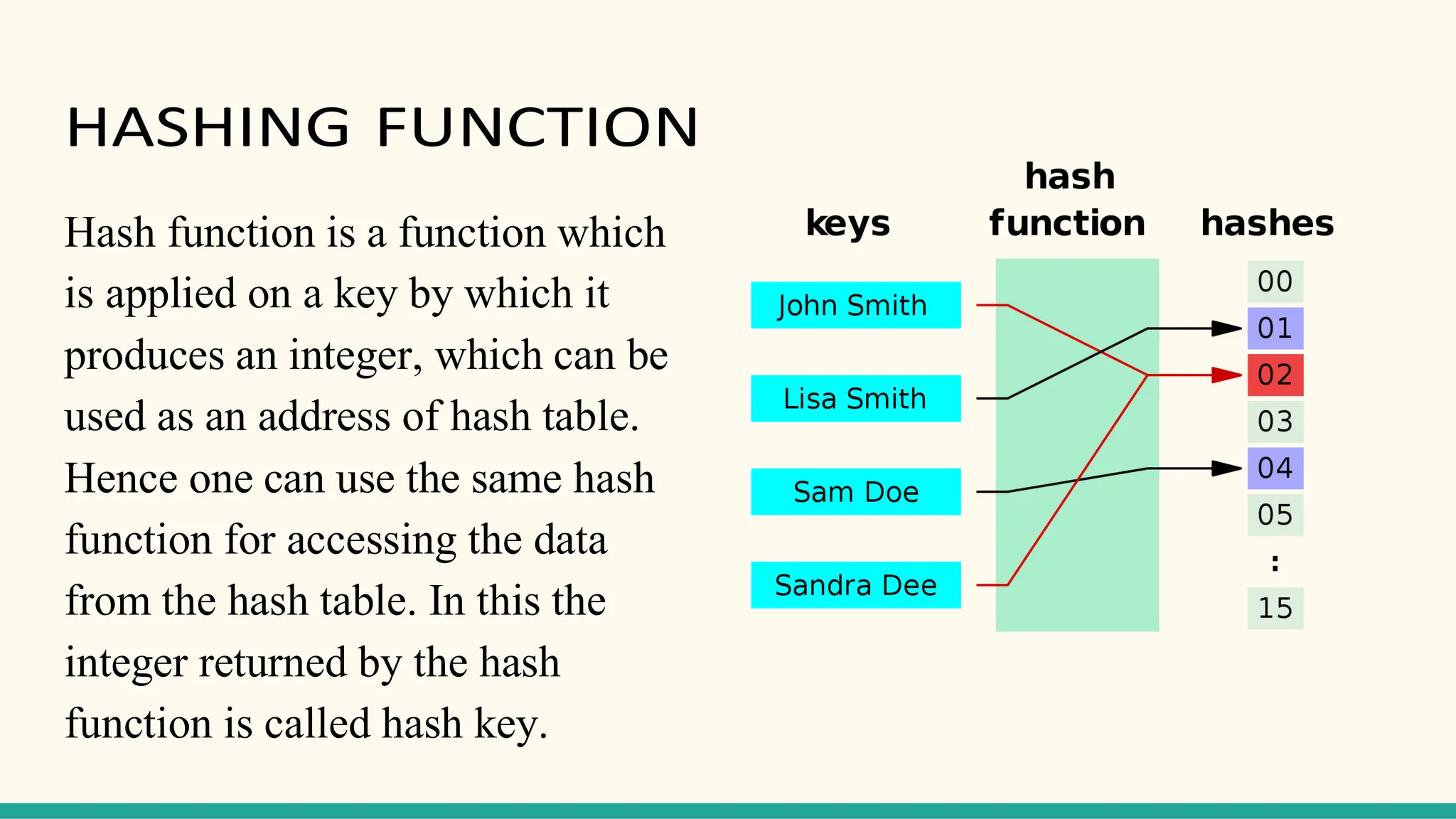
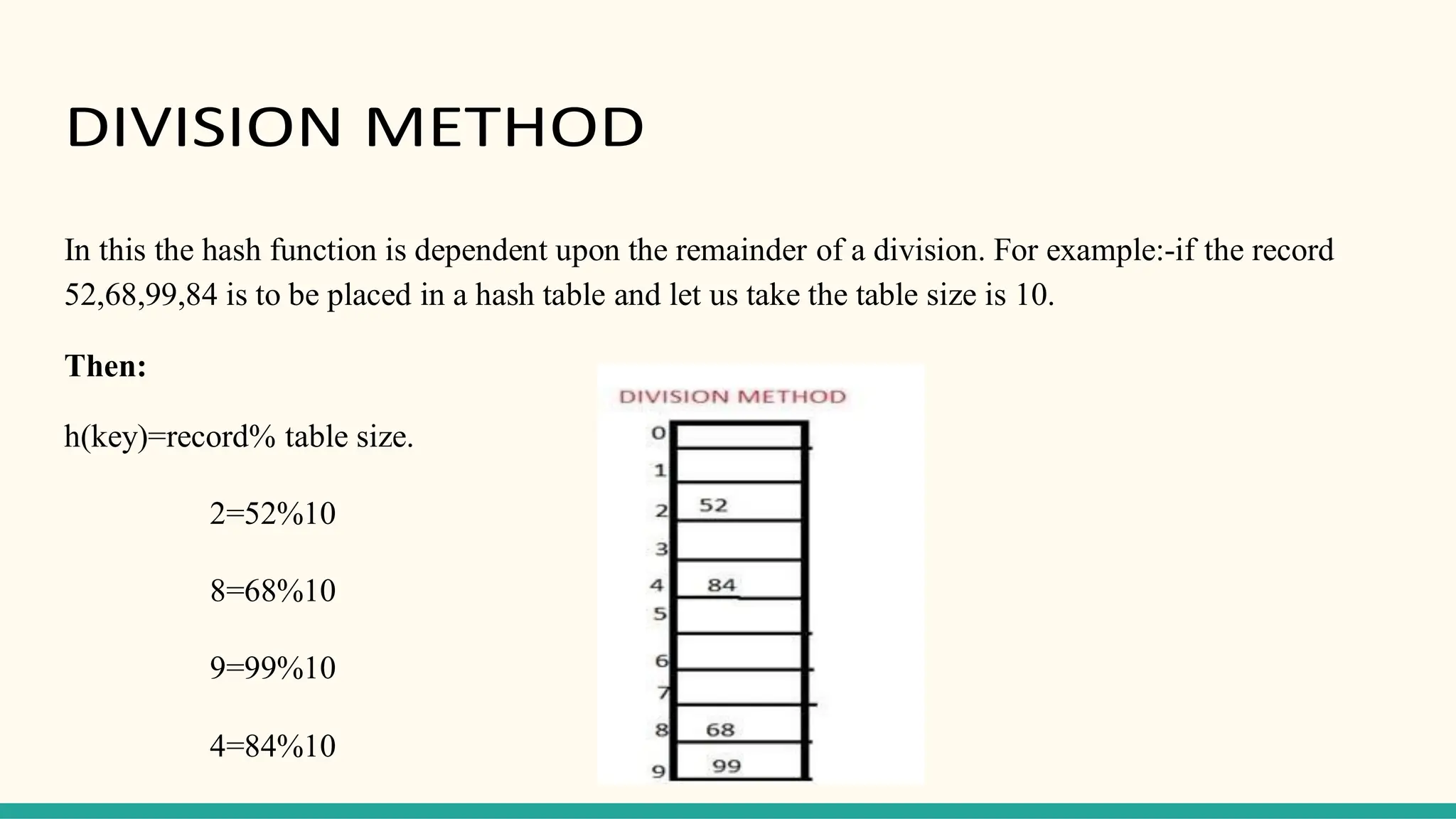
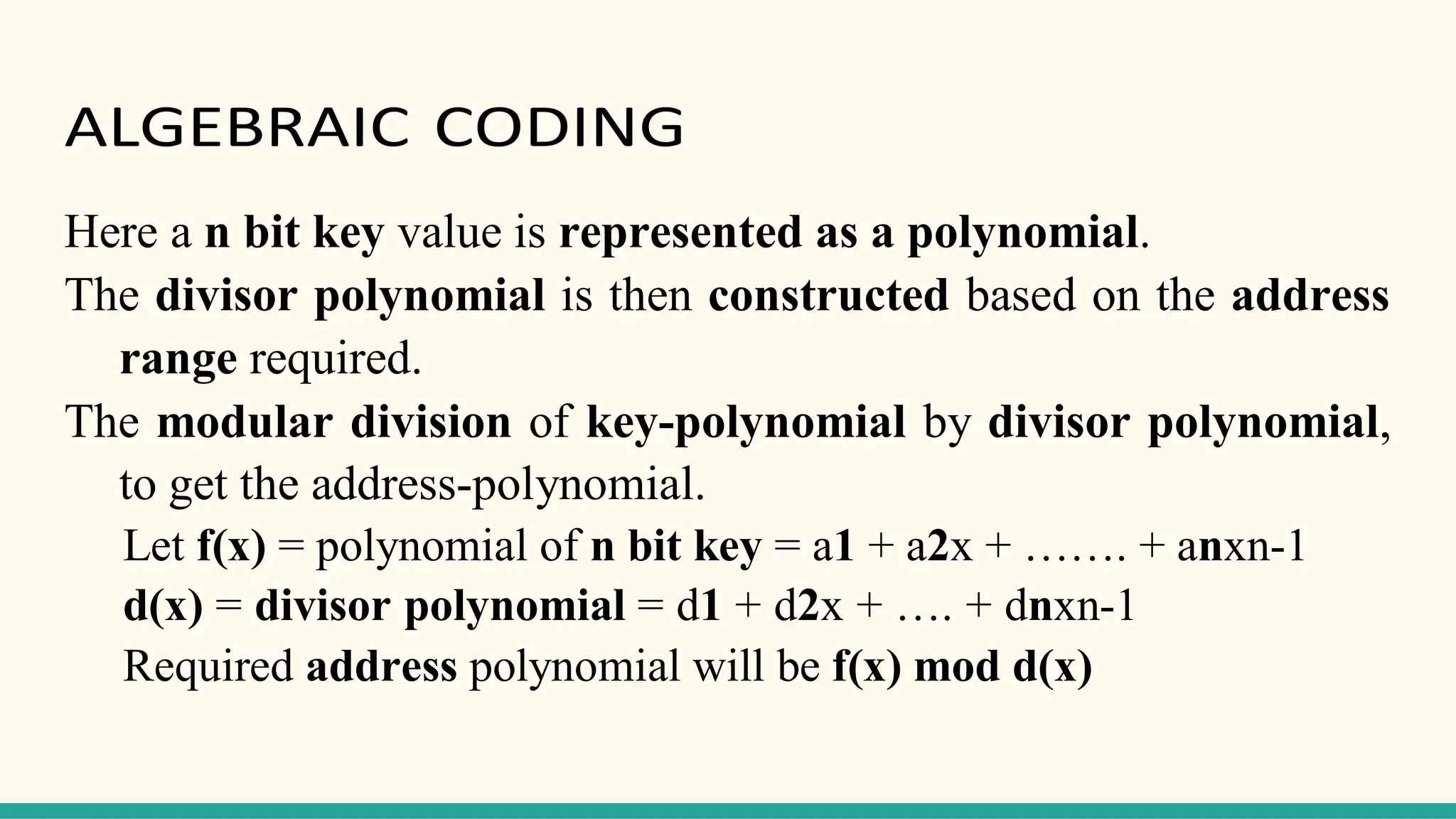
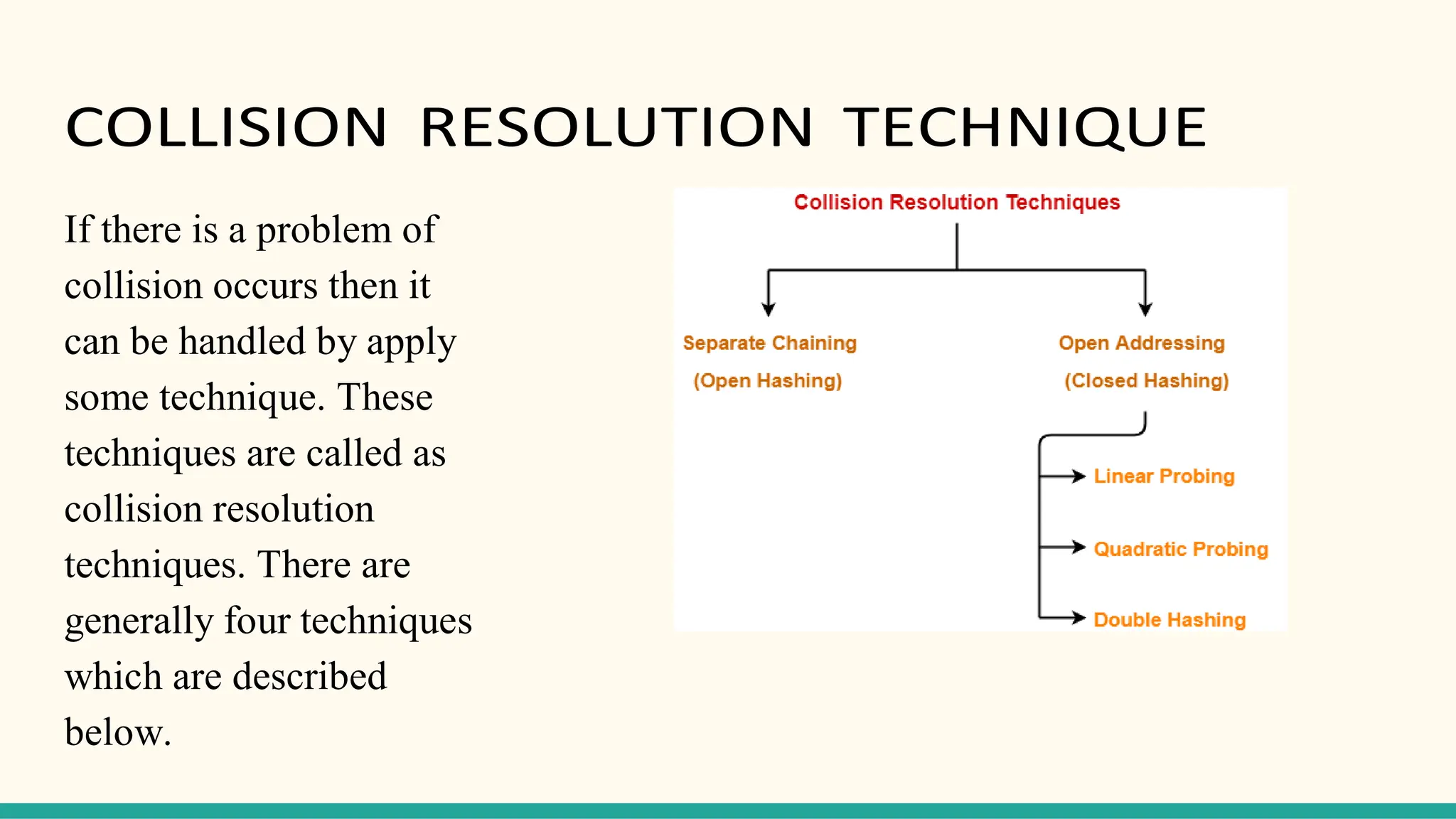
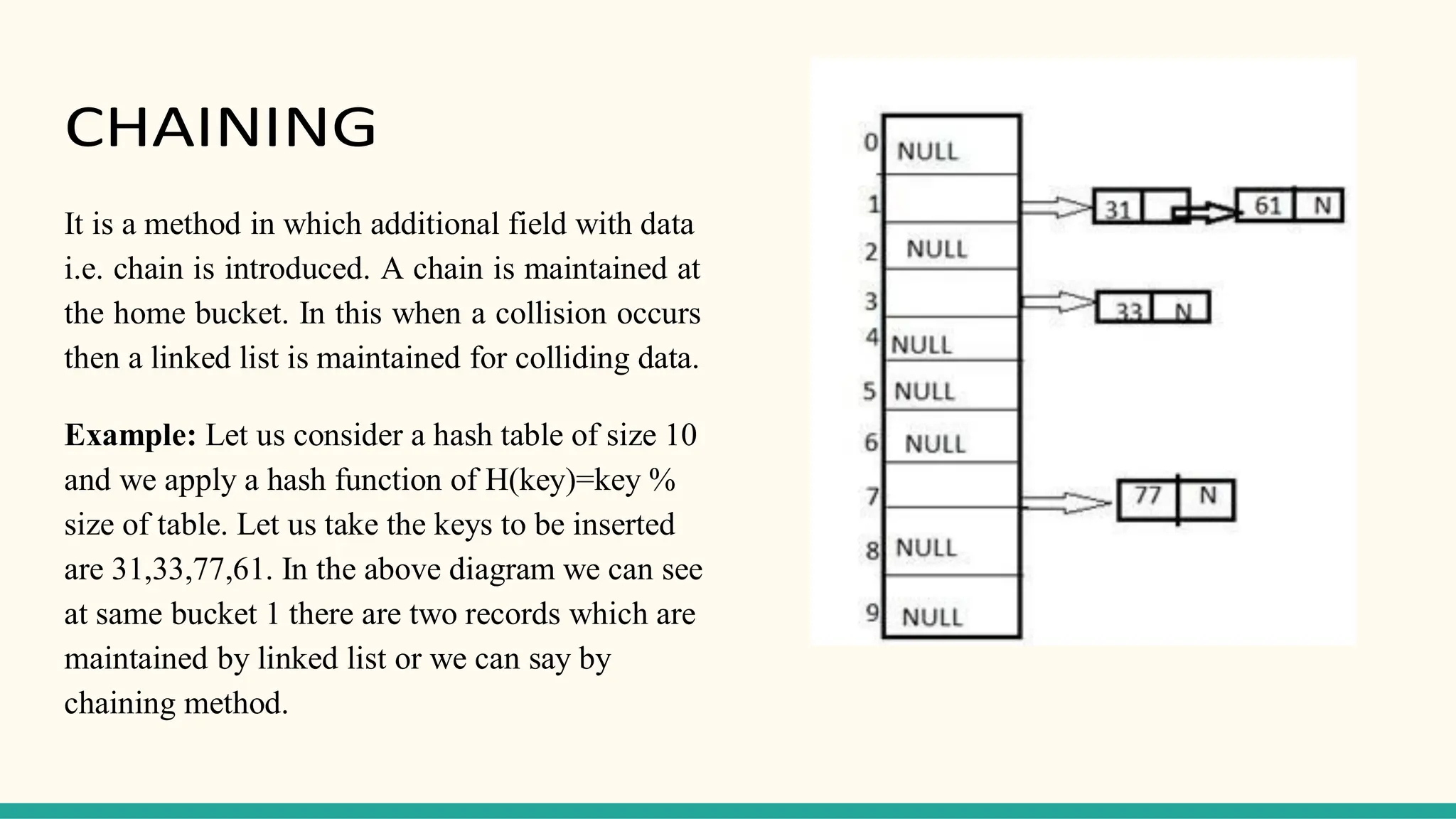
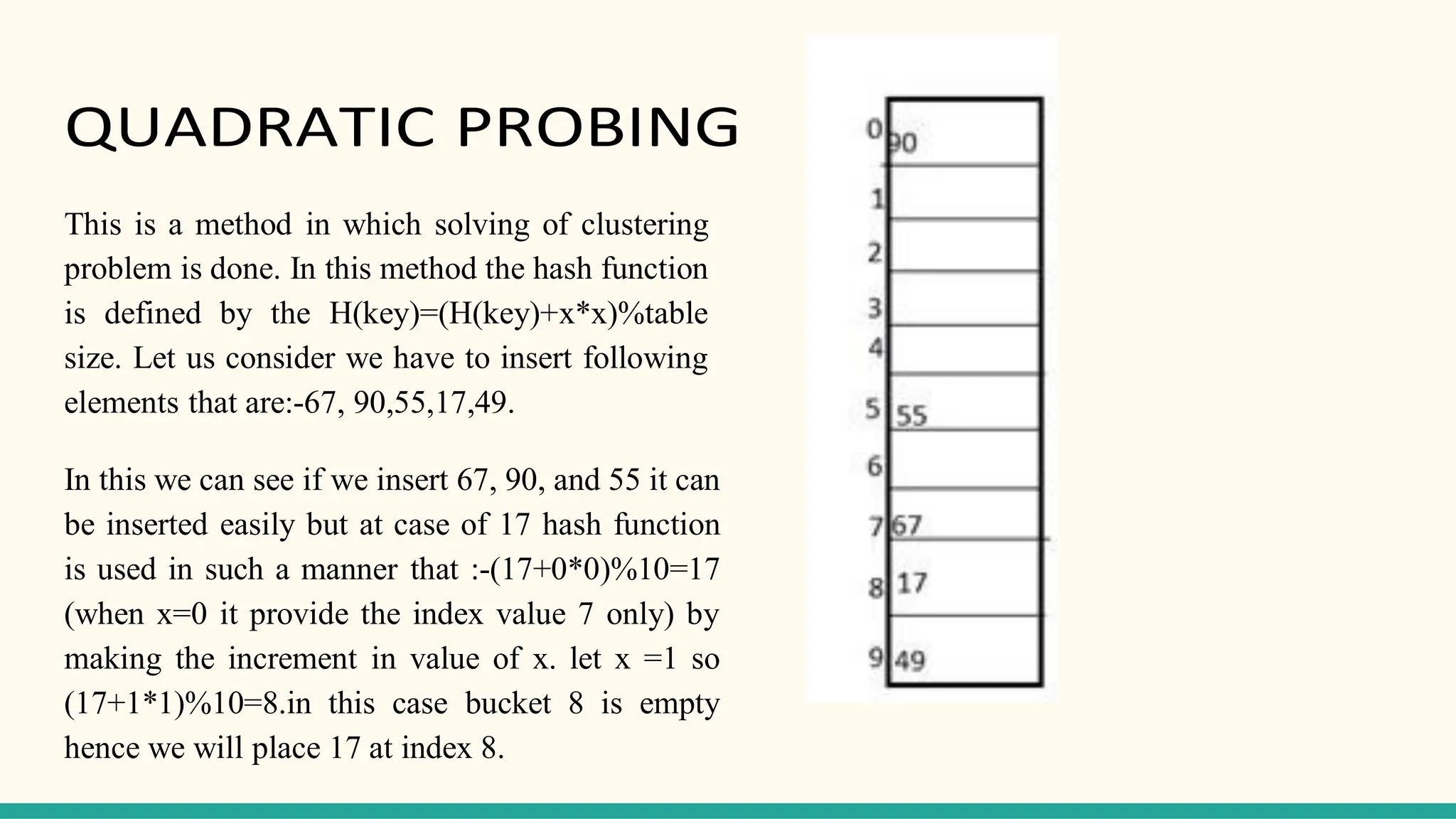
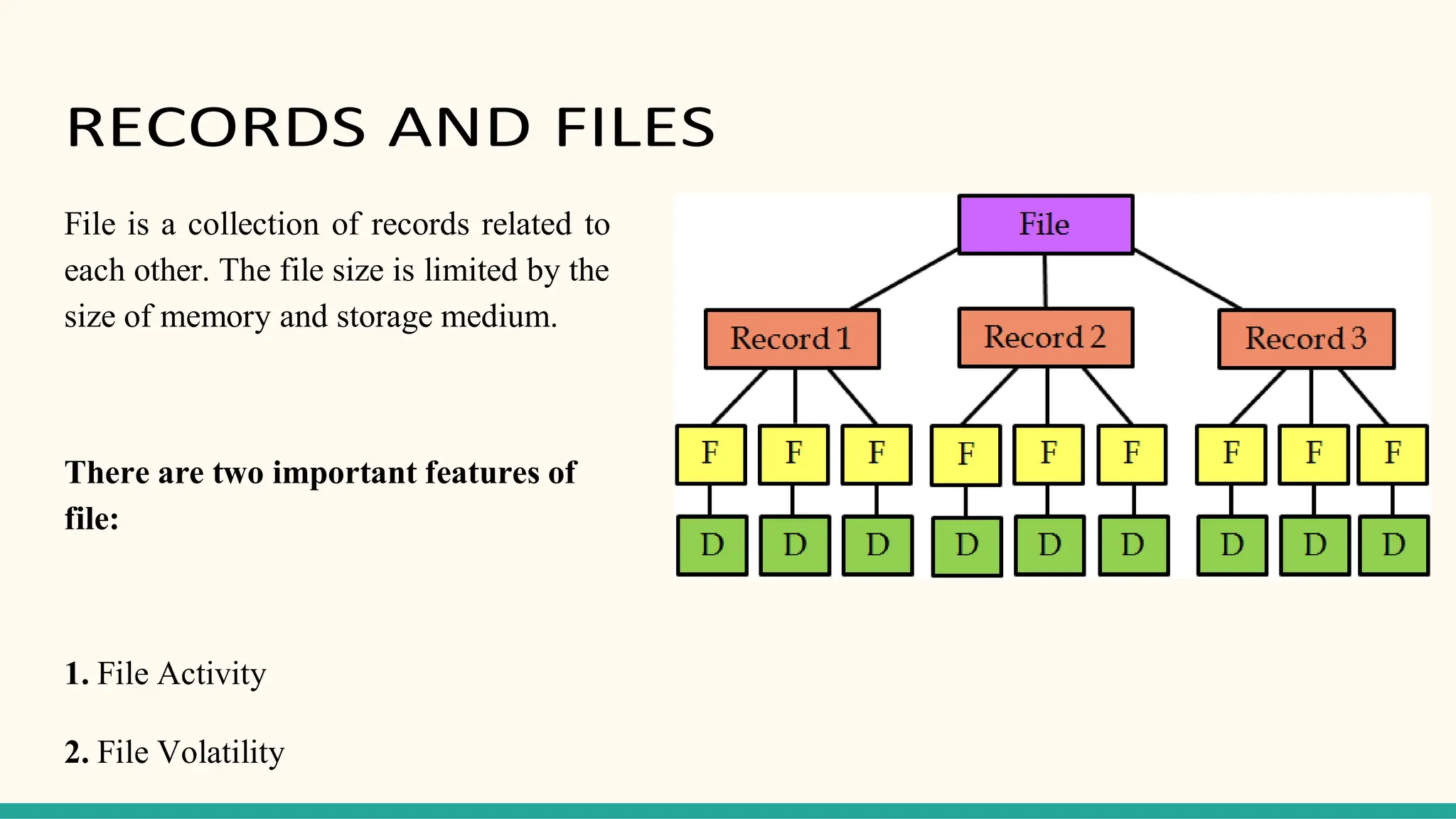
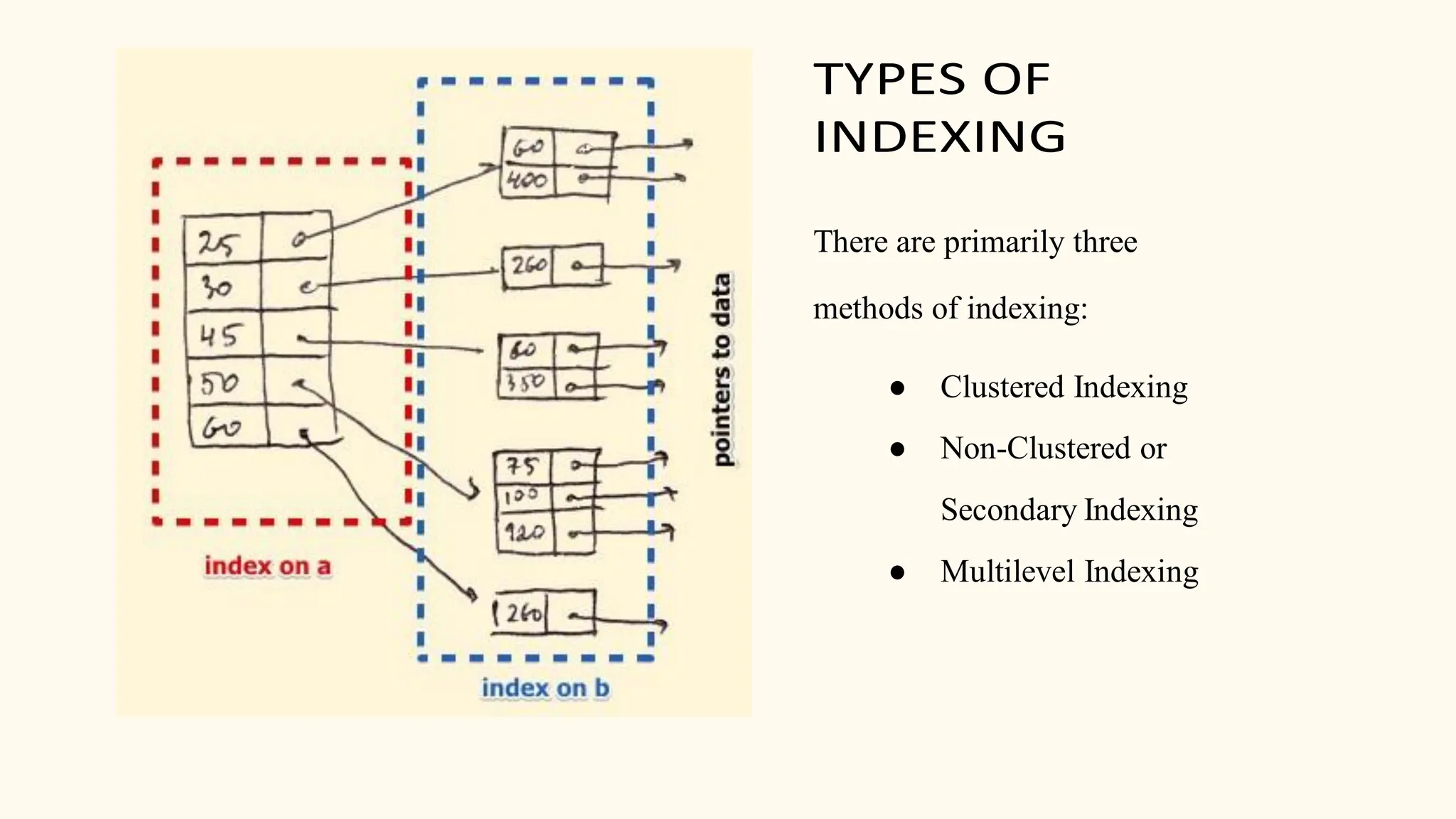
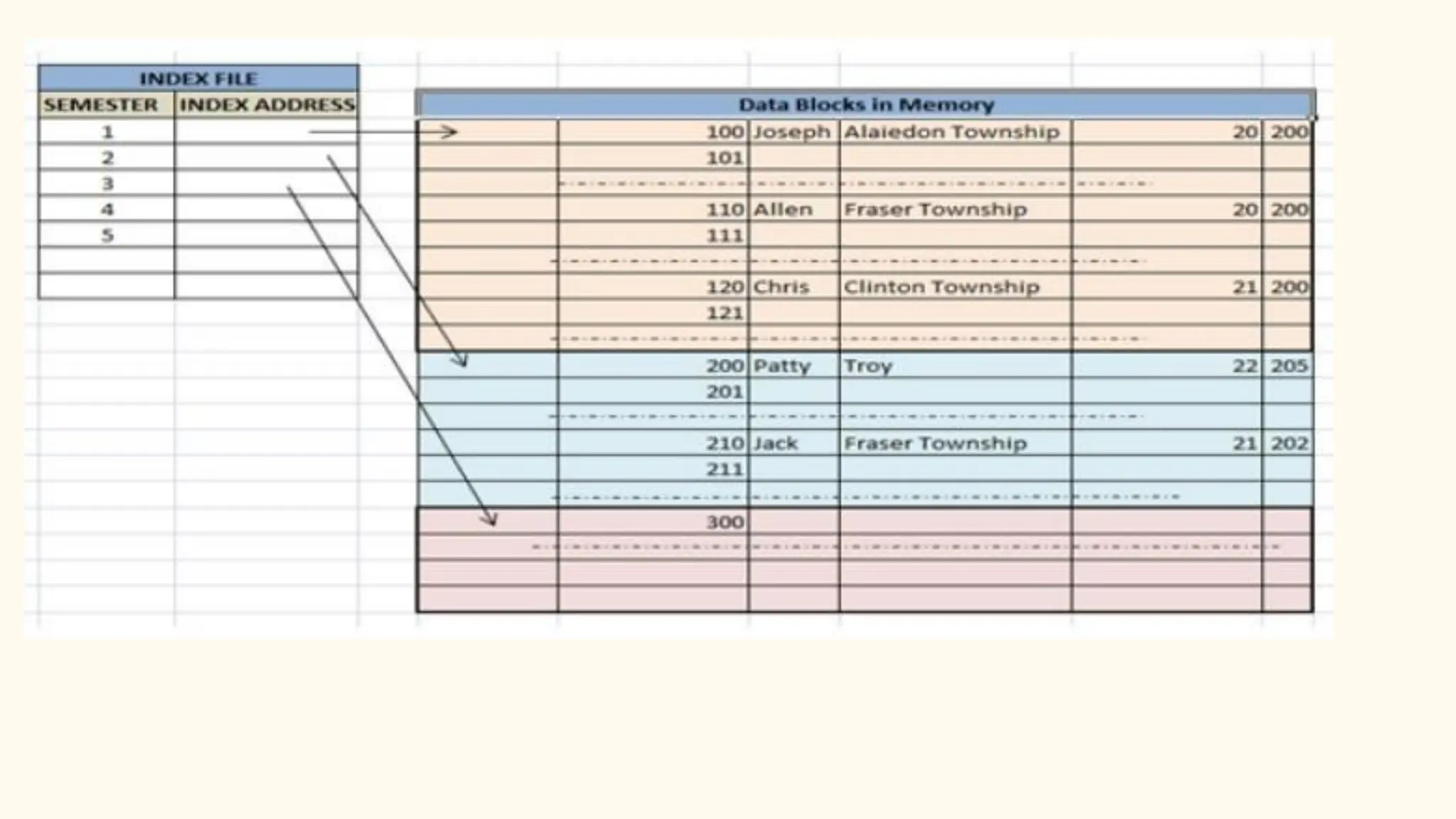
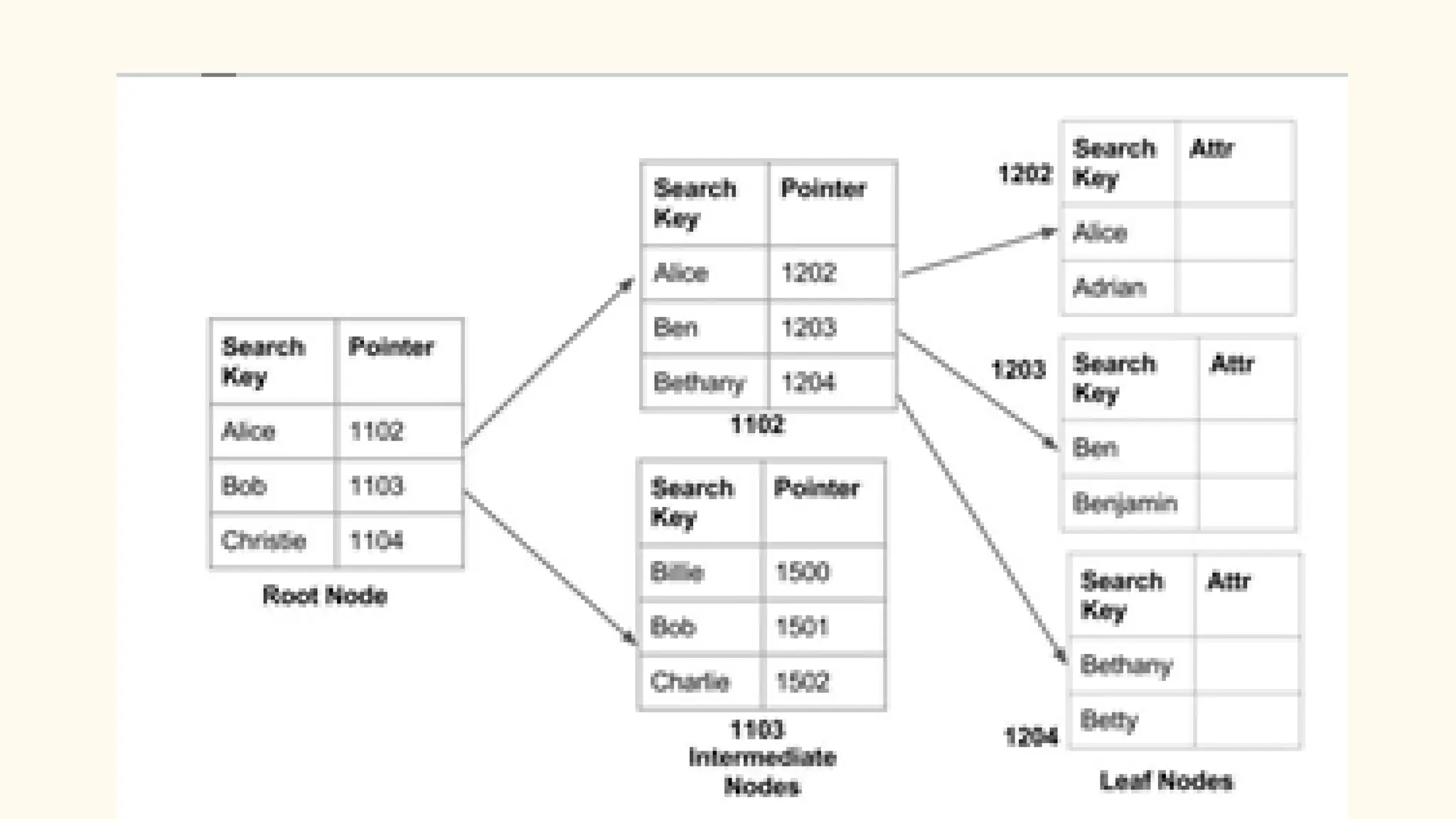
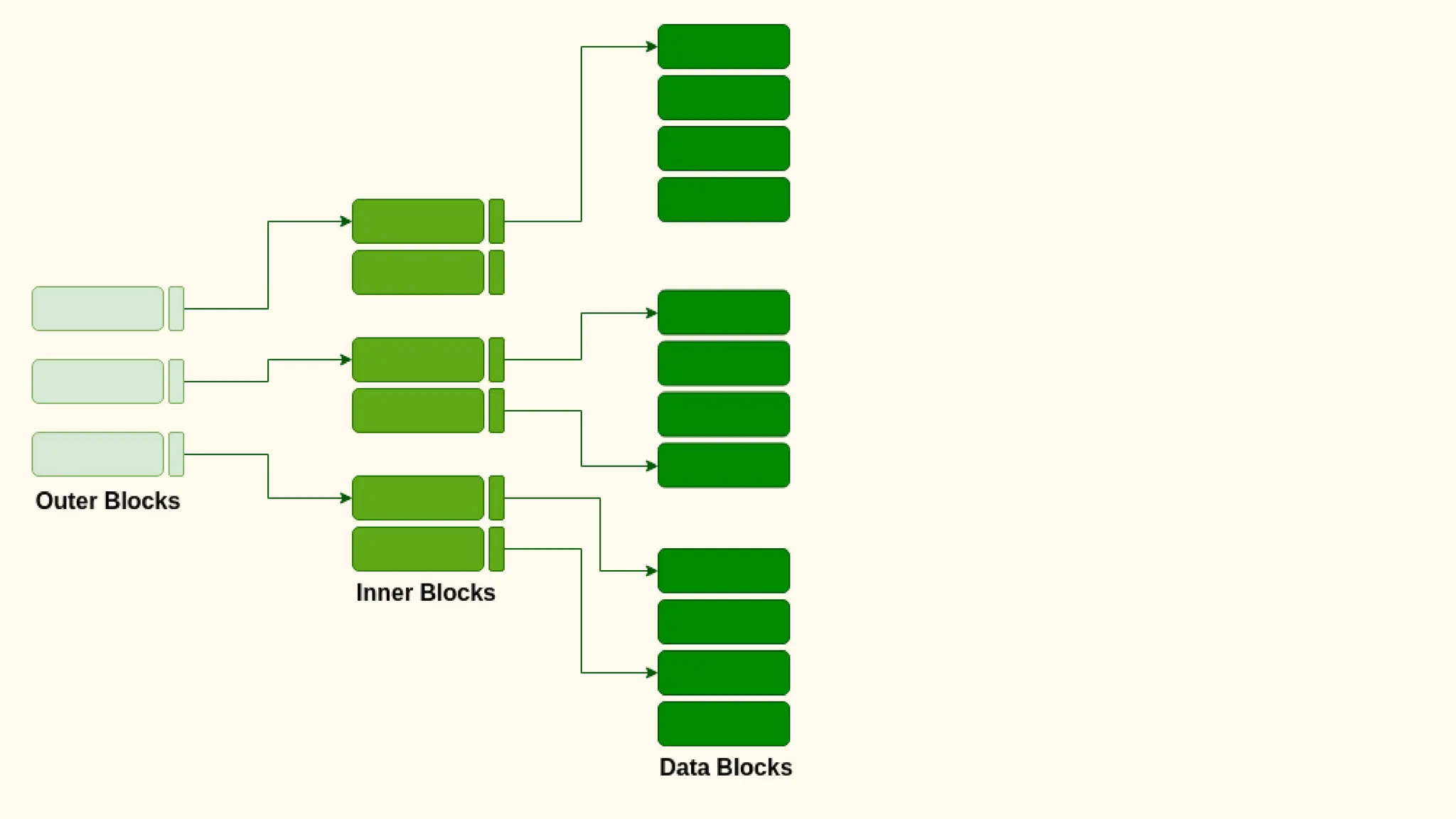
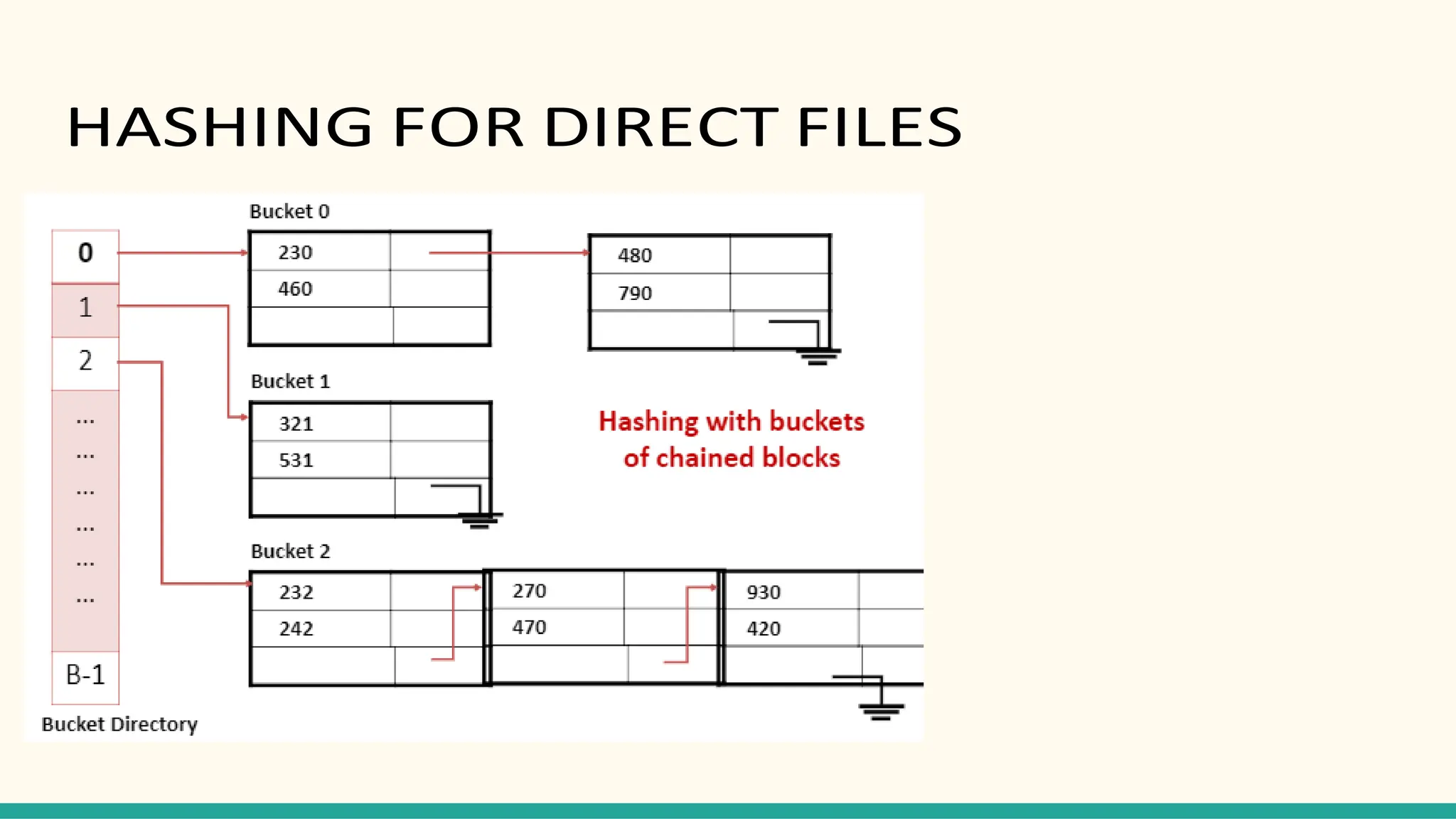
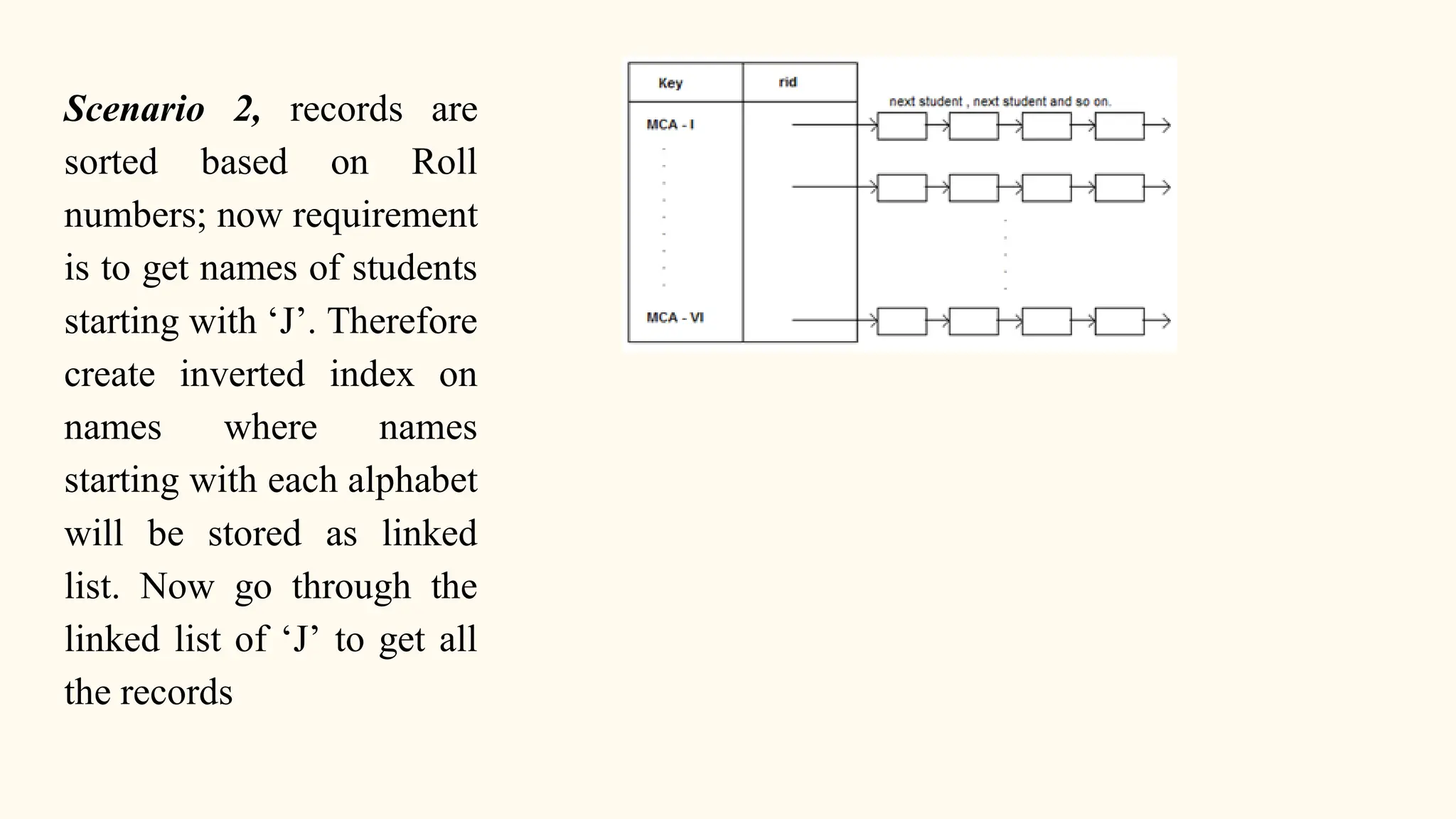
Hashing is a technique for storing data in an array such that each element is assigned a unique location based on its key value. This allows for constant time retrieval but collisions can occur when two elements hash to the same location. Collision resolution techniques like chaining, linear probing, quadratic probing, and double hashing are used to handle collisions. File structures like sequential, indexed, and relative organization are used to store records on storage devices efficiently with different access methods. Indexing uses a separate index file to speed up retrieval by mapping keys to record locations.