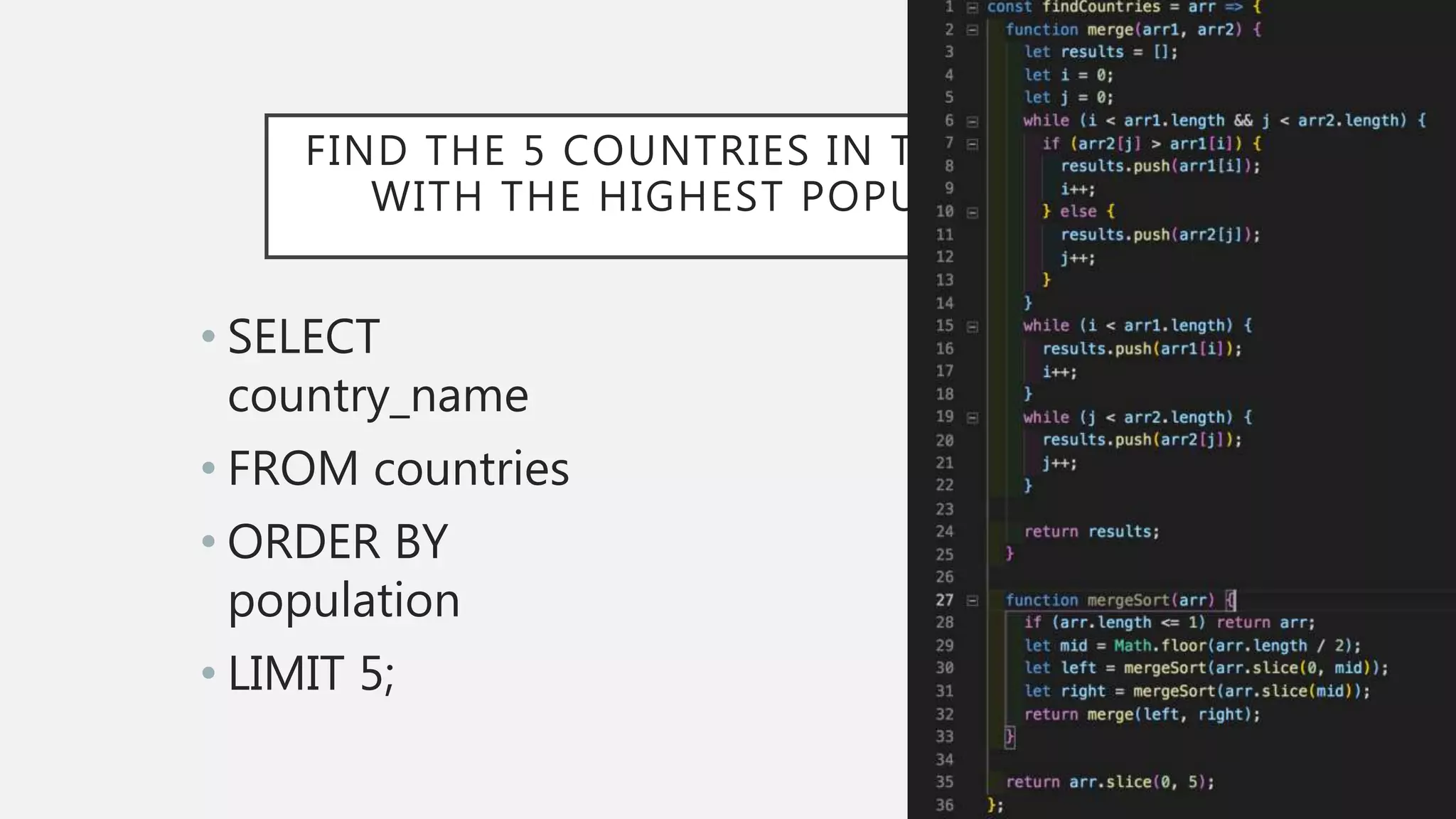
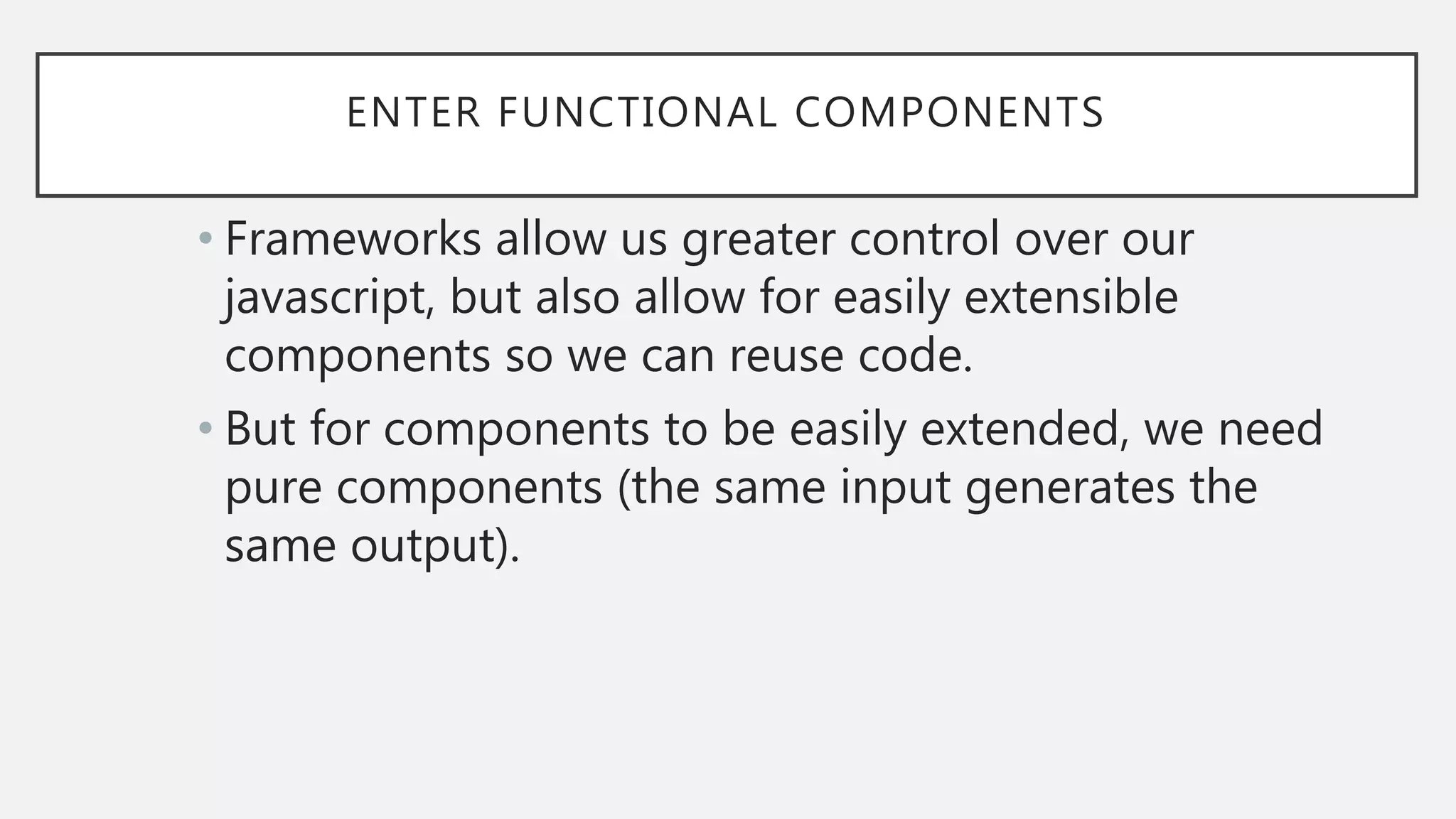
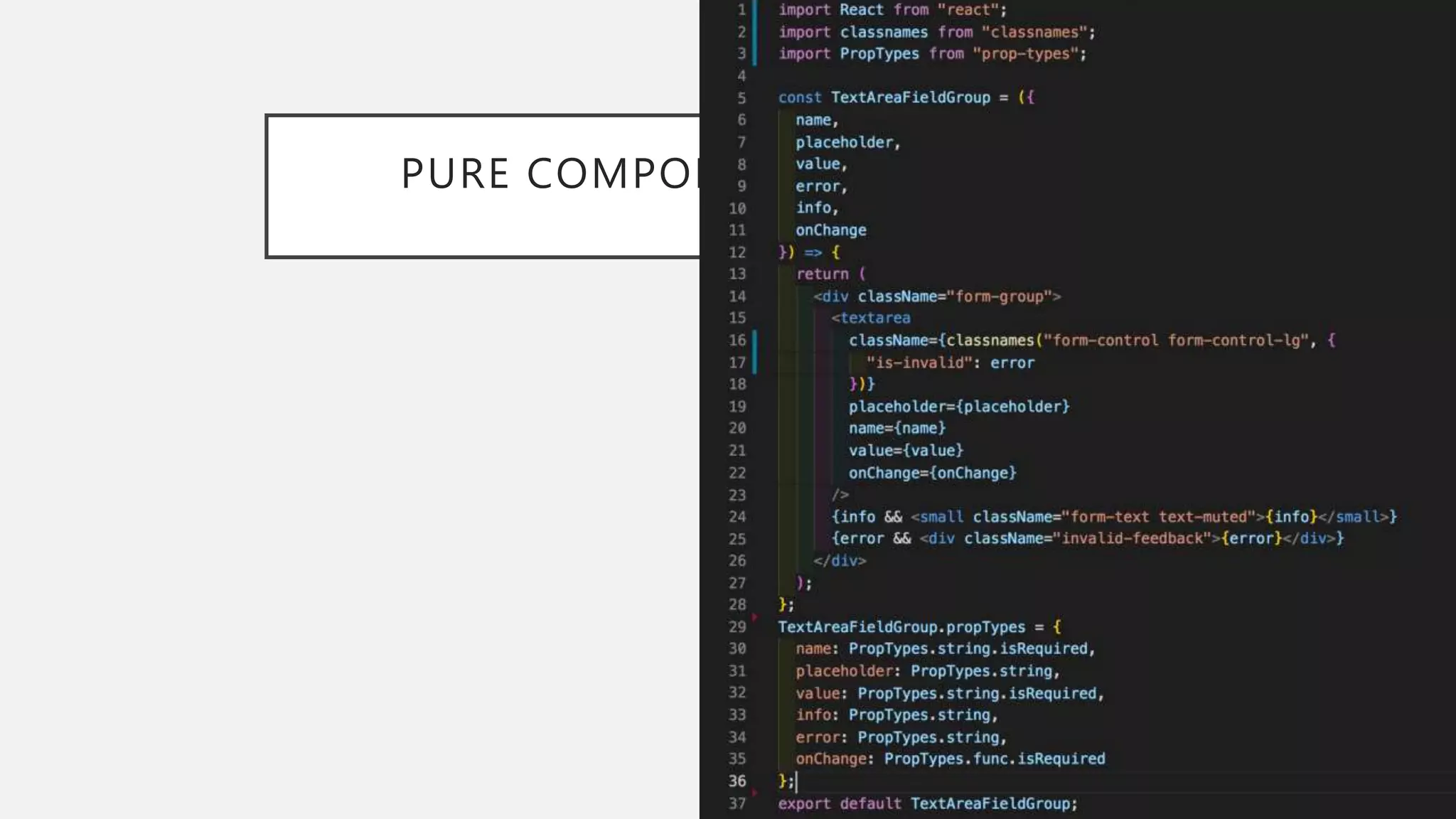
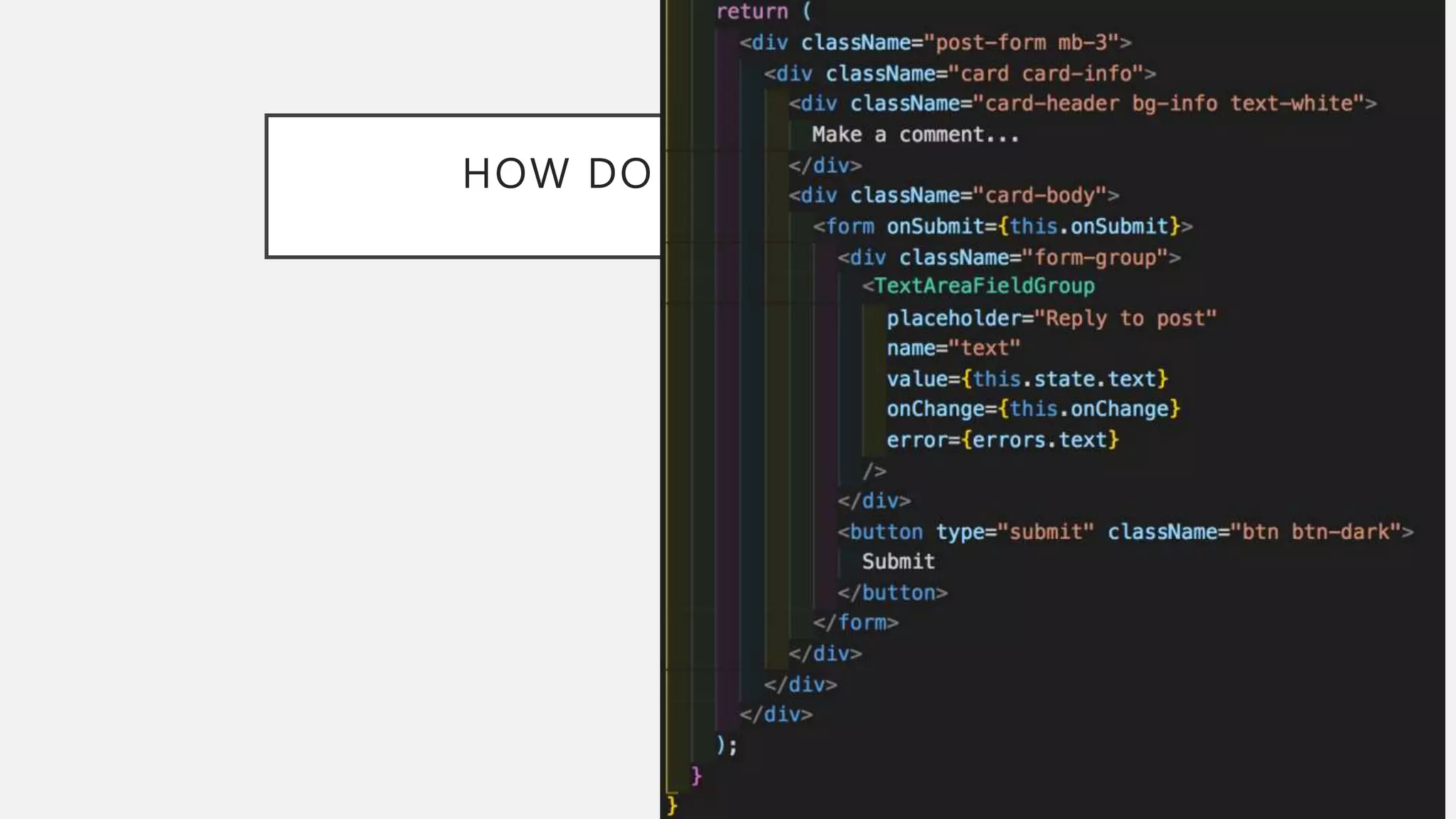
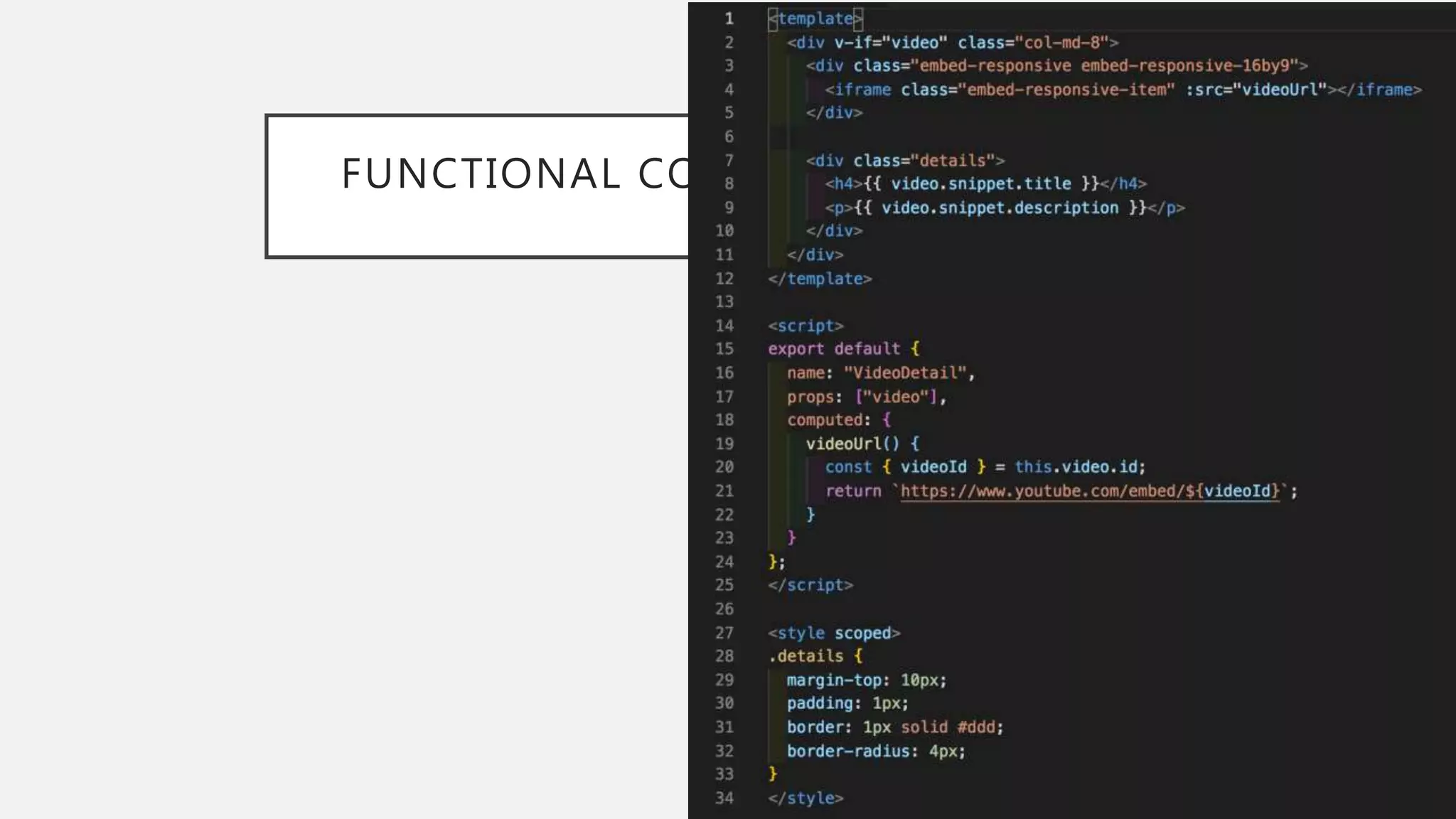
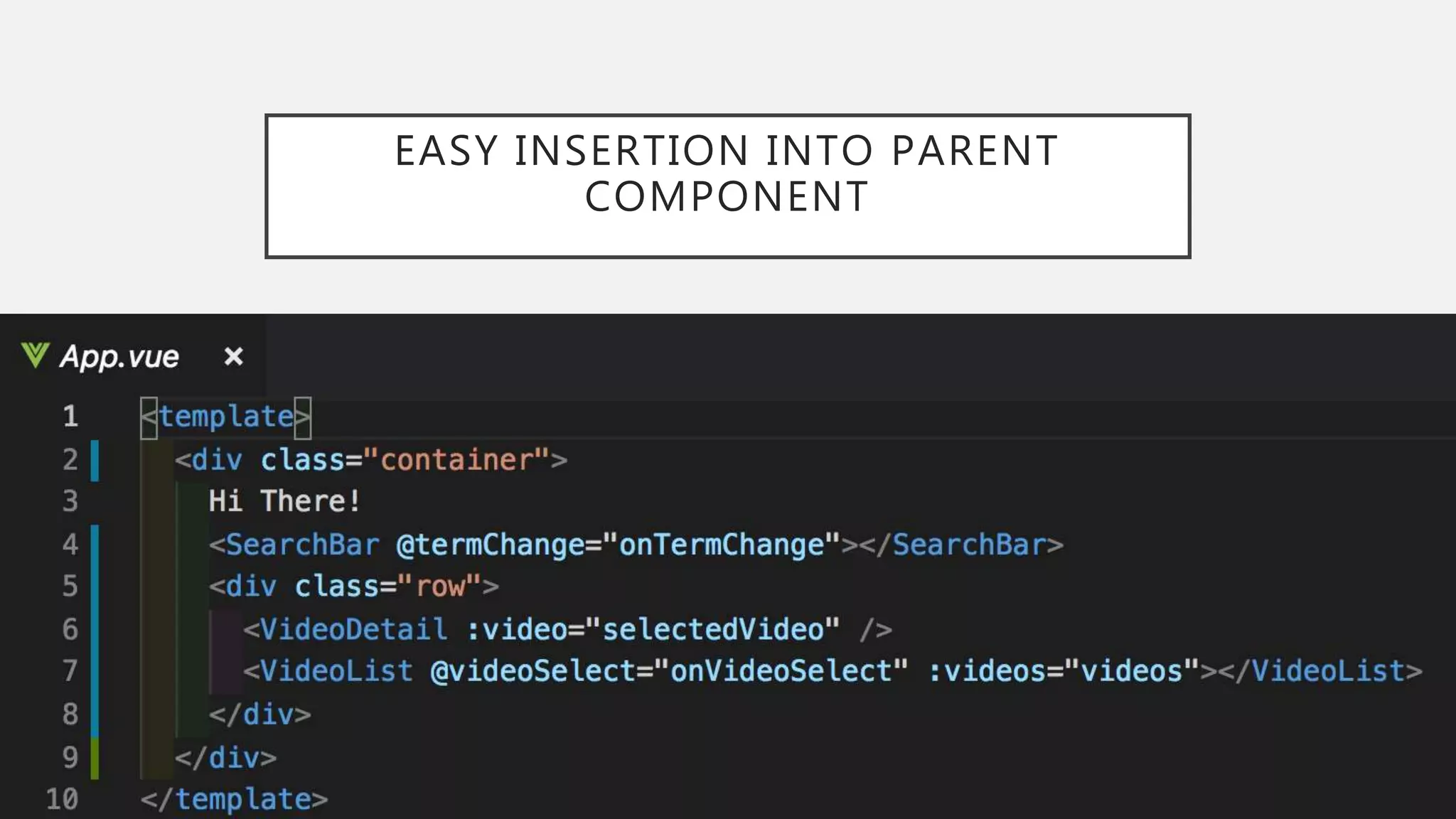
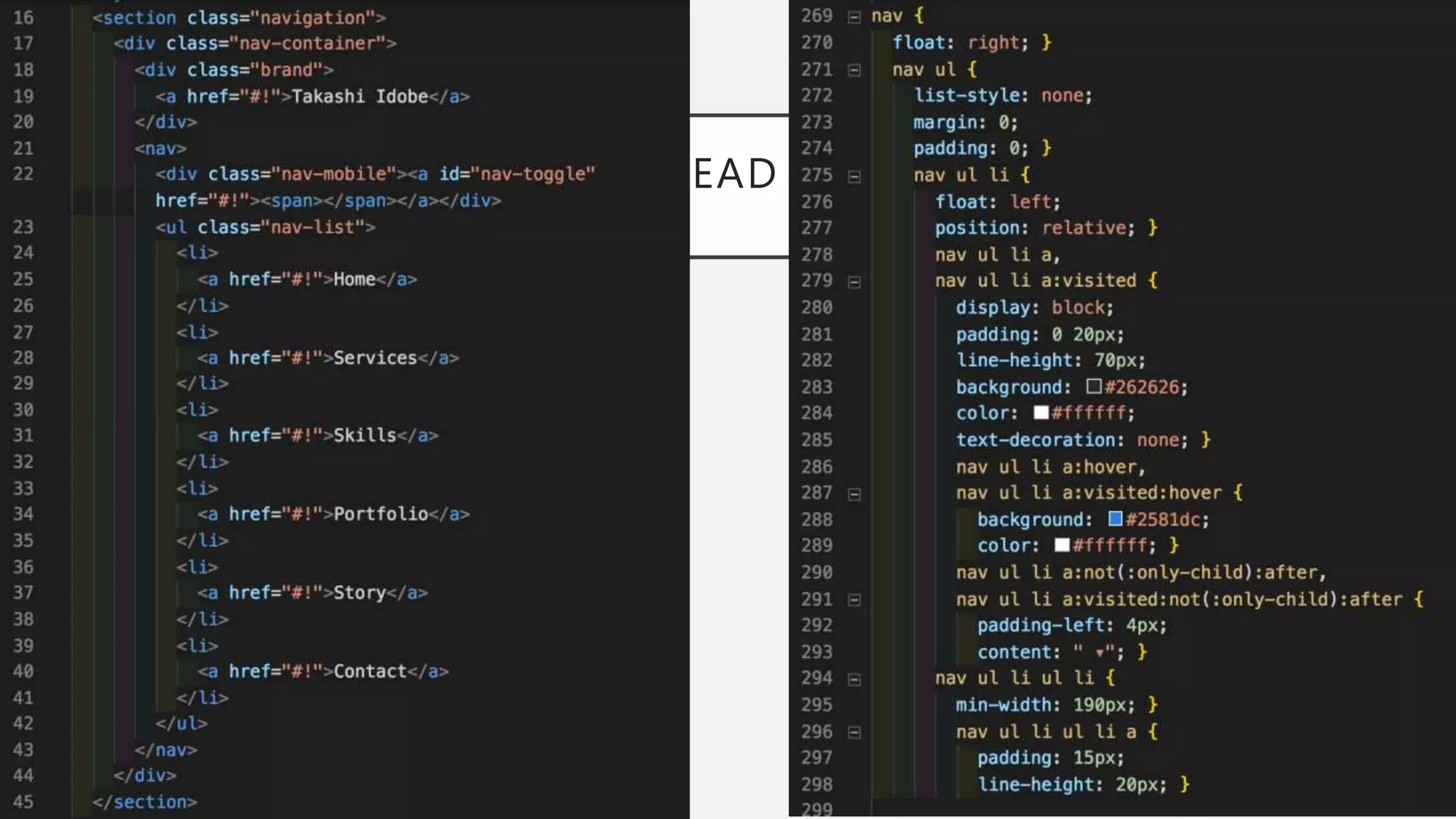
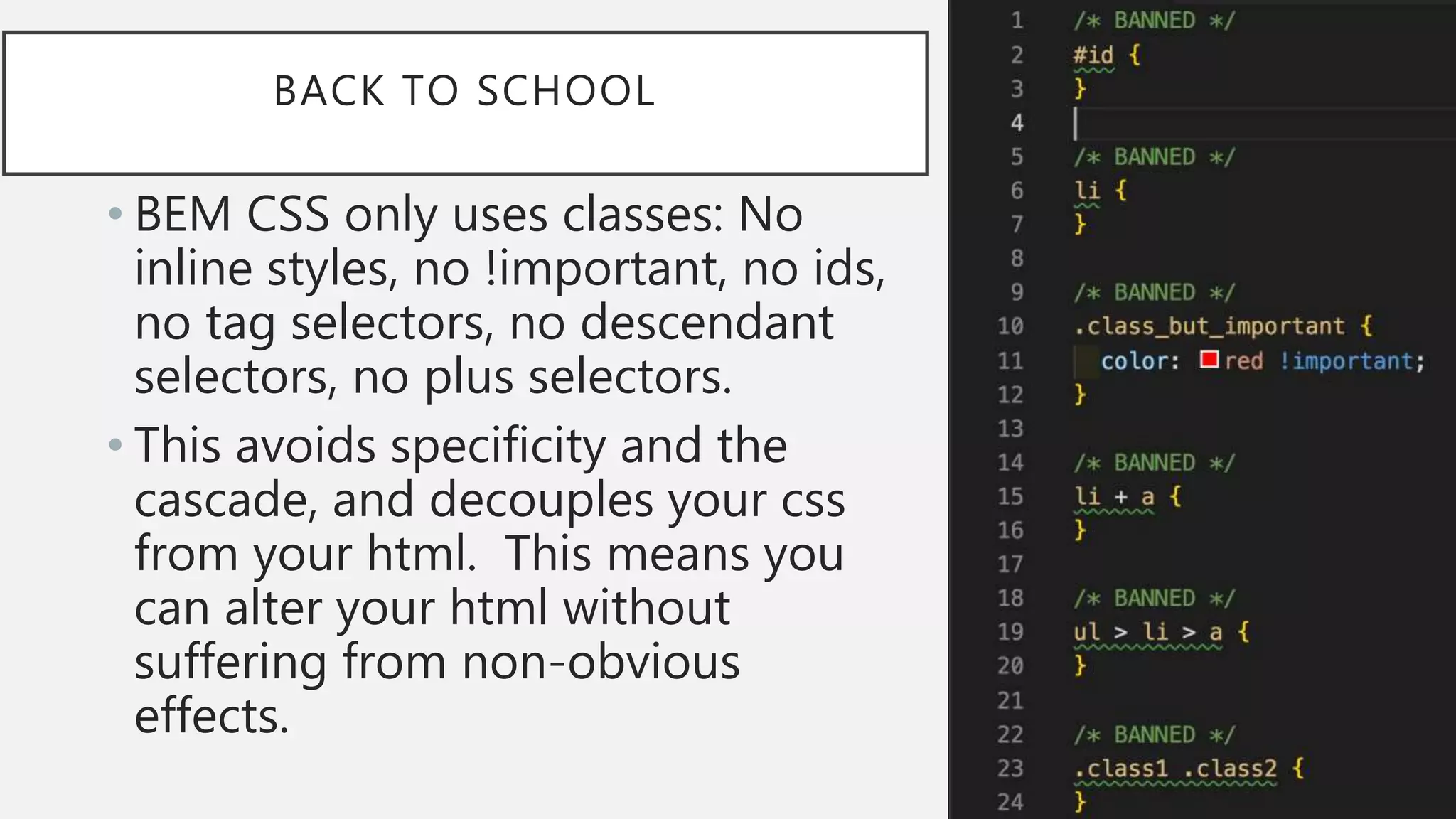
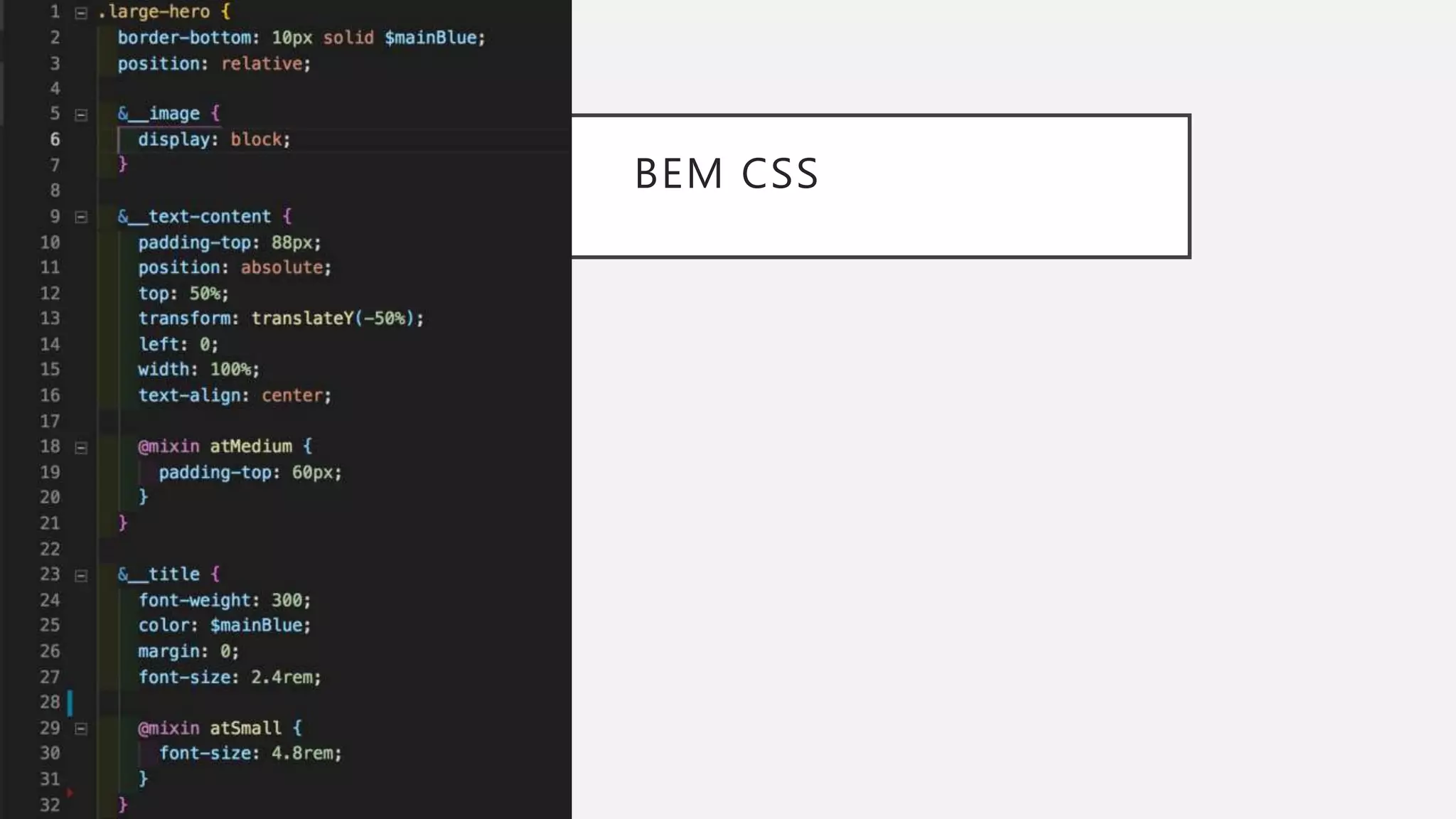
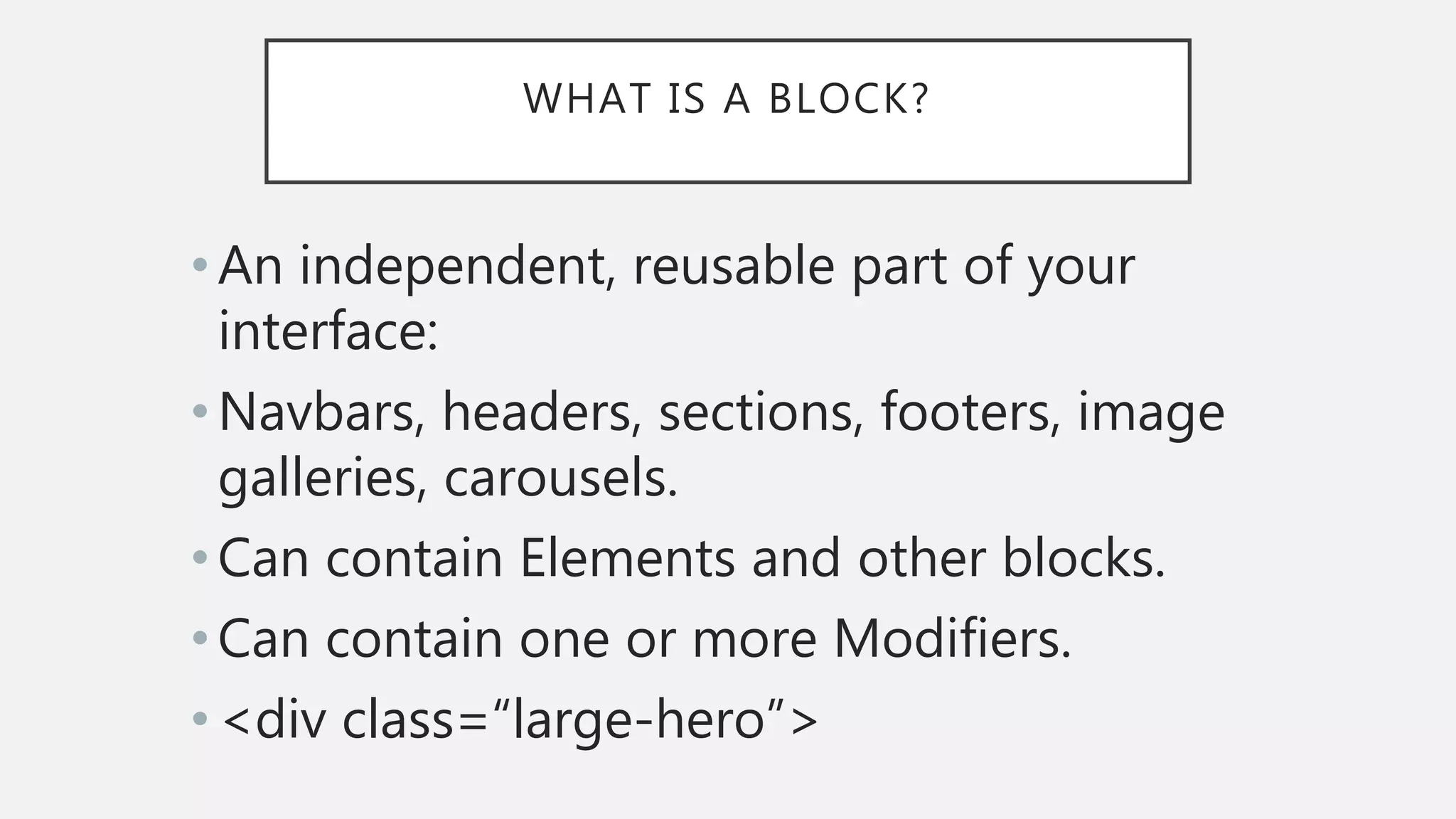
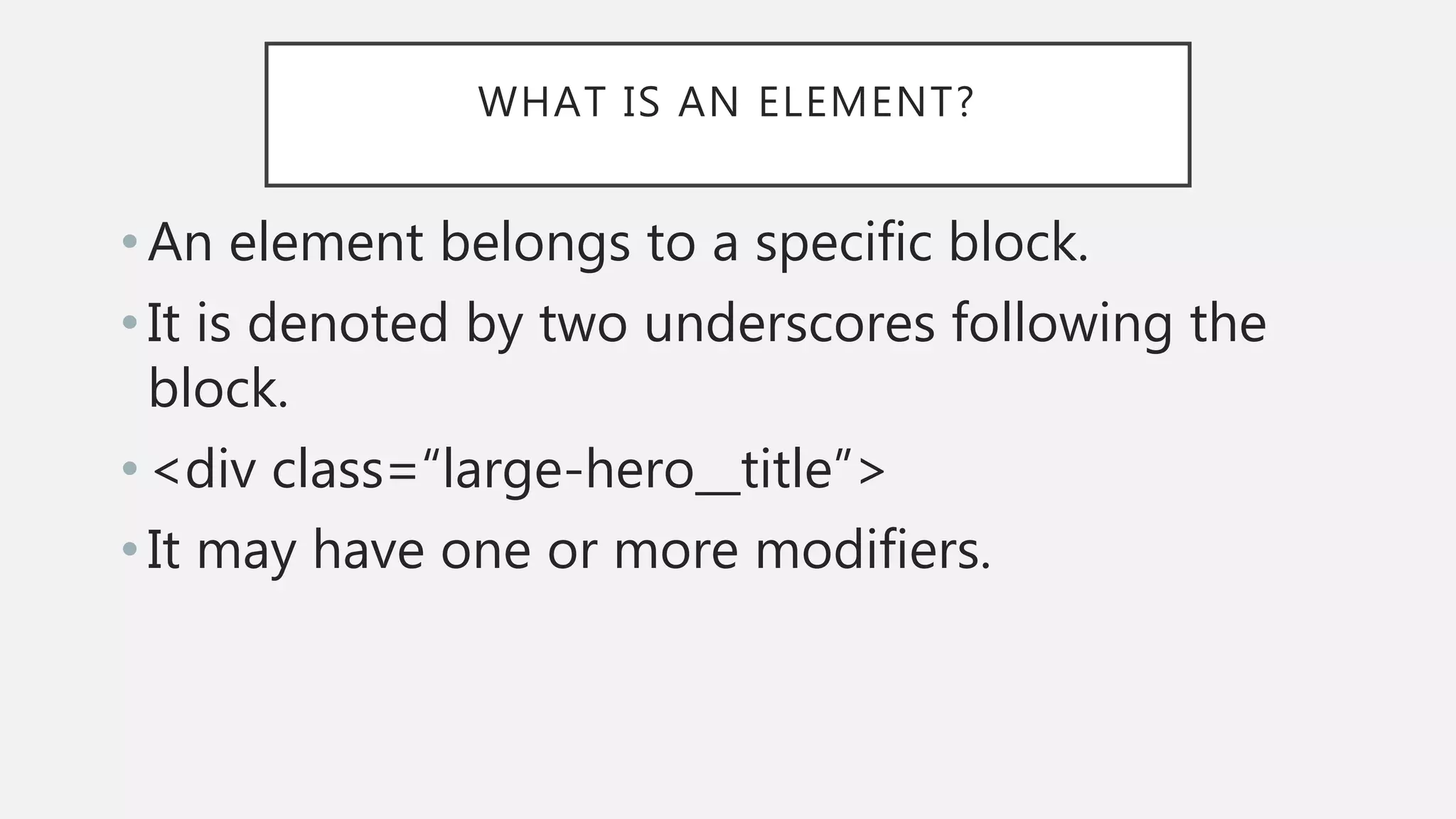
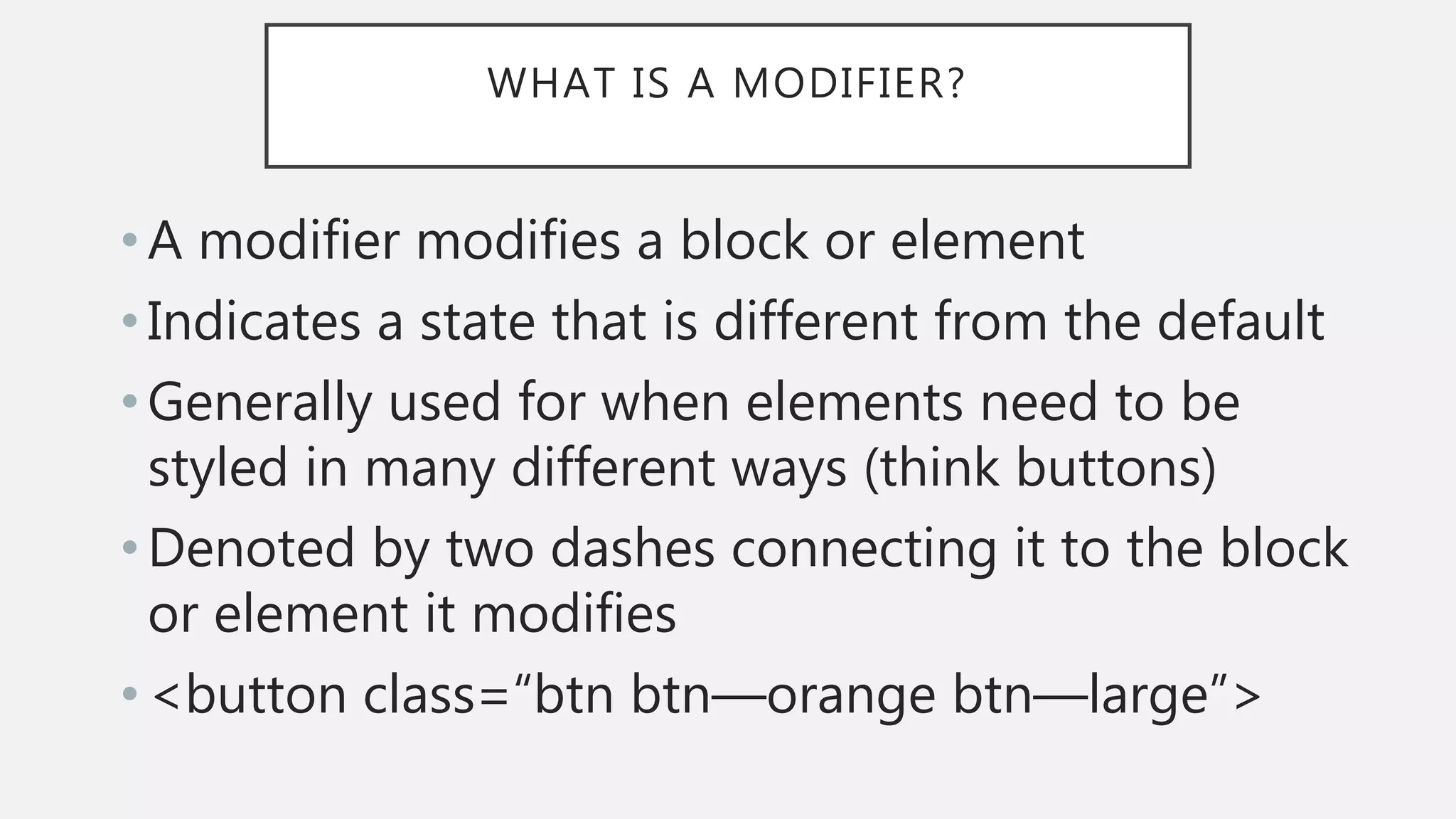
The document discusses functional CSS and JavaScript. It advocates using BEM methodology for CSS, which separates blocks, elements, and modifiers to avoid specificity and cascading issues. This makes CSS more predictable and reusable. The document also discusses writing pure, reusable components in React and Vue using a functional programming paradigm. Components should be decoupled from data sources to promote reusability. Frameworks provide tools like props, computed properties, and templates to build extensible functional components.















![FUNCTIONAL JAVASCRIPT WITH REACT
AND VUE
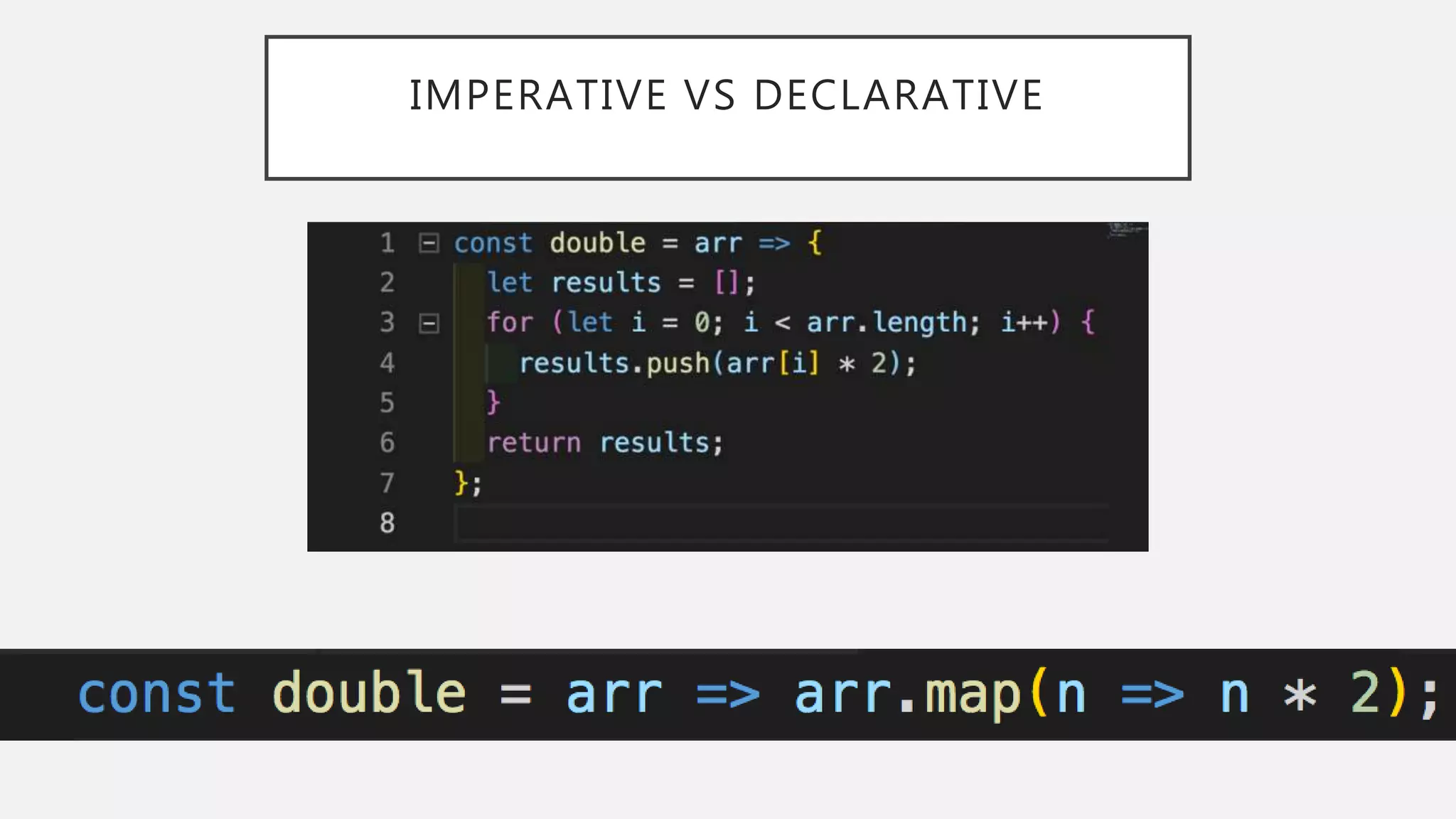
• Let’s talk about paradigms:
• Write a function in your favorite language that takes
in an array of numbers and returns a new array which
has doubled all of the items in the array.
• [1,2,3] => [2, 4, 6];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalcss-181116125125/75/Functional-Css-25-2048.jpg)