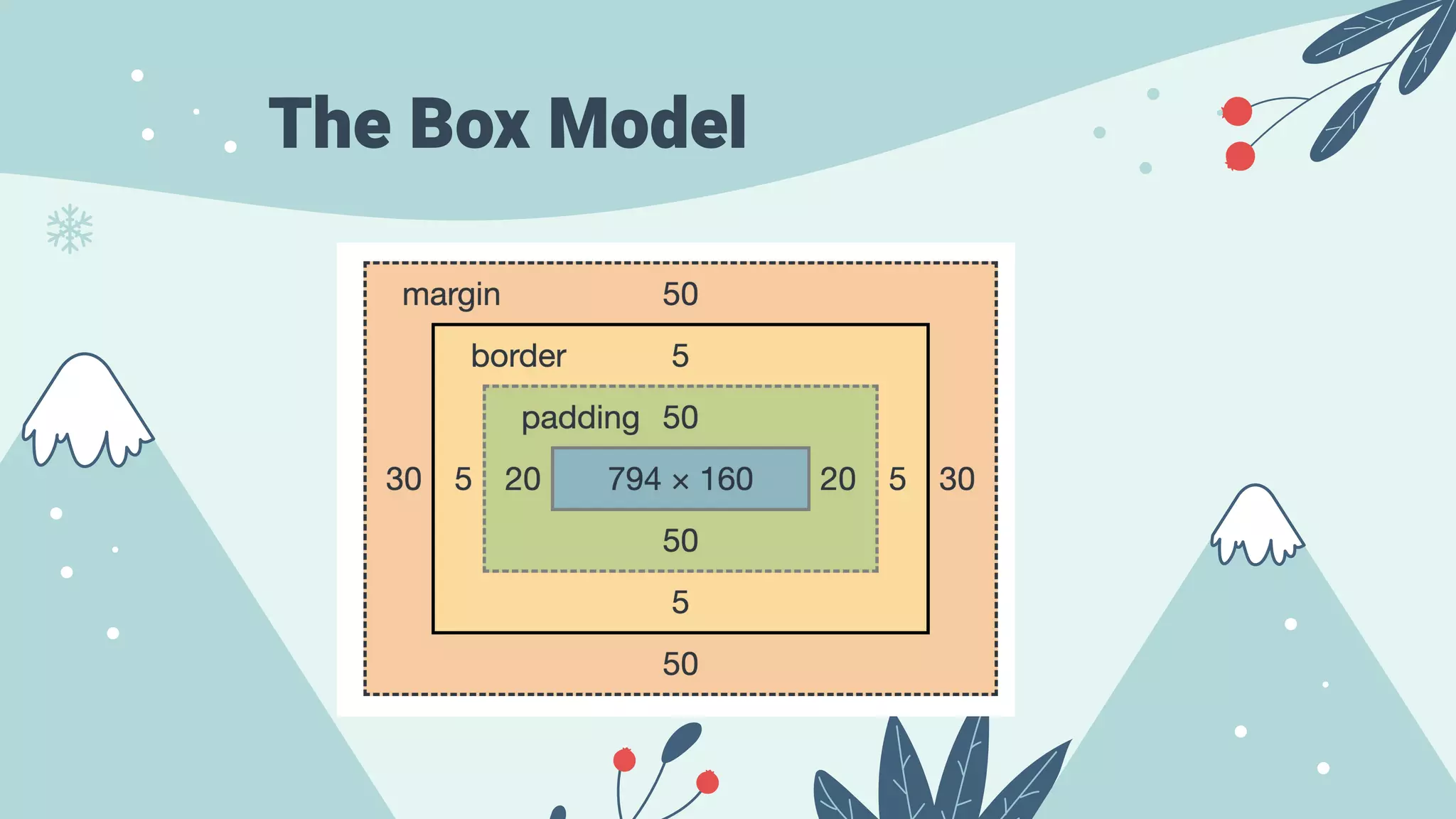
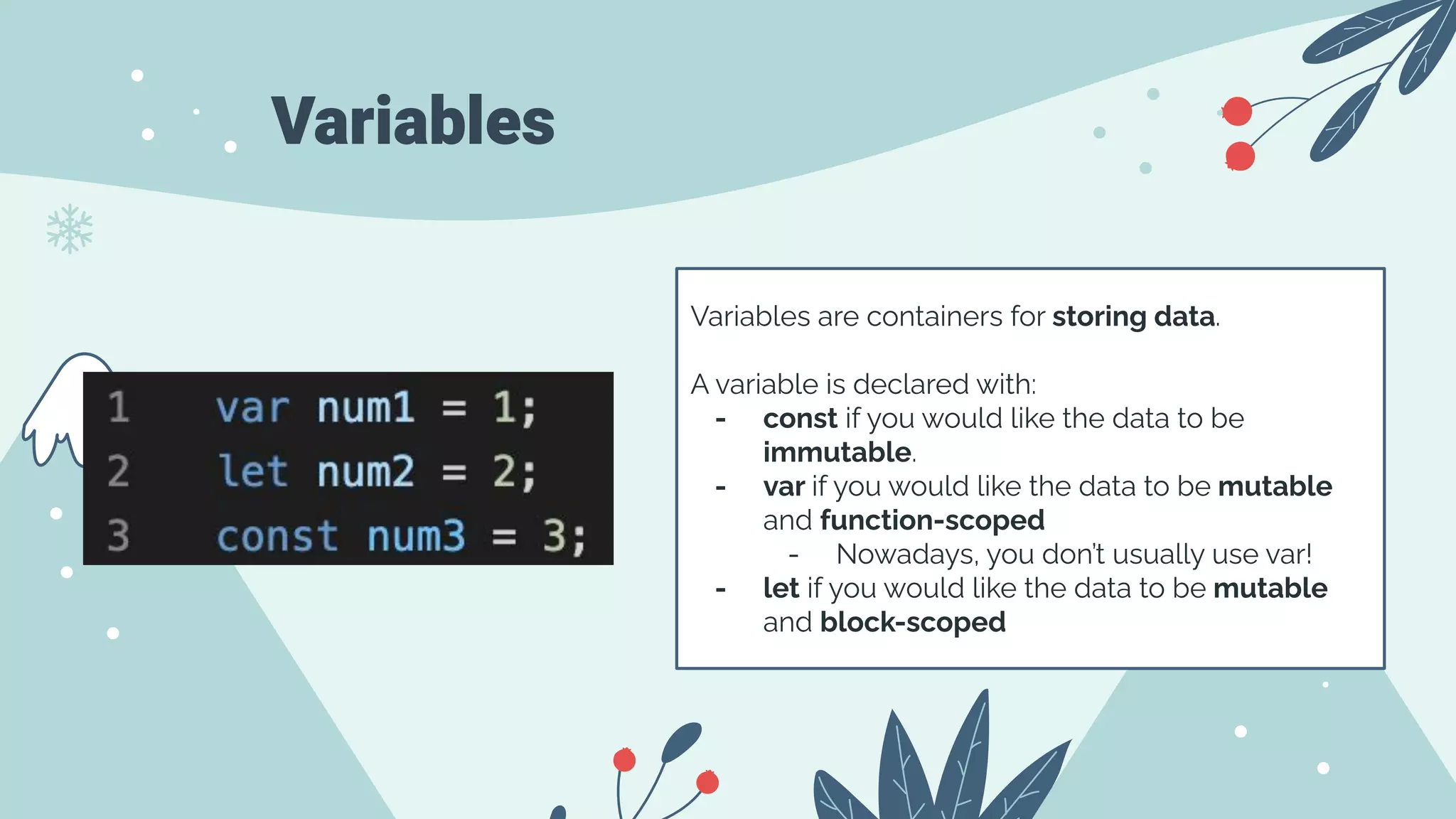
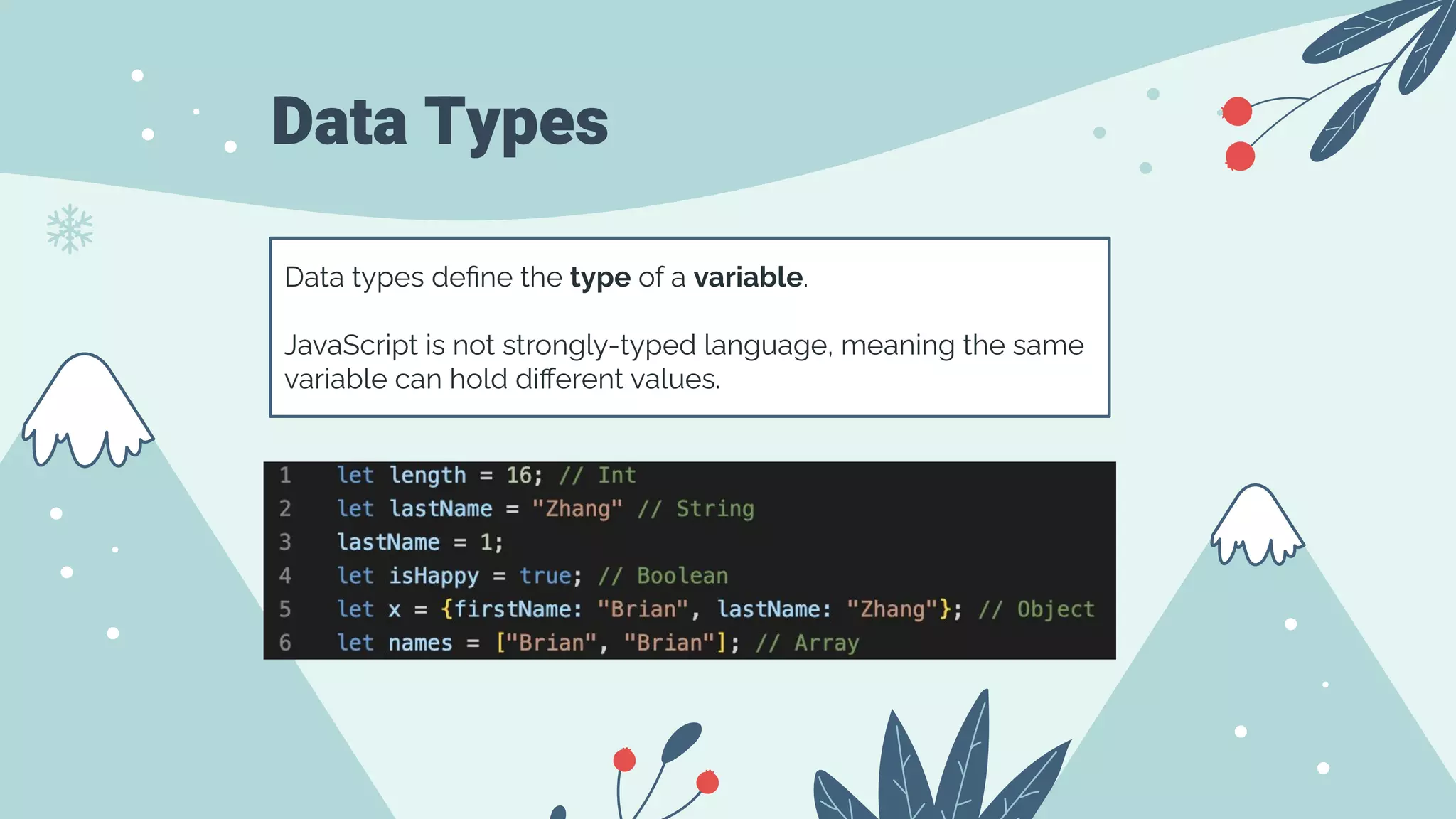
The document serves as an introduction to front-end development, covering HTML, CSS, and JavaScript basics. HTML is presented as the fundamental markup language for creating web pages, while CSS is used for styling and JavaScript for programming page behavior. It also includes best practices for accessibility in HTML and a brief guide on variable declaration and functions in JavaScript.