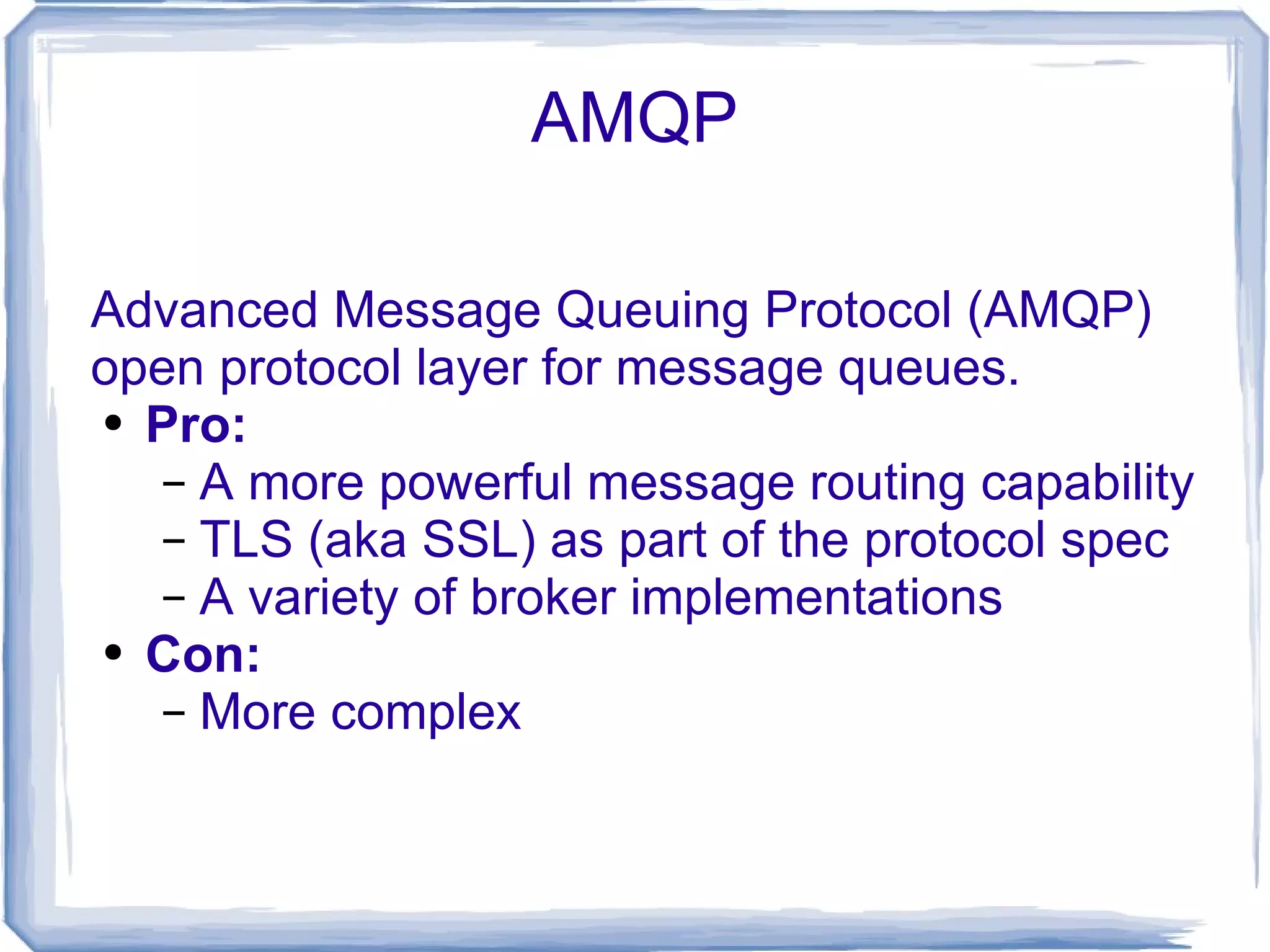
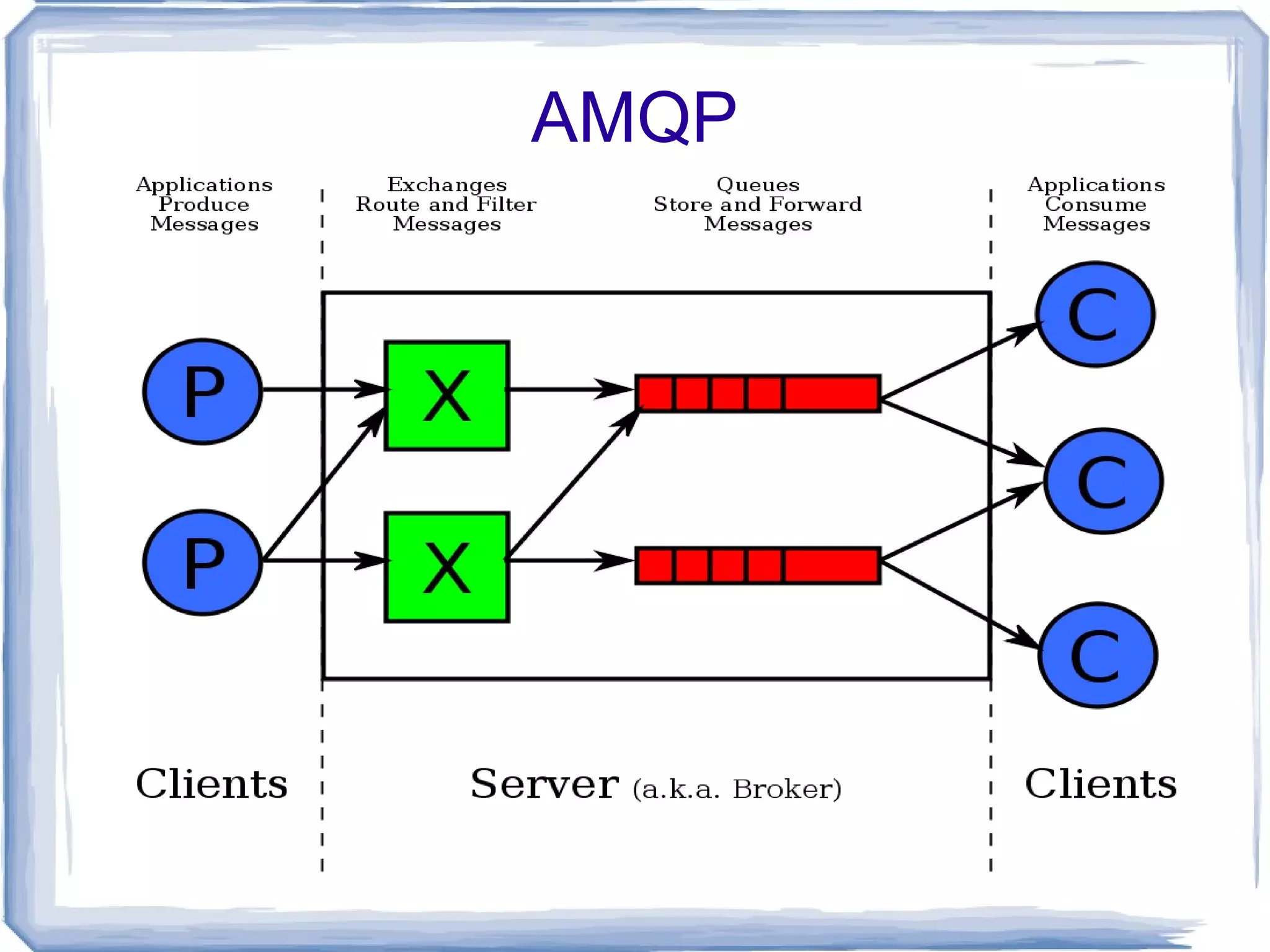
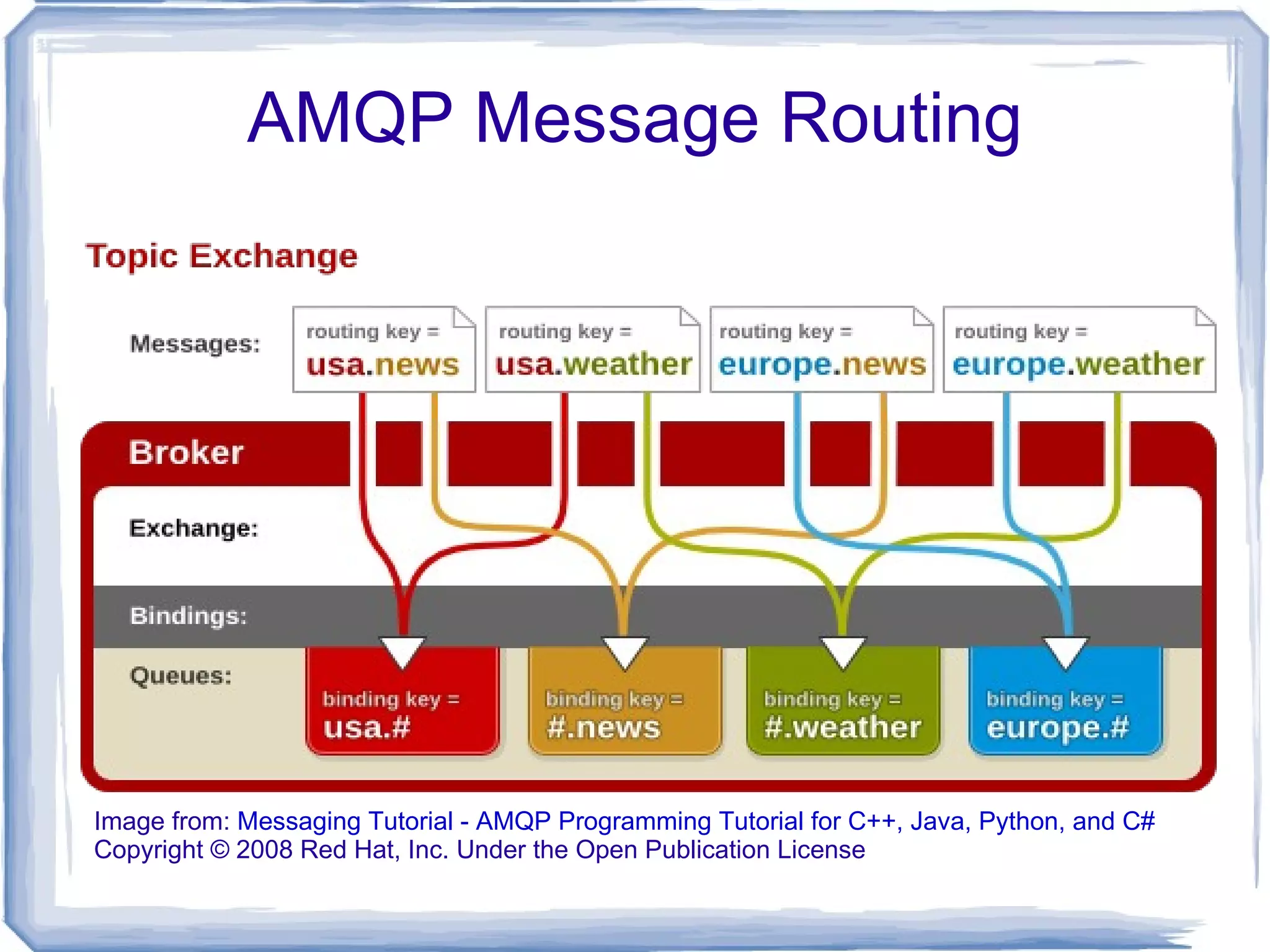
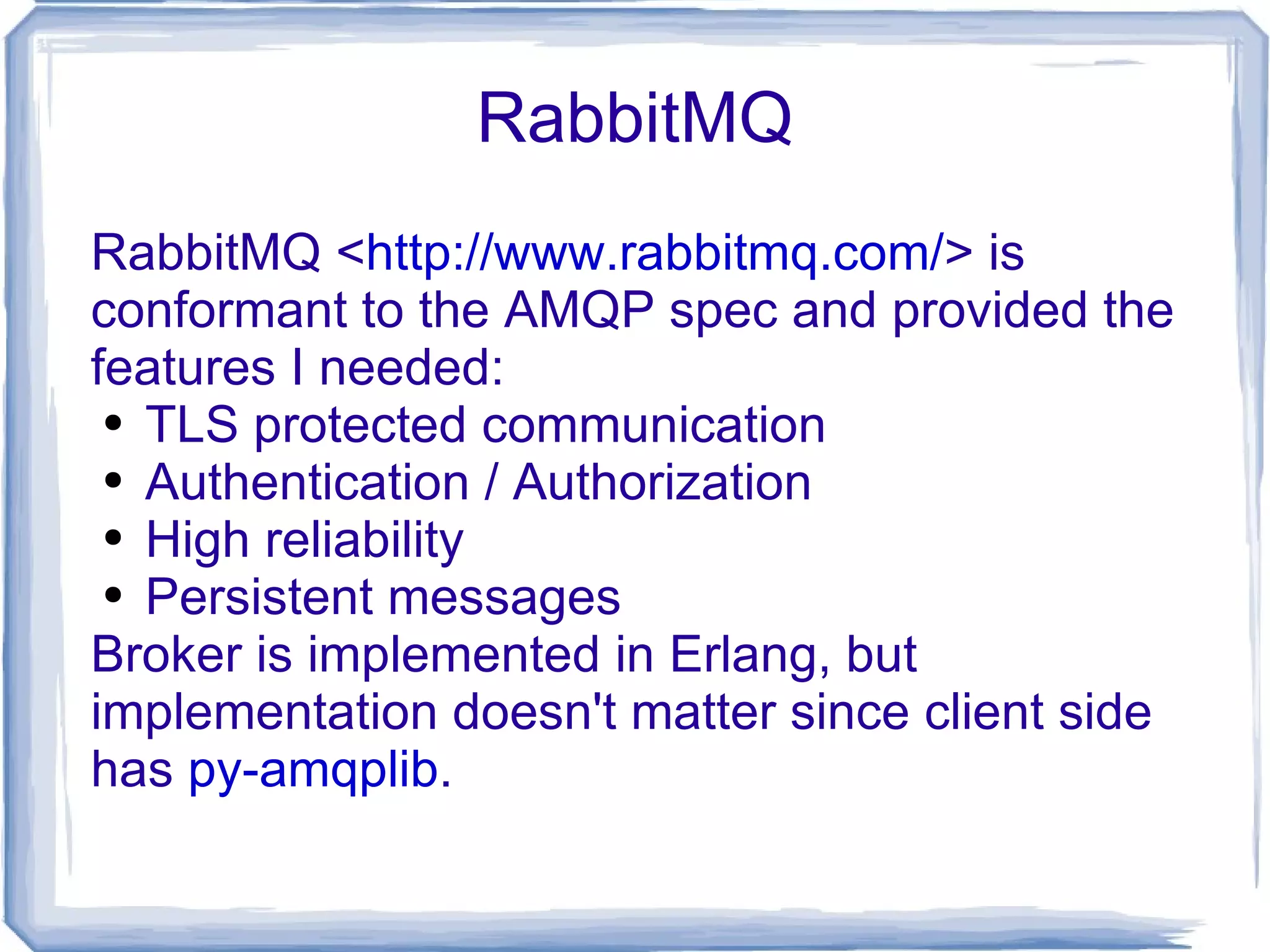
The document discusses various methods of inter-process communication using message queues, highlighting the challenges faced in coordinating long-running processes with web requests. It evaluates different message queuing systems, including Beanstalkd, Memcacheq, and AMQP protocols such as RabbitMQ, outlining their pros and cons. The author expresses a preference for Beanstalkc and RabbitMQ with Carrot API for robust message handling and process coordination solutions.
![Inter-Process/Task Communication With Message Queues William McVey < [email_address] > PyOhio July 26, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyohio-message-queues-090727094523-phpapp02/75/Inter-Process-Task-Communication-With-Message-Queues-1-2048.jpg)






![beanstalkd/beanstalkc beanstalkd : A very simple text based-protocol with an simple yet powerful set of queue management primitives. http://xph.us/software/beanstalkd/ beanstalkc : A simple yet powerful client API that is well documented. http://github.com/earl/beanstalkc/ [demo here]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyohio-message-queues-090727094523-phpapp02/75/Inter-Process-Task-Communication-With-Message-Queues-9-2048.jpg)

![memcacheq Memcacheq uses the memcachedb protocol to implement queues. "Cache" look up of a queue name pop a value from the queue Pro: Fast, lightweight, and scales well. Persistent messages across reboots Con: Doesn't support either blocking or callback interfaces Have to poll to see if you have messages Didn't address authentication requirement [demo here]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyohio-message-queues-090727094523-phpapp02/75/Inter-Process-Task-Communication-With-Message-Queues-11-2048.jpg)



![carrot sample >>> from ConfigParser import ConfigParser >>> config = ConfigParser() >>> config . read( "application.ini" ) >>> from carrot.connection import AMQPConnection >>> amqpconn = AMQPConnection( ... hostname = config . get( "broker" , "host" ), ... port = config . get( "broker" , "port" ), ... userid = config . get( "broker" , "userid" ), ... password = config . get( "broker" , "password" ), ... vhost = config . get( "broker" , "vhost" )) >>> PostOfficePublisher(connection = amqpconn) . send( ... { "My message" : [ "foo" , "bar" , "baz" ]}) >>> PostOfficeConsumer(connection = amqpconn) . next() Received: { "My message" : [ "foo" , "bar" , "baz" ]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pyohio-message-queues-090727094523-phpapp02/75/Inter-Process-Task-Communication-With-Message-Queues-19-2048.jpg)

