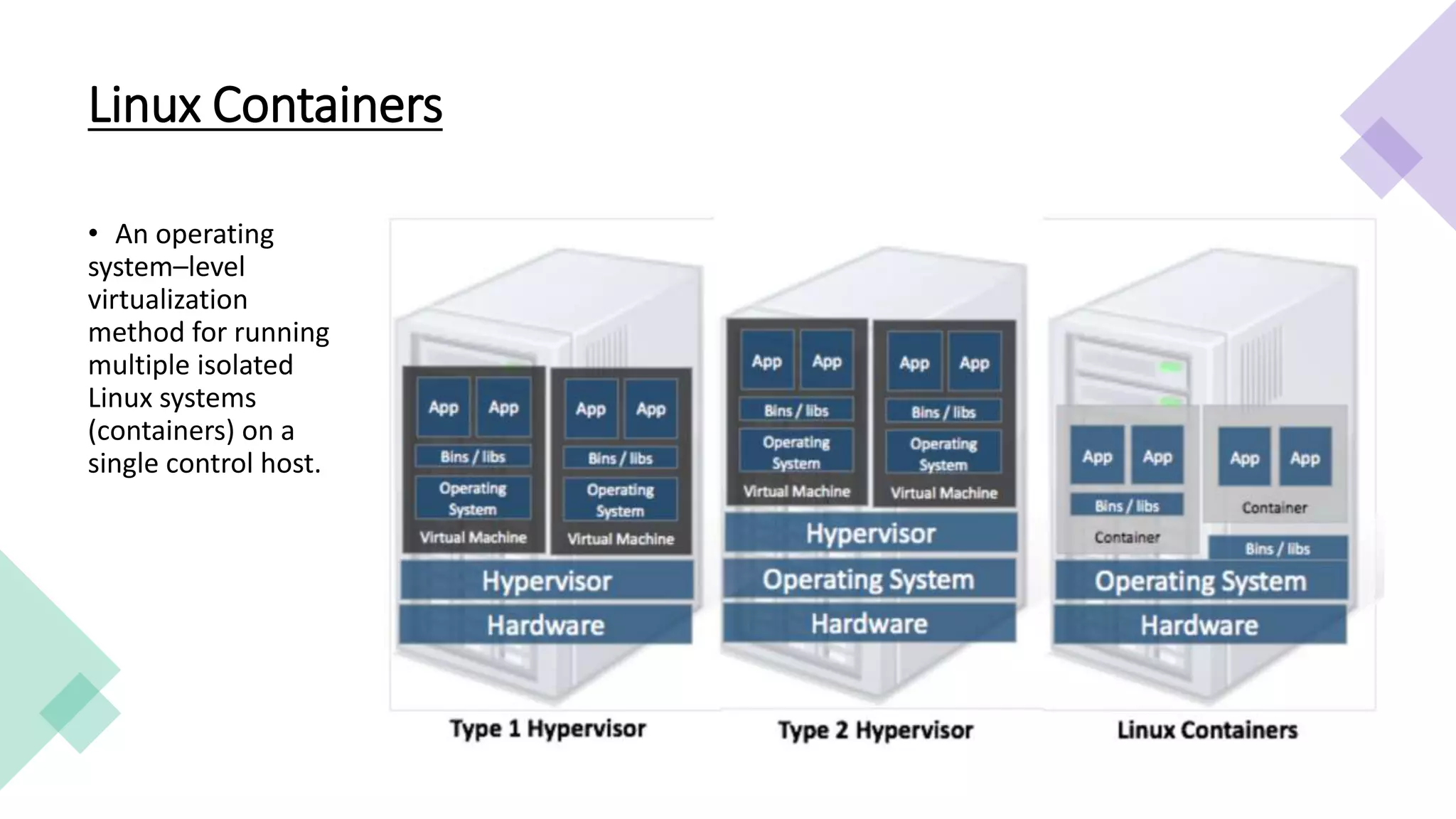
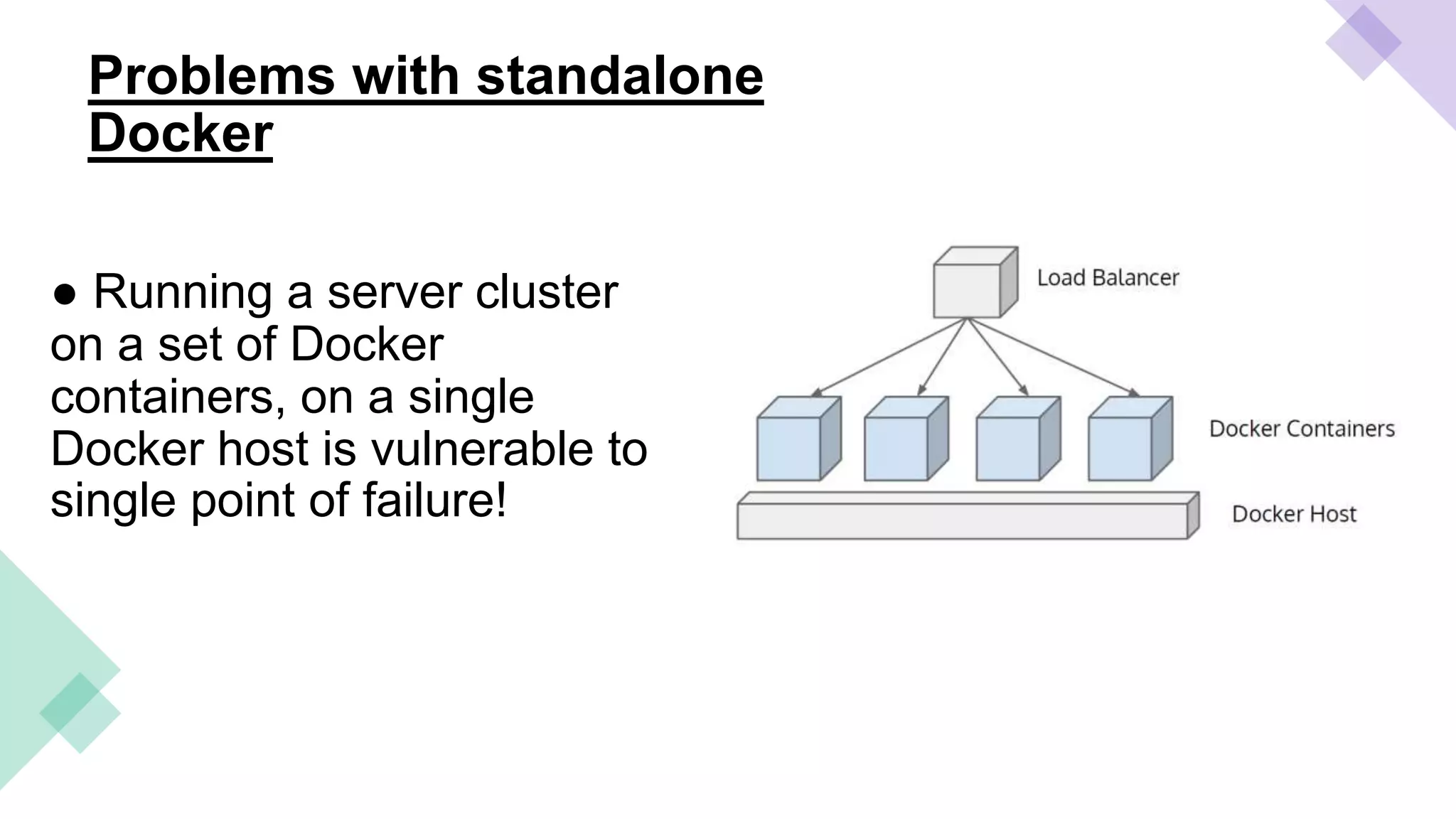
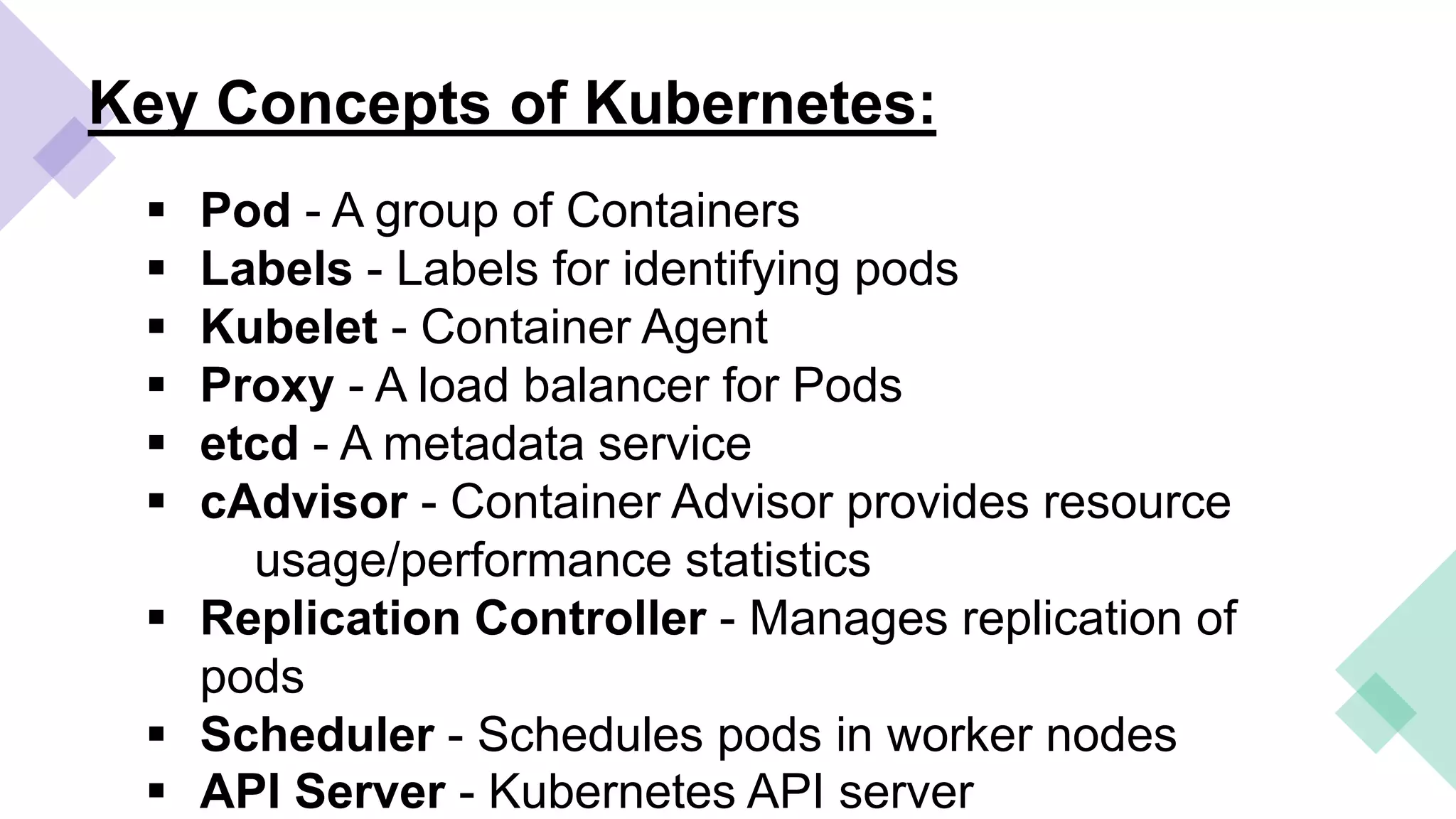
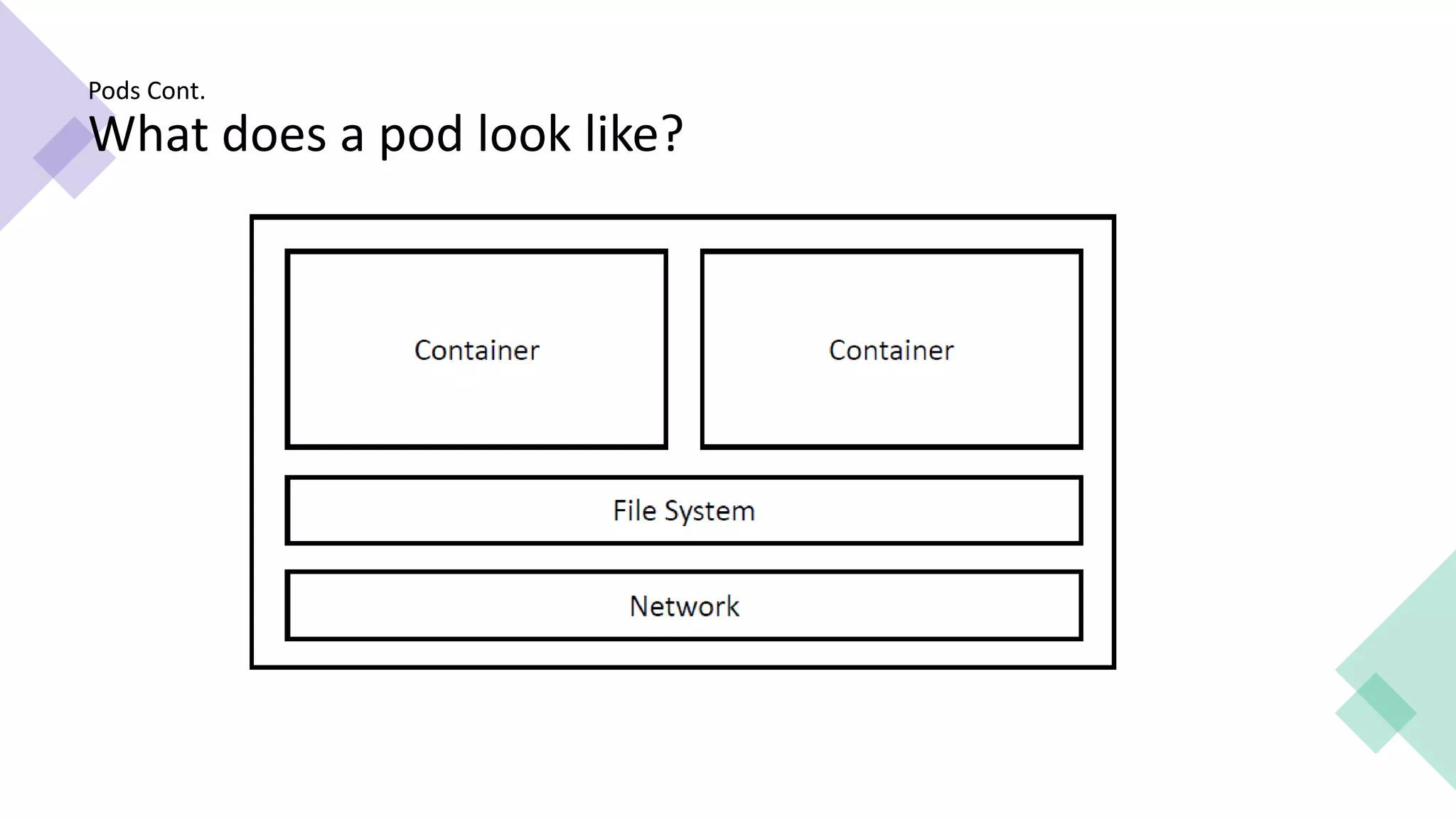
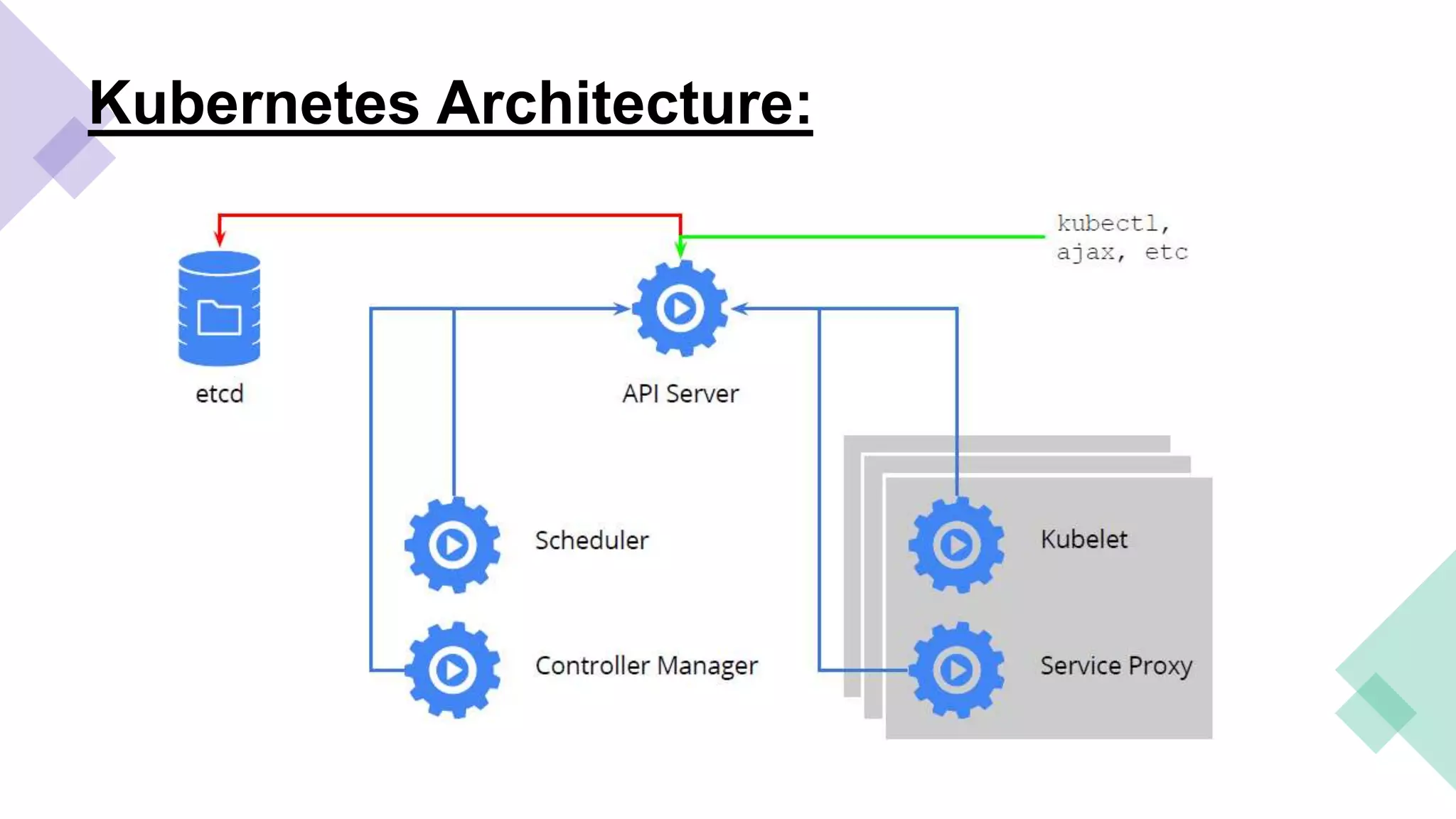
This document provides an overview of Linux containers, Docker, and Kubernetes. It discusses how Linux containers have limitations that Docker aimed to address by providing a platform for managing containers. However, standalone Docker has issues at scale, which Kubernetes was created to solve by offering clustering and orchestration of Docker containers across multiple hosts. Key Kubernetes concepts are explained such as pods, labels, services, and deployments. The document concludes with a reference to a Kubernetes demo.