The document is a presentation by Nate Peterson introducing F# to C# developers, focusing on the functional-first nature of F# and its differences from C#. It showcases code examples that illustrate concepts like immutability, concise syntax, and functional programming techniques through problems like the sum of squares and fizzbuzz. The presentation emphasizes a paradigm shift in thinking and coding style when transitioning to F# from C#.













![let square x = x * x
let sumOfSquares n =
[1..n] |>
List.map square|>
List.sum
sumOfSquares 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fsharpcsharp-150615123201-lva1-app6891/75/Introduction-to-F-for-the-C-developer-20-2048.jpg)

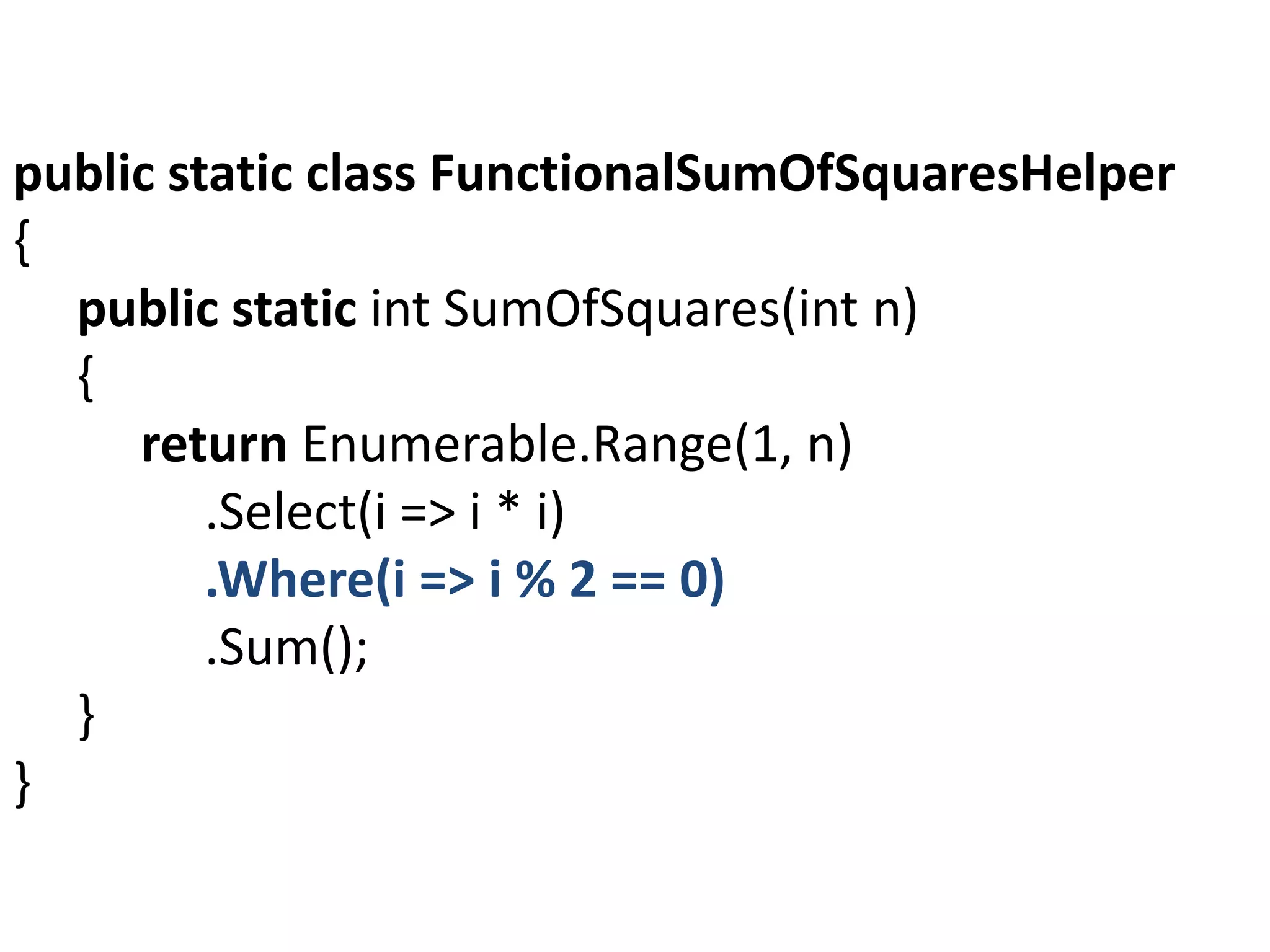
![let square x = x * x
let isEven x = x % 2 = 0
let sumOfSquares n =
[1..n] |>
List.filter
List.map square|>
List.filter isEven |>
List.sum
sumOfSquares 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fsharpcsharp-150615123201-lva1-app6891/75/Introduction-to-F-for-the-C-developer-25-2048.jpg)





![let FizzBuzz number =
match number % 3, number % 5 with
| 0, 0 -> "FizzBuzz"
| 0, _ -> "Fizz"
| _, 0 -> "Buzz"
| _ -> string number
[1..100]
|> List.map FizzBuzz
|> List.reduce (sprintf "%srn%s")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fsharpcsharp-150615123201-lva1-app6891/75/Introduction-to-F-for-the-C-developer-31-2048.jpg)









