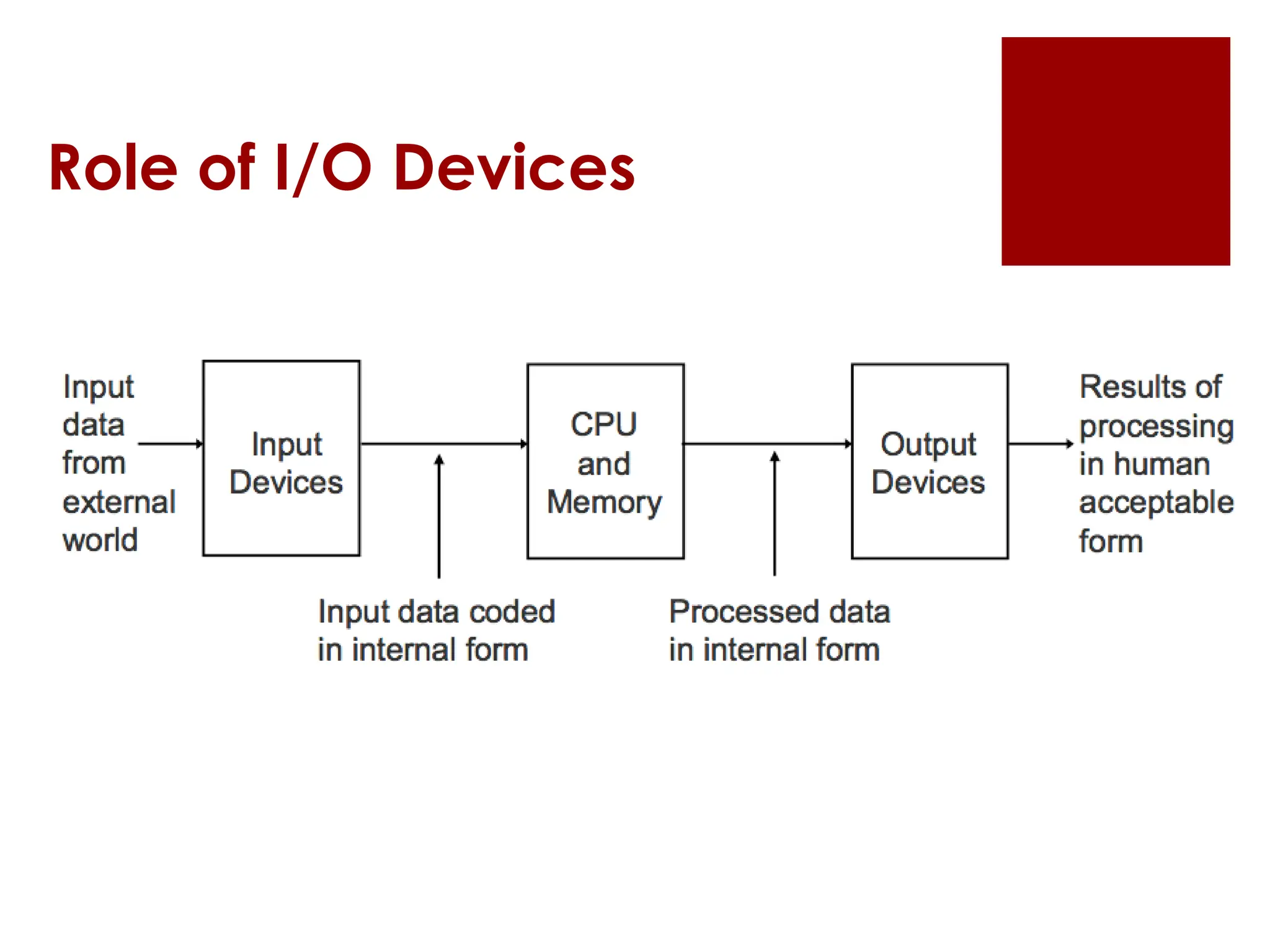
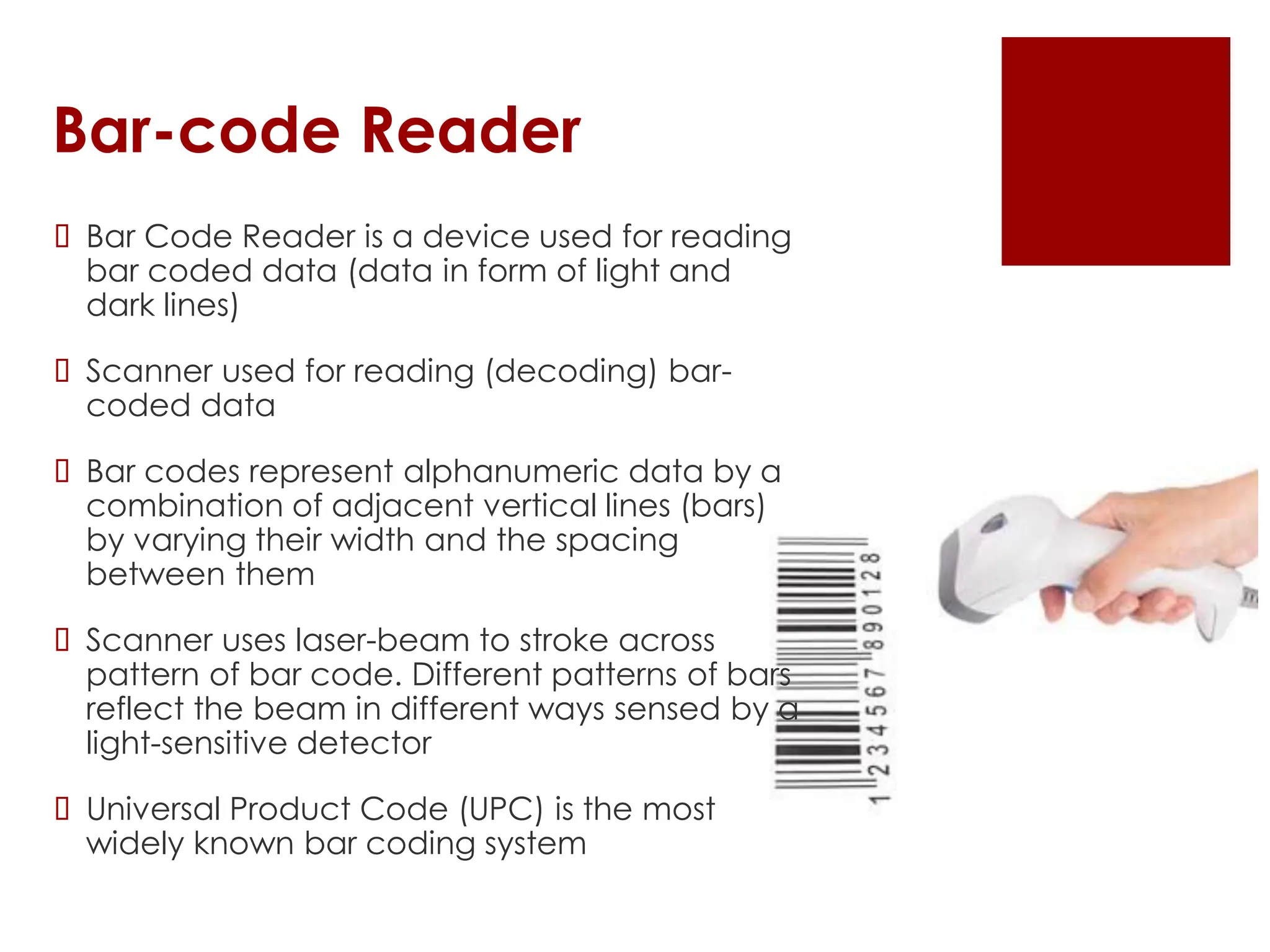
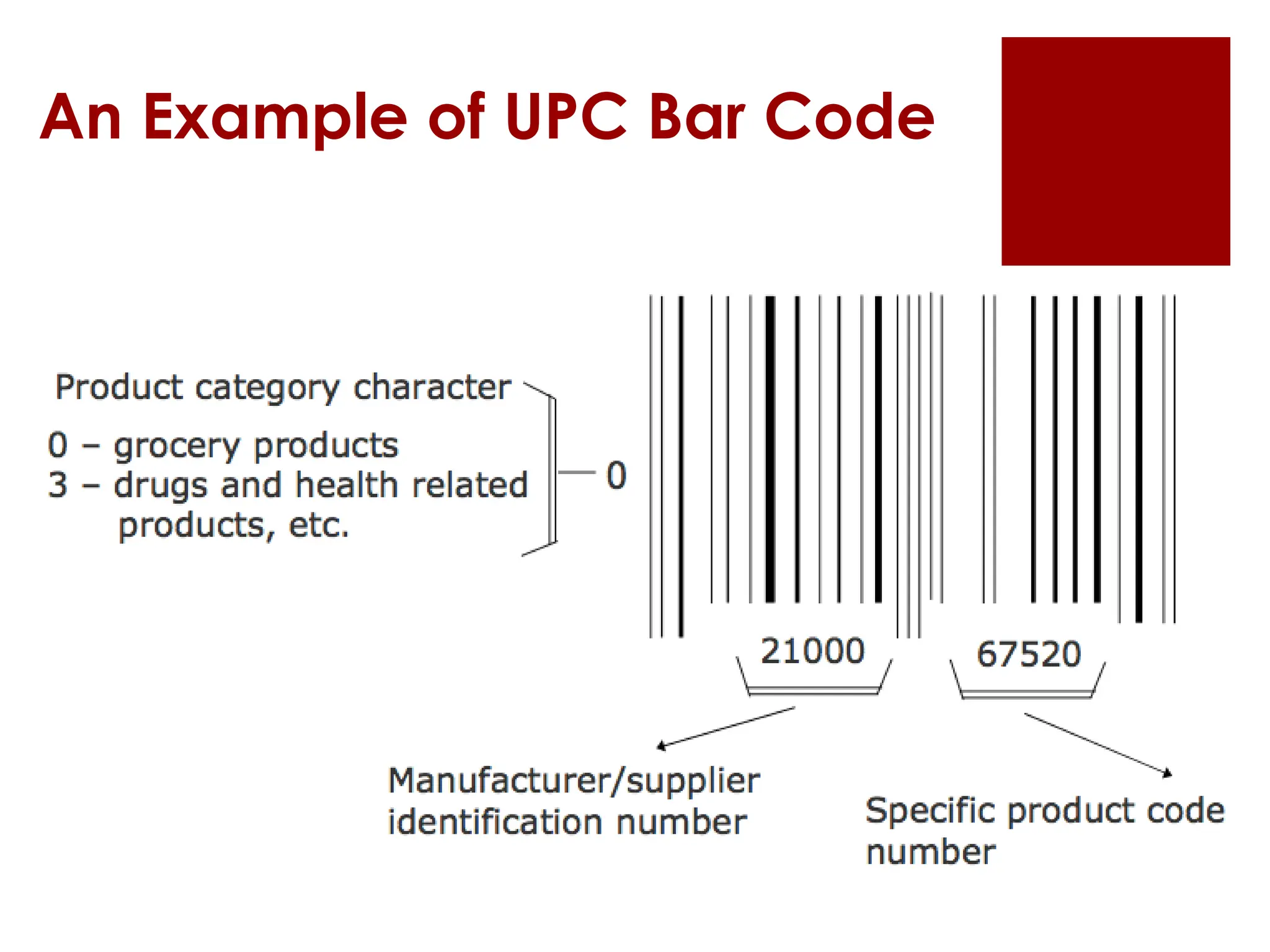
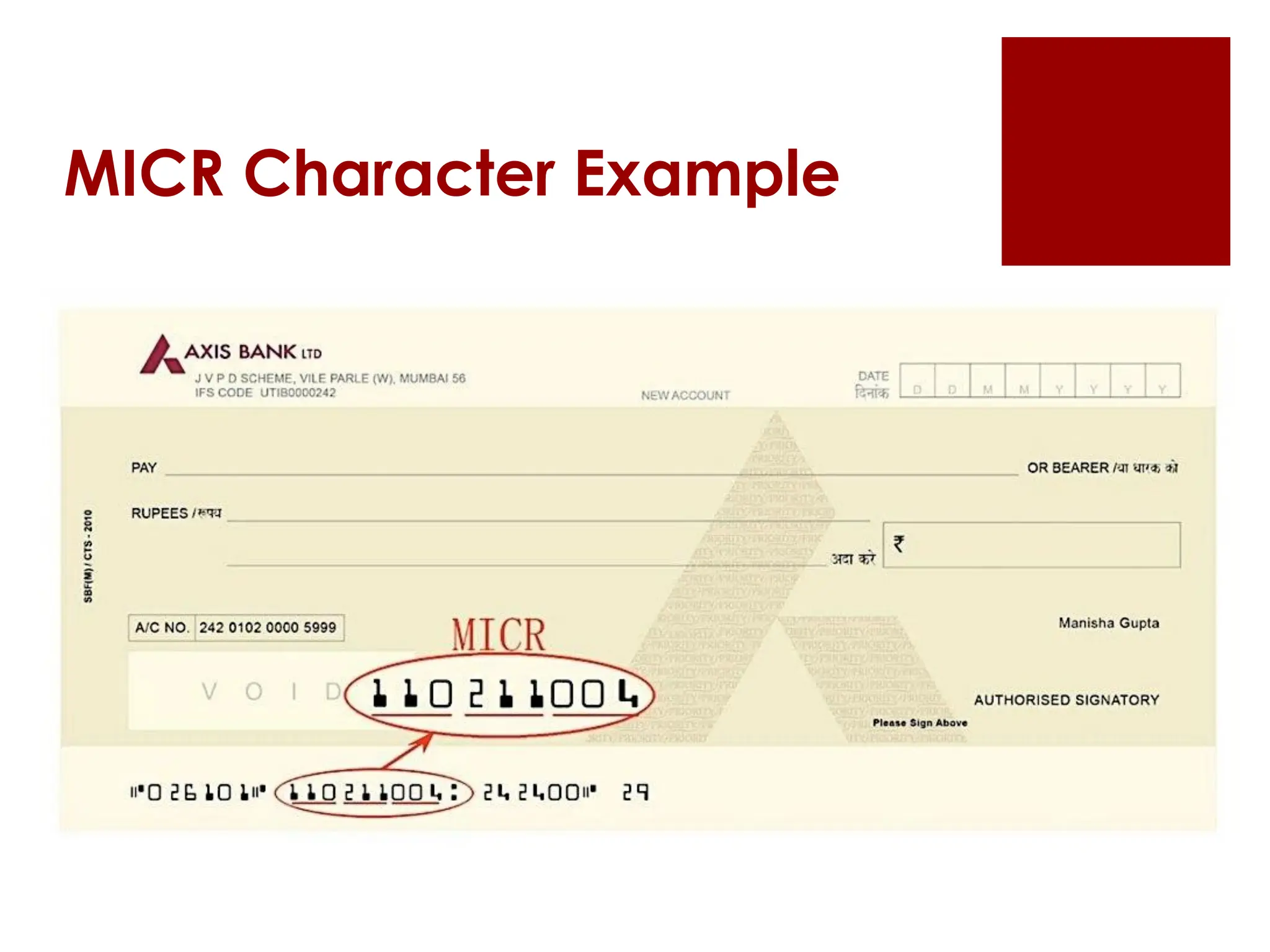
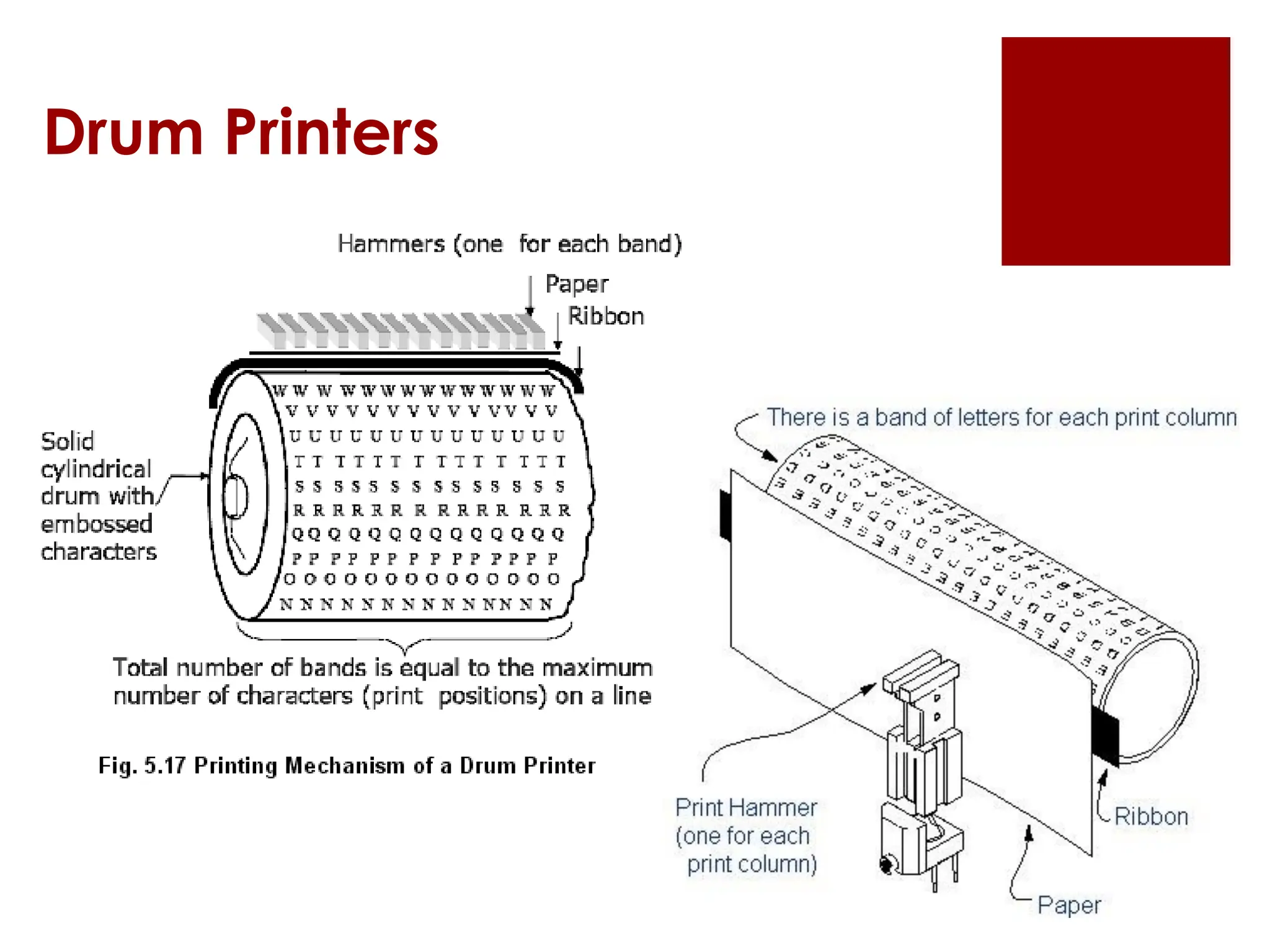
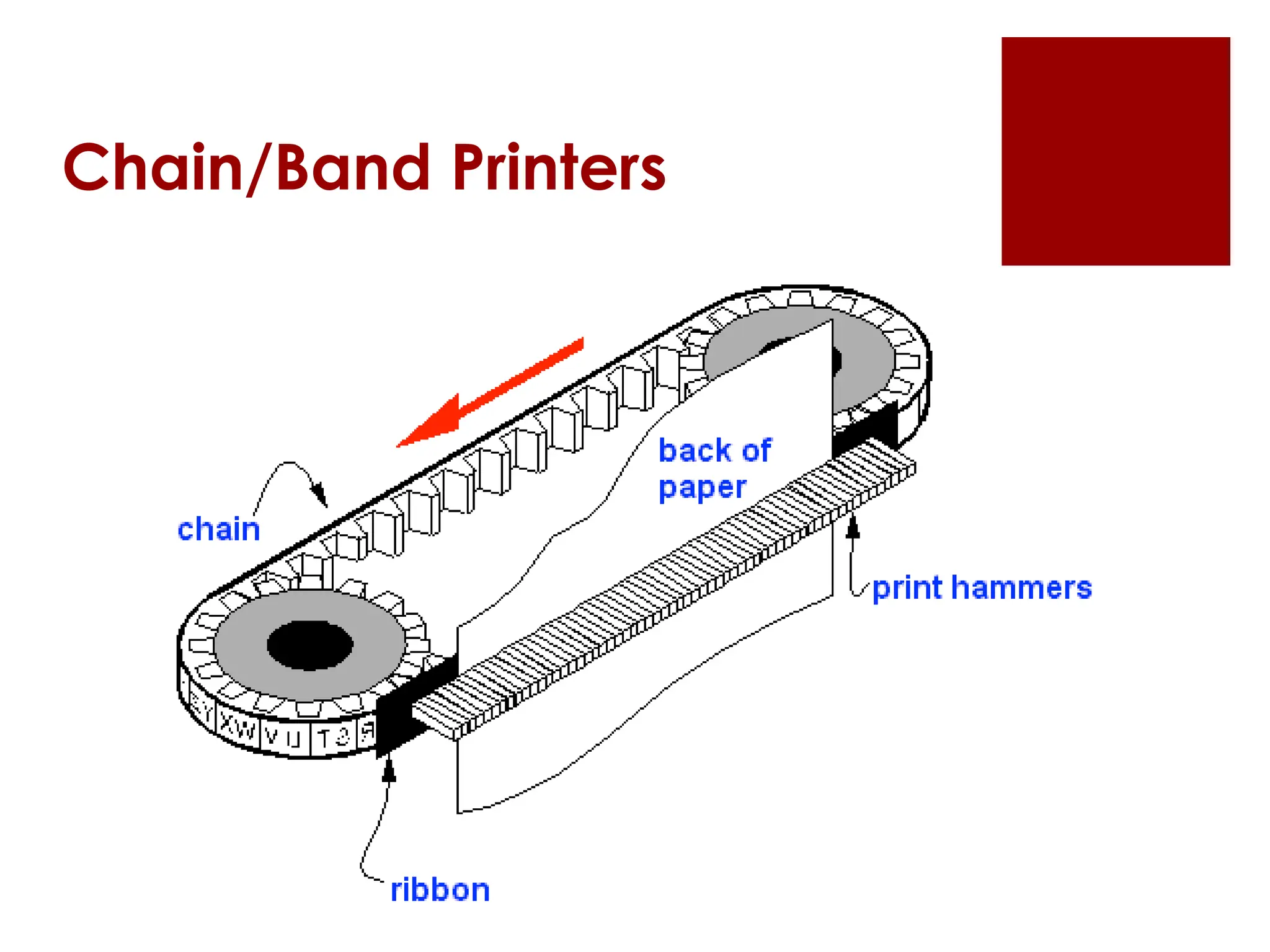
The document provides an overview of input/output (I/O) devices, including their roles, types, and functionalities. It covers common input devices such as keyboards and mice, as well as output devices like monitors and printers, detailing their characteristics and uses. Additionally, it discusses various specialized devices like scanners and speech recognition systems, highlighting their importance in enhancing human-computer interaction.