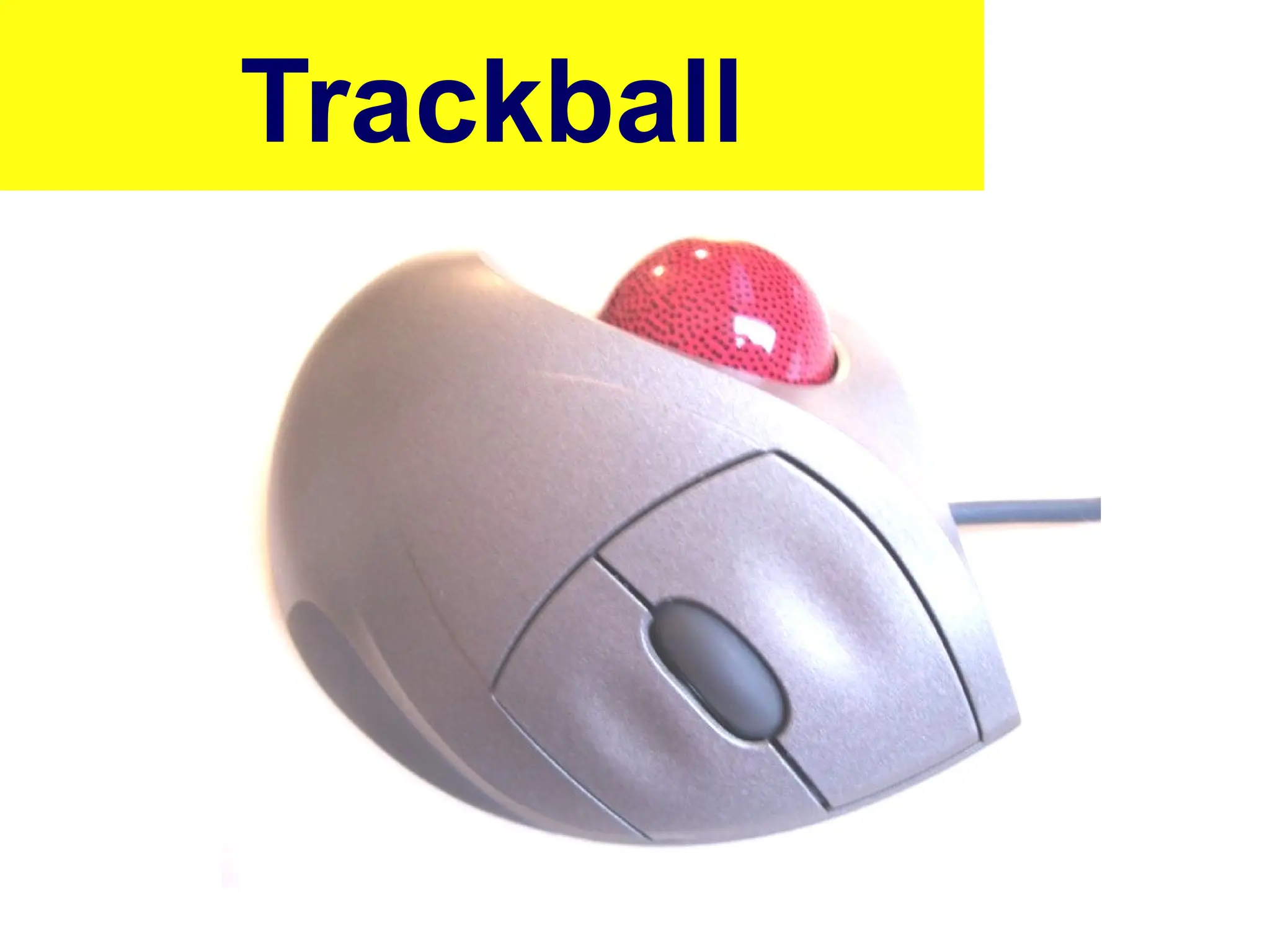
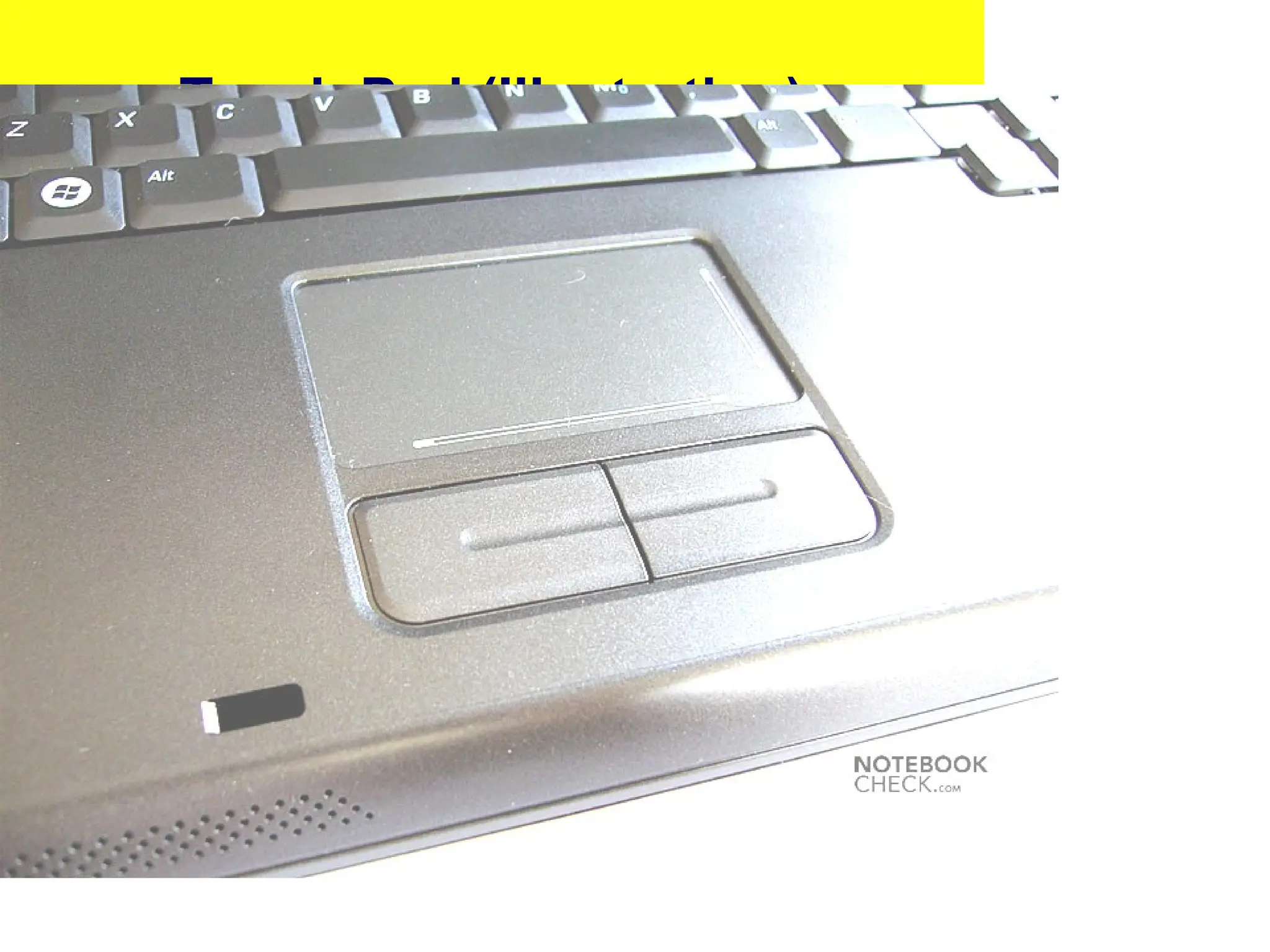
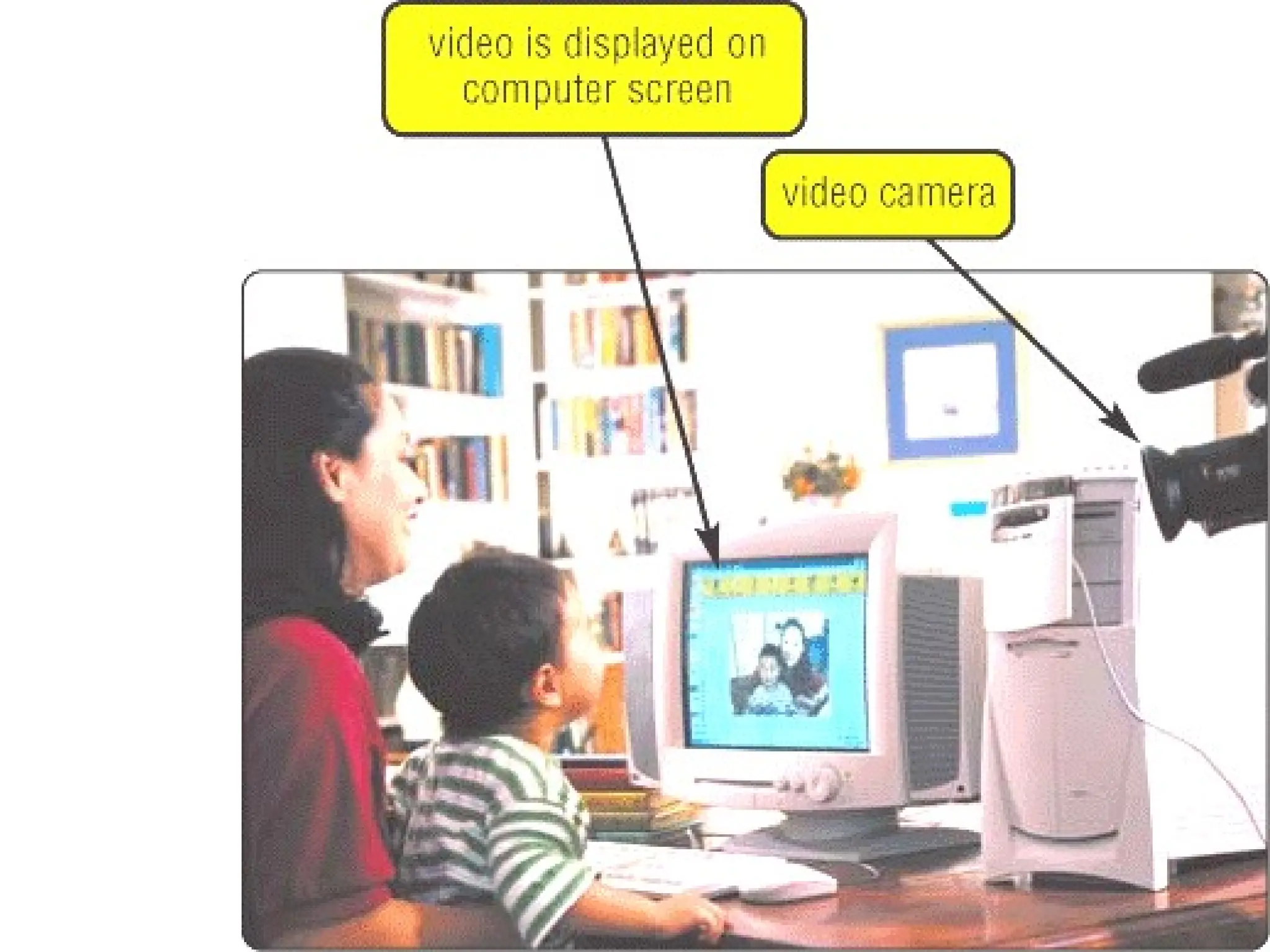
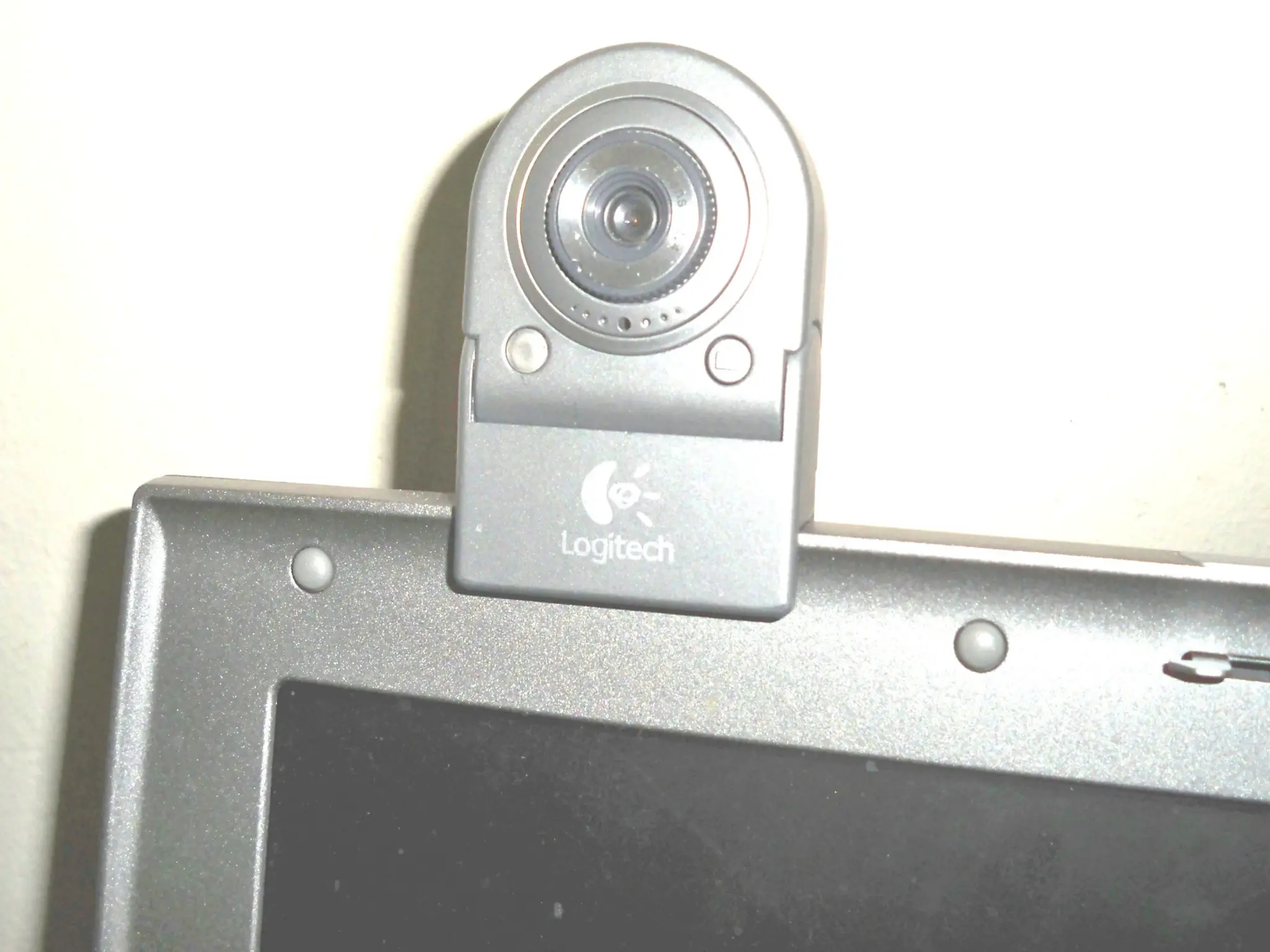
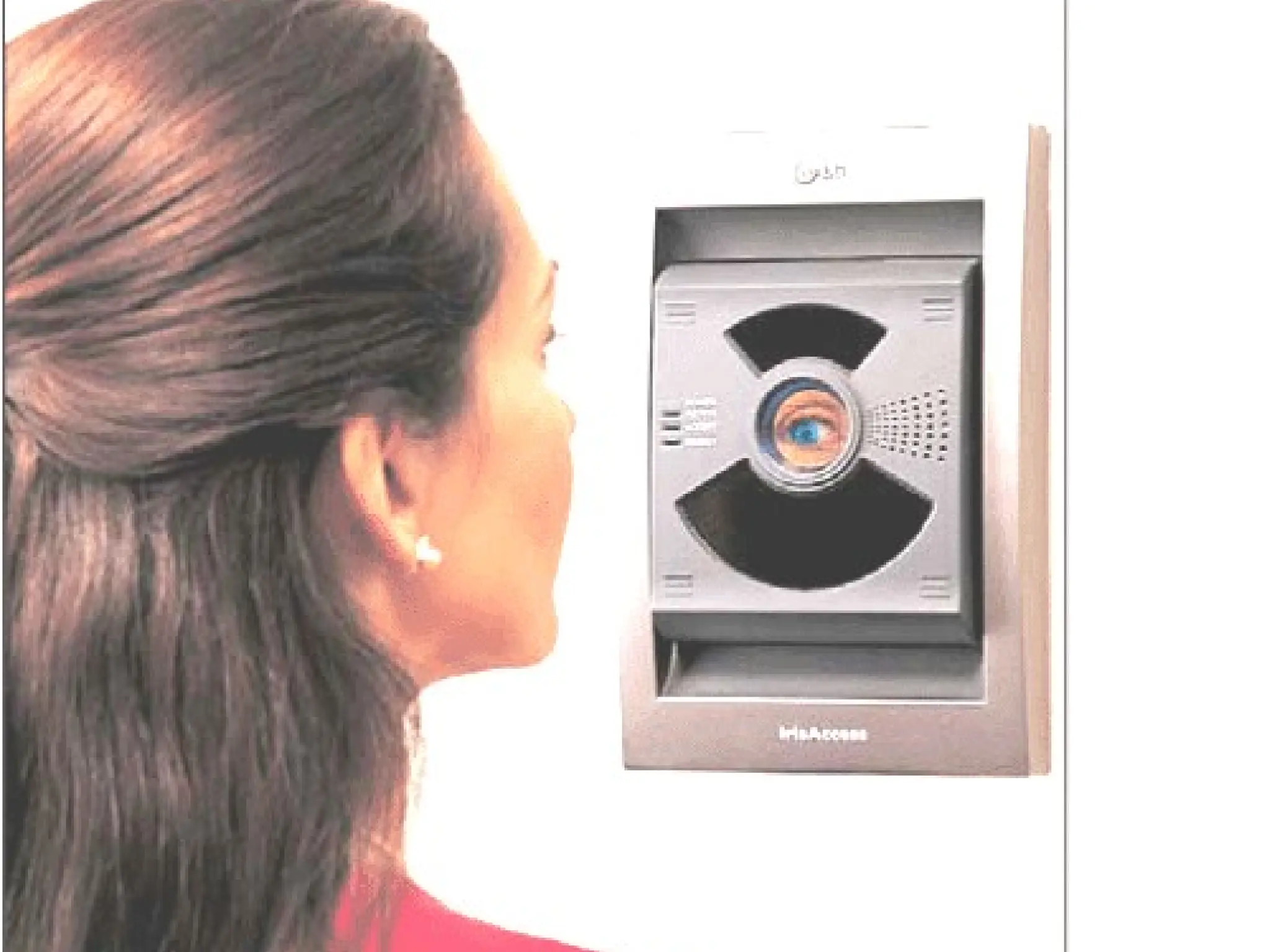
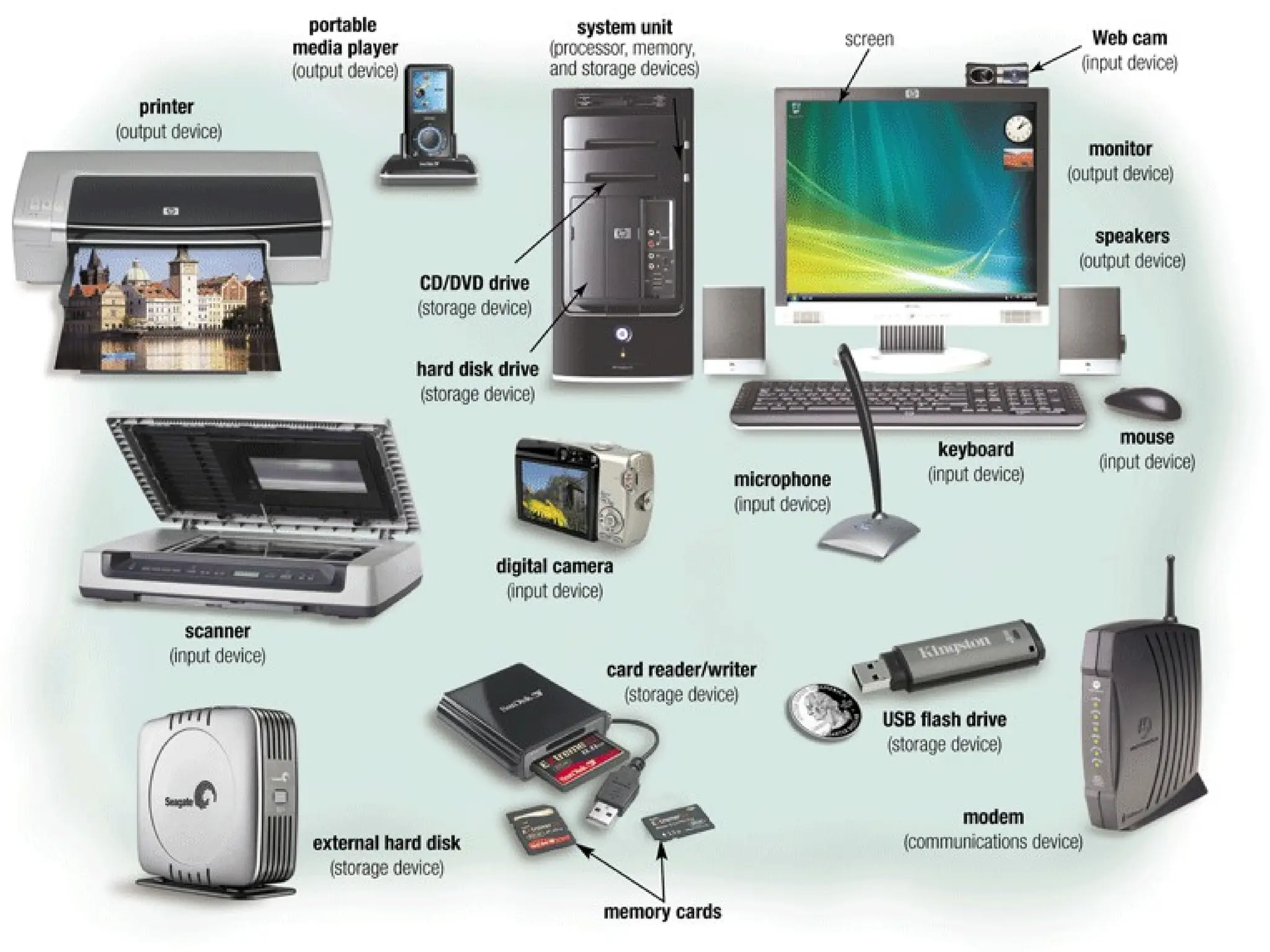
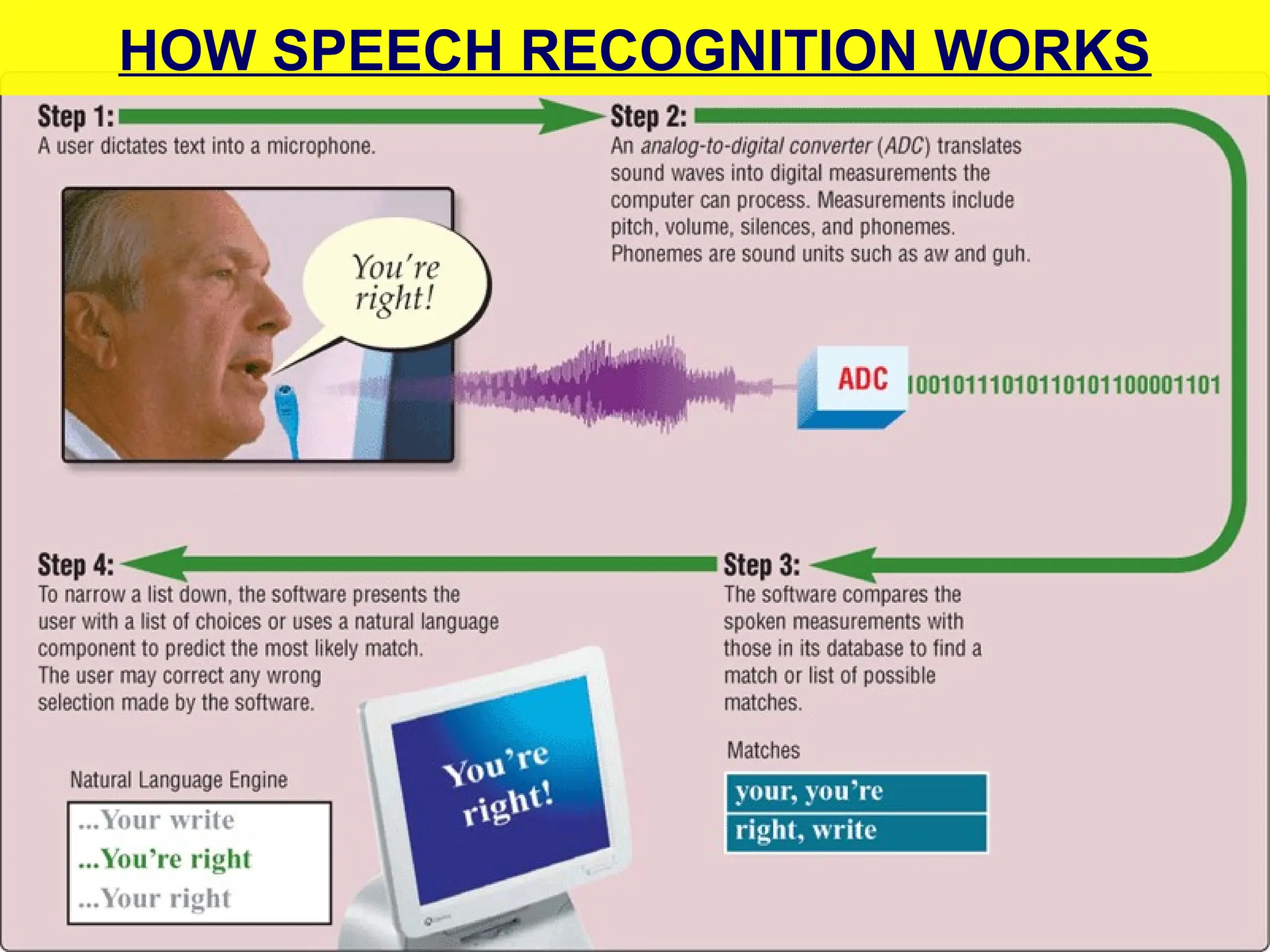
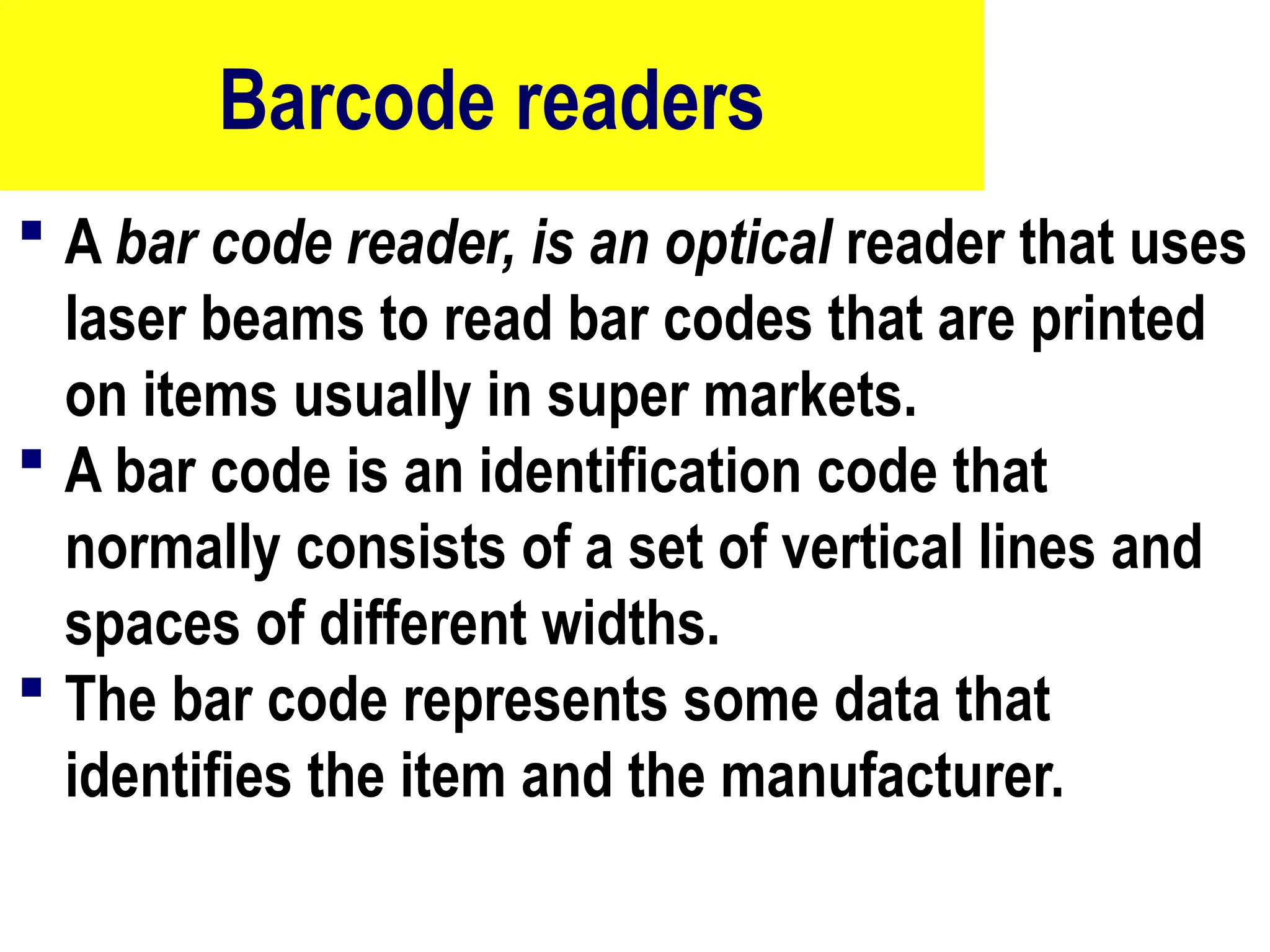
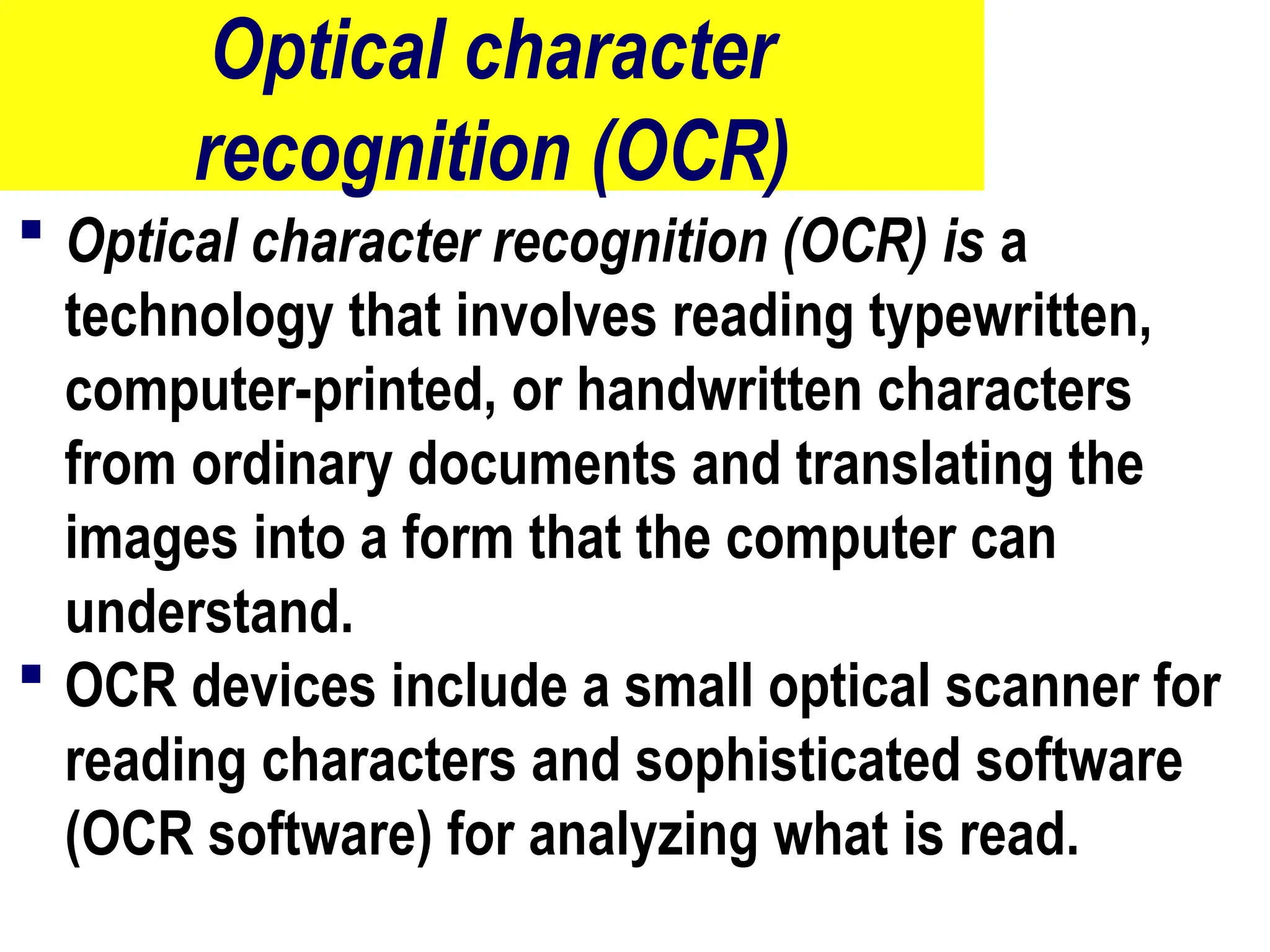
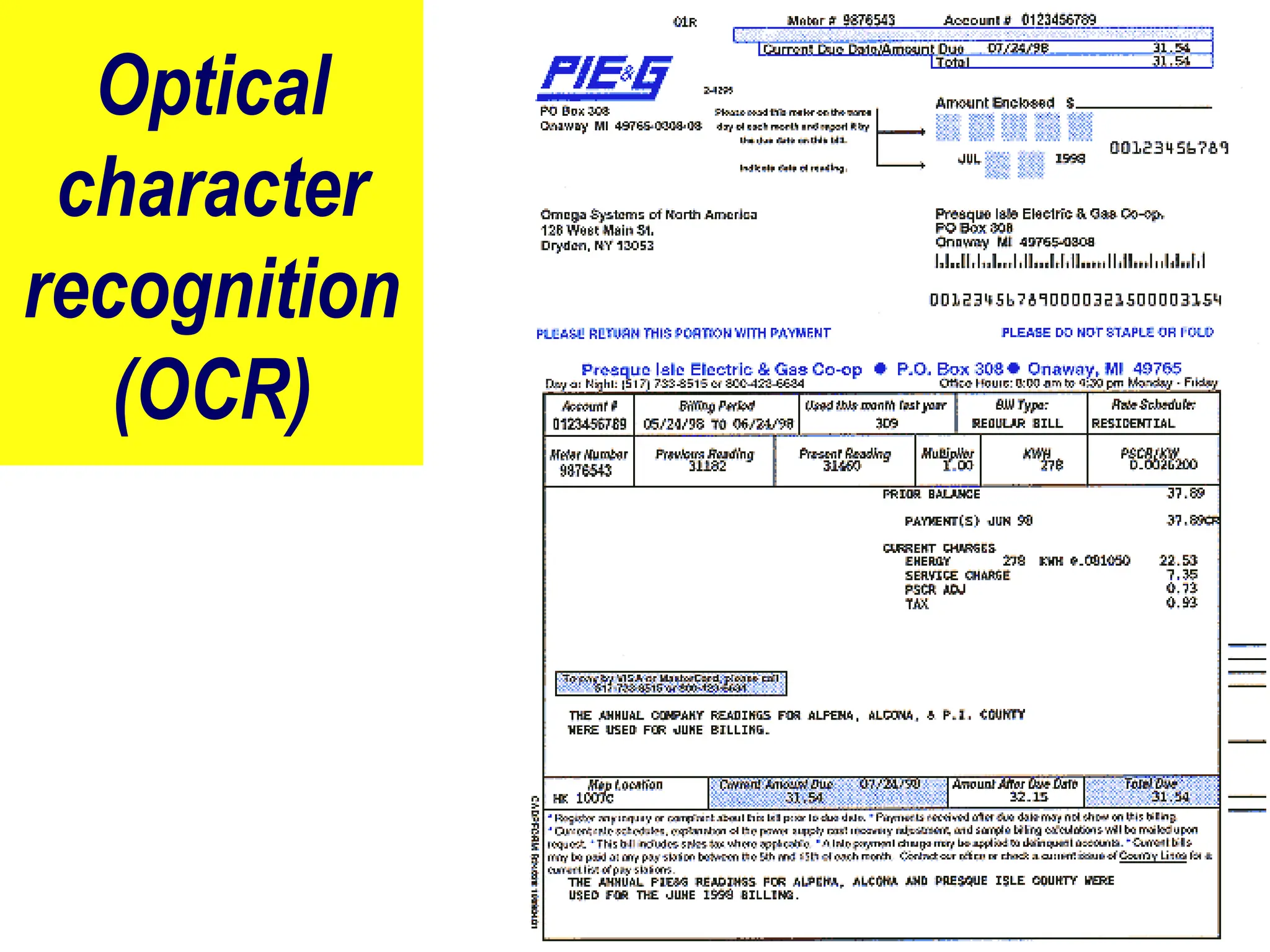
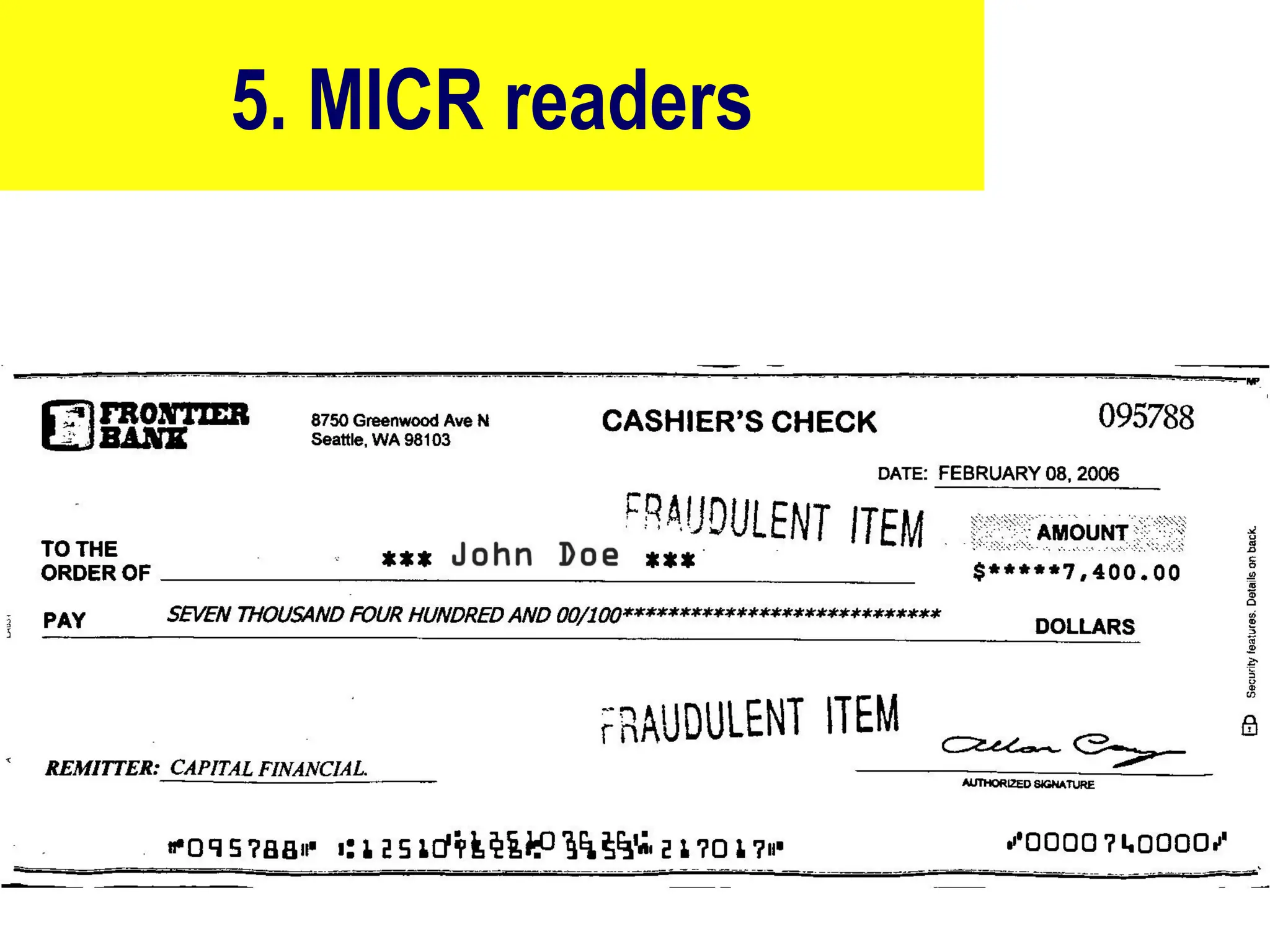
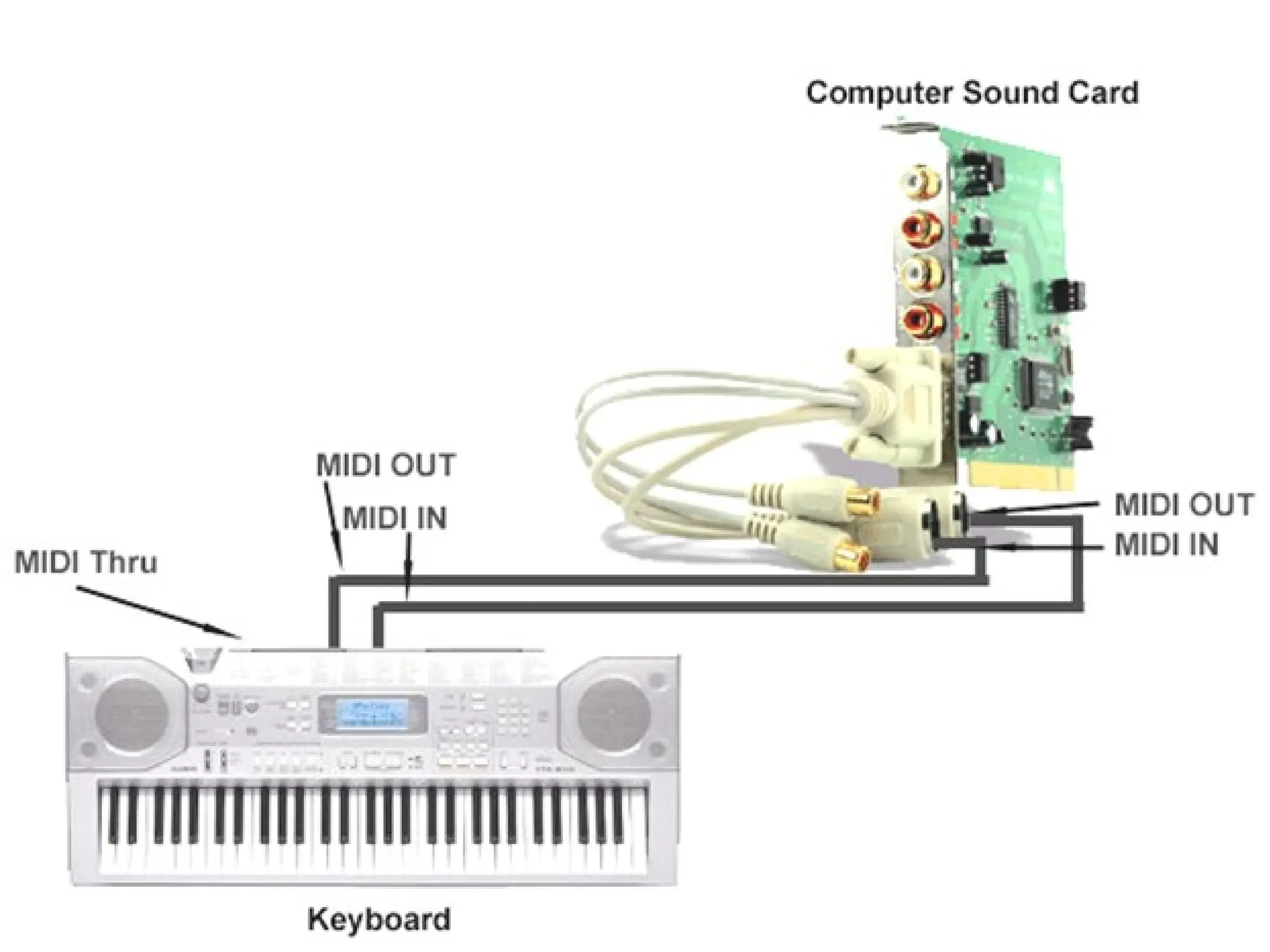
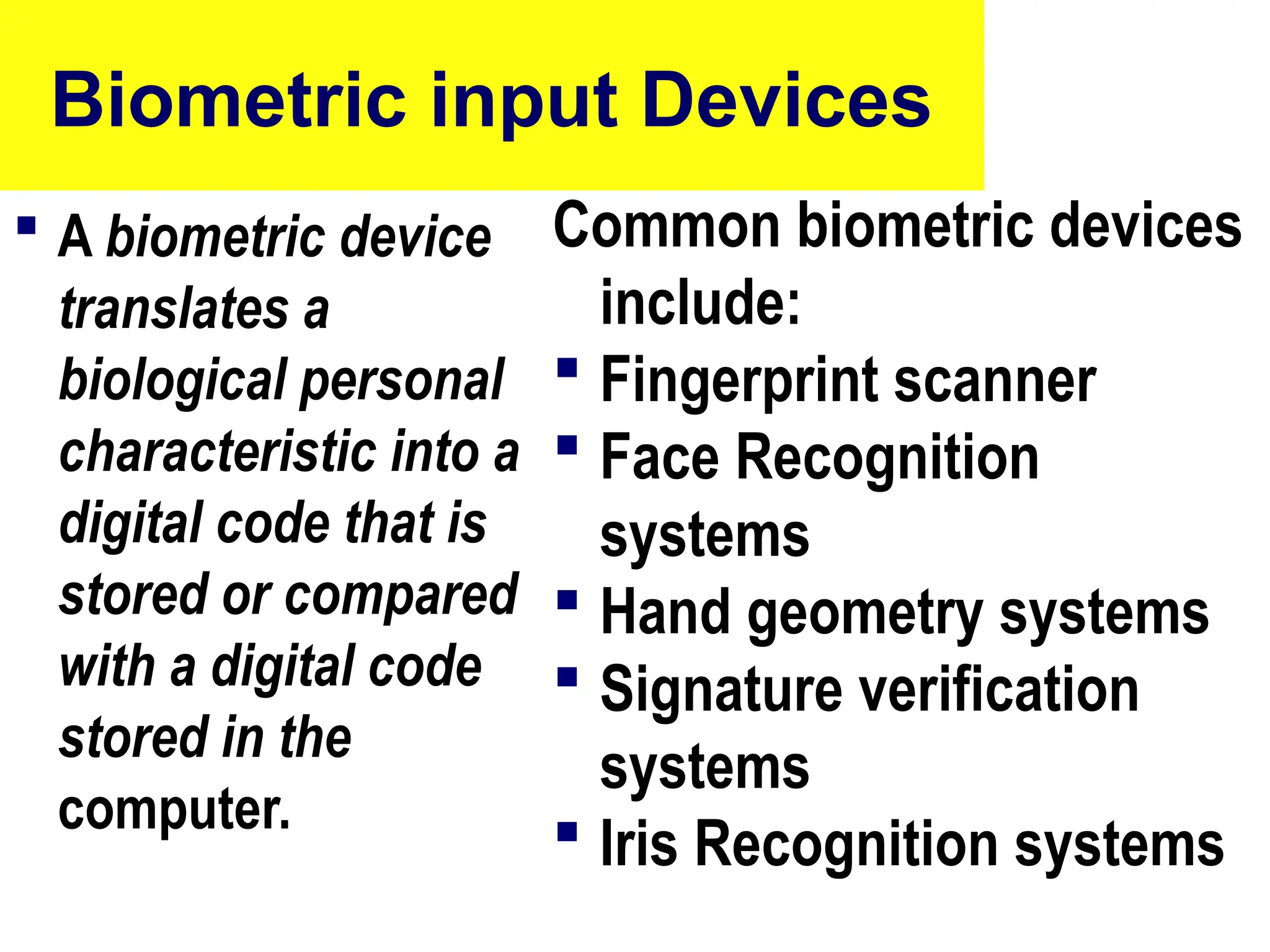
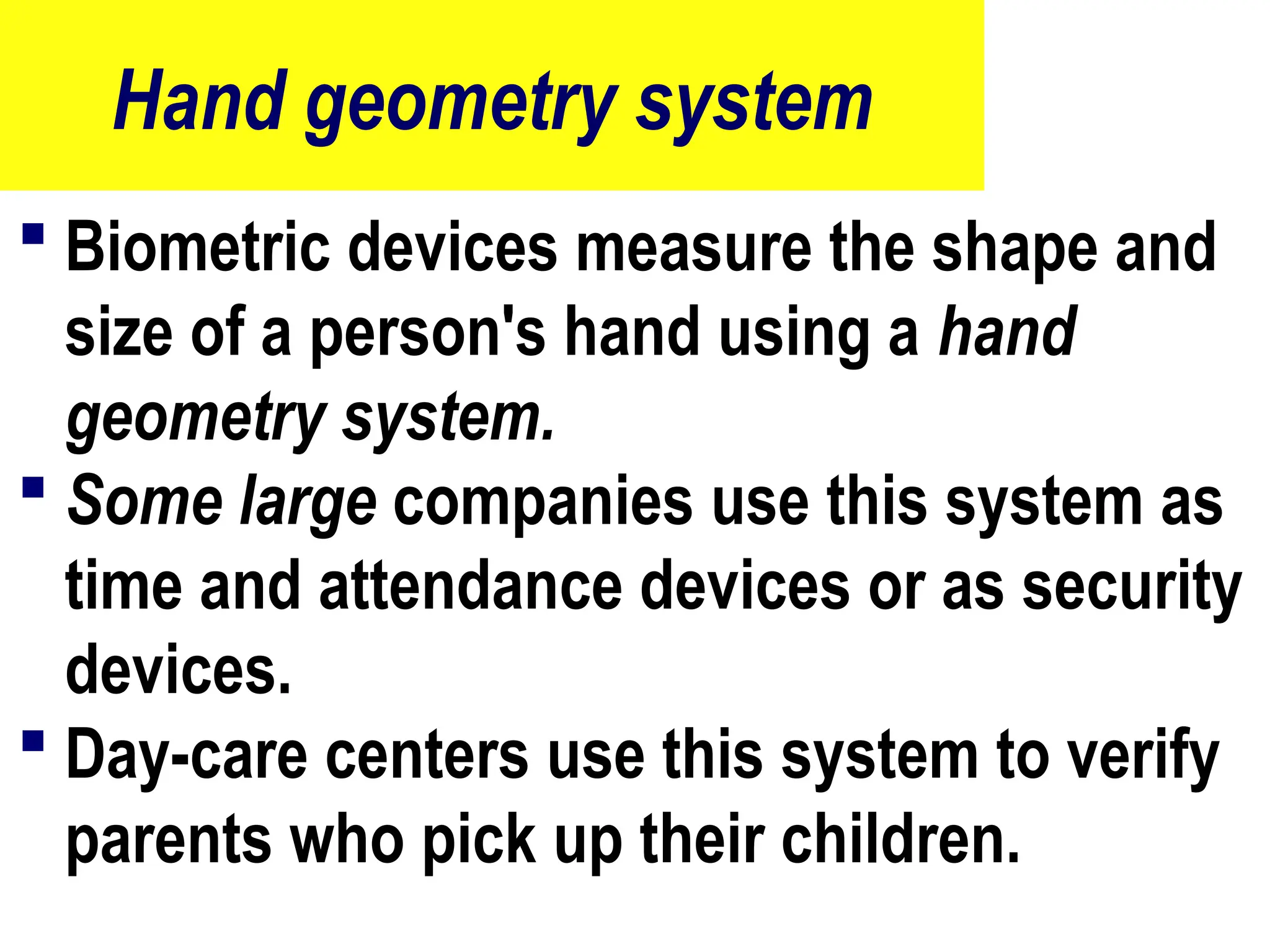
The document provides an overview of computer hardware, focusing on input devices used to enter data into a computer. It categorizes input devices into text, pointing, imaging, gaming, audio, and biometric types, detailing each type's functionalities and examples, such as keyboards, mice, scanners, and voice recognition systems. The information is targeted towards students in computer studies, helping them understand the roles and characteristics of various input devices.