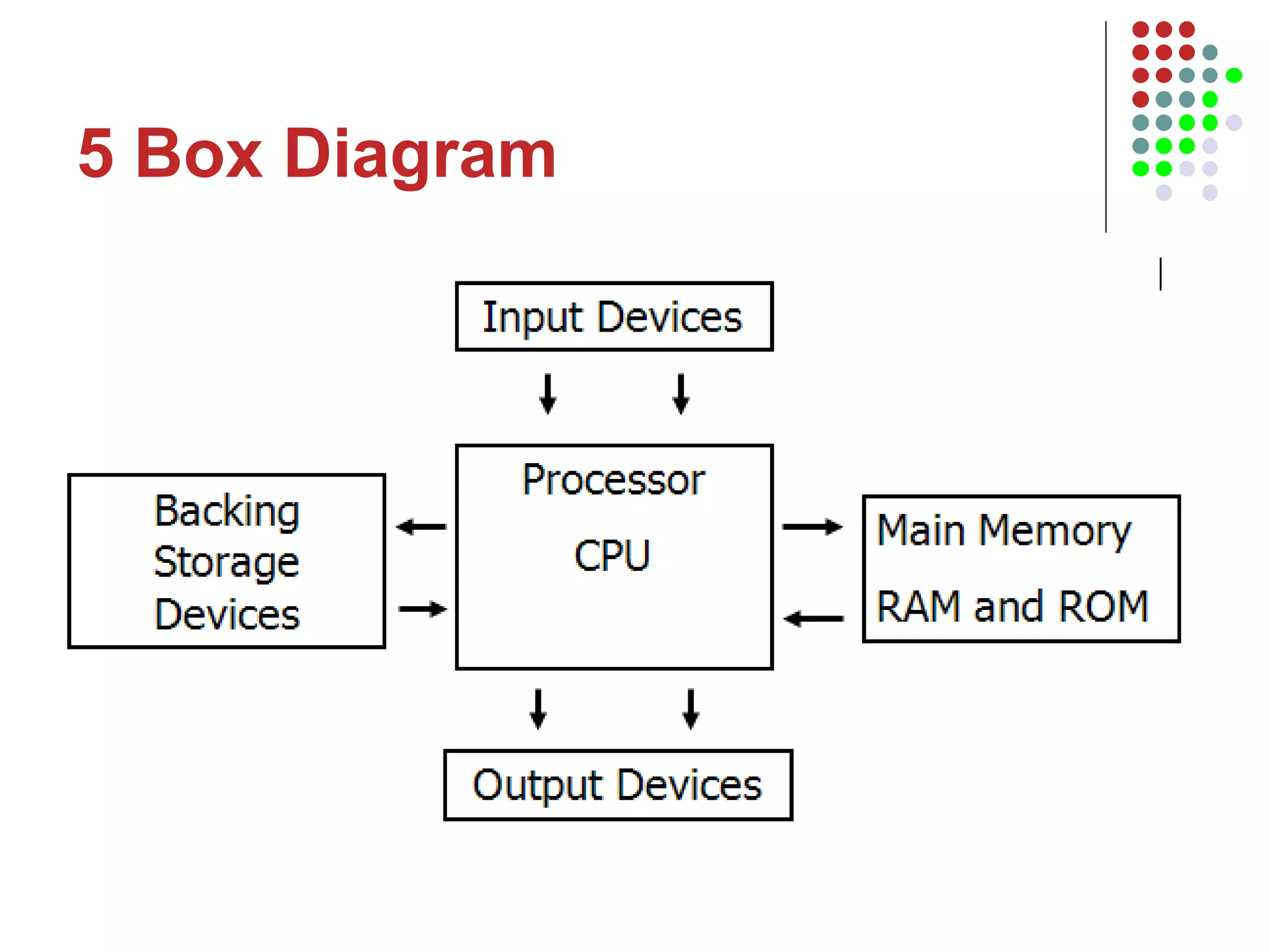
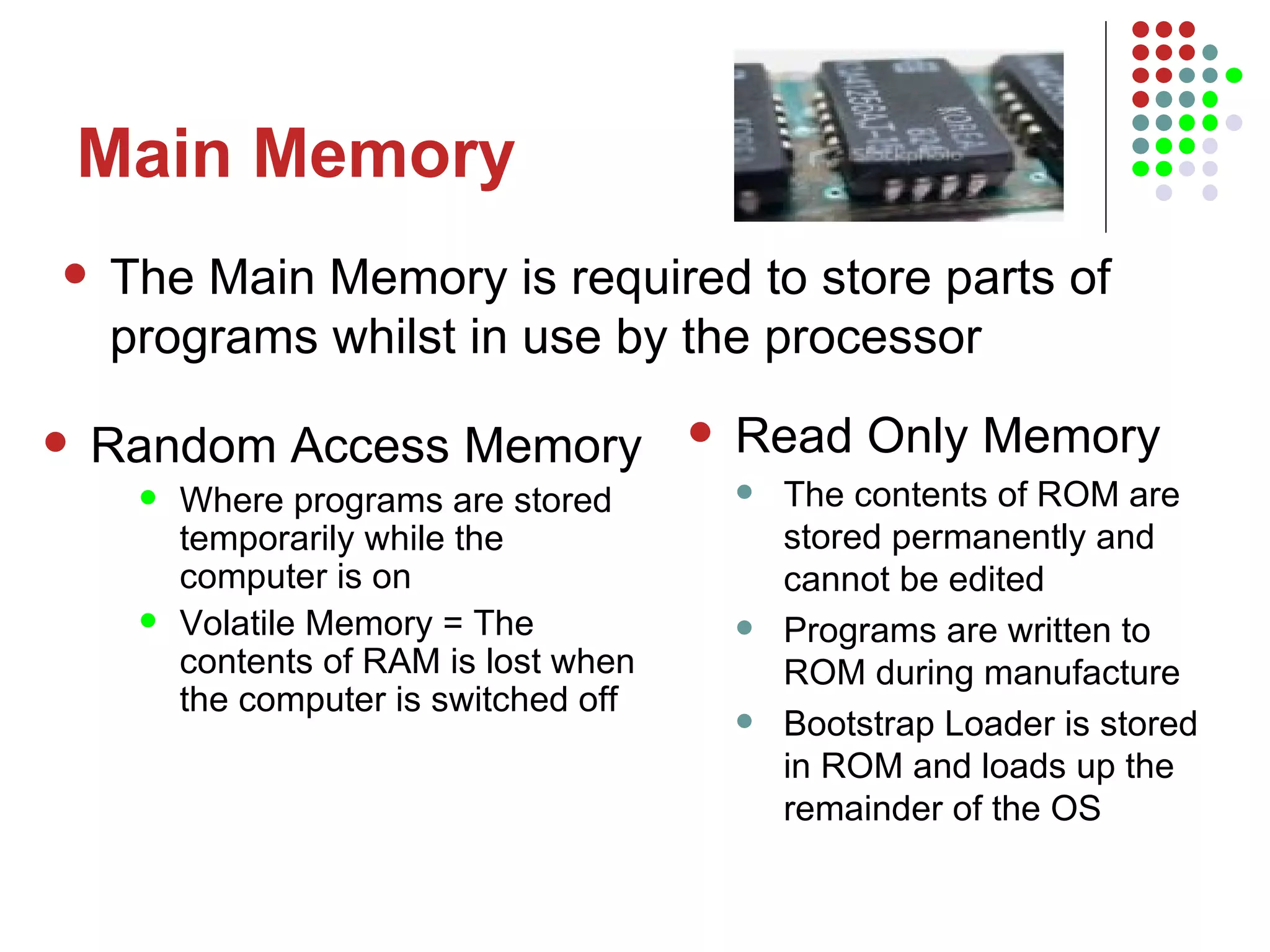
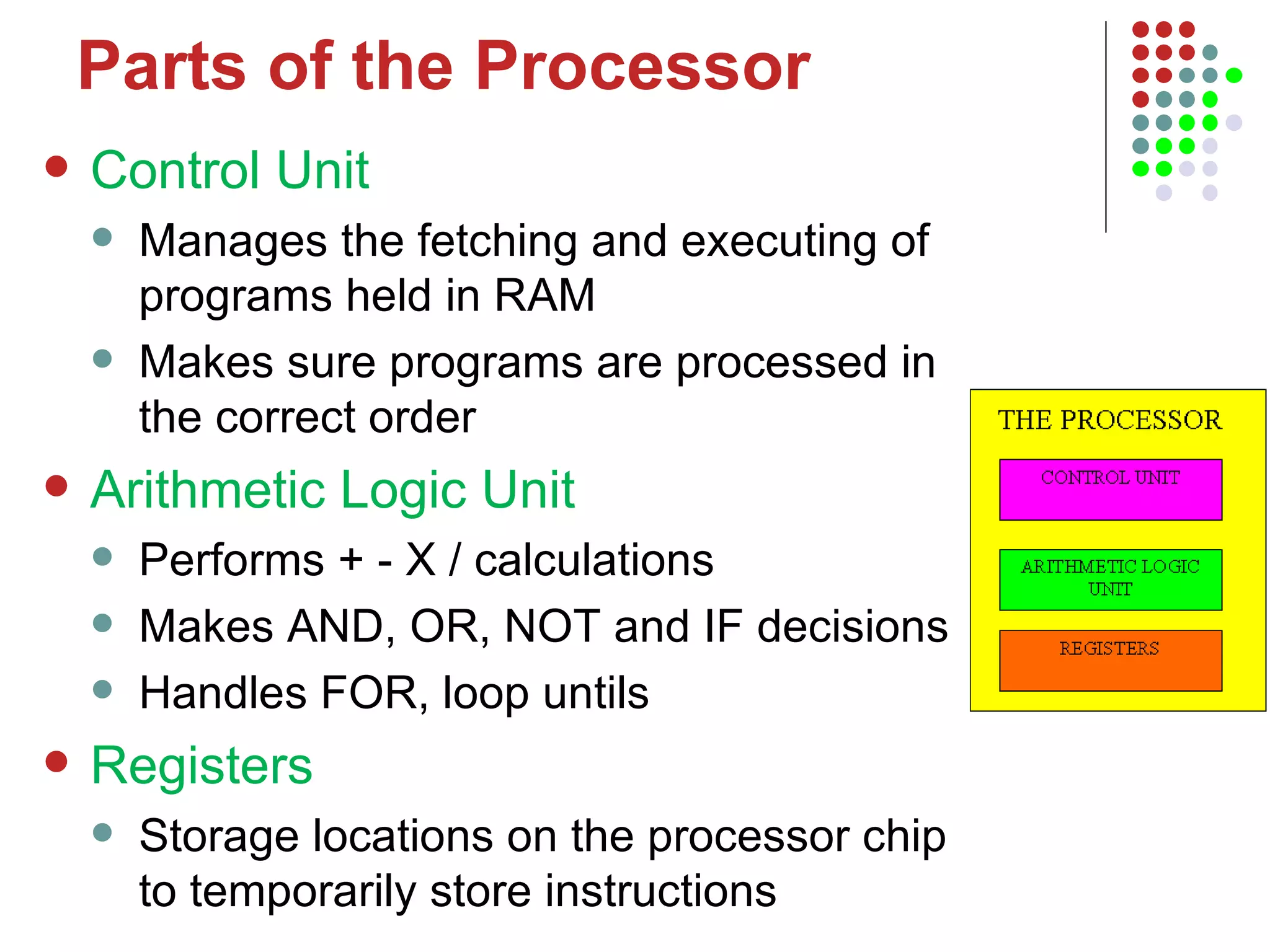
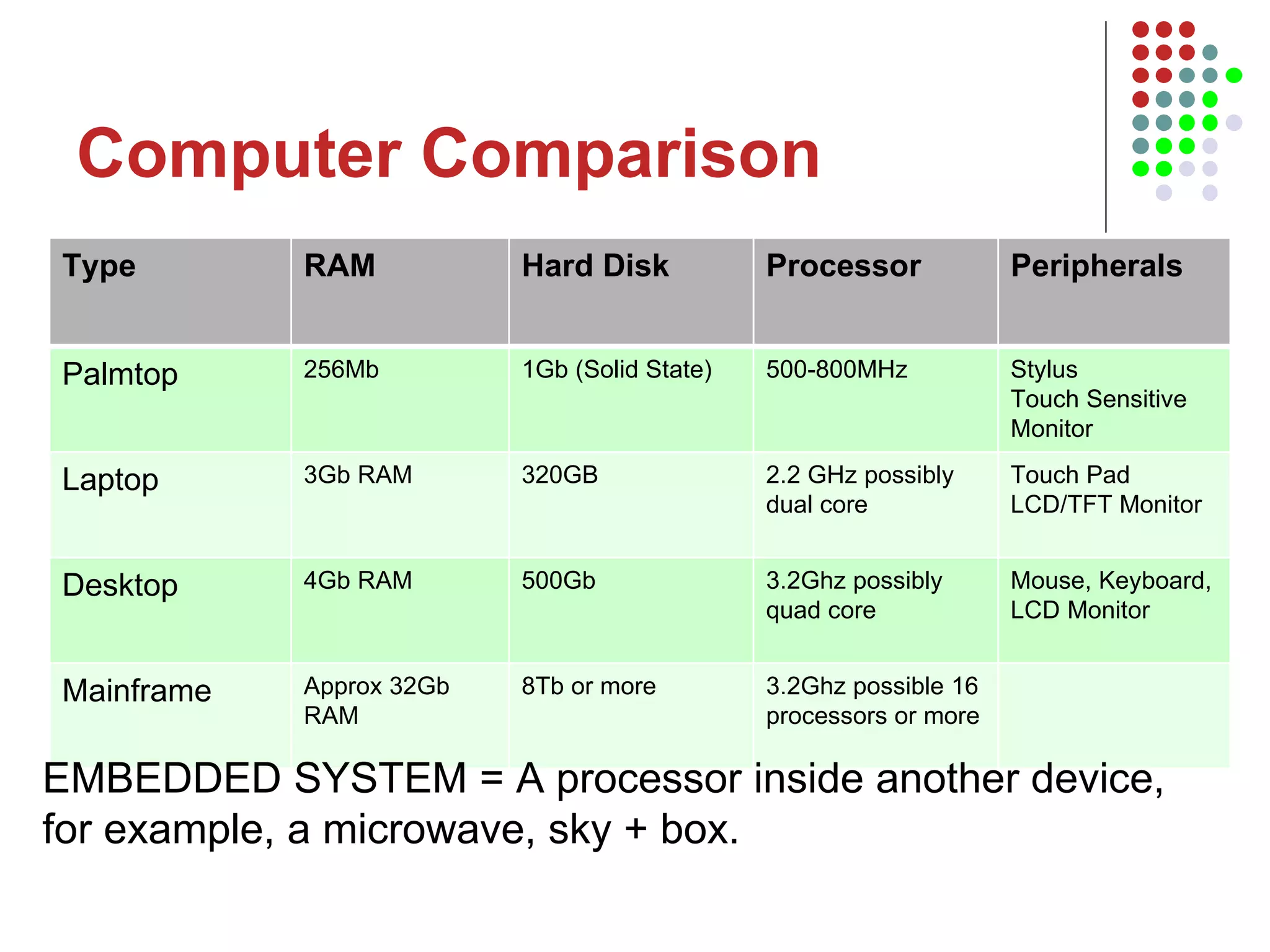
The document discusses the structure and components of a basic computer system. It describes the five main components as input devices, processor, main memory, output devices, and backing storage. It explains random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM), and how they differ. It also defines the processor as the central processing unit that processes instructions and programs, and lists its main parts as the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and registers. The control unit manages program execution and timing.