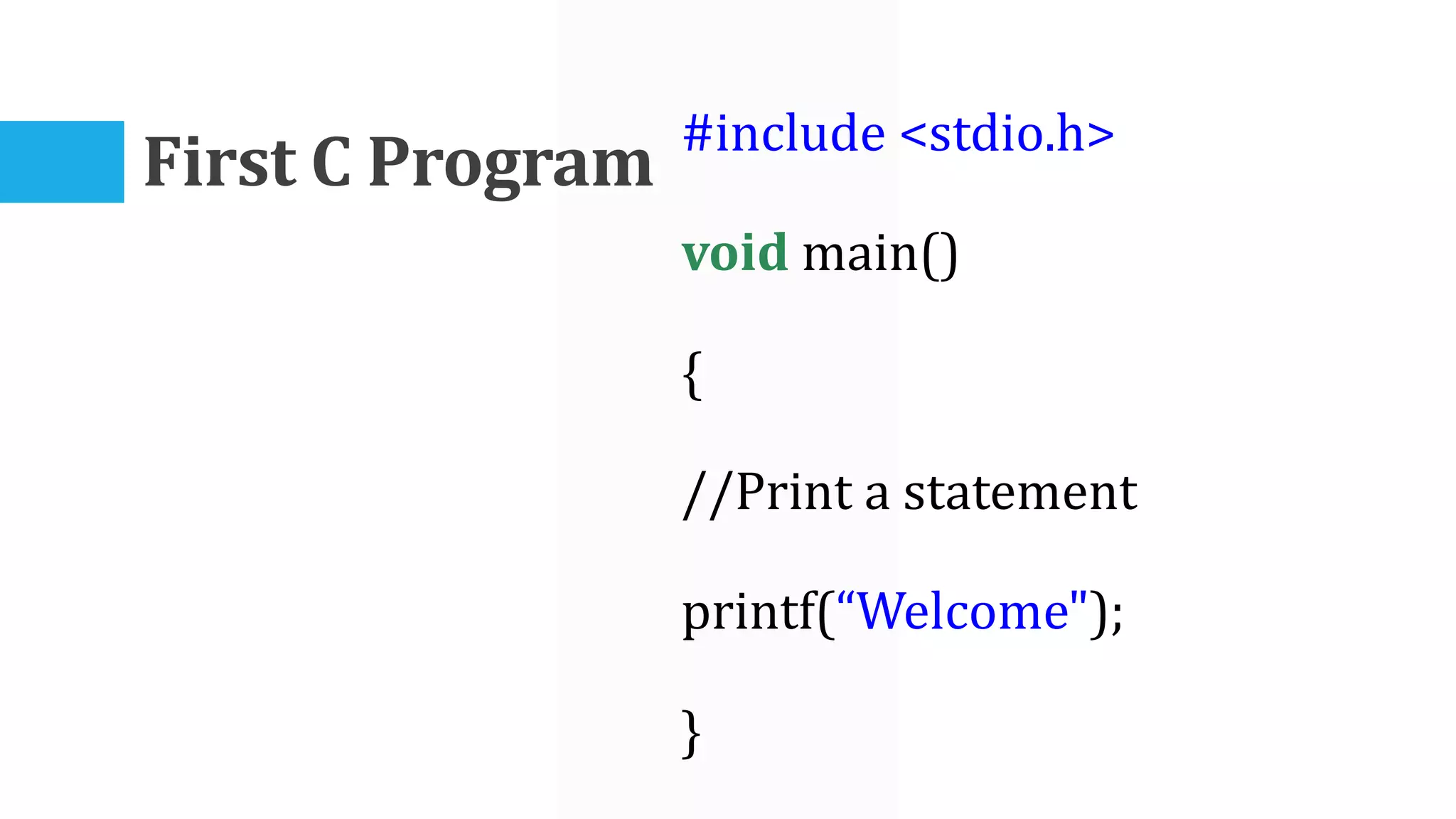
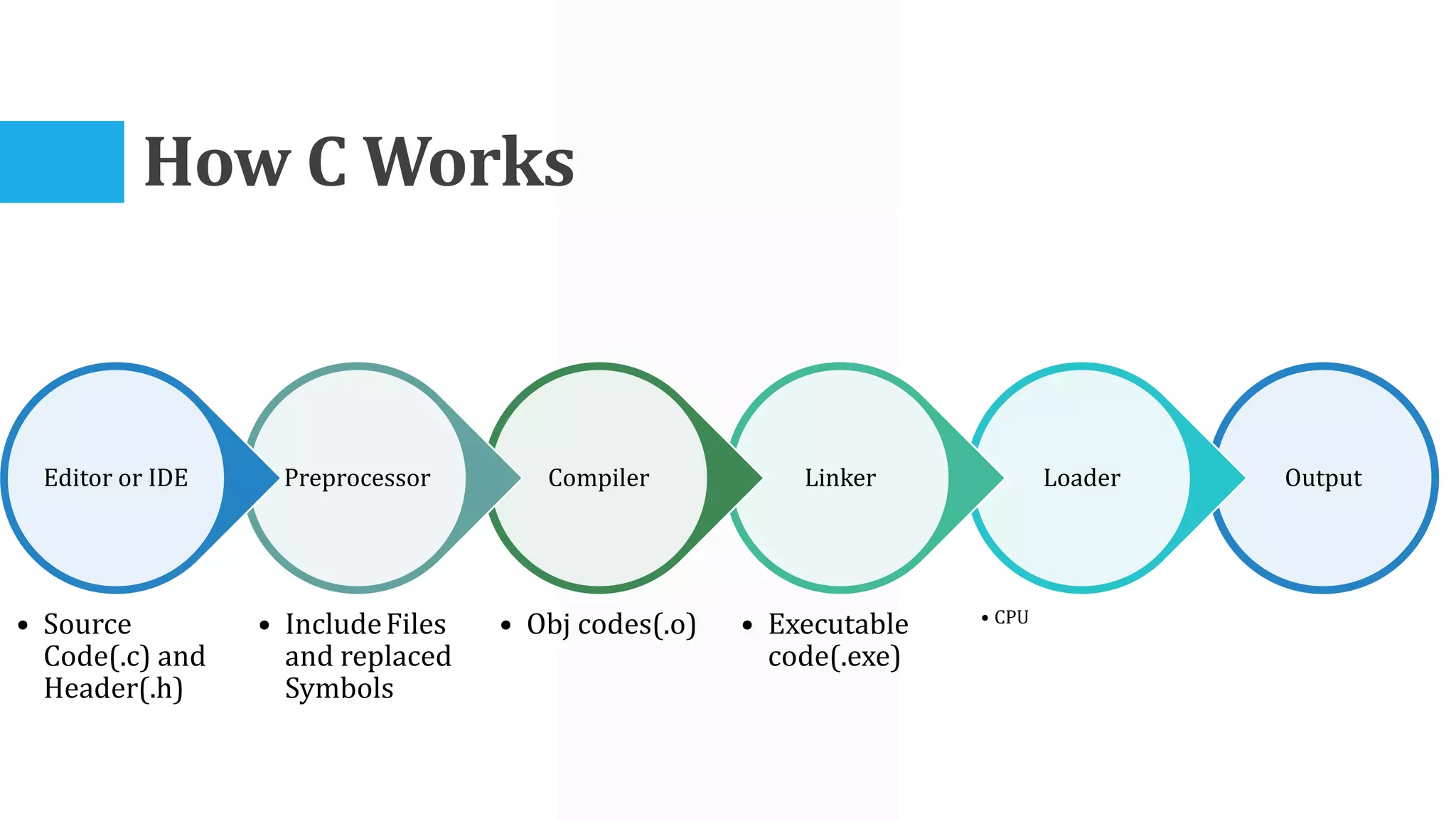
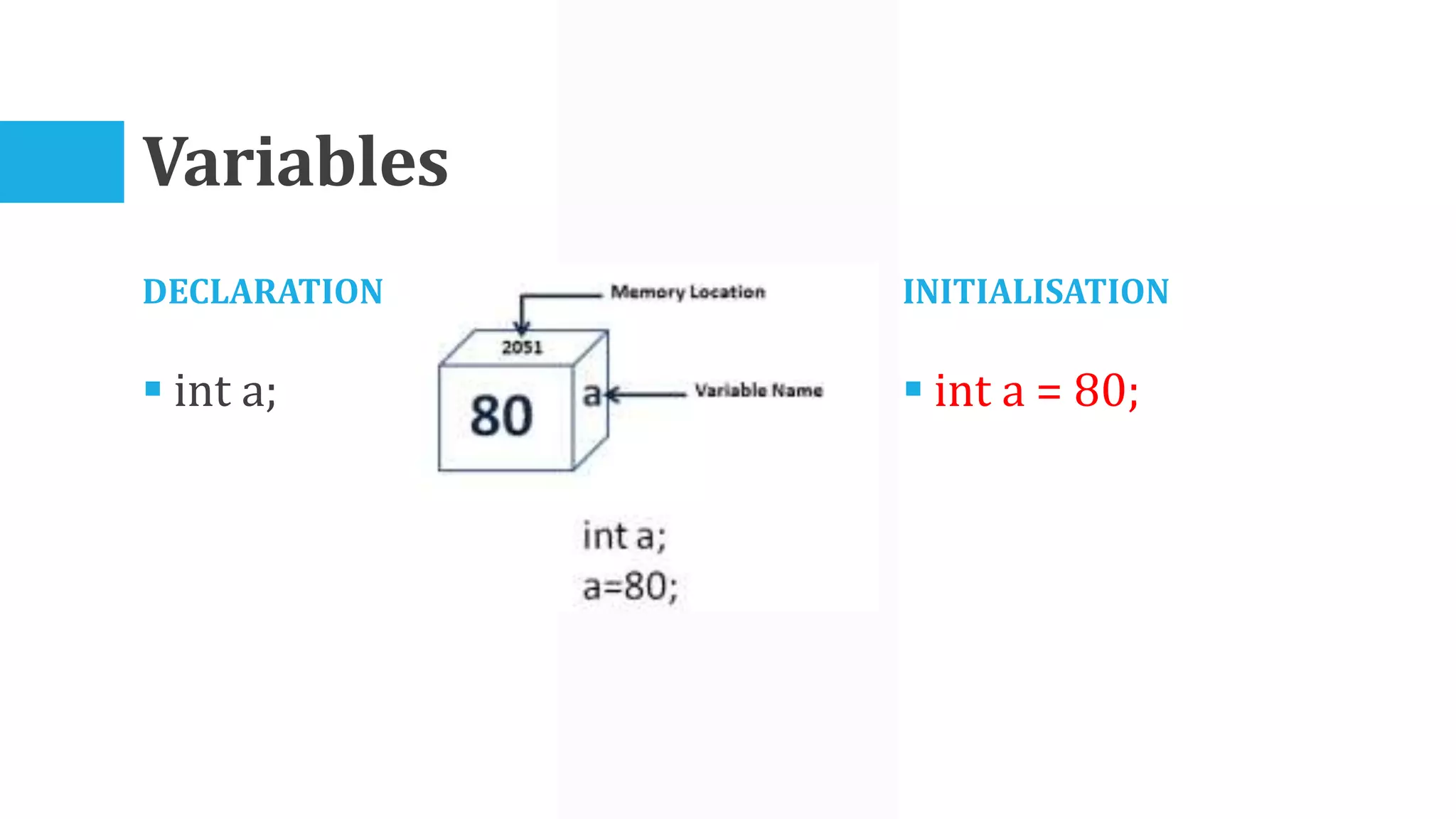
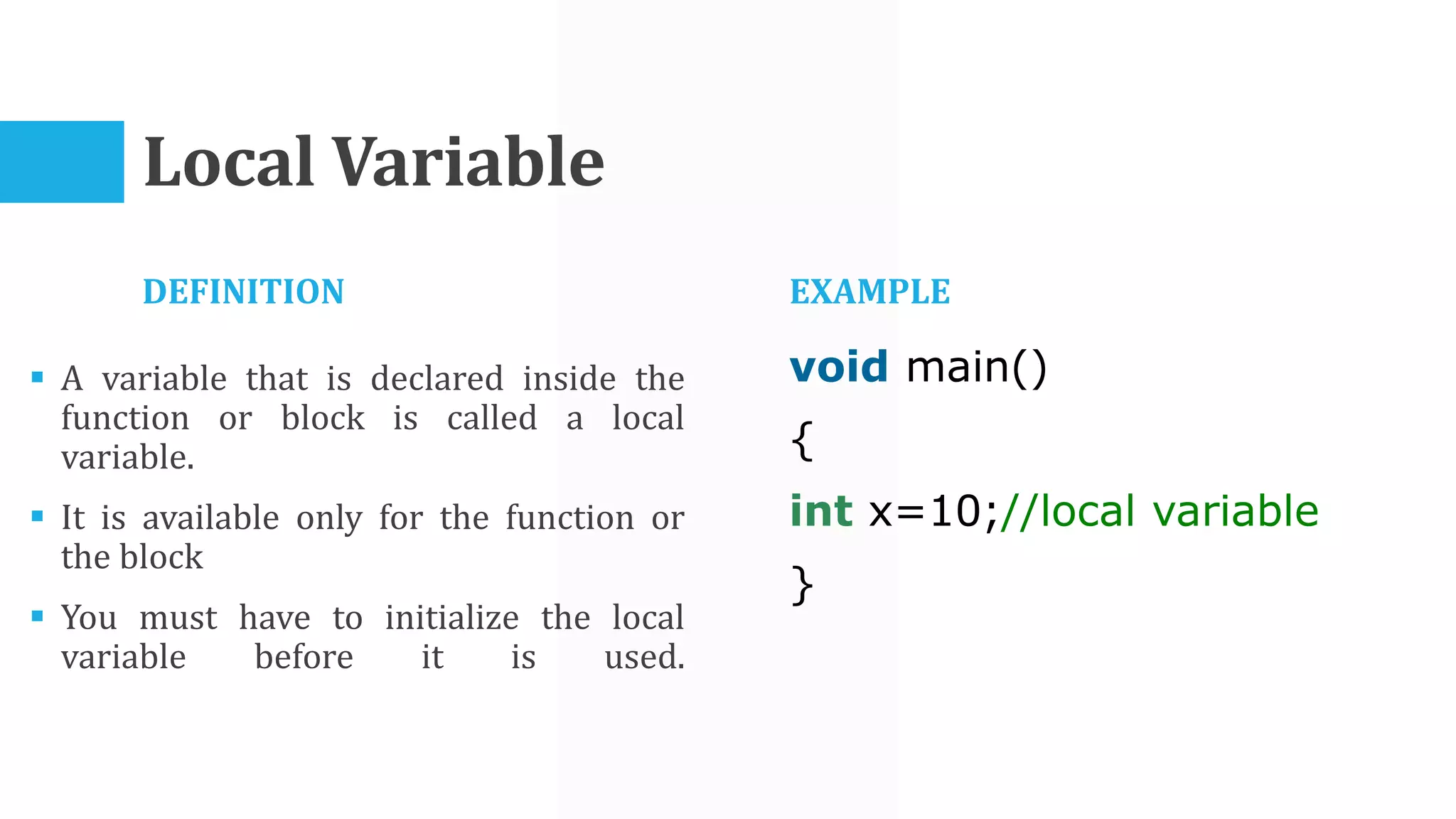
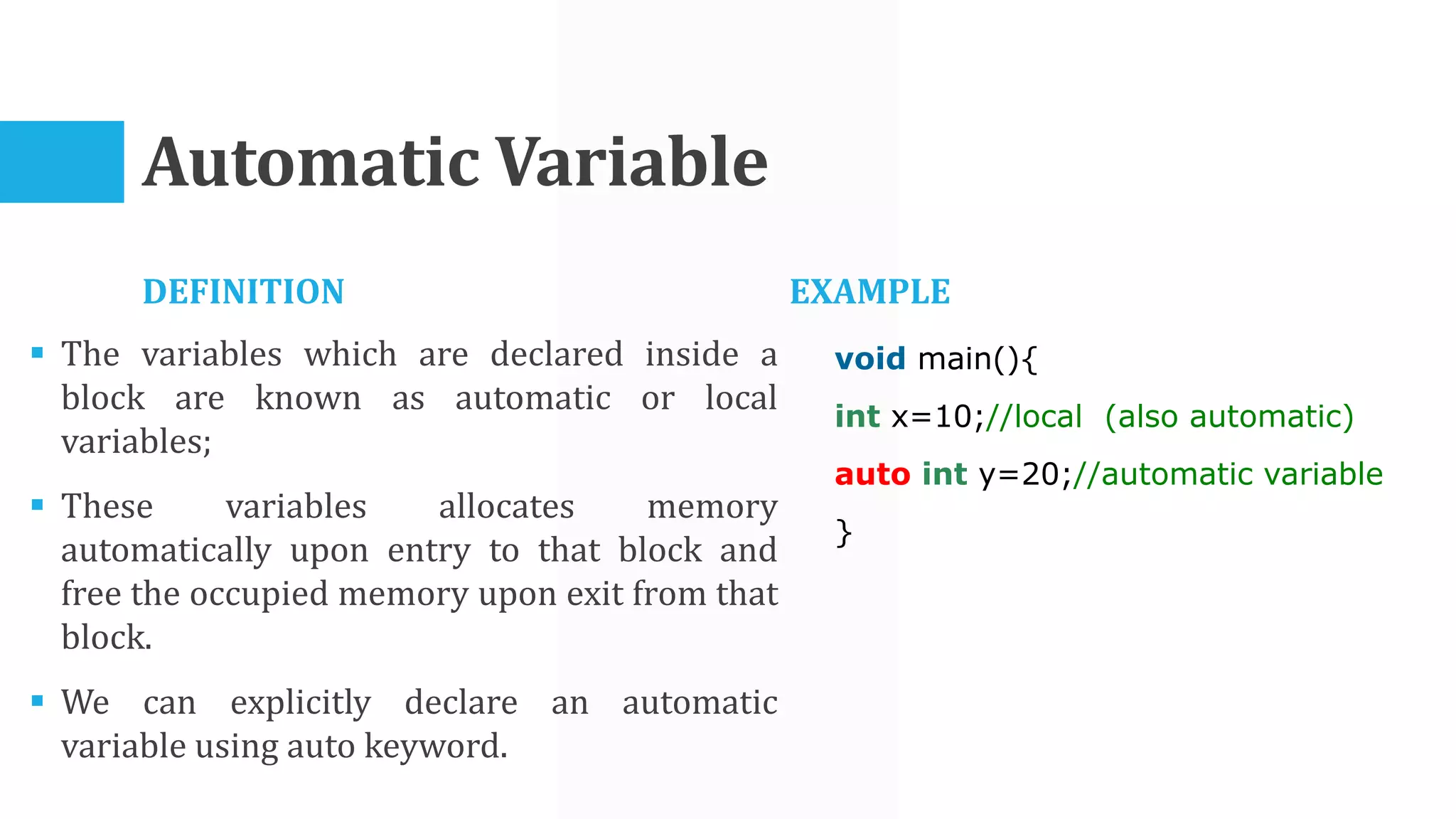
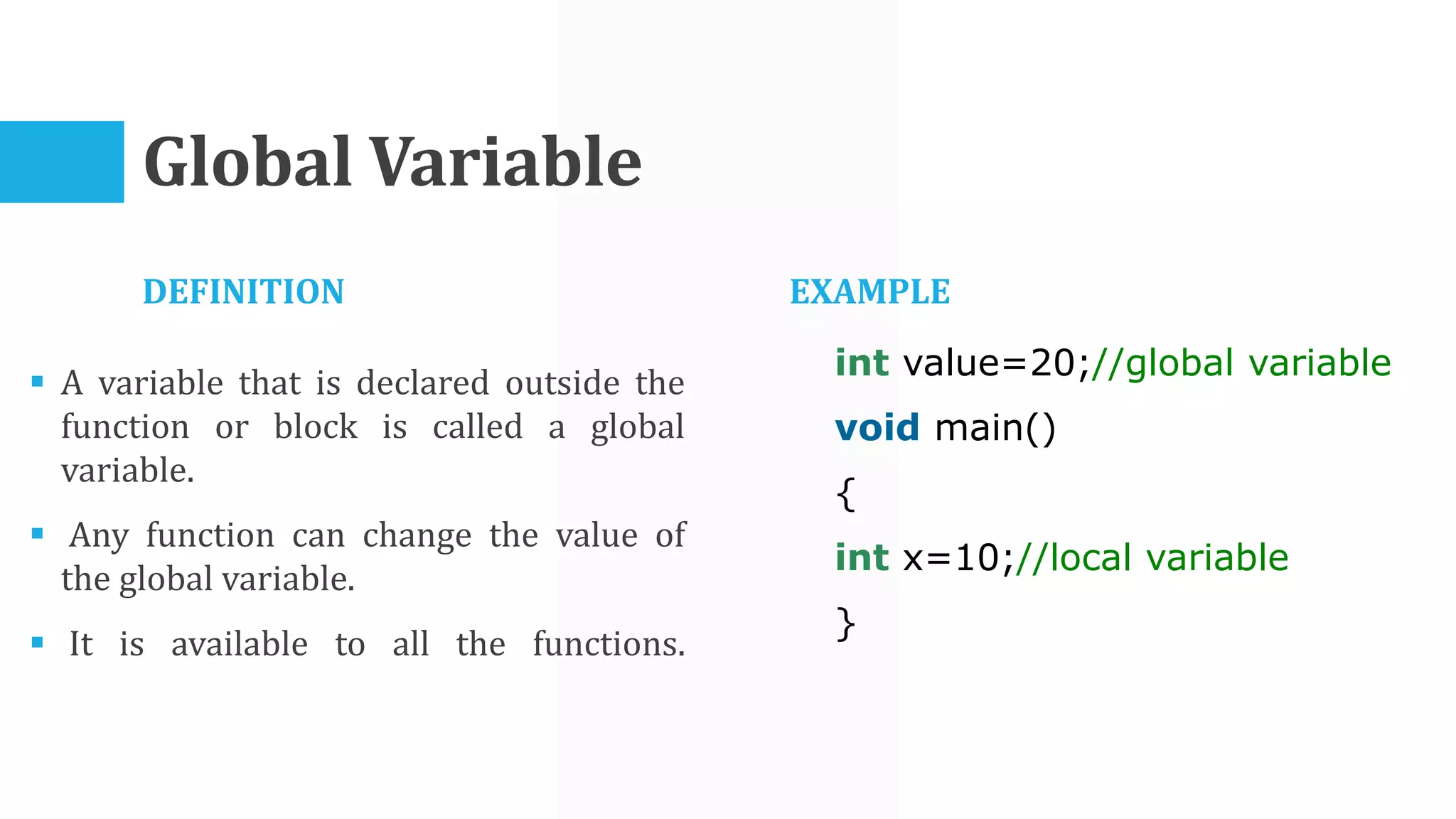
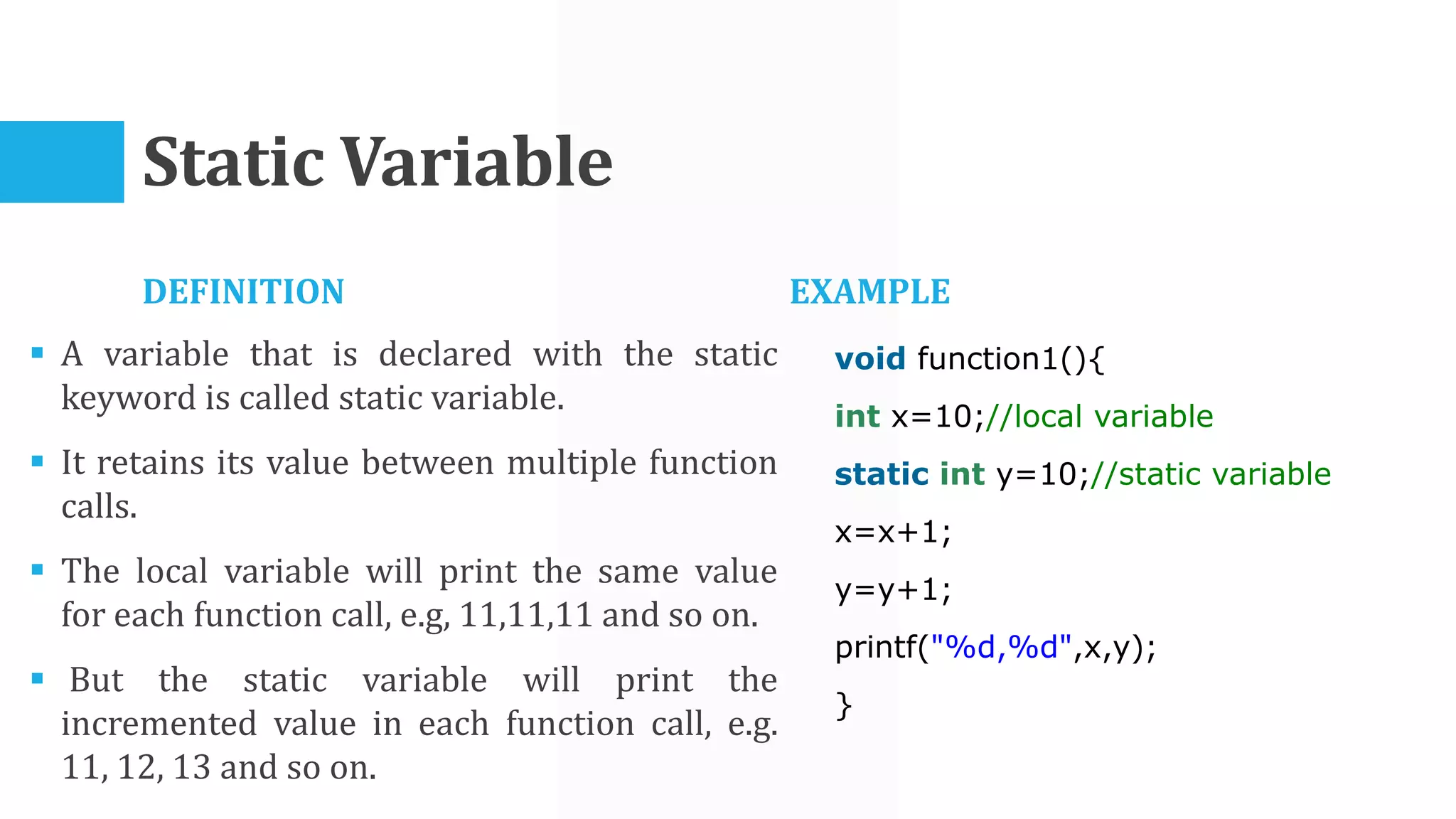
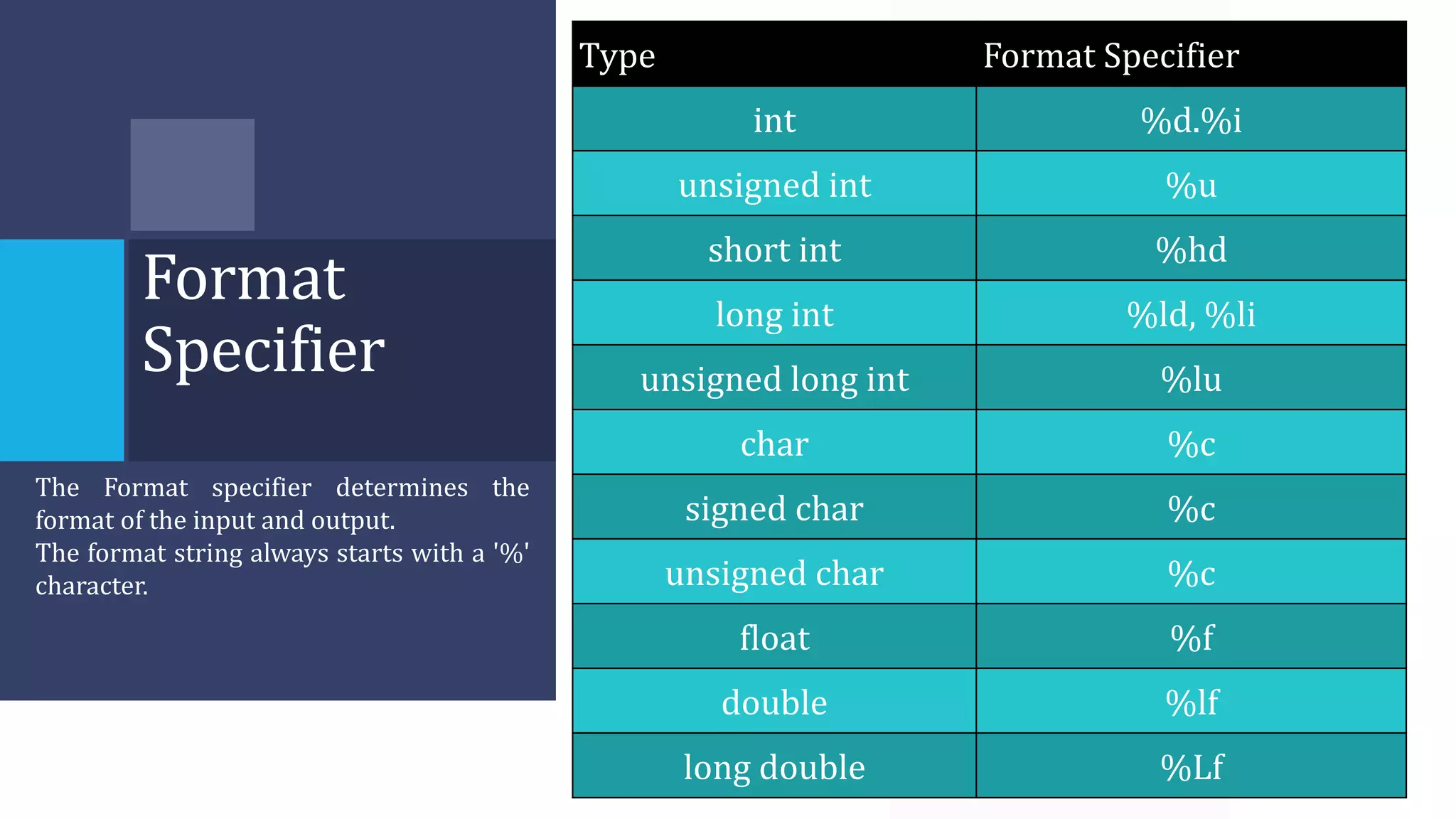
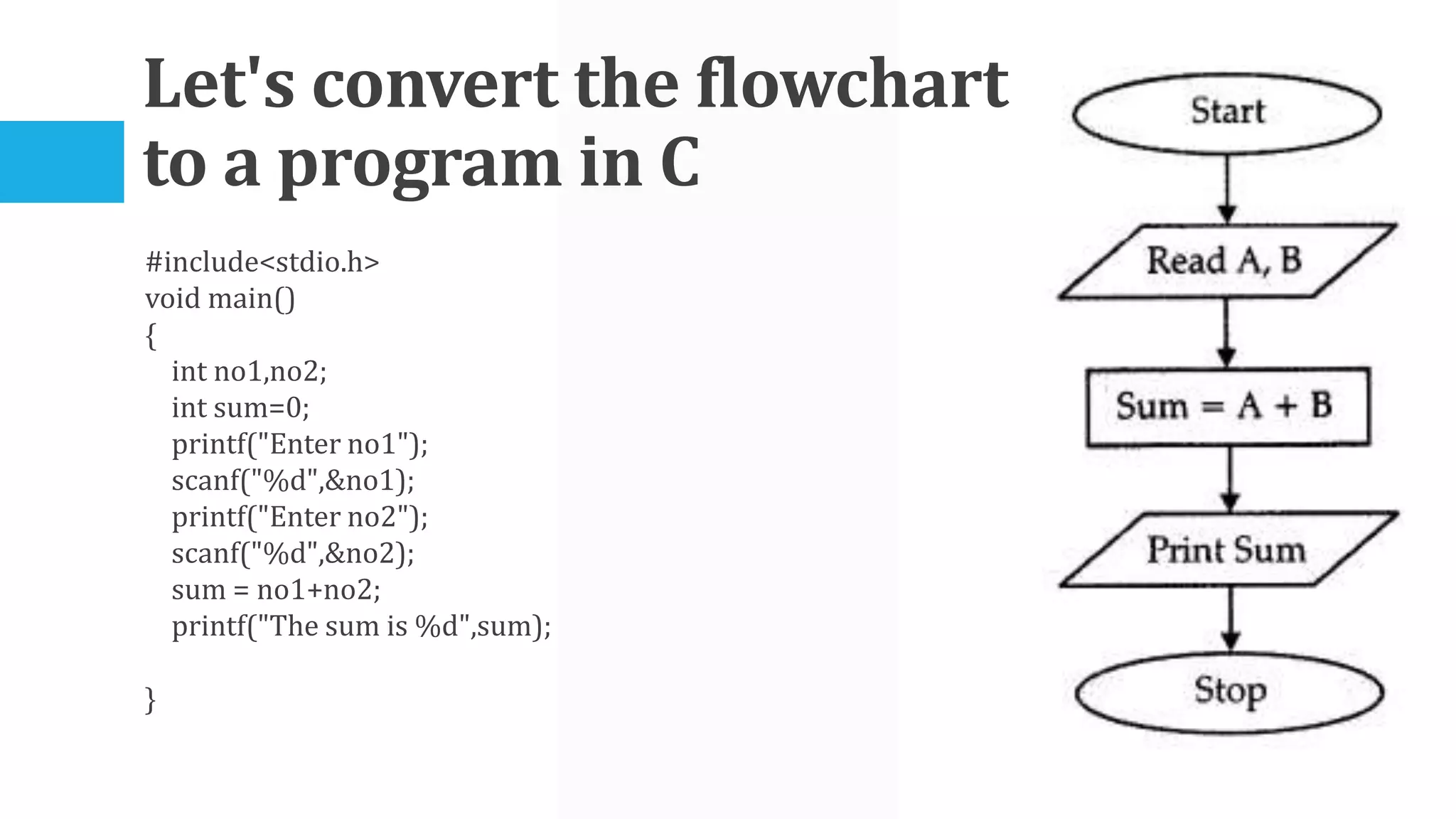
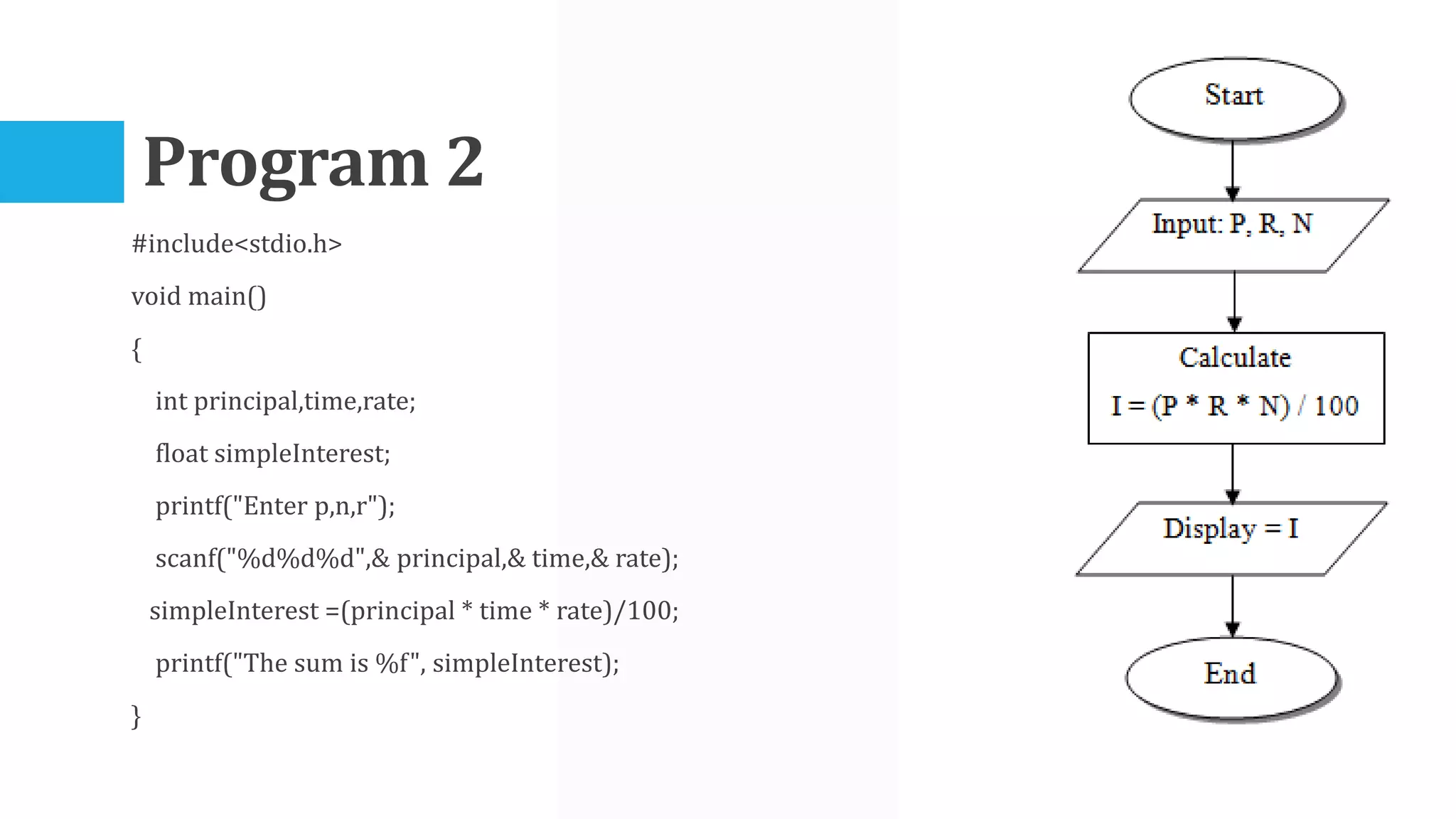
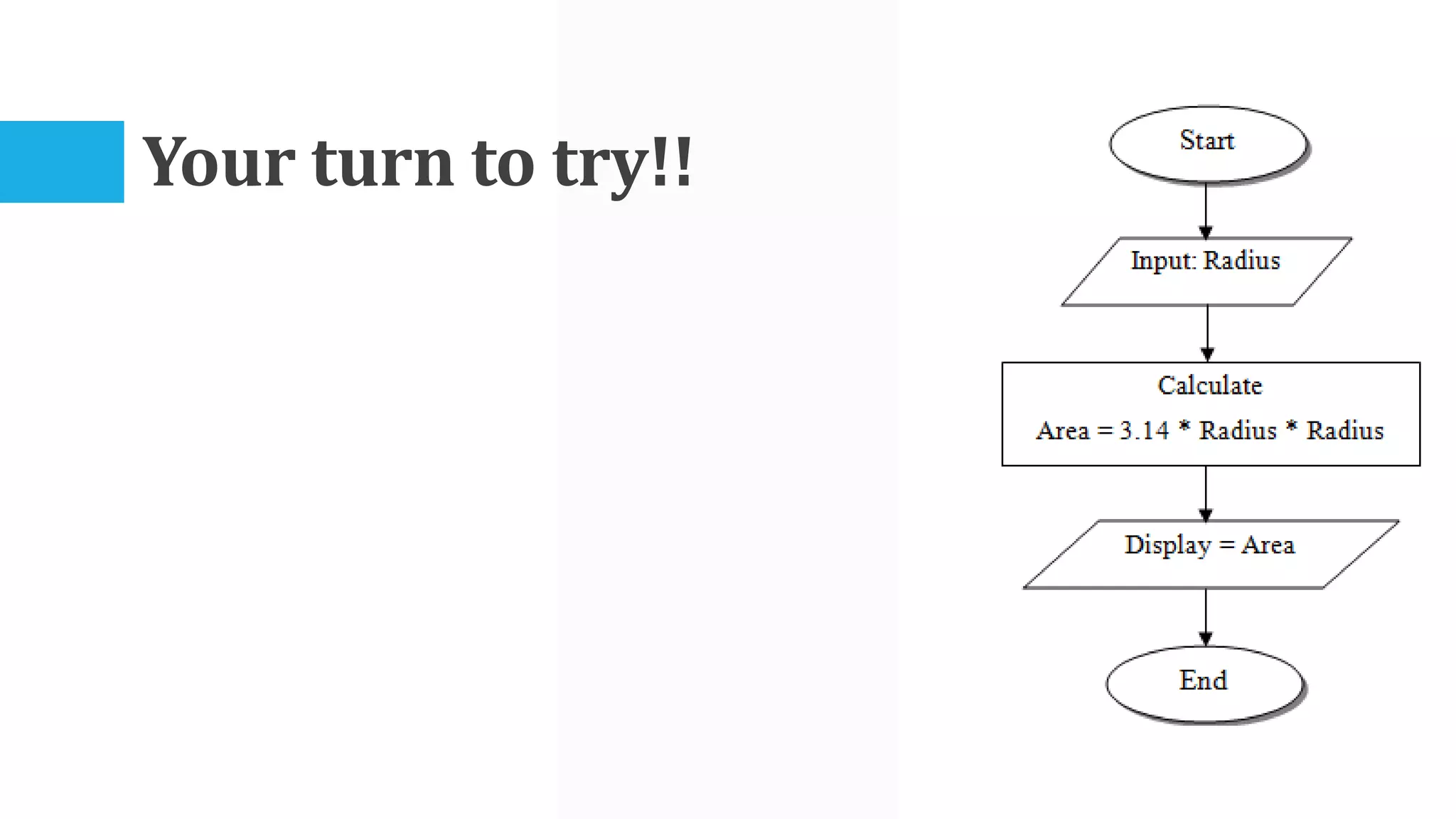
The algorithm involves taking Celsius temperature as input, multiplying it by 1.8 and adding 32 to convert it to Fahrenheit. This is implemented in a C program that takes Celsius input, performs the conversion calculation and prints the Fahrenheit output.