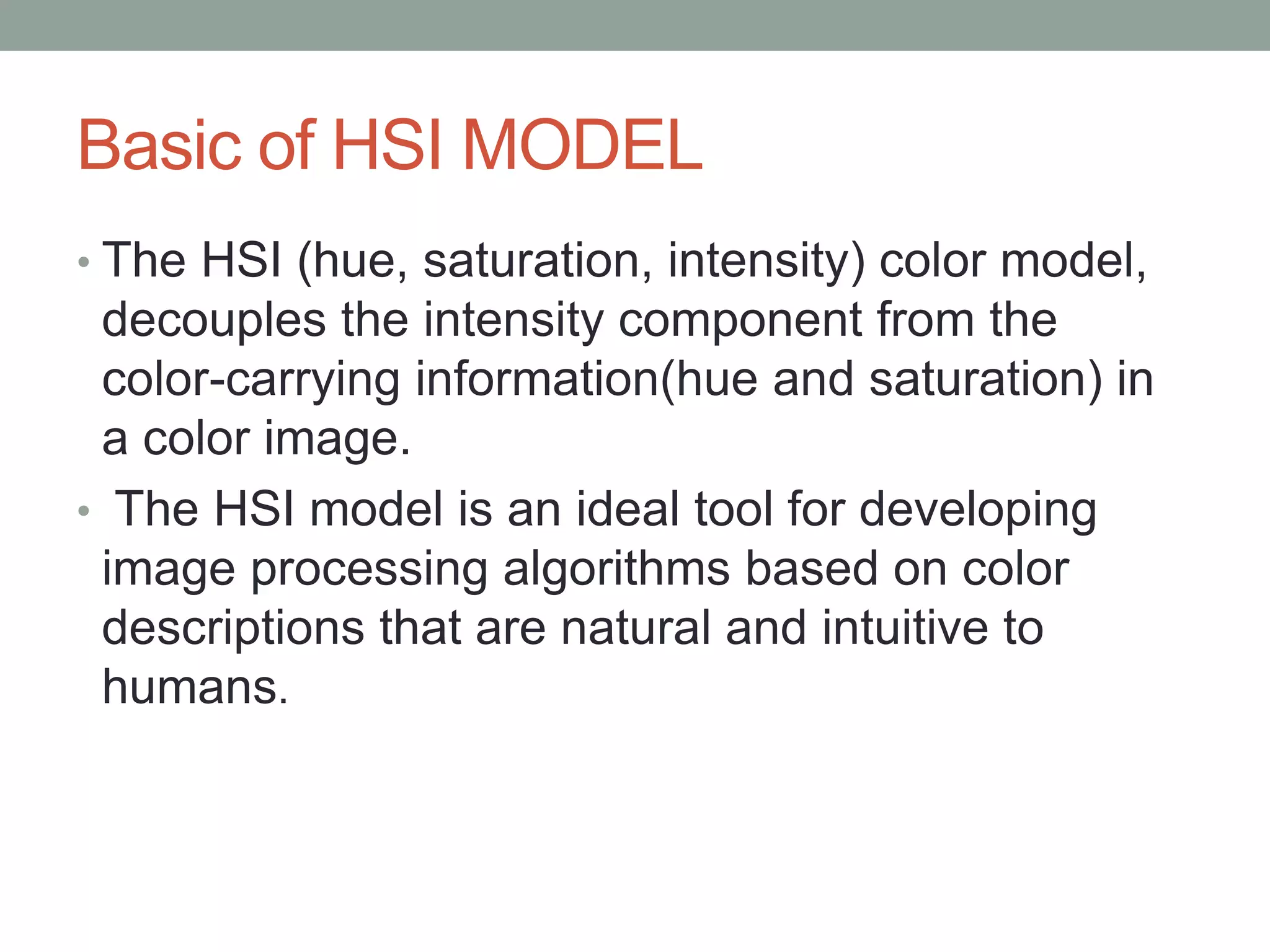
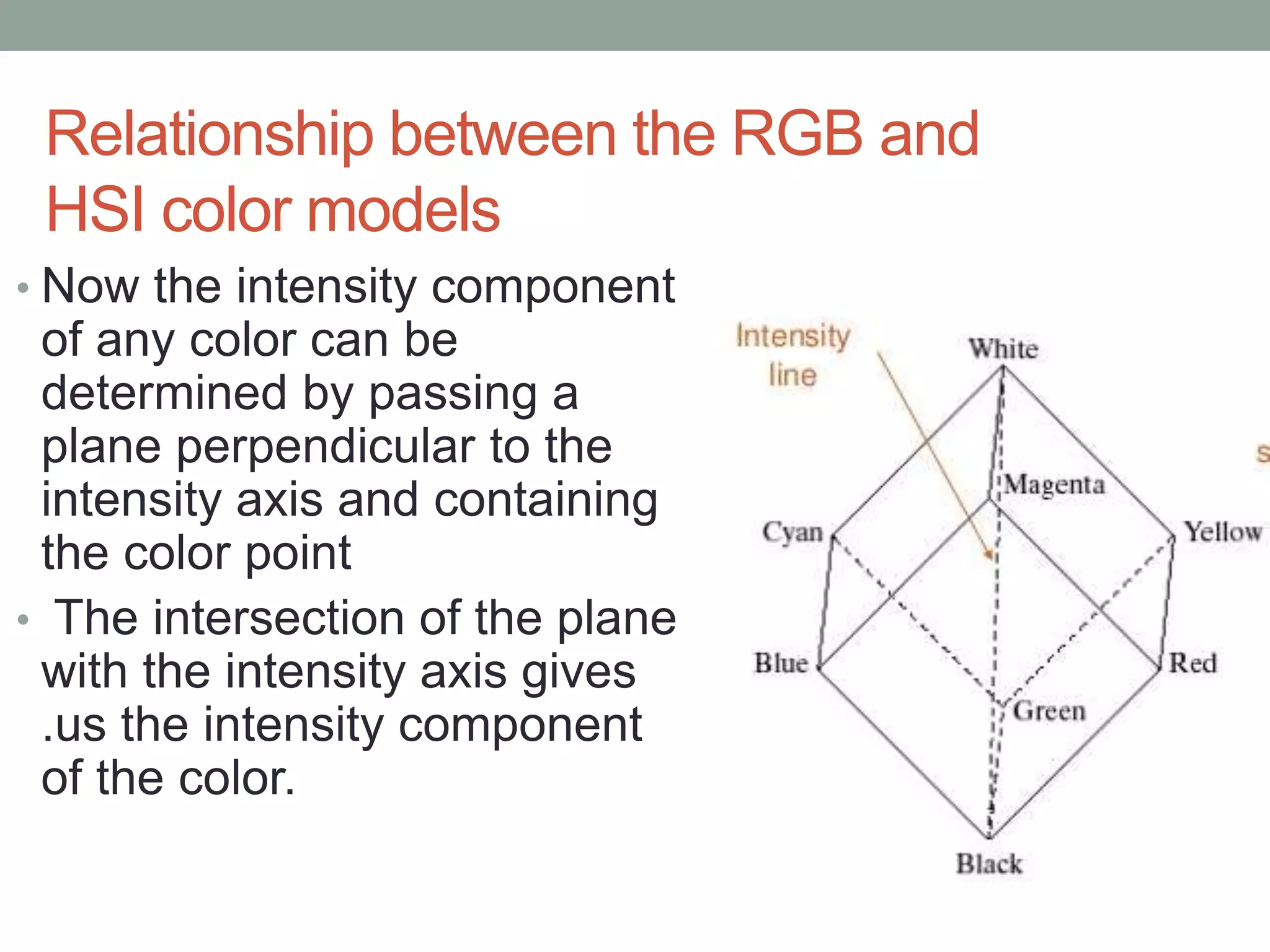
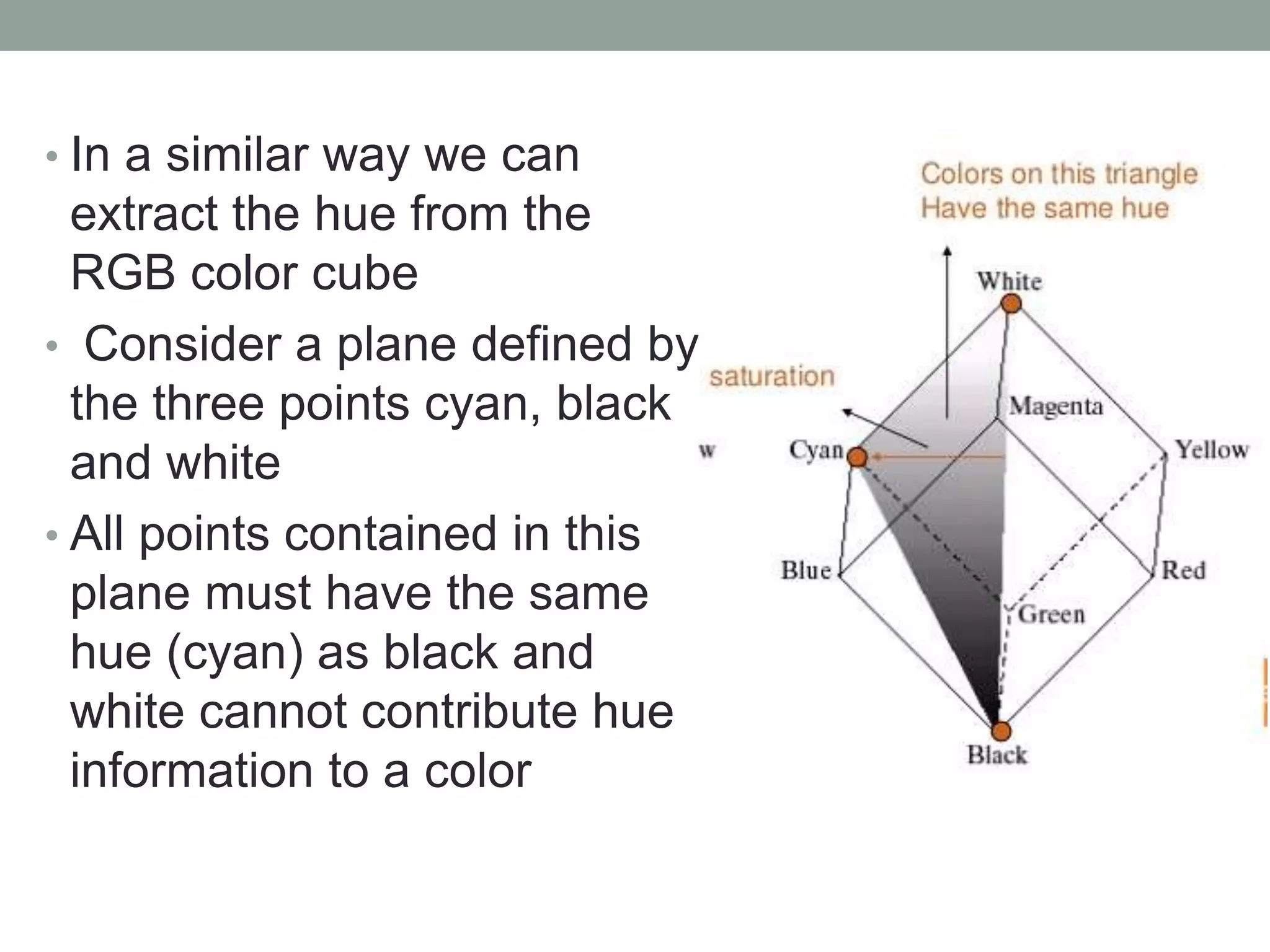
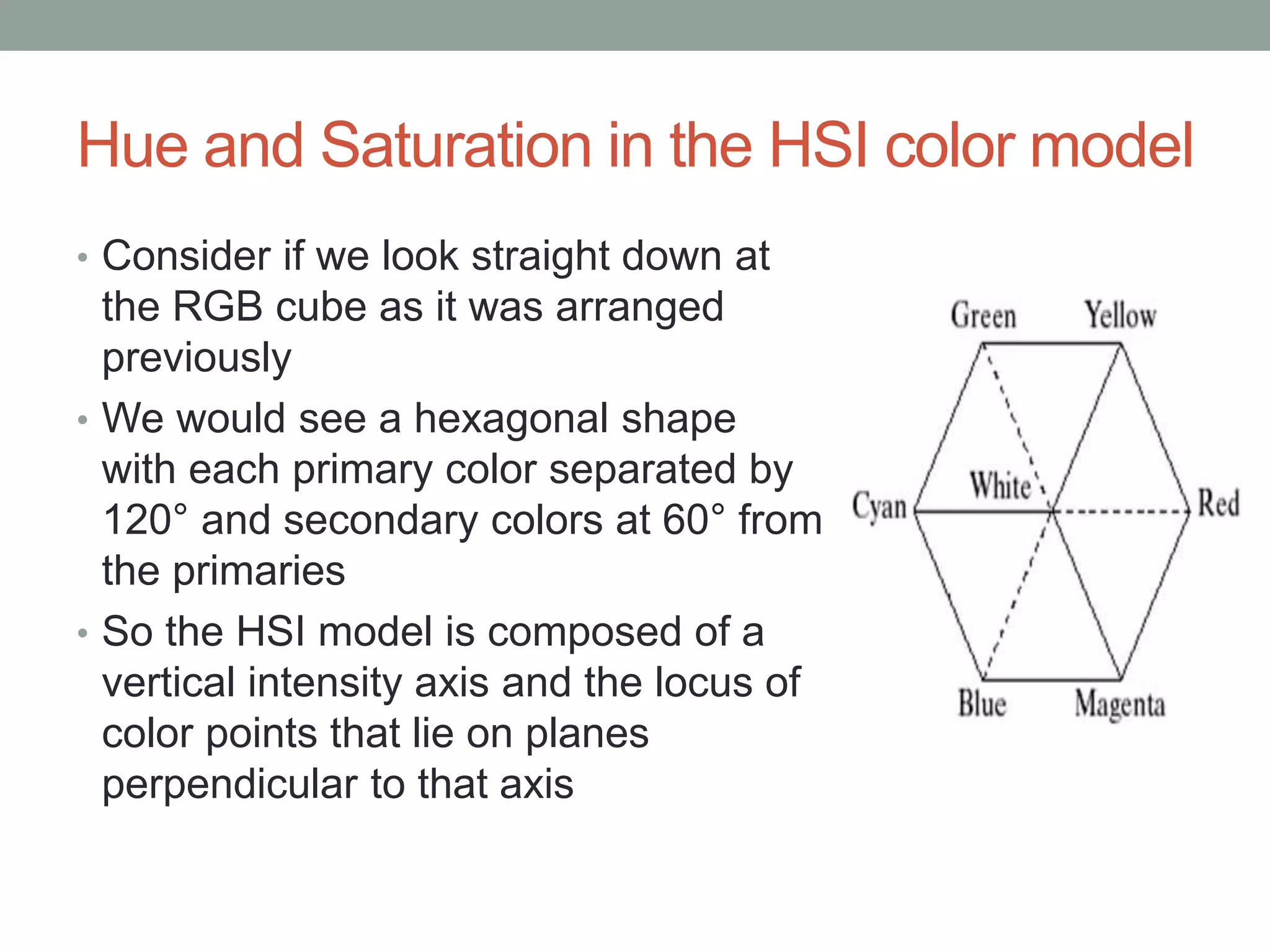
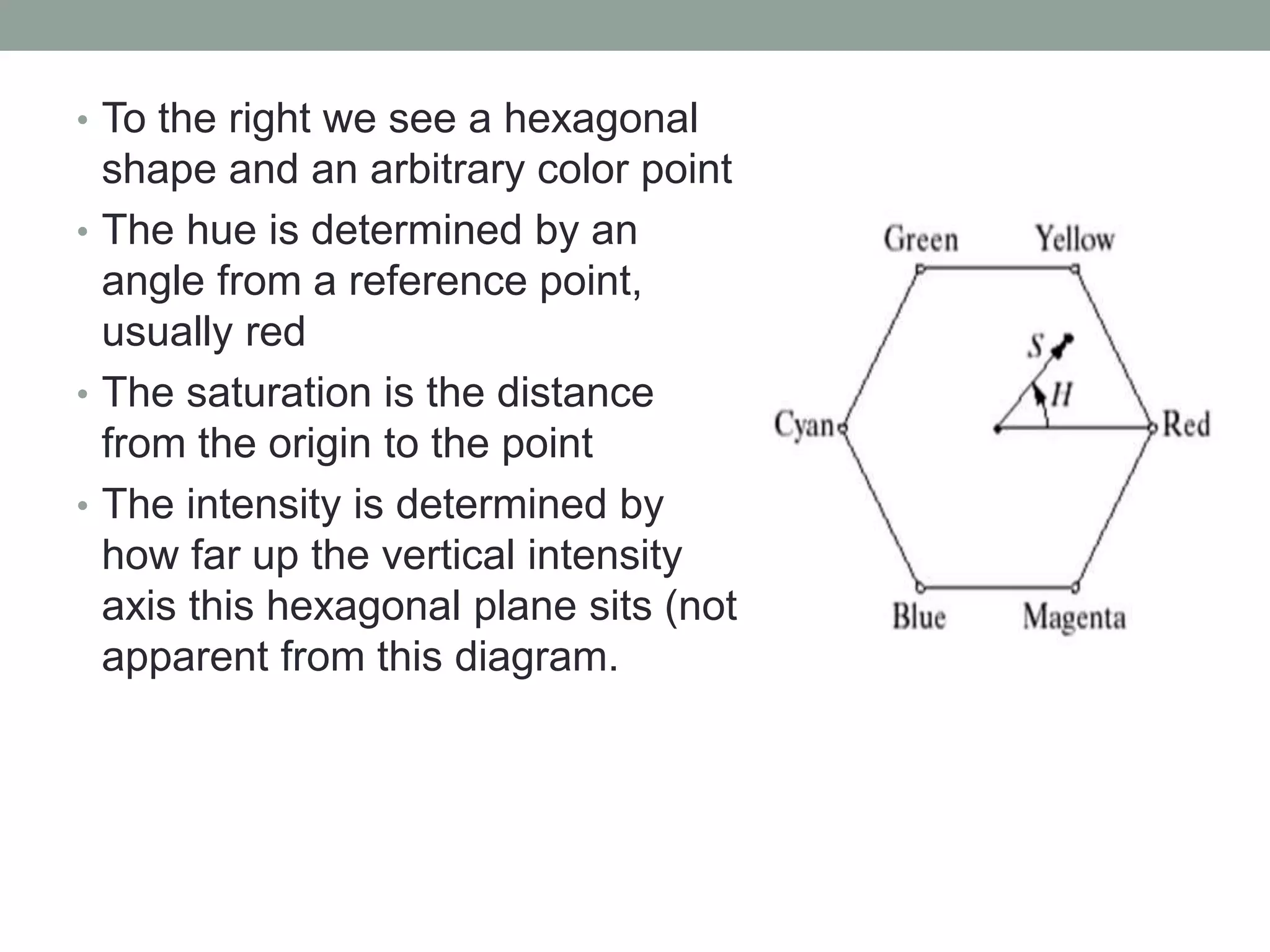
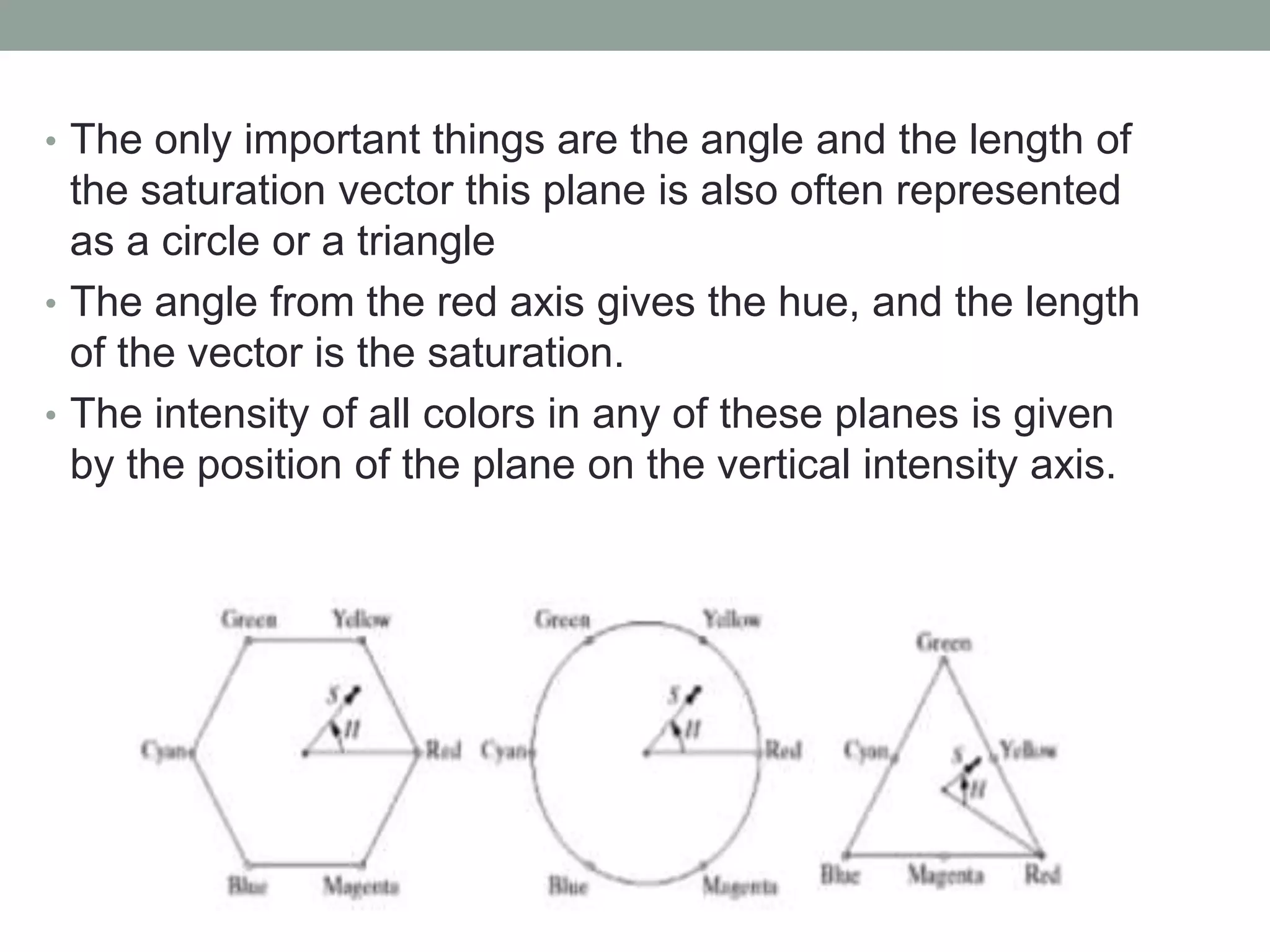
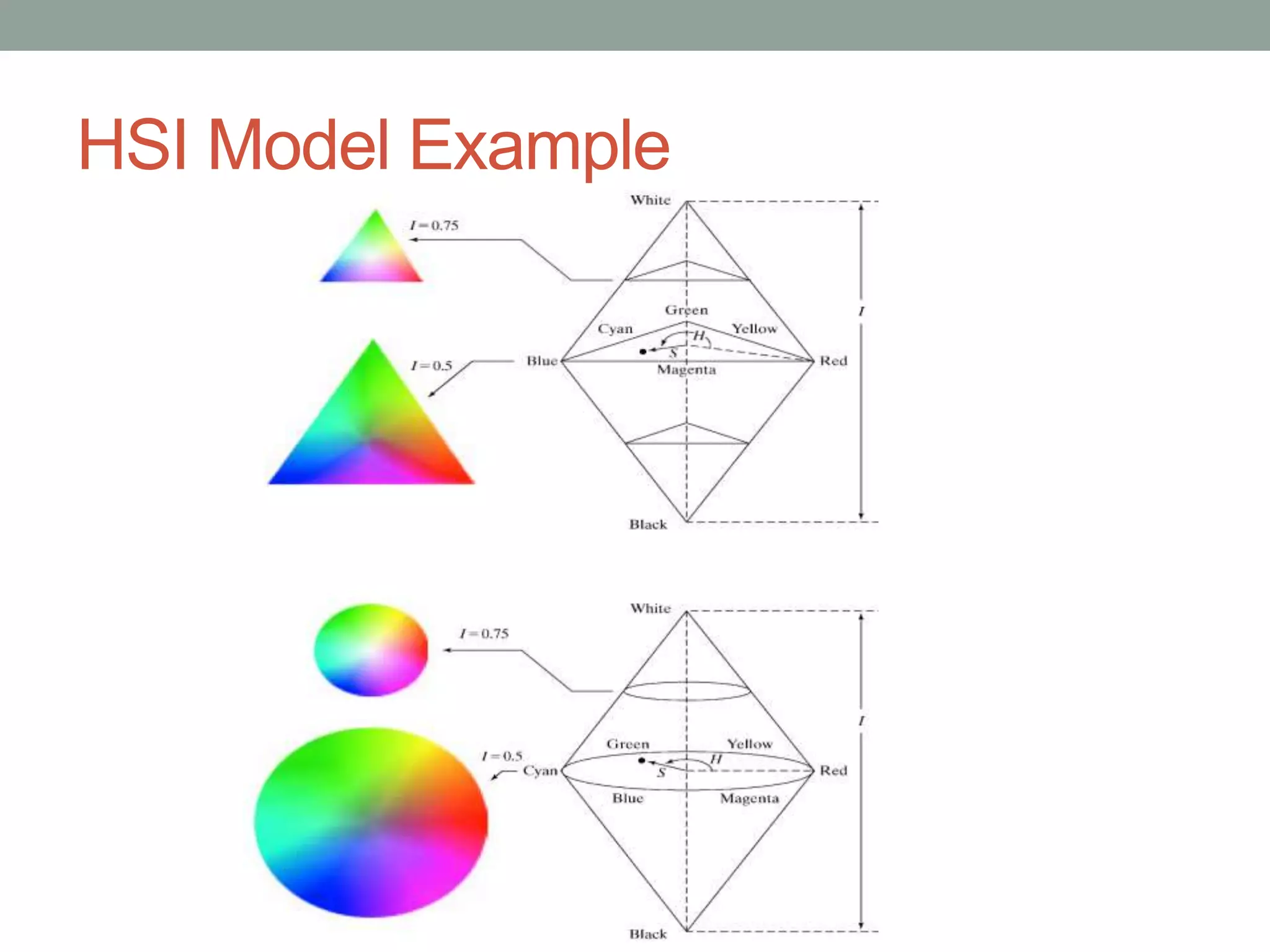
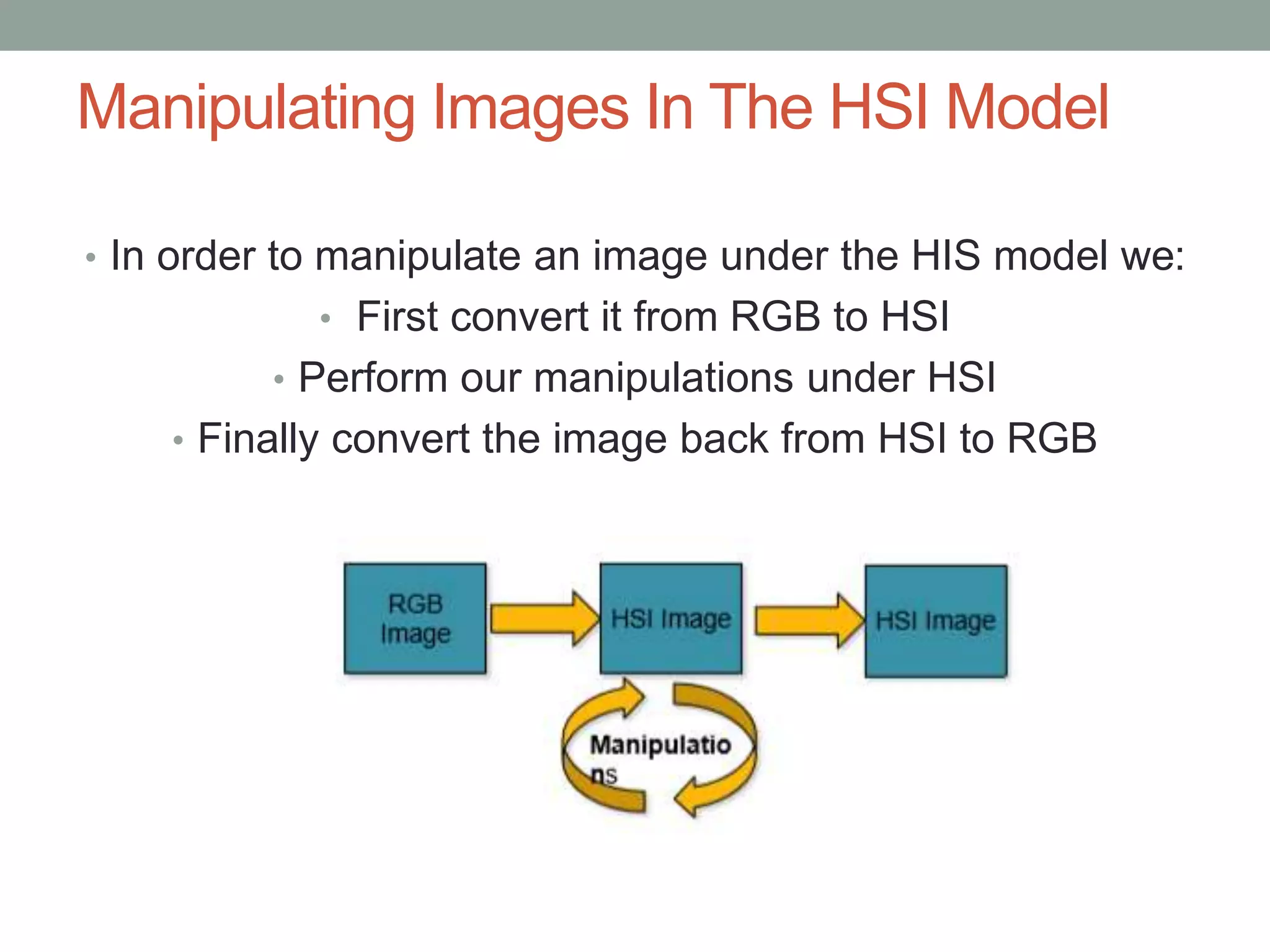
The HSI (hue, saturation, intensity) color model represents color in a way that is more perceptually relevant to humans compared to the RGB (red, green, blue) model. Hue represents the color (such as red, yellow, blue), saturation represents the amount of gray, and intensity represents the brightness. The HSI model separates intensity from color information. Converting an image to HSI allows color manipulations like changing hue or saturation before converting back to RGB for display.