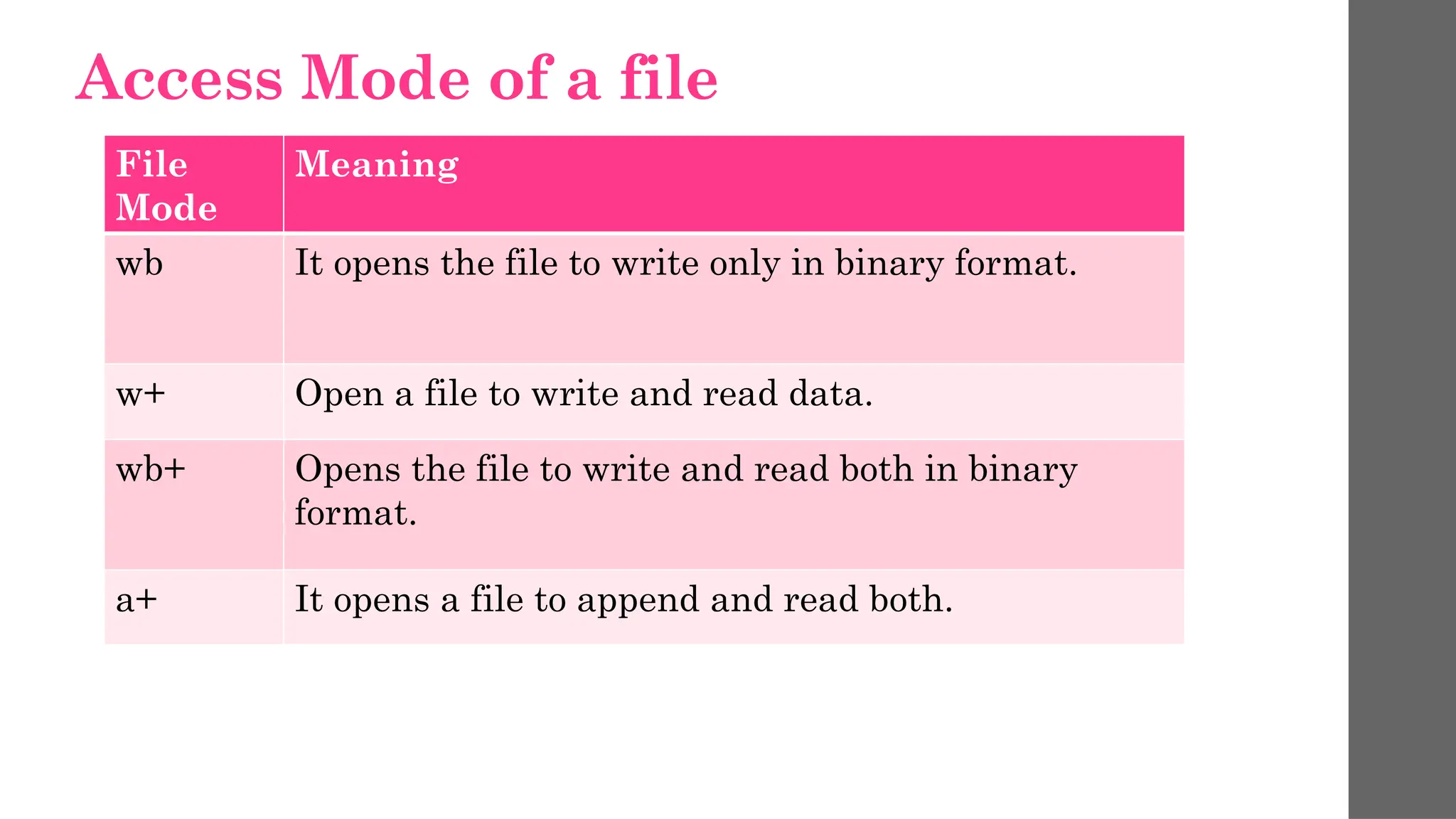
The document provides an overview of file operations in Python, covering functions for creating, opening, reading, writing, and deleting files. It explains various file access modes and introduces methods like seek() and tell() for file pointer manipulation. Additionally, it mentions the use of the os and shutil modules for checking file existence, size, and copying files and directories.