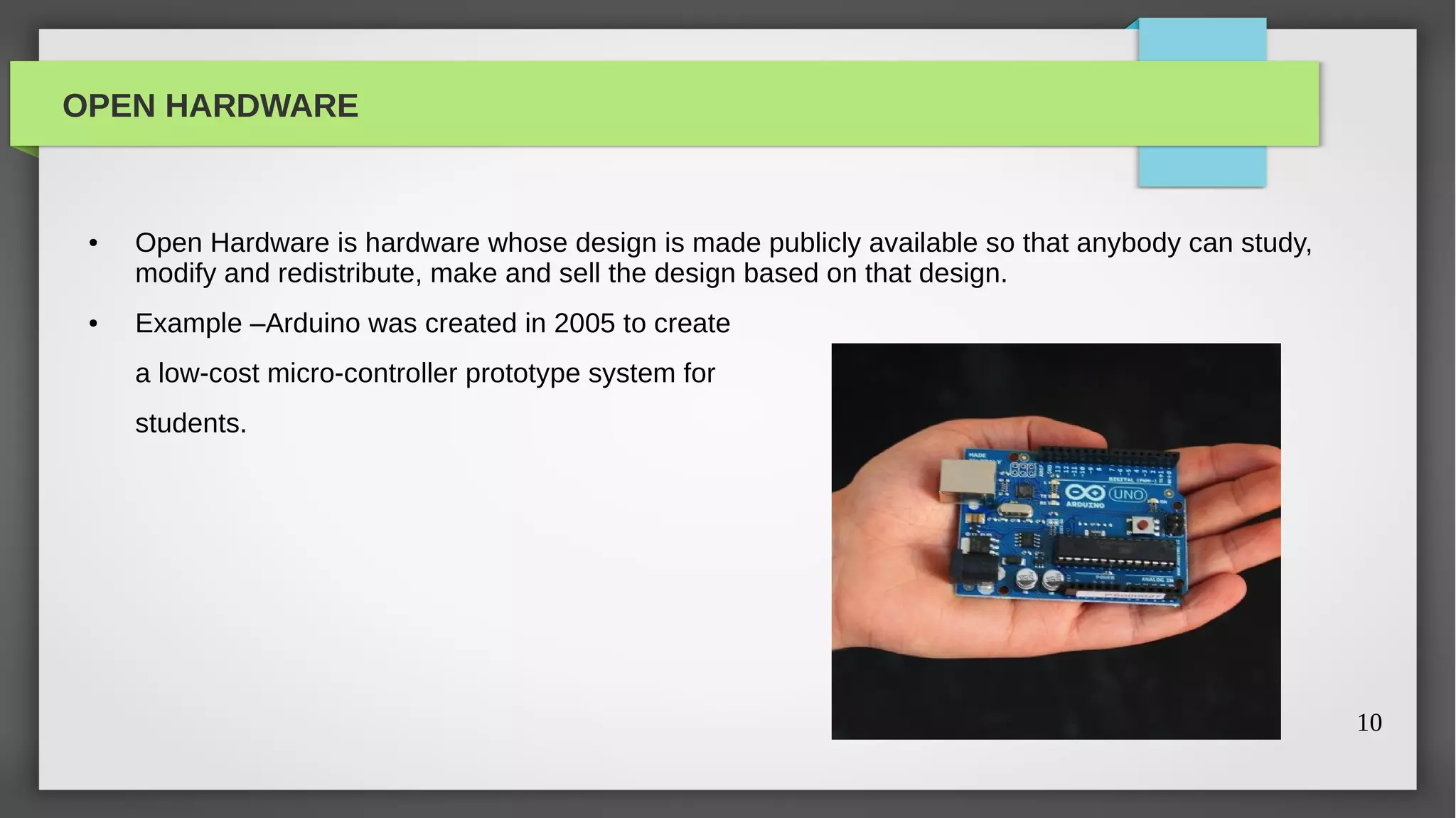
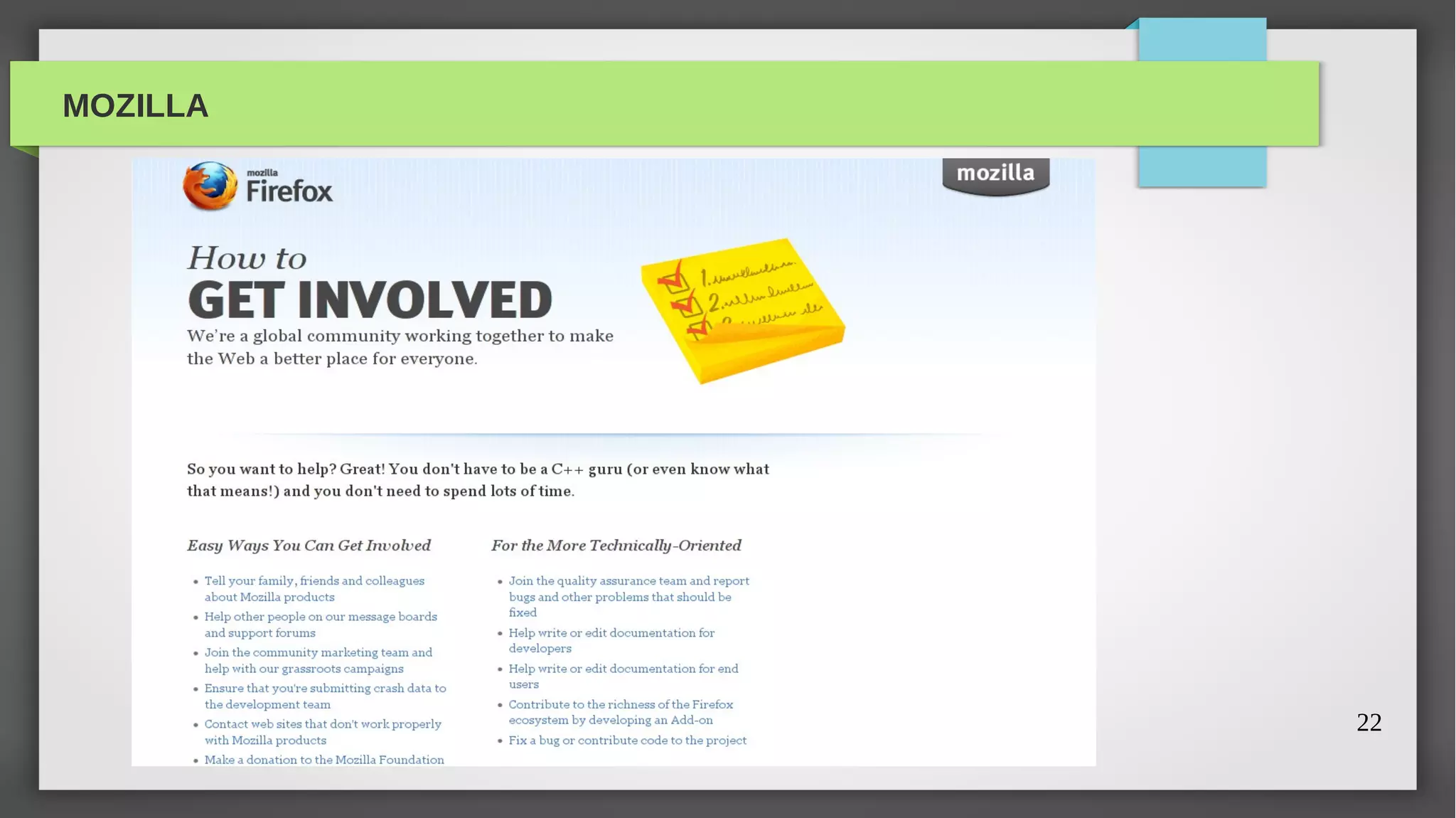
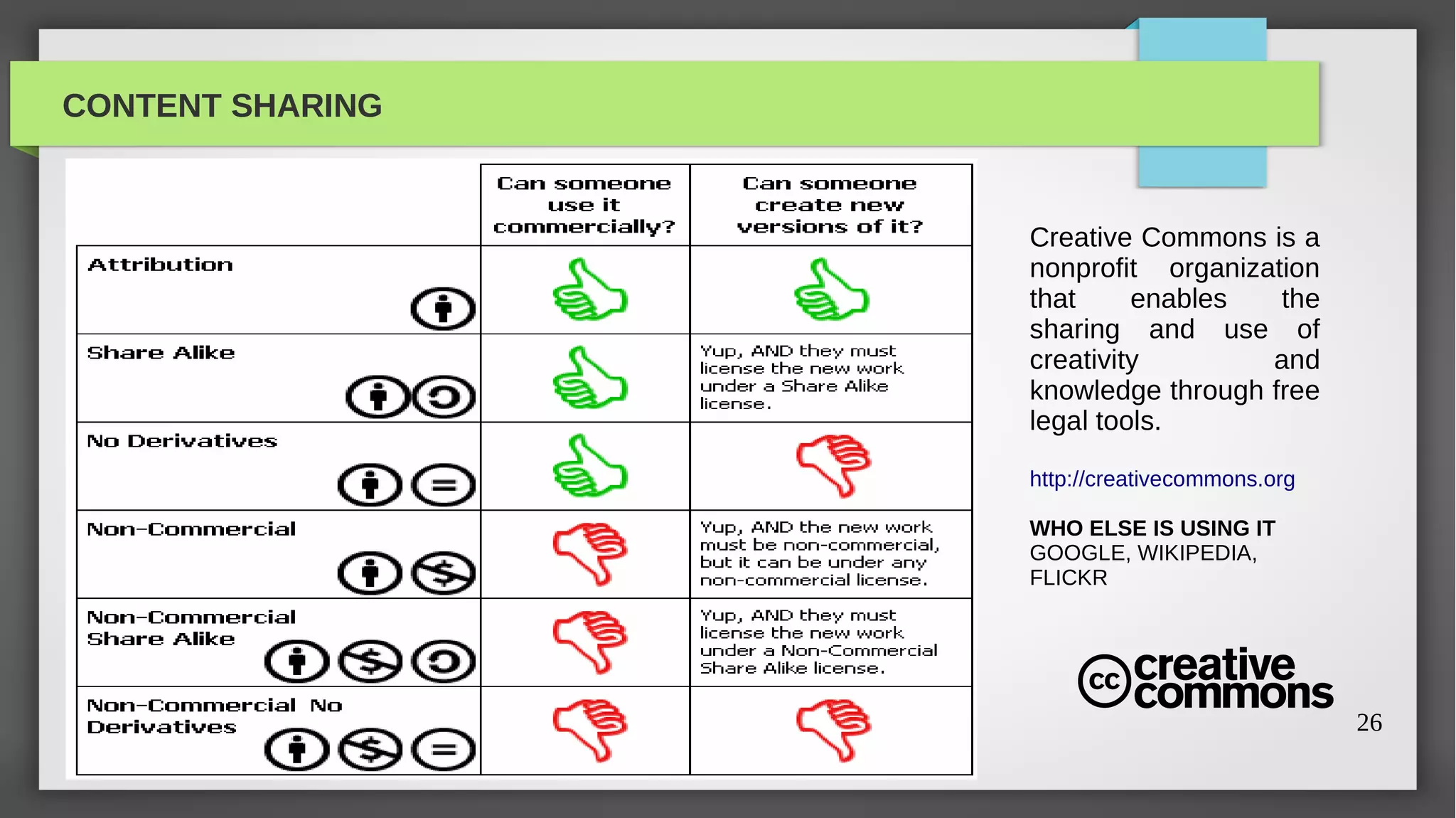
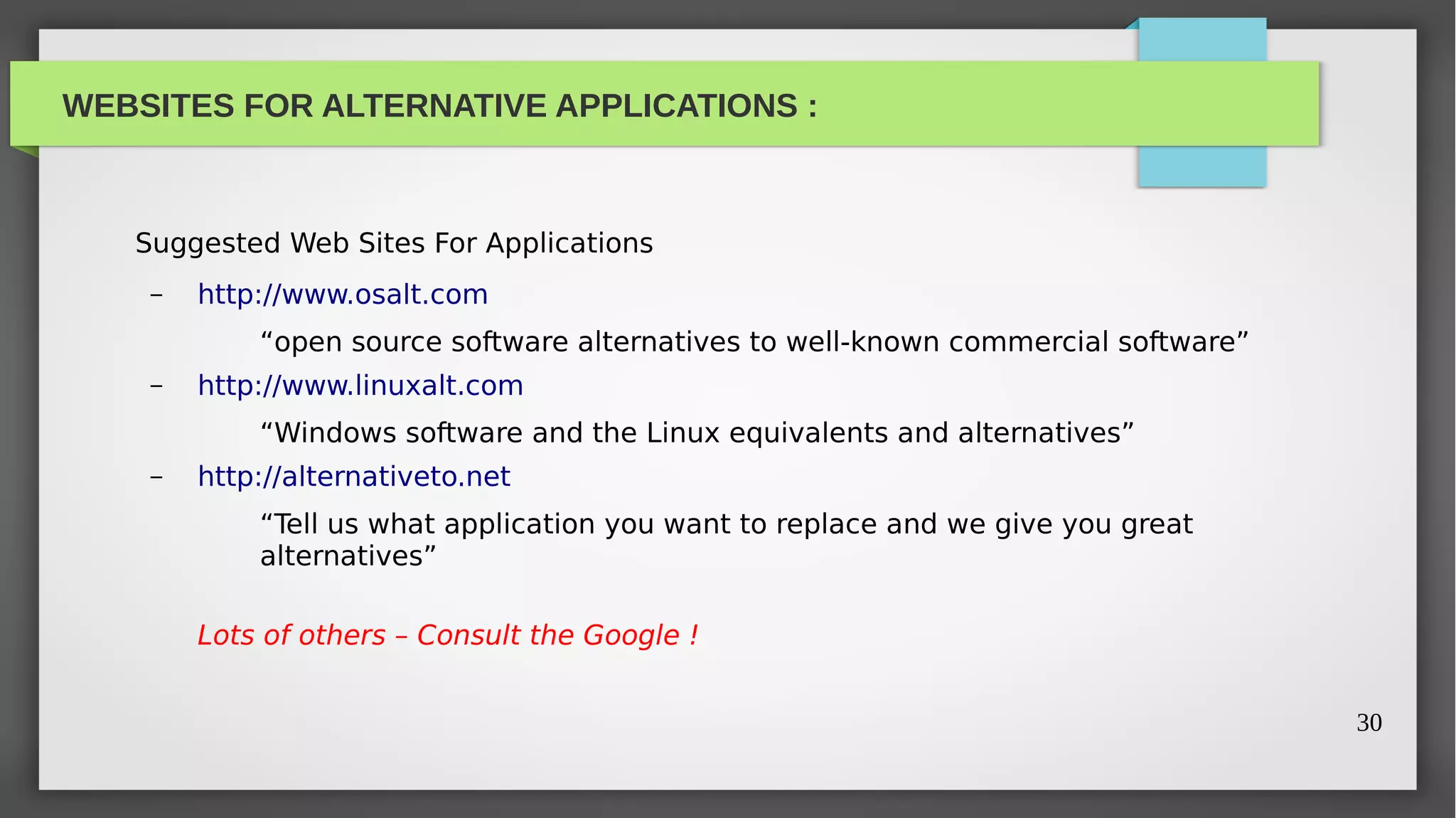
The document provides a comprehensive overview of open source software, its history, and its significance in modern technology. It traces the evolution of open source from its academic origins in the 1960s to its popularization in the late 1990s, highlighting key projects like the GNU and Linux. The text emphasizes the importance of participation in open source through contributions and outlines various categories including open software, open hardware, and open content.