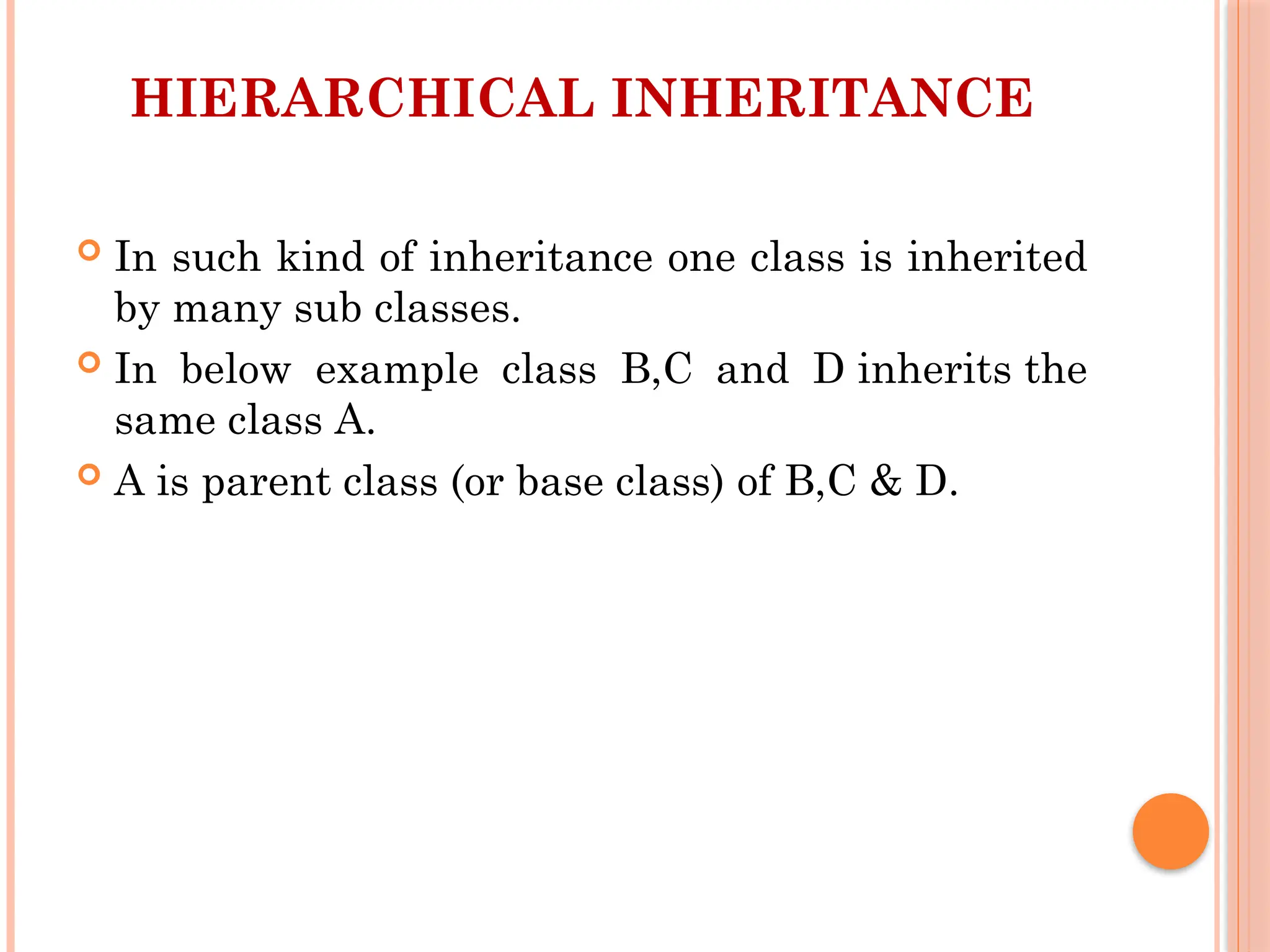
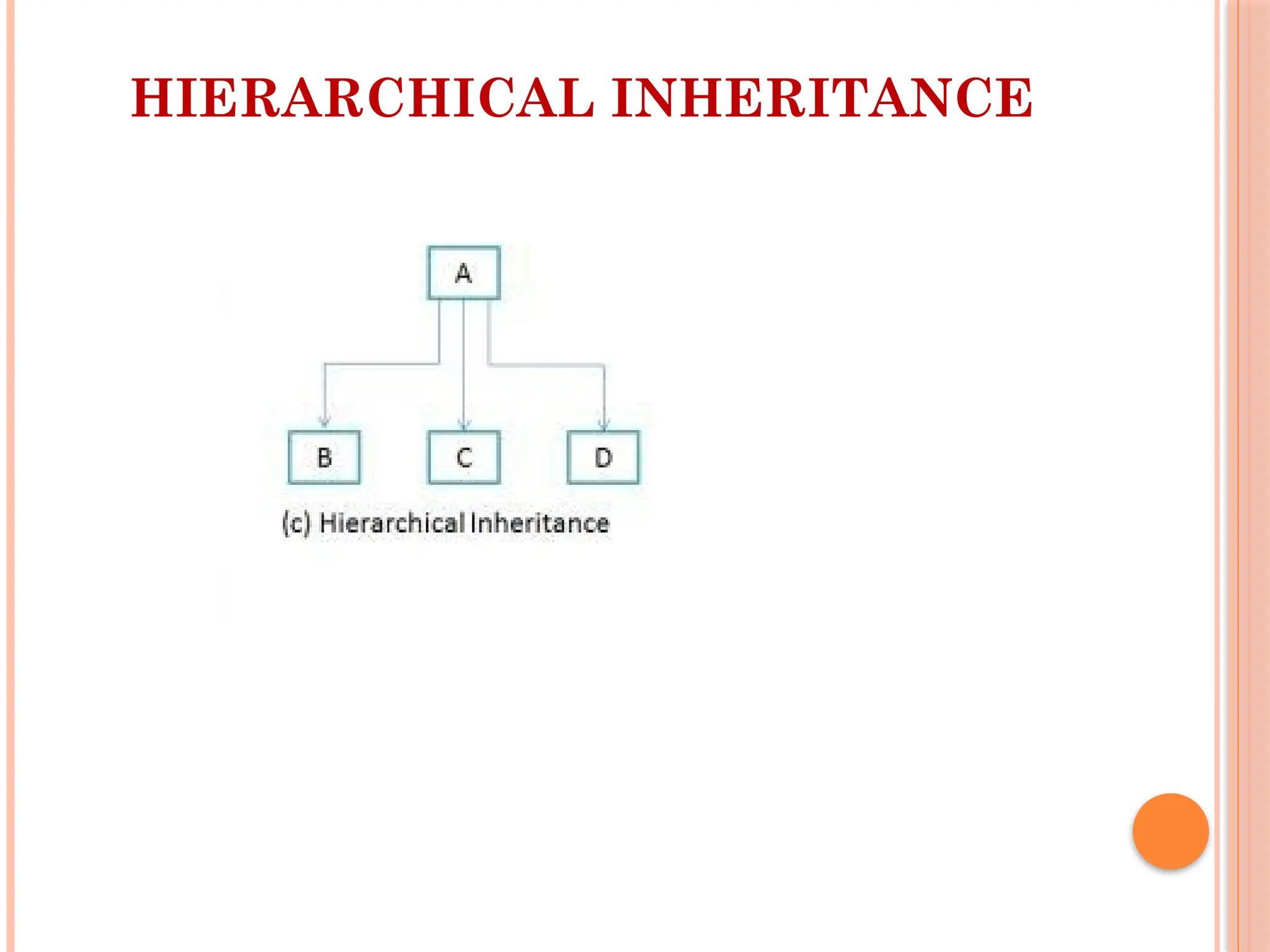
Inheritance in Java is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object. It is an important pillar of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). It allows for code reusability, where a class (subclass) can inherit fields and methods from another class (superclass).



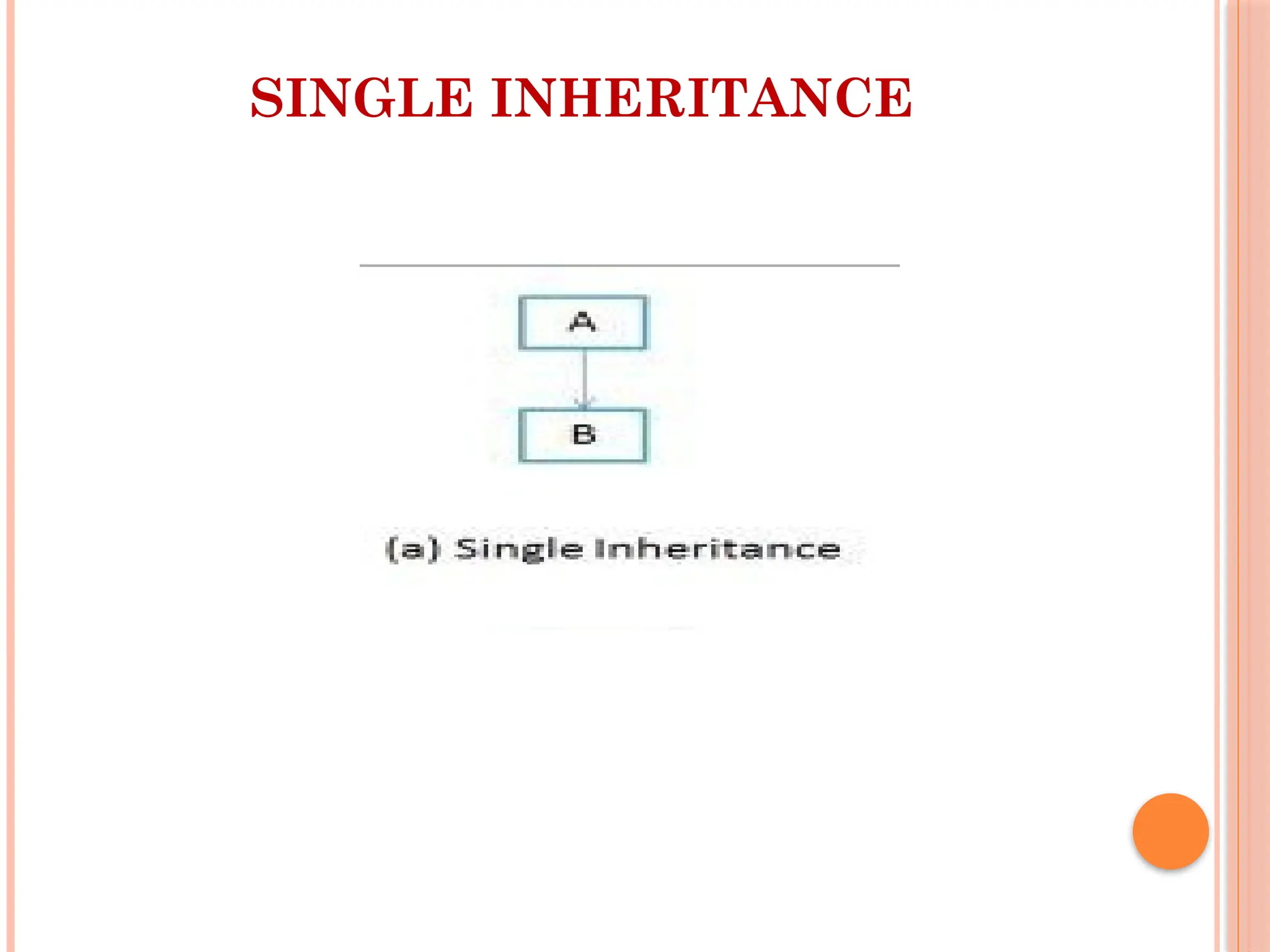
![ Single Inheritance example program in Java
Class A { public void methodA()
{ System.out.println("Base class method");
} } Class B extends A
{ public void methodB()
{ System.out.println("Child class method");
} public static void main(String args[])
{ B obj = new B(); obj.methodA();
//calling super class method obj.methodB();
//calling local method } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-250425085445-ebe8adc7/75/Inheritance-in-Java-An-Introduction-types-5-2048.jpg)

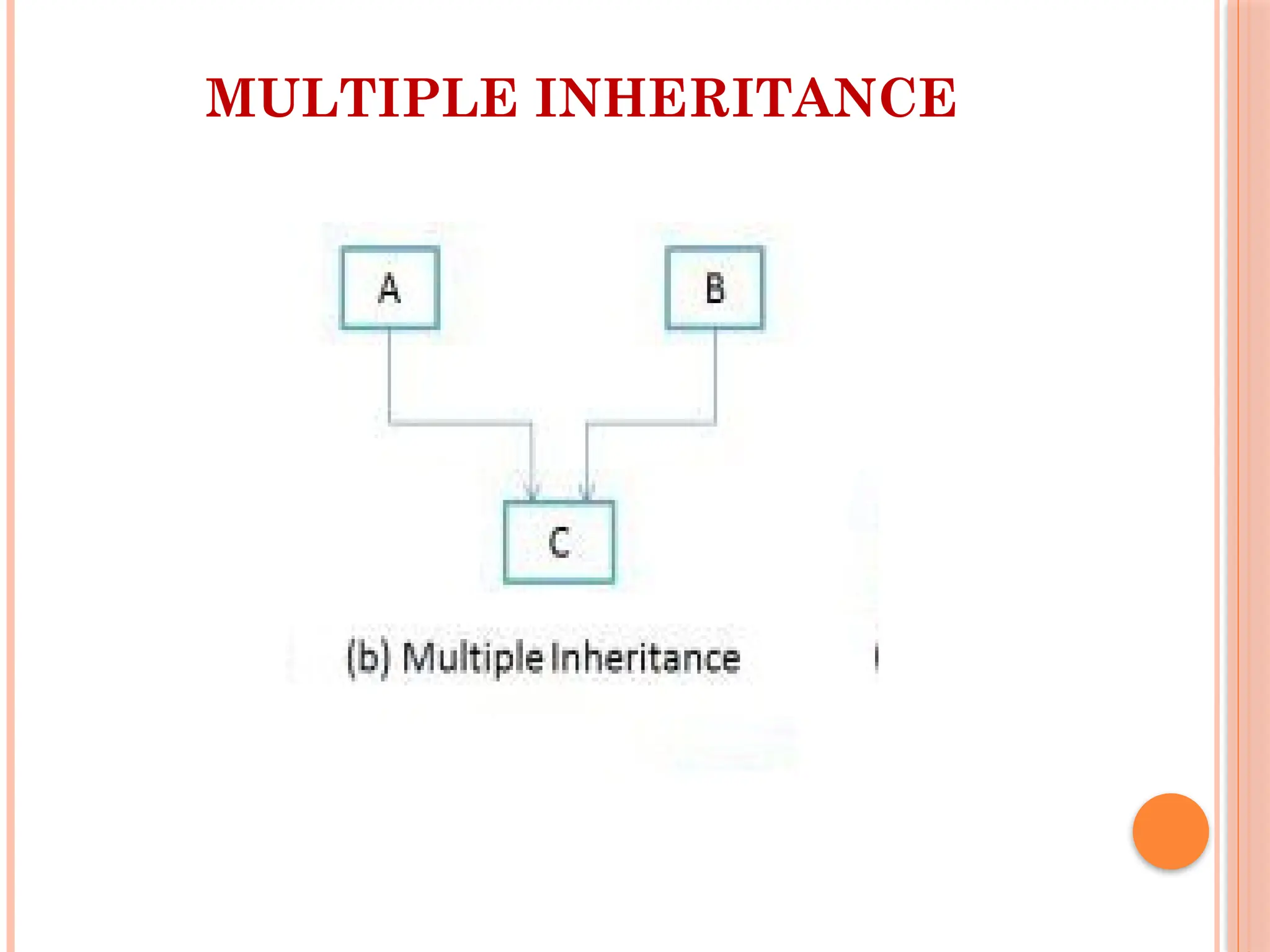



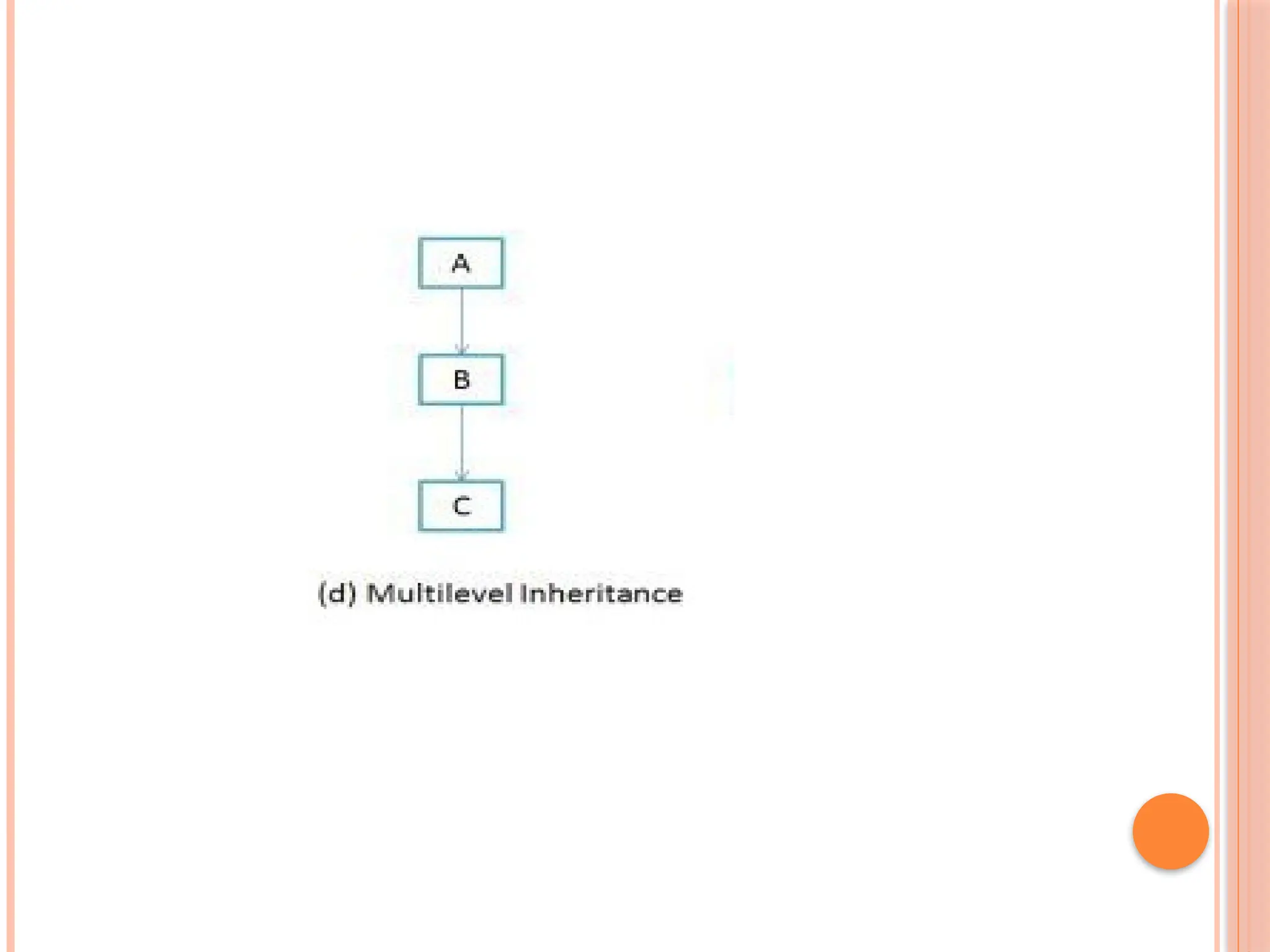
![MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE EXA
MPLE PROGRAM IN JAVA
public static void main(String args[])
{ Z obj = new Z(); obj.methodX();
//calling grand parent class method
obj.methodY();
//calling parent class method obj.methodZ();
//calling local method }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-250425085445-ebe8adc7/75/Inheritance-in-Java-An-Introduction-types-13-2048.jpg)