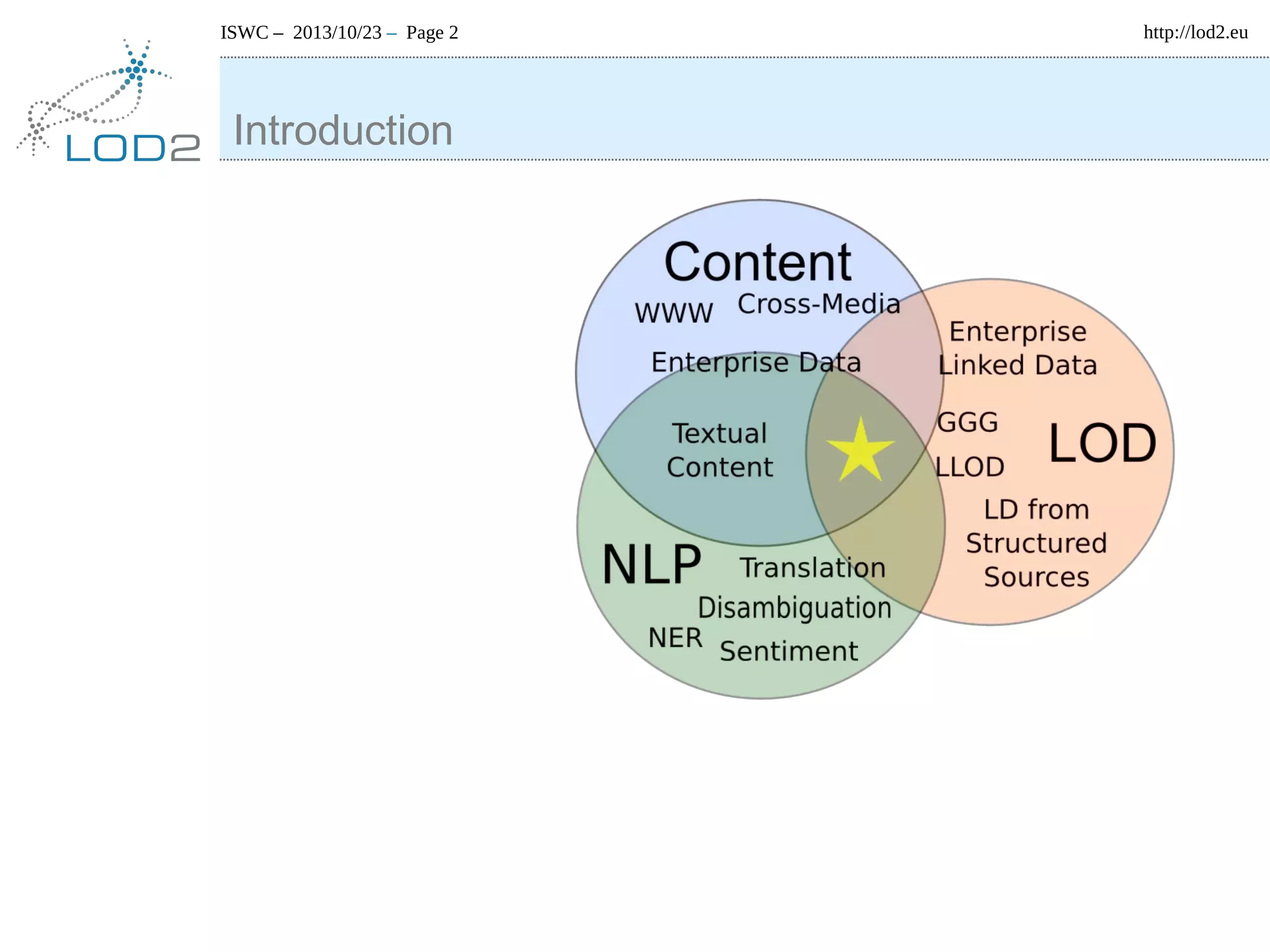
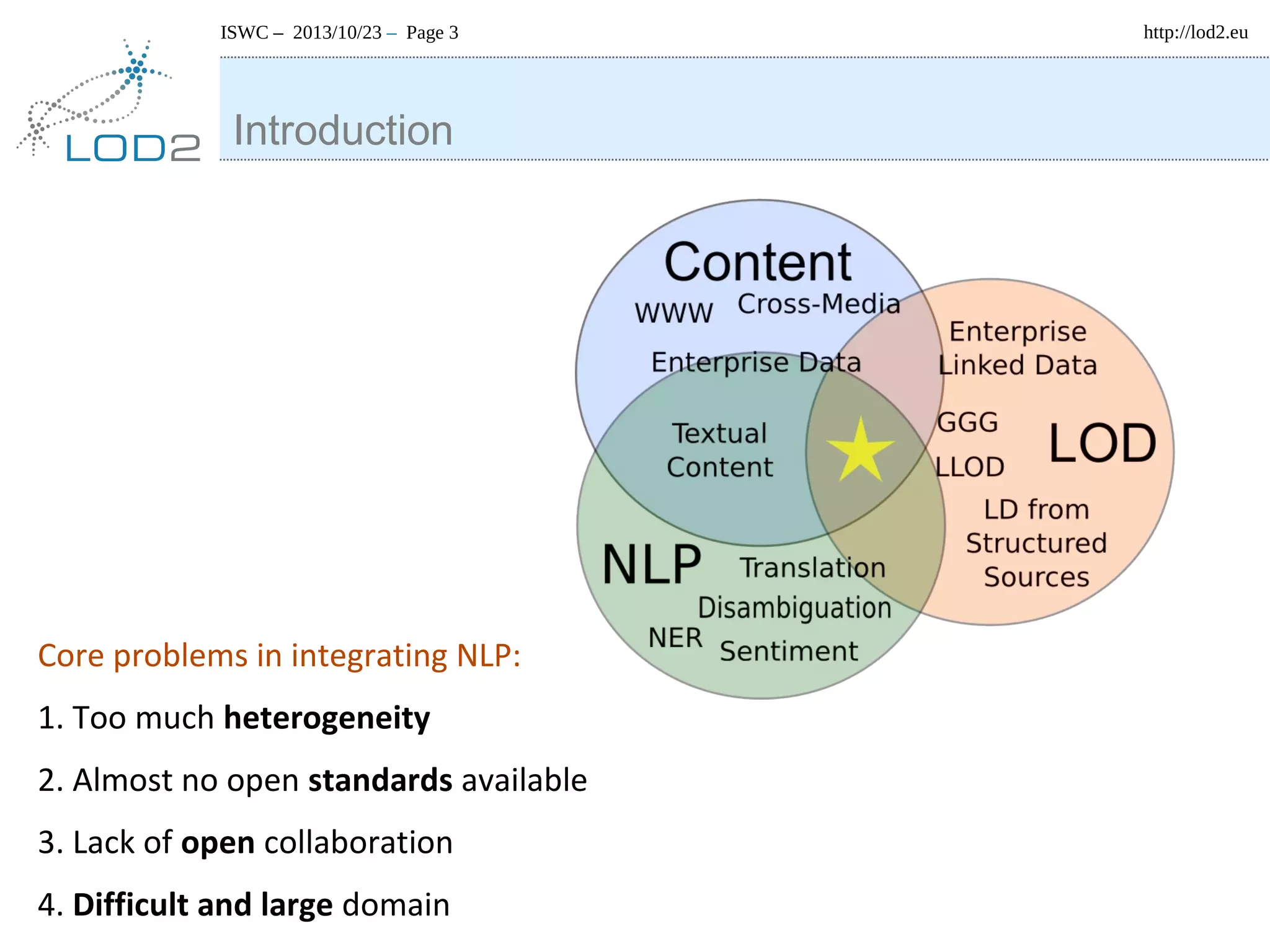
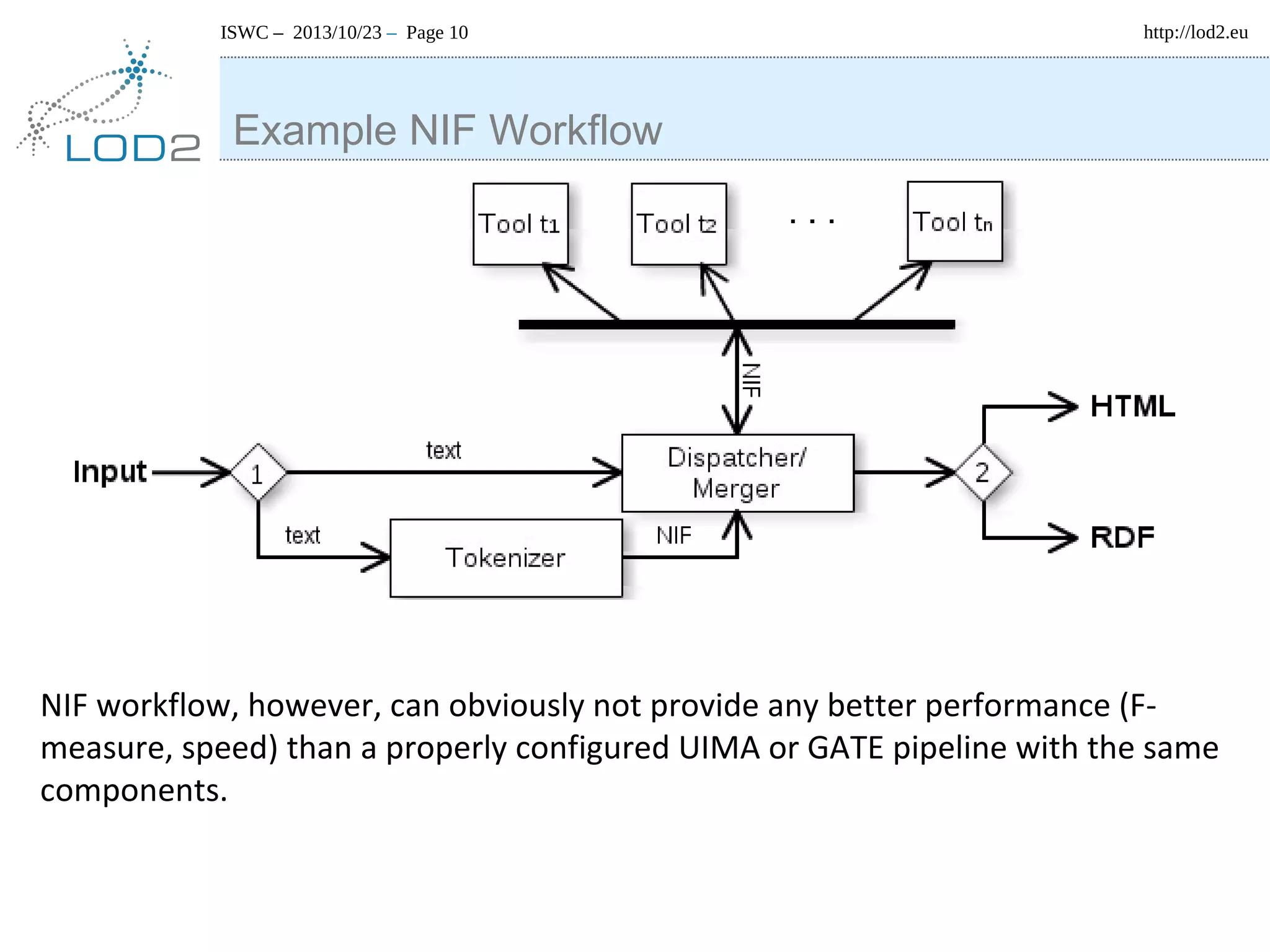
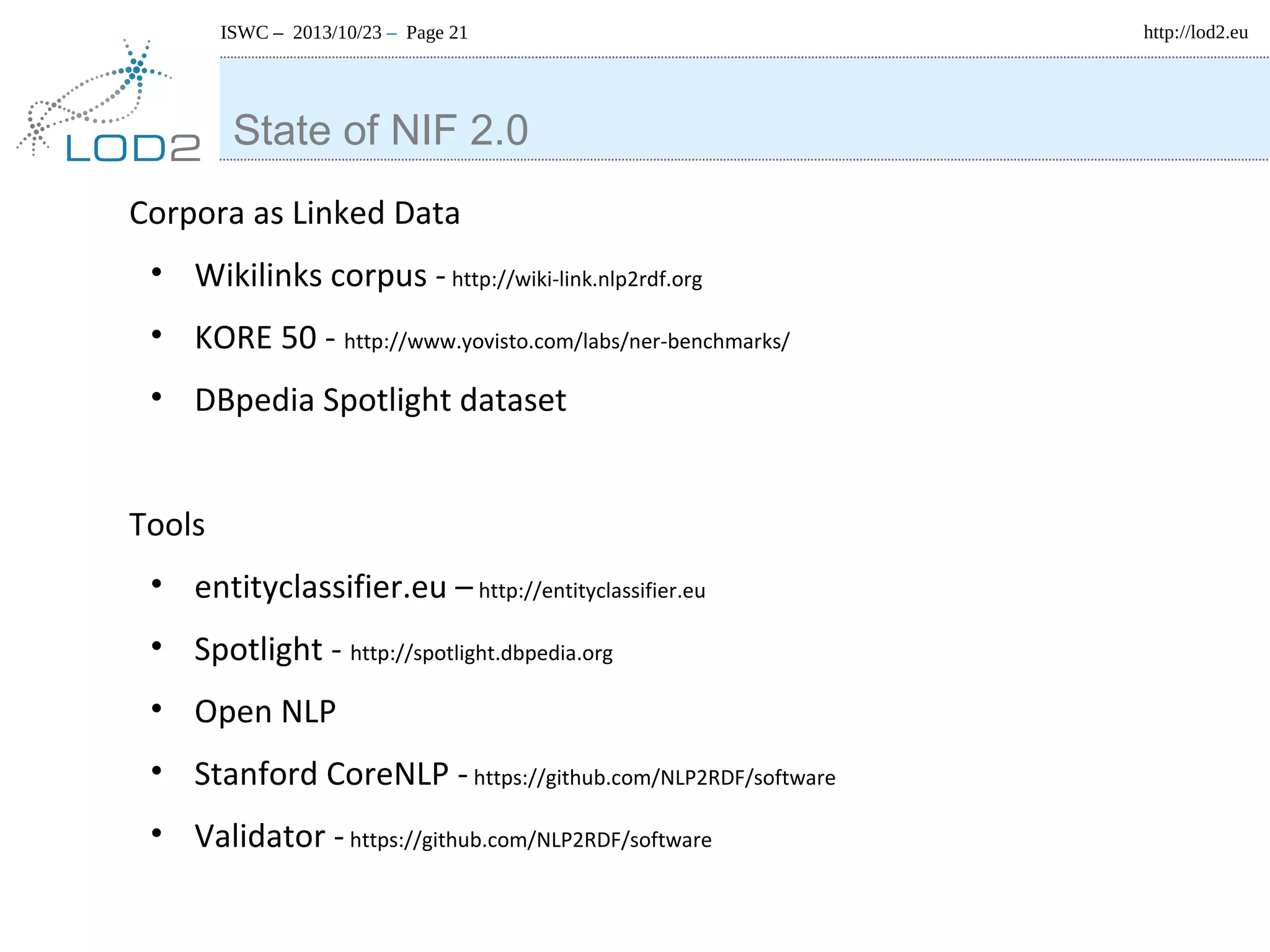
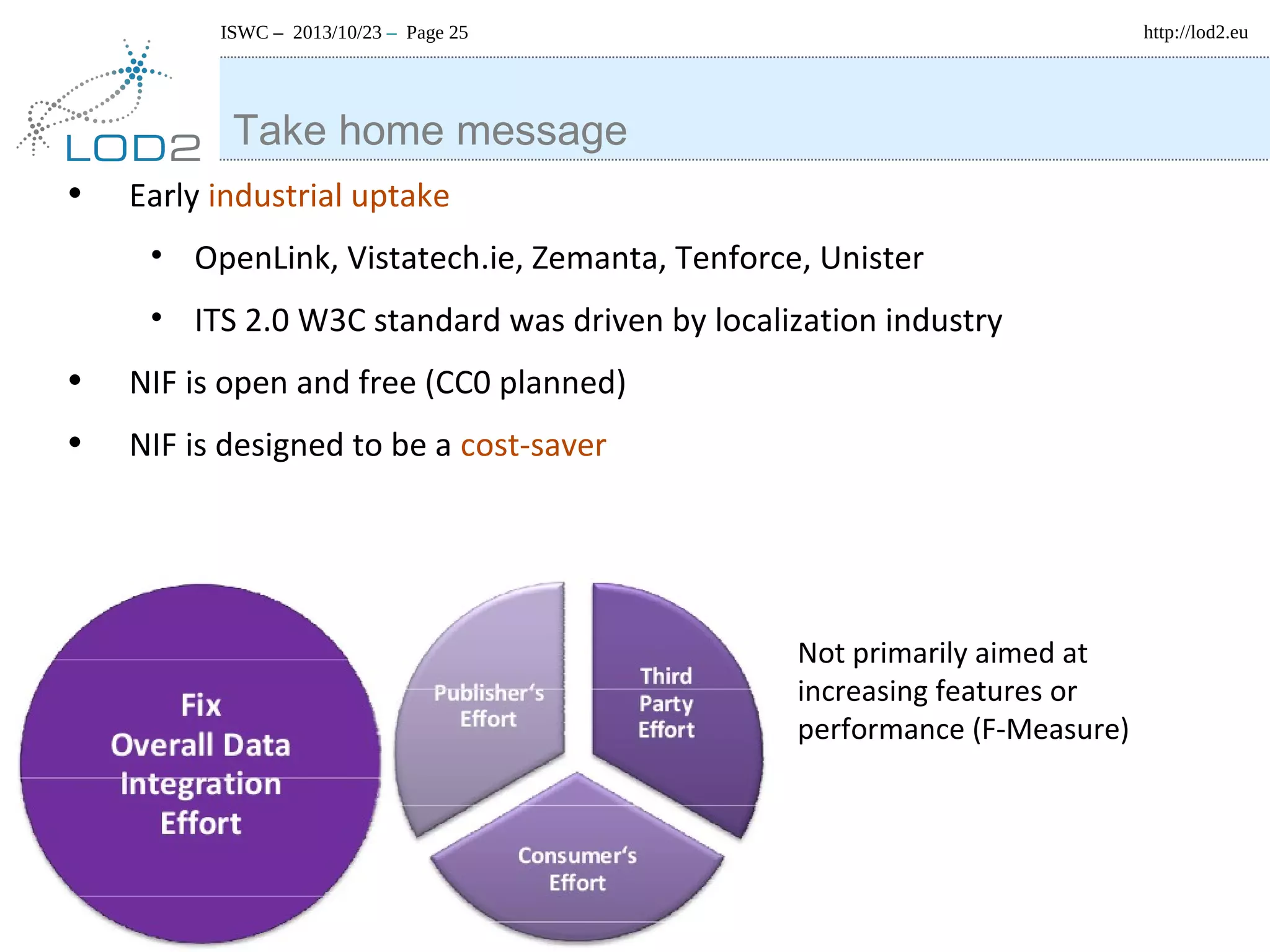
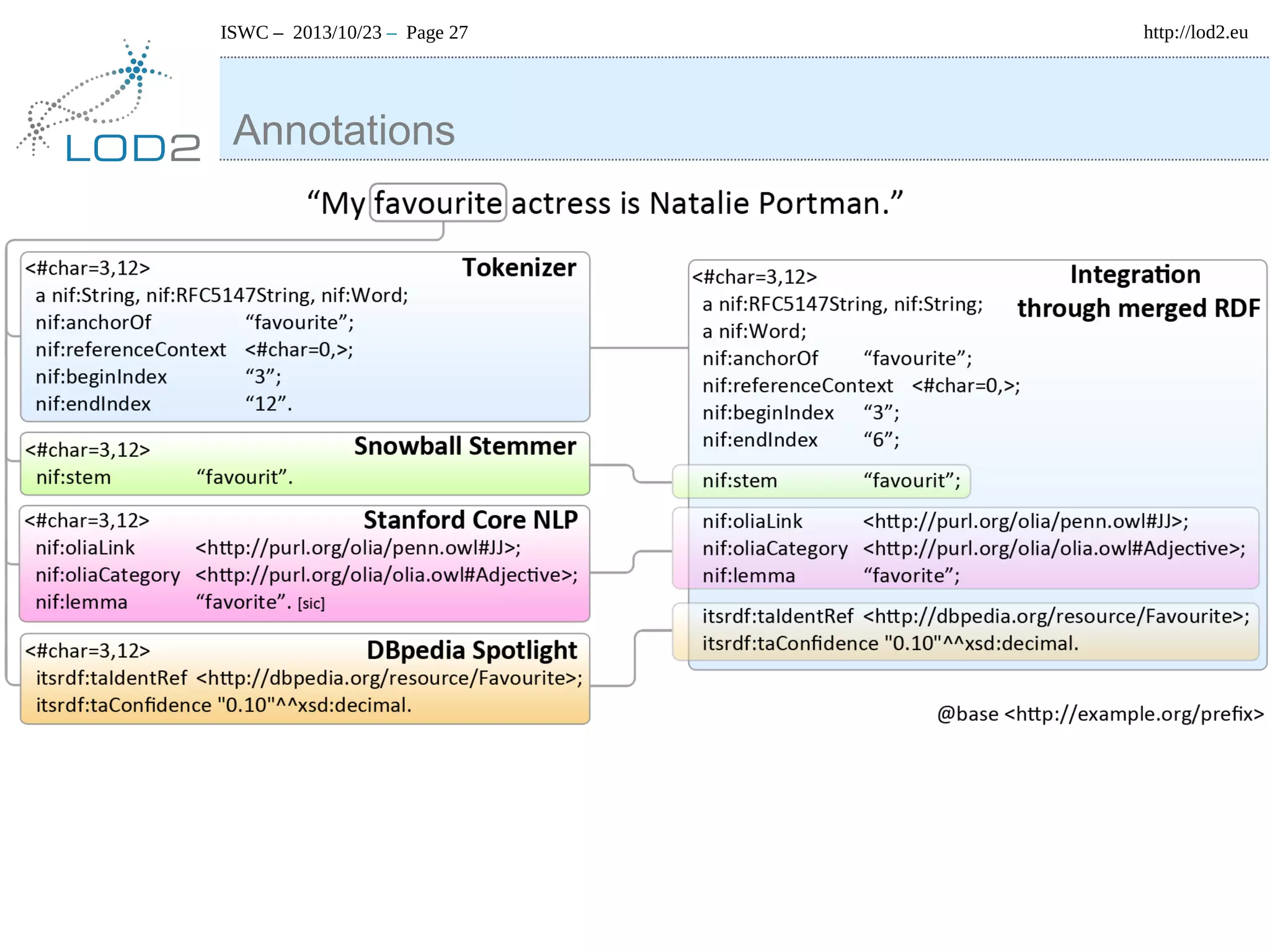
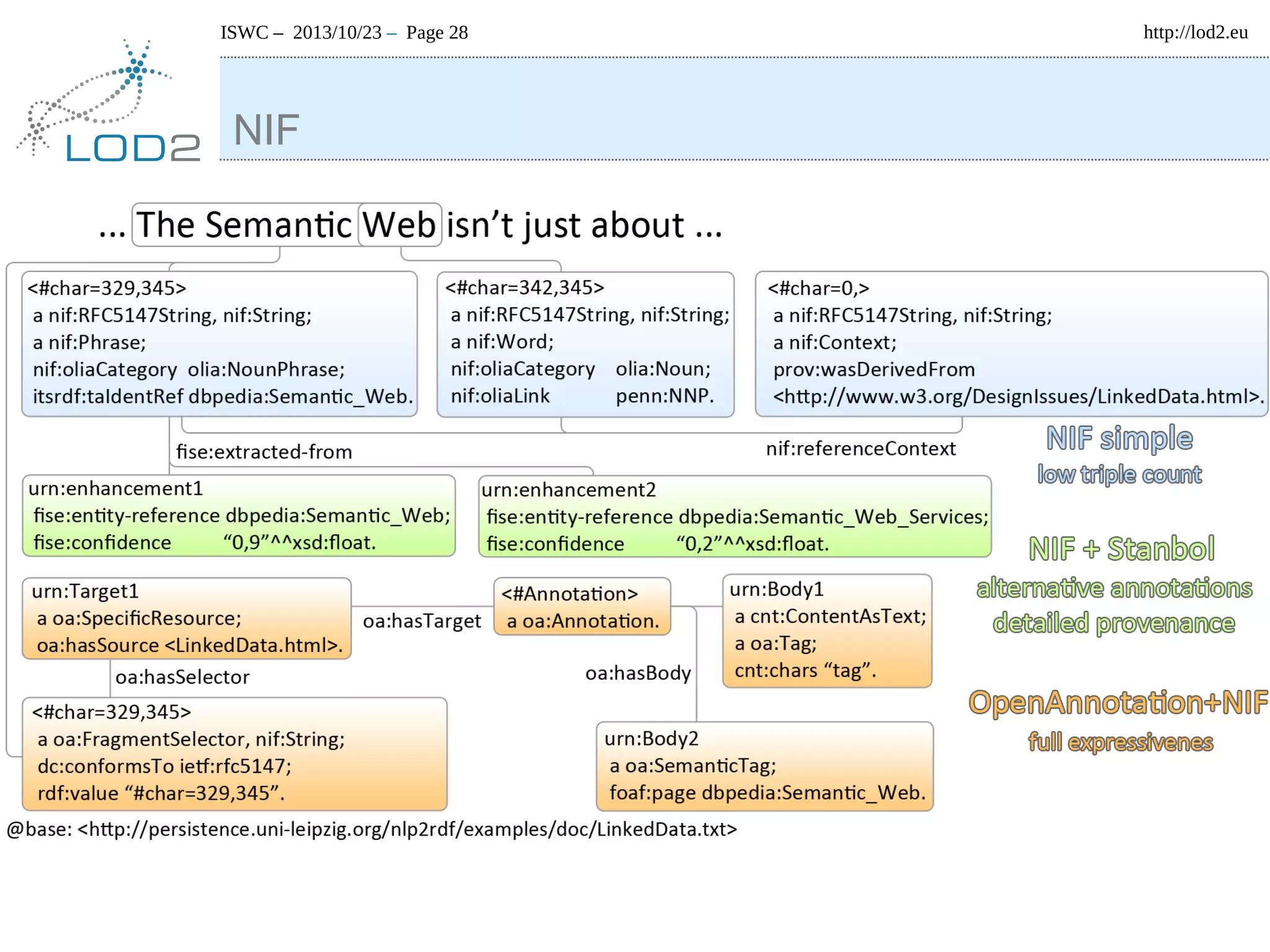
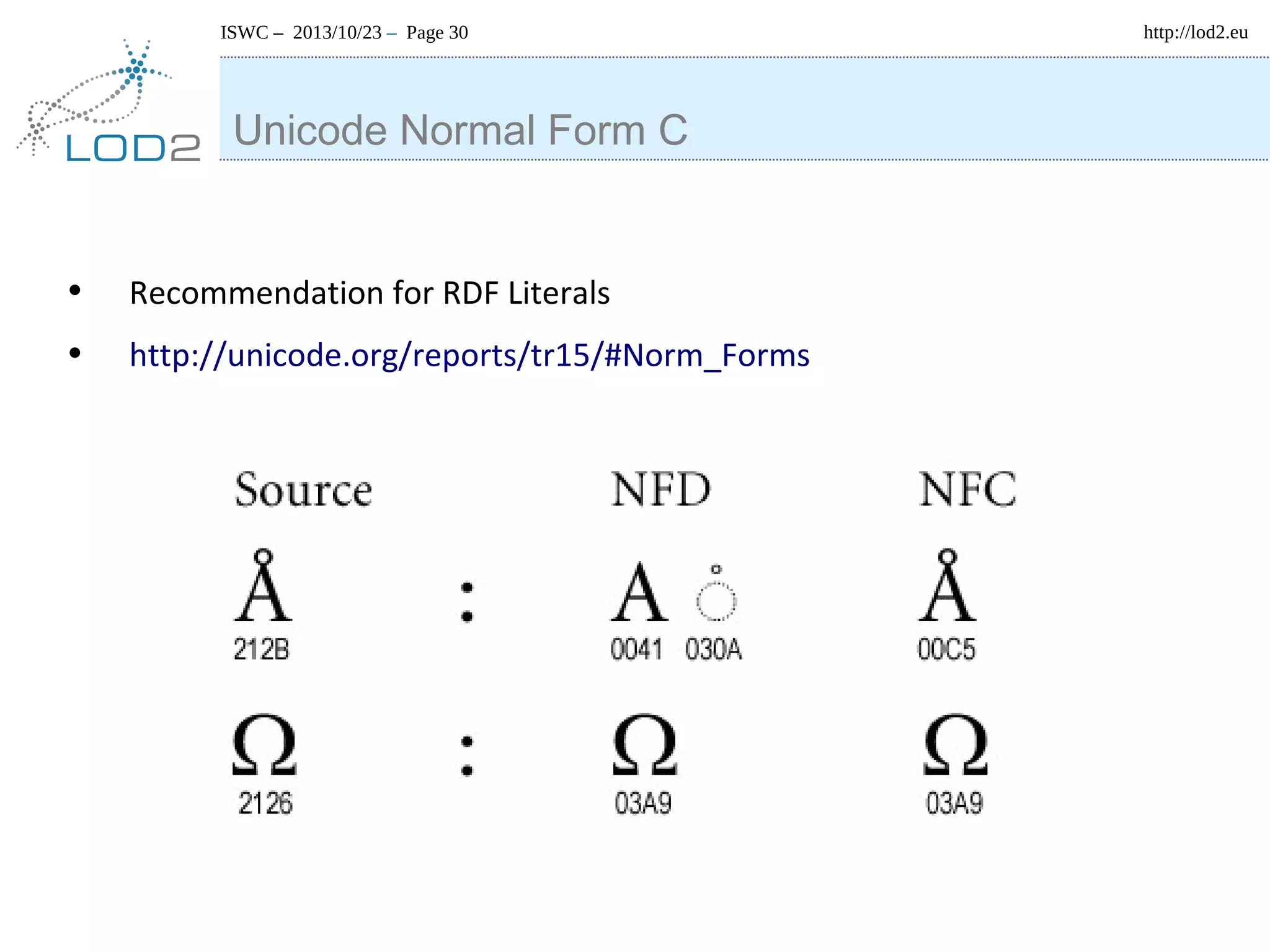
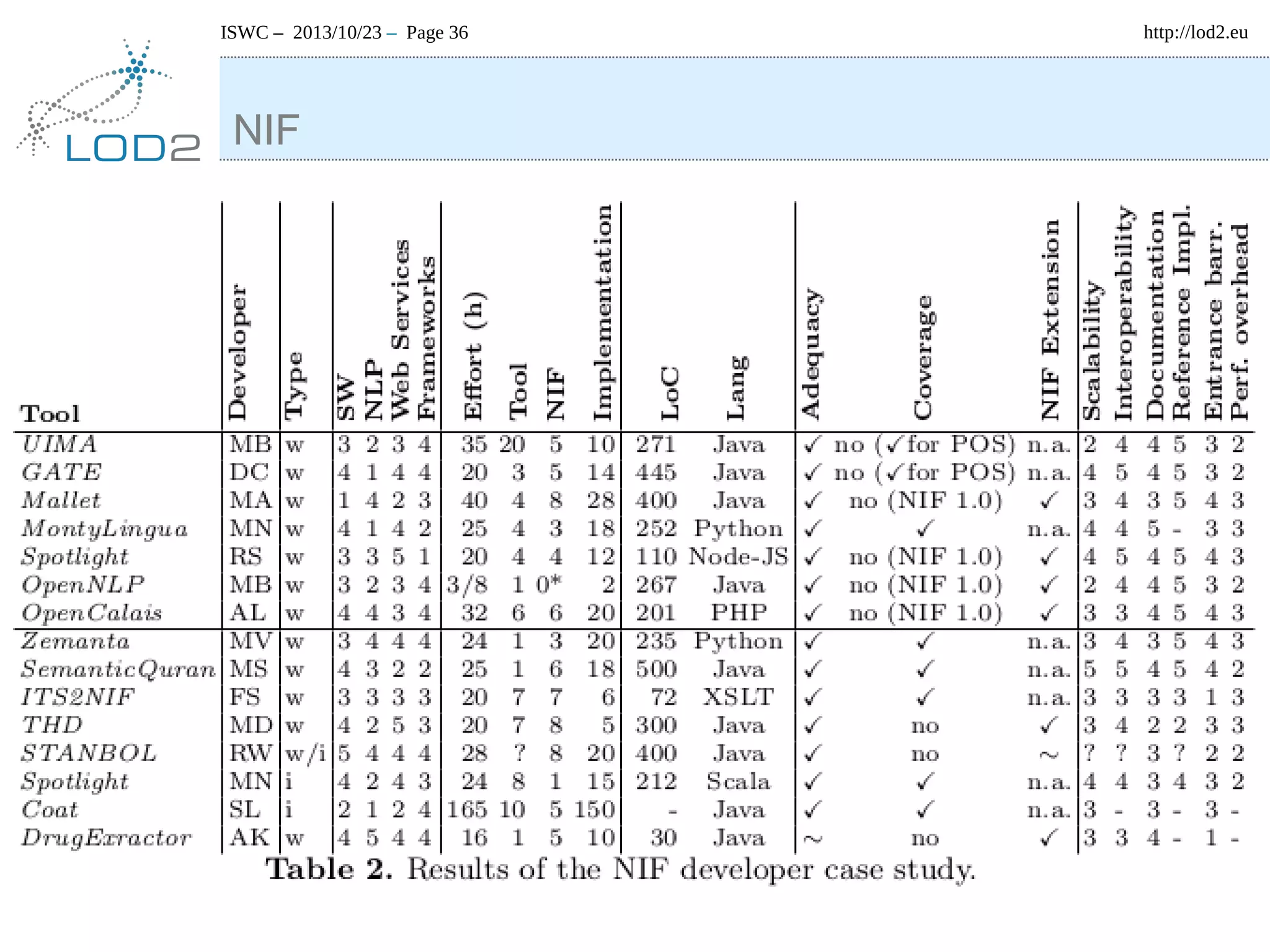
The document discusses using linked data and the NLP Interchange Format (NIF) to improve interoperability in natural language processing. It describes NIF as an RDF/OWL-based format that aims to allow interoperability between NLP tools, resources, and annotations. The document outlines several use cases for NIF, including part-of-speech tagging and entity linking, and evaluates its adoption and impact on lowering barriers to NLP tool integration and reuse. It encourages more ontology creators and developers to join the NLP2RDF community and use NIF.