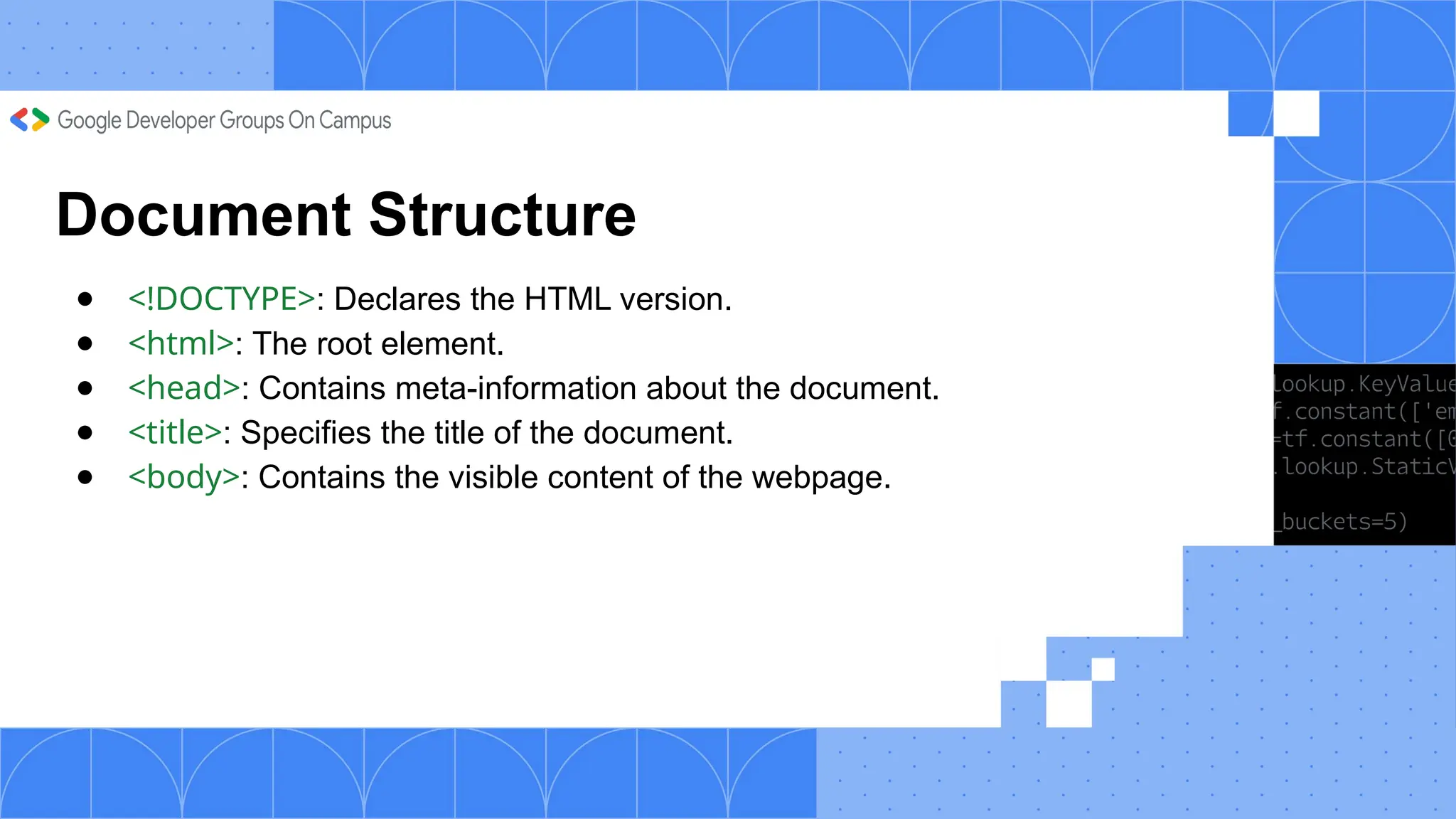
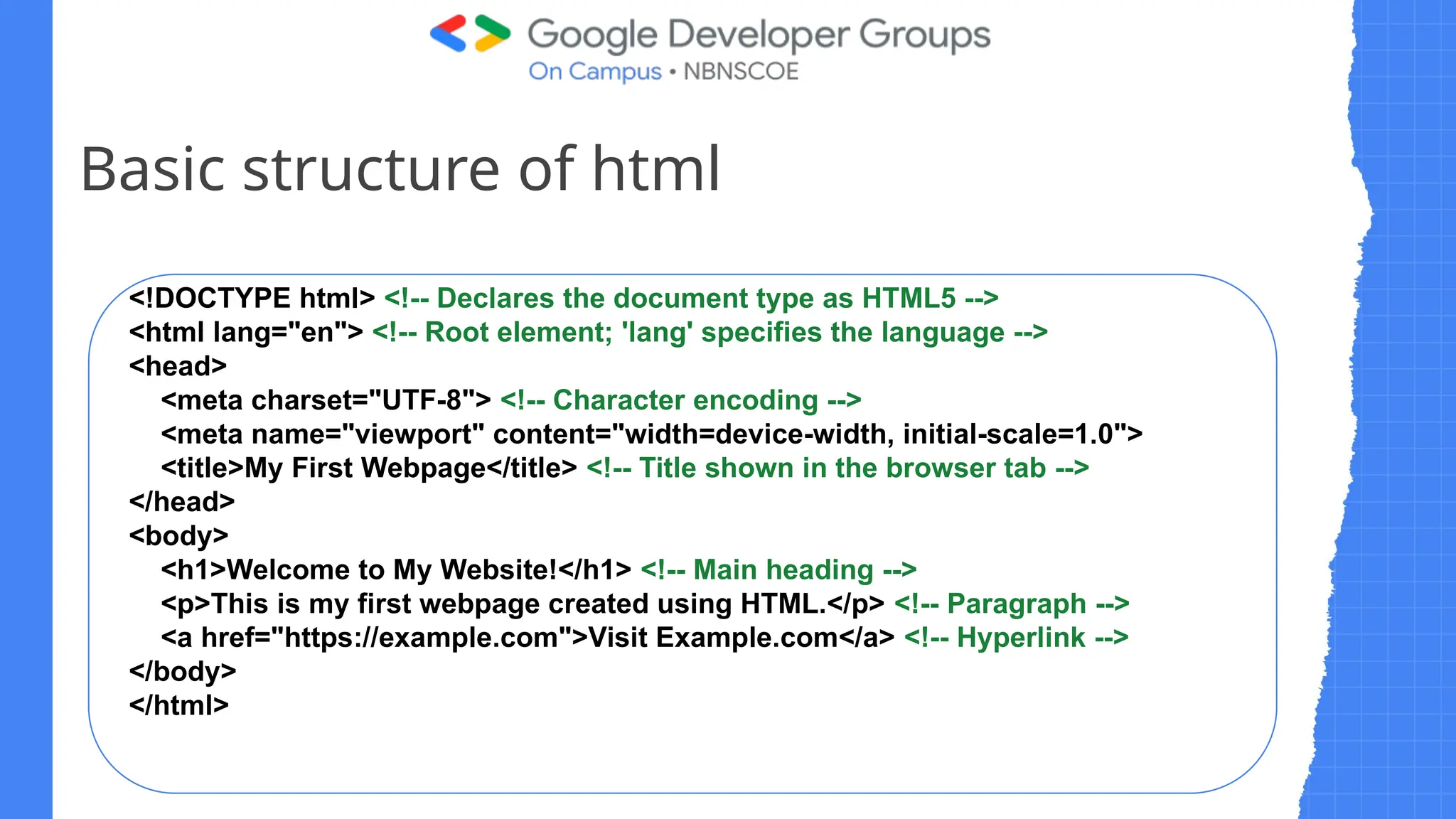
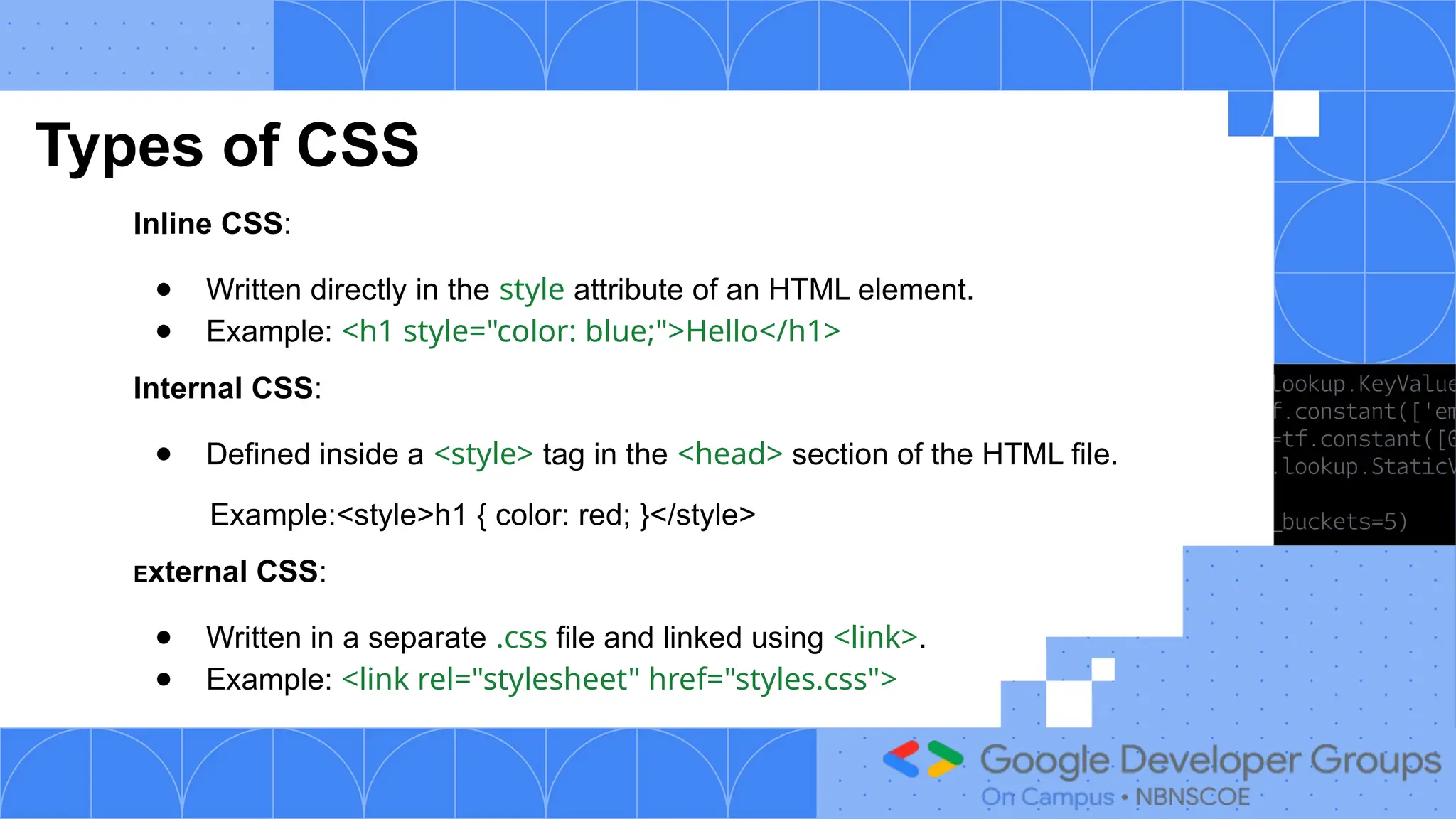
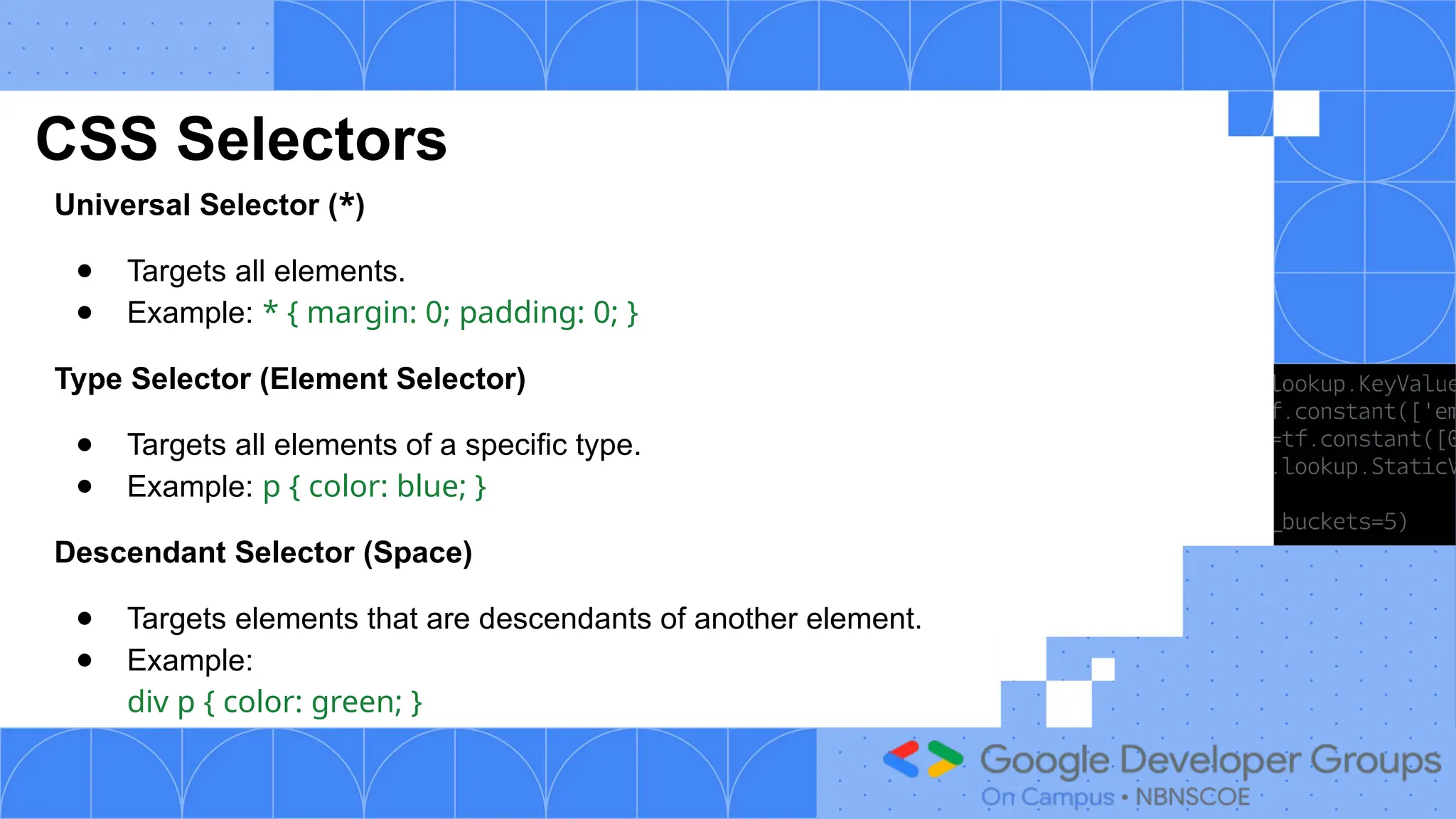
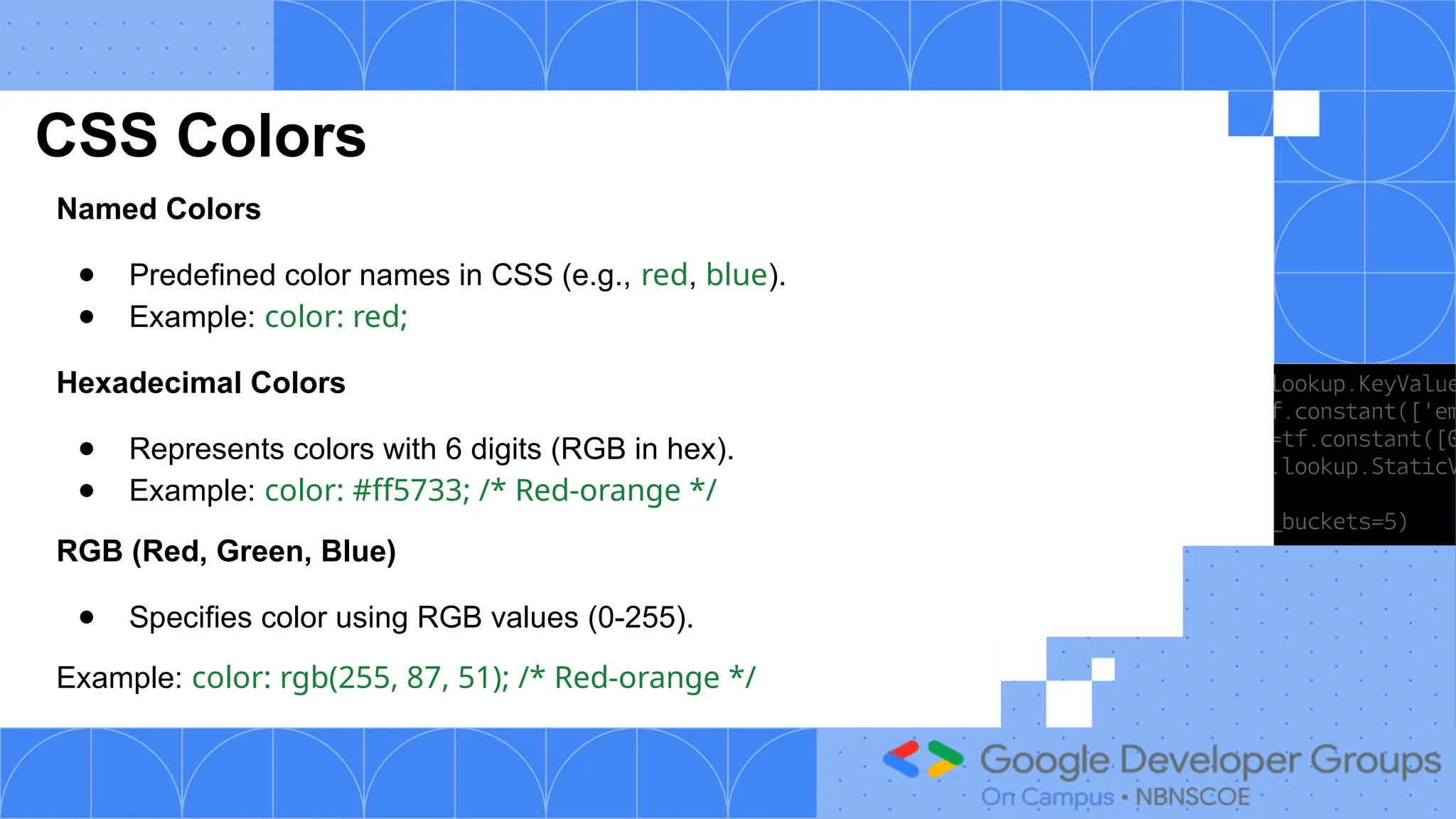
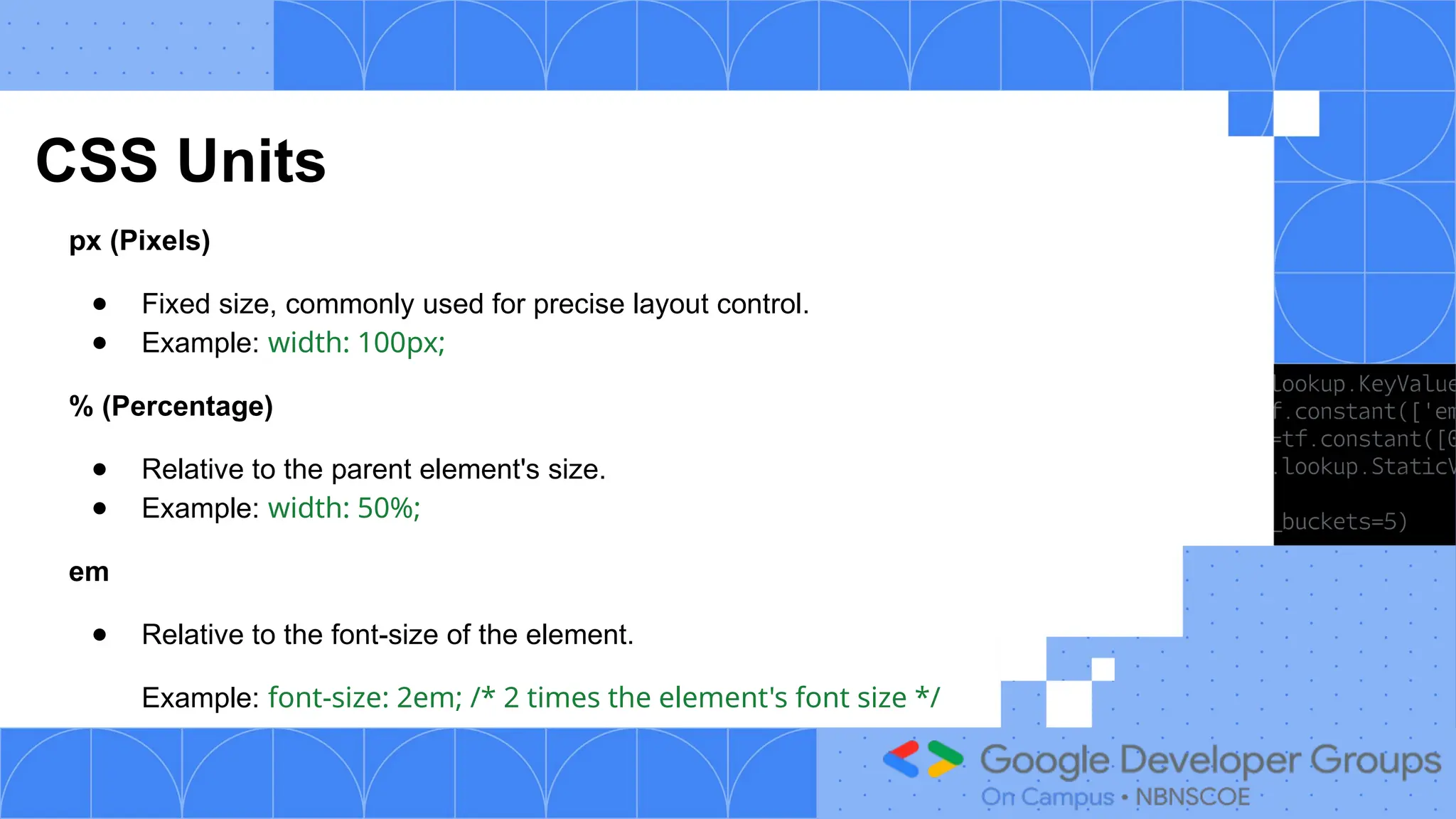
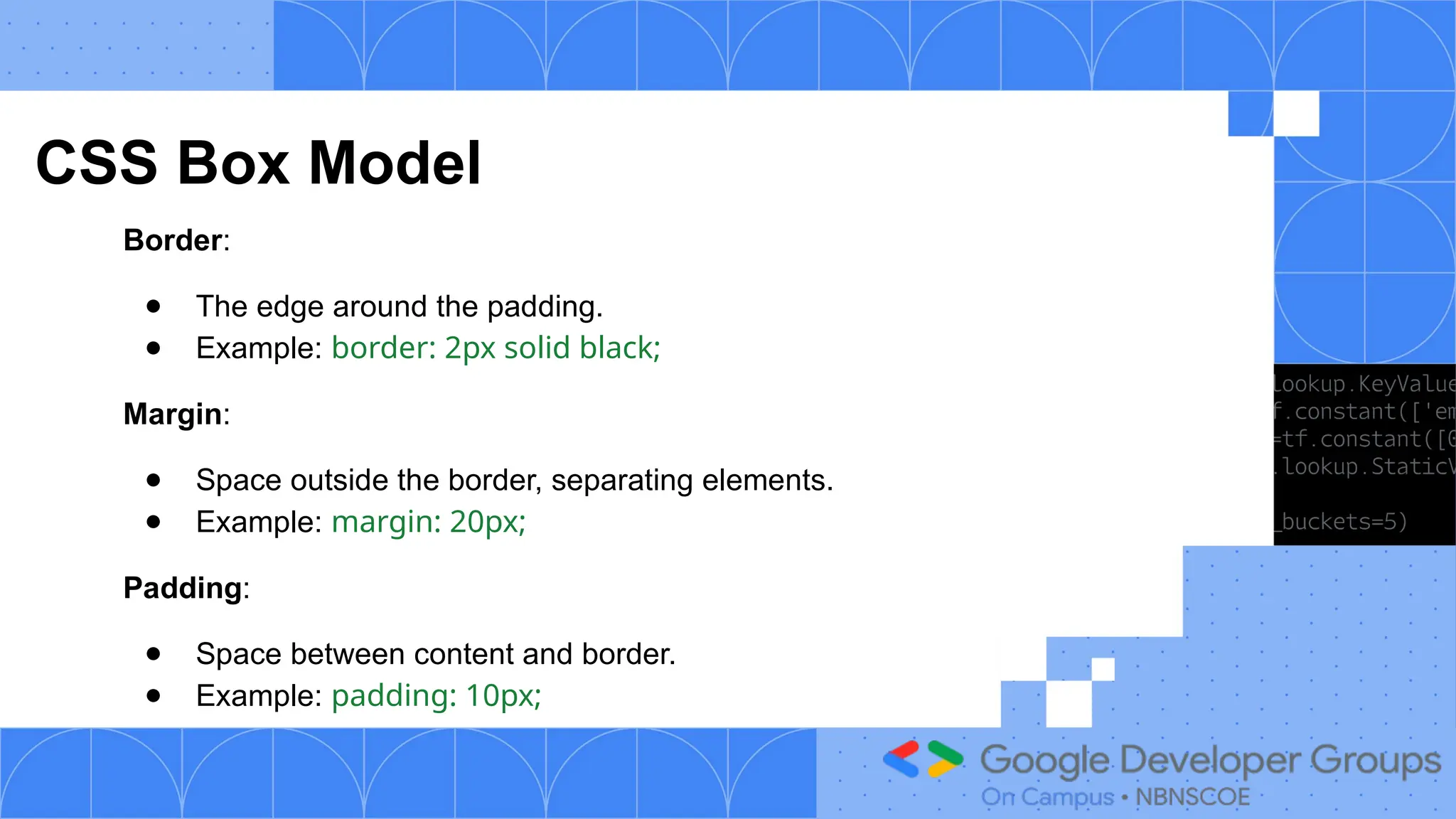
The document outlines a three-day web development workshop focused on HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React/Node.js, featuring speakers Mayuresh and Tanuja. It provides an introduction to HTML's structure, elements, and forms, as well as CSS's syntax, selectors, and layout models like Flexbox. Participants are encouraged to engage in tasks throughout the workshop and can access further updates via a WhatsApp channel.