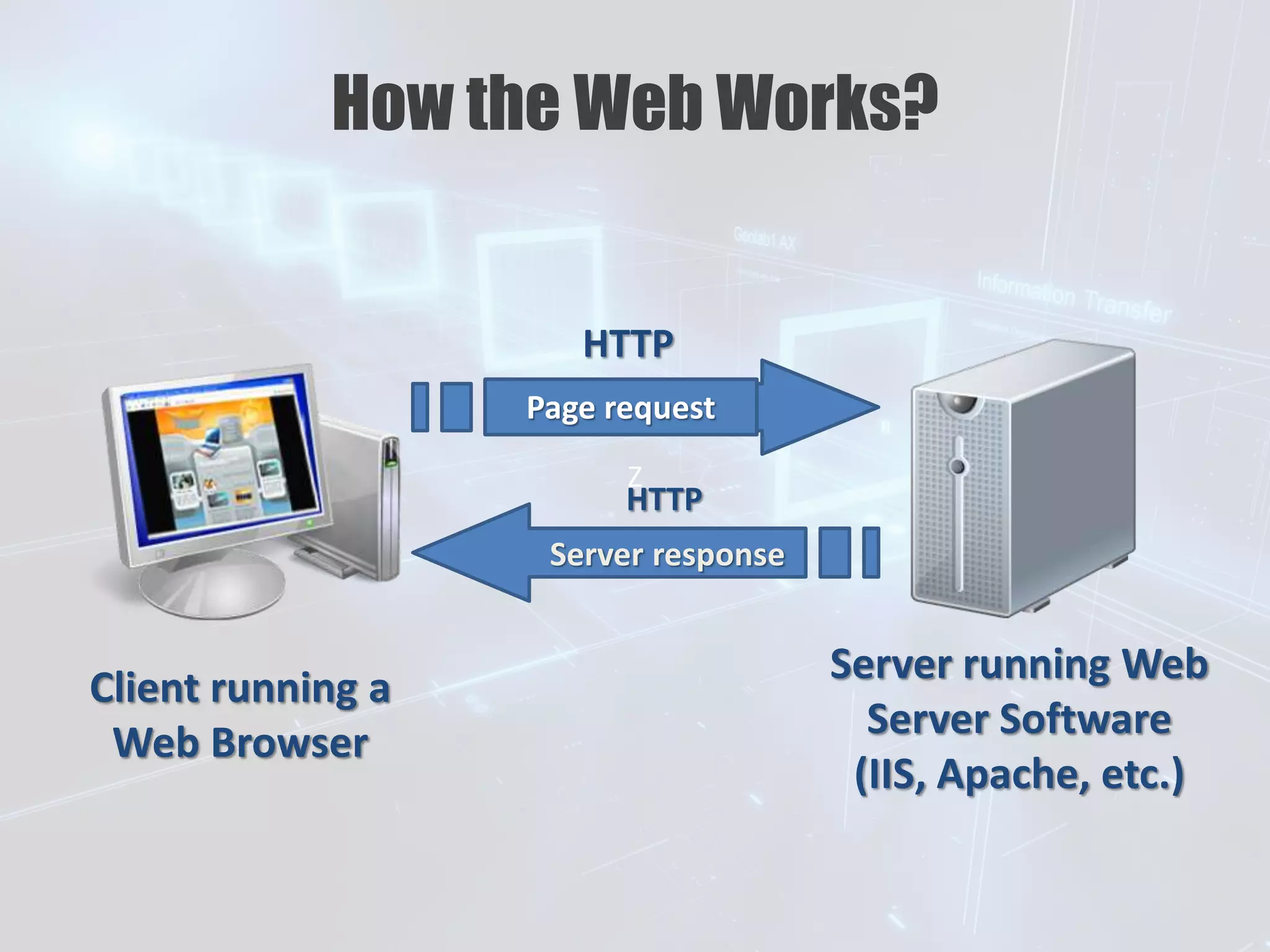
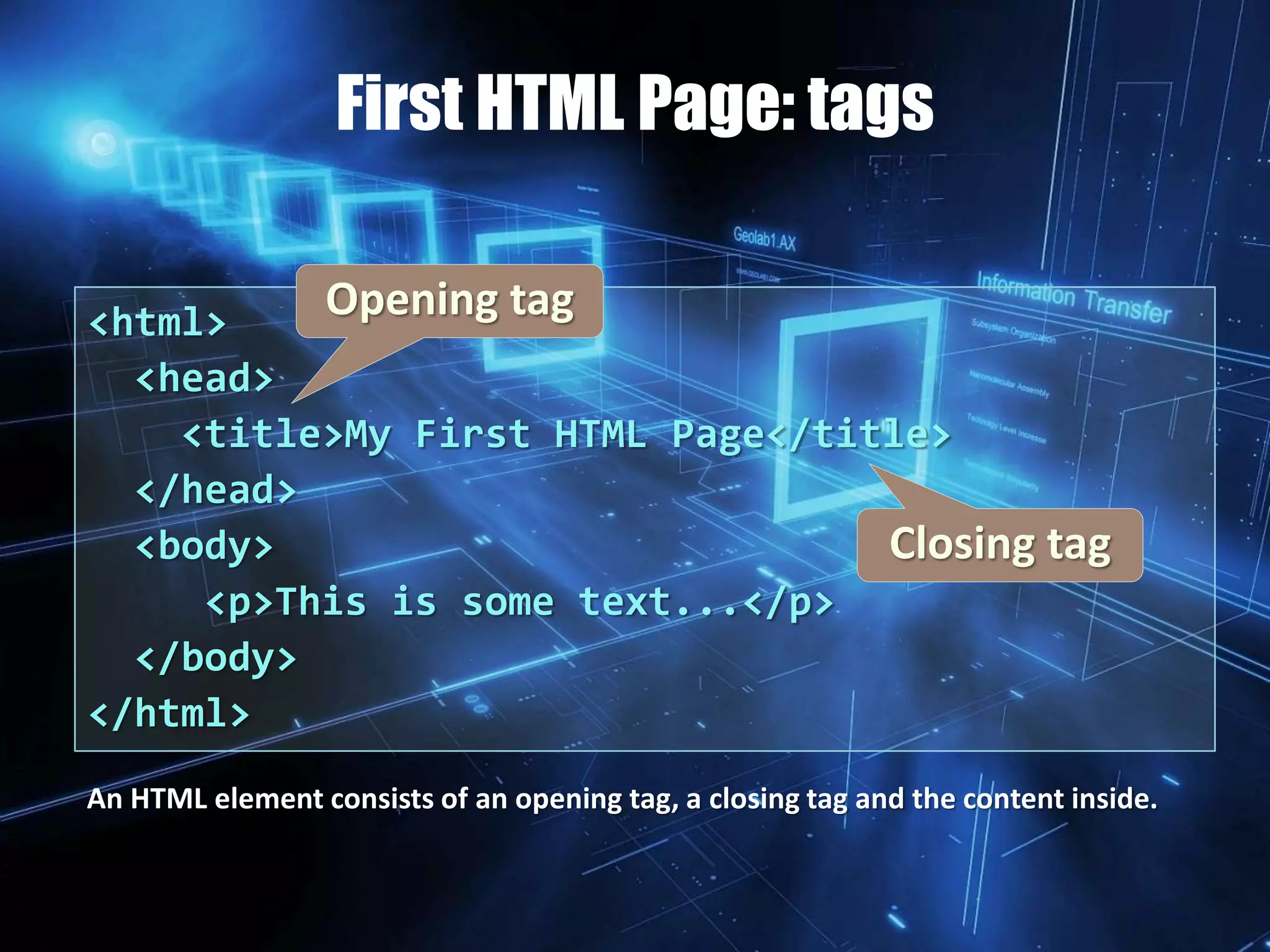
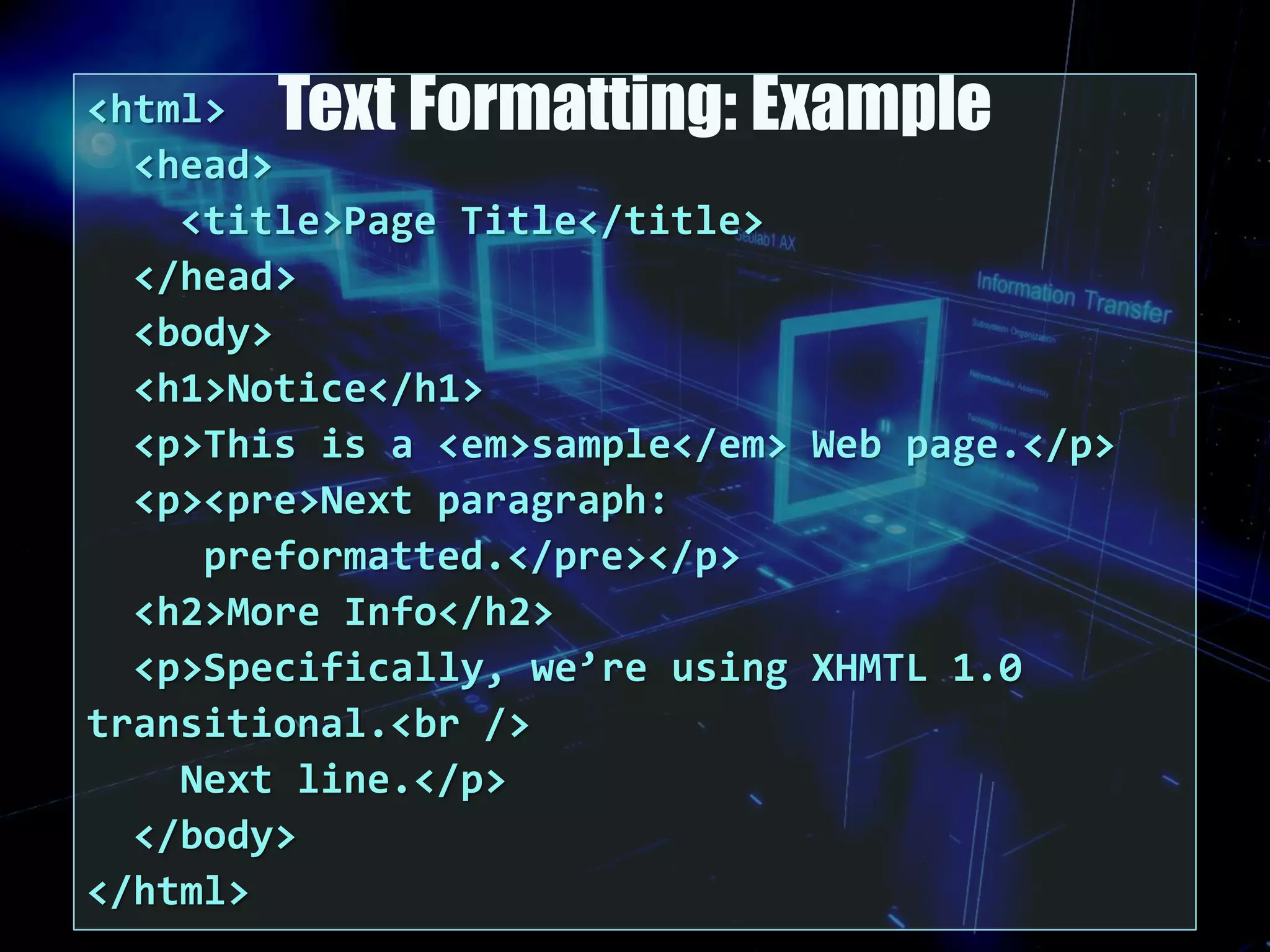
This document provides an overview of HTML and how websites work. It discusses HTML elements and tags, how to structure an HTML page using the <head>, <body>, and other tags. It also covers how to format text, add headings and paragraphs, and change background and text colors. The learning outcomes are to understand basic HTML coding syntax and styles and how they are used to code websites.