Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) use two neural networks, a generator and discriminator, that compete against each other. The generator learns to generate fake images that look real, while the discriminator learns to tell real images apart from fakes. This document discusses various GAN architectures and applications, including conditional GANs, image-to-image translation, style transfer, semantic image editing, and data augmentation using GAN-generated images. It also covers evaluation metrics for GANs and societal impacts such as bias and deepfakes.







![25
Papers and Websites
• Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization (Park, Liu, Wang, and Zhu, 2019): https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.07291
• Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network (Ledig et al., 2017): https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04802
• Multimodal Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation (Huang et al., 2018): https://github.com/NVlabs/MUNIT
• StackGAN: Text to Photo-realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks (Zhang et al., 2017): https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03242
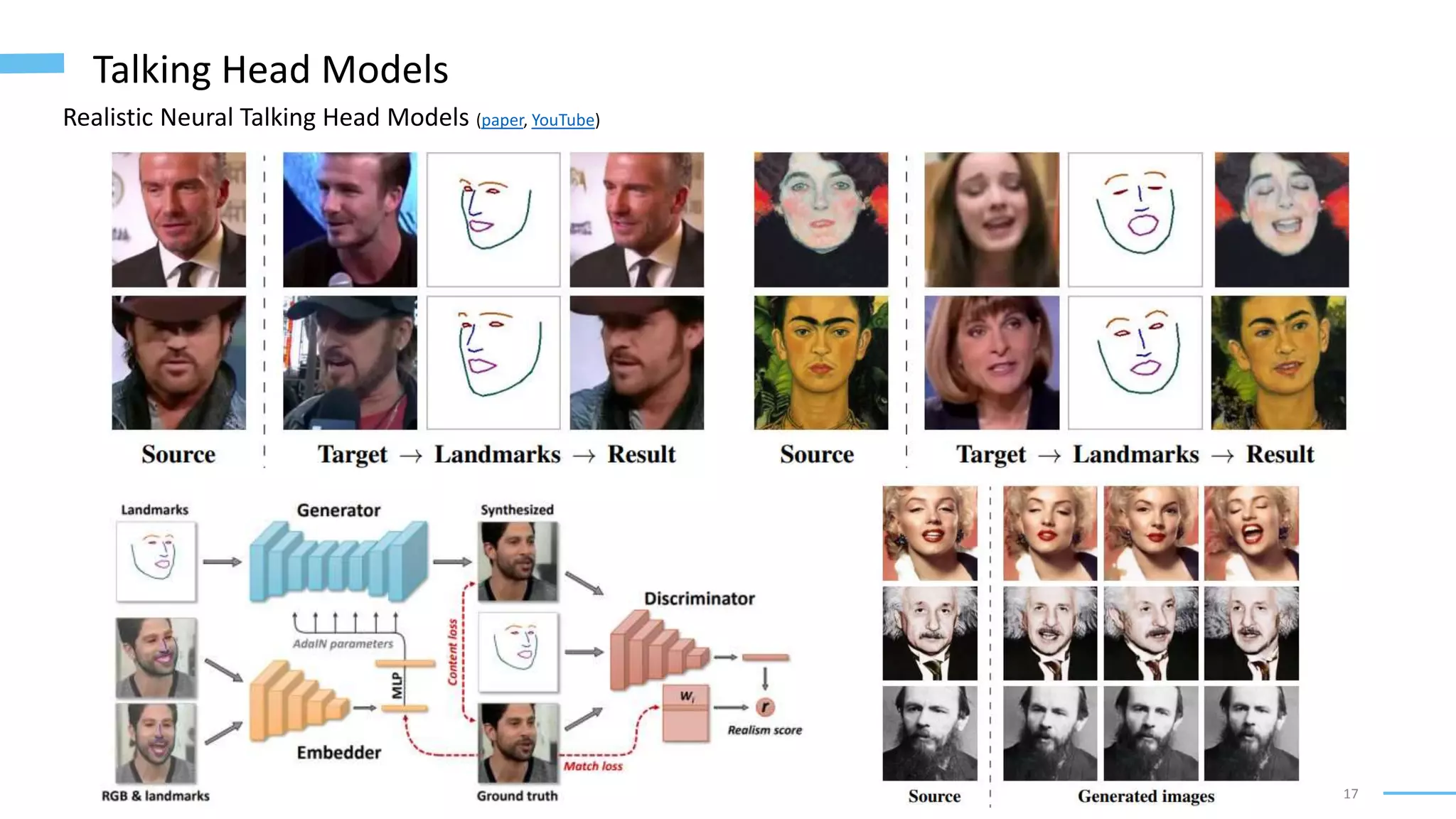
• Few-Shot Adversarial Learning of Realistic Neural Talking Head Models (Zakharov, Shysheya, Burkov, and Lempitsky, 2019): https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.08233
• Snapchat: https://www.snapchat.com
• MaskGAN: Towards Diverse and Interactive Facial Image Manipulation (Lee, Liu, Wu, and Luo, 2020): https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11922
• When AI generated paintings dance to music... (2019): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=85l961MmY8Y
• Data Augmentation Generative Adversarial Networks (Antoniou, Storkey, and Edwards, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.04340
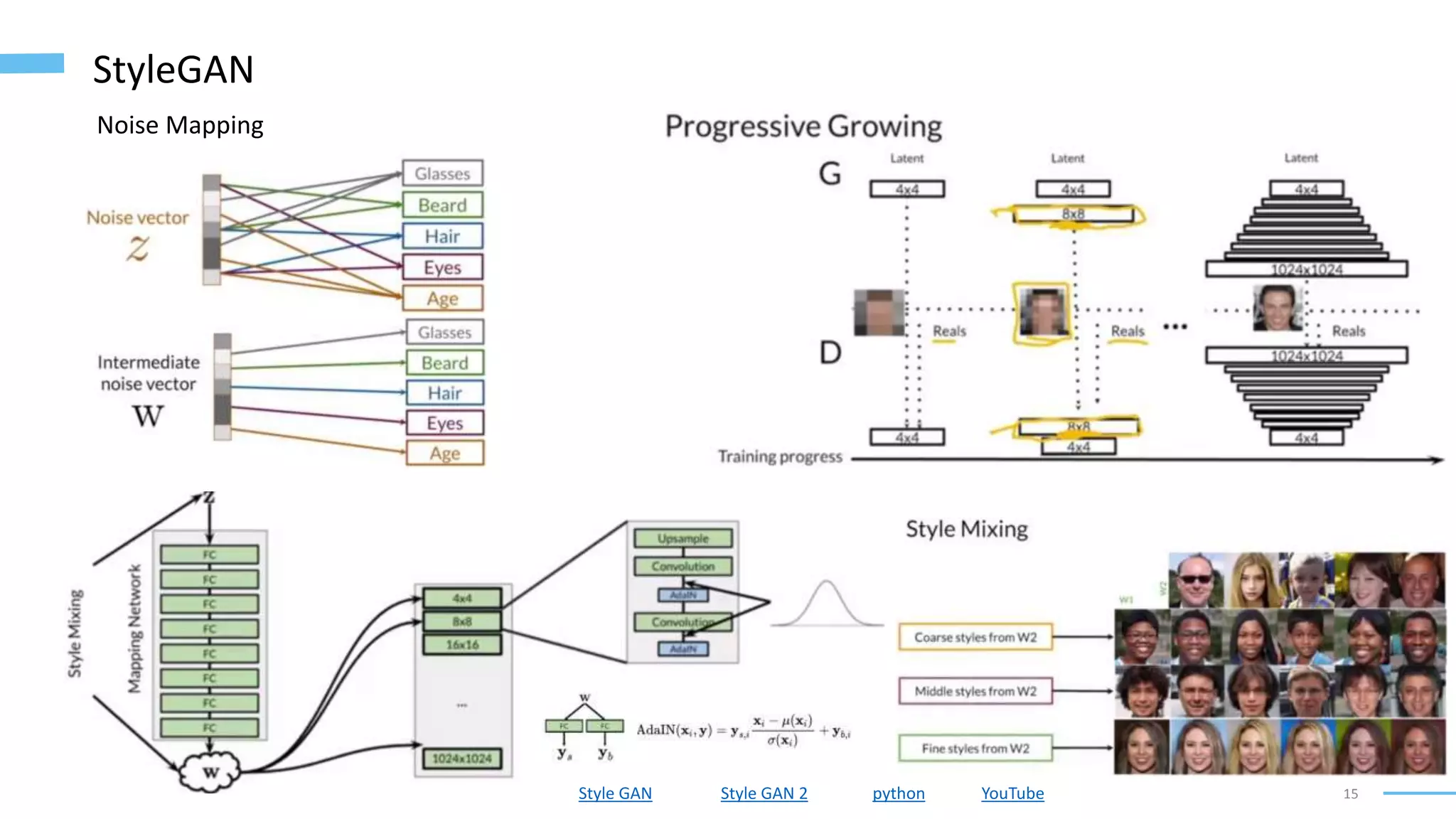
• Training progression of StyleGAN on H&E tissue fragments (Zhou, 2019): https://twitter.com/realSharonZhou/status/1182877446690852867
• Establishing an evaluation metric to quantify climate change image realism (Sharon Zhou, Luccioni, Cosne, Bernstein, and Bengio, 2020): https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2632-2153/ab7657/meta
• Deepfake example (2019): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Deepfake_example.gif
• Introduction to adversarial robustness (Kolter and Madry): https://adversarial-ml-tutorial.org/introduction/
• Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis (Brock, Donahue, and Simonyan, 2019): https://openreview.net/pdf?id=B1xsqj09Fm
• GazeGAN - Unpaired Adversarial Image Generation for Gaze Estimation (Sela, Xu, He, Navalpakkam, and Lagun, 2017): https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09767
• Data Augmentation using GANs for Speech Emotion Recognition (Chatziagapi et al., 2019): https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/395b/ea6f025e599db710893acb6321e2a1898a1f.pdf
• GAN-based Synthetic Medical Image Augmentation for increased CNN Performance in Liver Lesion Classification (Frid-Adar et al., 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01229
• GANsfer Learning: Combining labelled and unlabelled data for GAN based data augmentation (Bowles, Gunn, Hammers, and Rueckert, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.10669
• Data augmentation using generative adversarial networks (CycleGAN) to improve generalizability in CT segmentation tasks (Sandfort, Yan, Pickhardt, and Summers, 2019): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-52737-
x/figures/3
• De-identification without losing faces (Li and Lyu, 2019): https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.04202
• Privacy-Preserving Generative Deep Neural Networks Support Clinical Data Sharing (Beaulieu-Jones et al., 2019): https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epub/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005122
• DeepPrivacy: A Generative Adversarial Network for Face Anonymization (Hukkelås, Mester, and Lindseth, 2019): https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.04538
• GAIN: Missing Data Imputation using Generative Adversarial Nets (Yoon, Jordon, and van der Schaar, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.02920
• Conditional Infilling GANs for Data Augmentation in Mammogram Classification (E. Wu, K. Wu, Cox, and Lotter, 2018): https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-00946-5_11
• The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation in Image Classification using Deep Learning (Perez and Wang, 2017): https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.04621
• CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 Dataset; Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images (Krizhevsky, 2009): https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/learning-features-2009-TR.pdf
• DeOldify... (Antic, 2019): https://twitter.com/citnaj/status/1124904251128406016
• pix2pixHD (Wang et al., 2018): https://github.com/NVIDIA/pix2pixHD
• [4k, 60 fps] Arrival of a Train at La Ciotat (The Lumière Brothers, 1896) (Shiryaev, 2020): https://youtu.be/3RYNThid23g
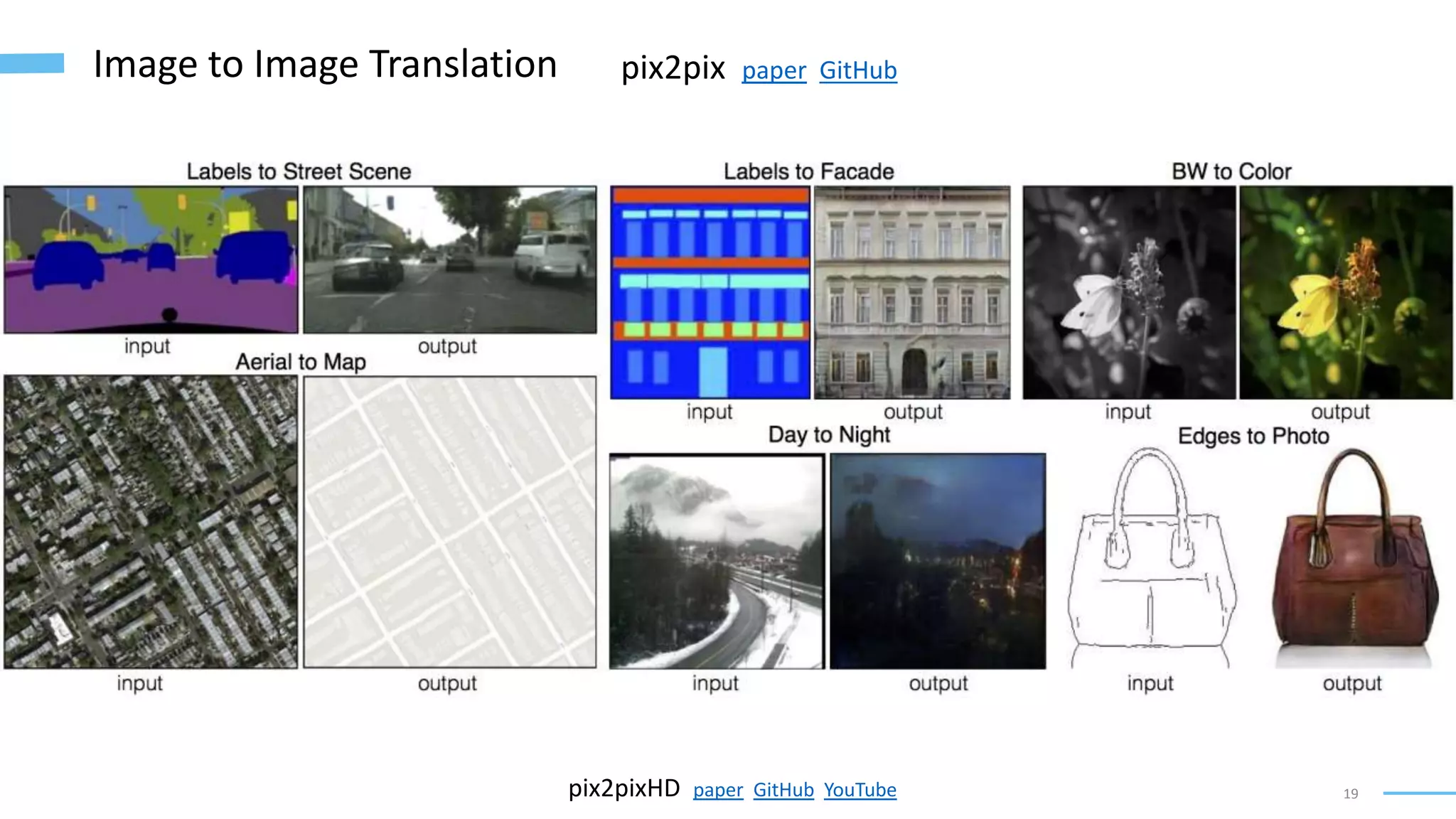
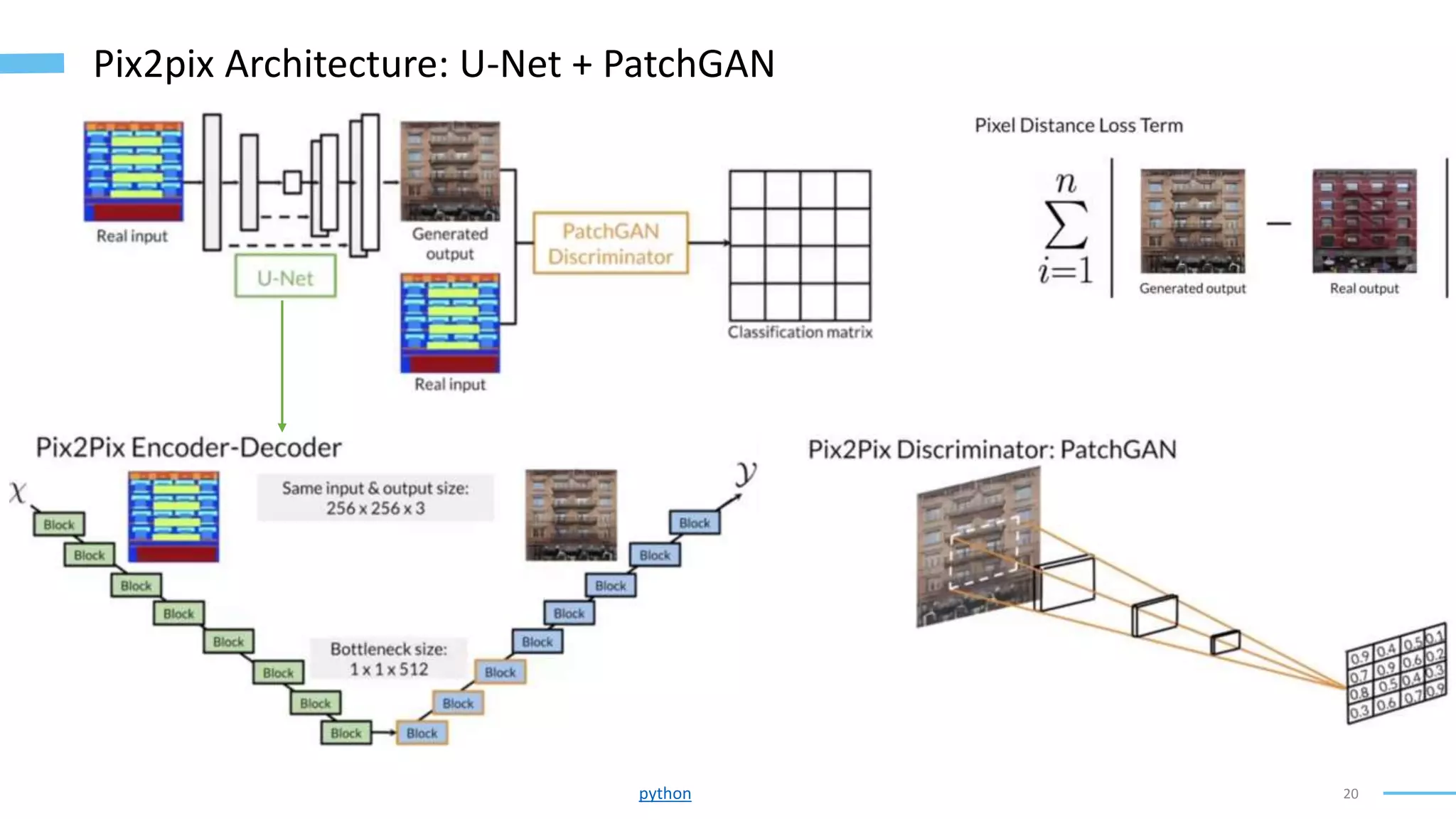
• Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks (Isola, Zhu, Zhou, and Efros, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004
• Pose Guided Person Image Generation (Ma et al., 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.09368
• AttnGAN: Fine-Grained Text to Image Generation with Attentional Generative Adversarial Networks (Xu et al., 2017): https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10485
• Few-Shot Adversarial Learning of Realistic Neural Talking Head Models (Zakharov, Shysheya, Burkov, and Lempitsky, 2019): https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.08233
• Patch-Based Image Inpainting with Generative Adversarial Networks (Demir and Unal, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.07422
• Image Segmentation Using DIGITS 5 (Heinrich, 2016): https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/image-segmentation-using-digits-5/
• Stroke of Genius: GauGAN Turns Doodles into Stunning, Photorealistic Landscapes (Salian, 2019): https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2019/03/18/gaugan-photorealistic-landscapes-nvidia-research/
• Crowdsourcing the creation of image segmentation algorithms for connectomics (Arganda-Carreras et al., 2015): https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnana.2015.00142/full
• U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation (Ronneberger, Fischer, and Brox, 2015): https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
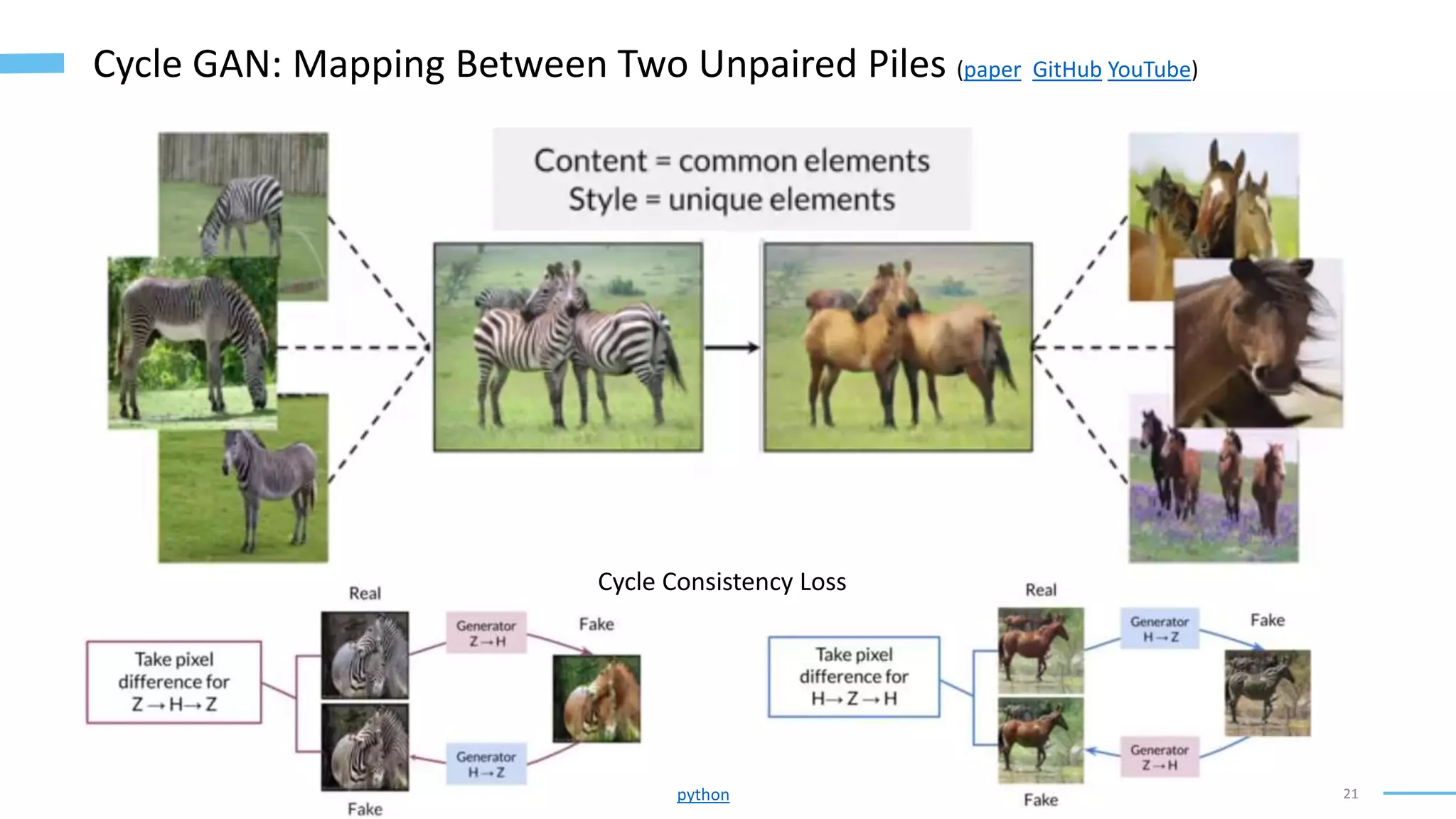
• Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks (Zhu, Park, Isola, and Efros, 2020): https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.10593
• PyTorch implementation of CycleGAN (2017): https://github.com/togheppi/CycleGAN
• Distribution Matching Losses Can Hallucinate Features in Medical Image Translation (Cohen, Luck, and Honari, 2018): https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.08841
• Data augmentation using generative adversarial networks (CycleGAN) to improve generalizability in CT segmentation tasks (Sandfort, Yan, Pickhardt, and Summers, 2019): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-52737-x.pdf
• Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation (NVIDIA, 2018): https://github.com/mingyuliutw/UNIT
• Multimodal Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation (Huang et al., 2018): https://github.com/NVlabs/MUNIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generativeadversarialnetworks-220212125010/75/Generative-adversarial-networks-25-2048.jpg)