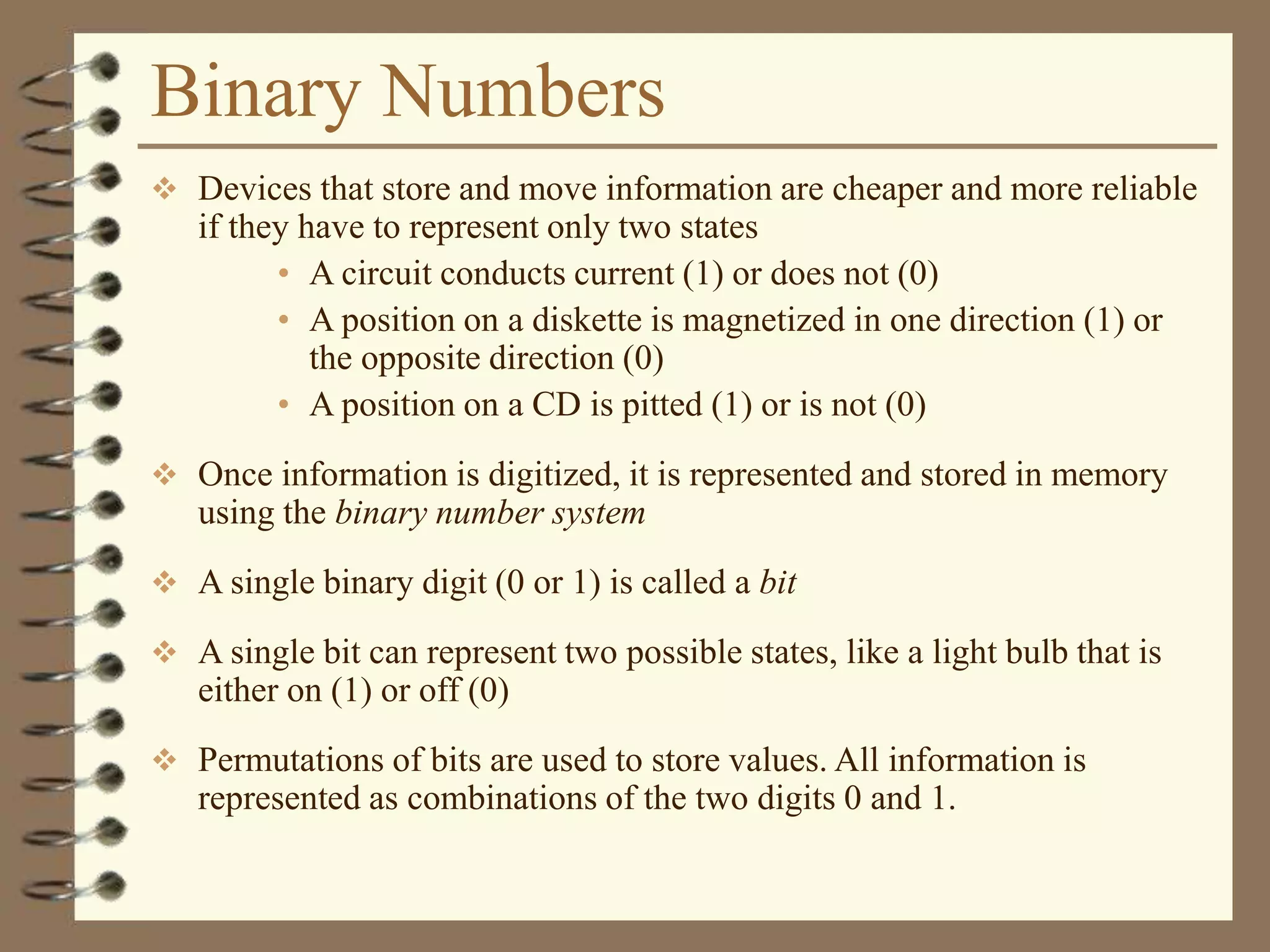
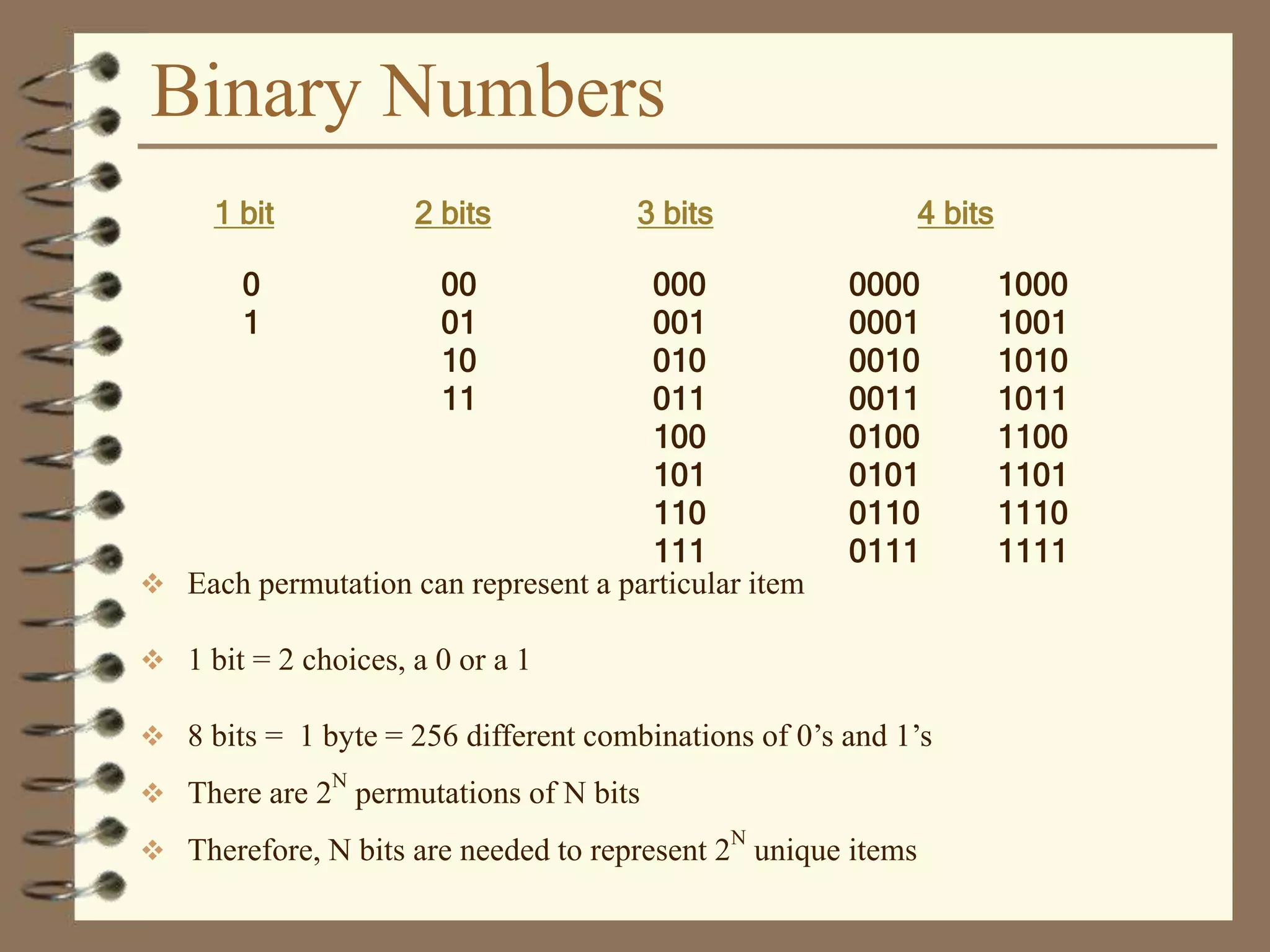
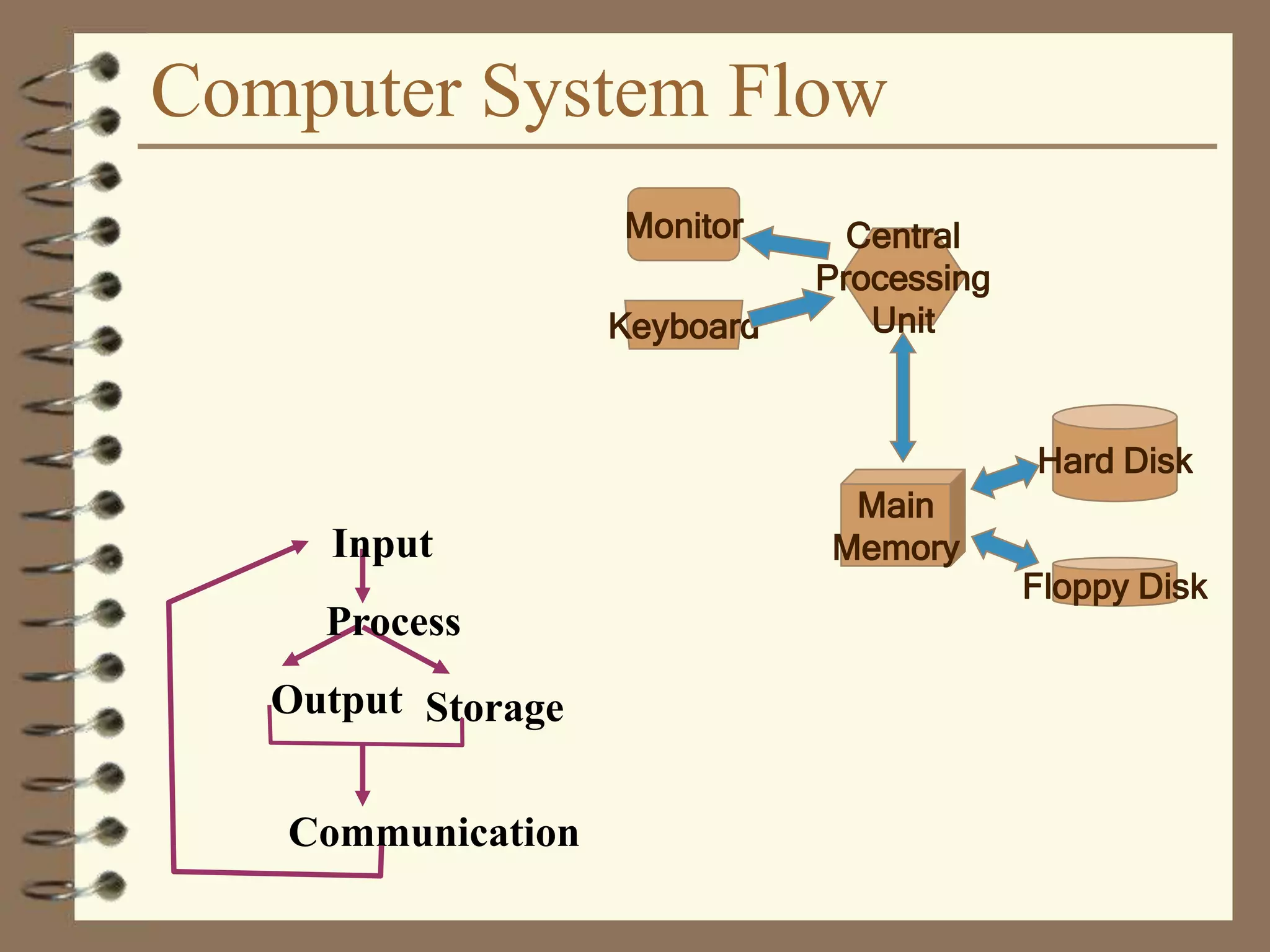
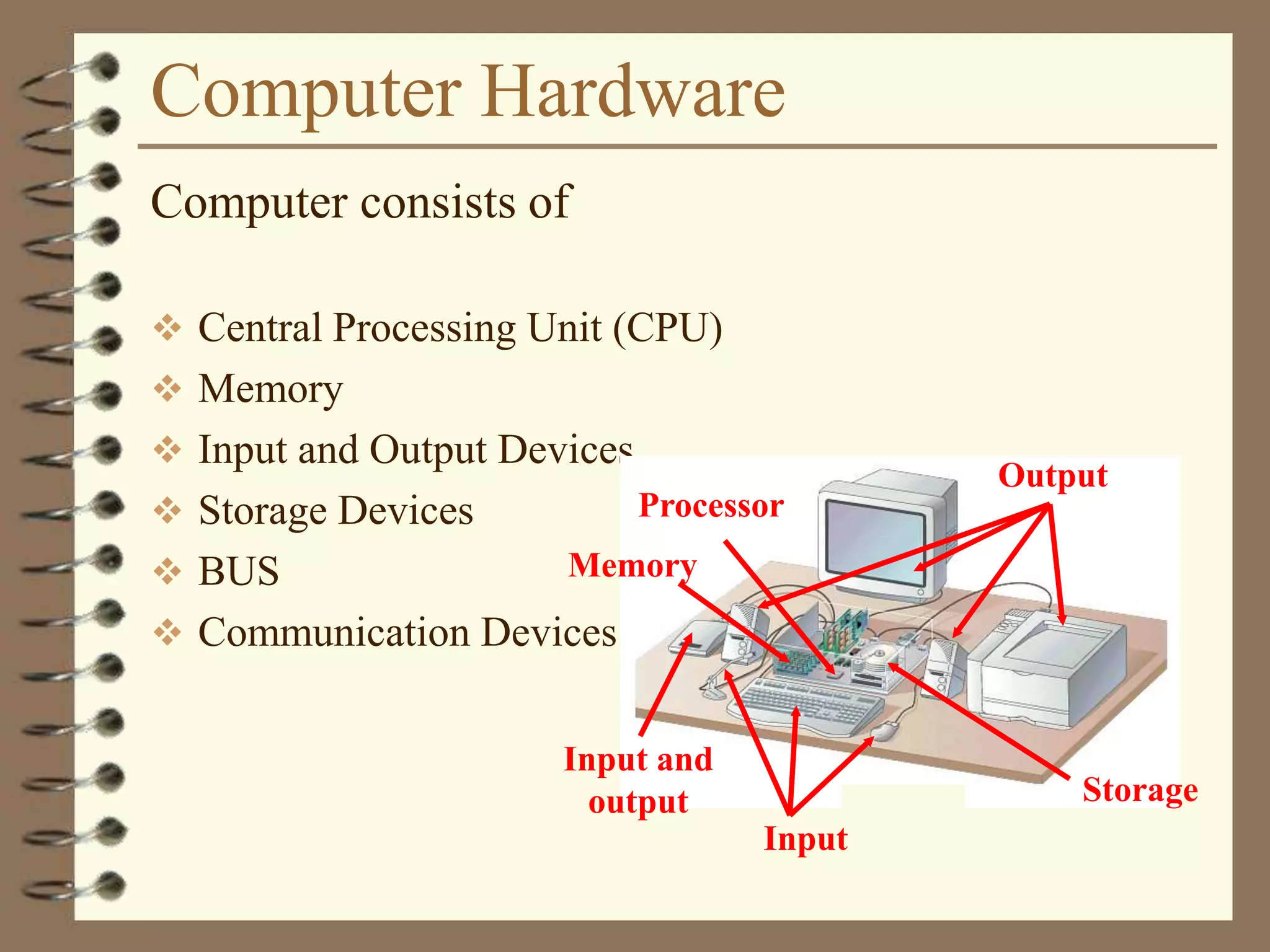
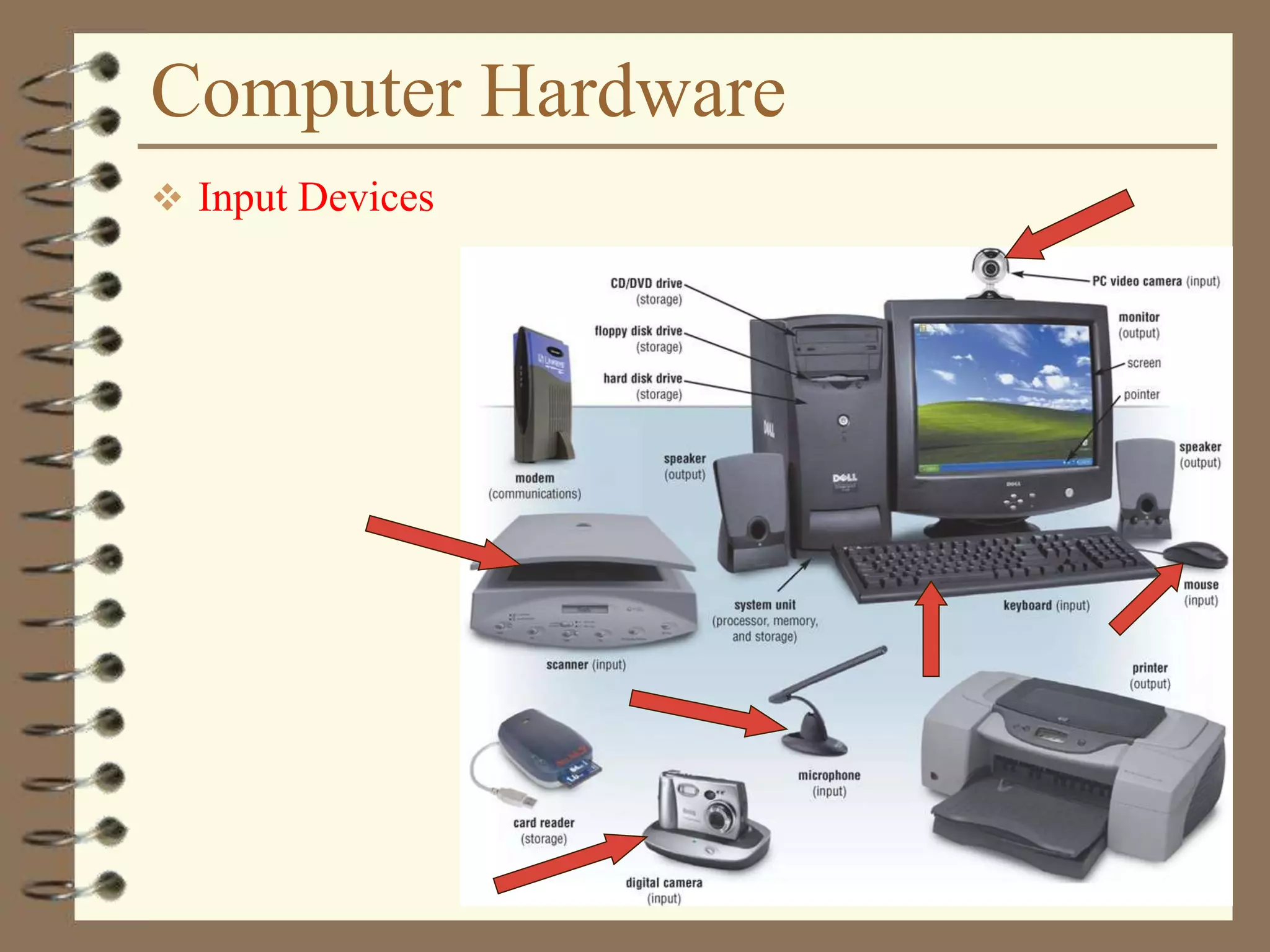
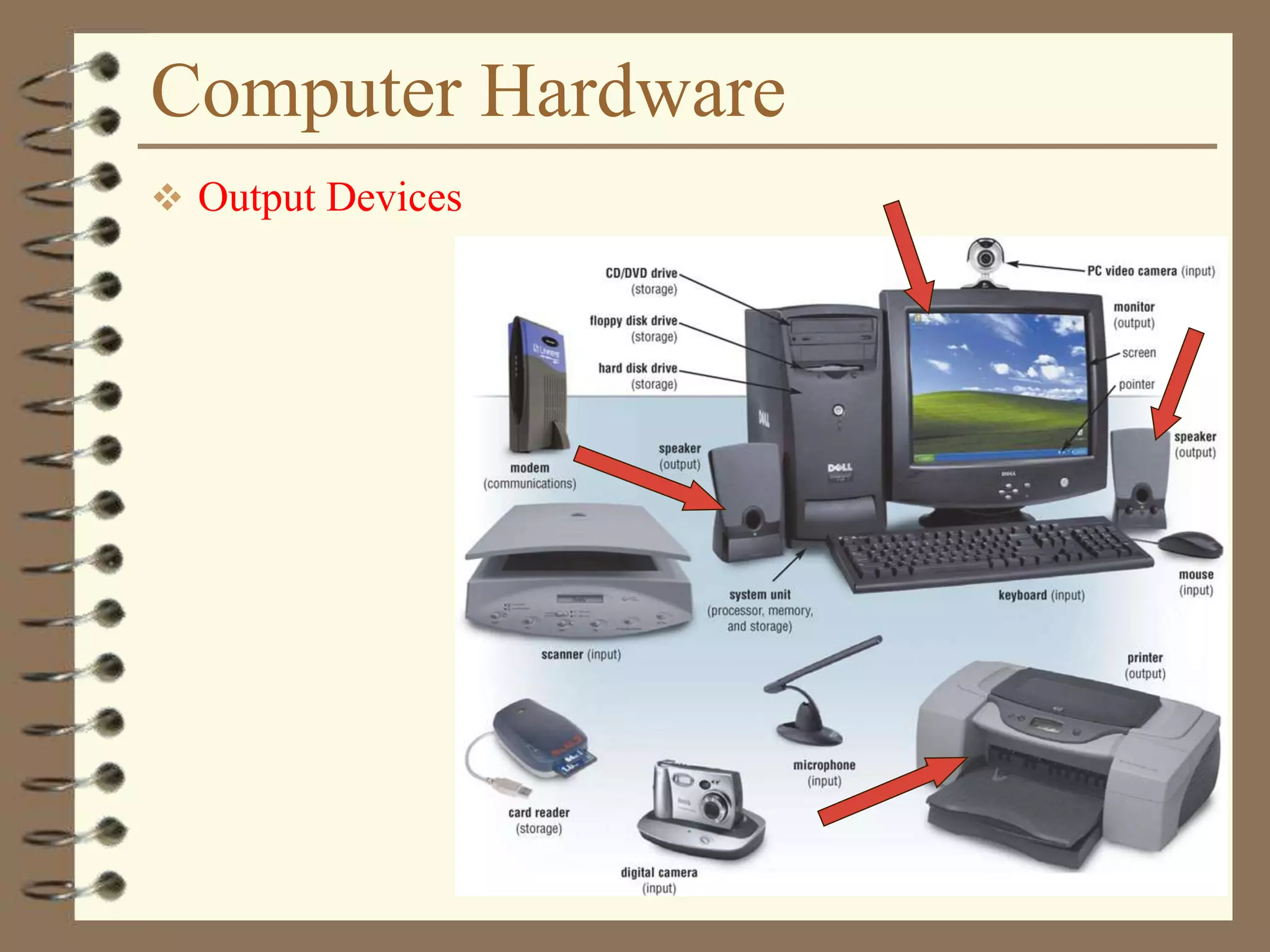
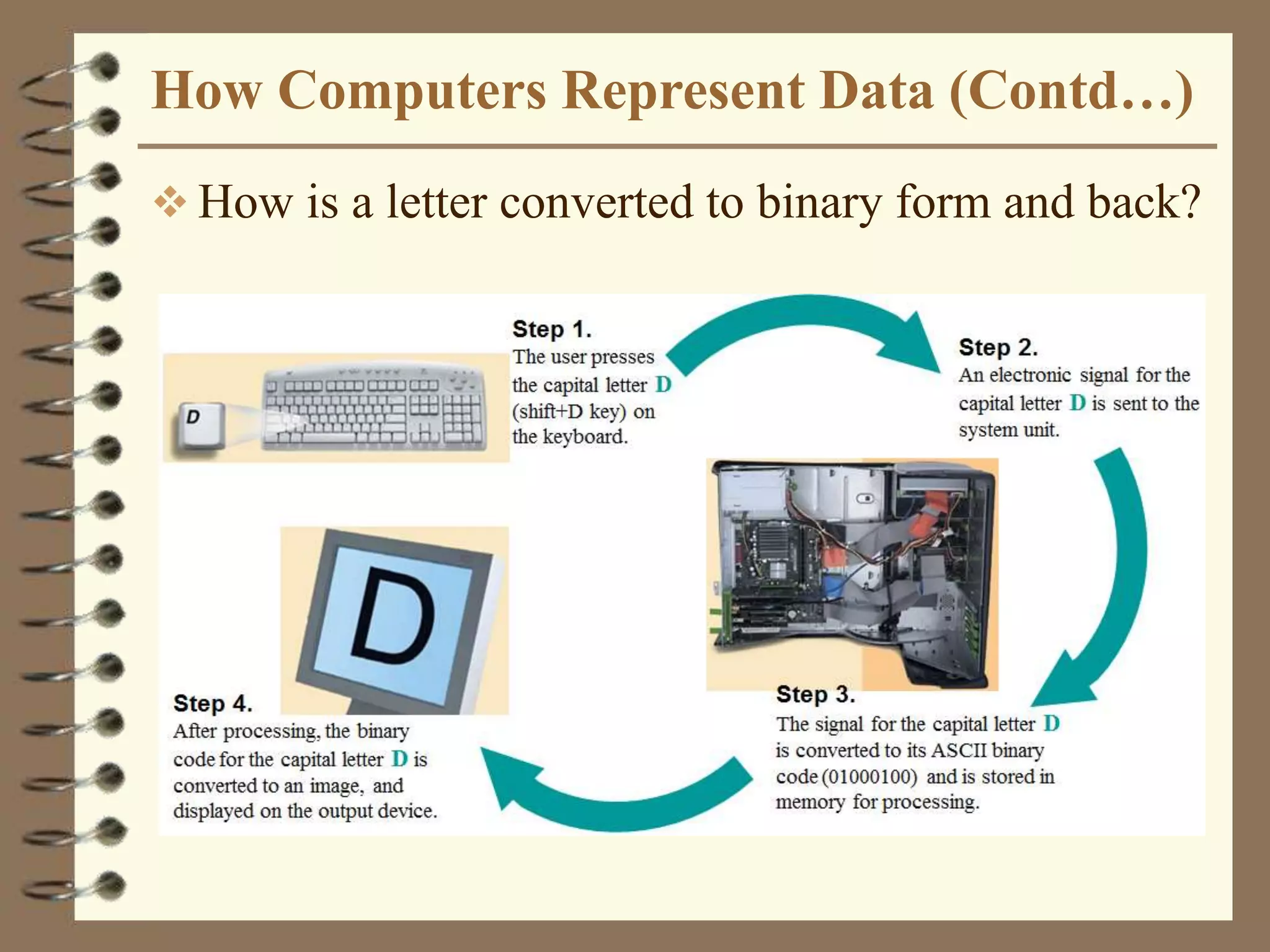
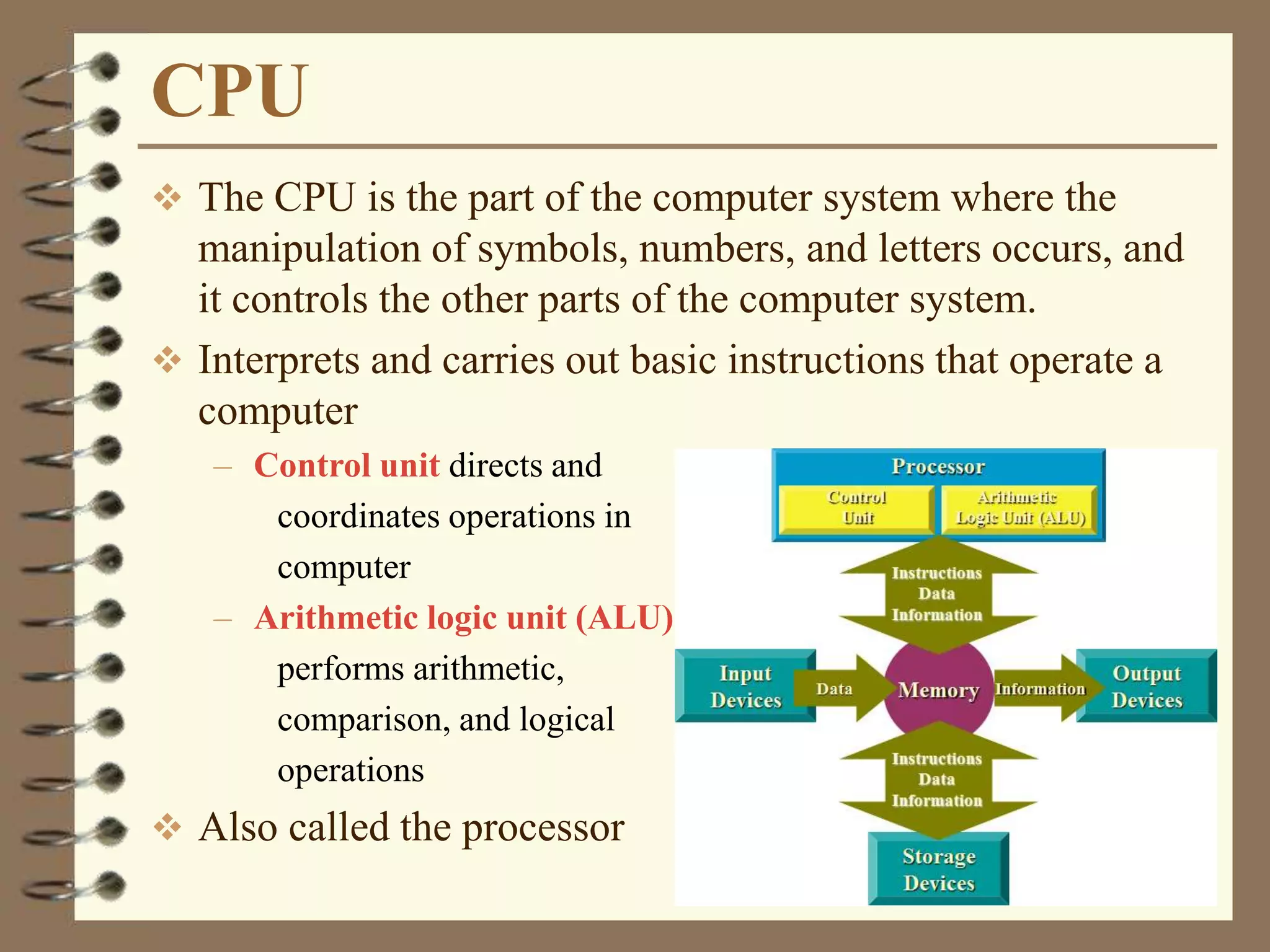
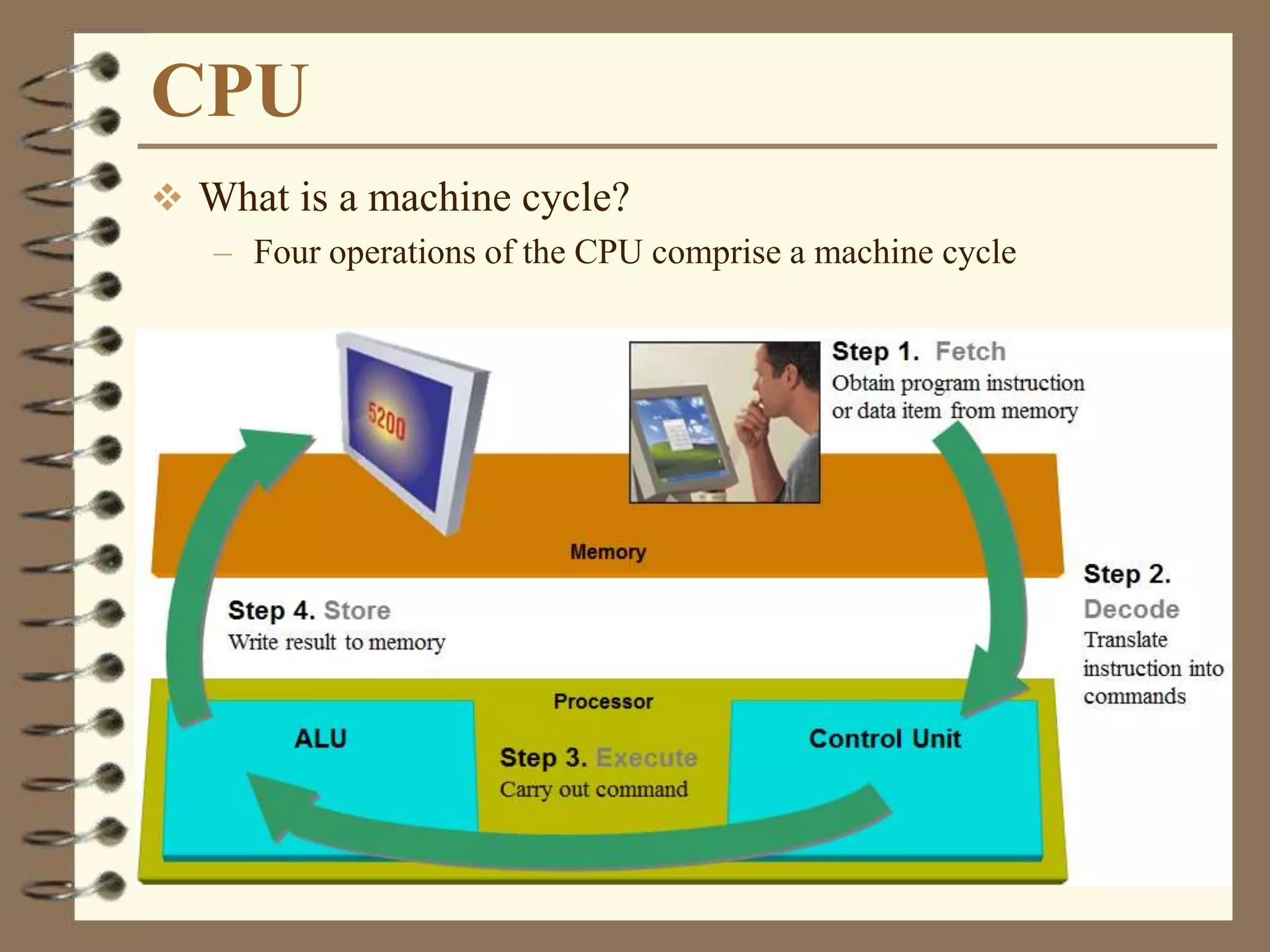
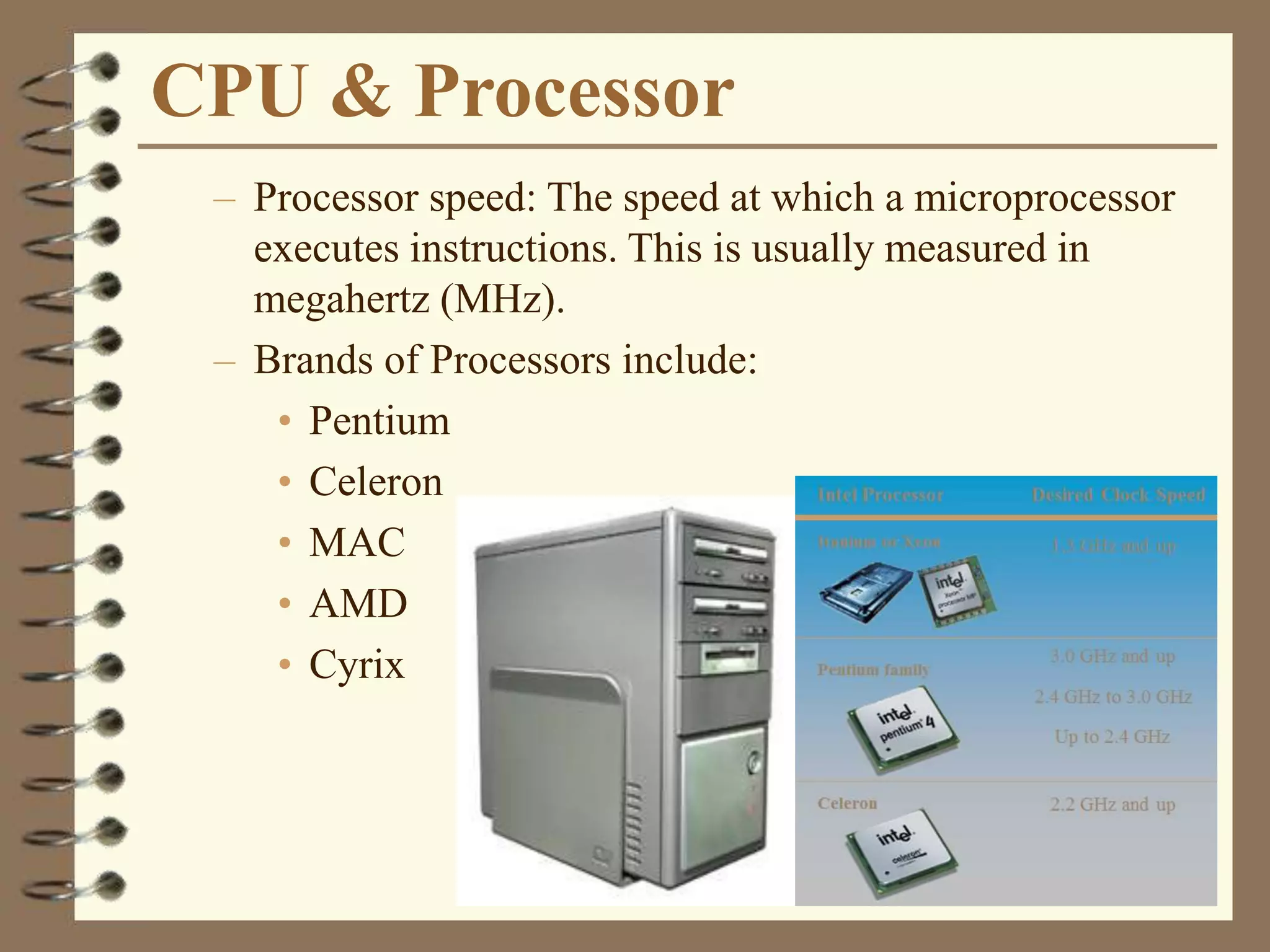
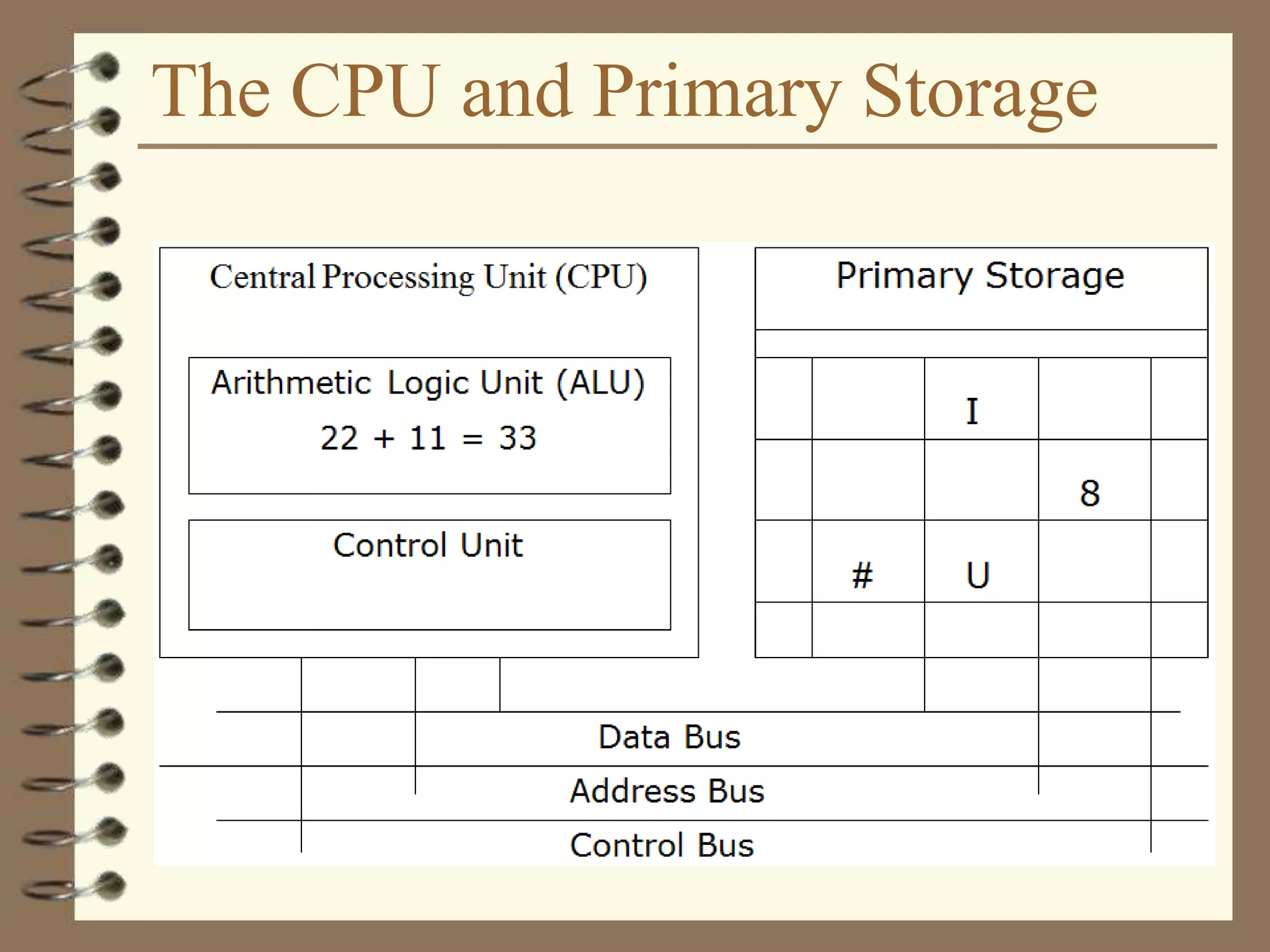
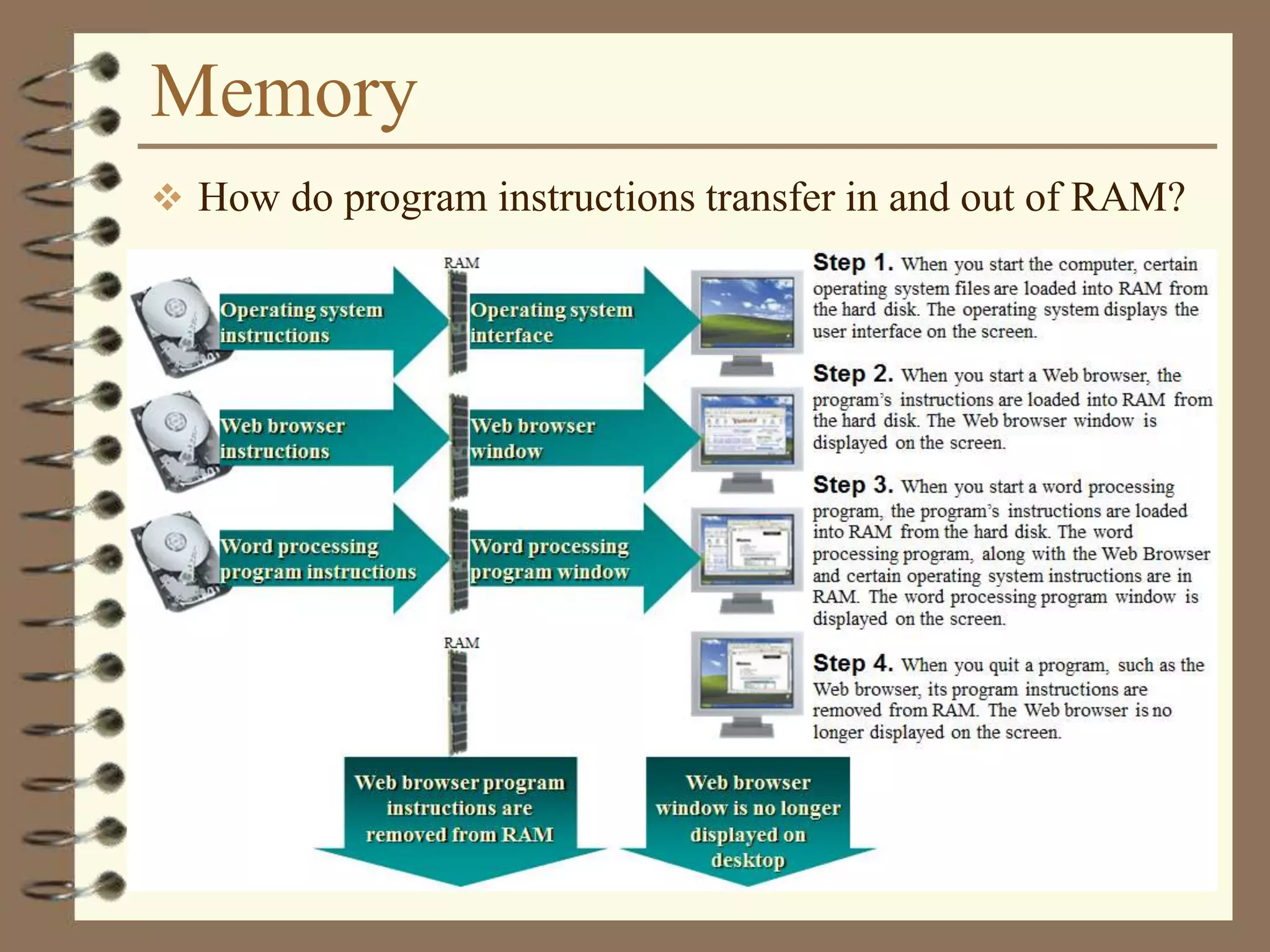
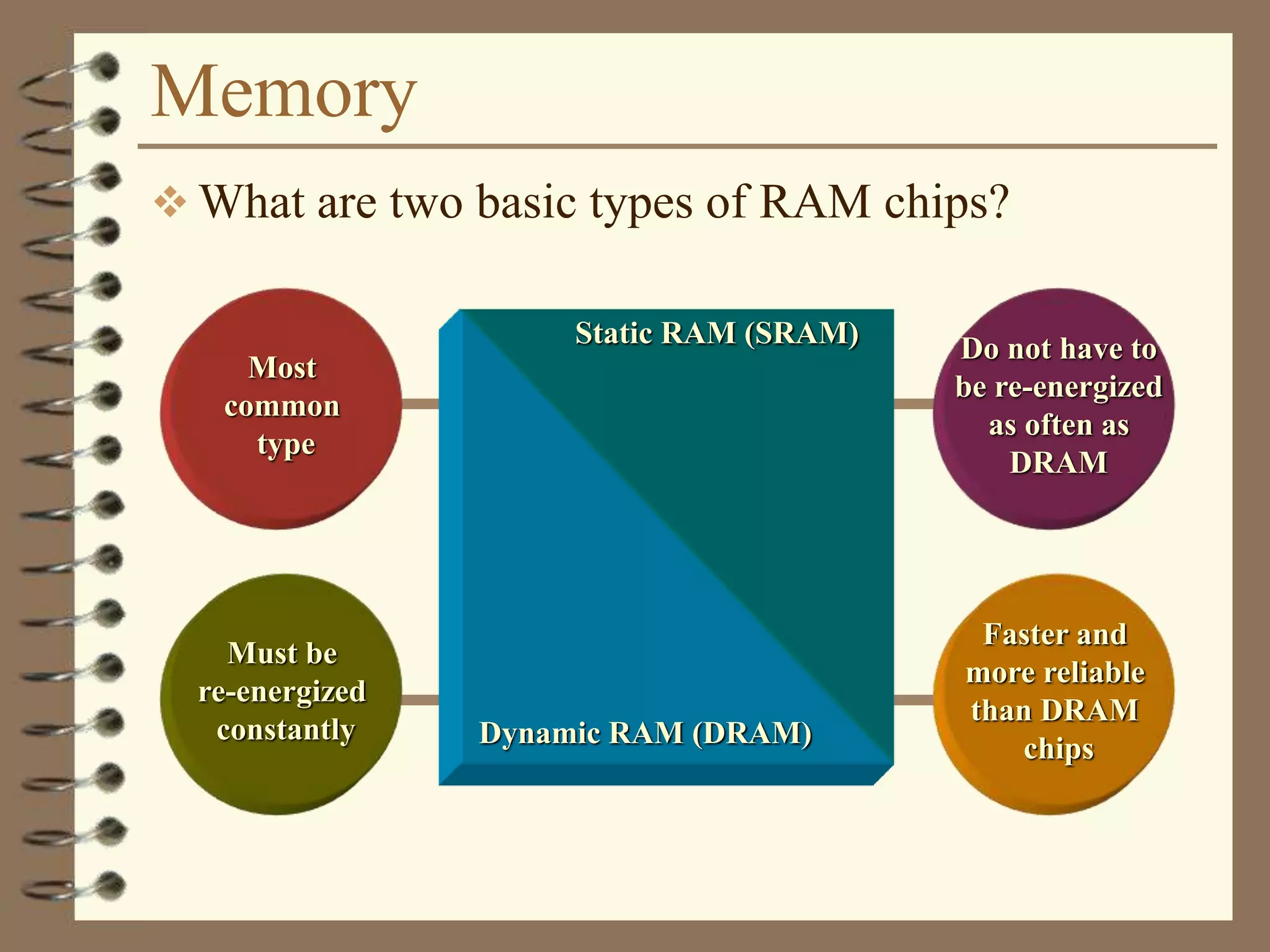
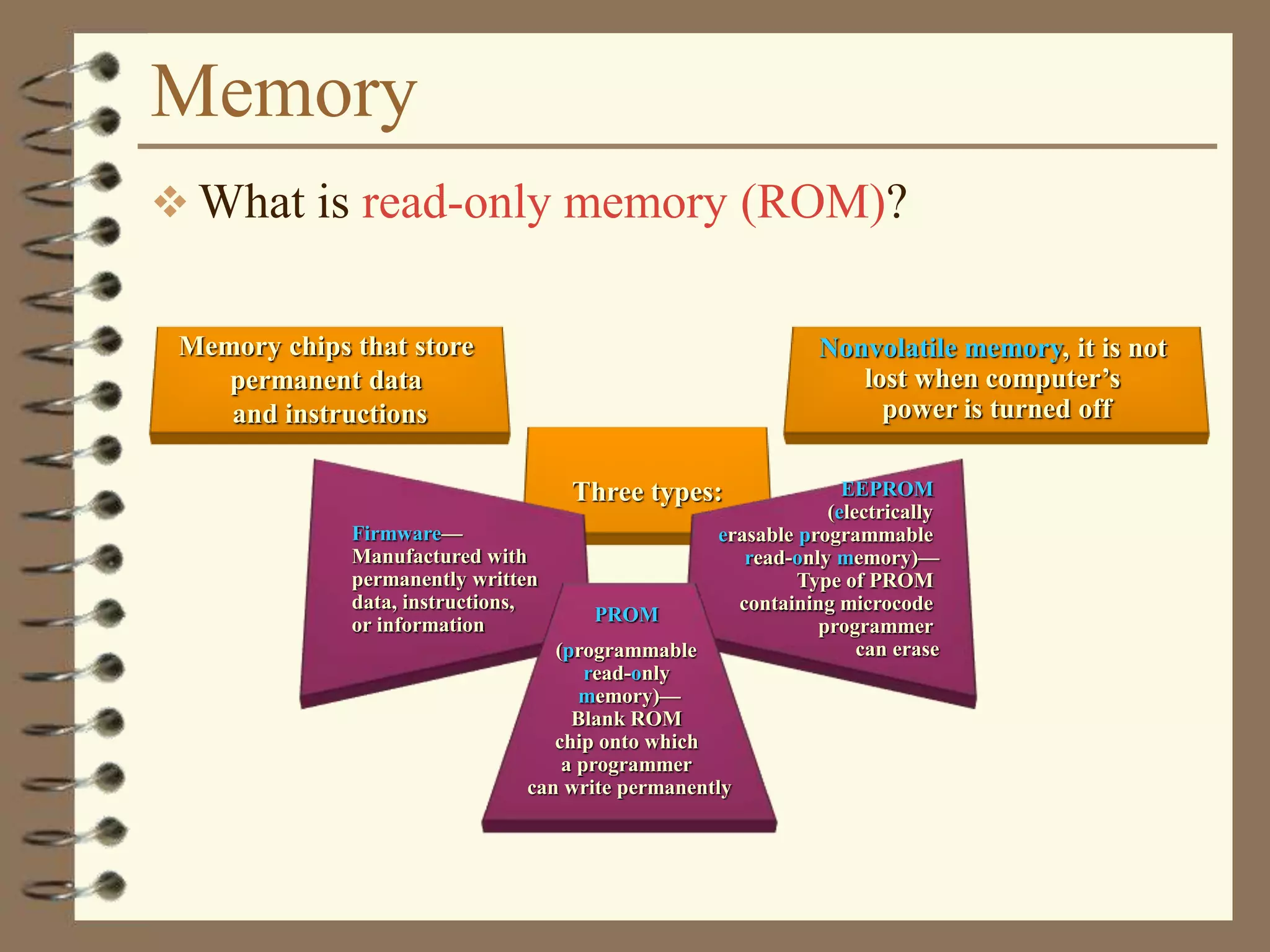
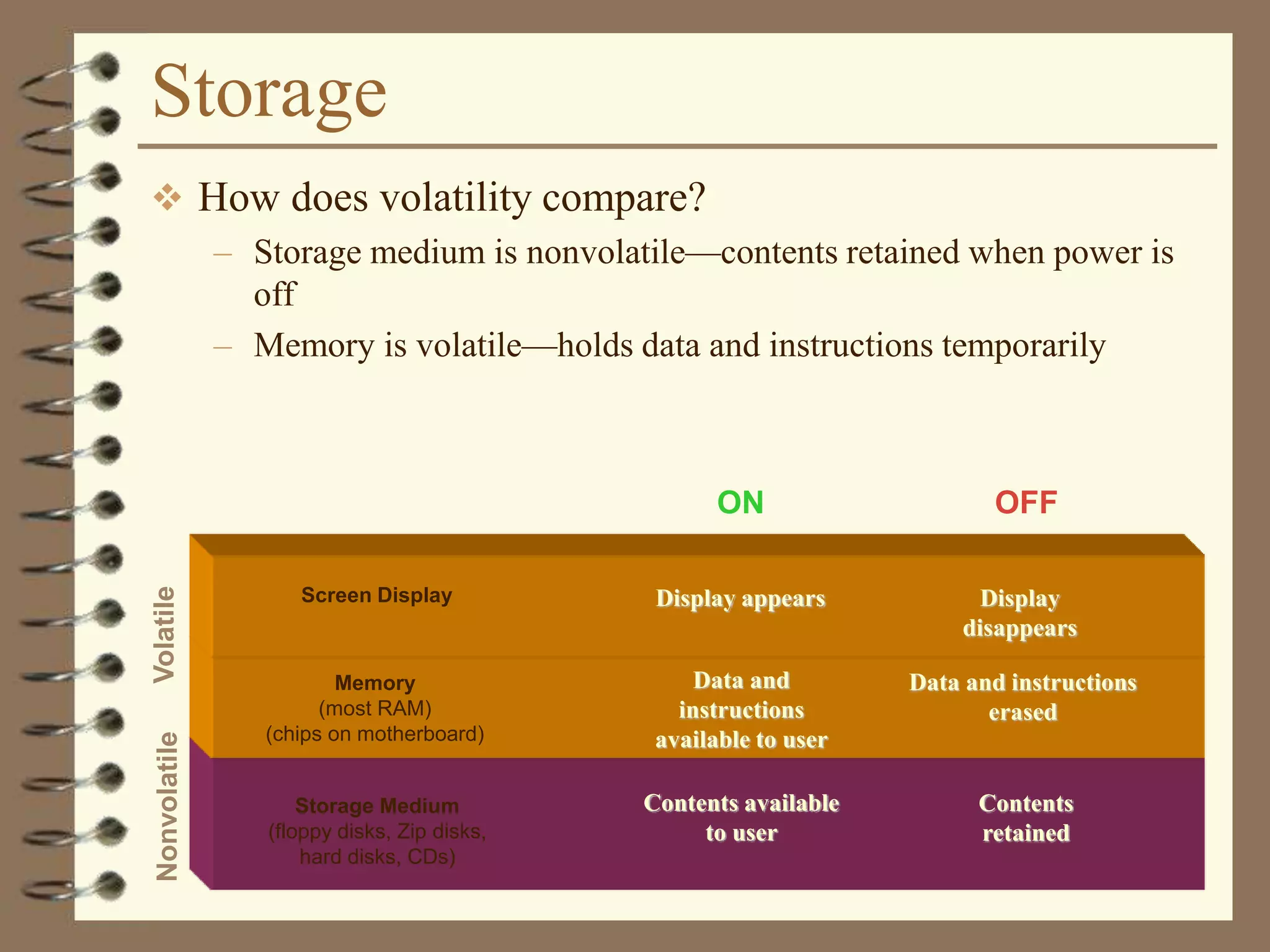
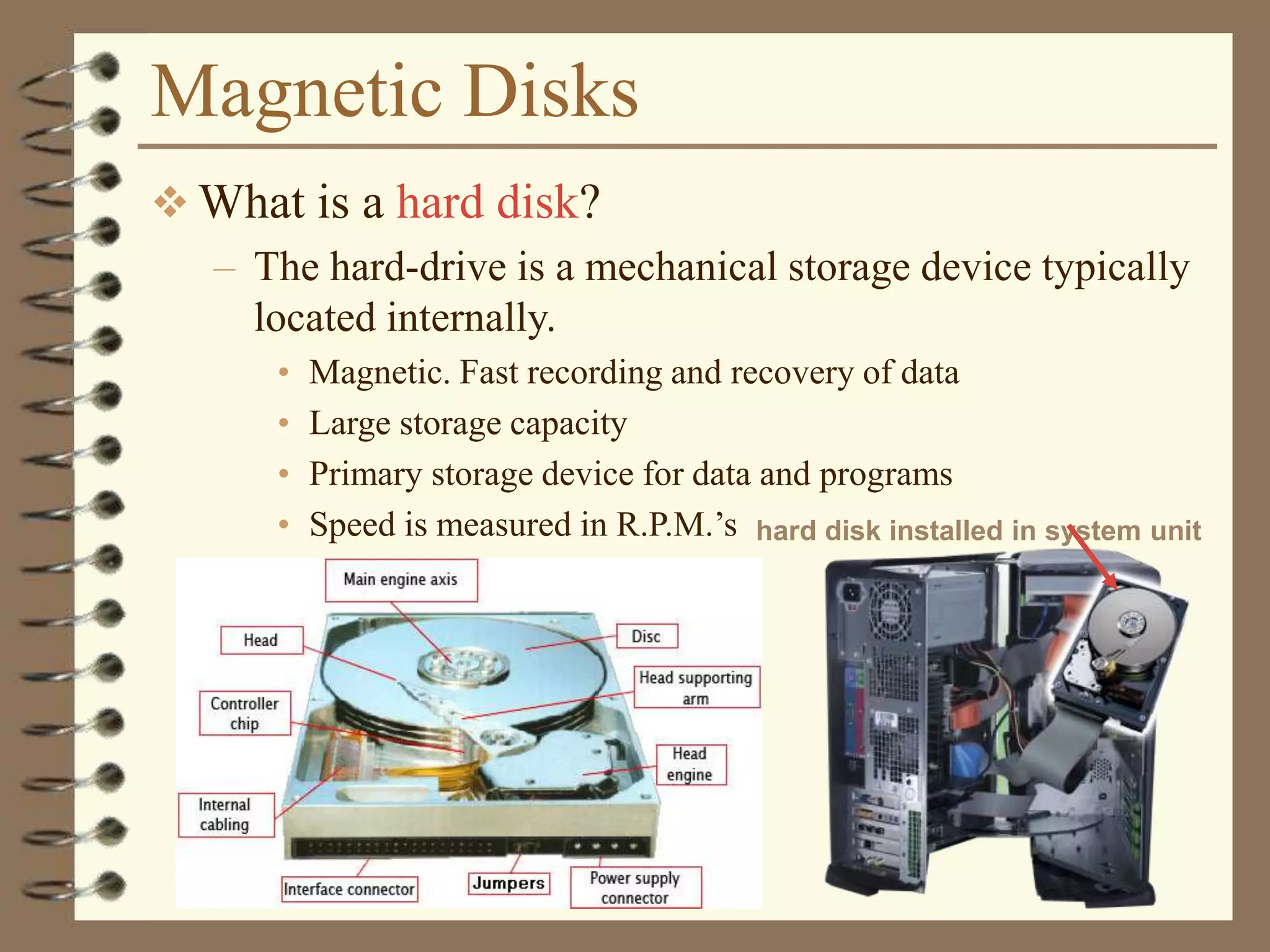
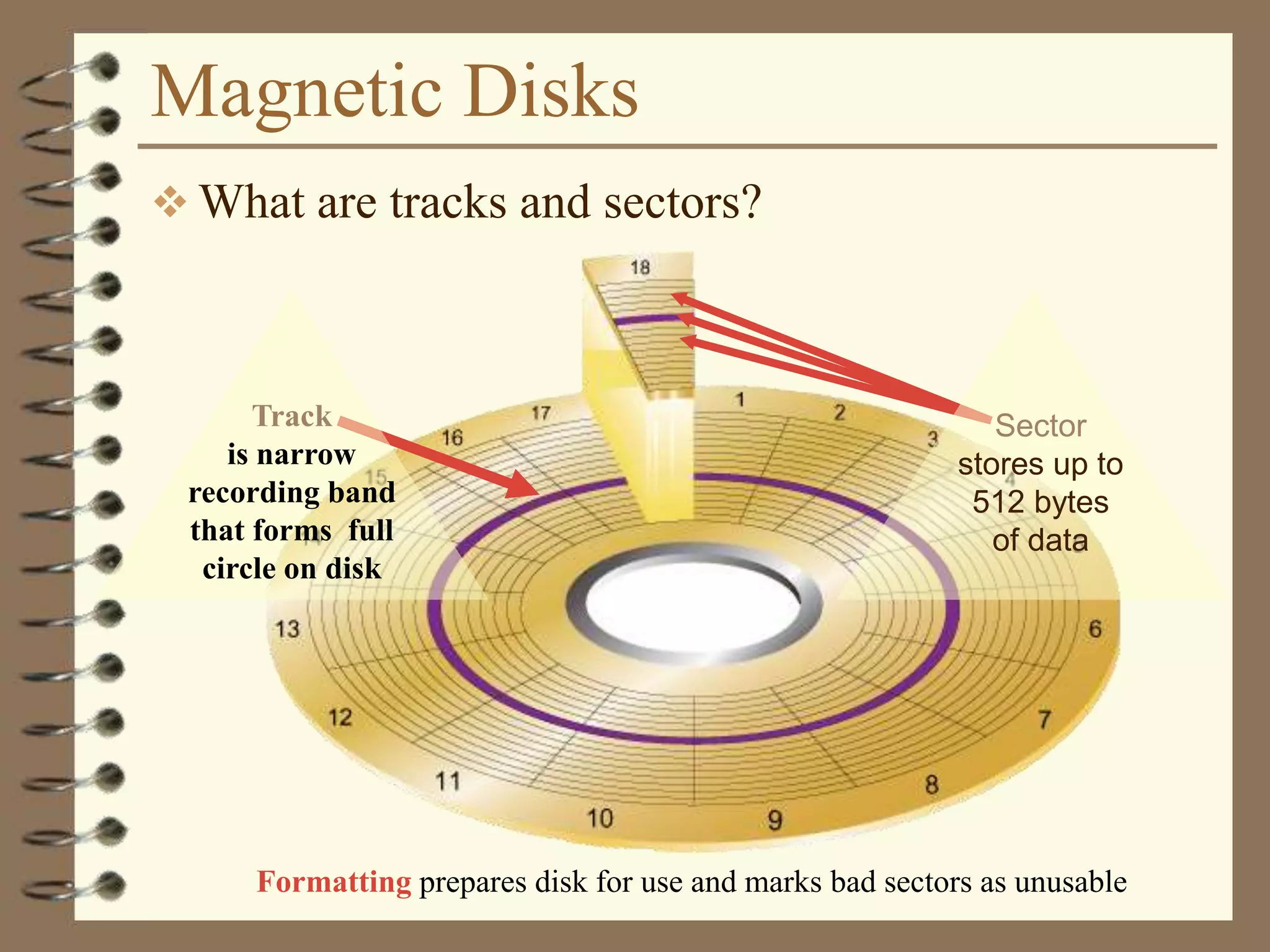
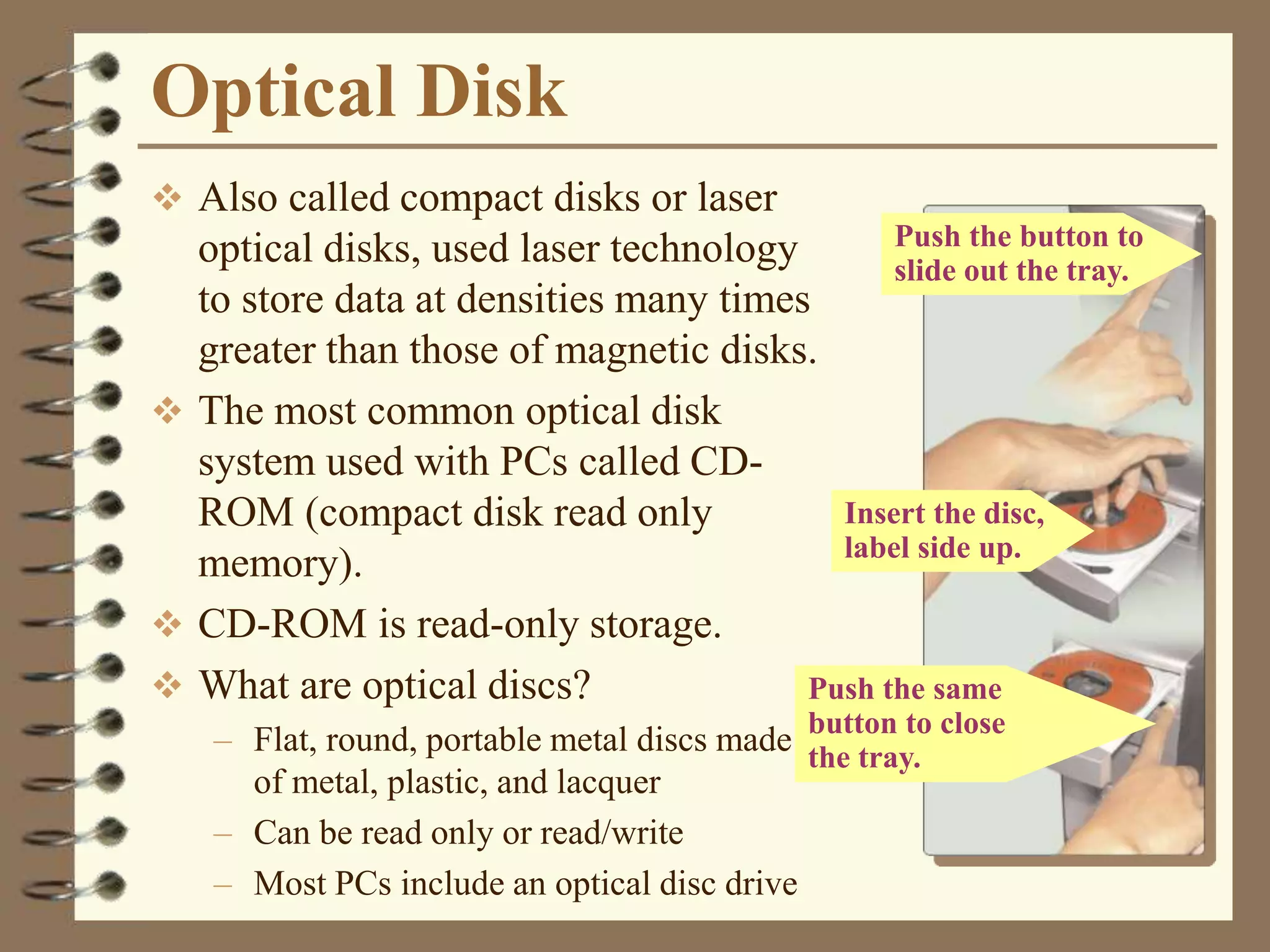
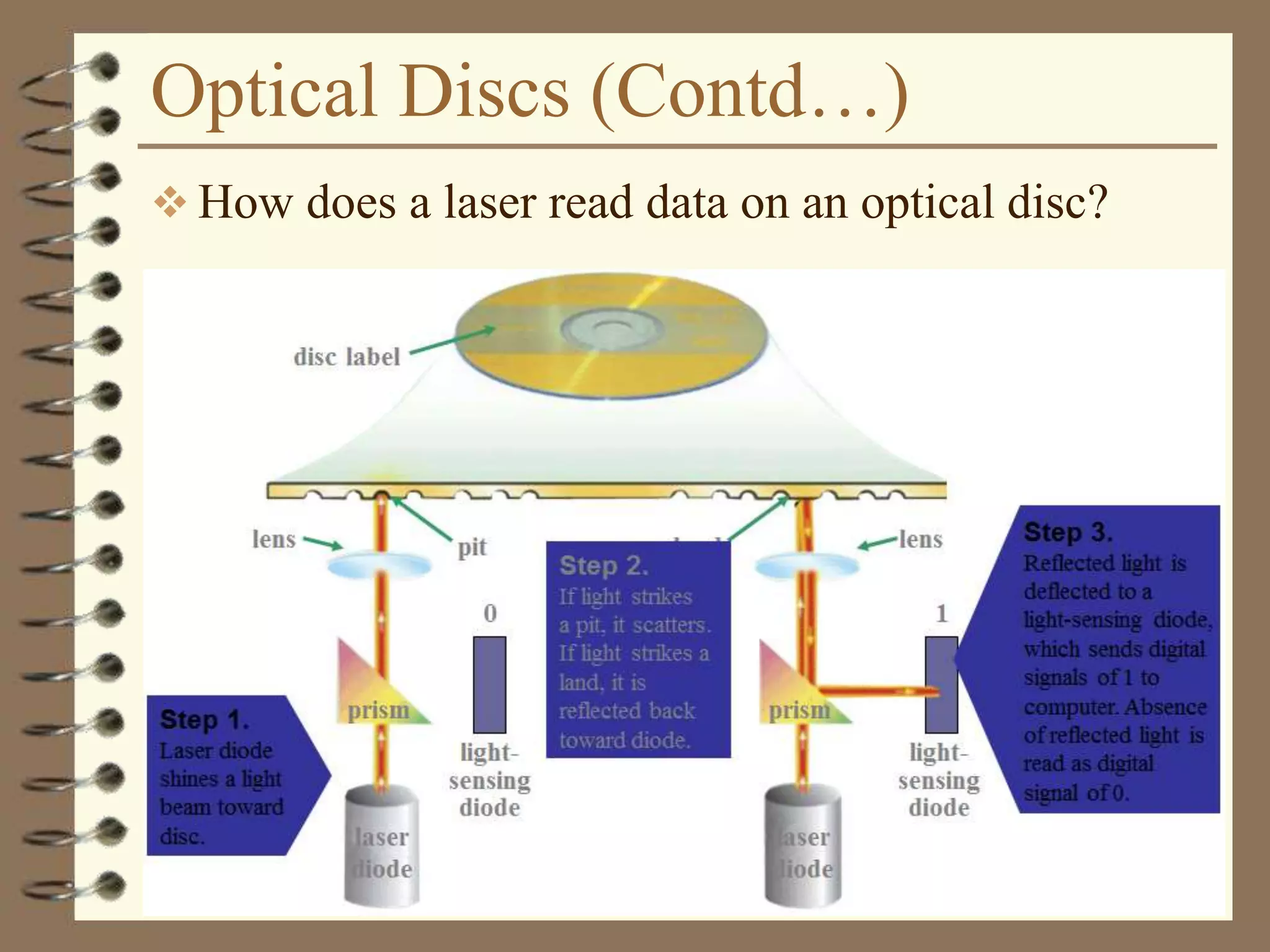
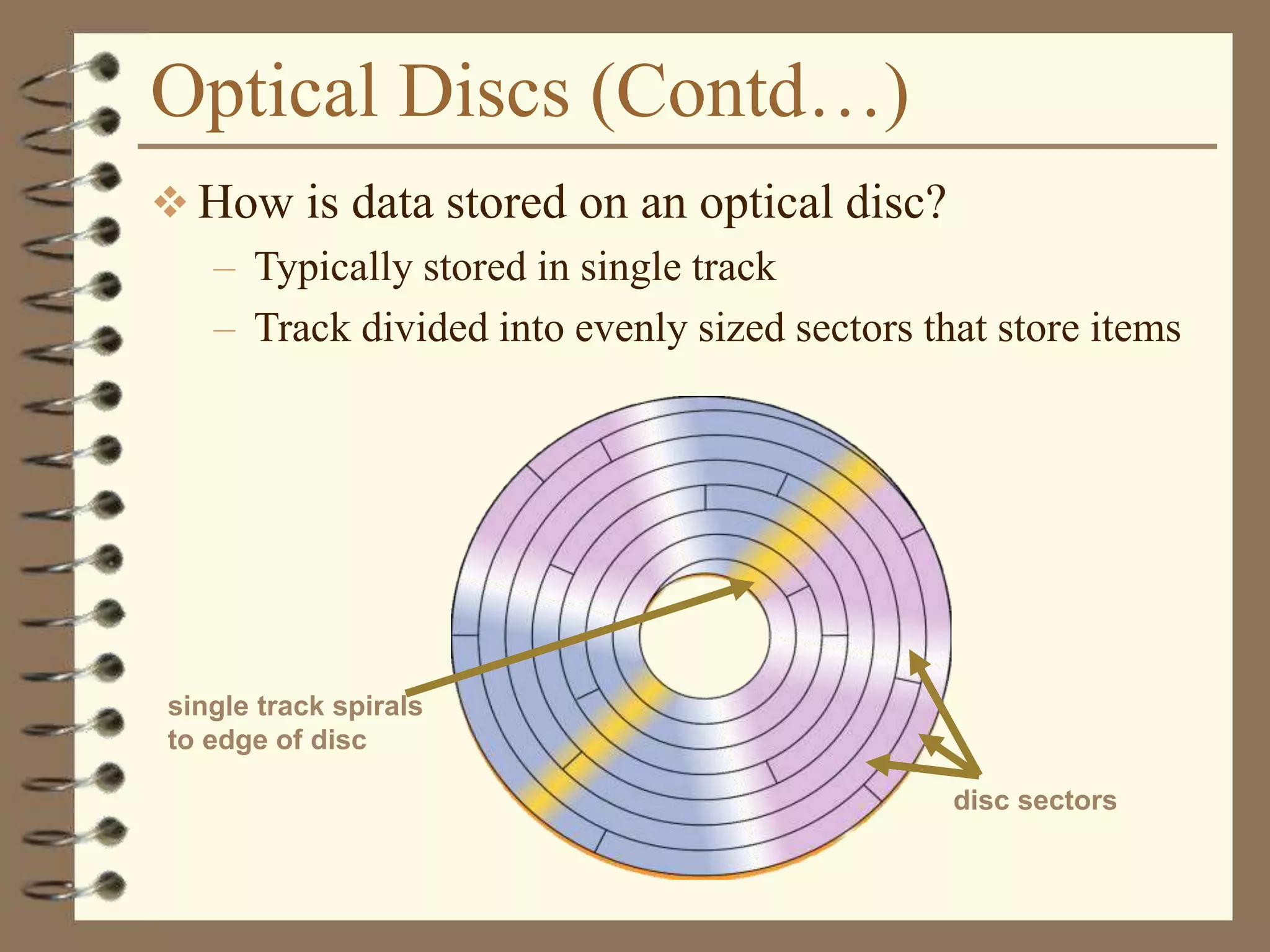
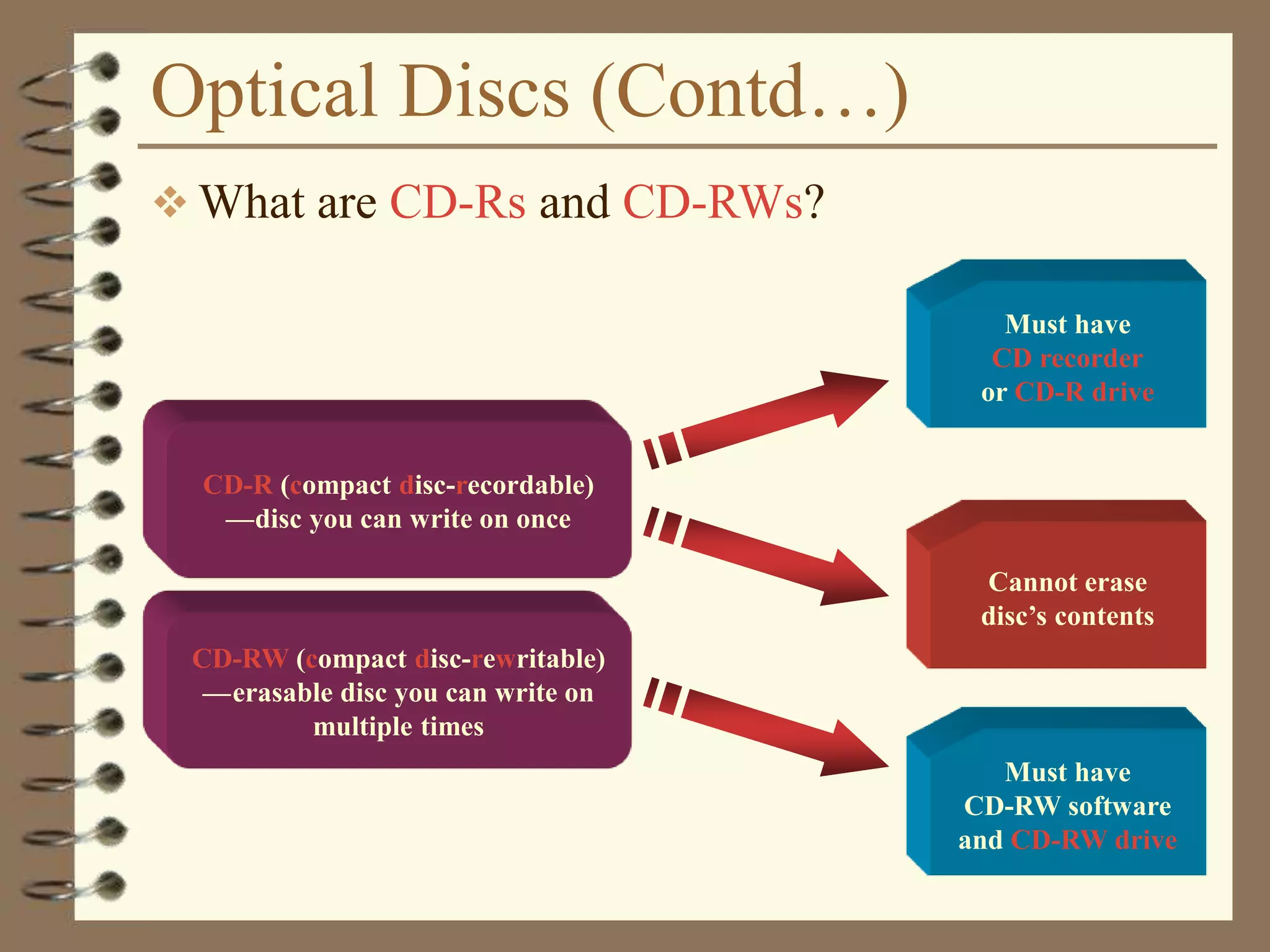
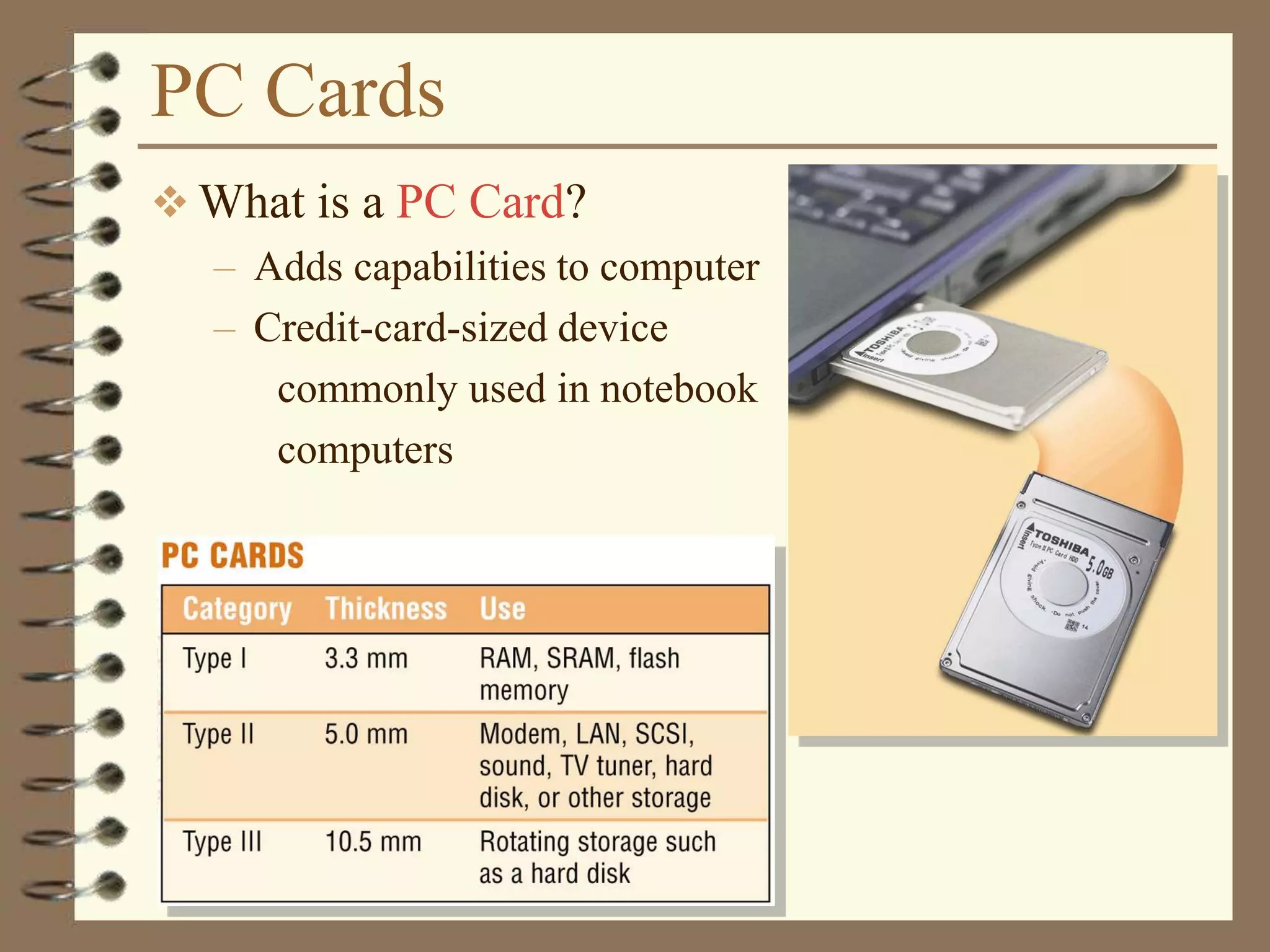
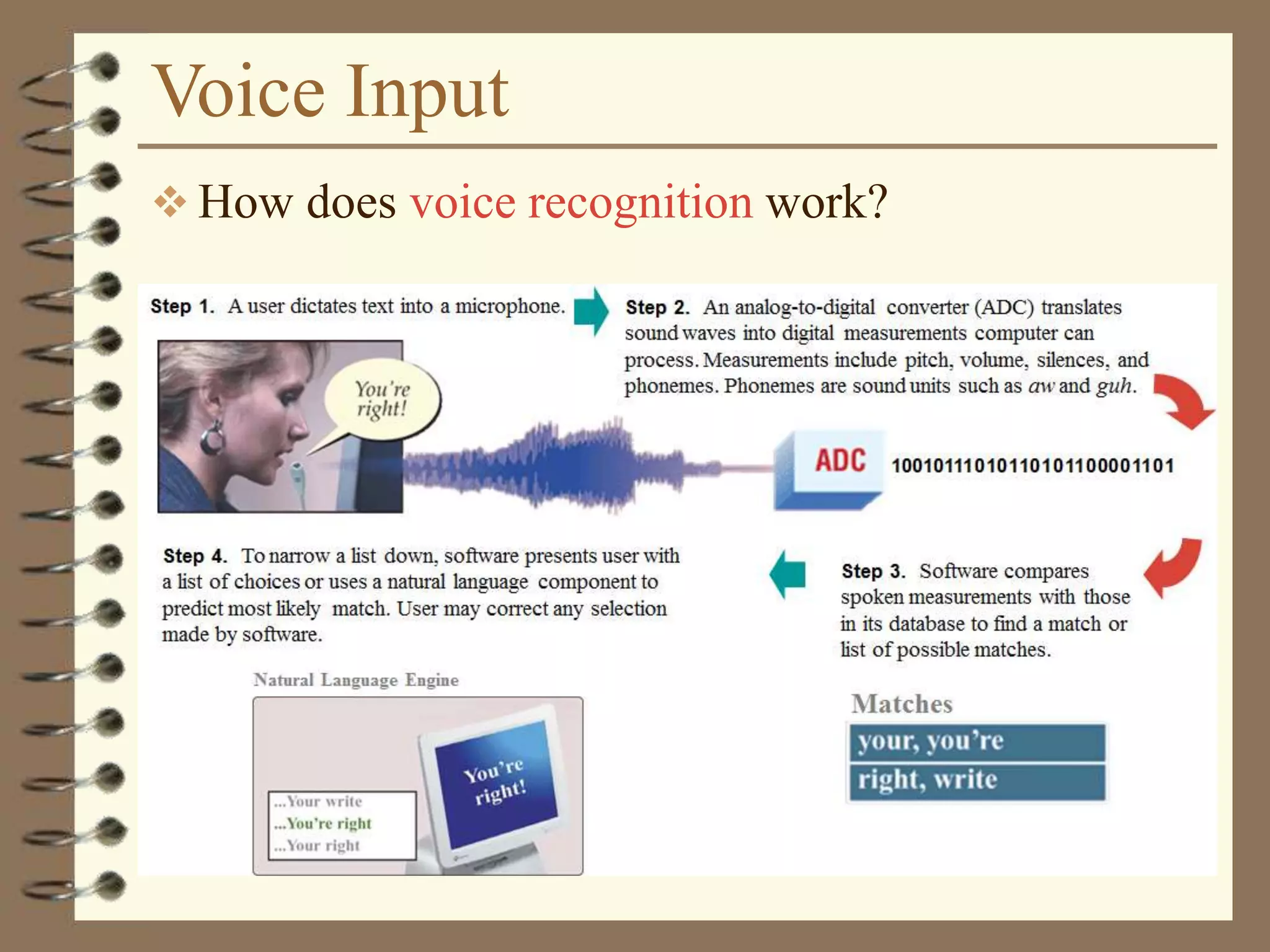
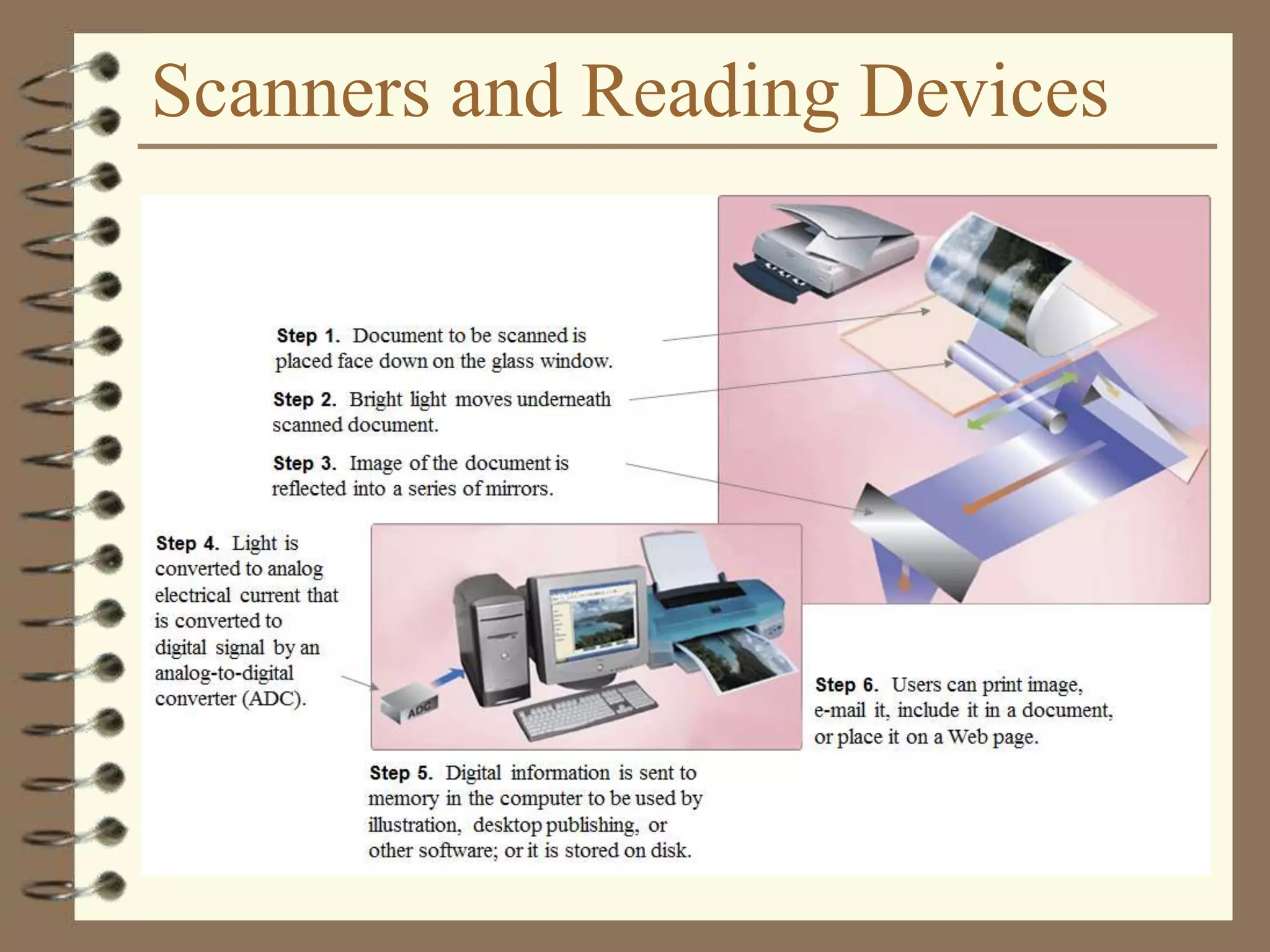
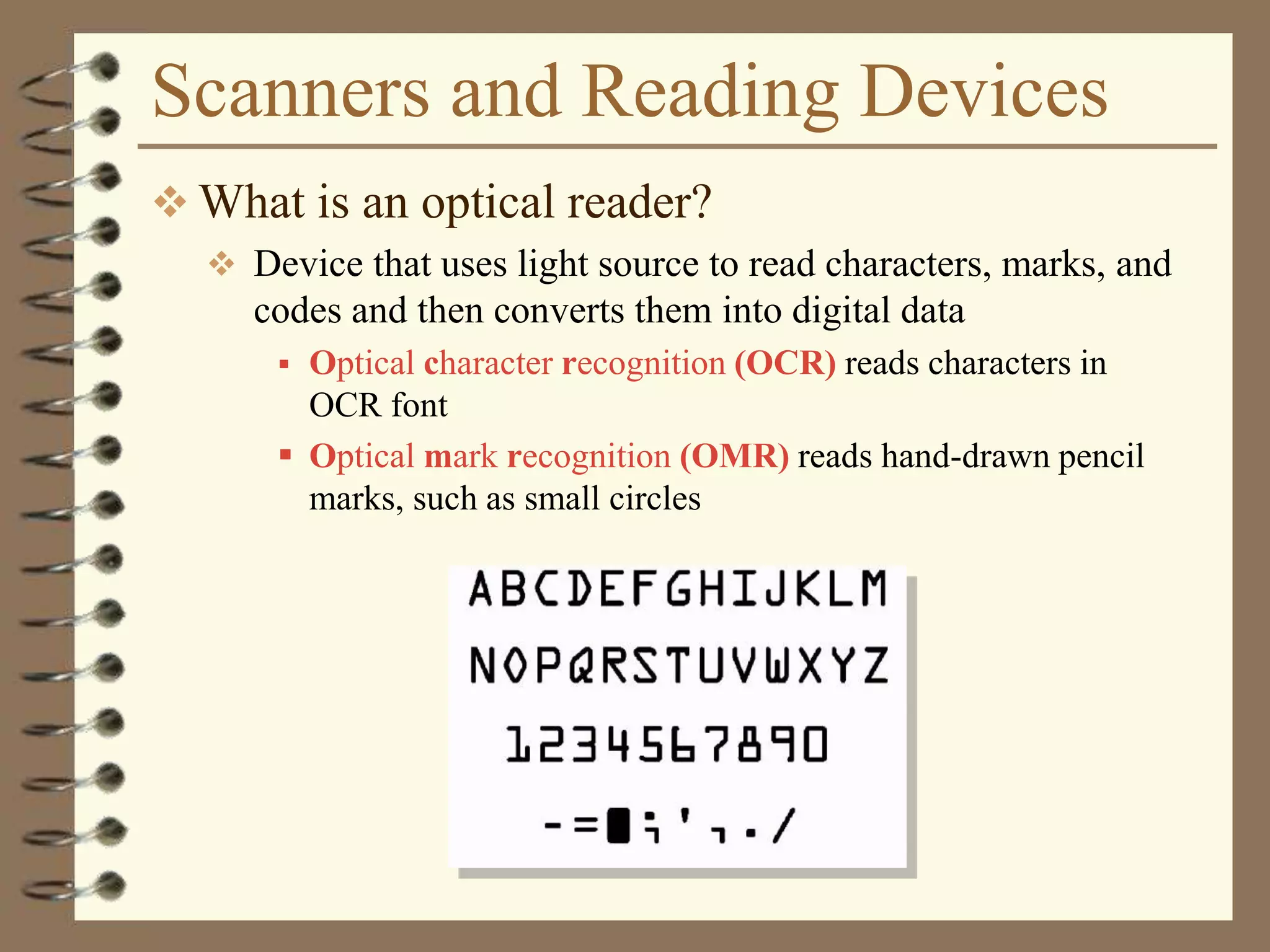
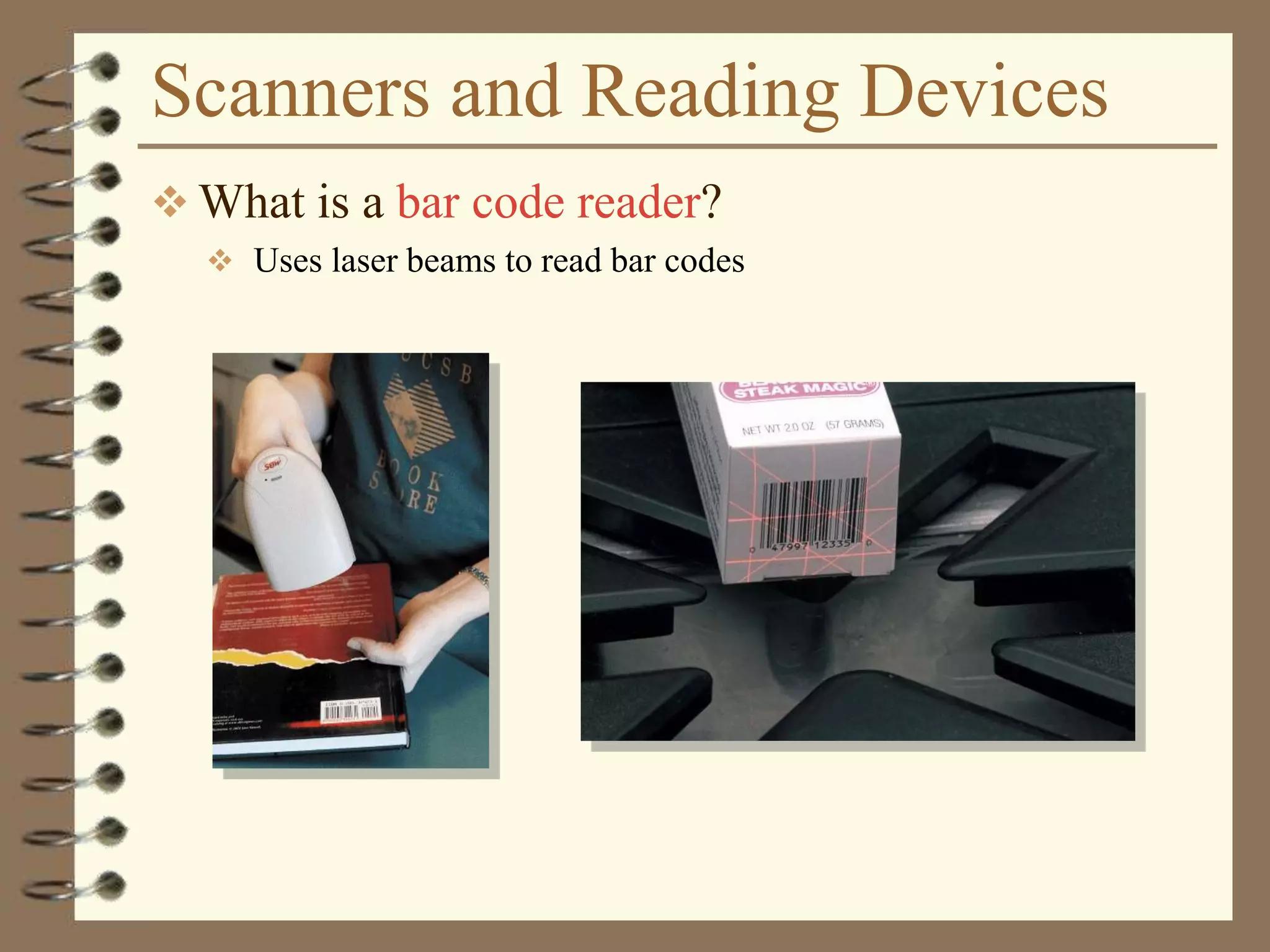
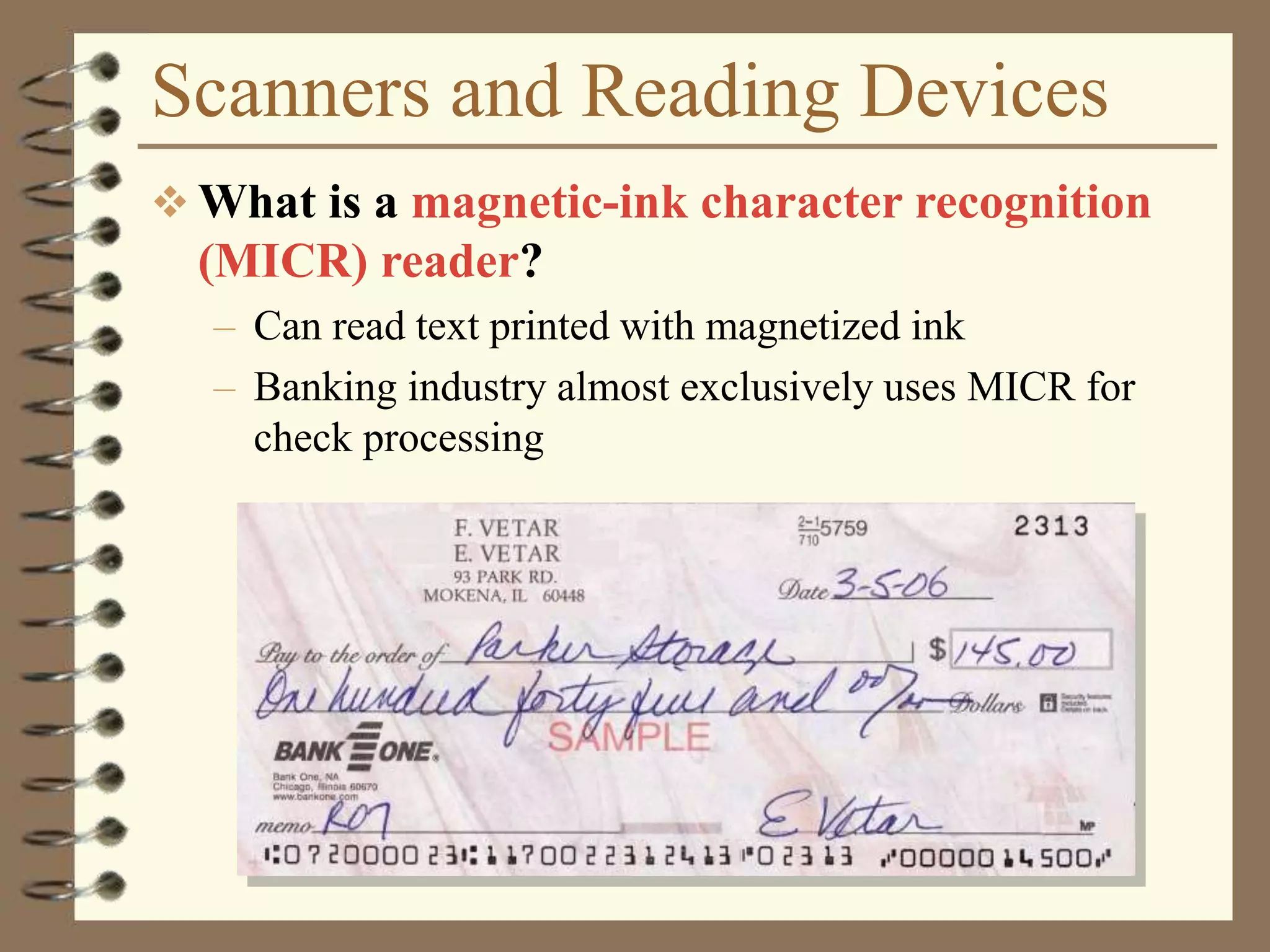
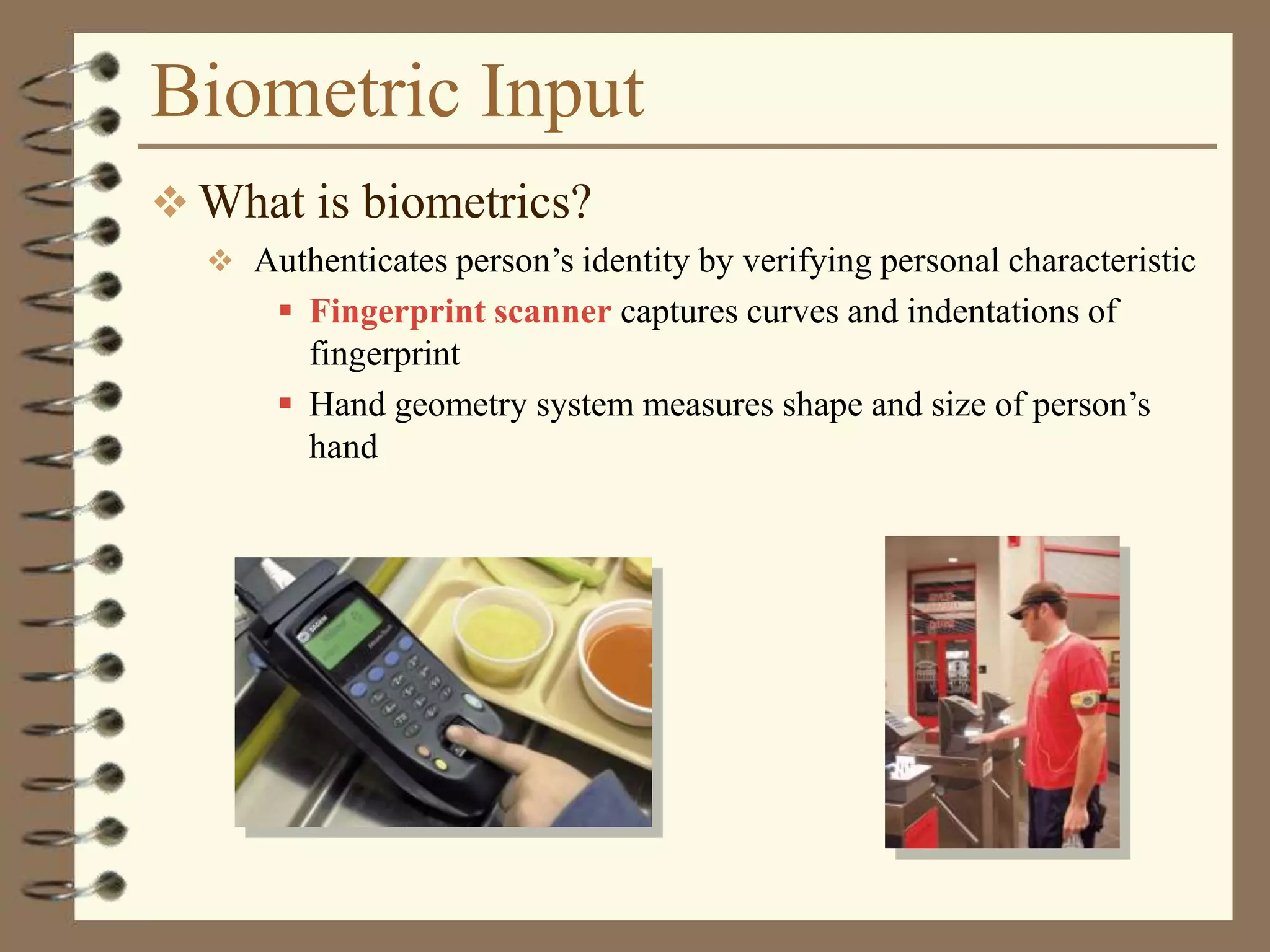
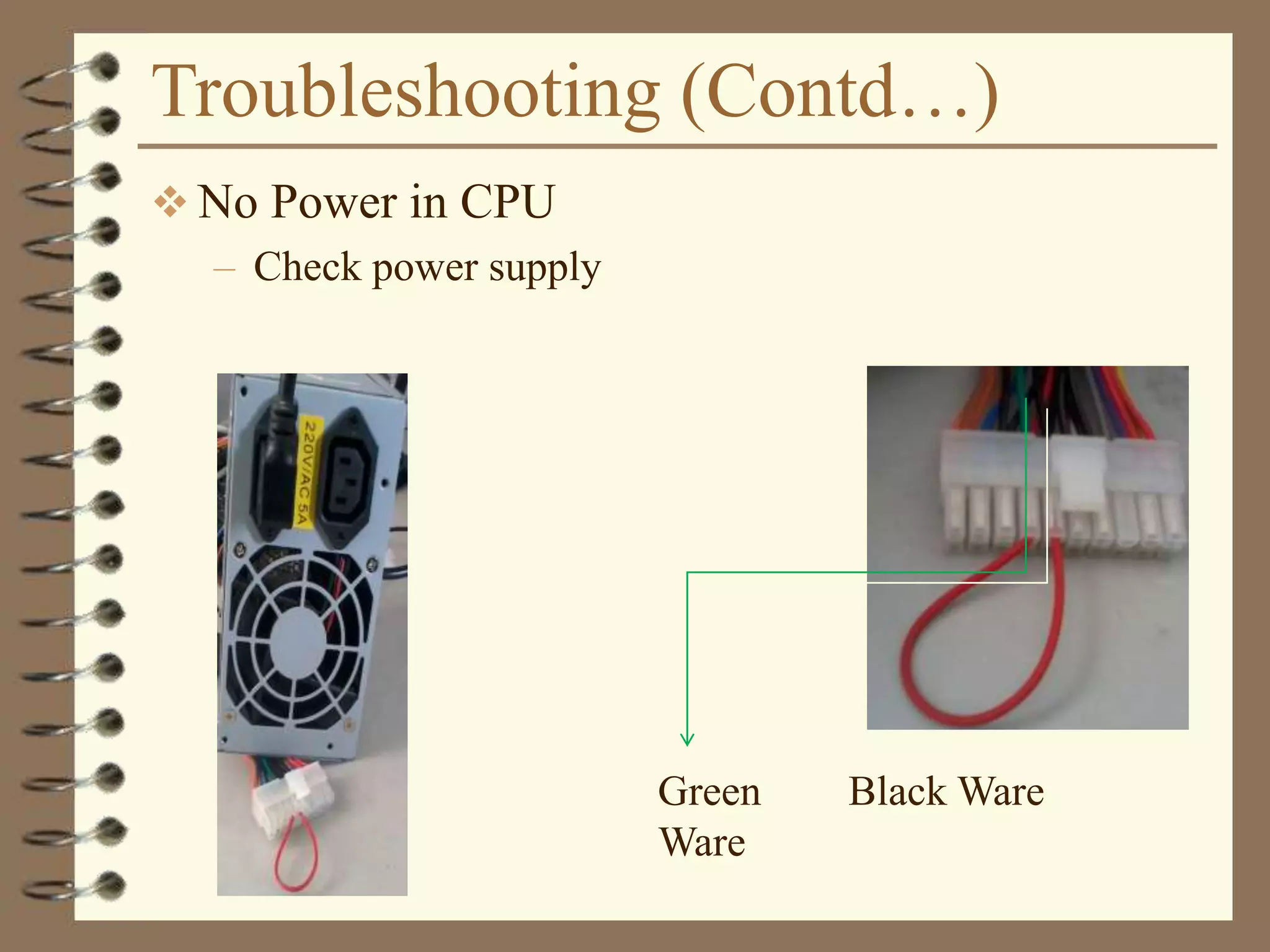
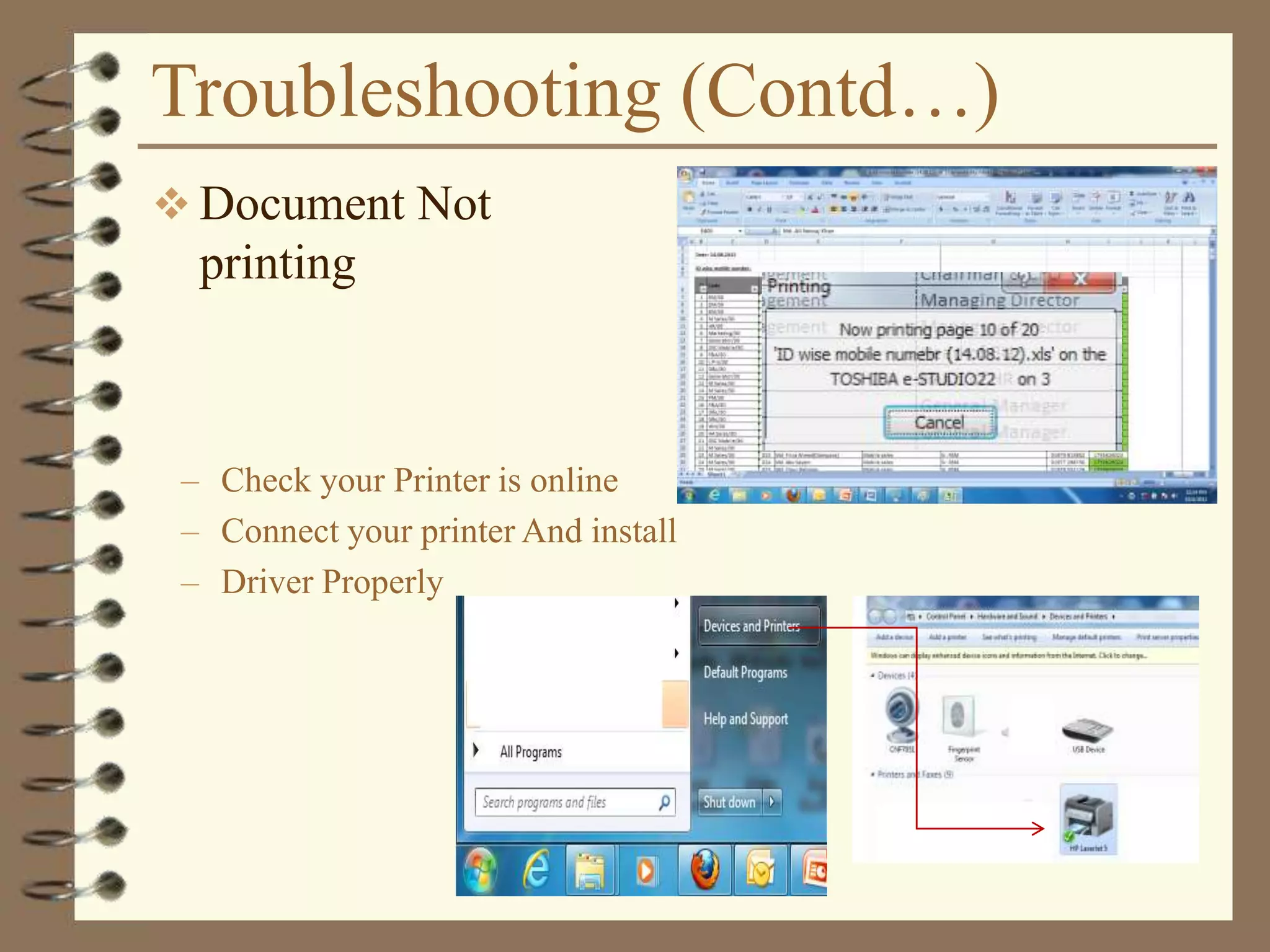
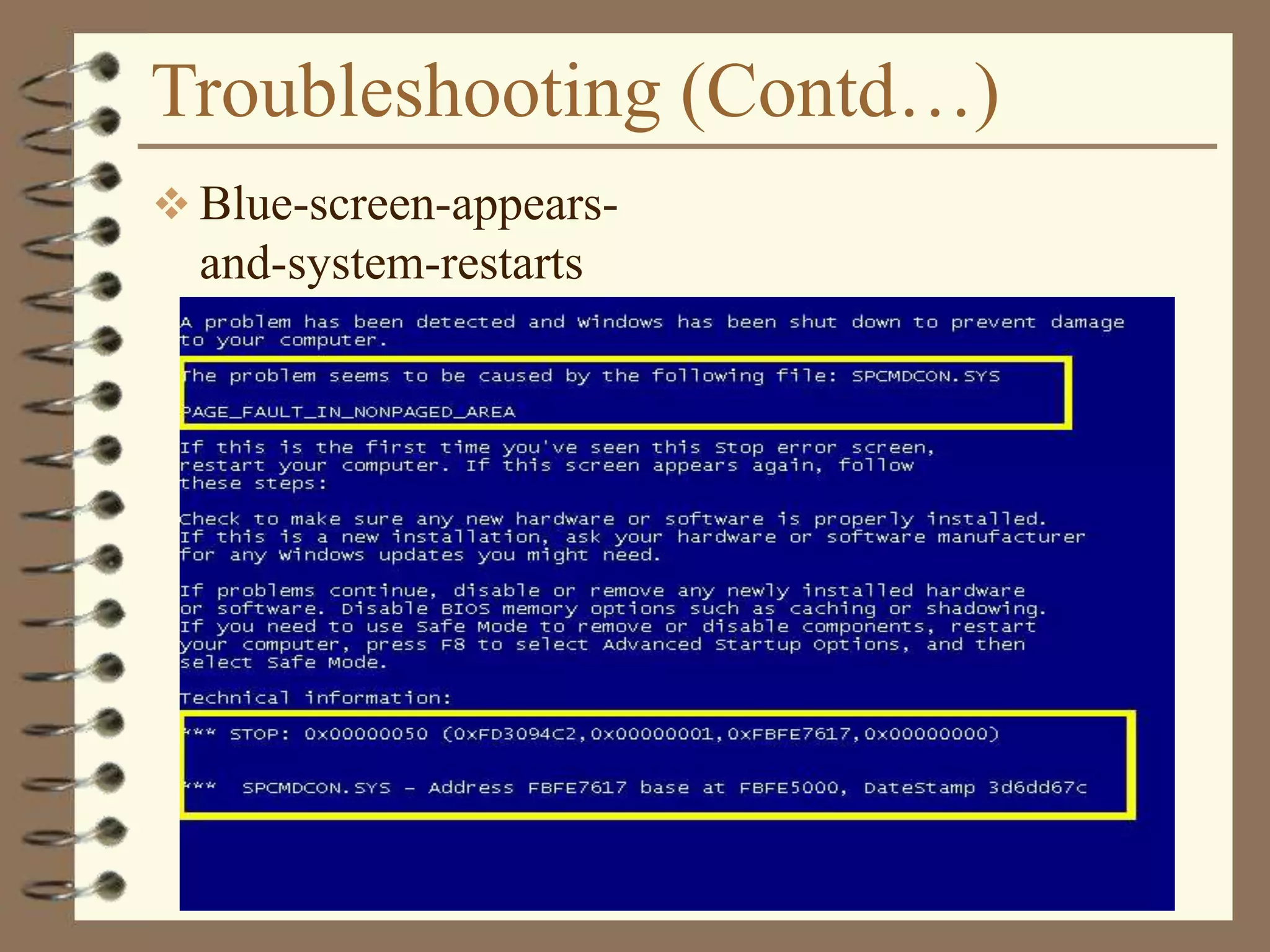
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to digital computers, outlining their key components, including hardware, software, and data storage. It explains the concept of digitization and binary representation, and details the functionality of input, output, and processing devices. It also covers various storage media, such as magnetic disks and optical discs, highlighting their characteristics and uses.