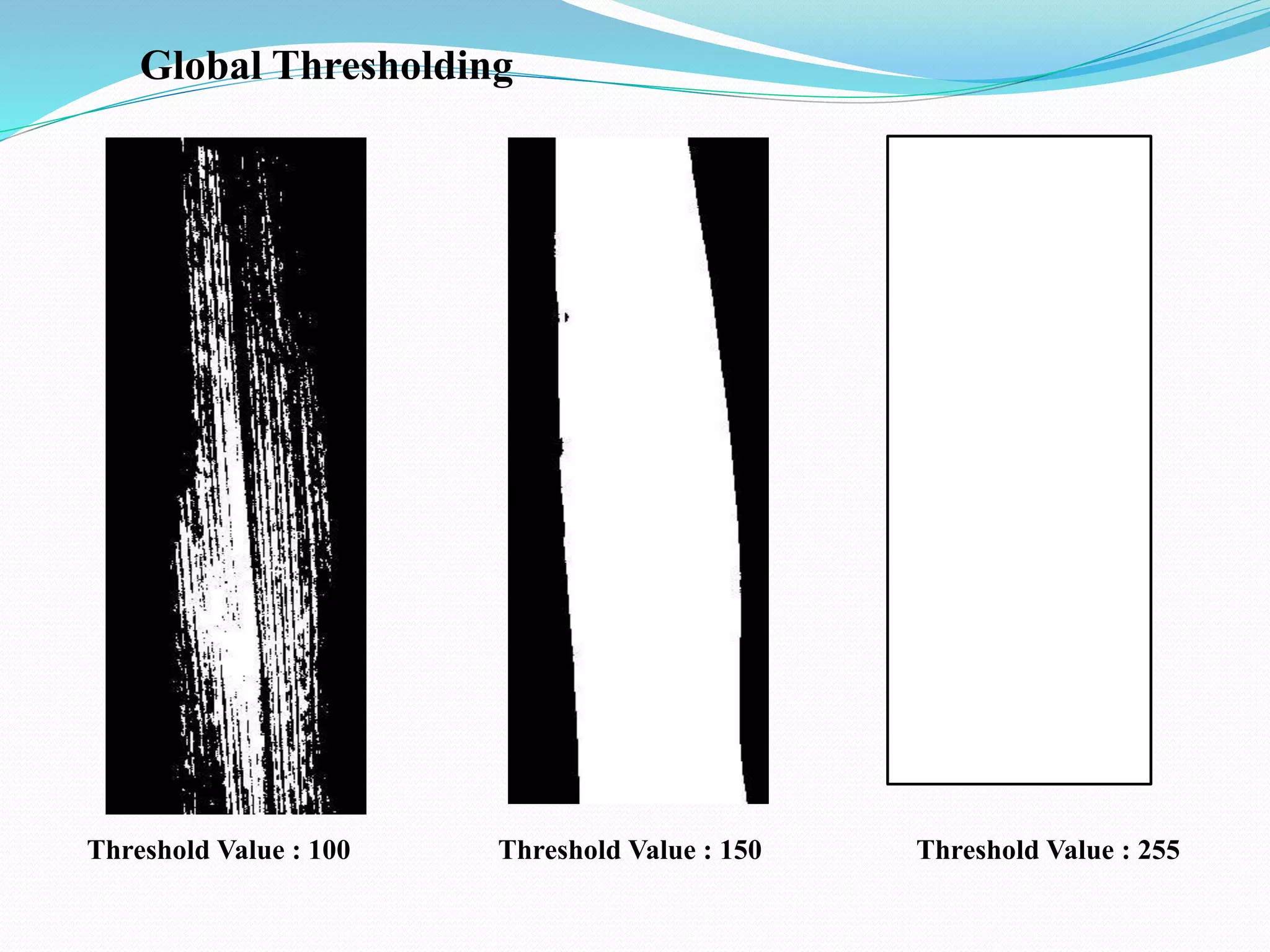
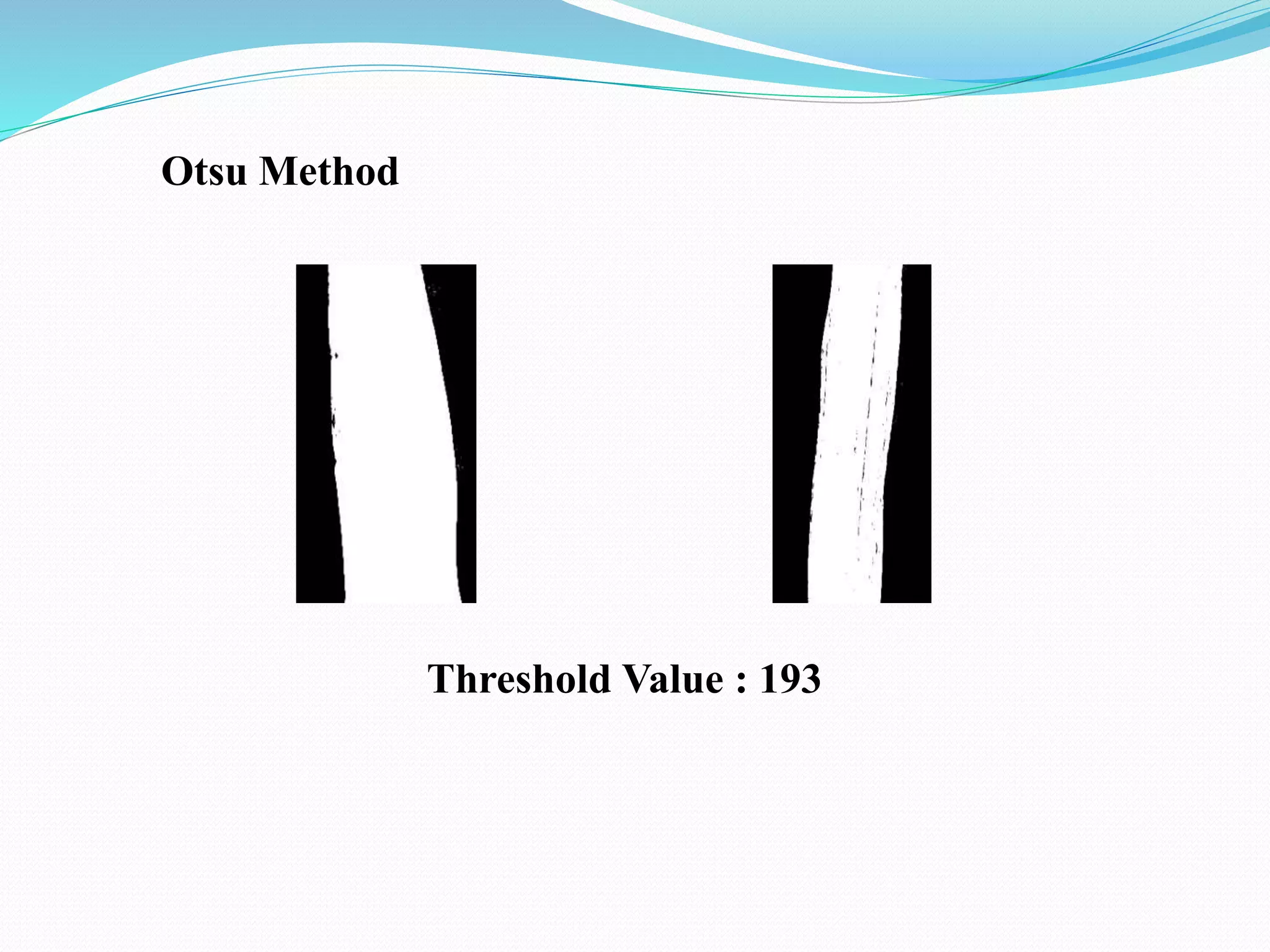
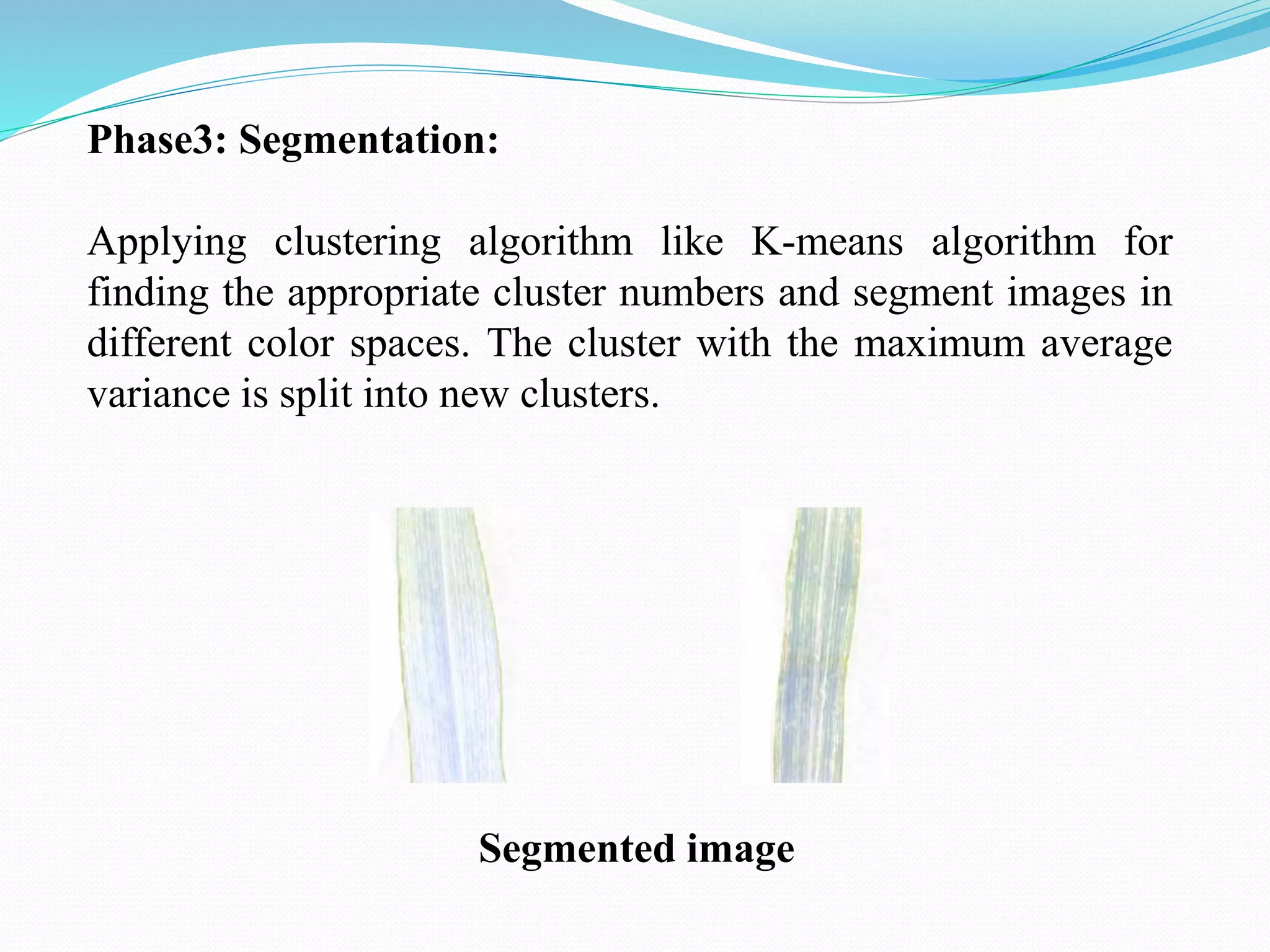
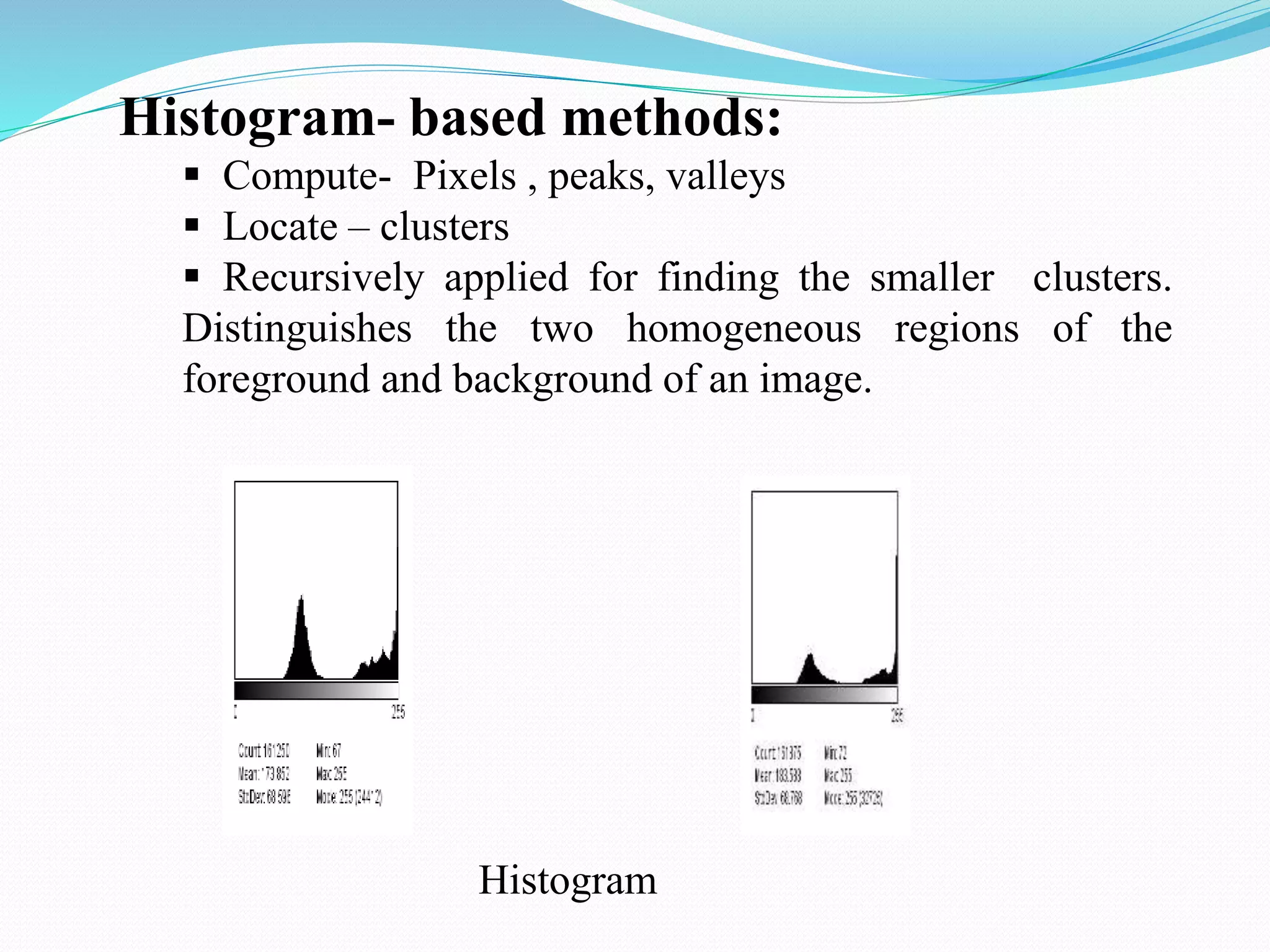
This document discusses various techniques for image processing and analysis, including image segmentation. It describes common segmentation techniques like thresholding, edge detection, color segmentation, and histogram-based methods. Thresholding techniques include global thresholding, local thresholding, and Otsu's method. Edge detection algorithms like Canny edge detection are also covered. The document provides examples of applying these techniques to extract features and segment objects from images.