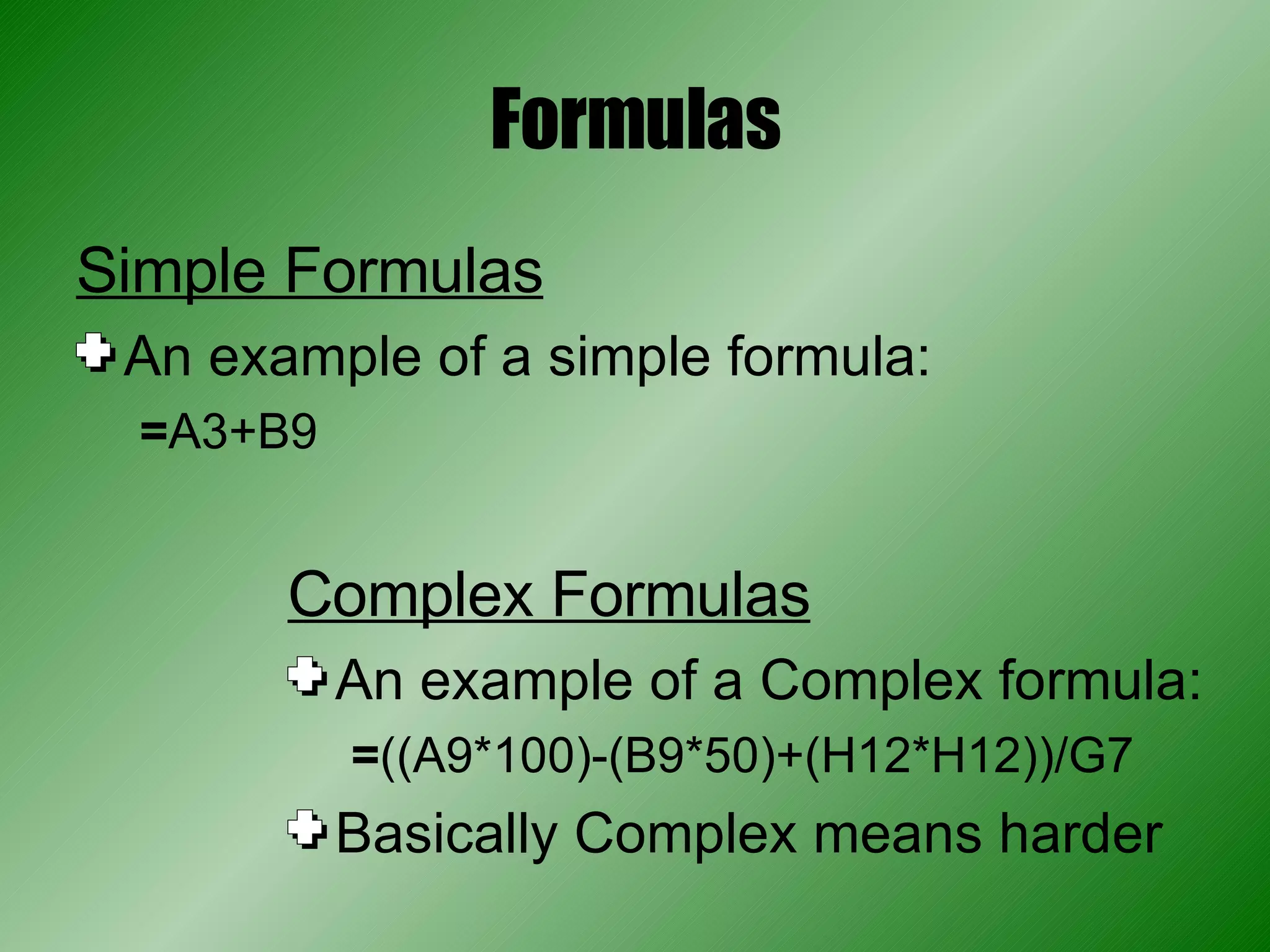
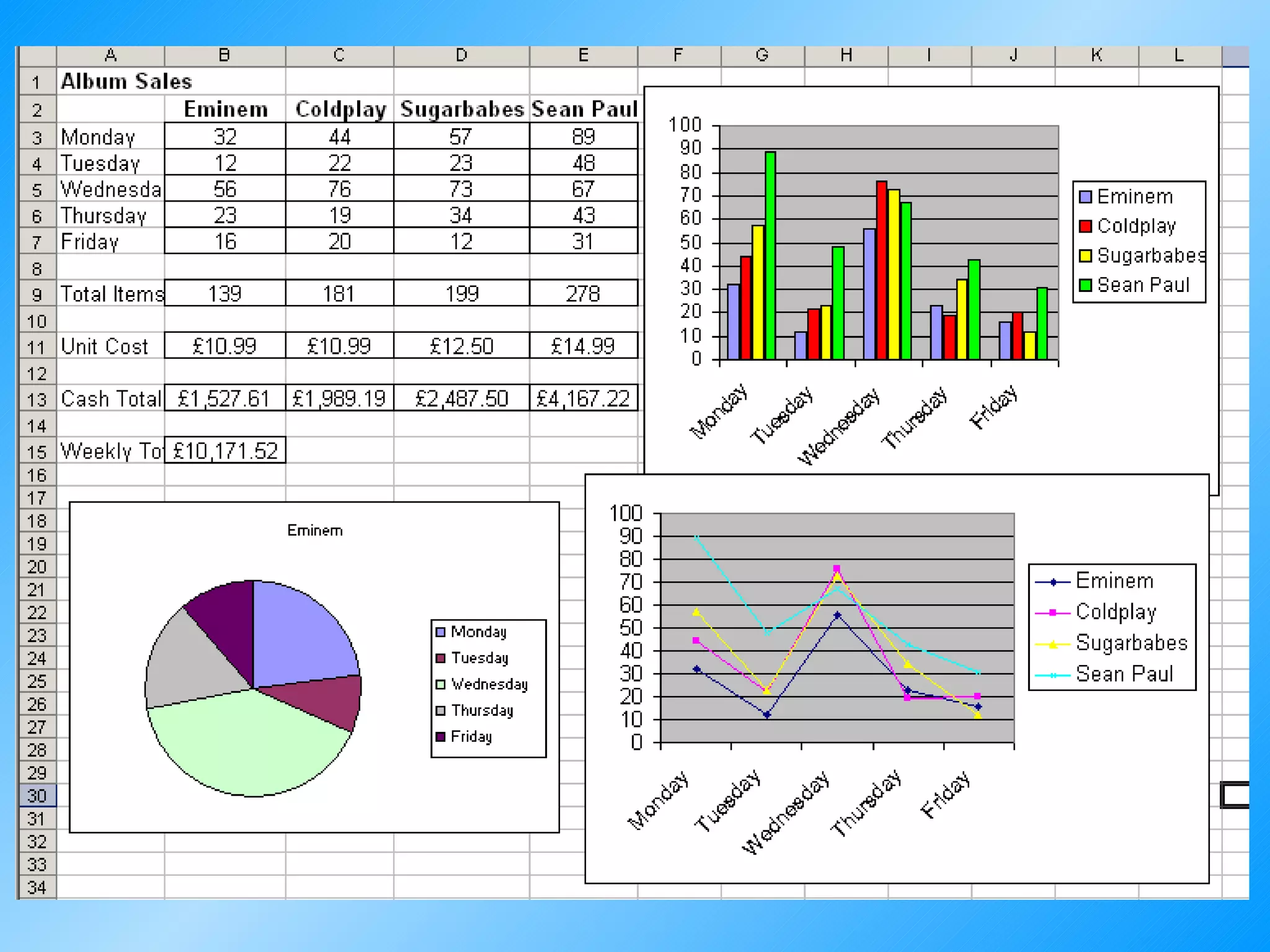
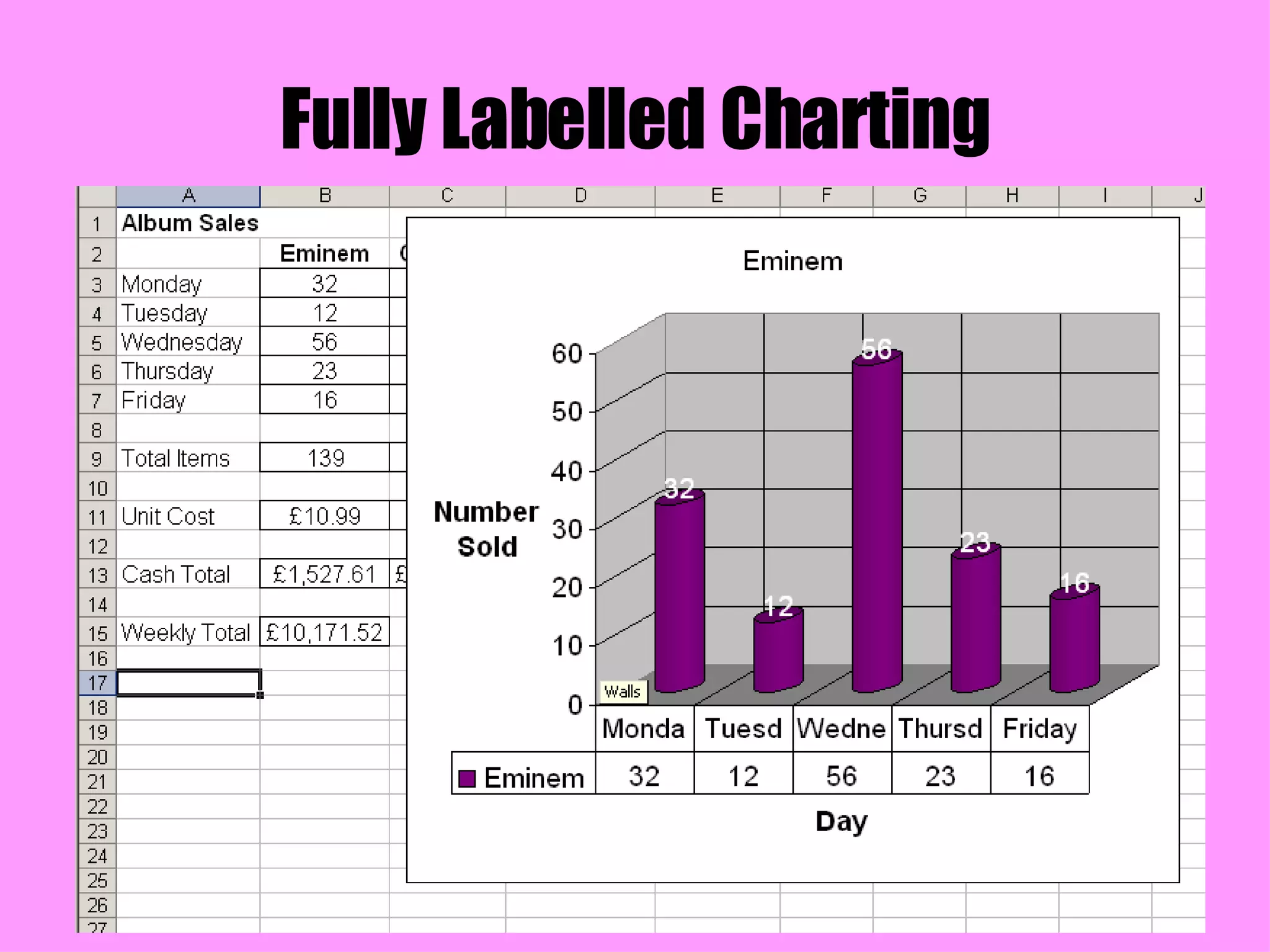
Spreadsheets are used to record and calculate numerical data through formulas in cells organized into rows and columns. Formulas can perform basic math operations and more complex calculations by referencing values in other cells. Spreadsheet programs offer formatting options, functions, charting capabilities, and other features to analyze and present calculated data.