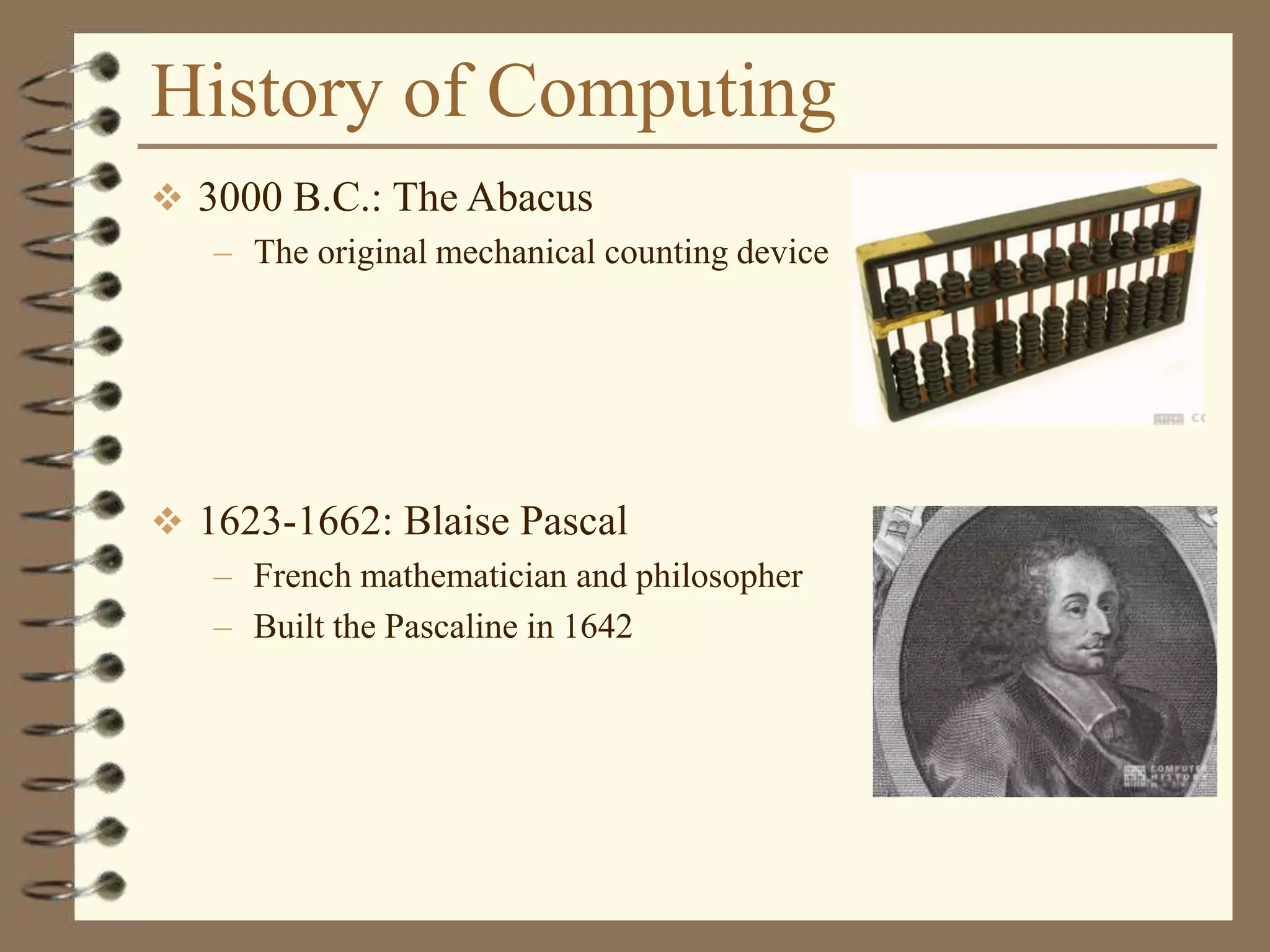
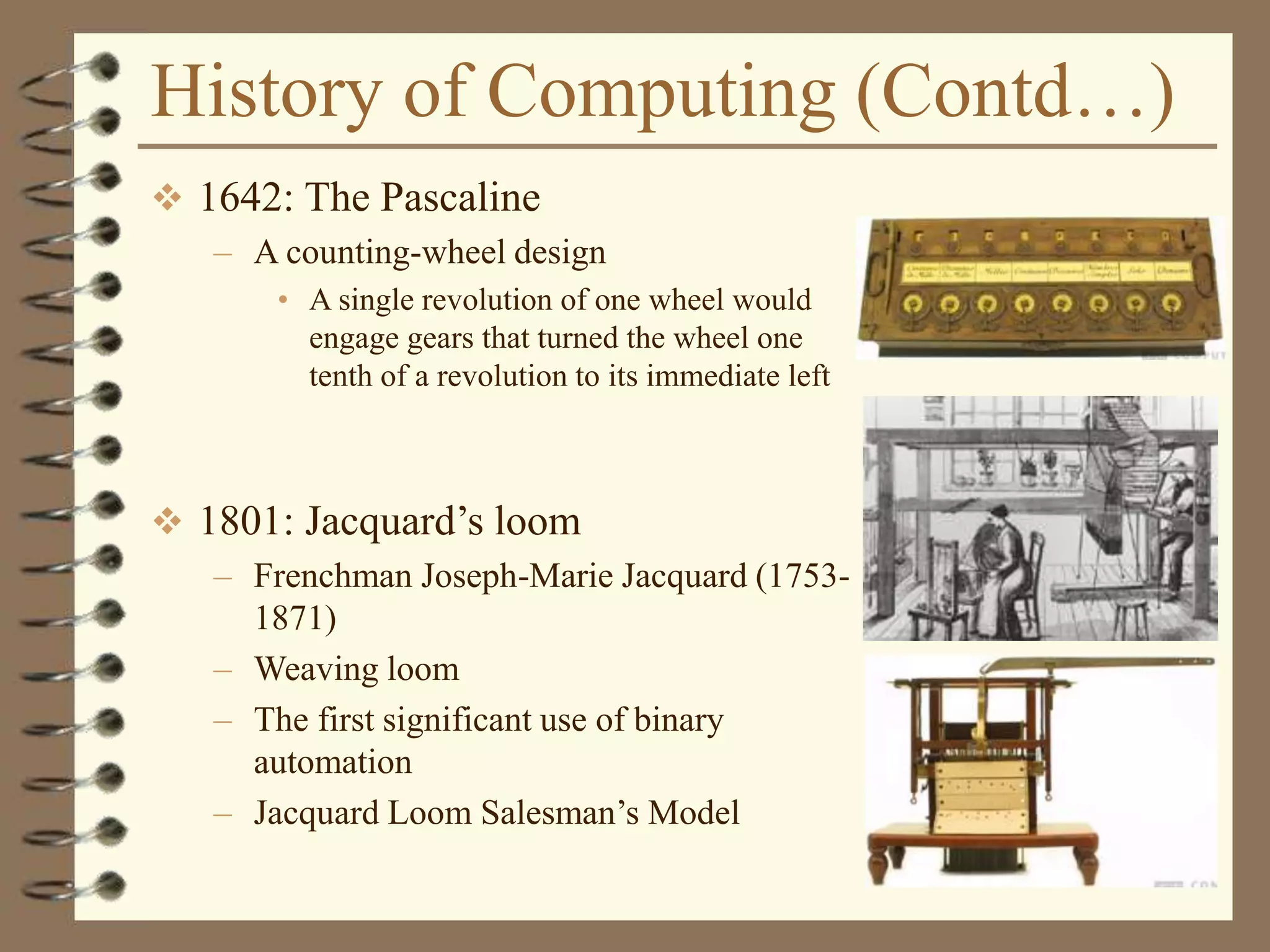
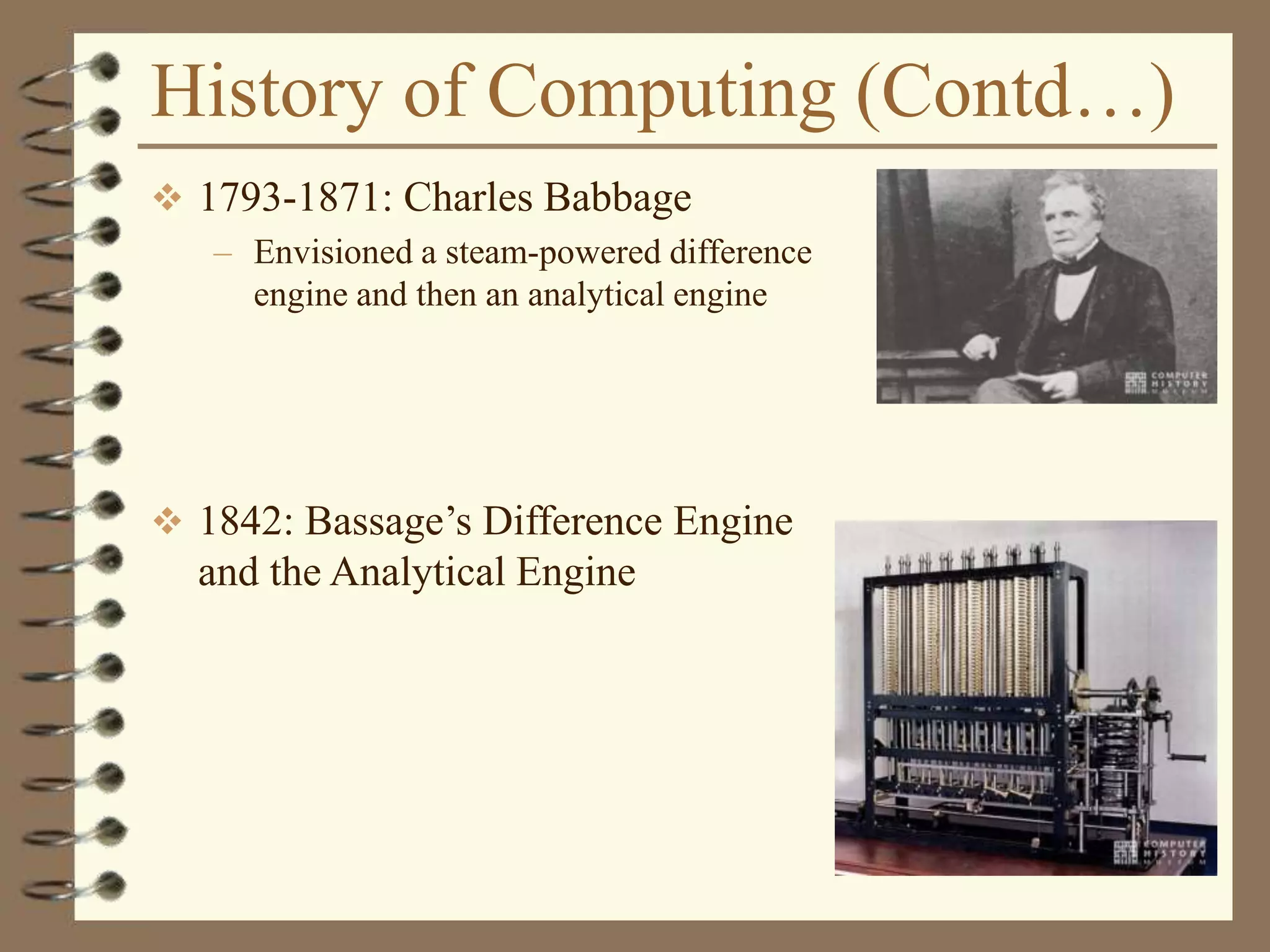
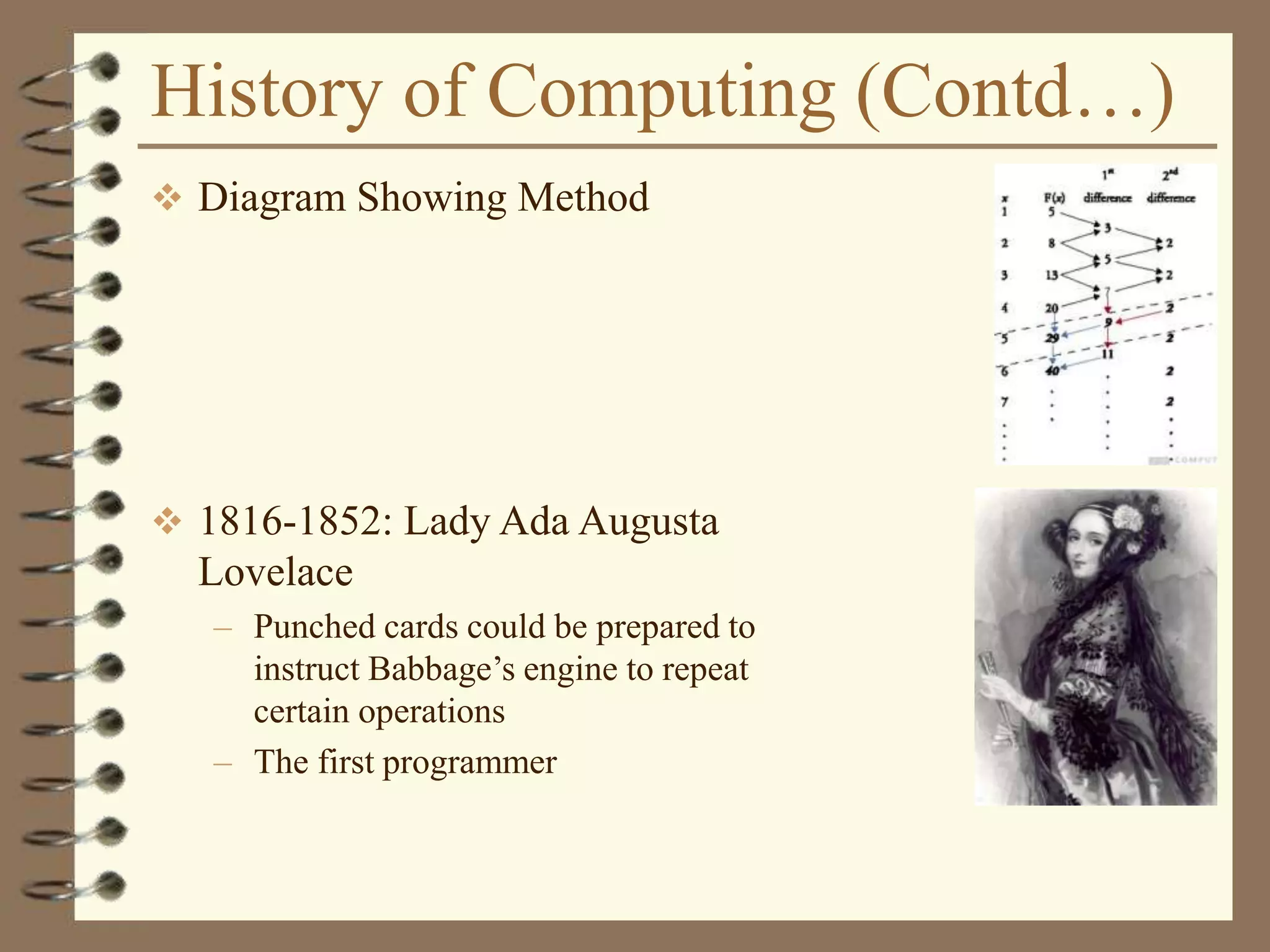
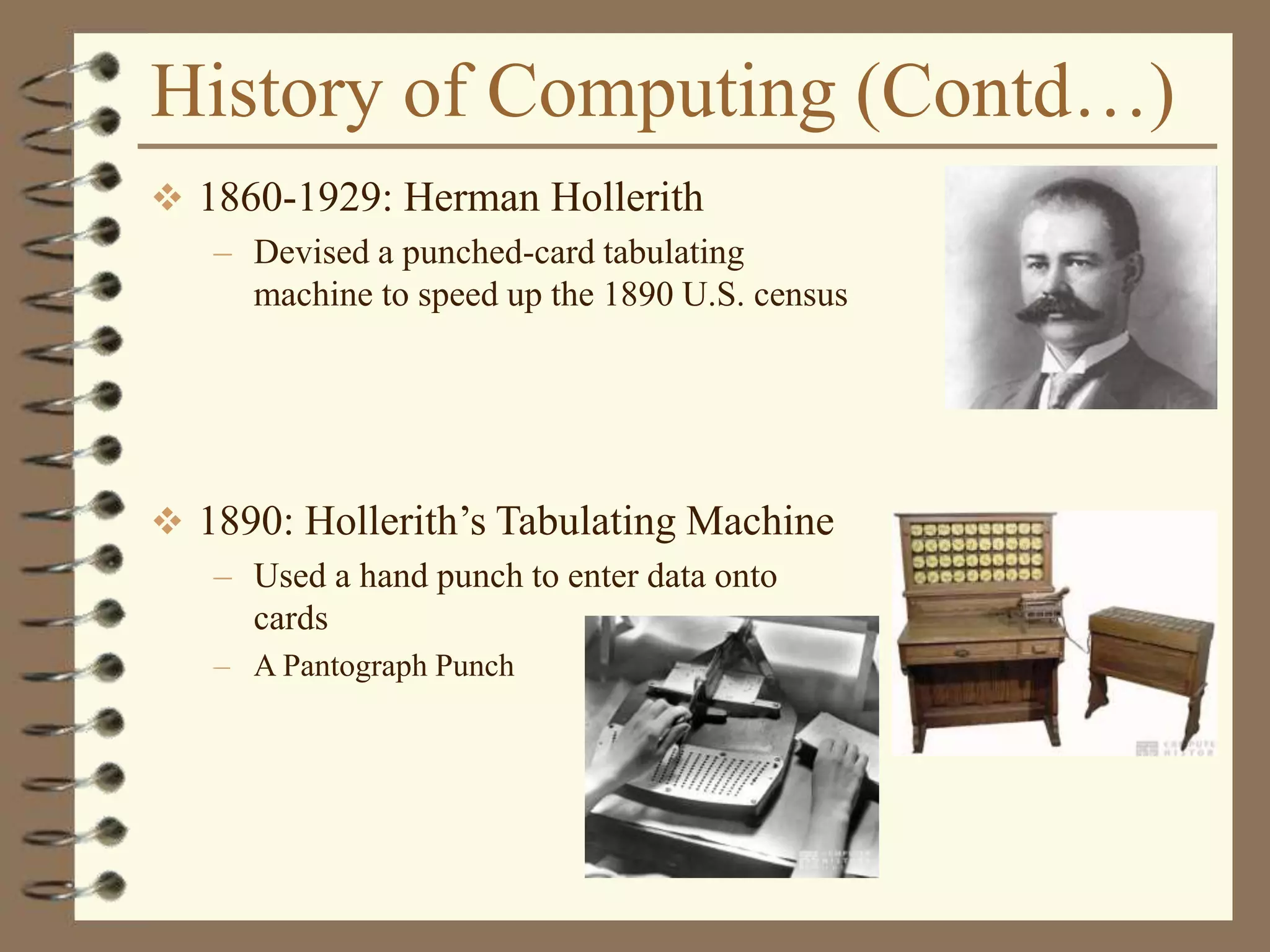
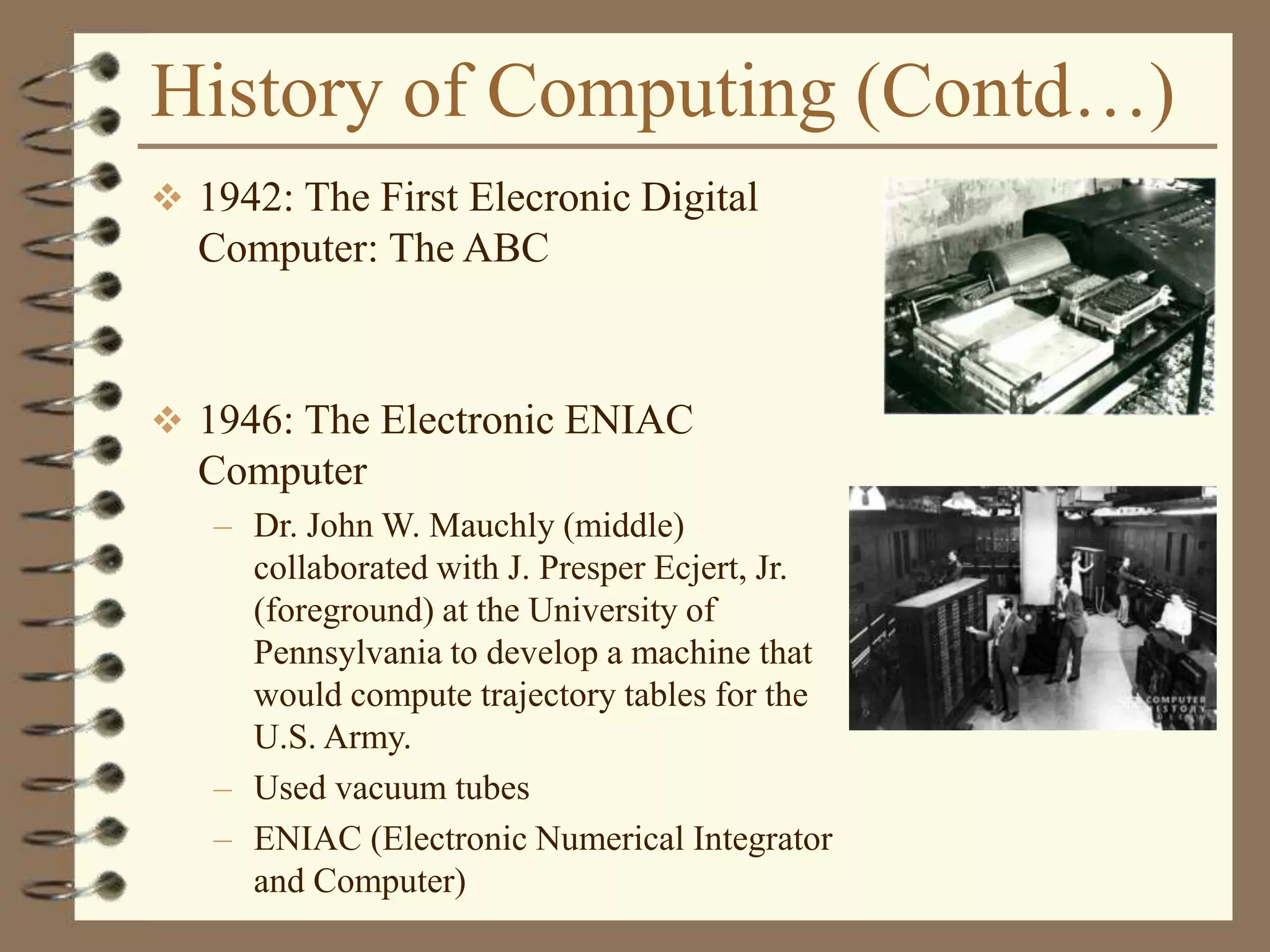
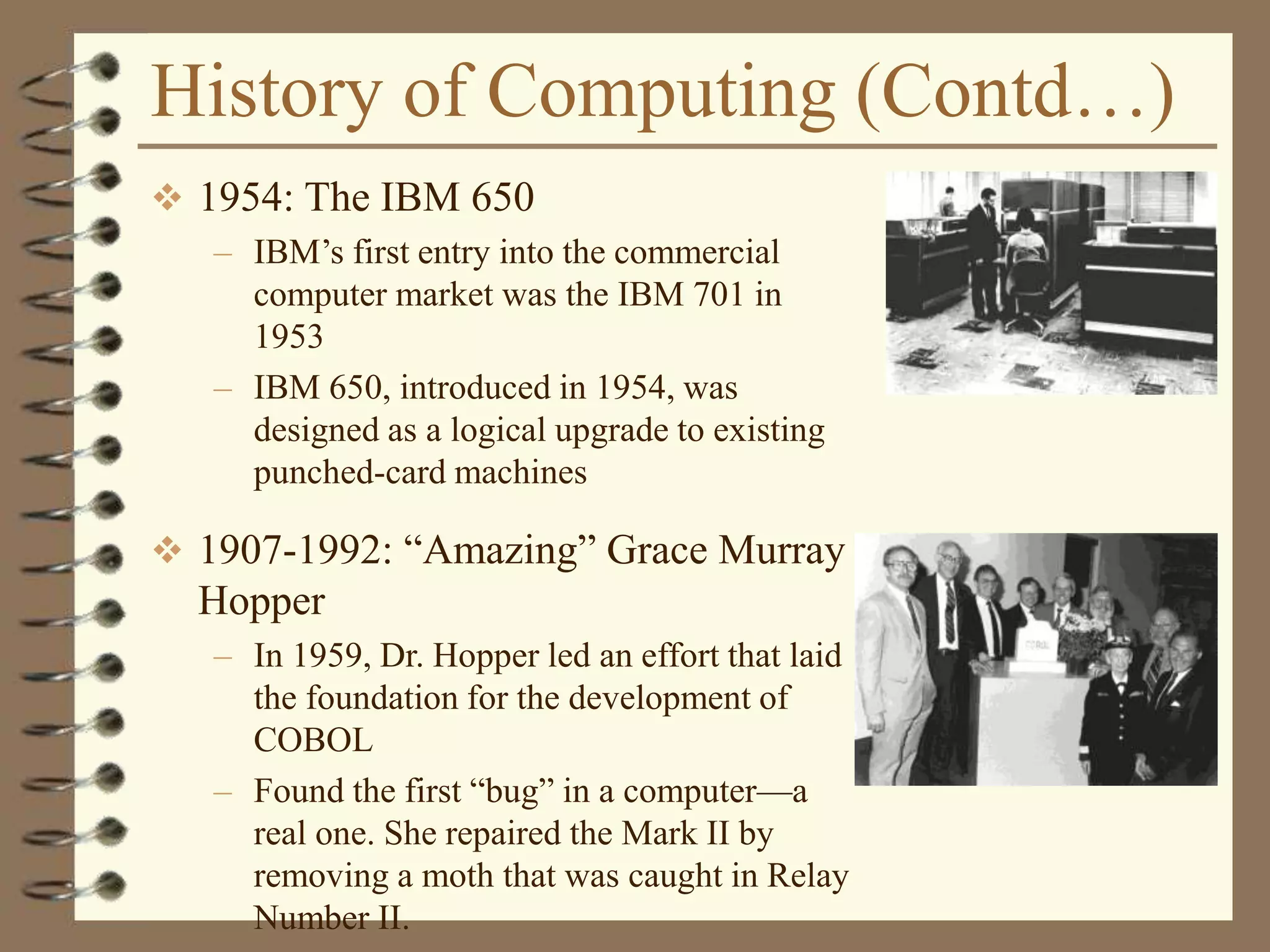
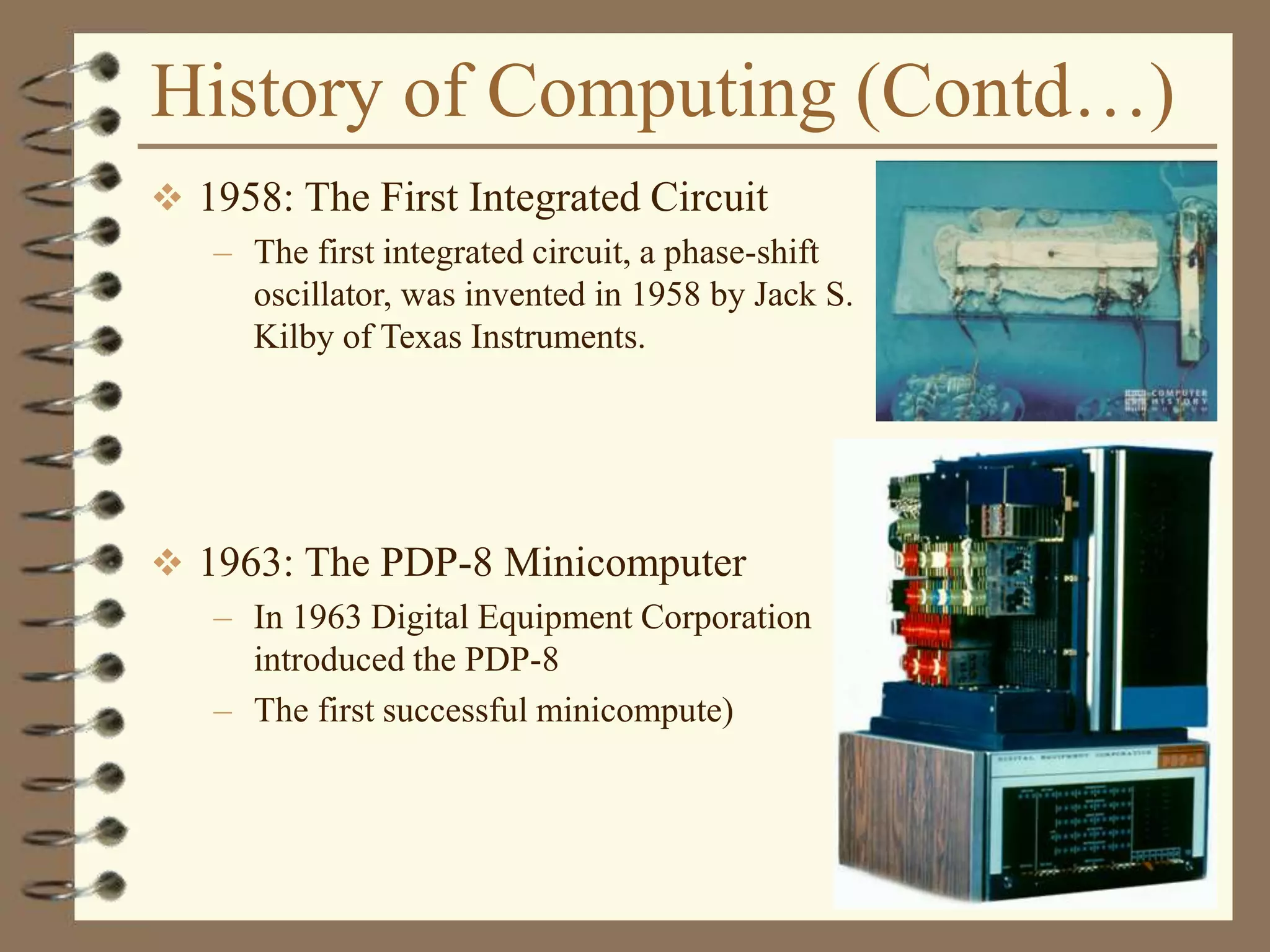
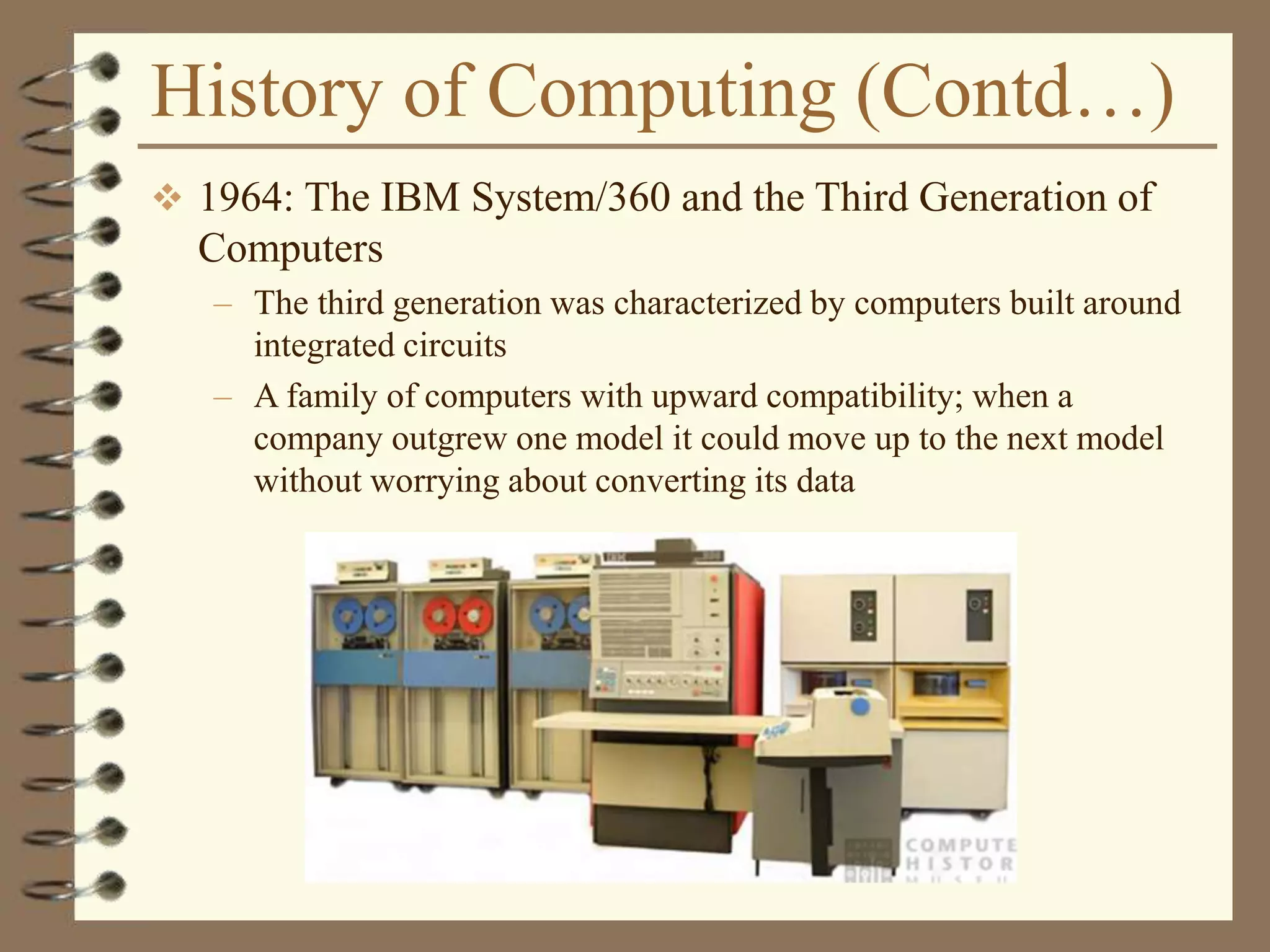
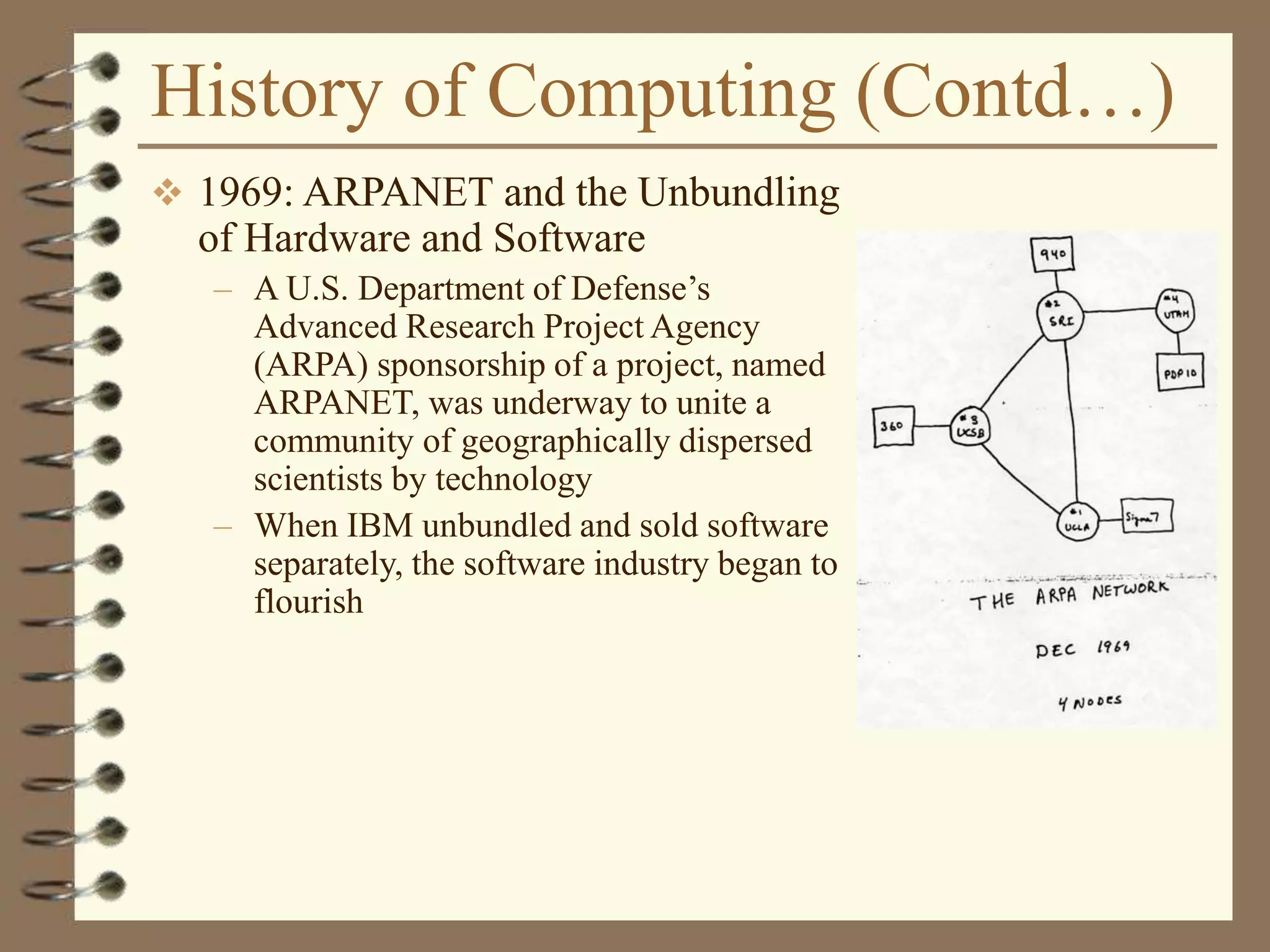
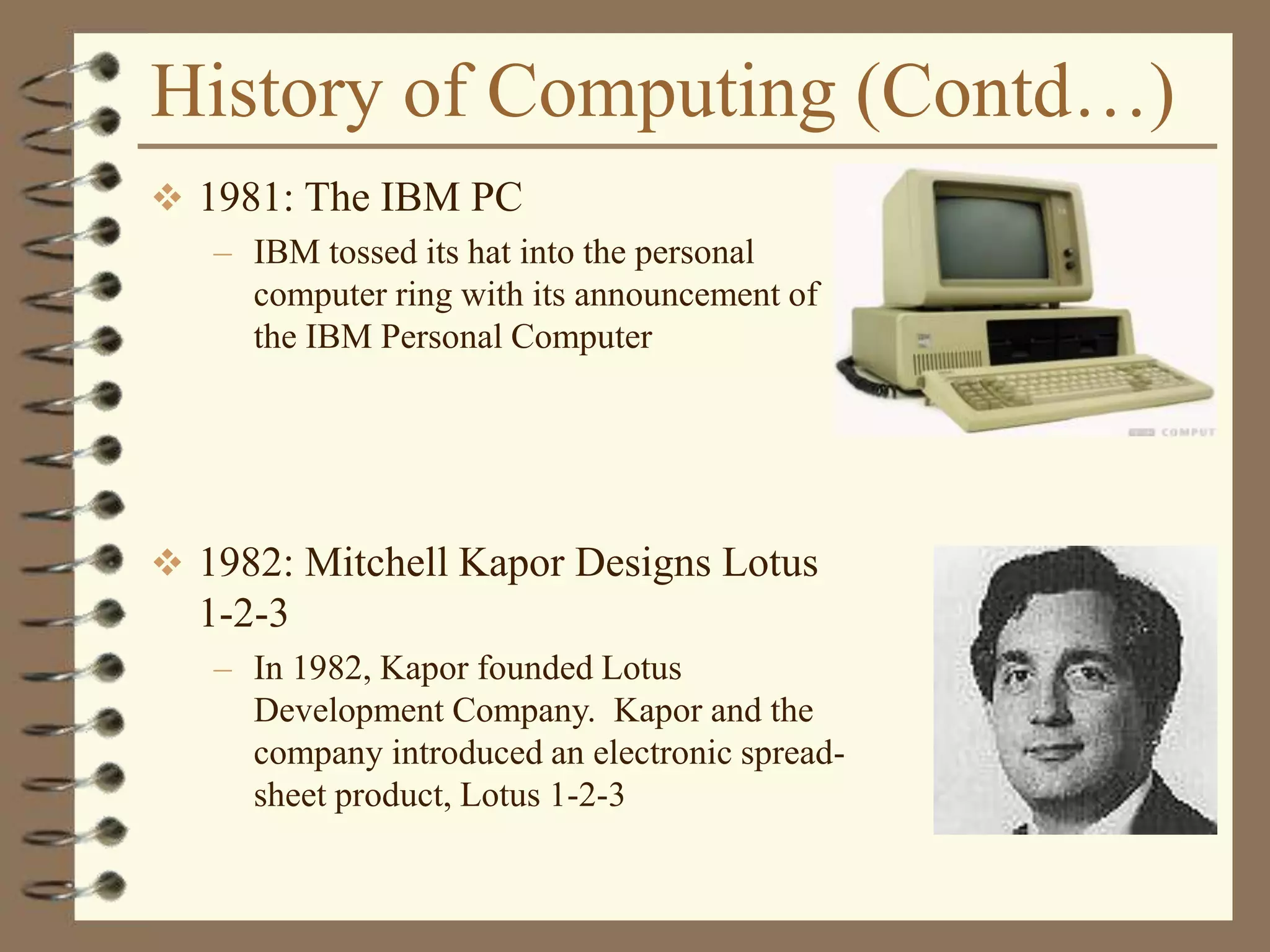
The document provides an introduction to computers including their components and functions. It discusses the history of computing from the abacus in 3000 BC to modern computers. It describes the different types of computers including special purpose computers like microwaves and general purpose computers like microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes, and supercomputers. The document outlines the evolution of computing technology over time from mechanical to electronic devices and the development of important innovations like integrated circuits, graphical user interfaces, the internet, and handheld devices.