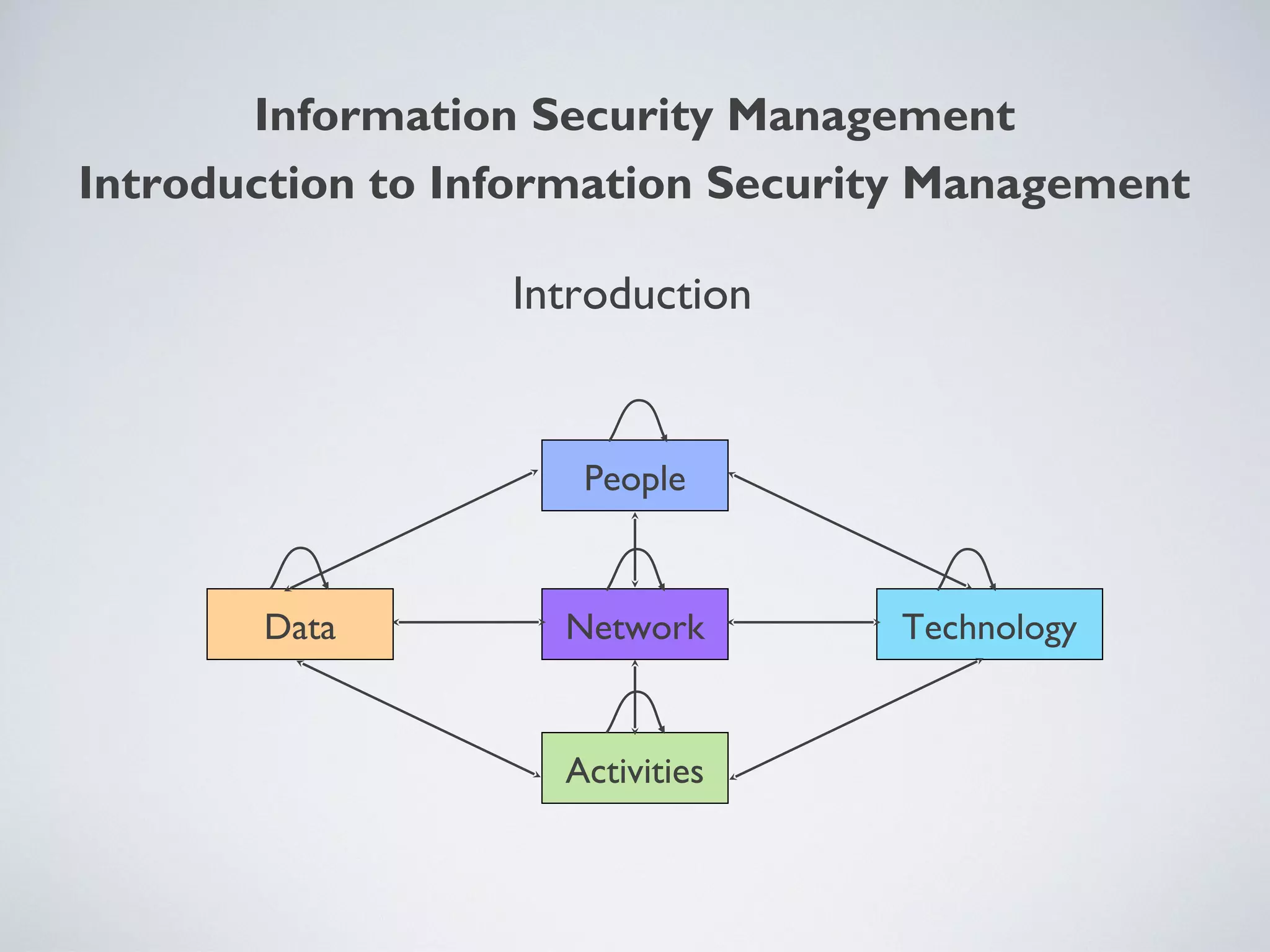
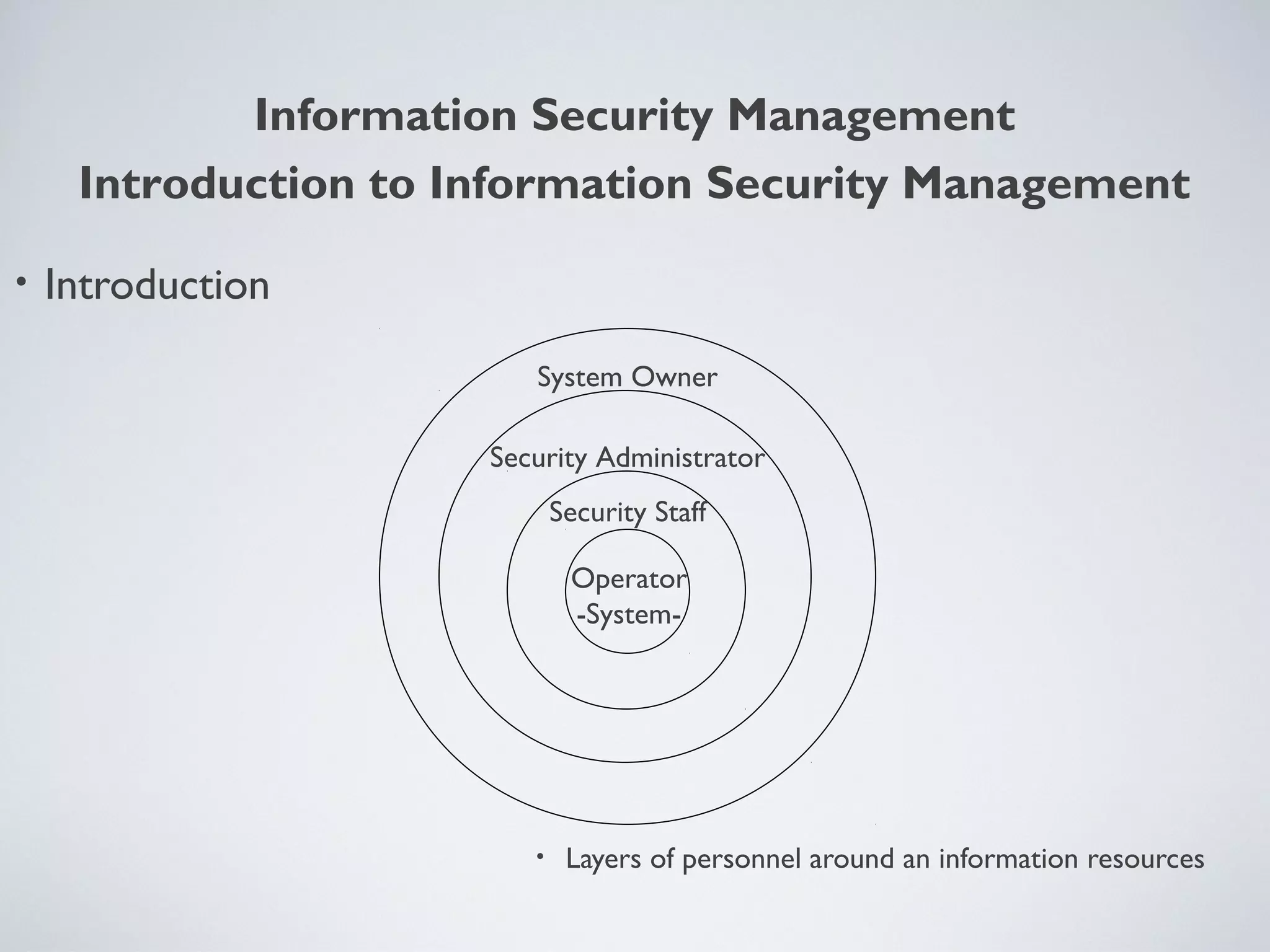
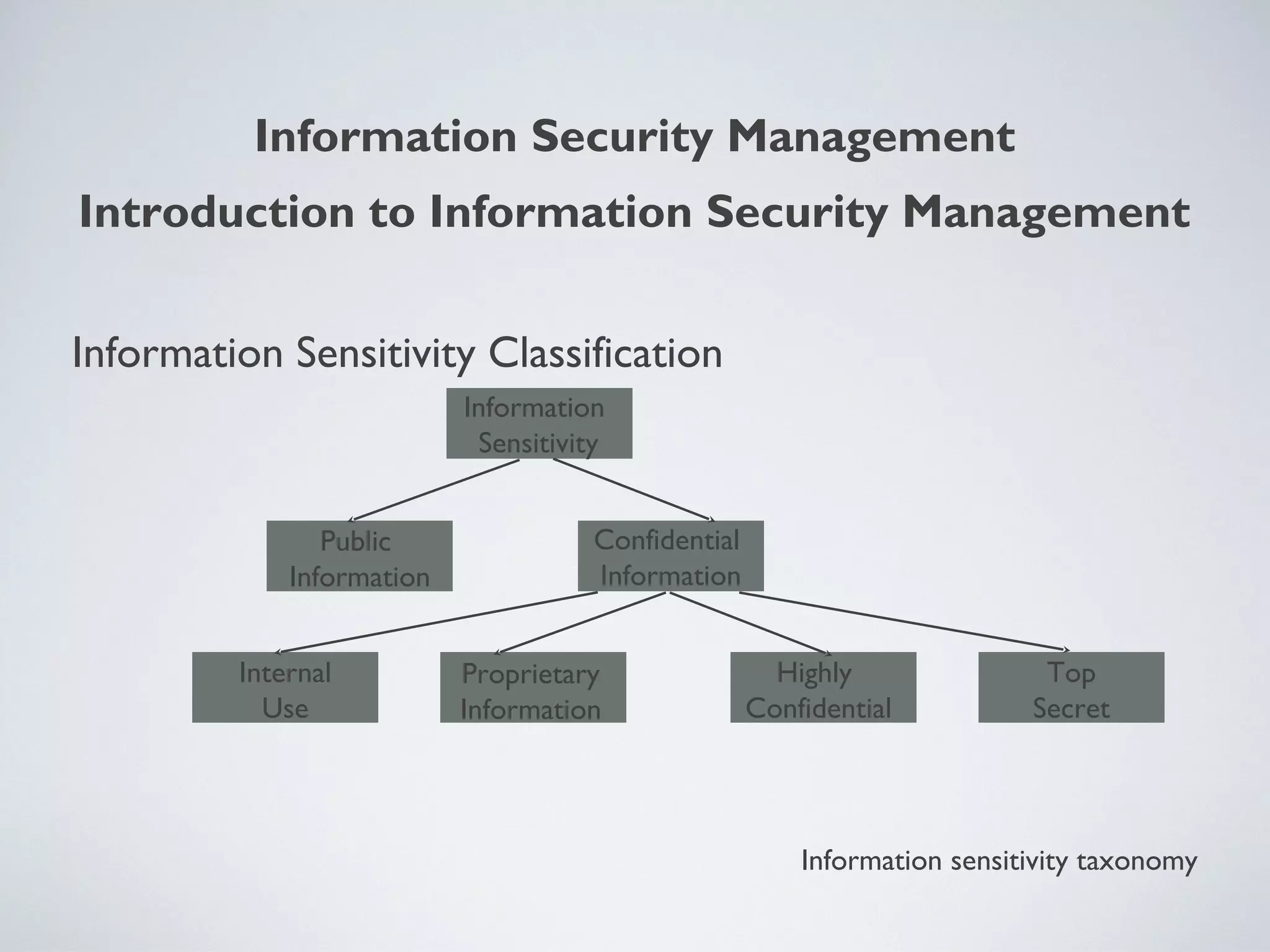
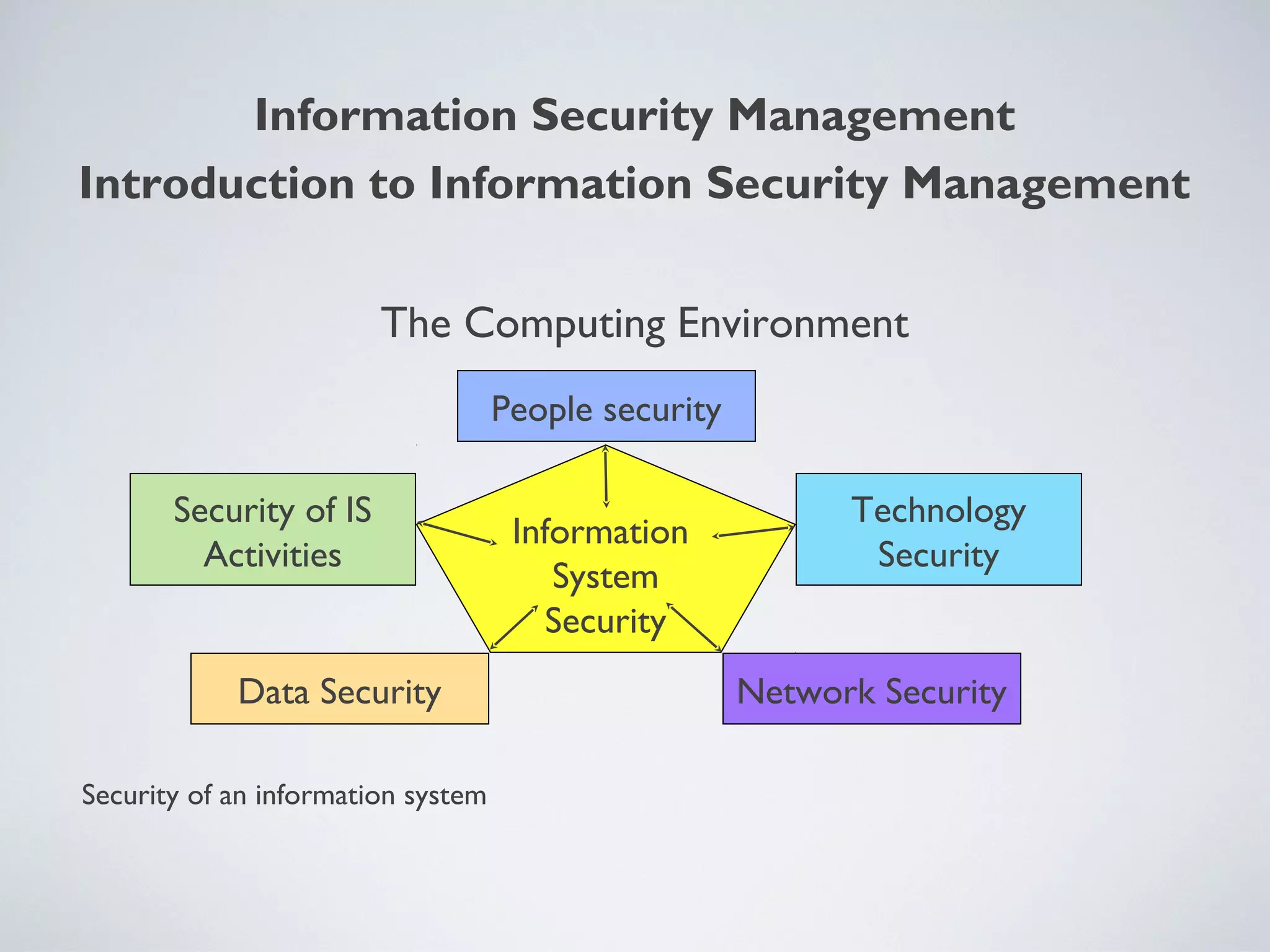
This document provides an overview of information security management, highlighting its significance in protecting organizational assets and facilitating business value generation. It discusses the classification of information sensitivity, the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, availability), and governance aspects of information security. Additionally, it outlines various security controls and assessment methodologies essential for maintaining a secure computing environment.