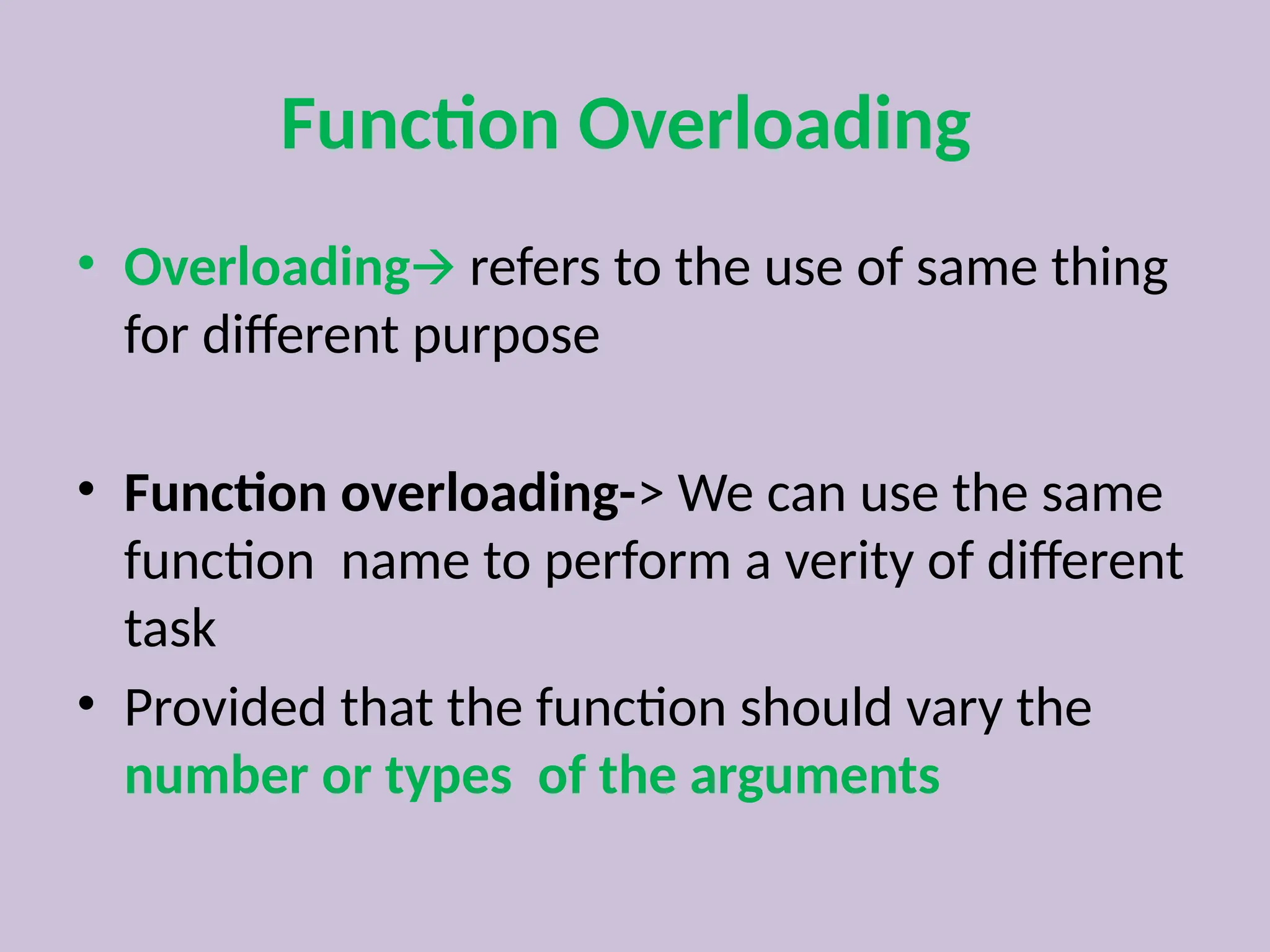
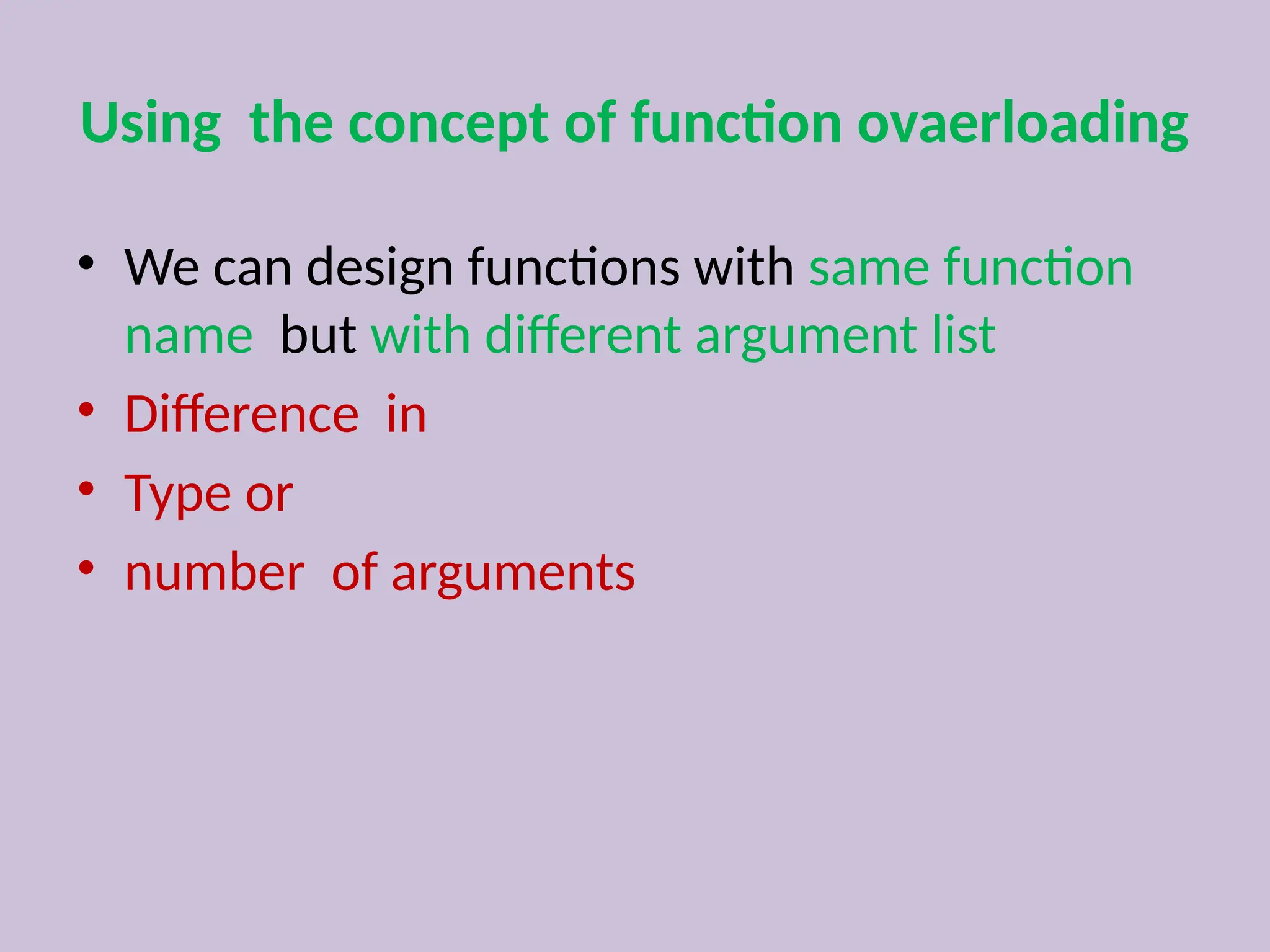
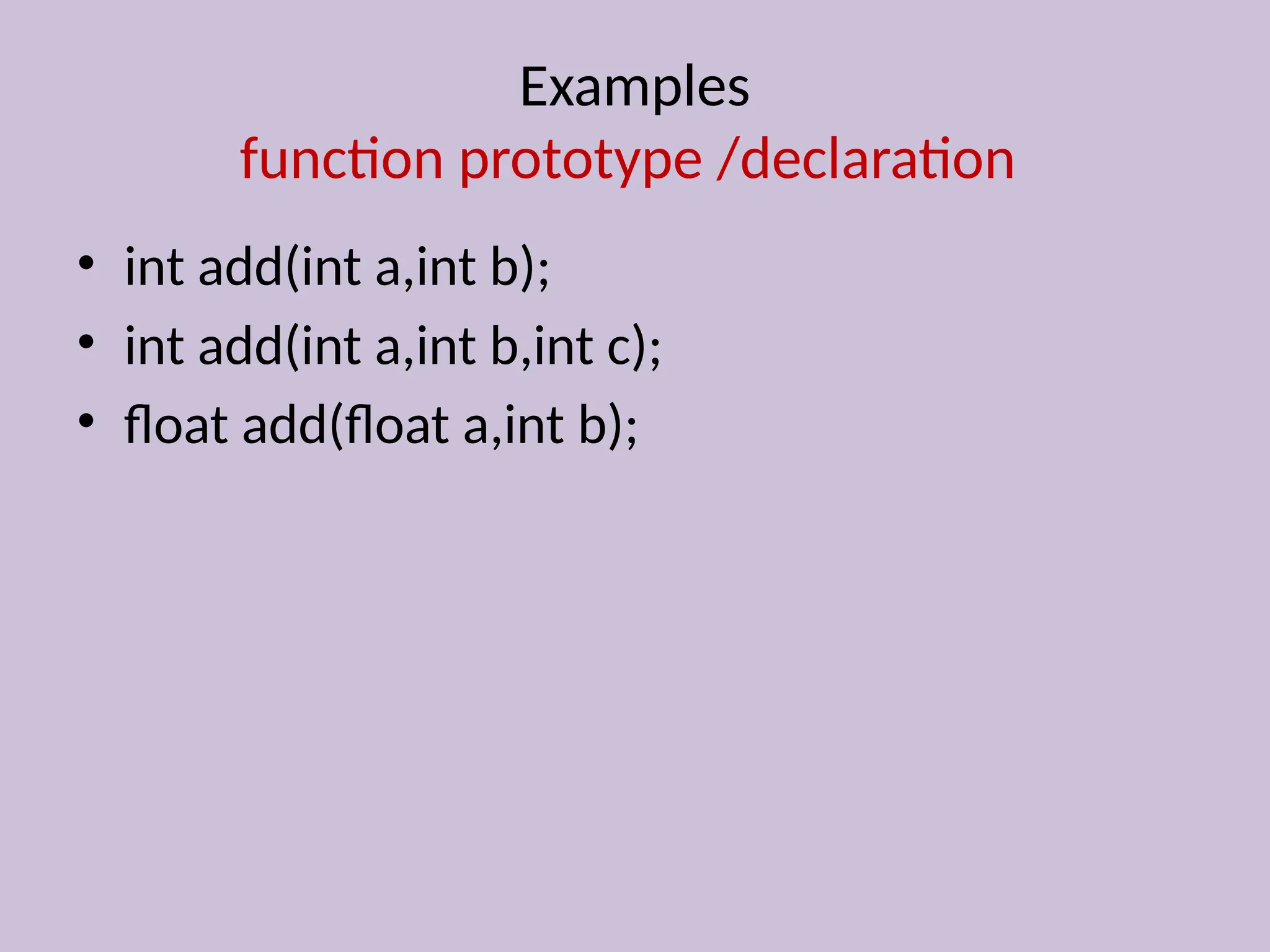
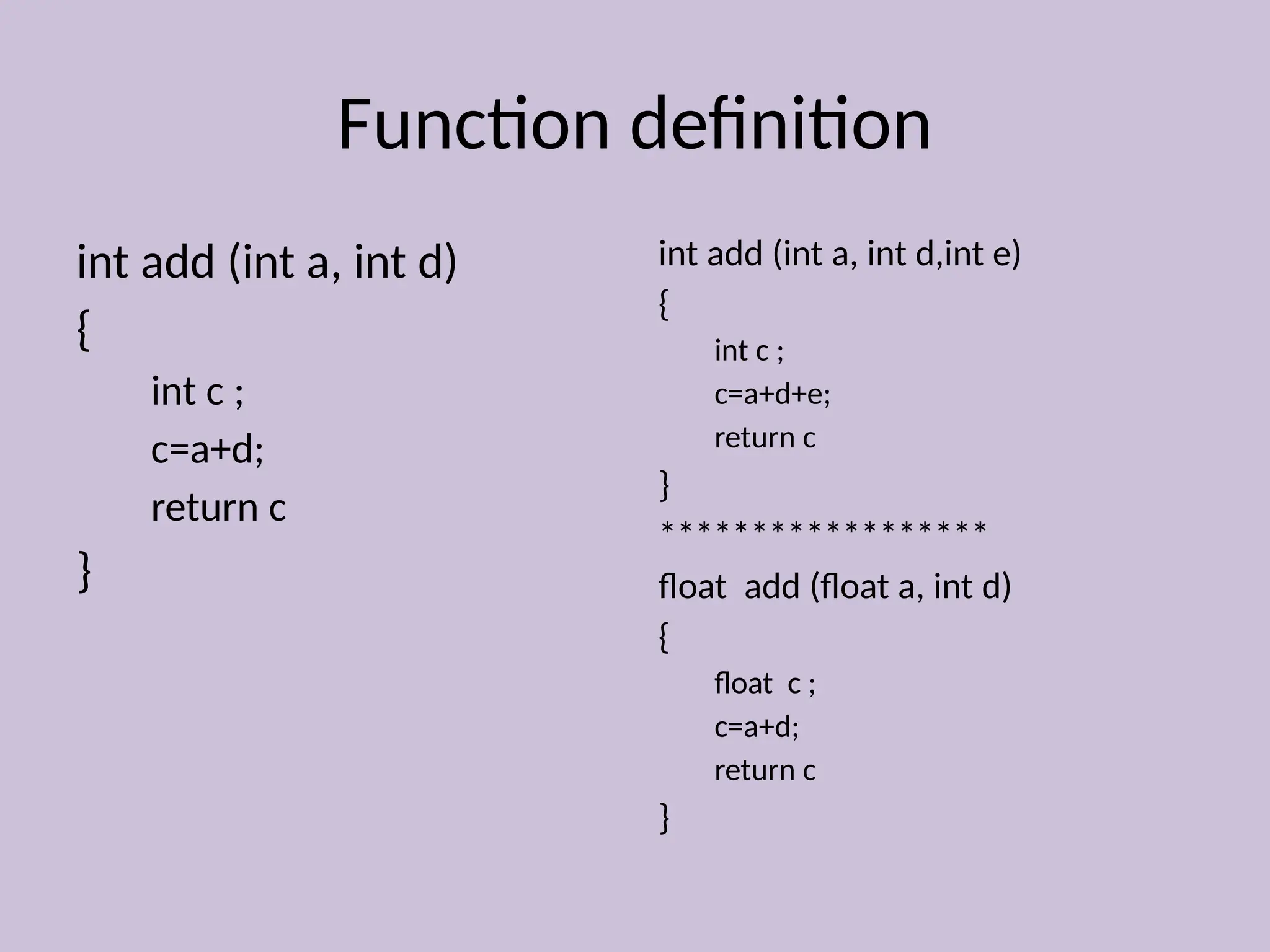
Function overloading allows the use of the same function name to perform different tasks based on varying numbers or types of arguments. Examples include different definitions for the 'add' and 'volume' functions, where the operation performed depends on the arguments provided. This approach illustrates compile-time polymorphism in programming.