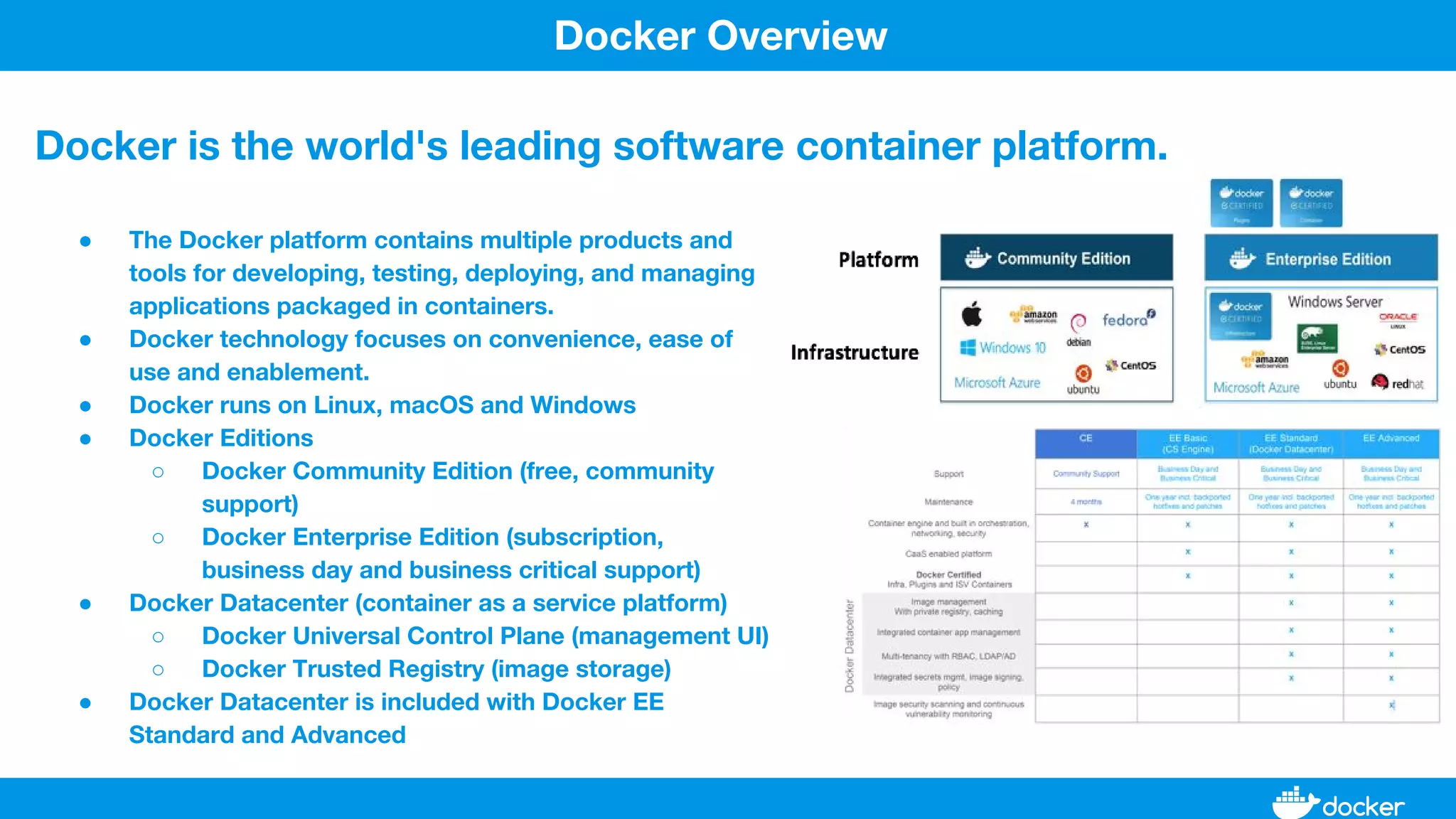
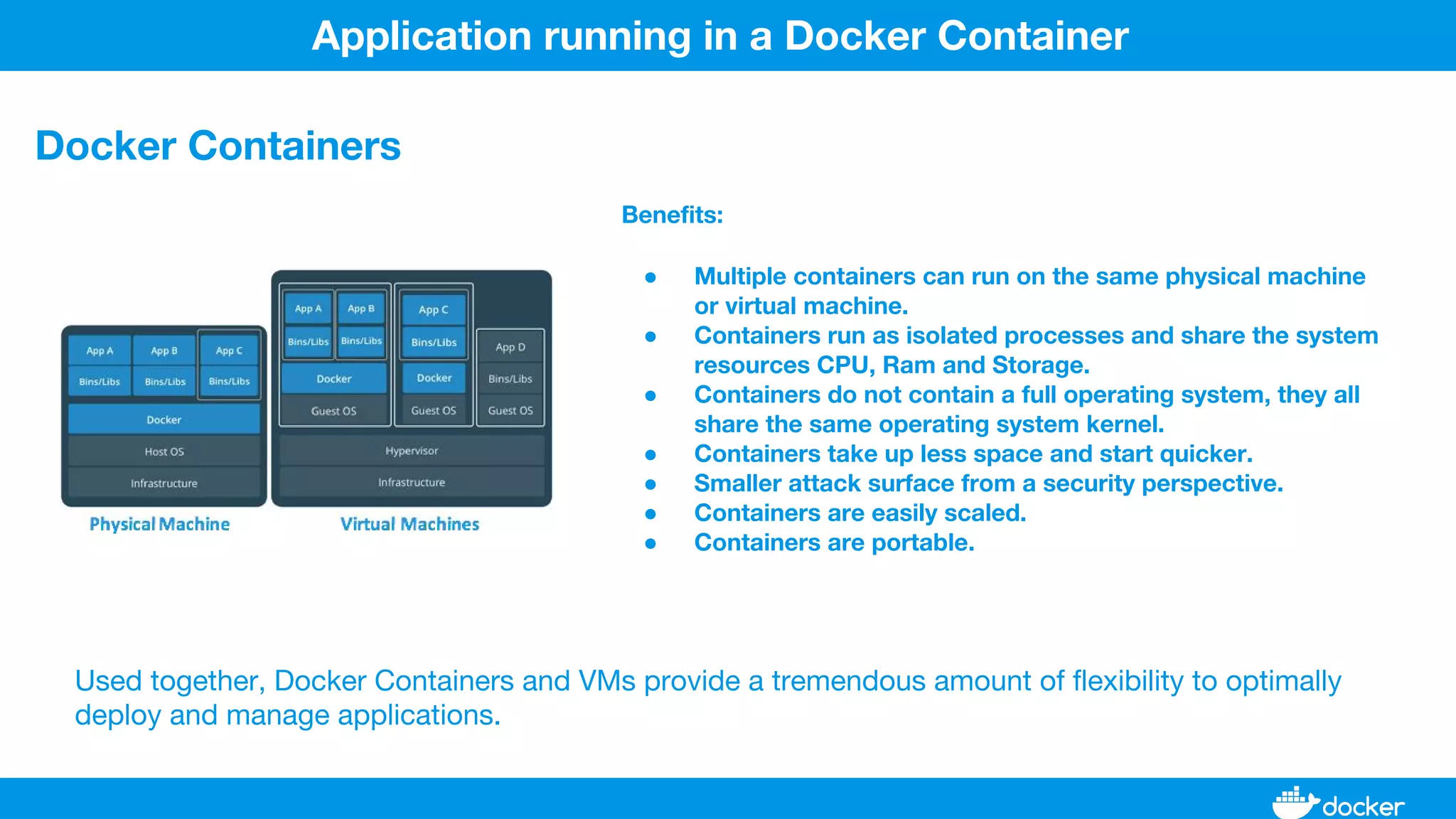
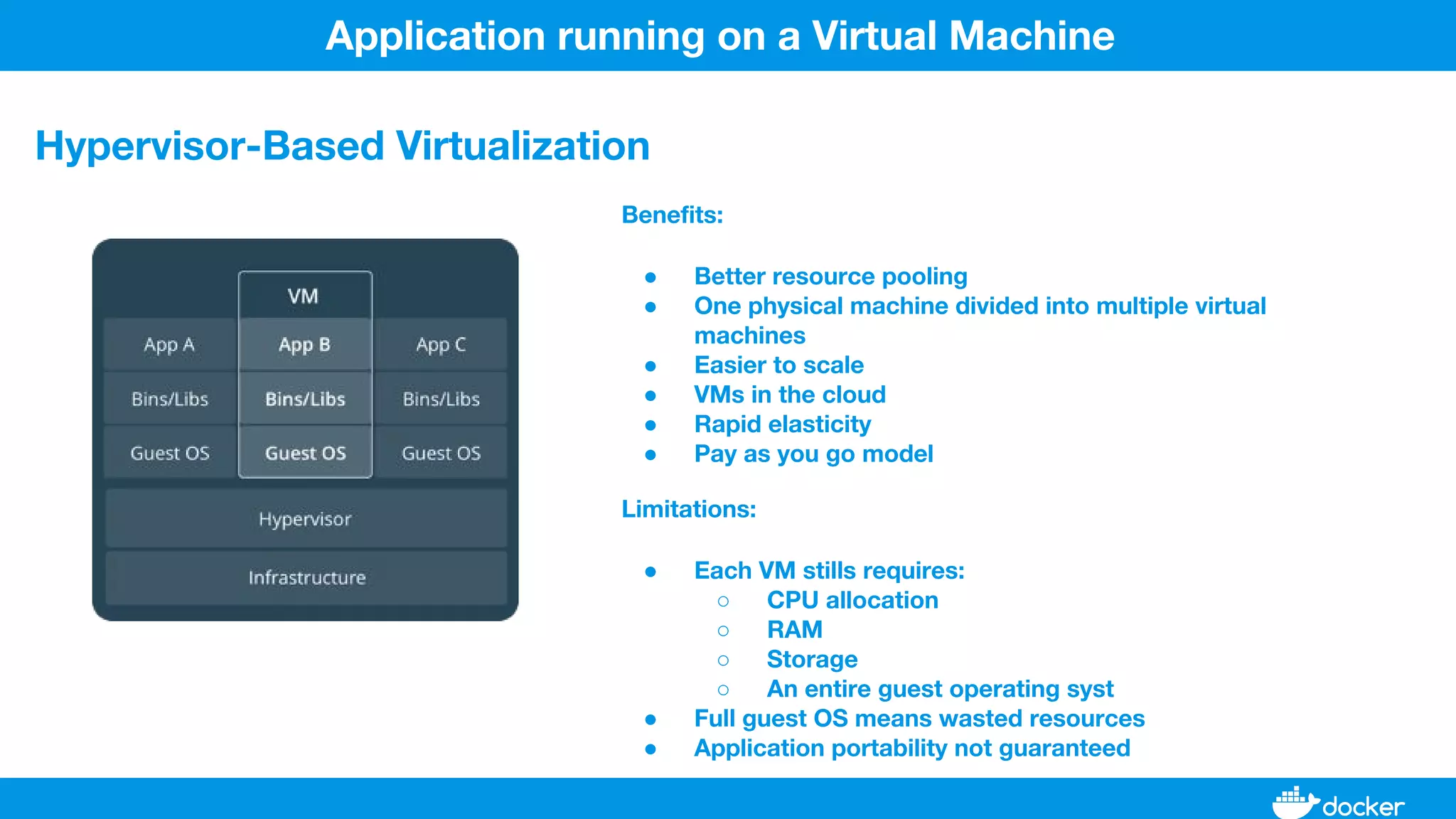
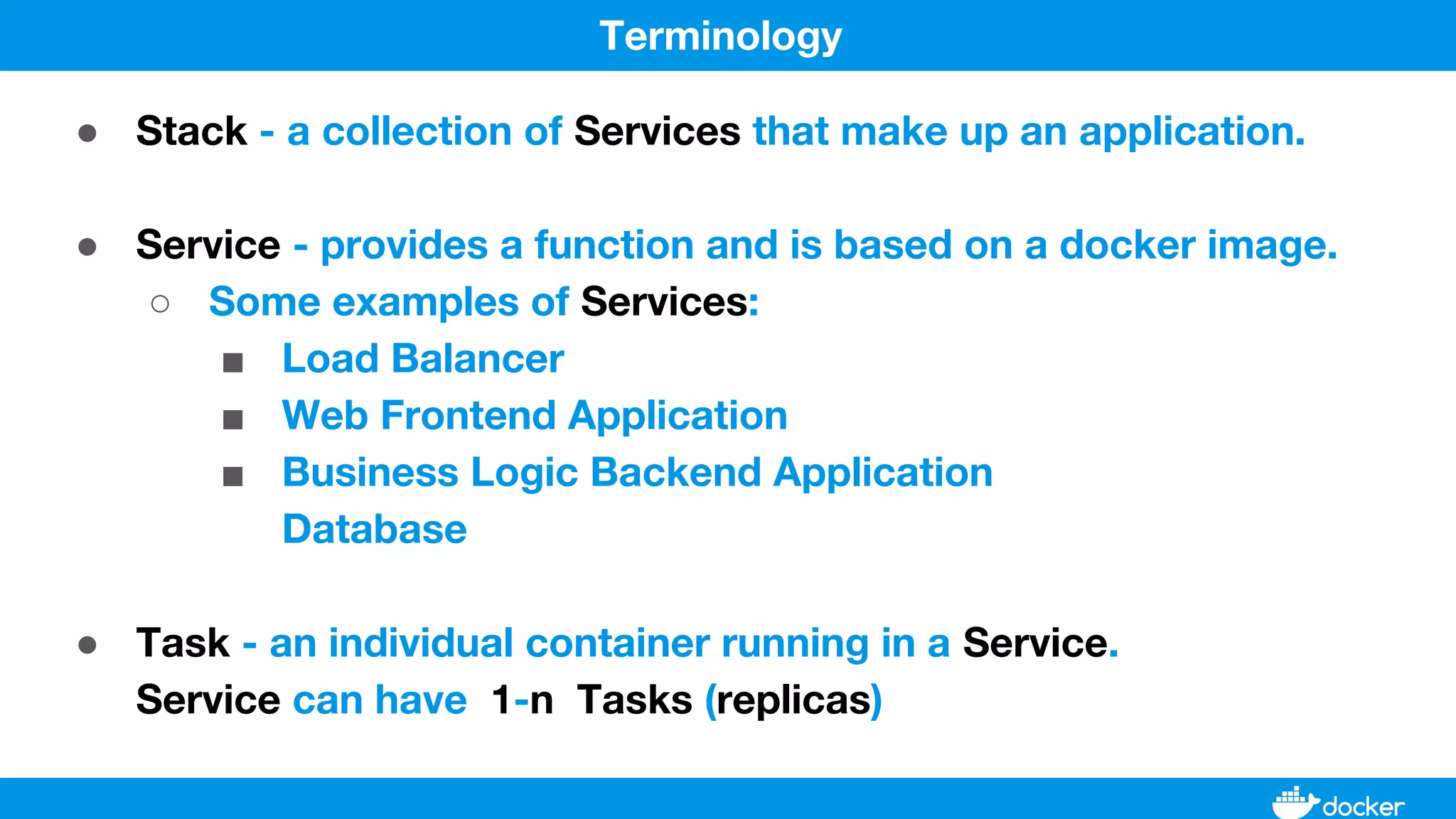
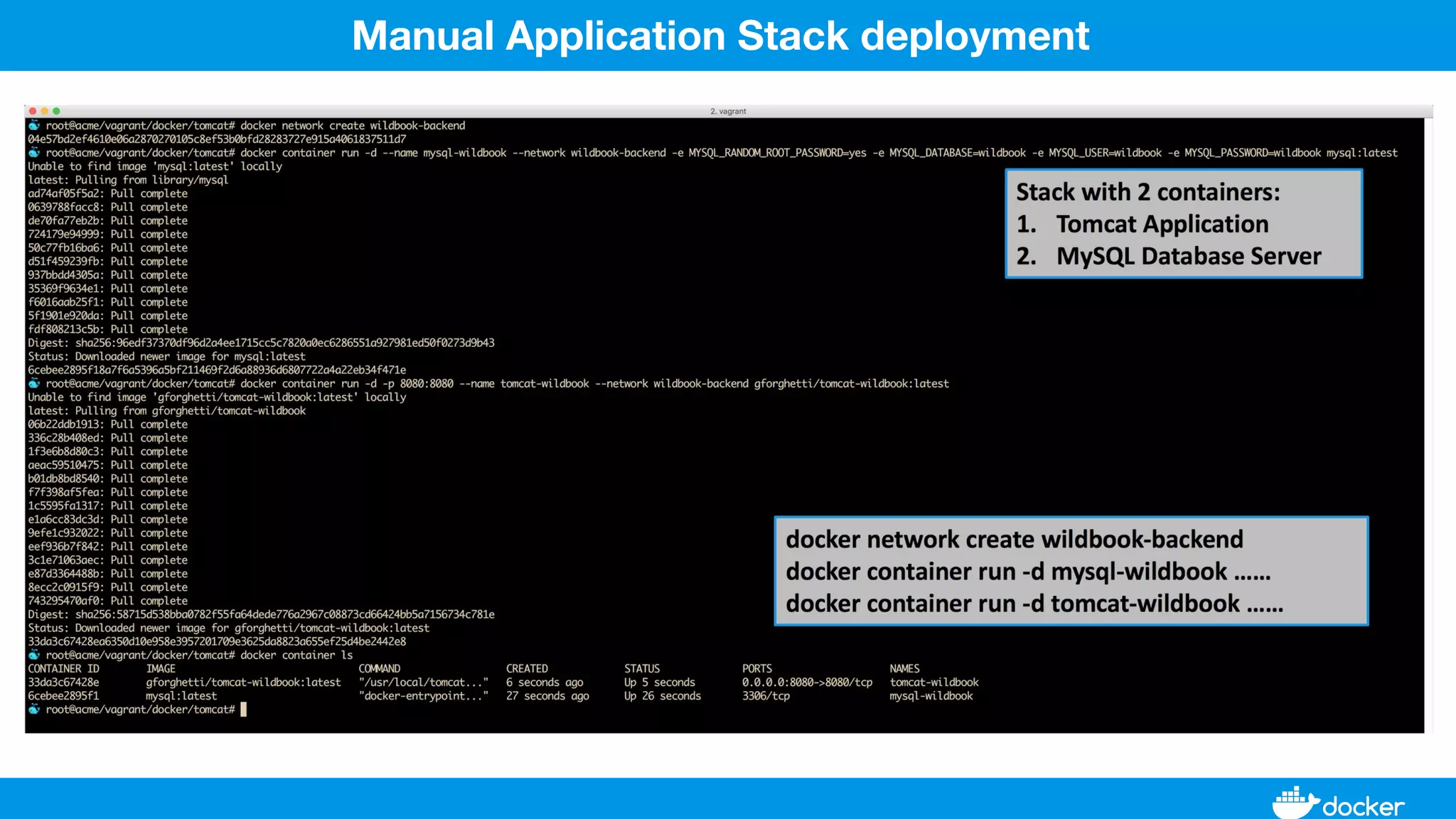
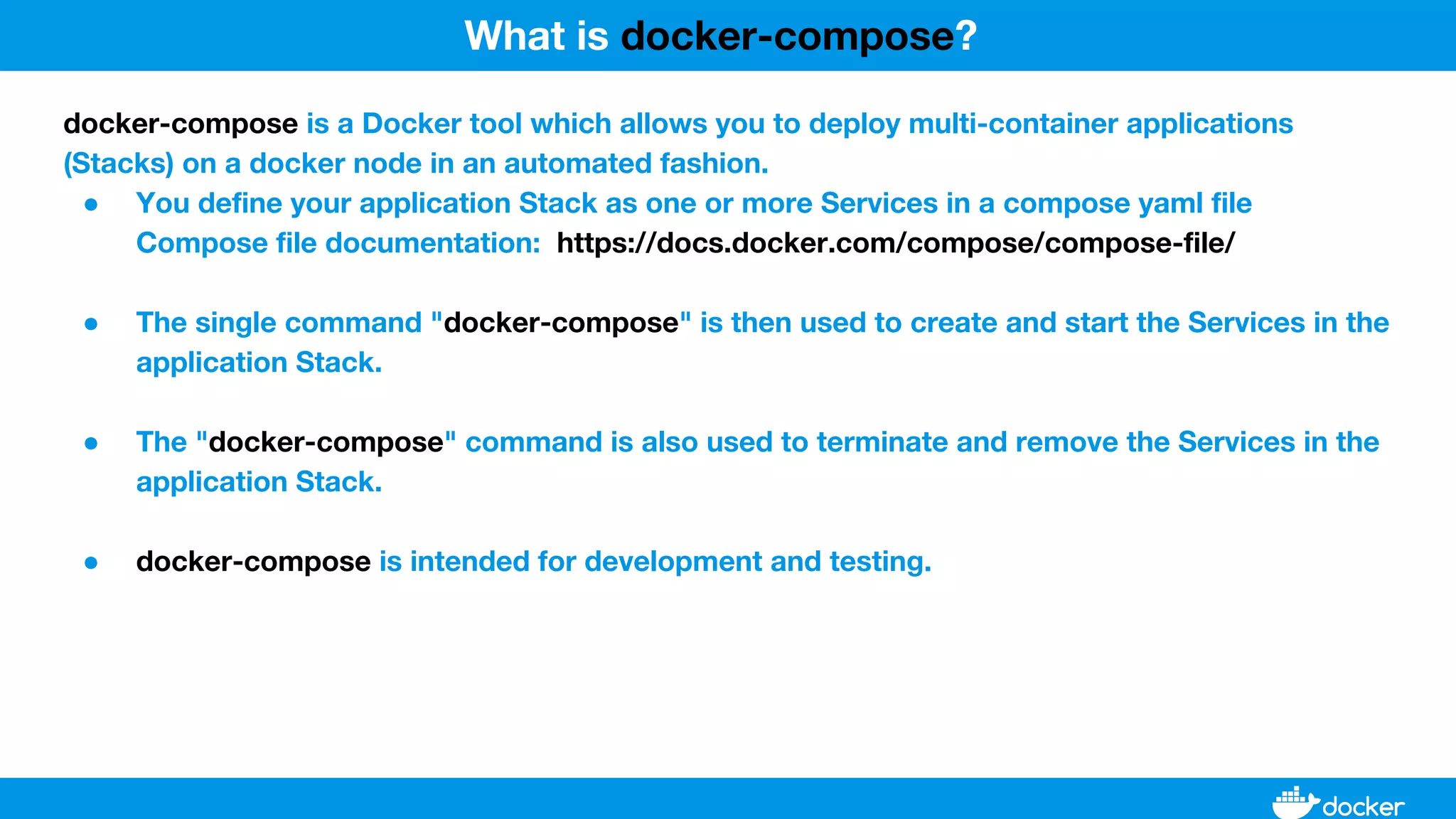
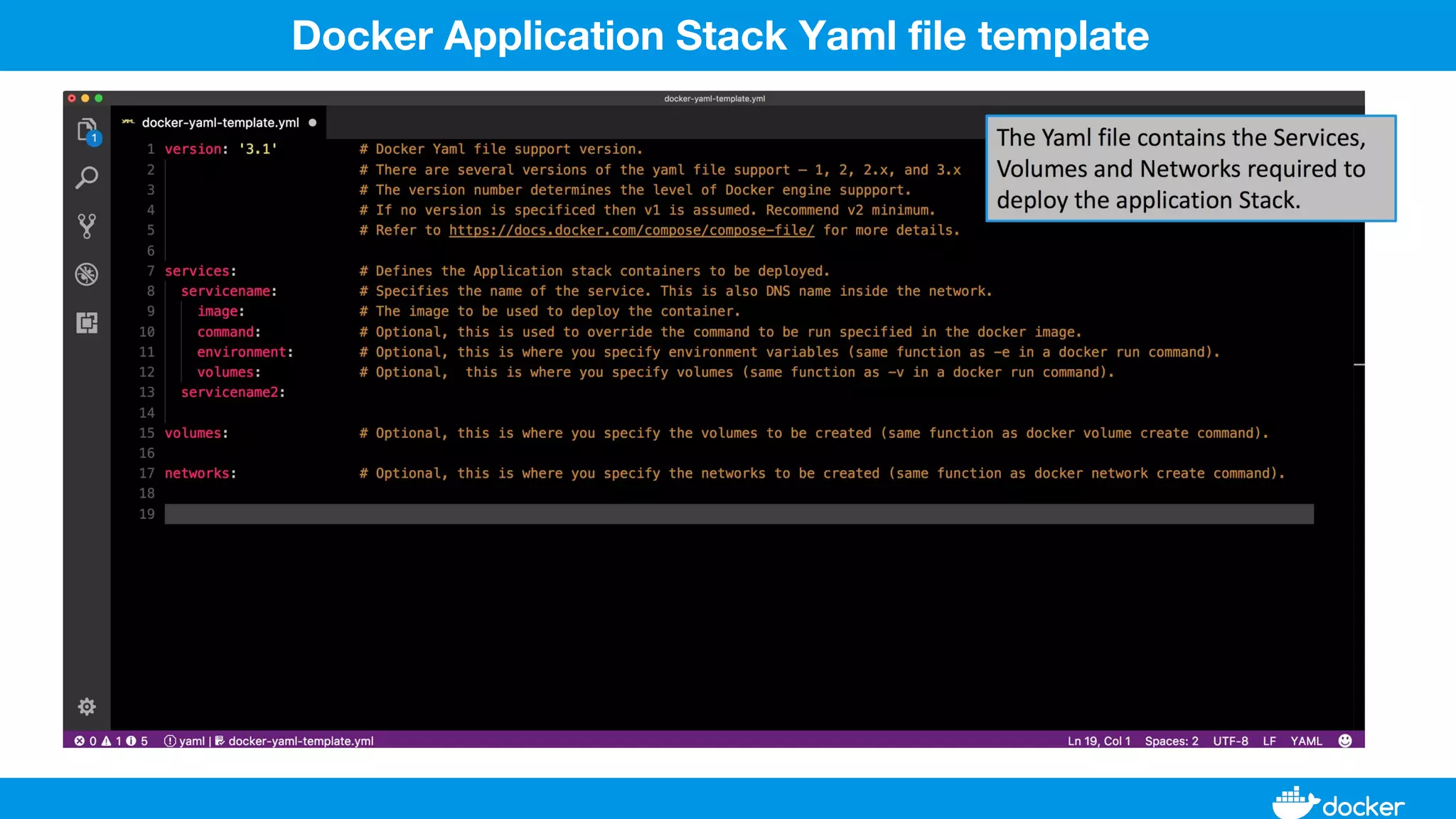
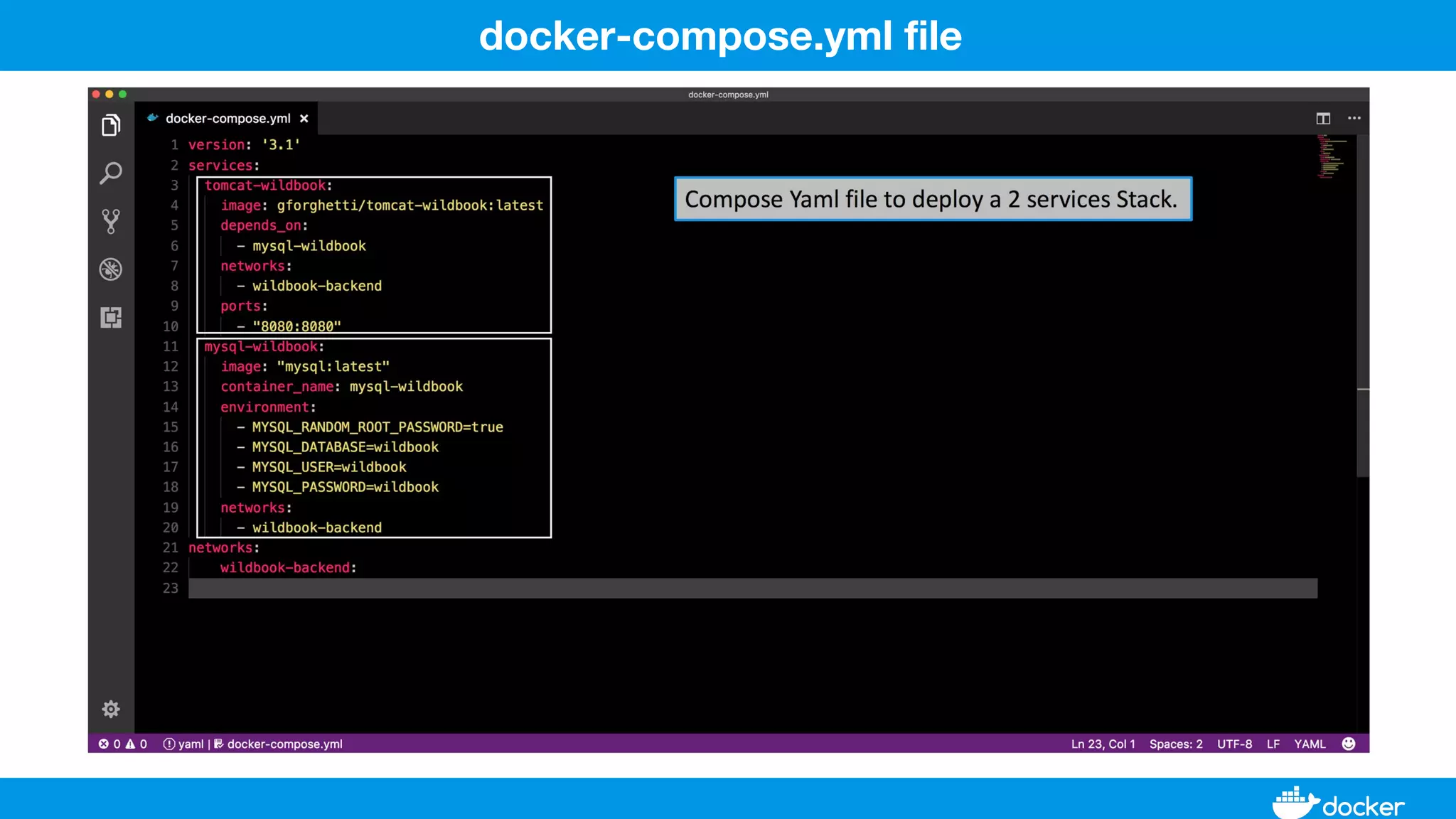
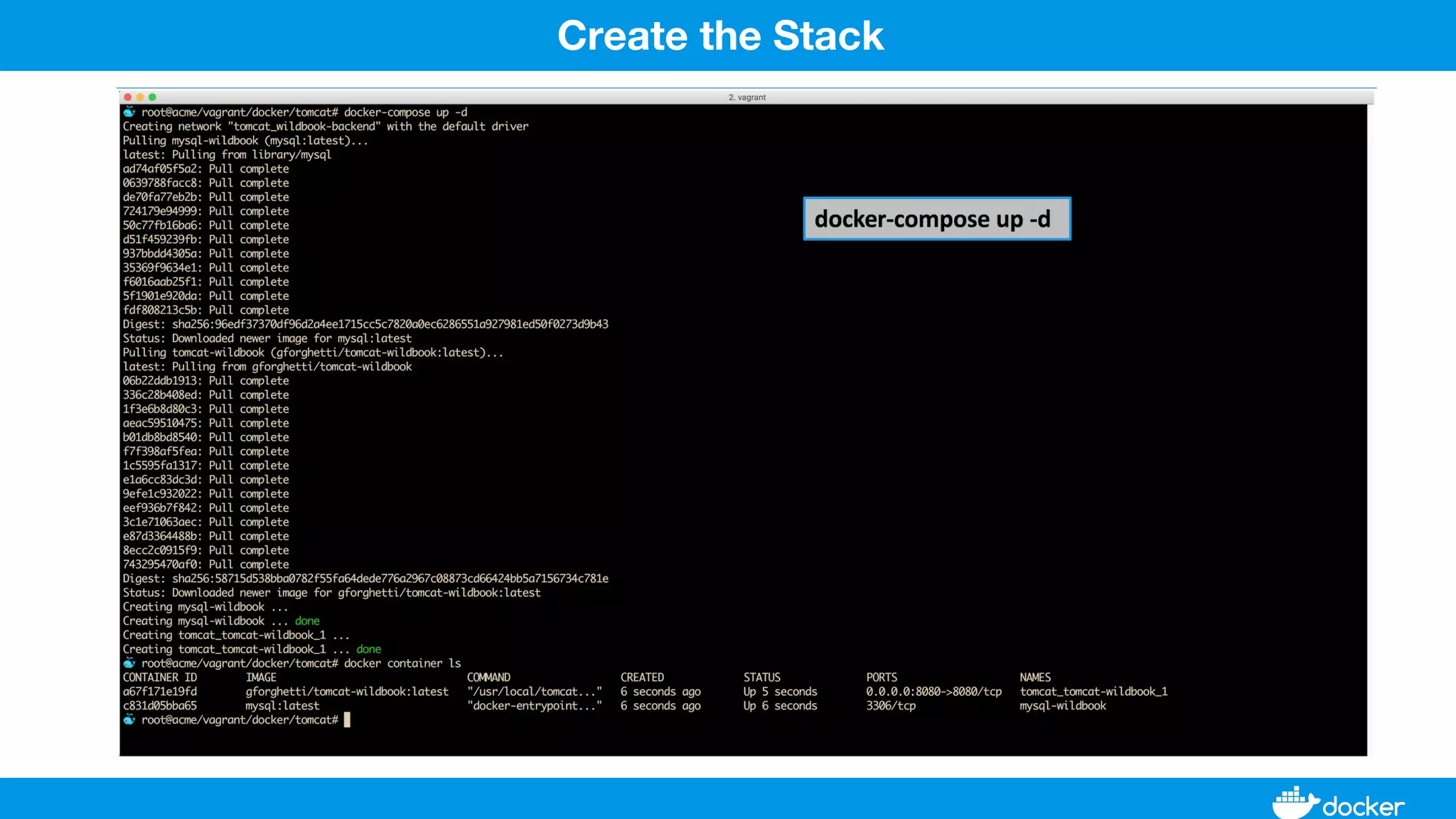
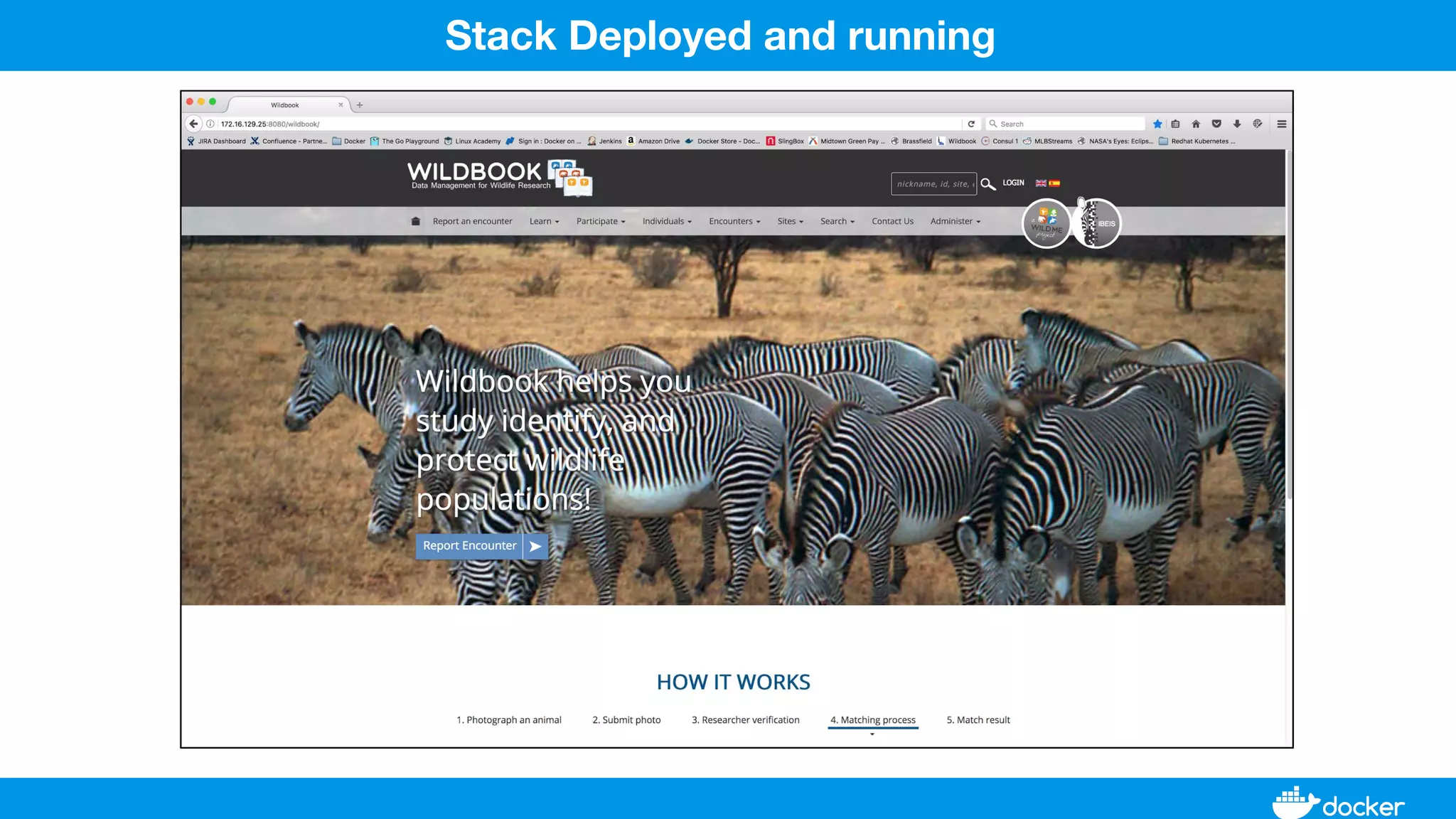
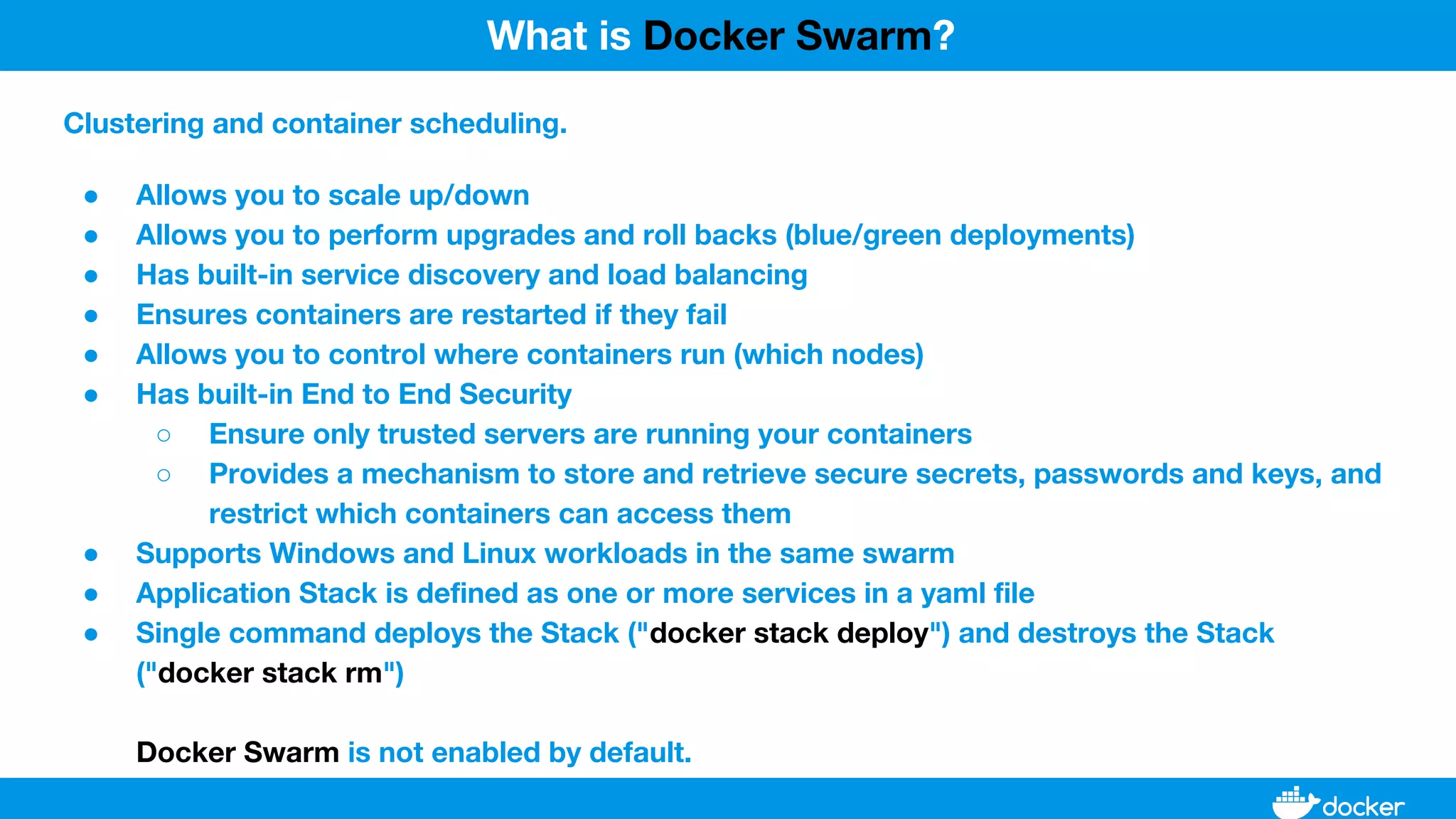
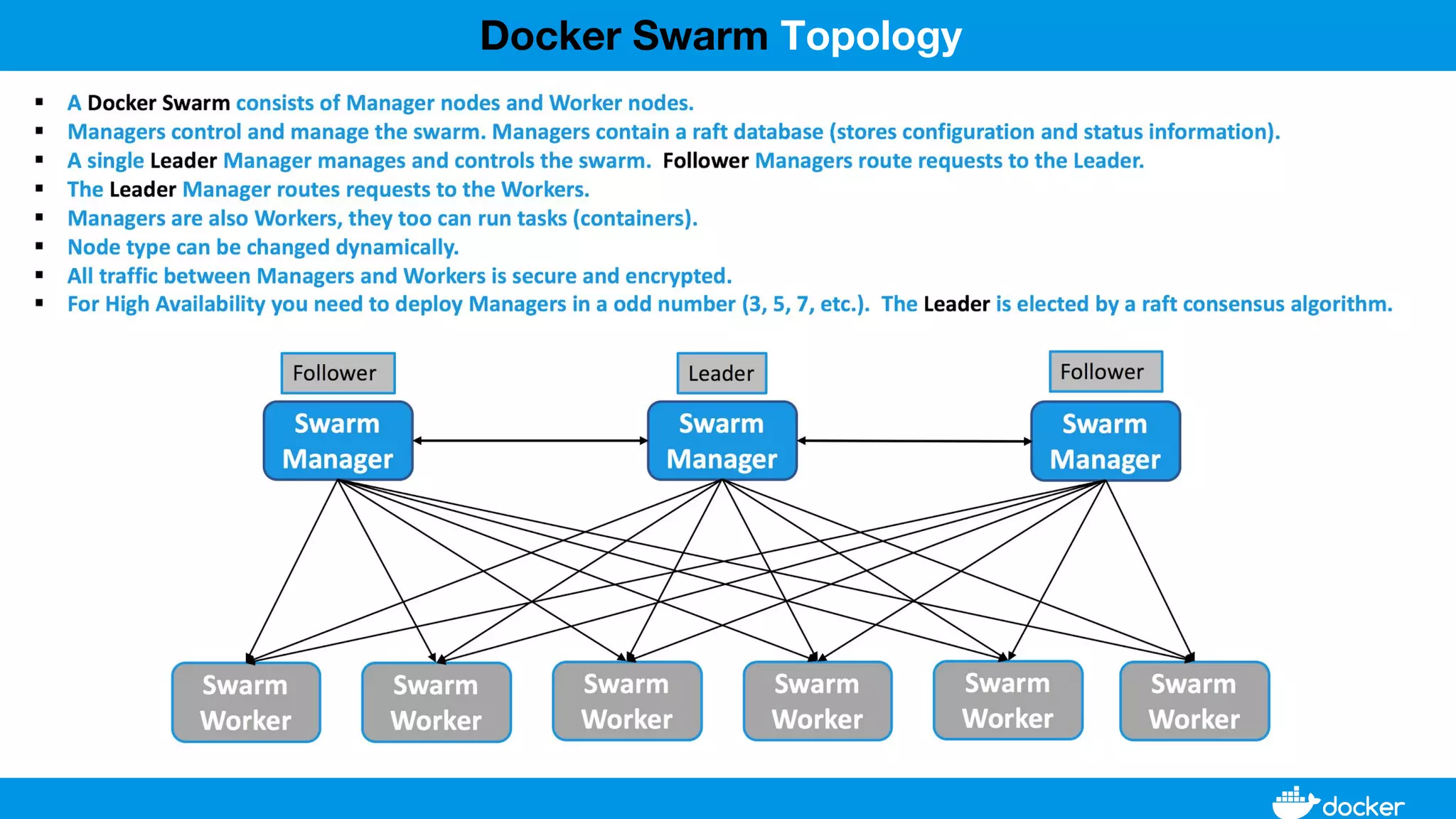
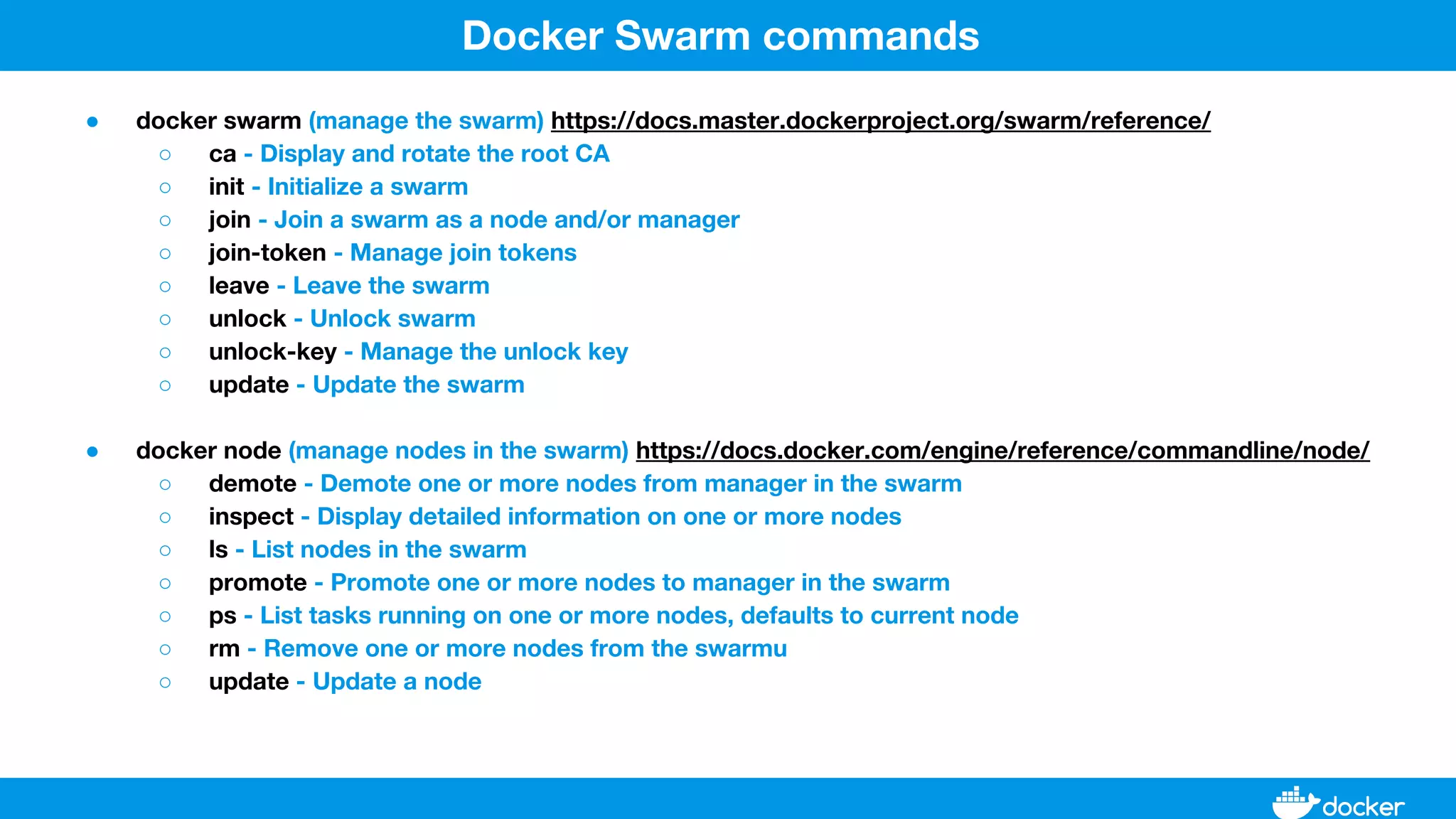
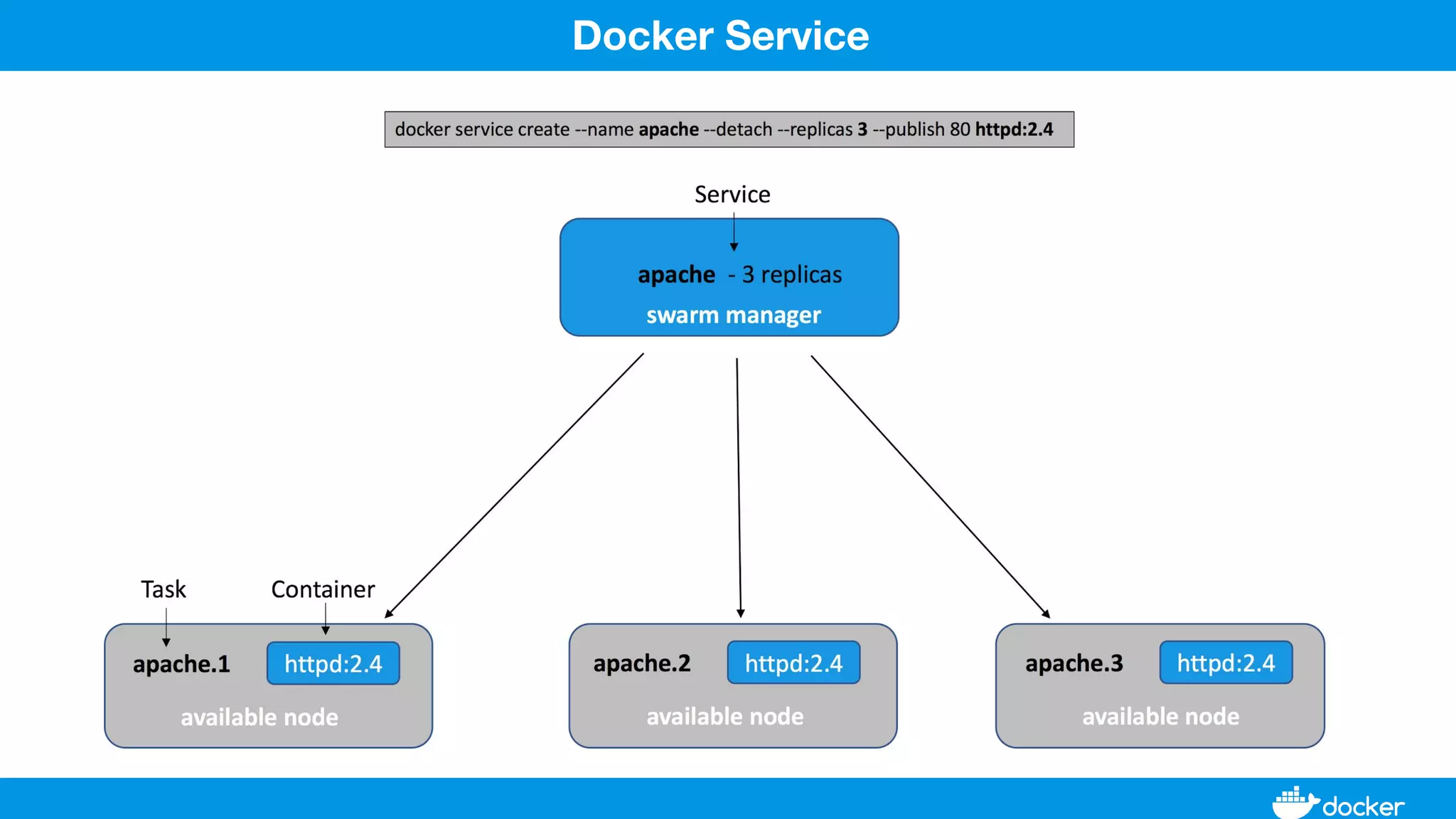
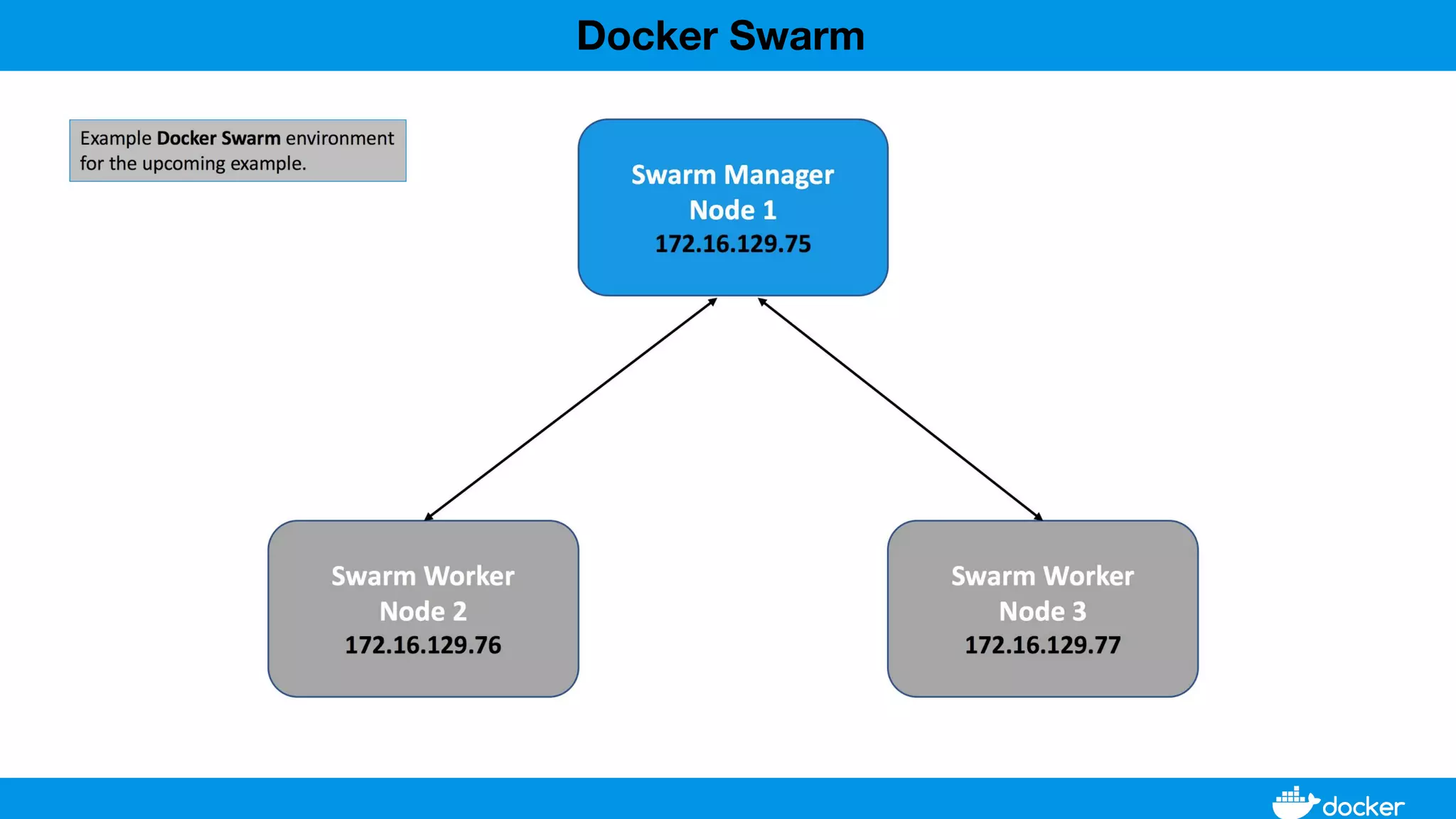
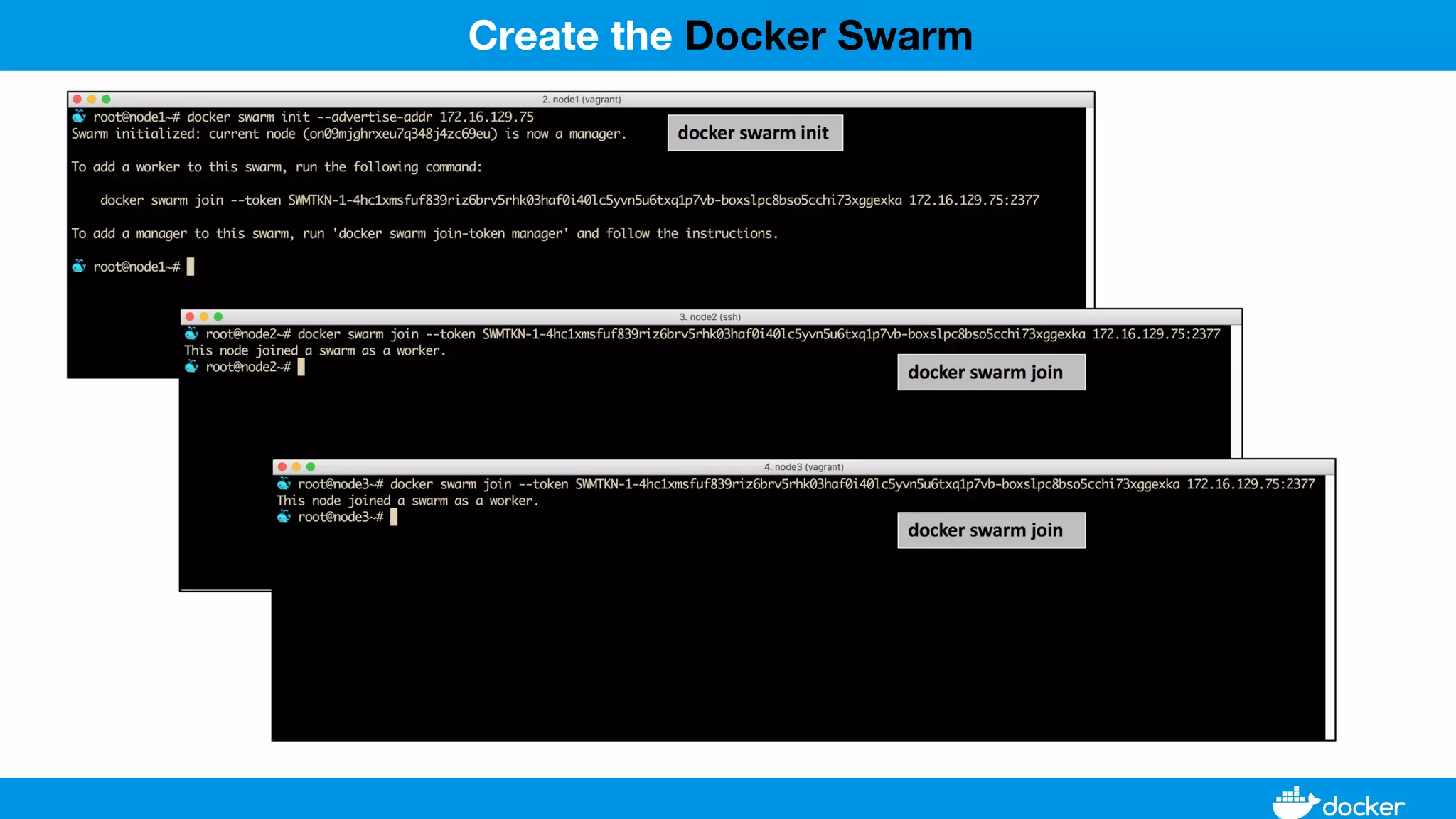
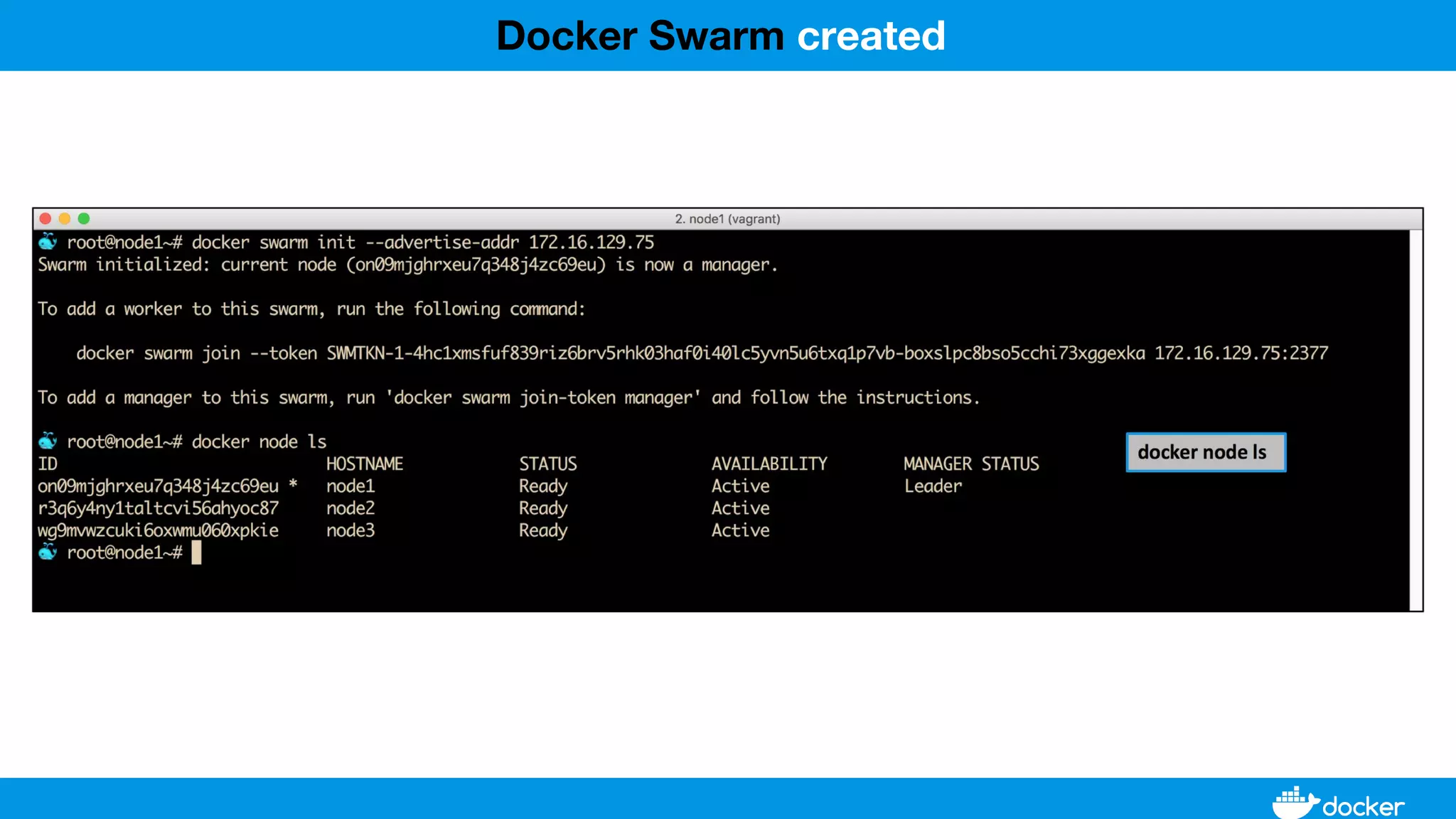
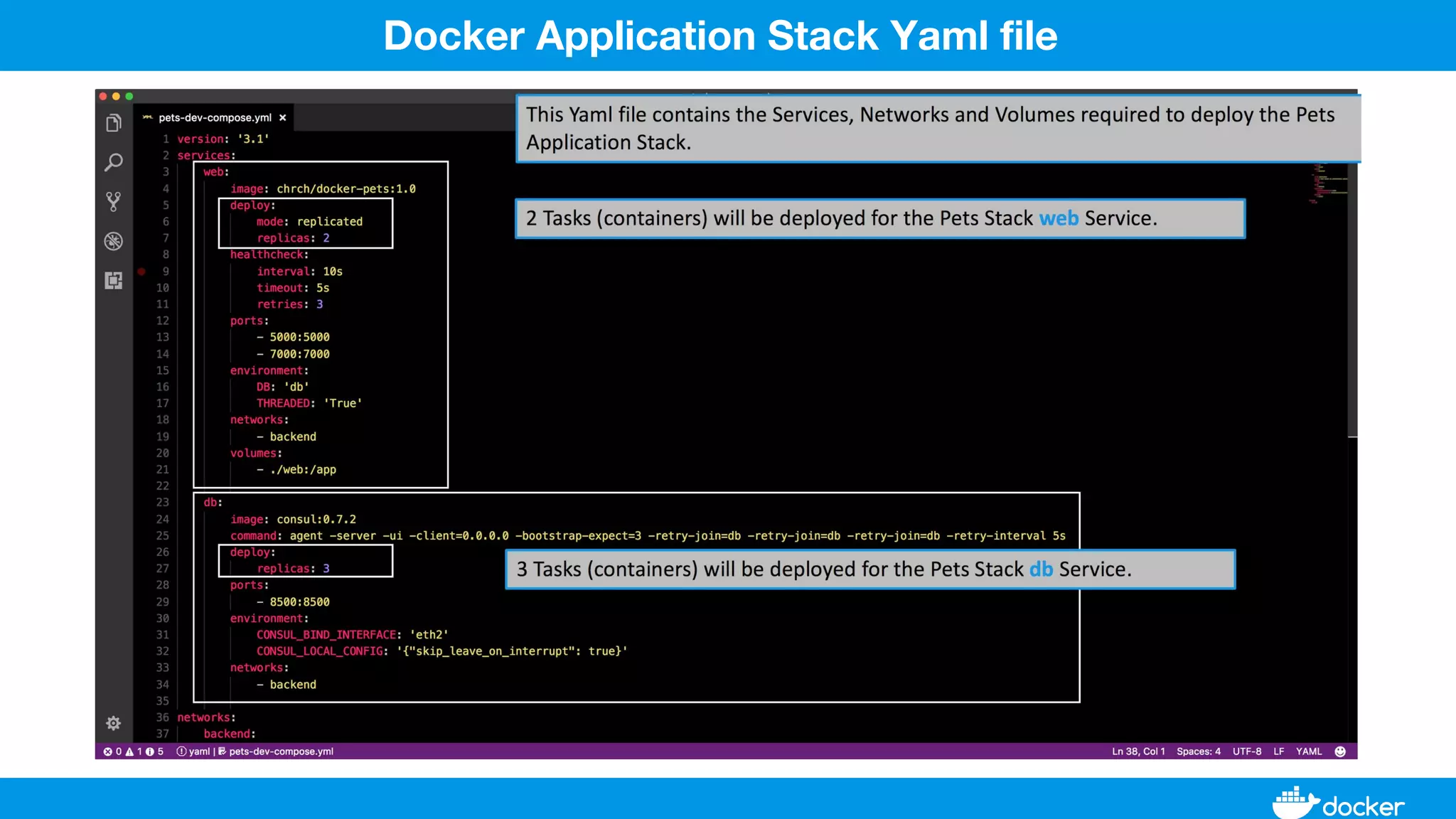
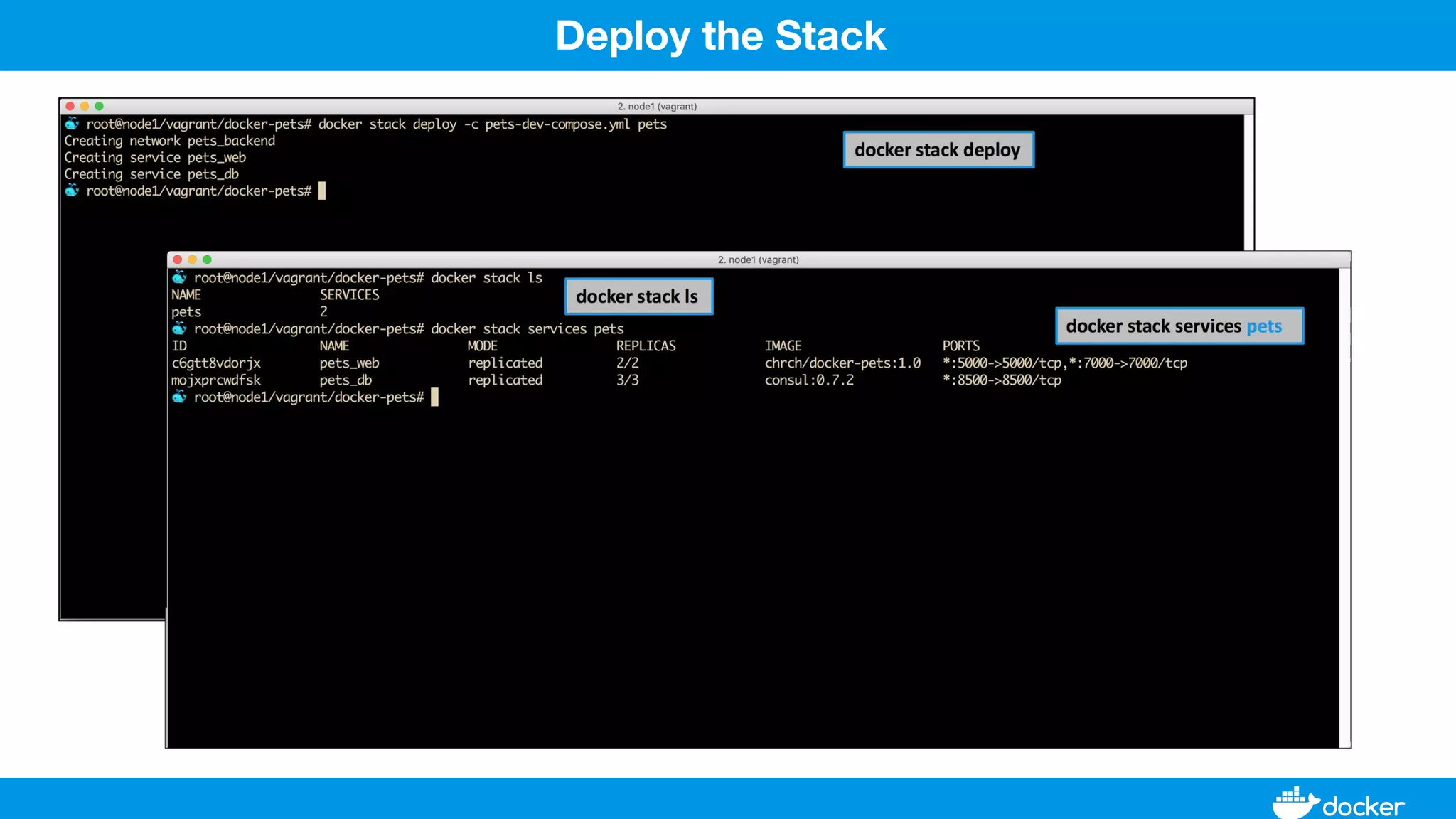
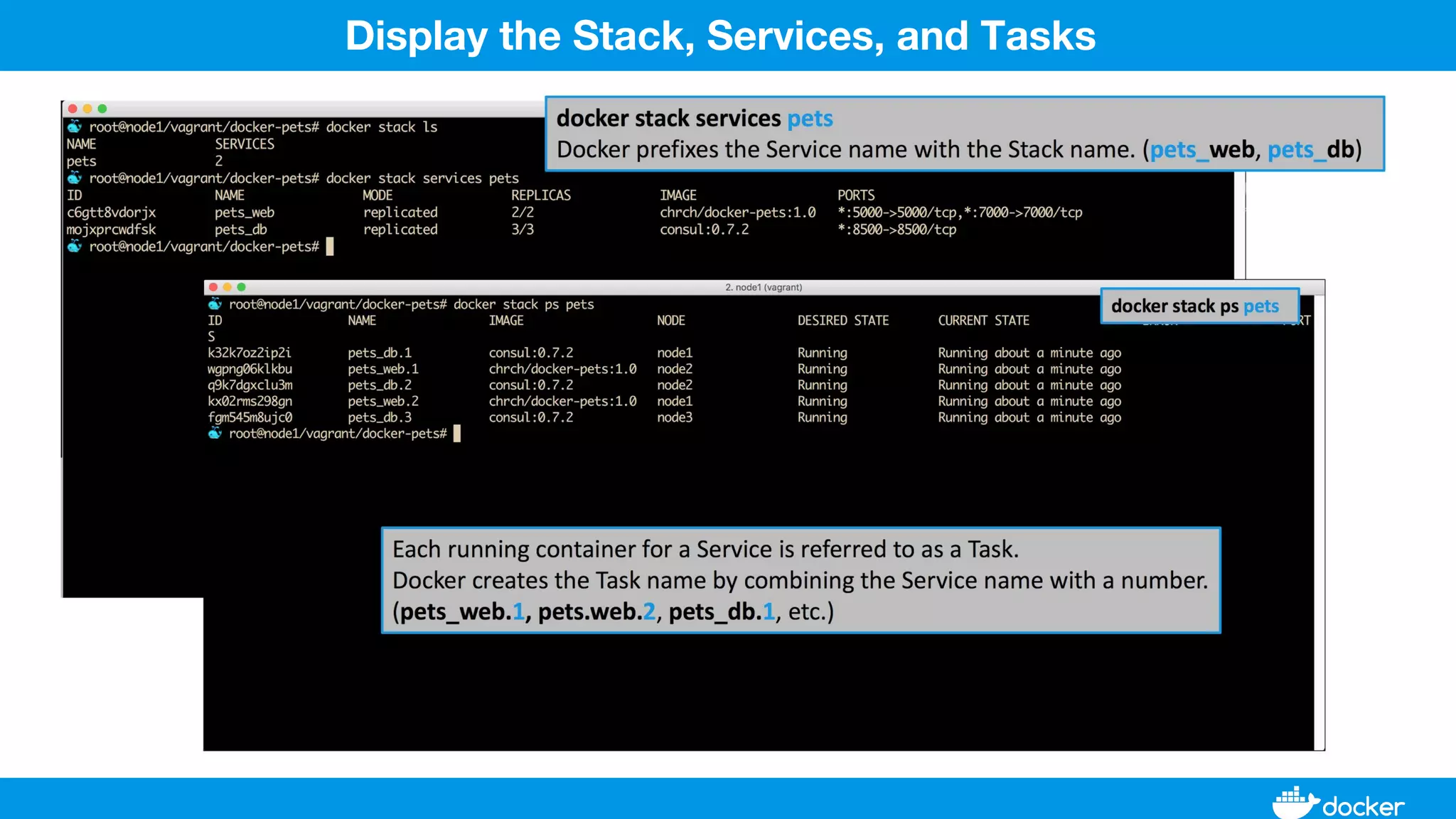
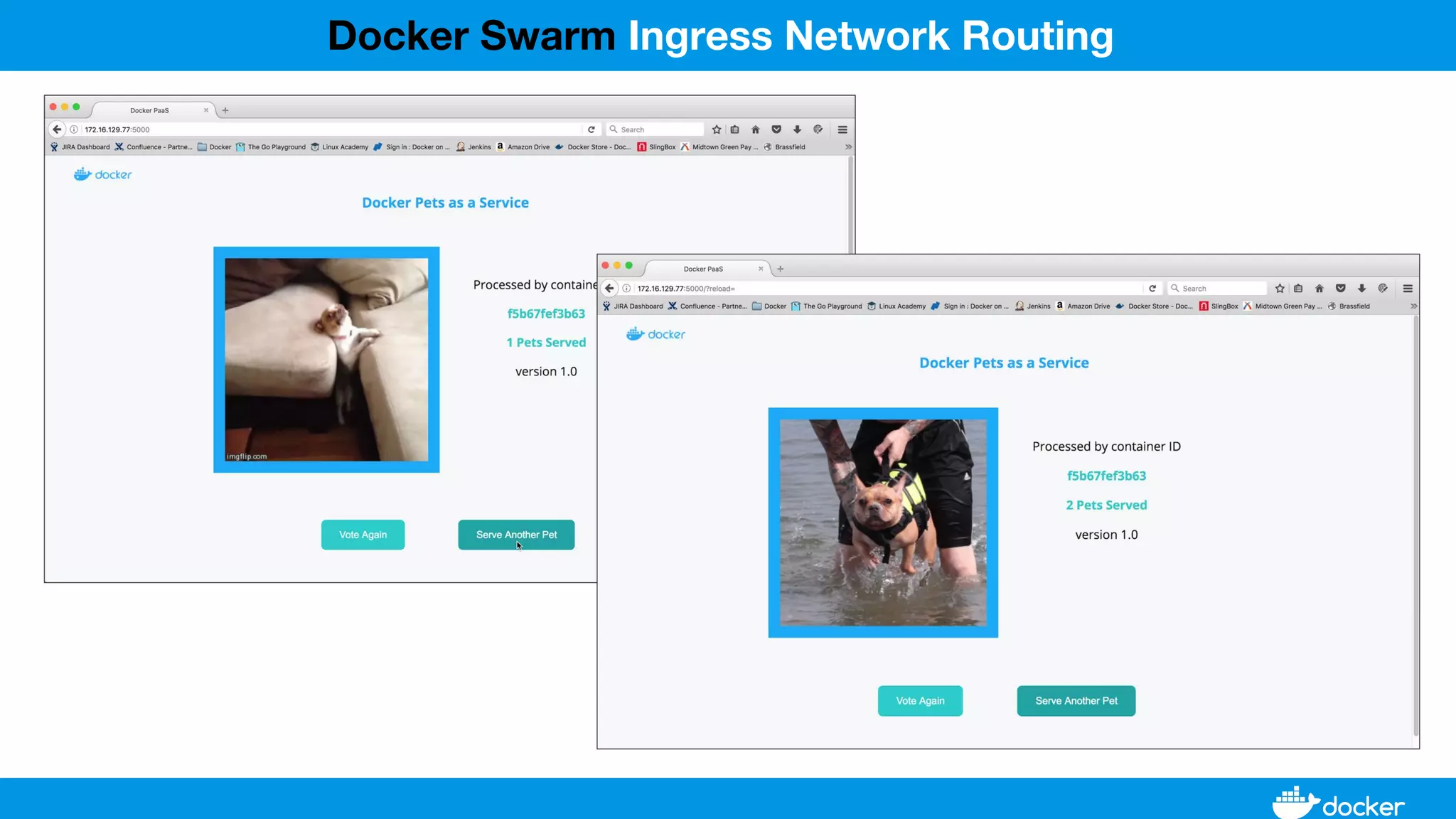
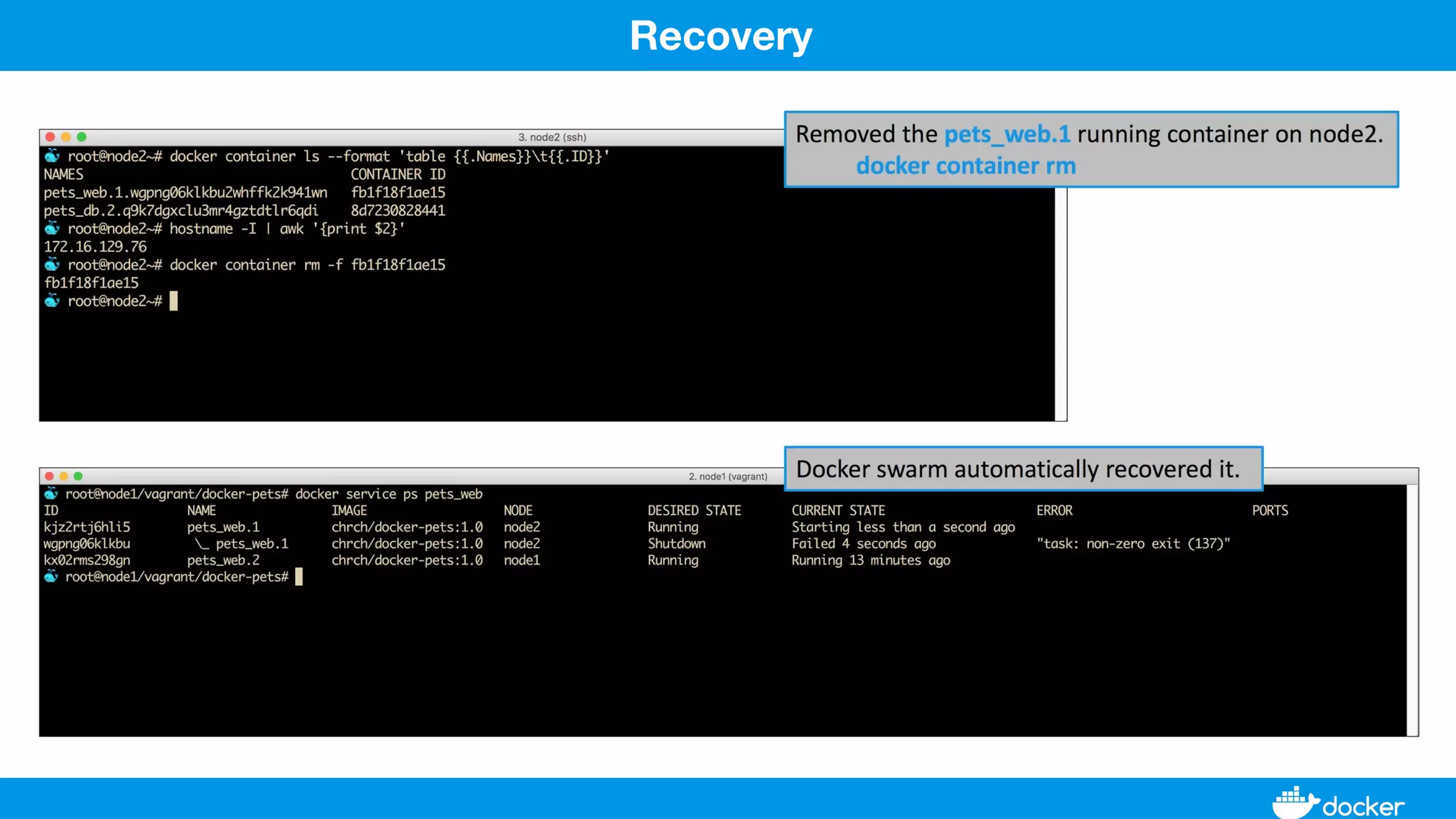
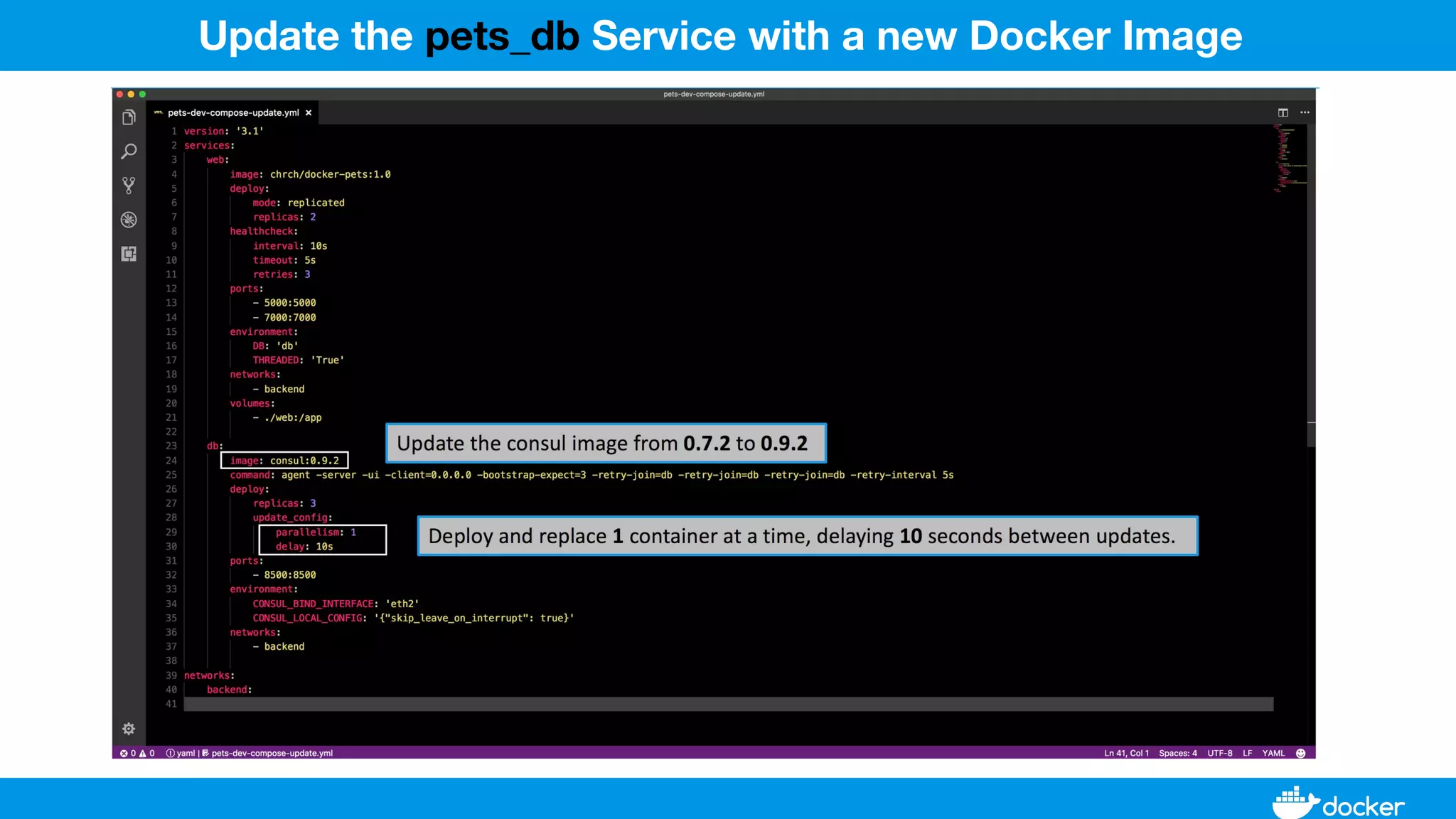
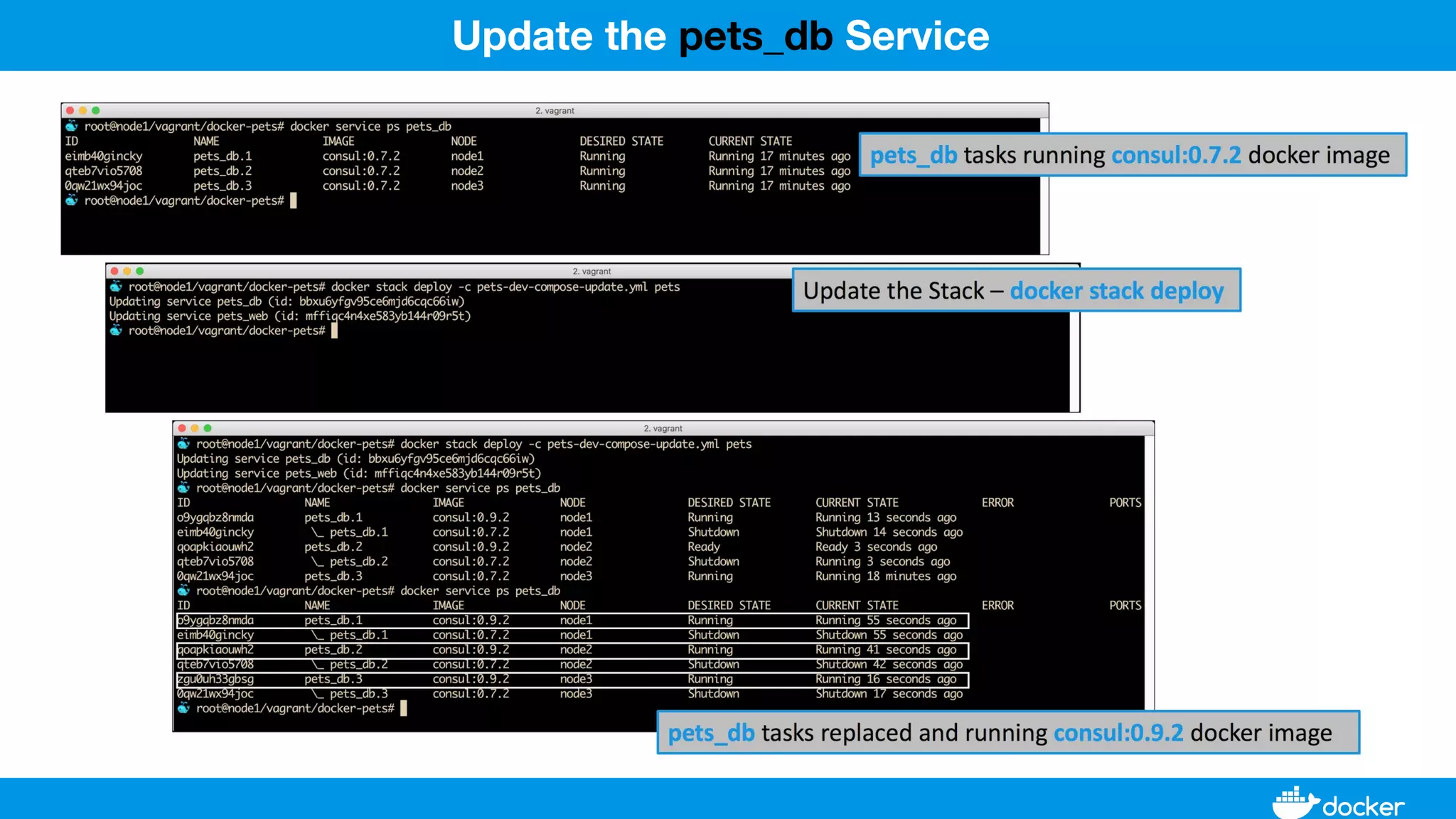
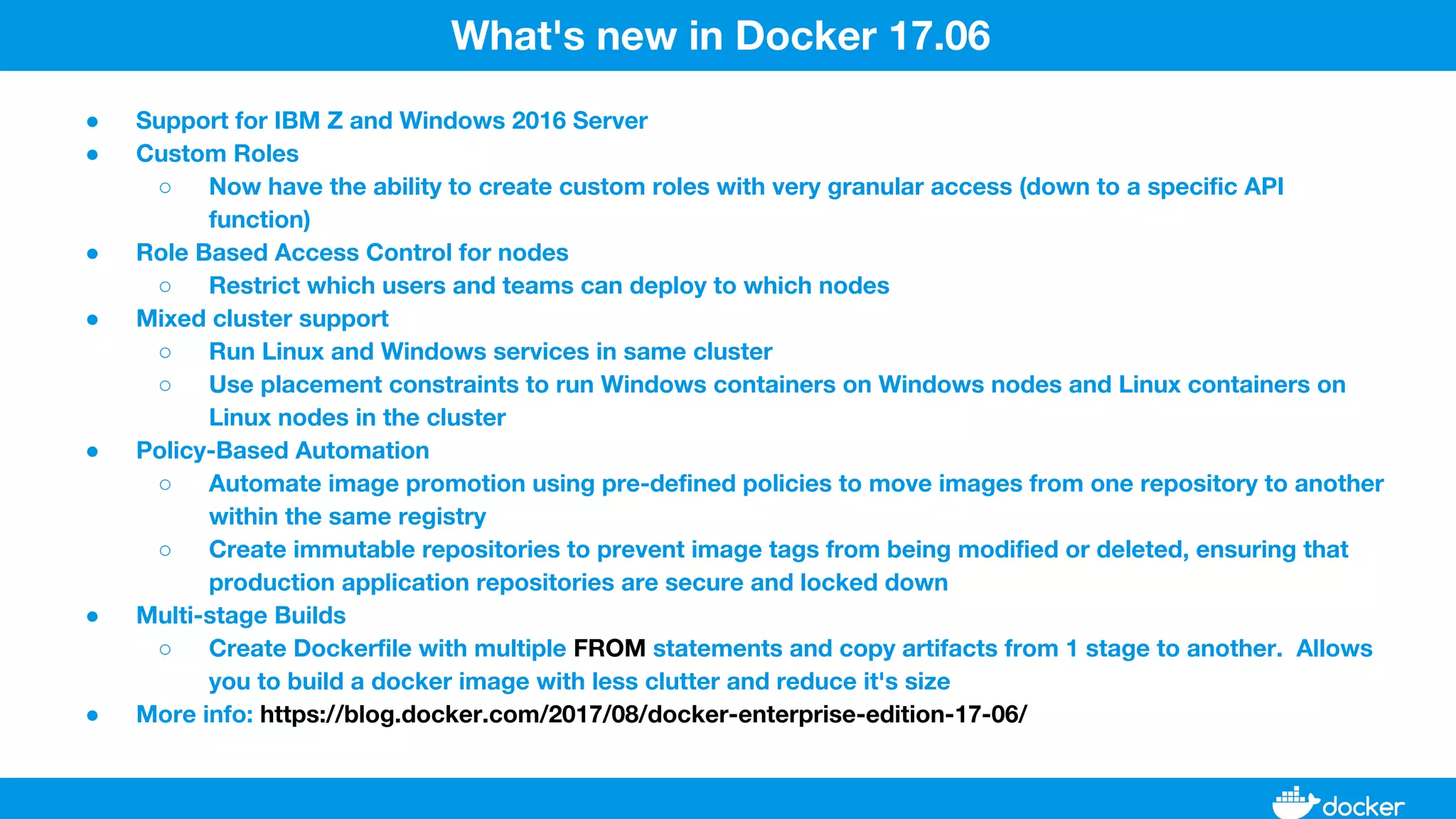
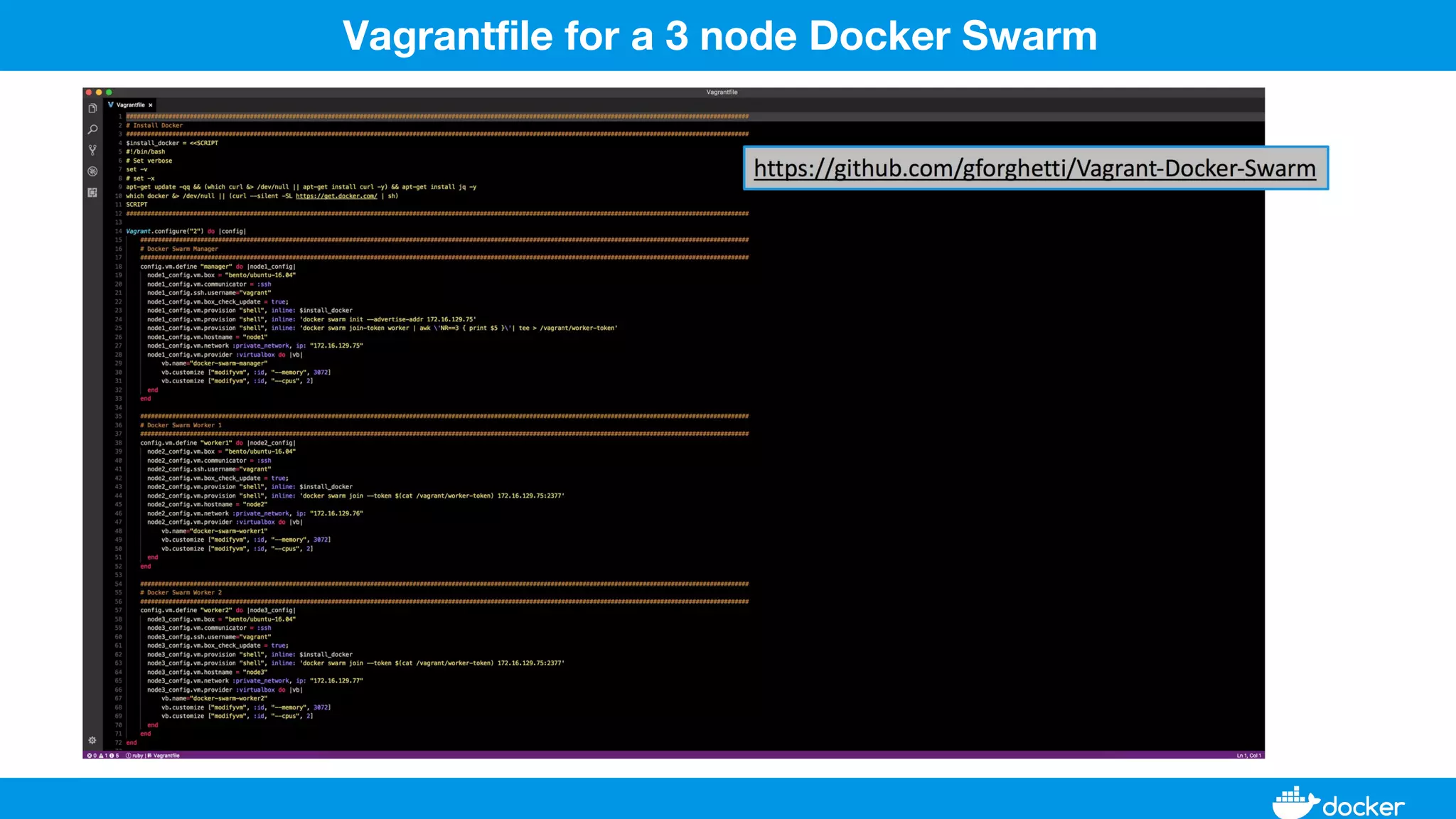
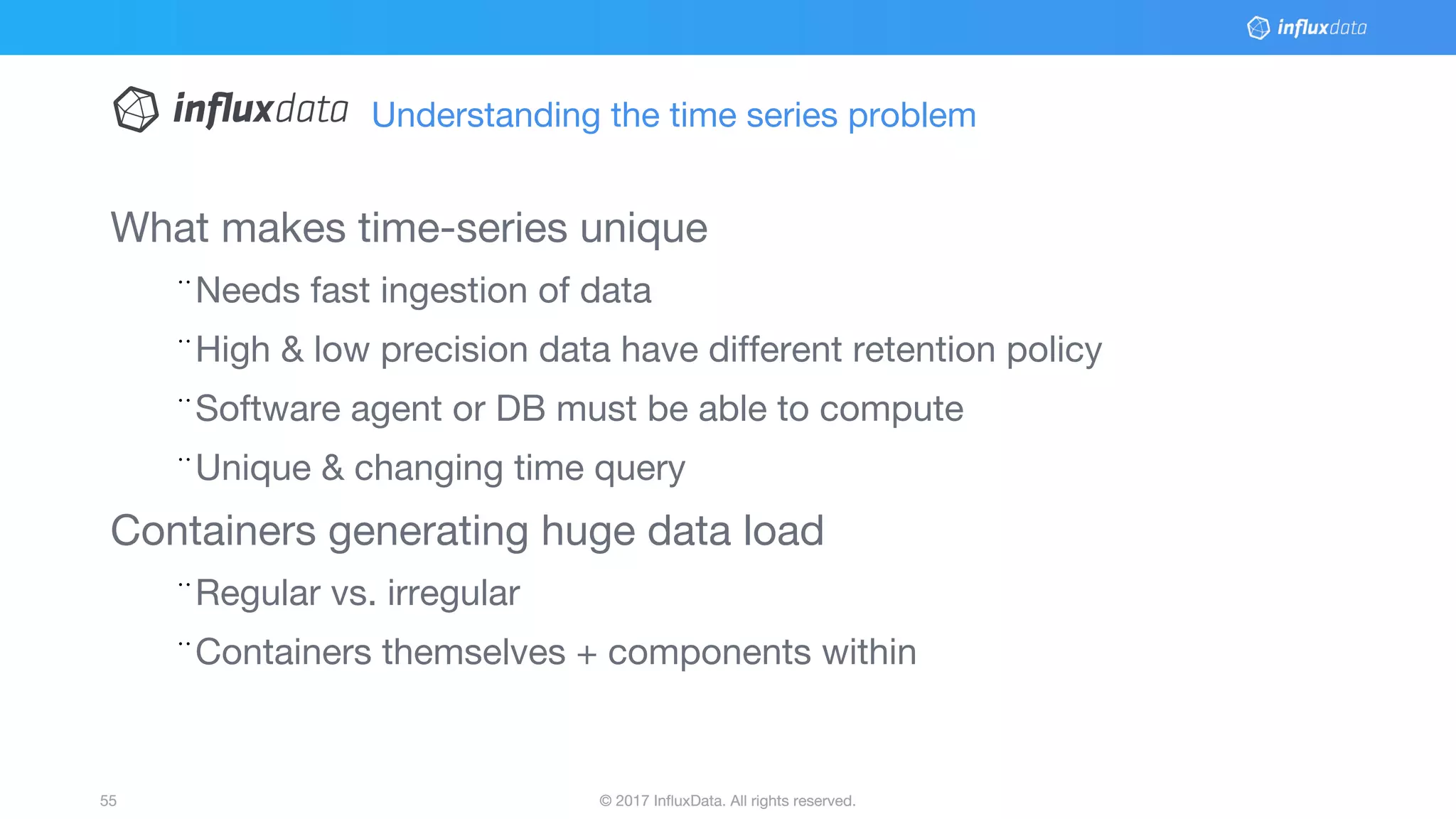
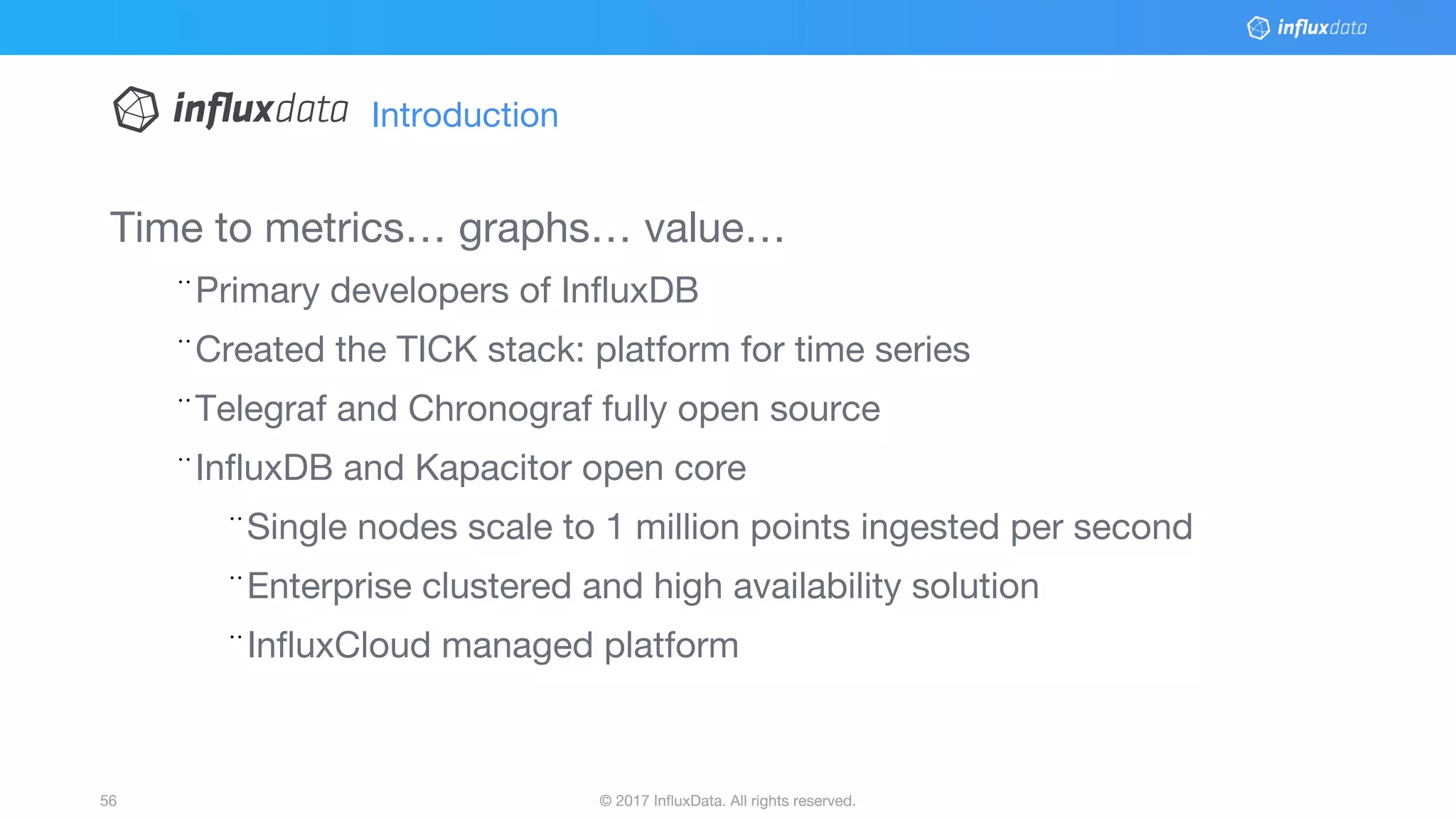
This document provides an overview of Docker, its applications, and how it manages time series data in container orchestration. It discusses Docker's features, such as images and containers, the use of Docker Compose and Swarm for deployment, and new updates in Docker 17.06. Additionally, it introduces InfluxData's tools for handling time series data, including Telegraf and InfluxDB, and outlines their architecture and performance capabilities.