This document provides an overview of Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) including:
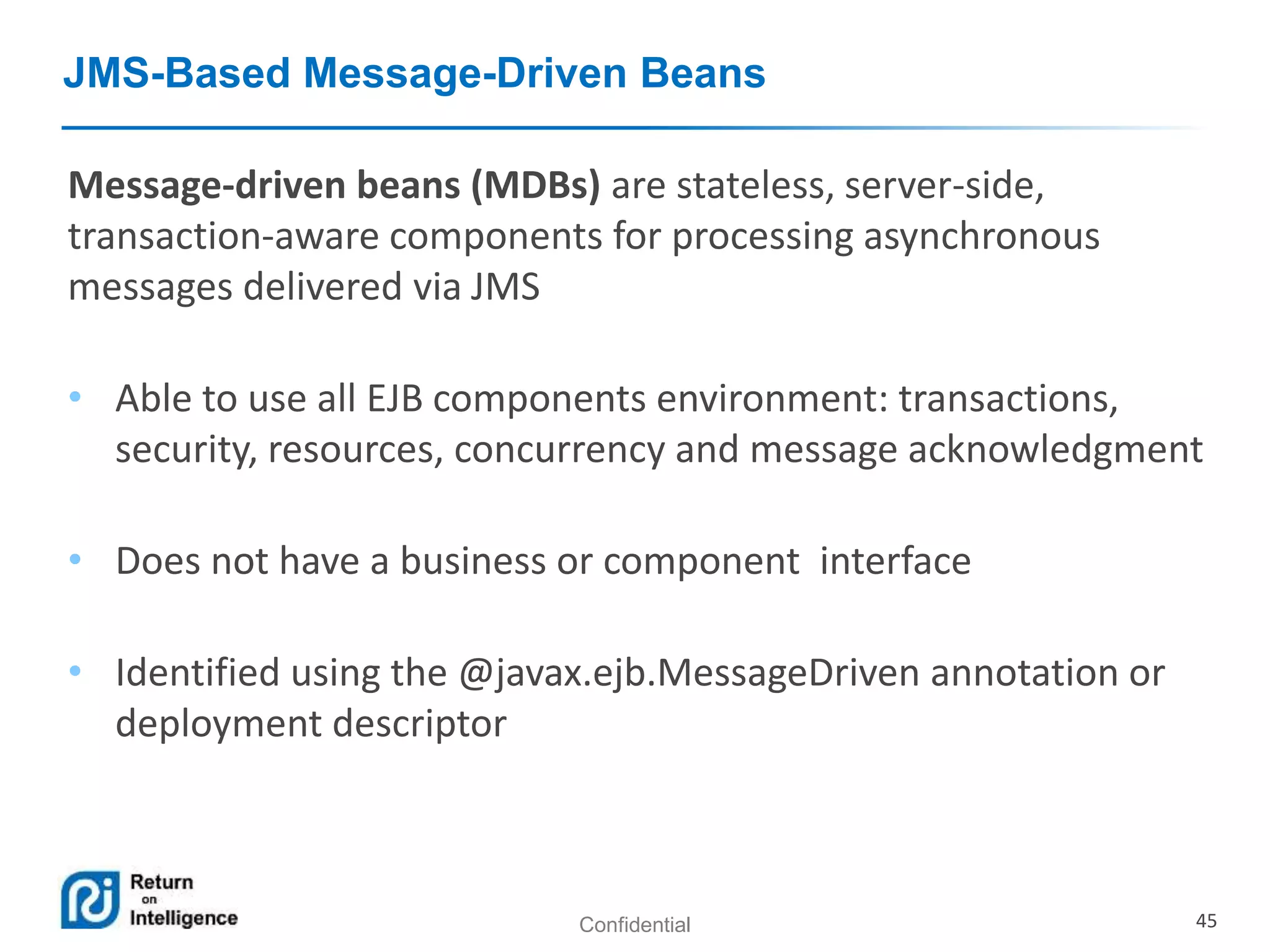
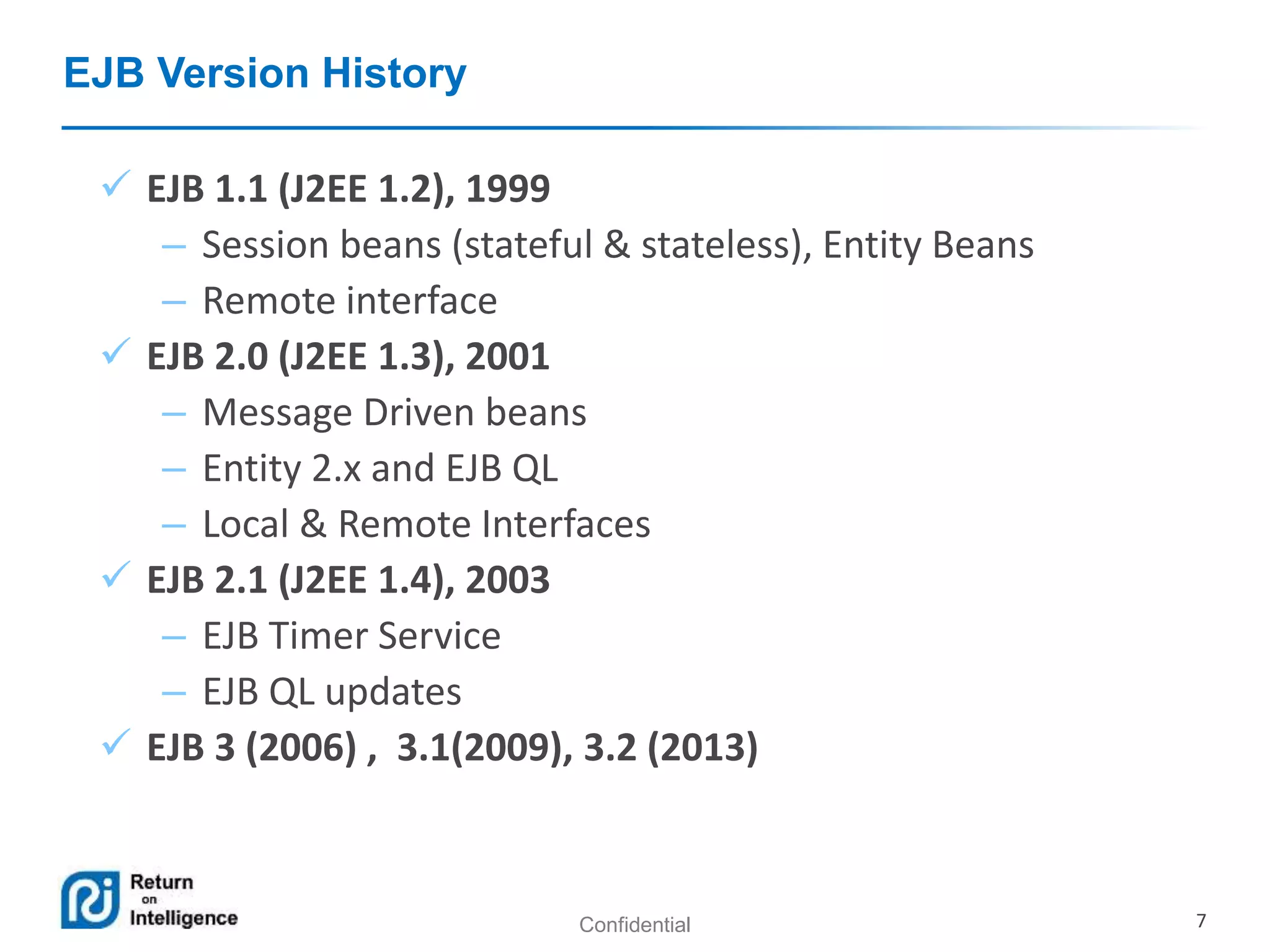
- The different types of EJB components including session beans, message-driven beans, and entities.
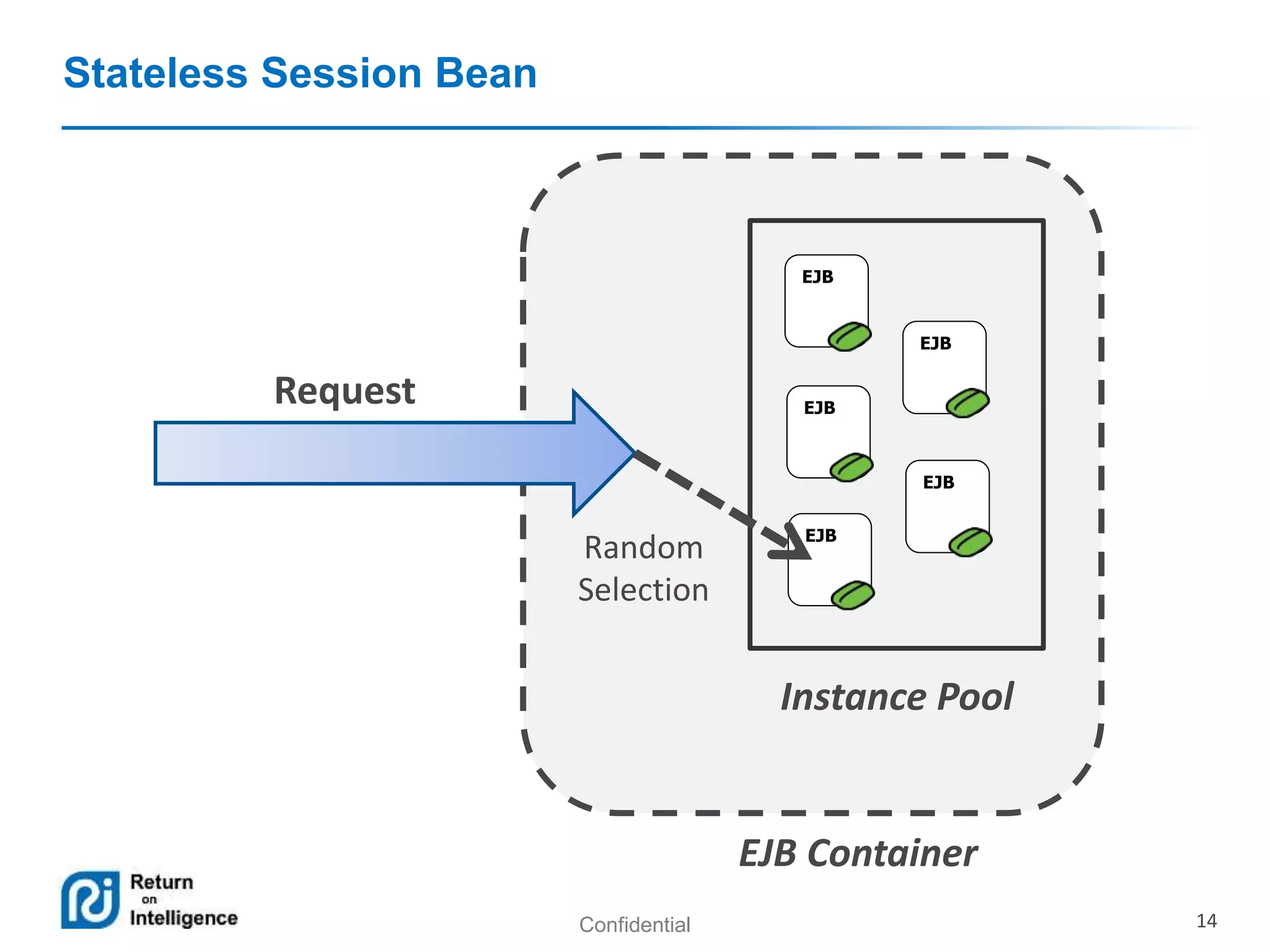
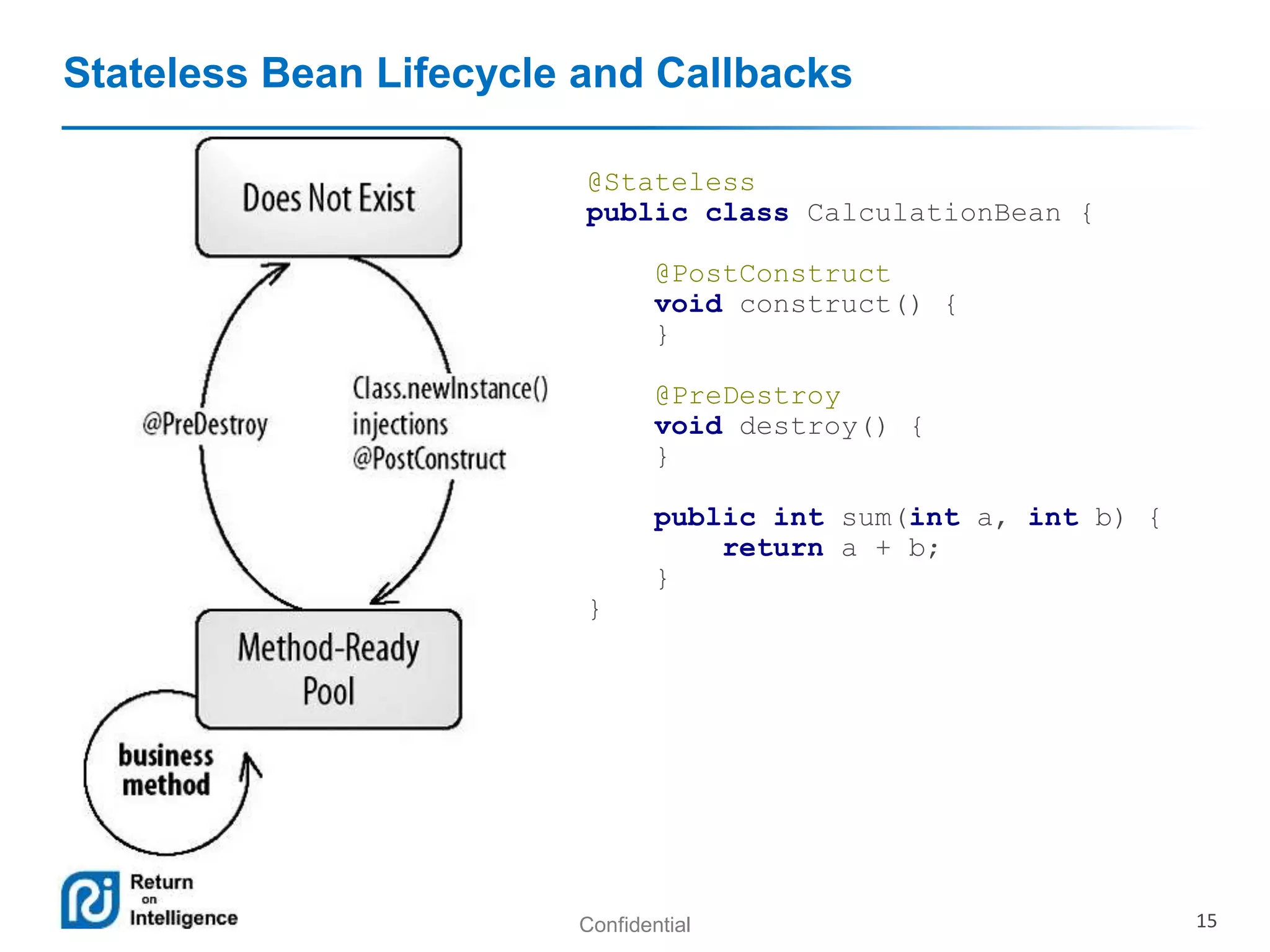
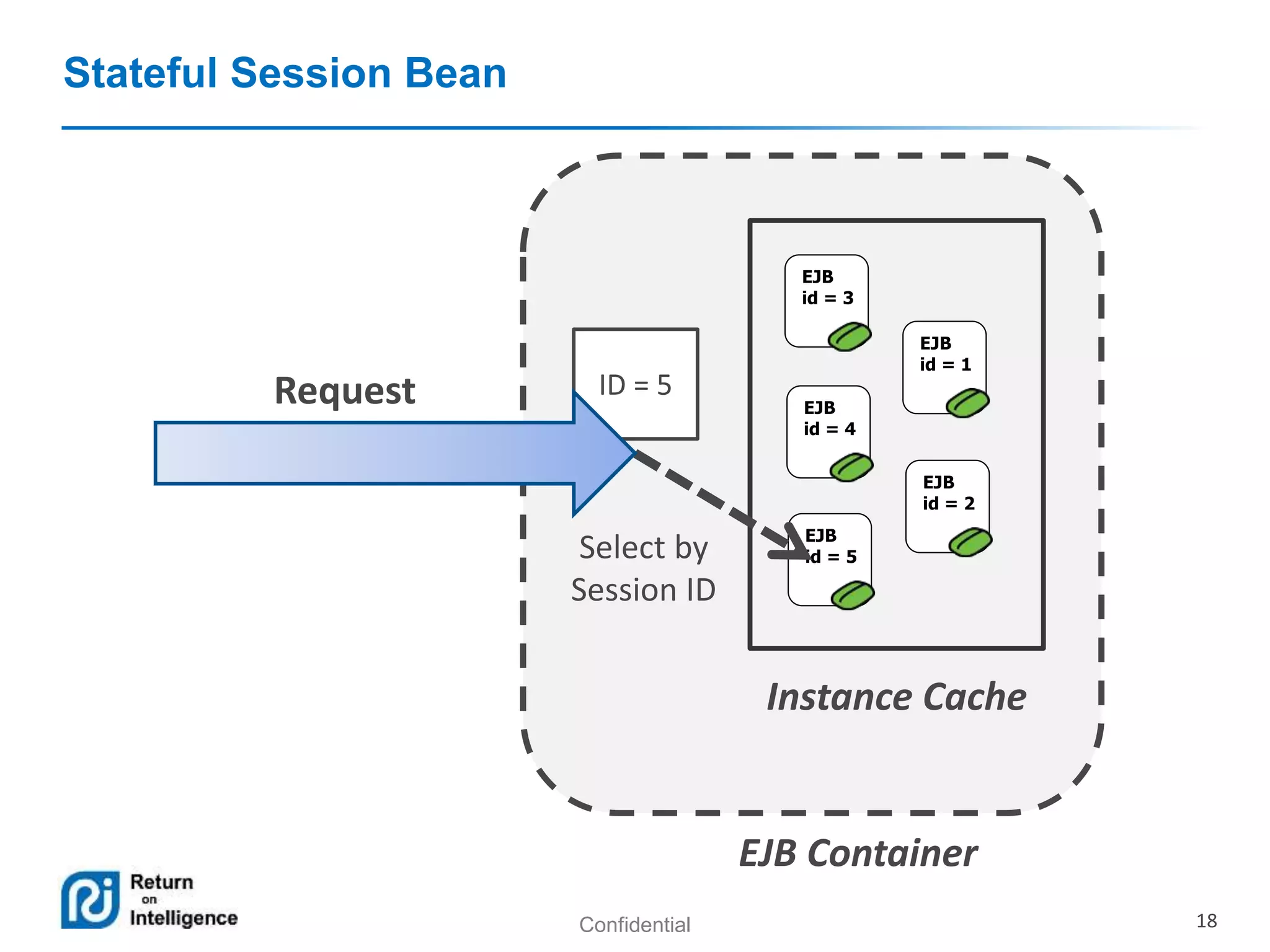
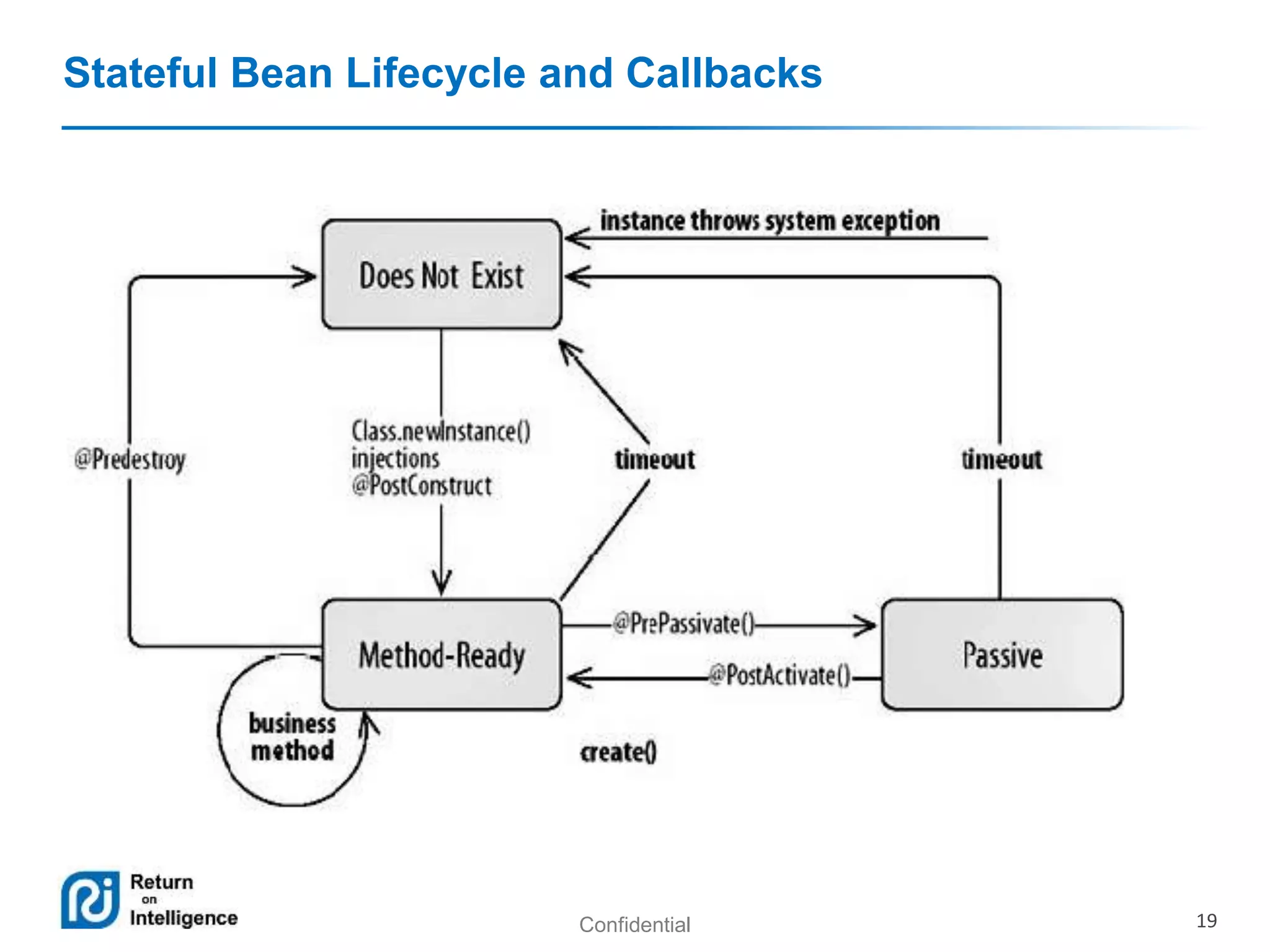
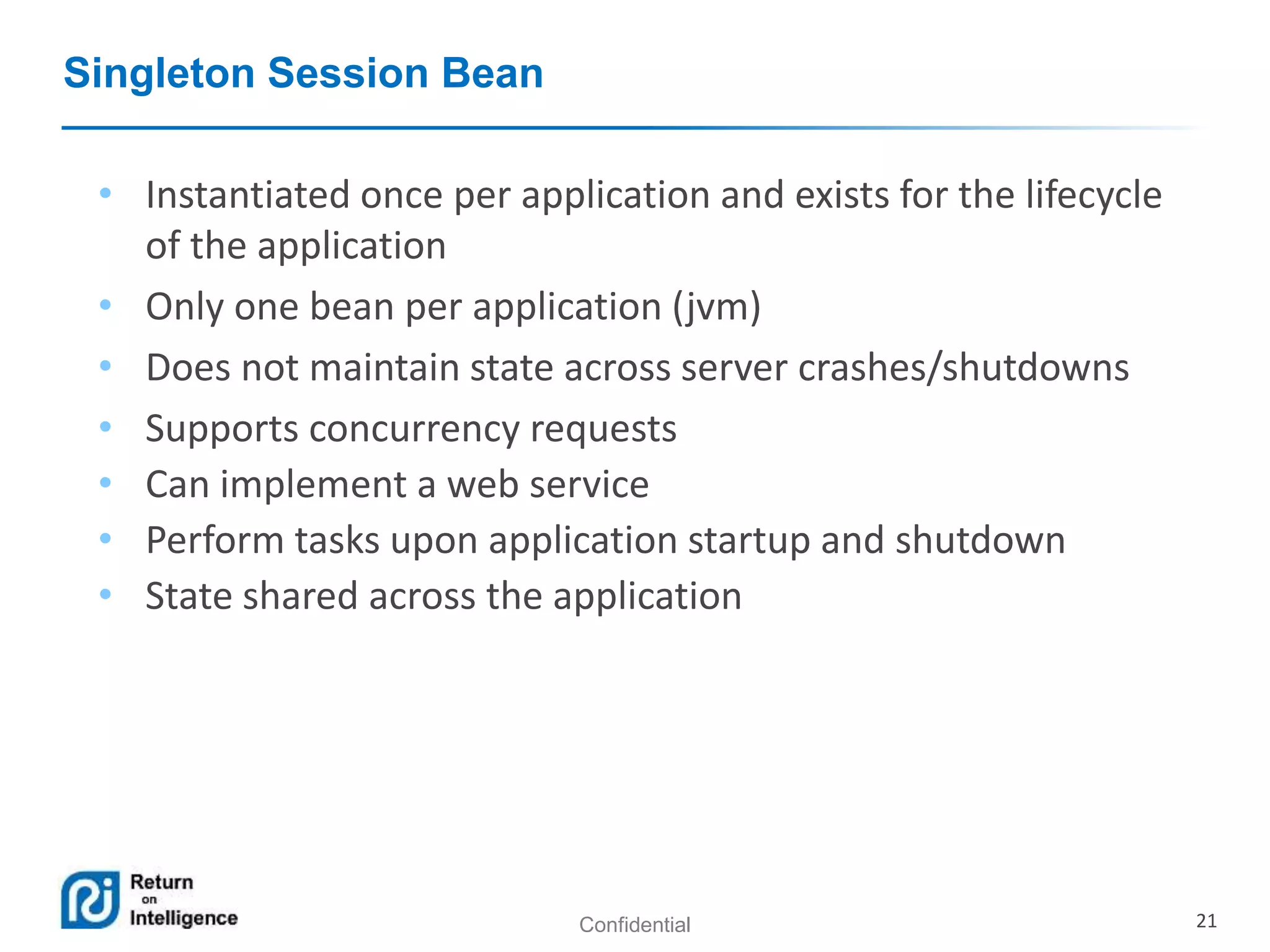
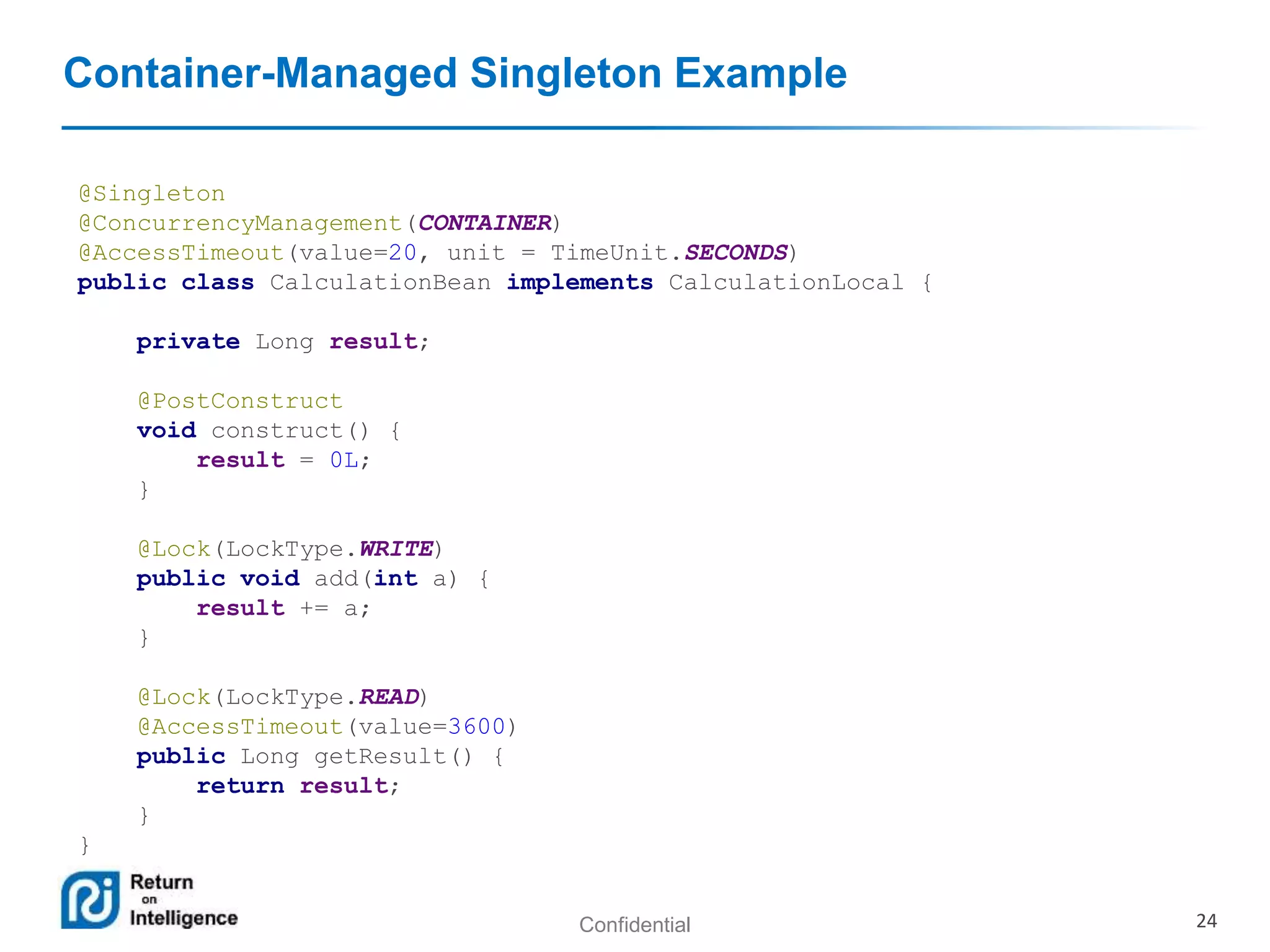
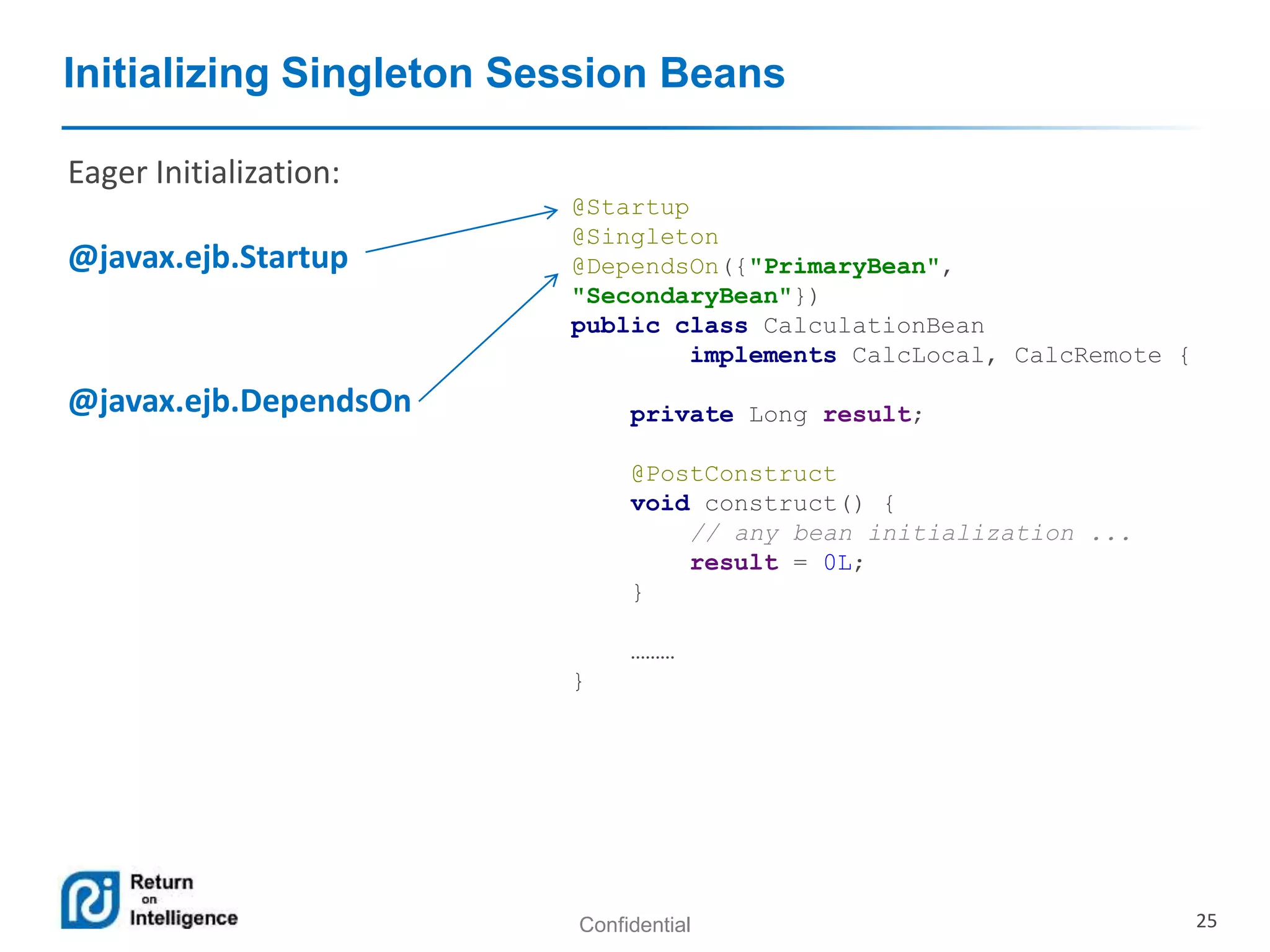
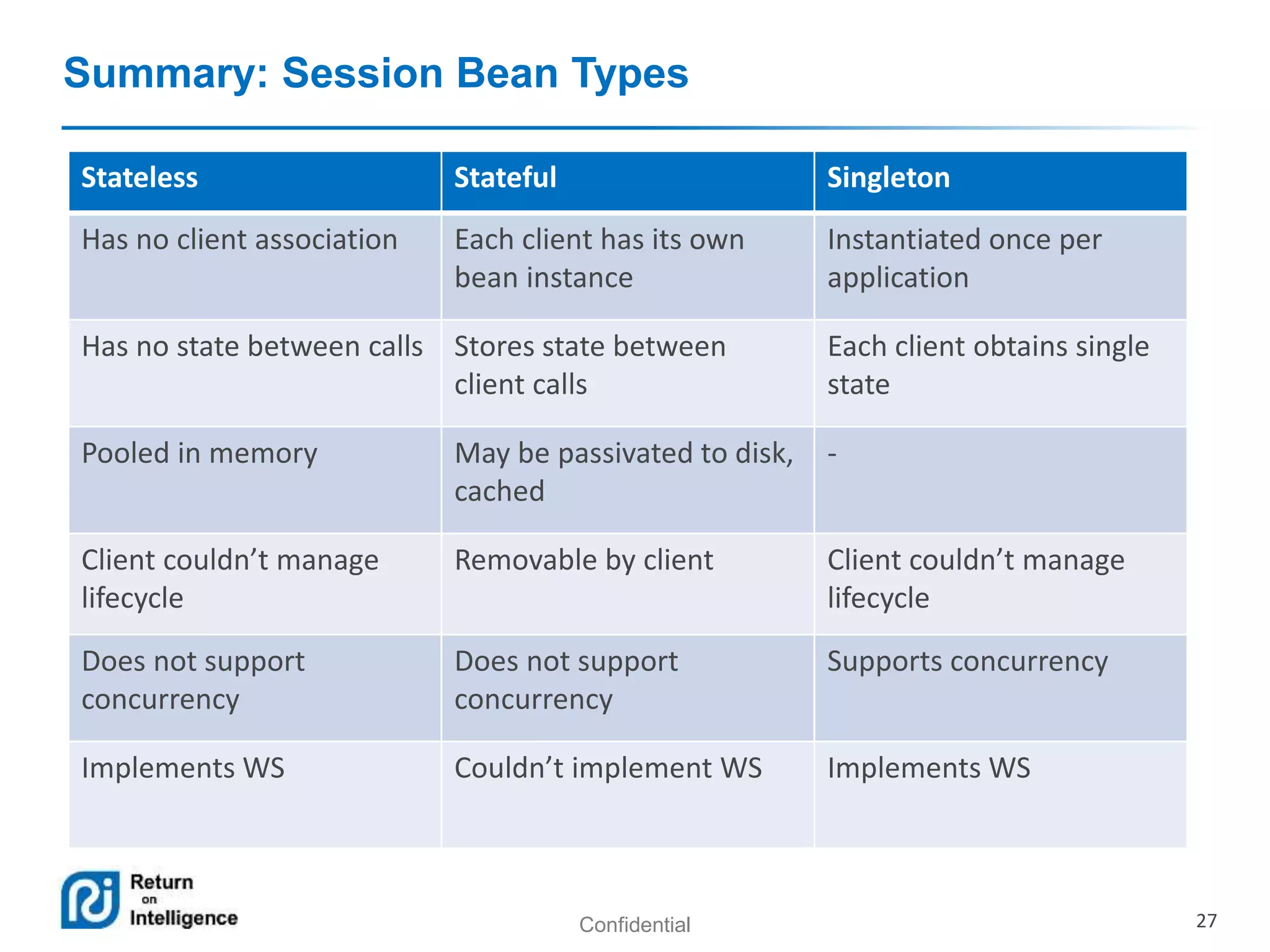
- Session beans can be stateless, stateful, or singleton and their differences are summarized.
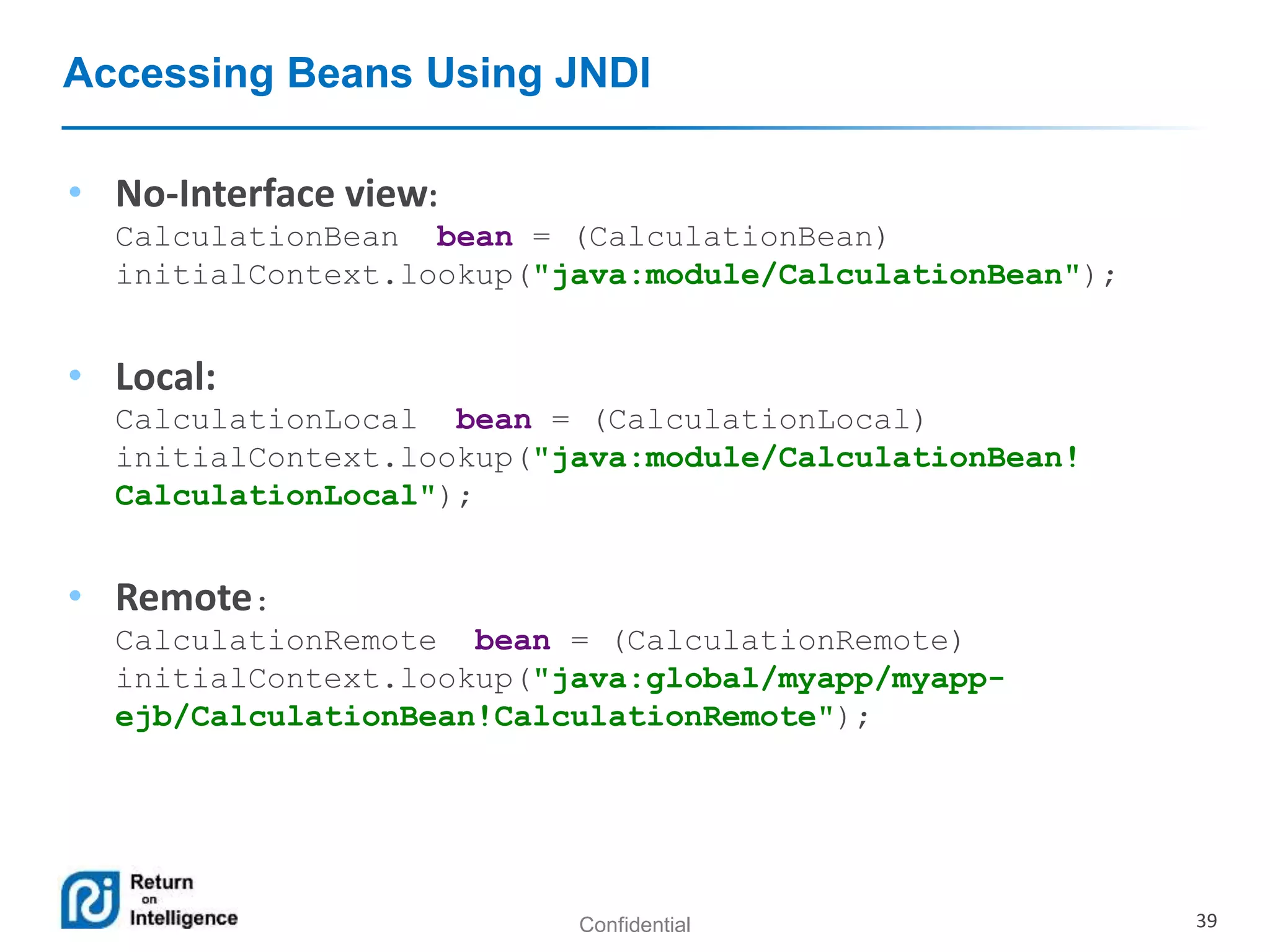
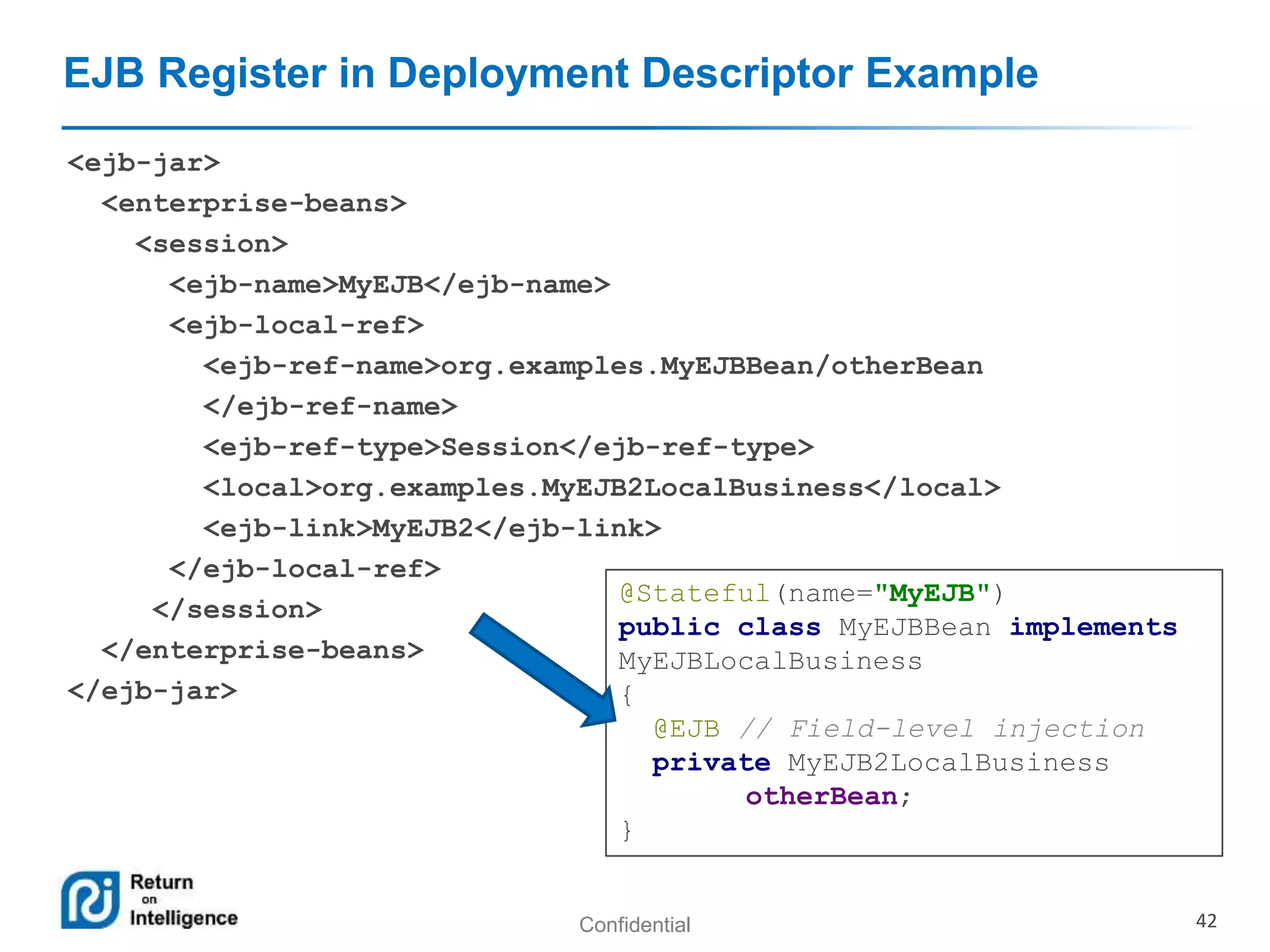
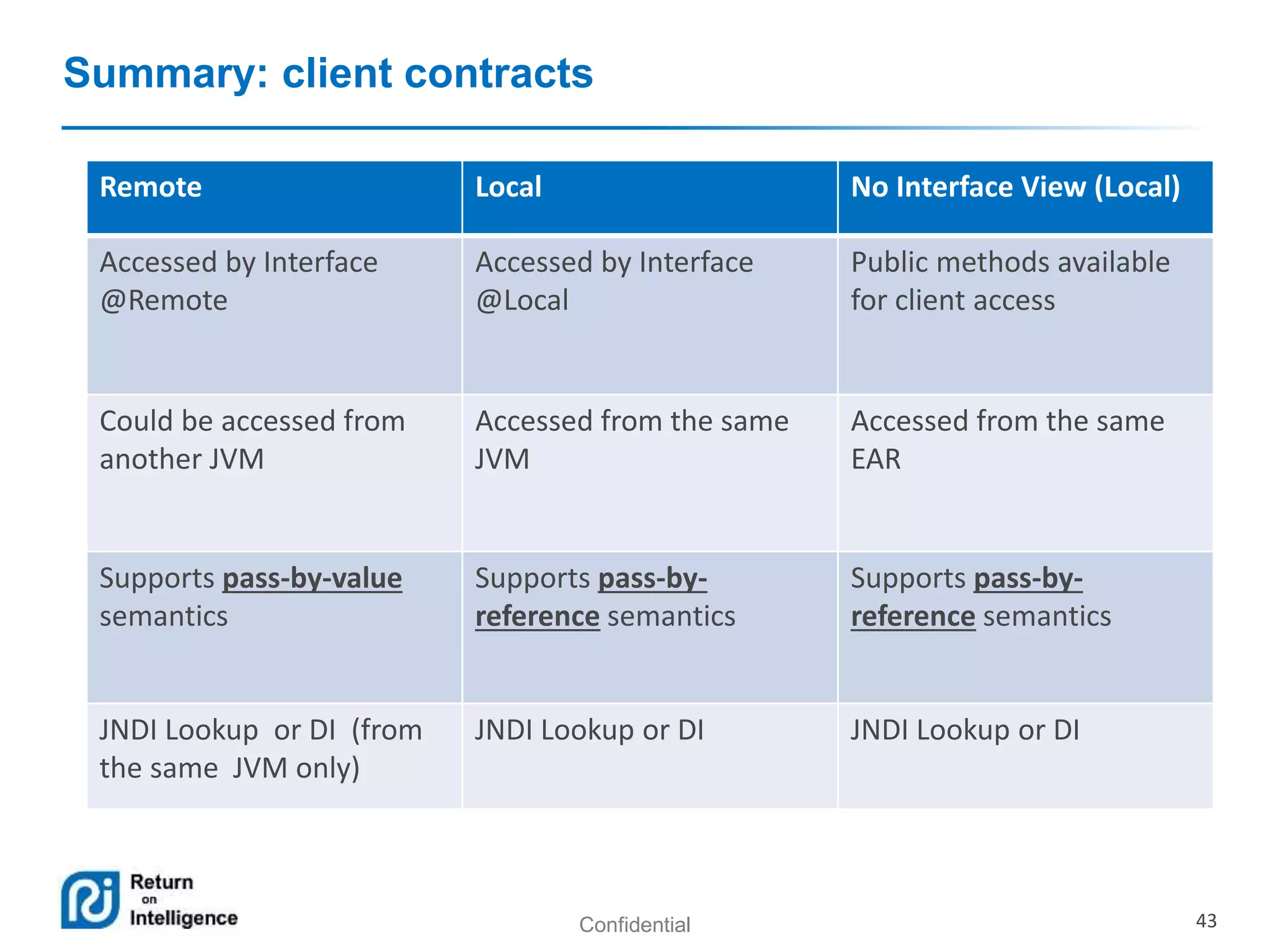
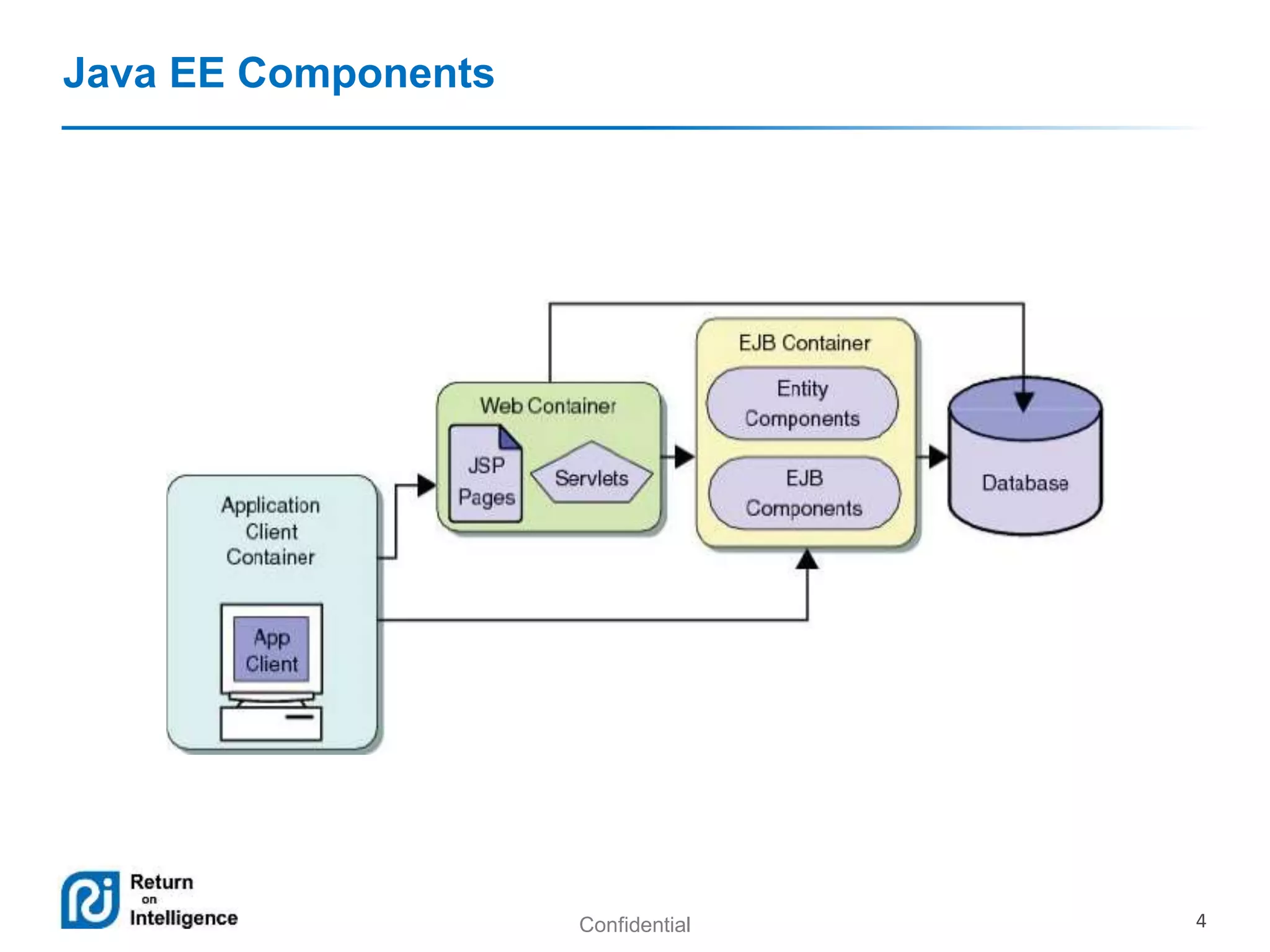
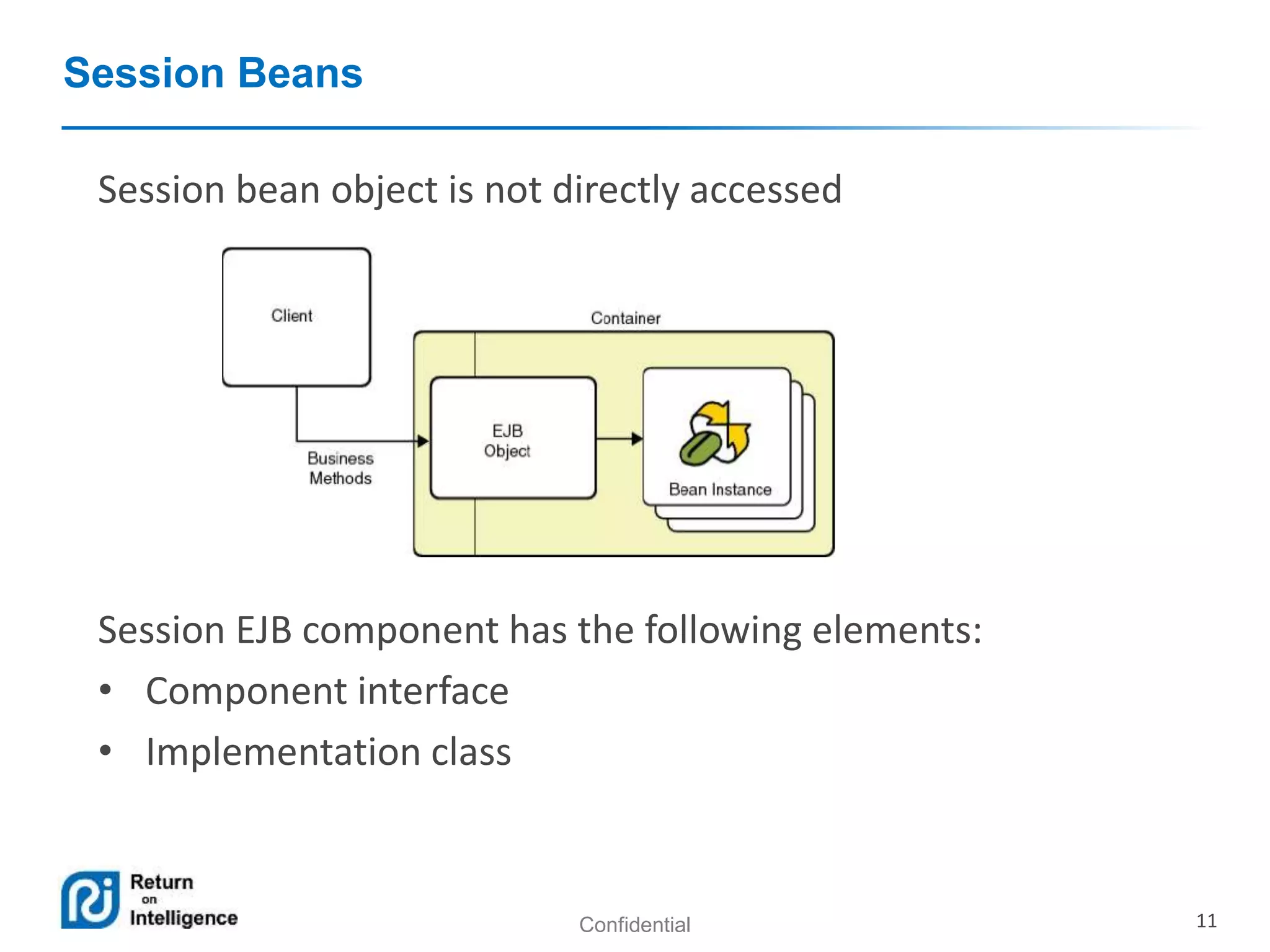
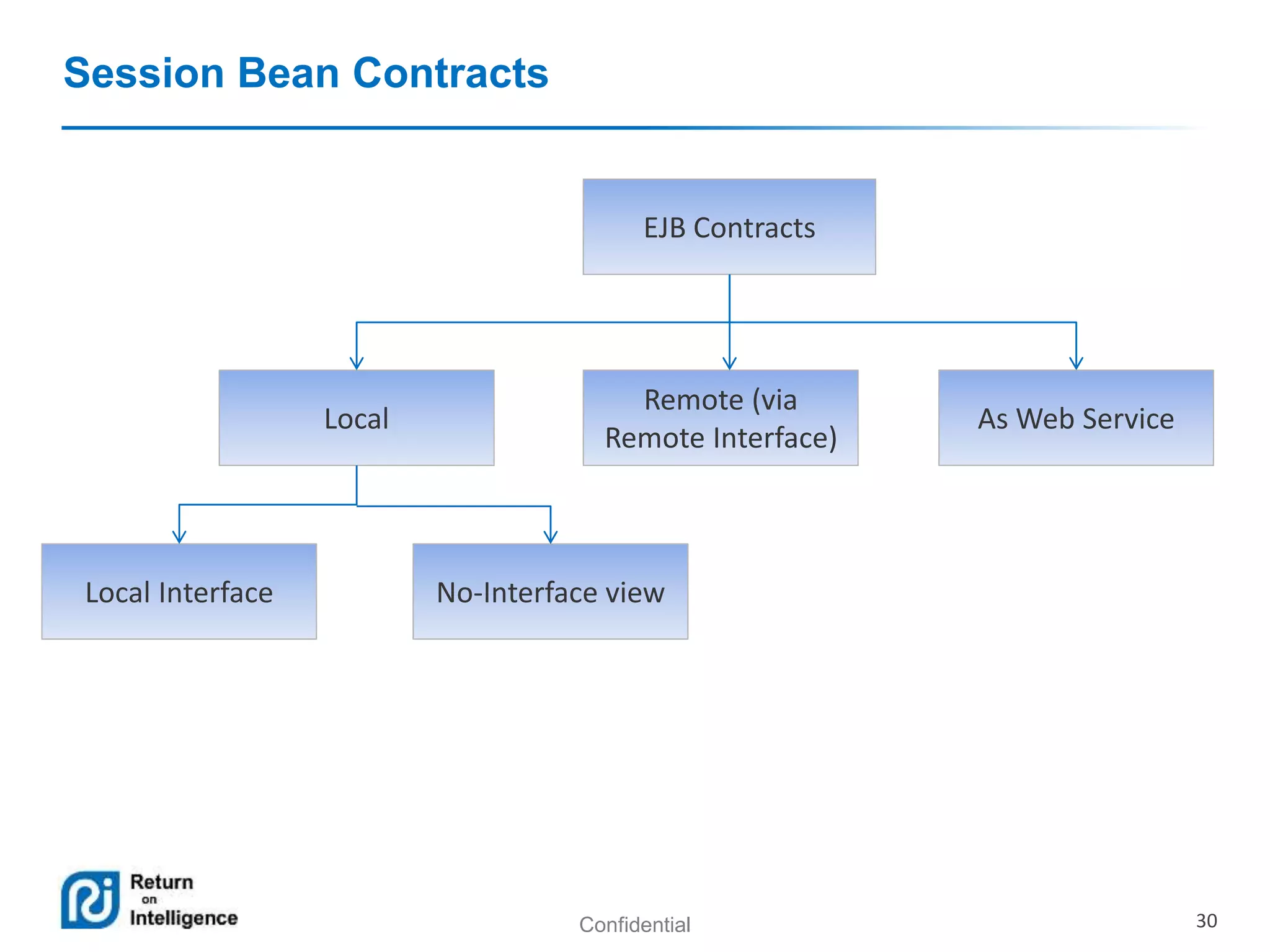
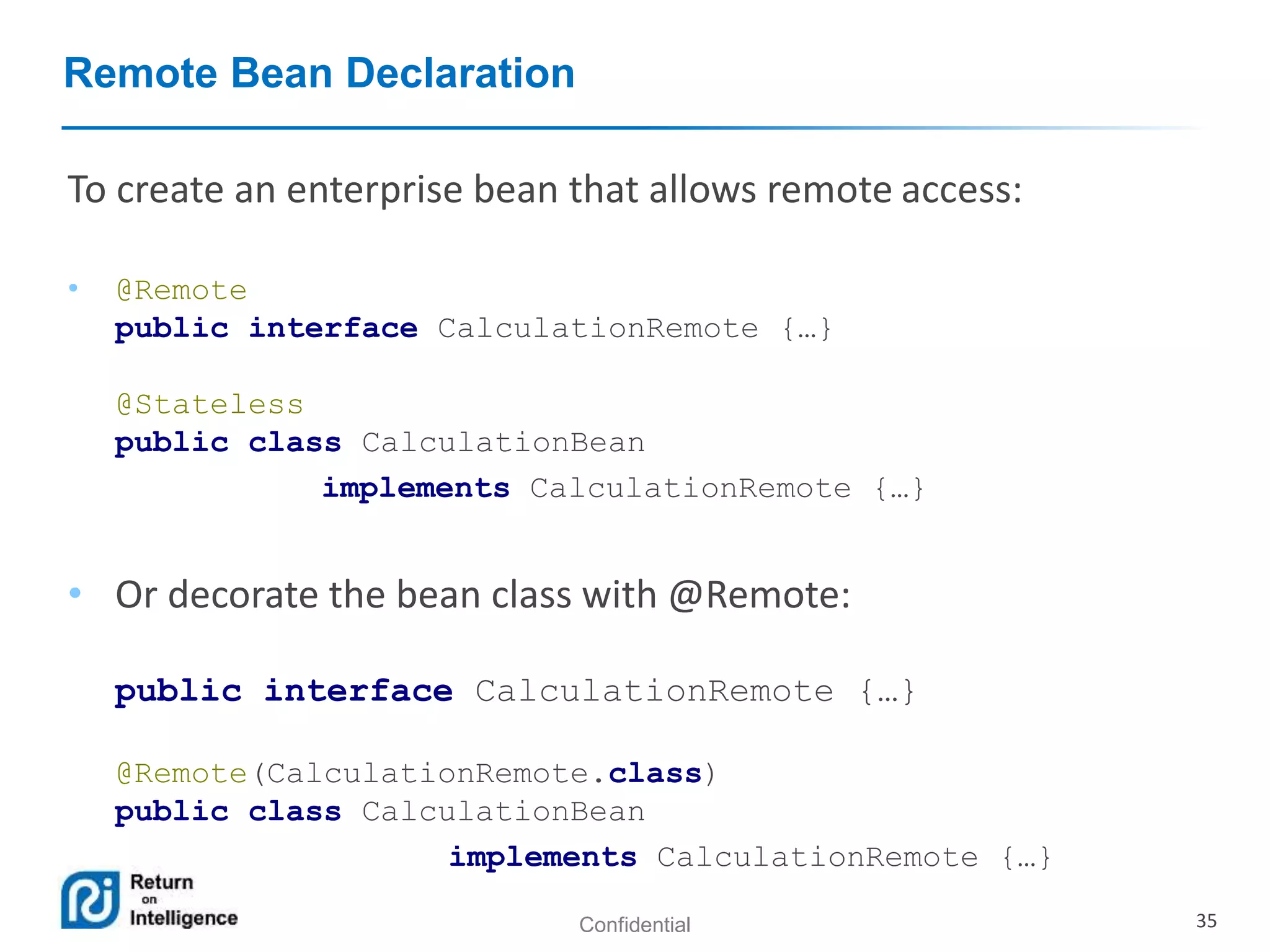
- How EJB components are accessed through local, remote, and no-interface views using dependency injection or JNDI lookups.
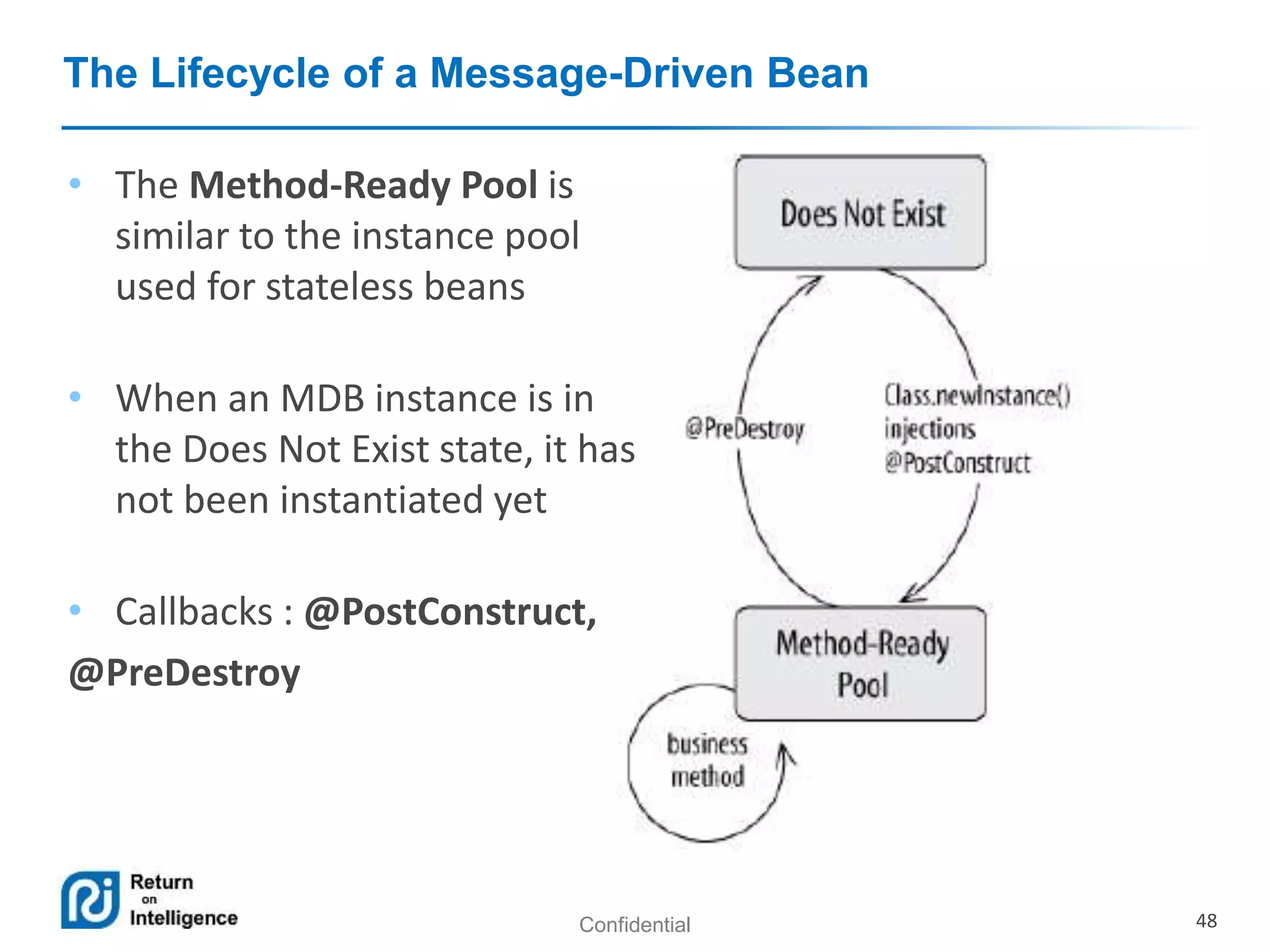
- Message-driven beans process asynchronous JMS messages.
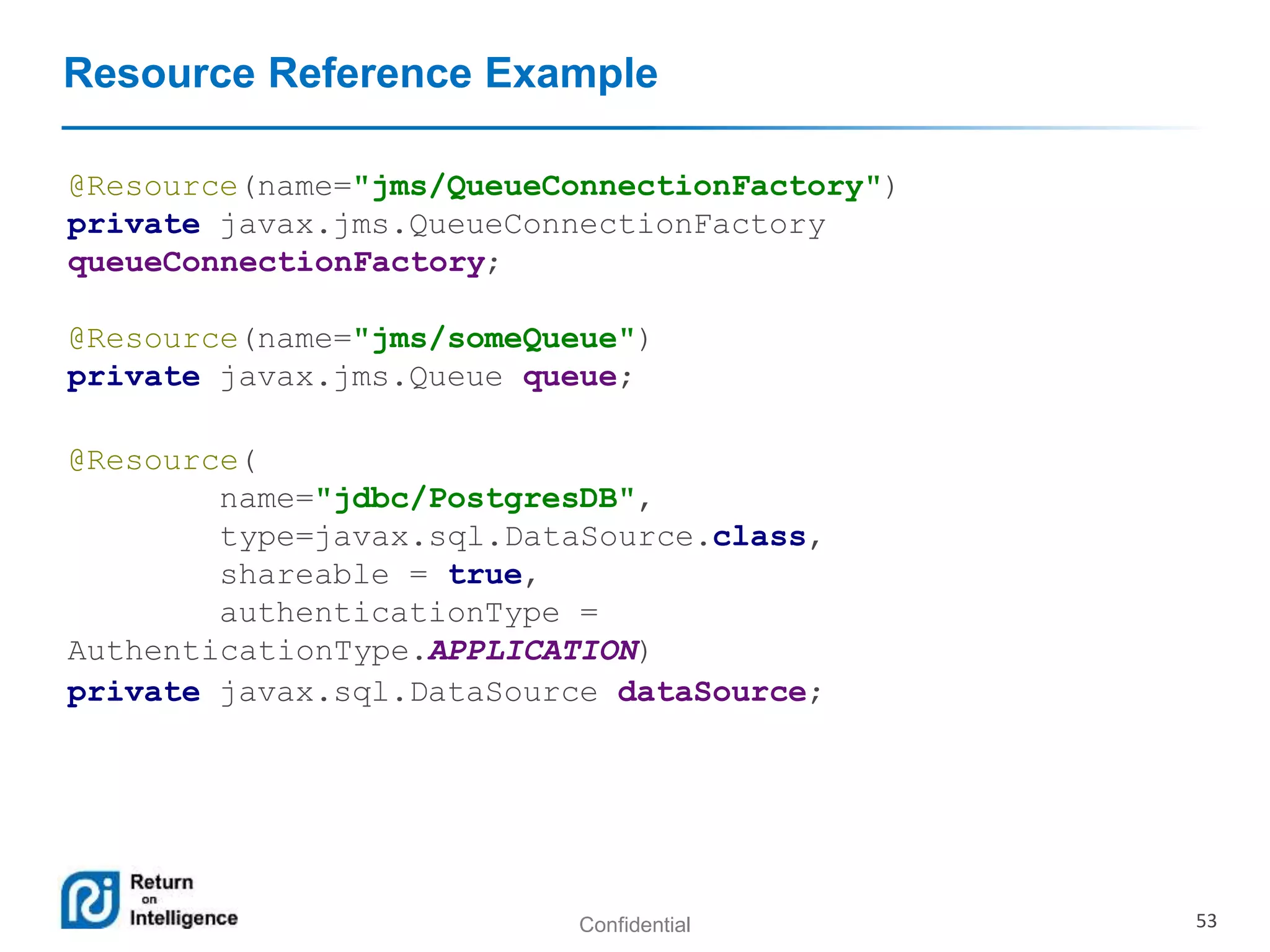
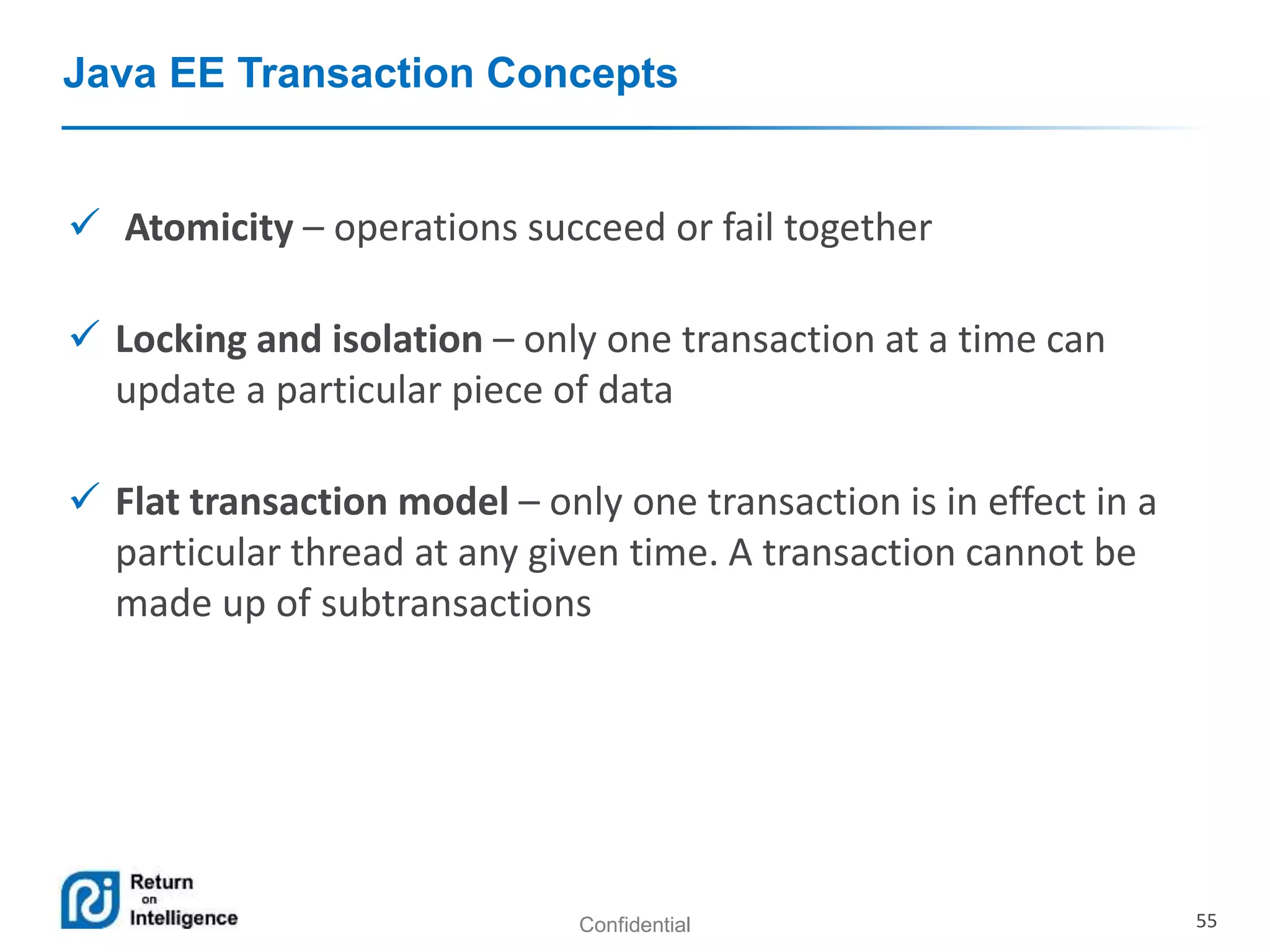
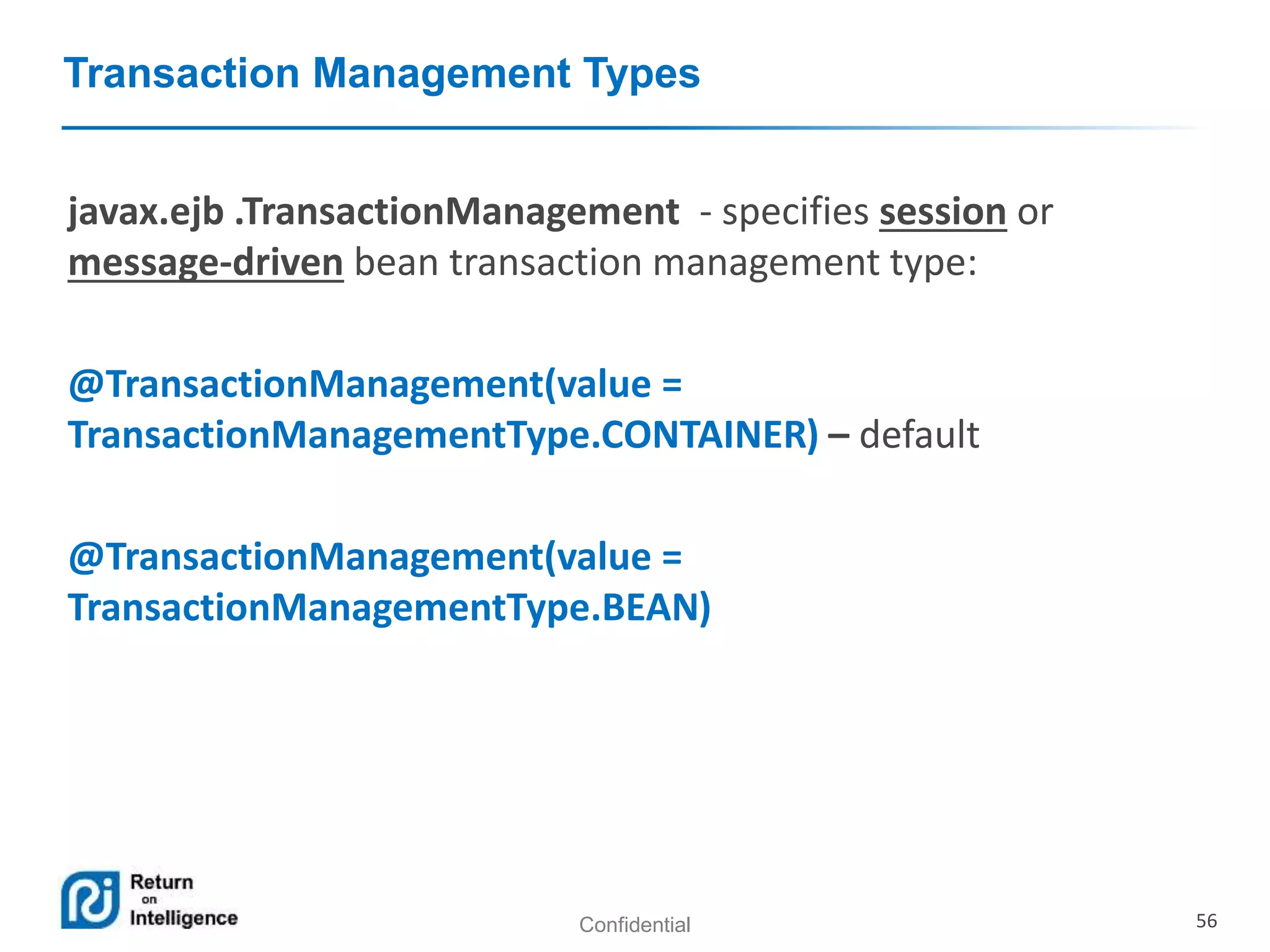
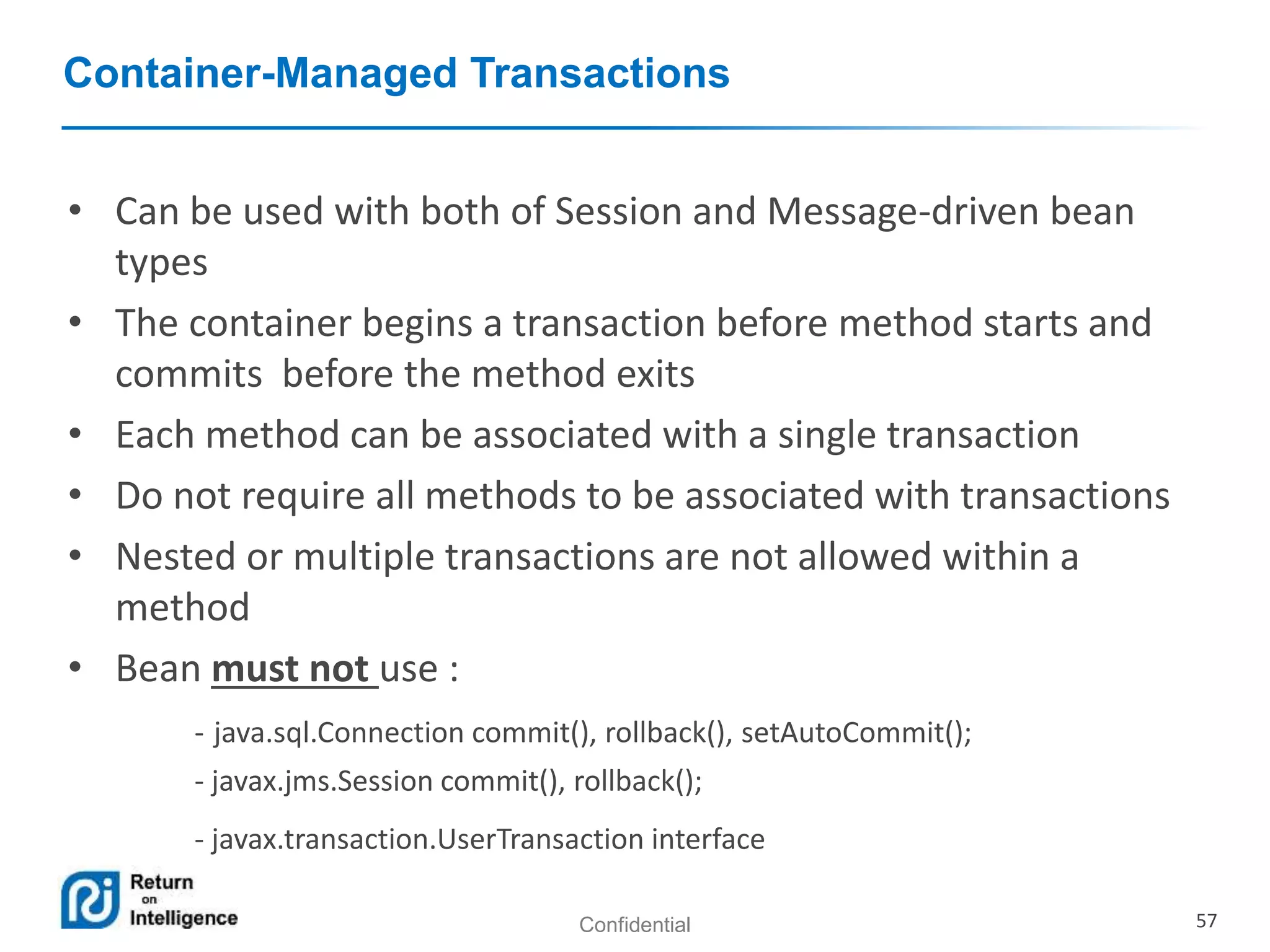
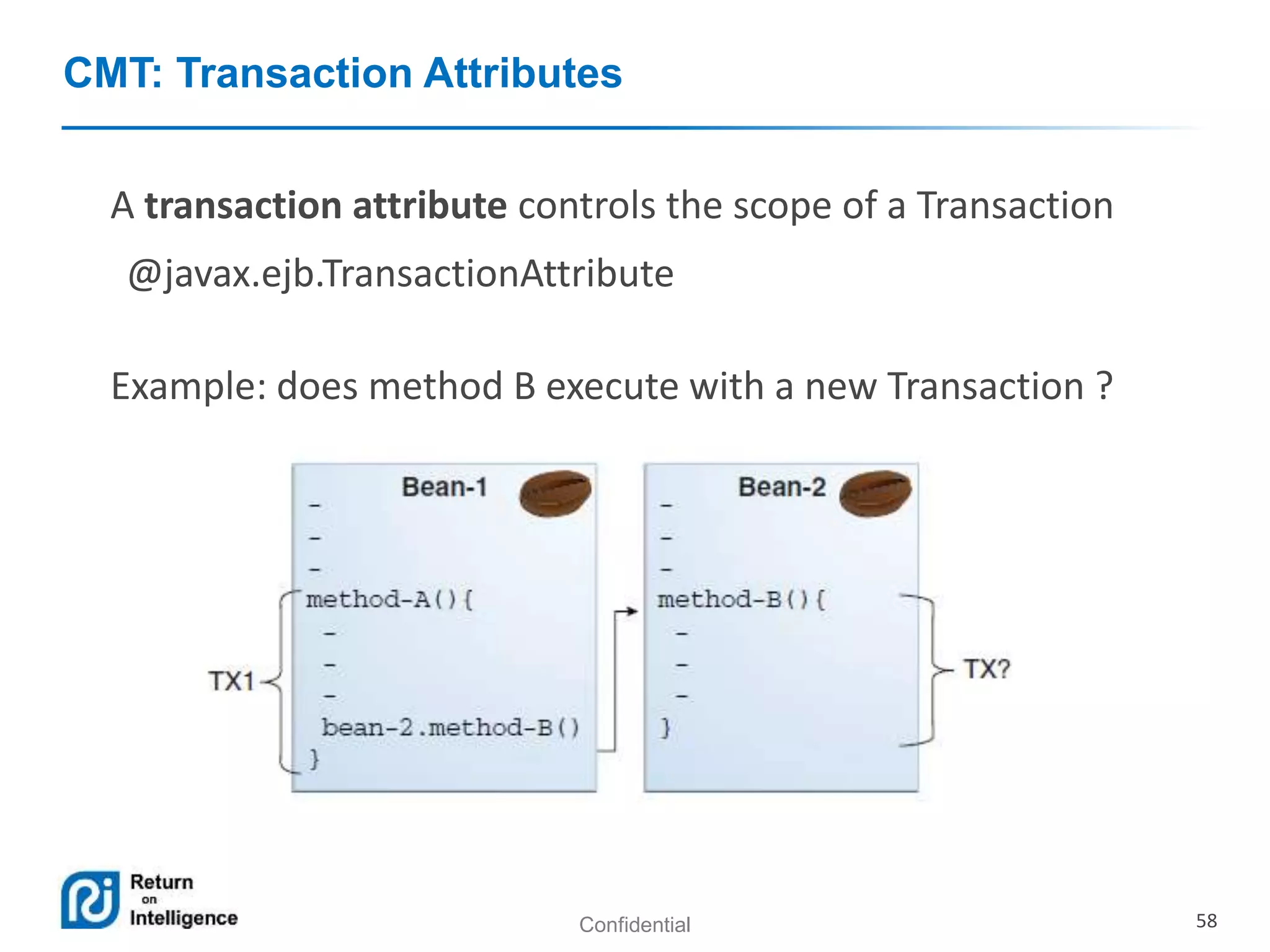
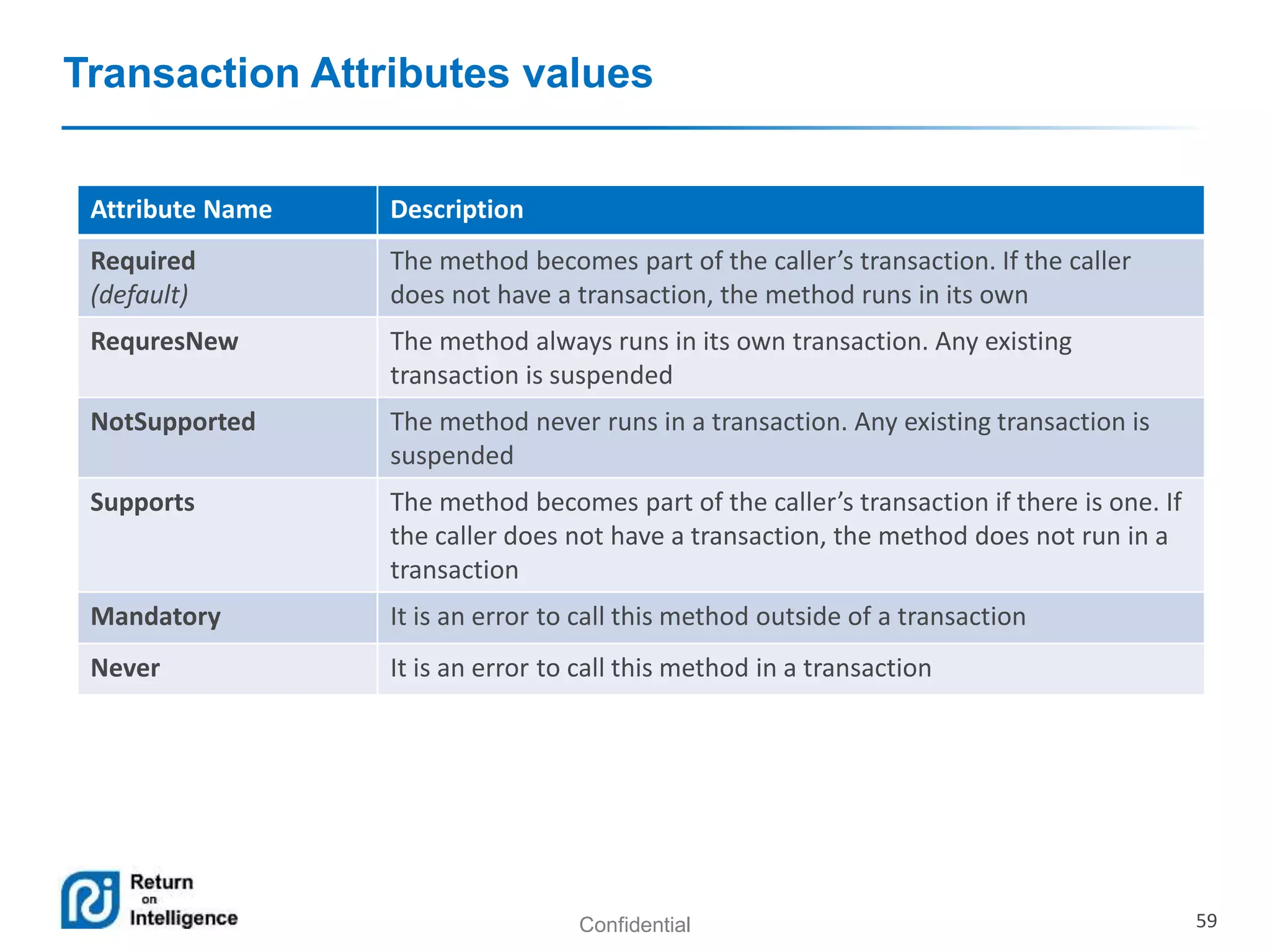
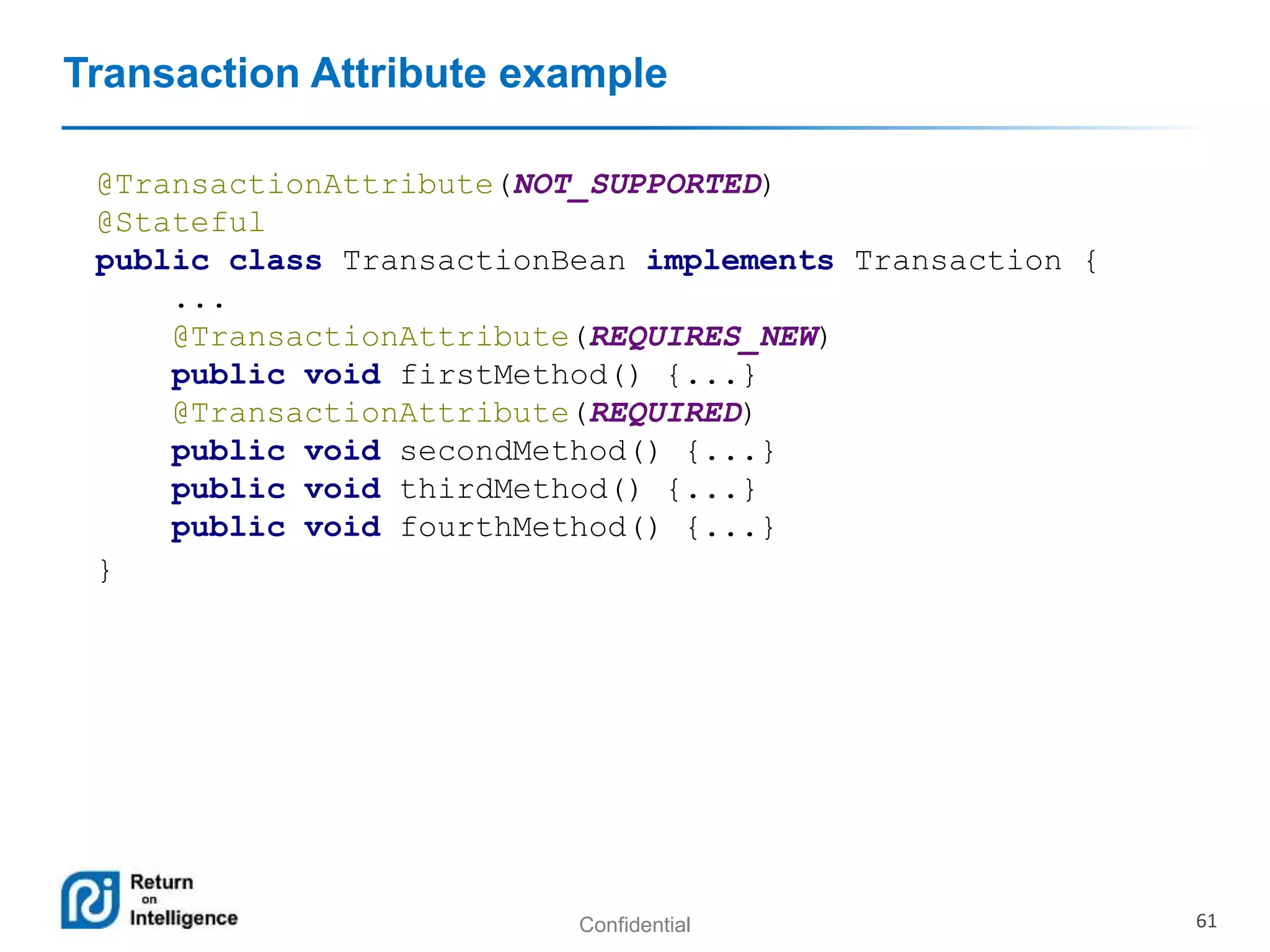
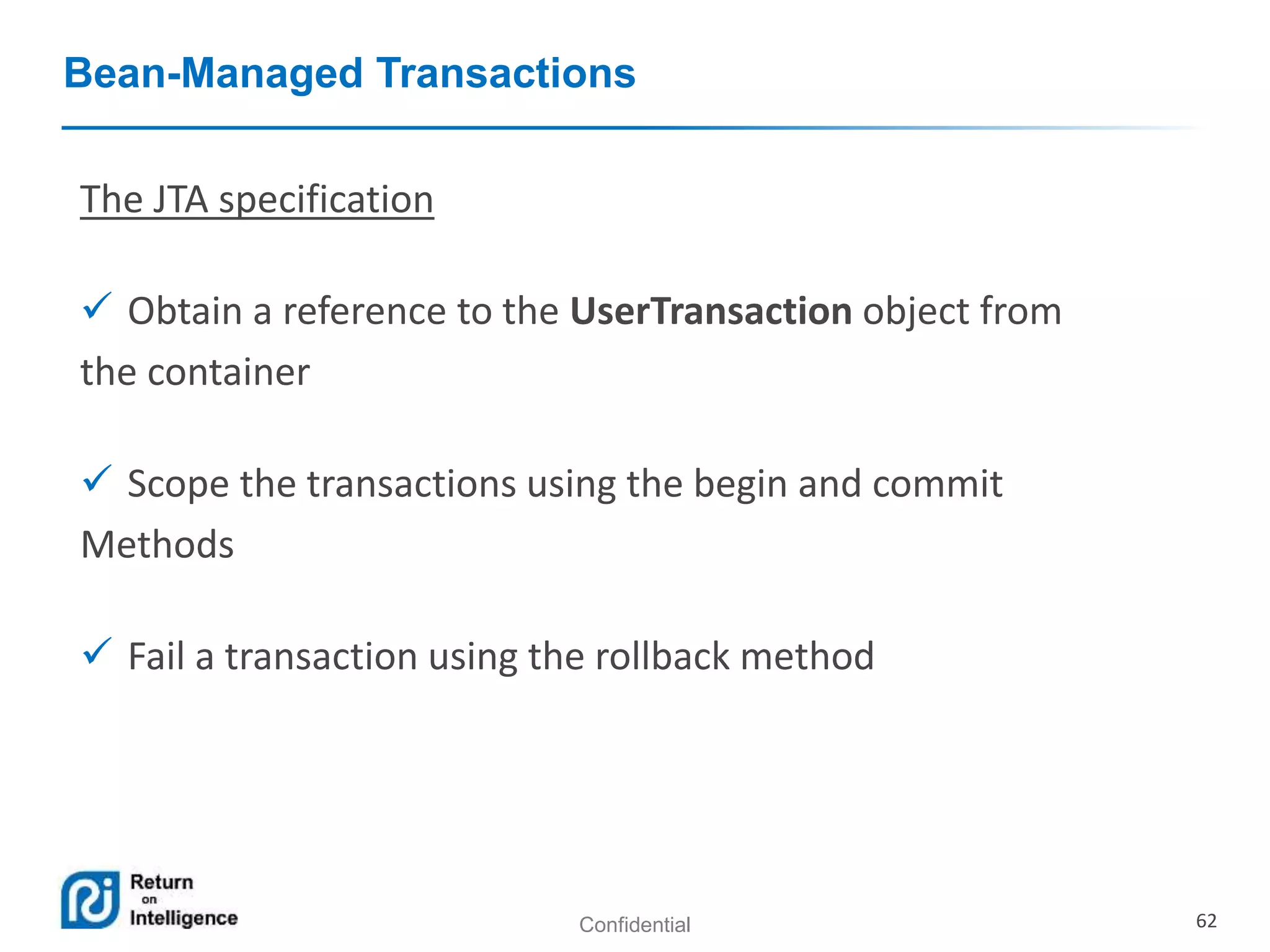
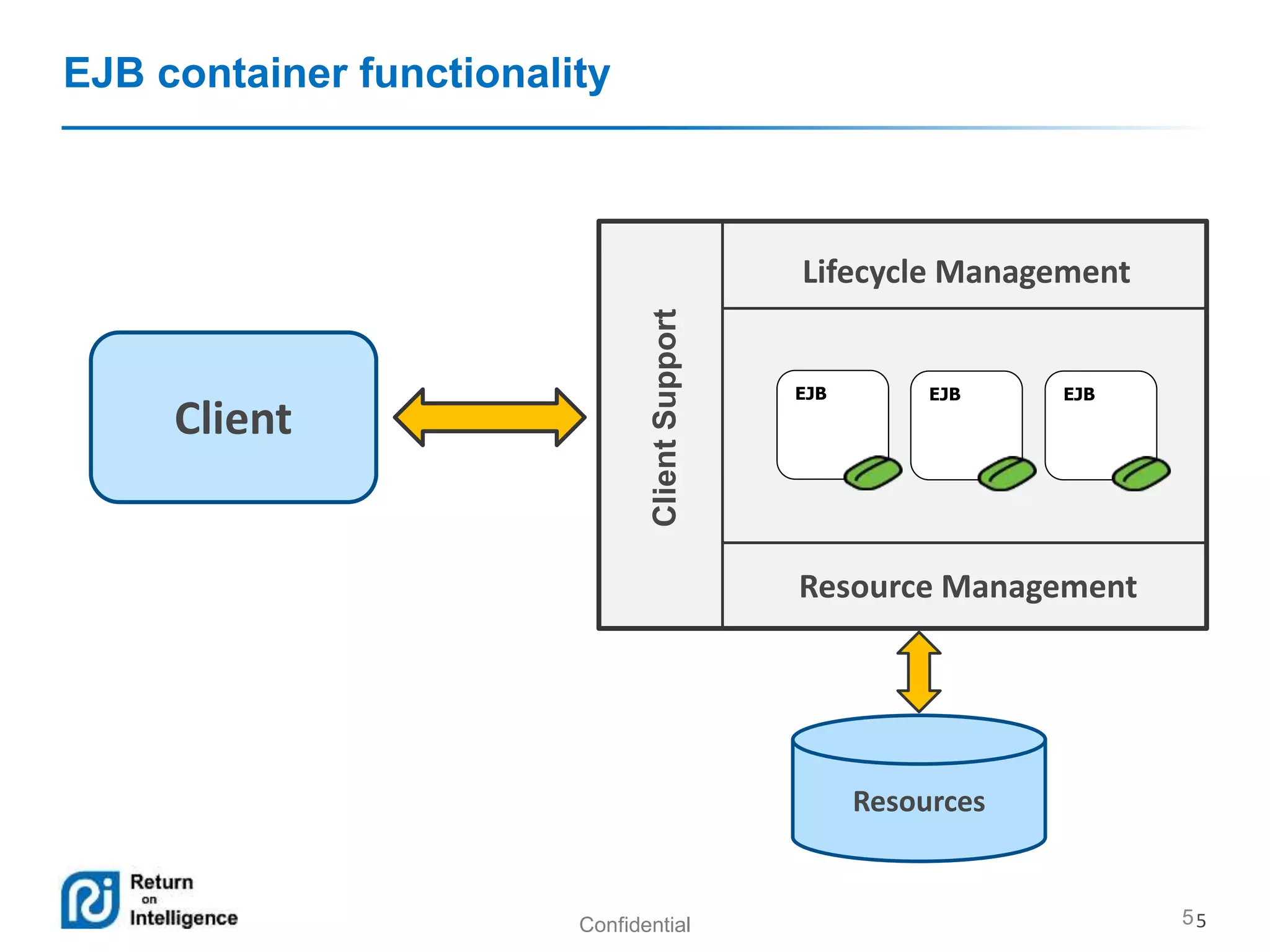
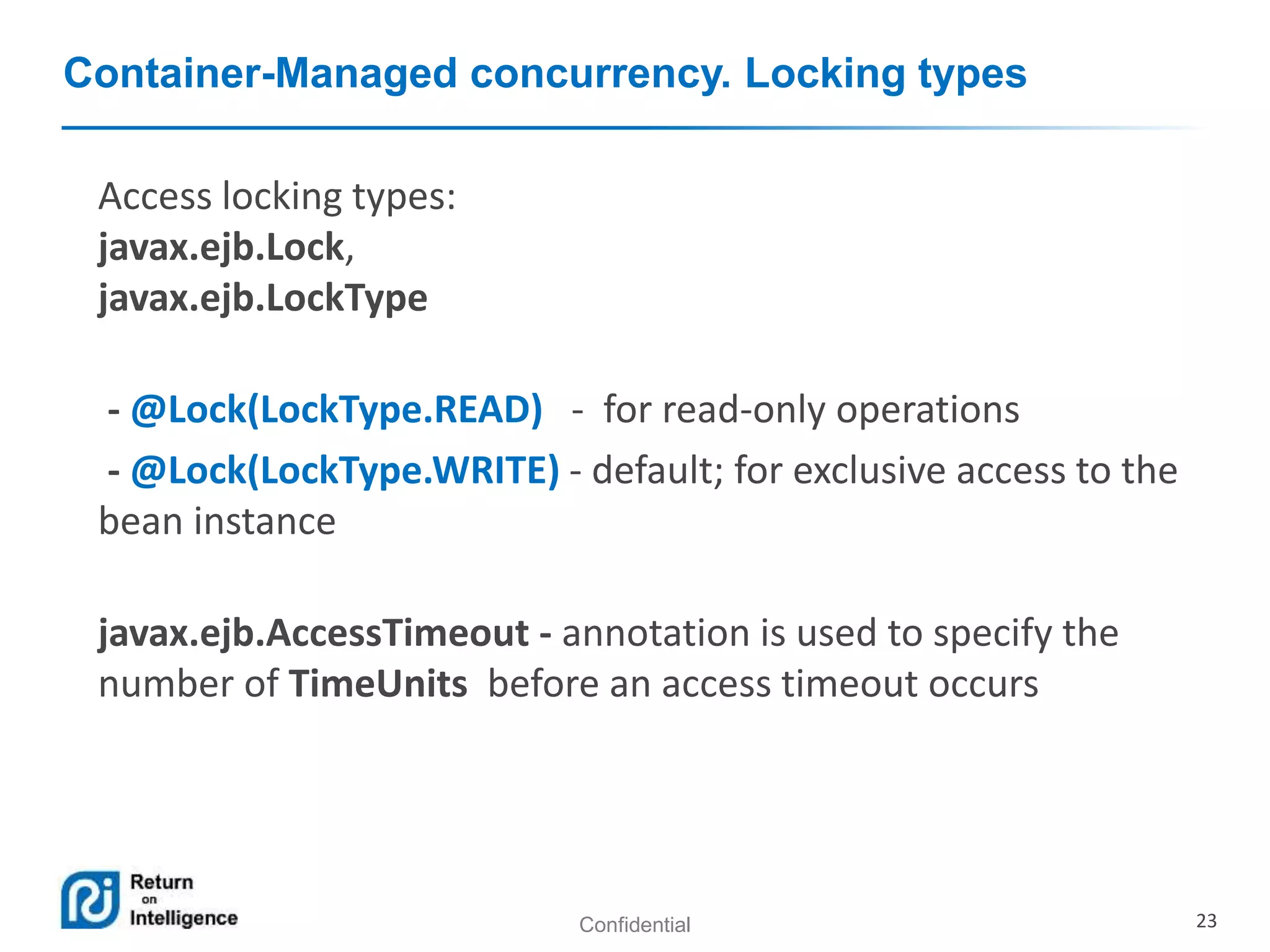
- Transactions, persistence contexts, and resources can be managed by the EJB container through annotations.





















![Confidential 37
Portable JNDI Syntax
Three JNDI namespaces are used for portable JNDI lookups:
java:global – remote beans using JNDI
java:global[/application name]/module name/enterprise bean
name[!interface name]
java:module - local enterprise beans within the same module
(JAR)
java:module/enterprise bean name[!interface name]
java:app - local enterprise beans packaged within the same
application (EAR)
java:app[/module name]/enterprise bean name[!interface name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterpricejavabeansoverview-part1-151015152259-lva1-app6891/75/Introduction-to-EJB-38-2048.jpg)