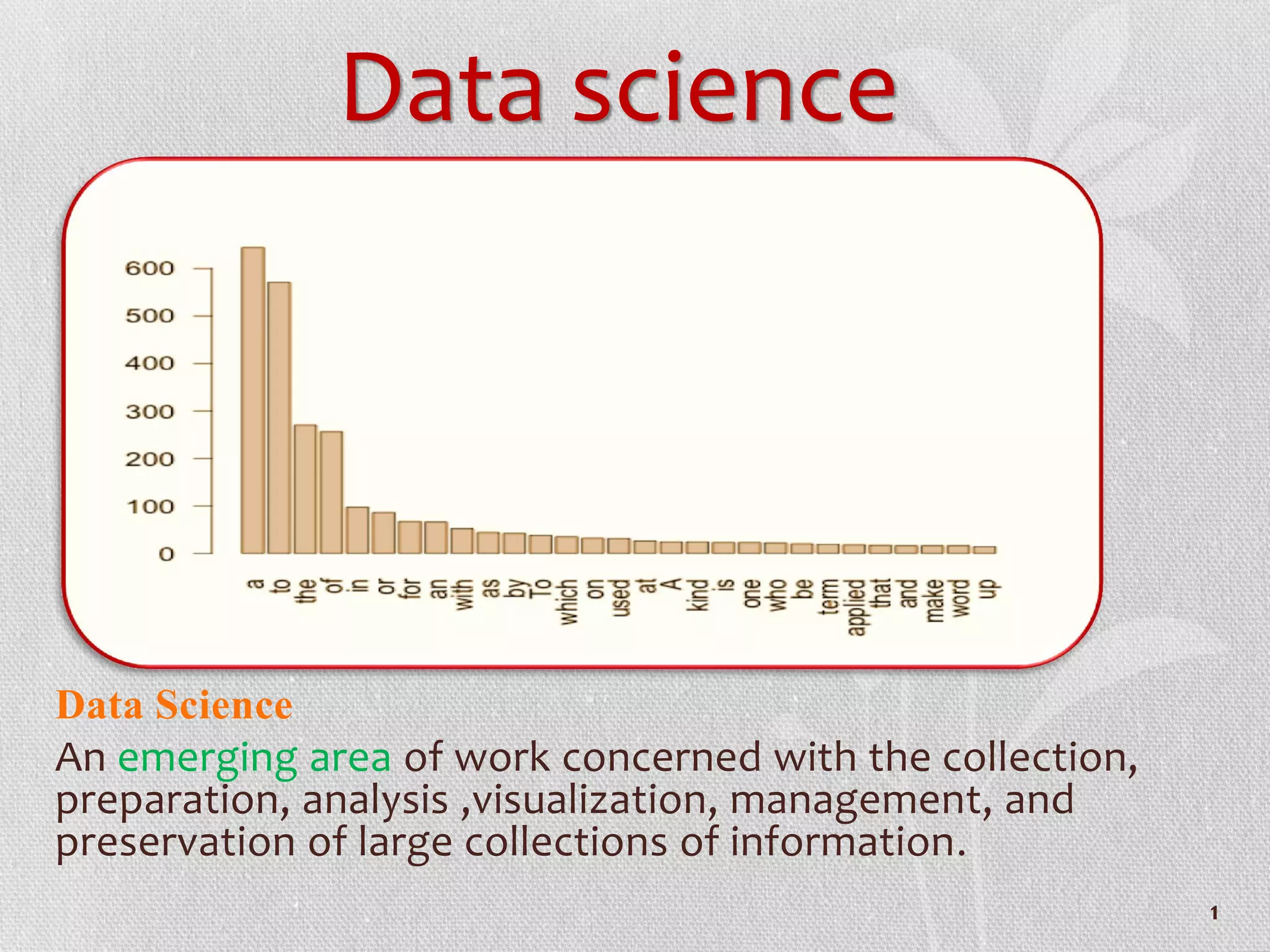
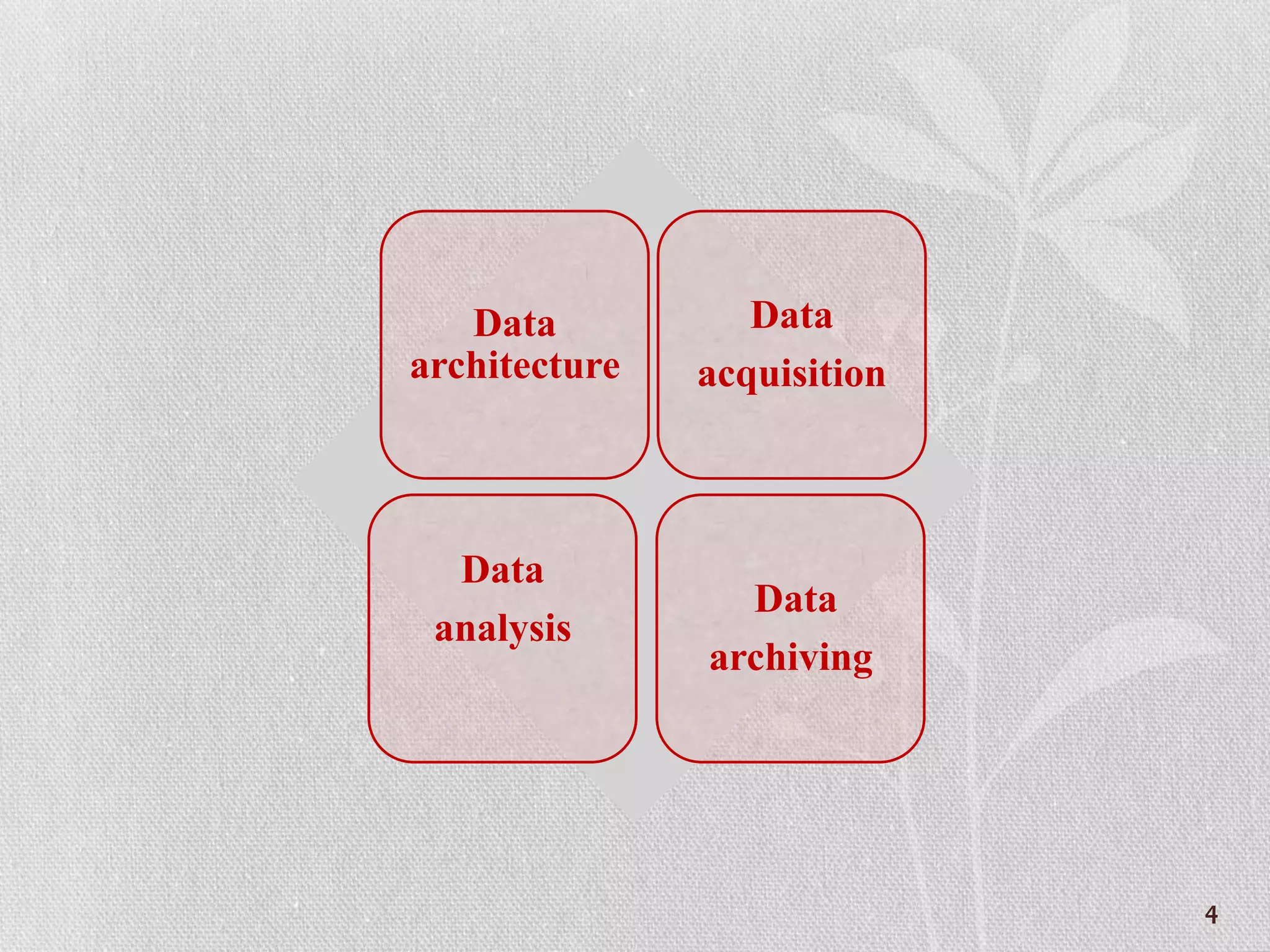
Data science is an emerging area concerned with collecting, preparing, analyzing, visualizing, managing, and preserving large collections of information. It involves data architecture, acquisition, analysis, archiving, and working with data architects, acquisition tools, analysis and visualization techniques, metadata, and ensuring quality and ethical use of data. R is an open source program for data manipulation, calculation, graphical display, and storage that is extensible and teaches skills applicable to other programs, though it is command line oriented and not always good at feedback.