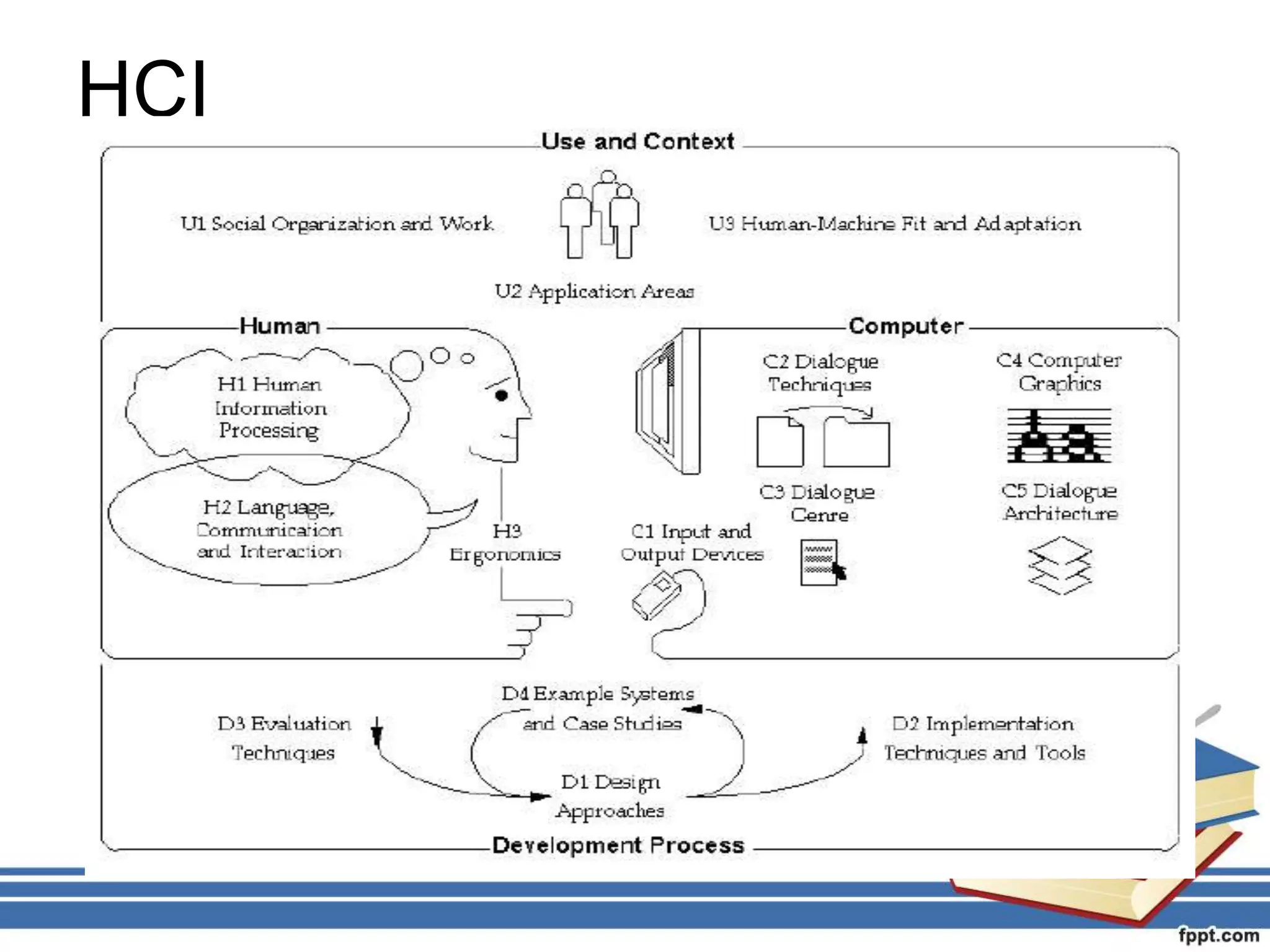
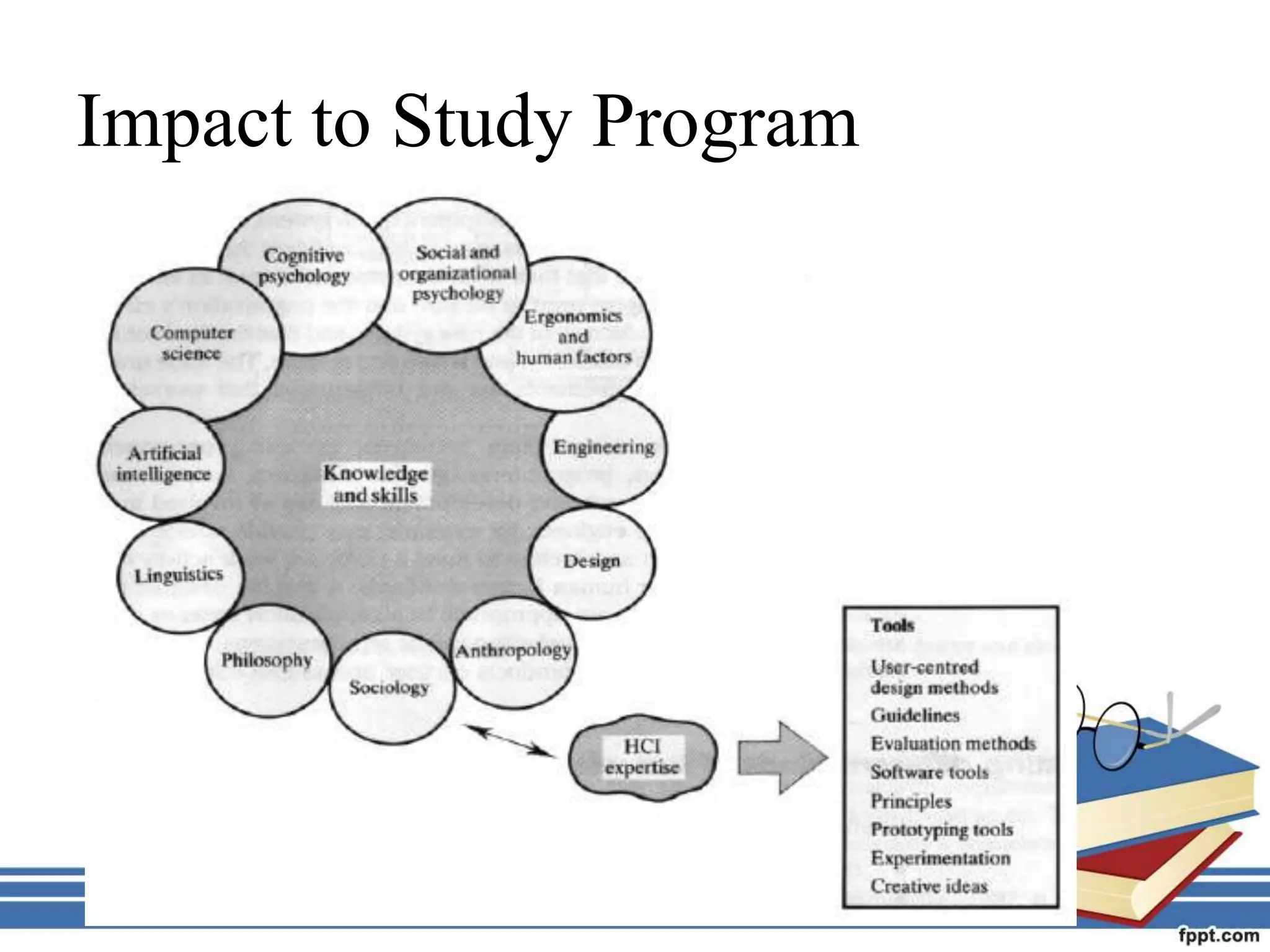
Human Computer Interaction (HCI) is the study of how humans interact with computers and how to design interfaces so that users can interact with systems effectively, efficiently and with satisfaction. HCI aims to make computers more usable by understanding users and designing appropriate input/output devices and interaction styles. The goals of HCI include improving safety, utility, effectiveness and efficiency of computer systems to benefit both users and organizations.