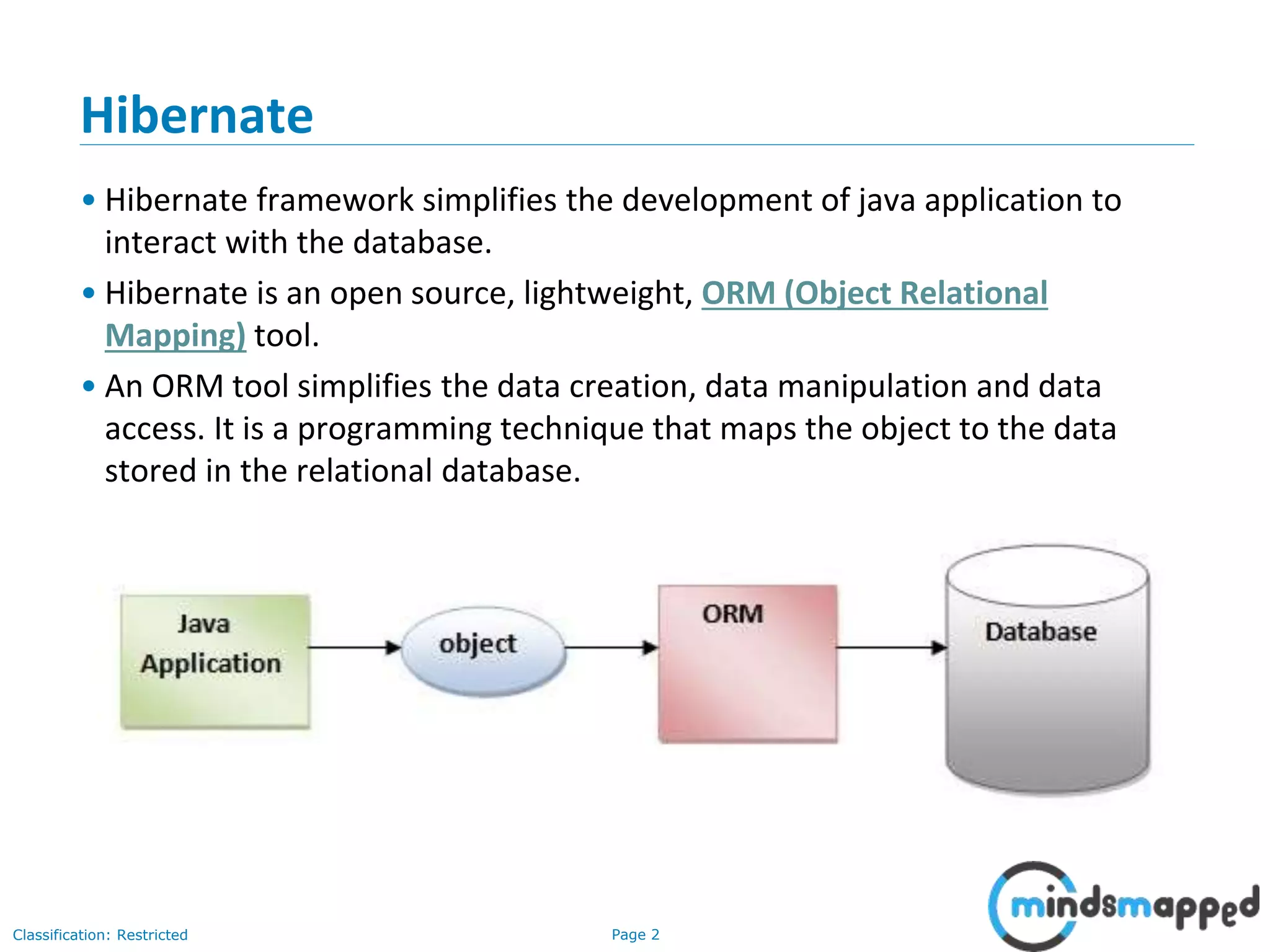
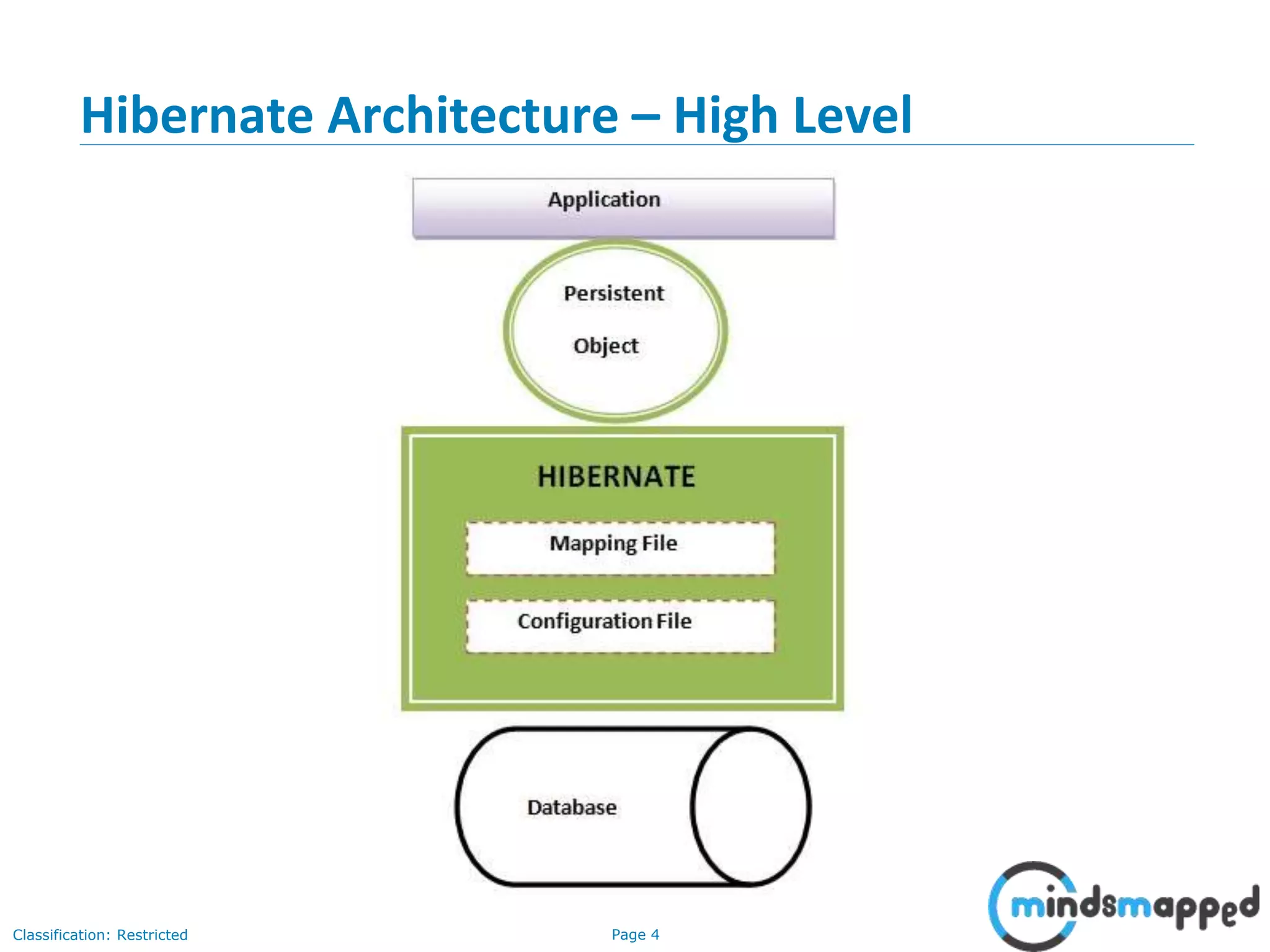
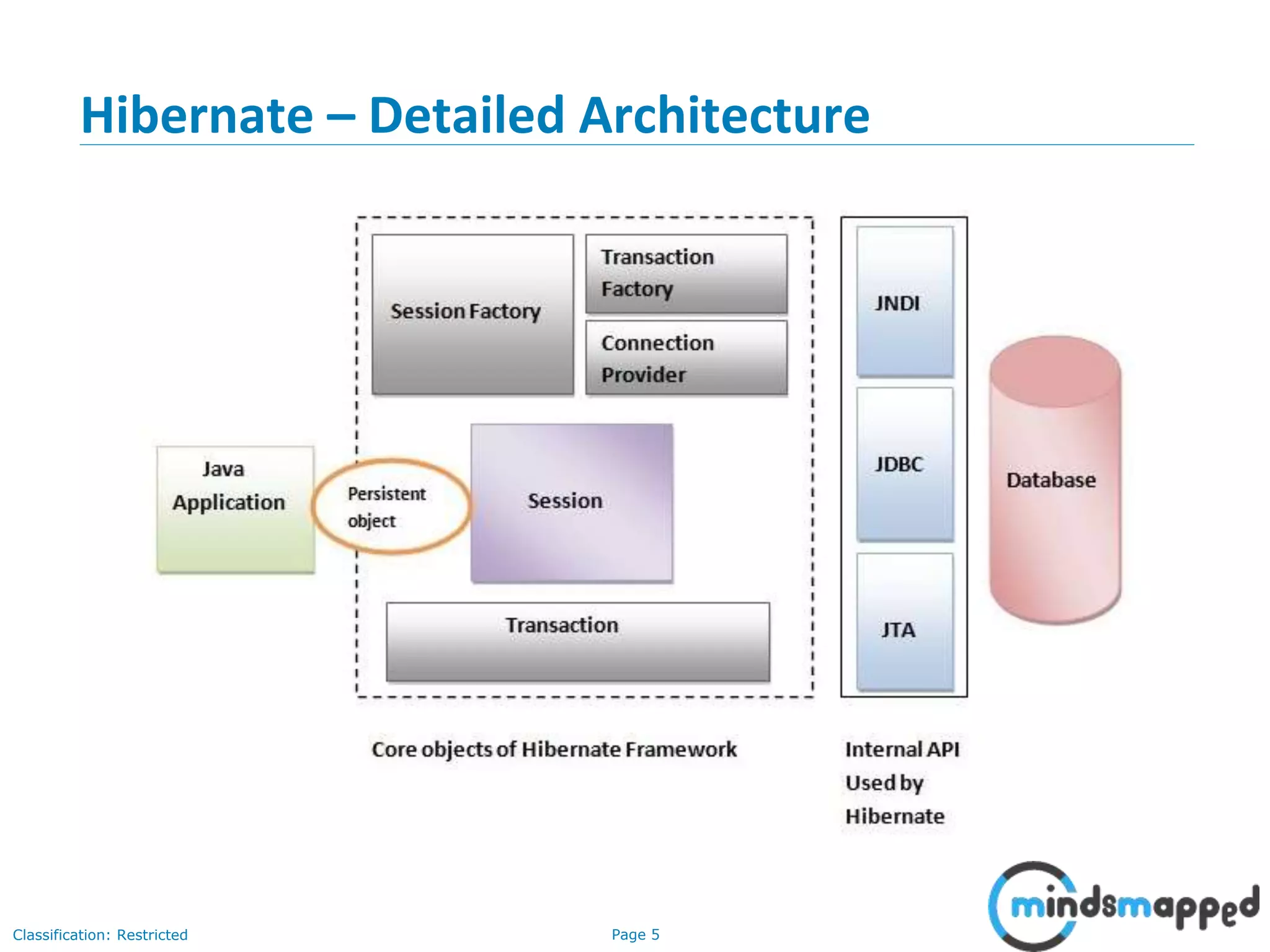
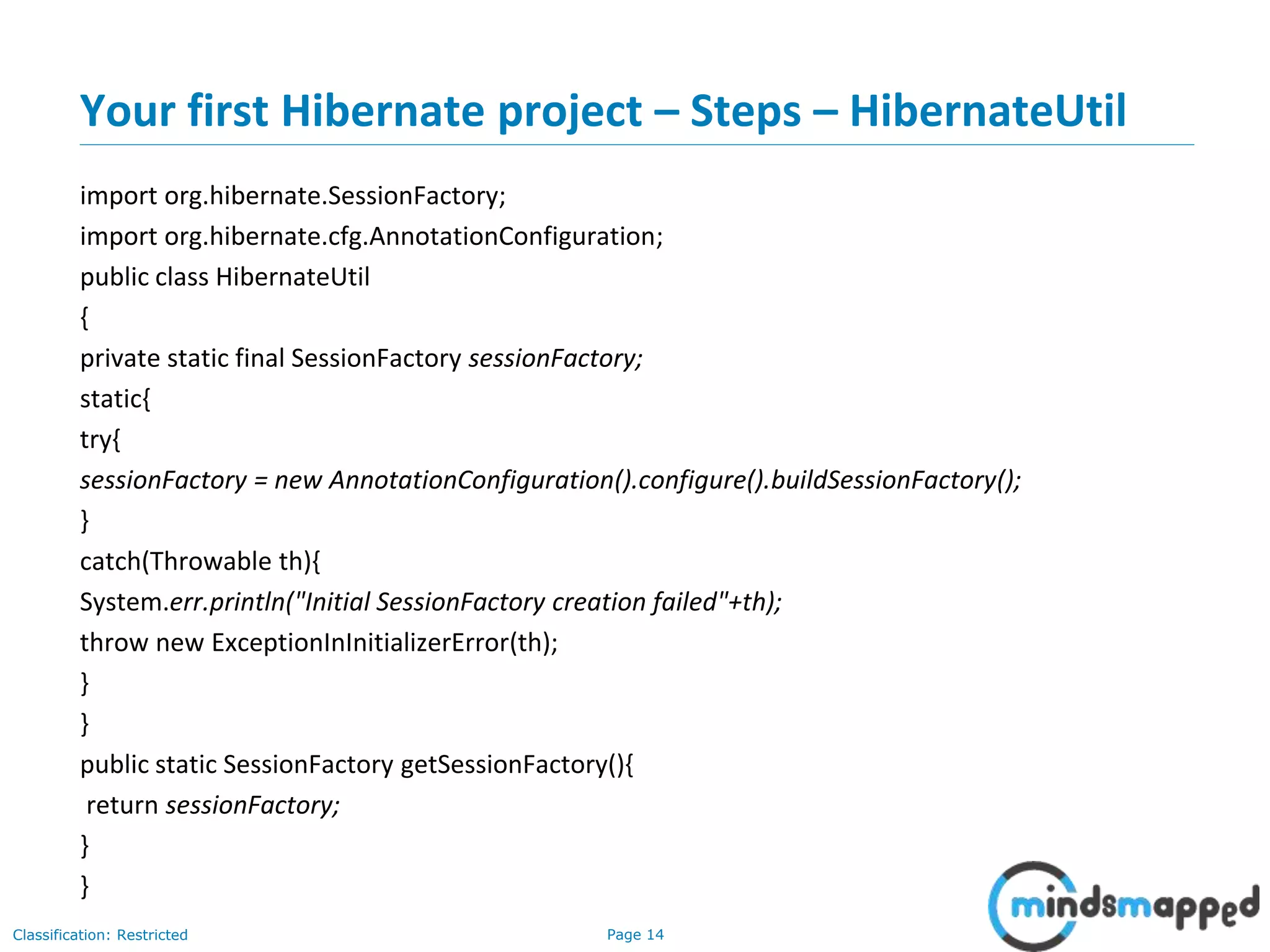
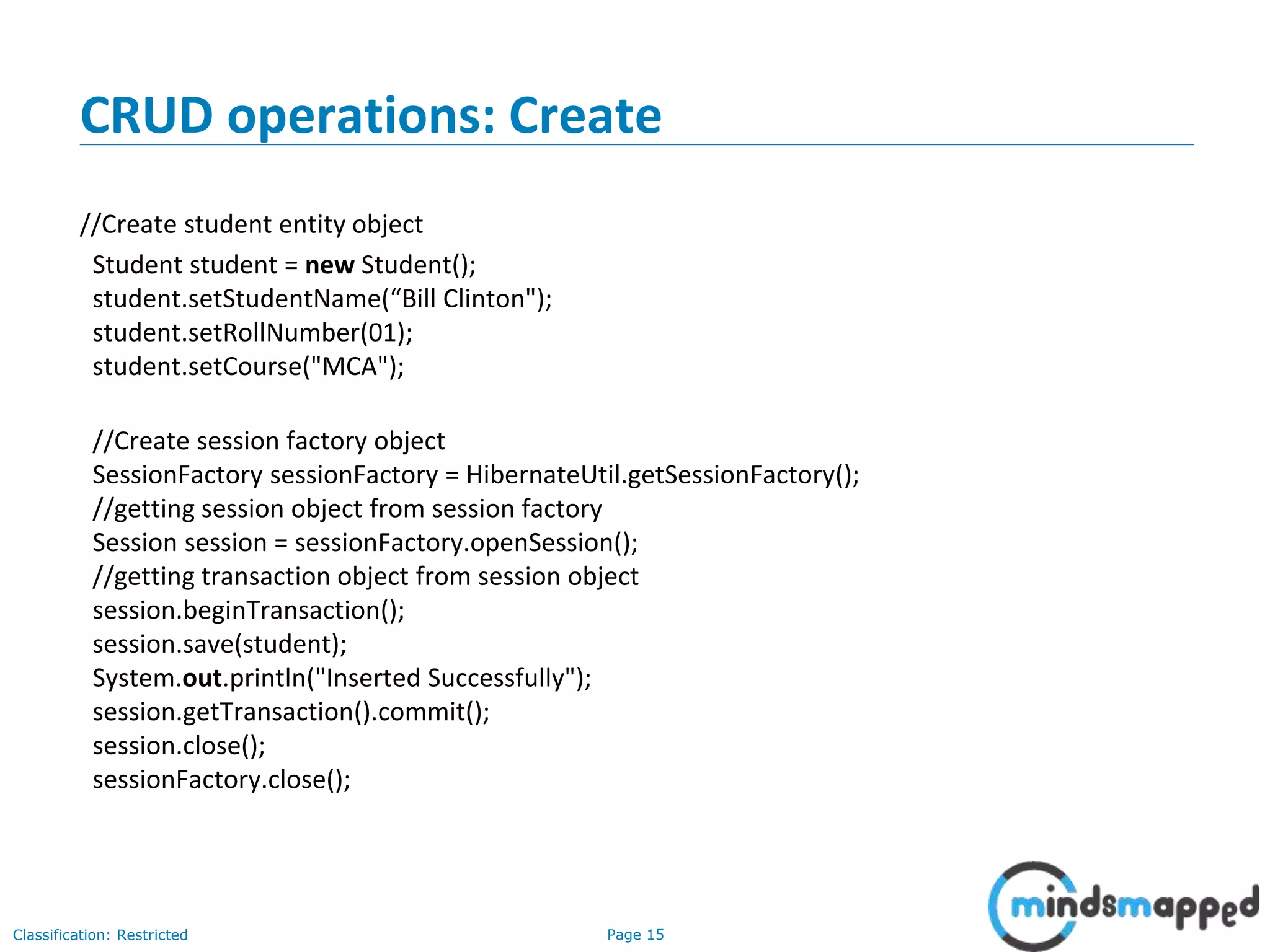
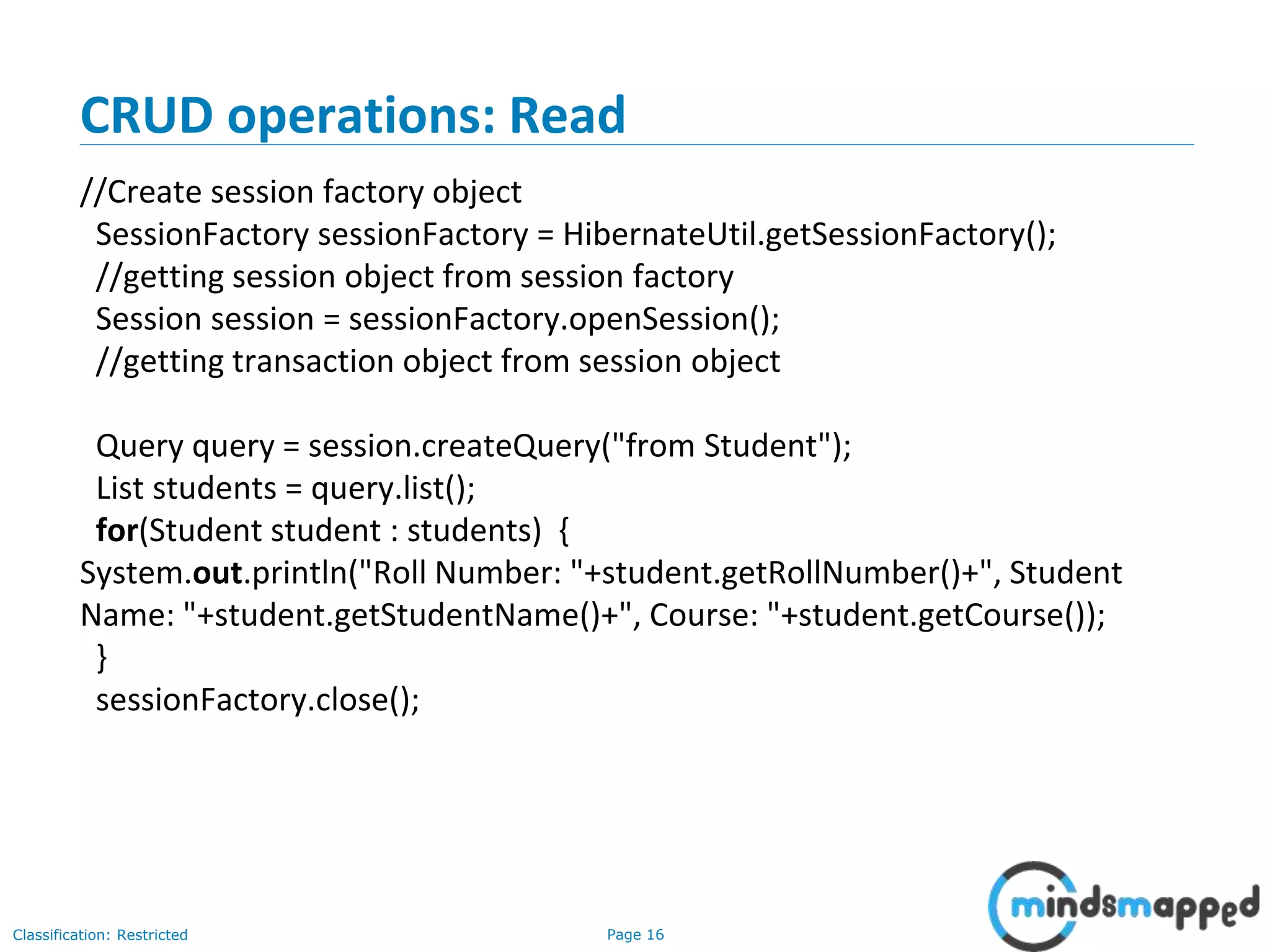
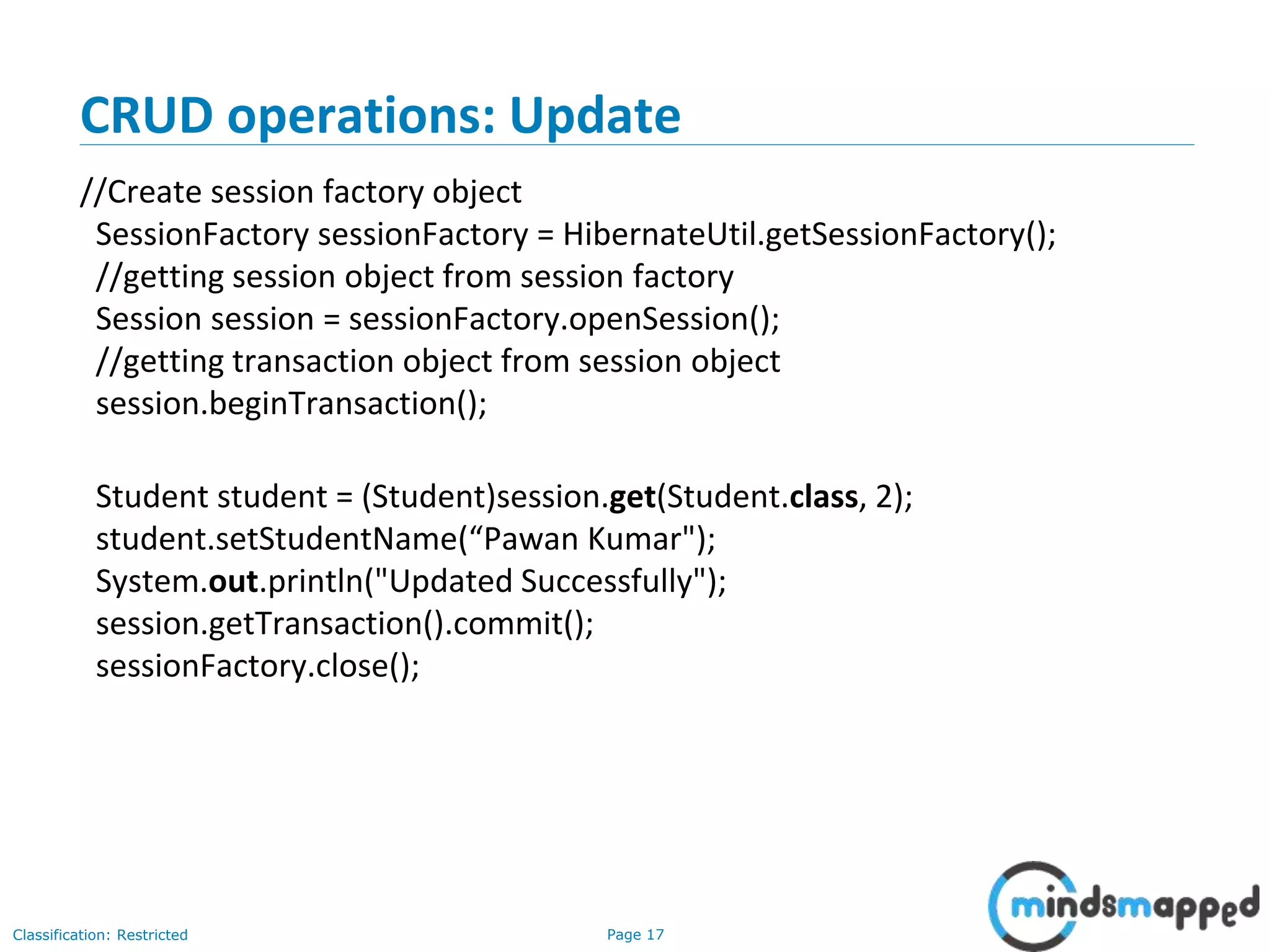
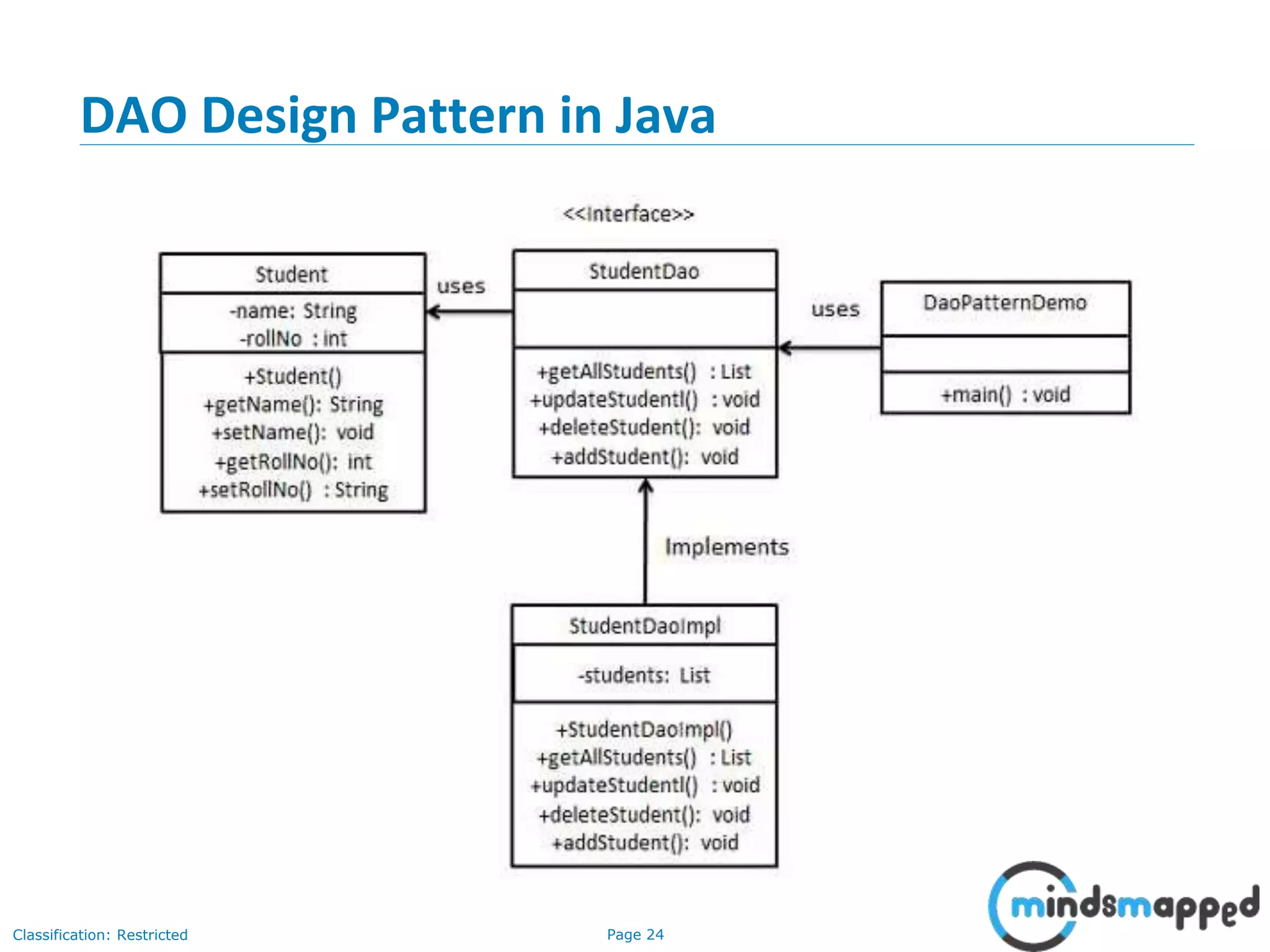
The document provides an overview of Hibernate, an open-source ORM framework that simplifies Java application development for database interactions. It outlines the advantages of Hibernate, such as fast performance, database independence, and automatic table creation, along with its architecture and components like SessionFactory and Session. Additionally, it includes instructions for creating a Hibernate project, detailed CRUD operations, and approaches for using Hibernate with annotations.