The document provides an introduction to embedded systems, including:
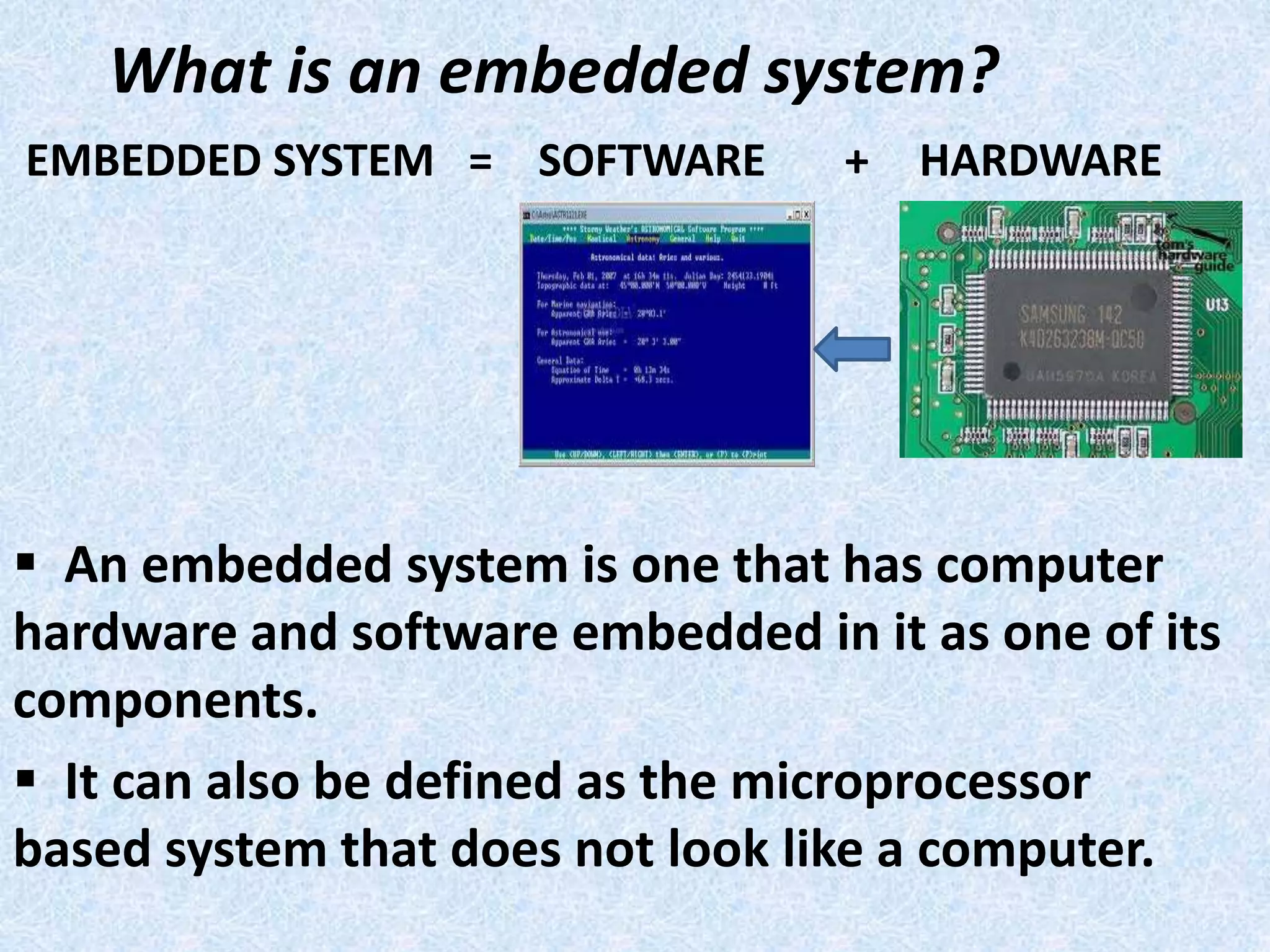
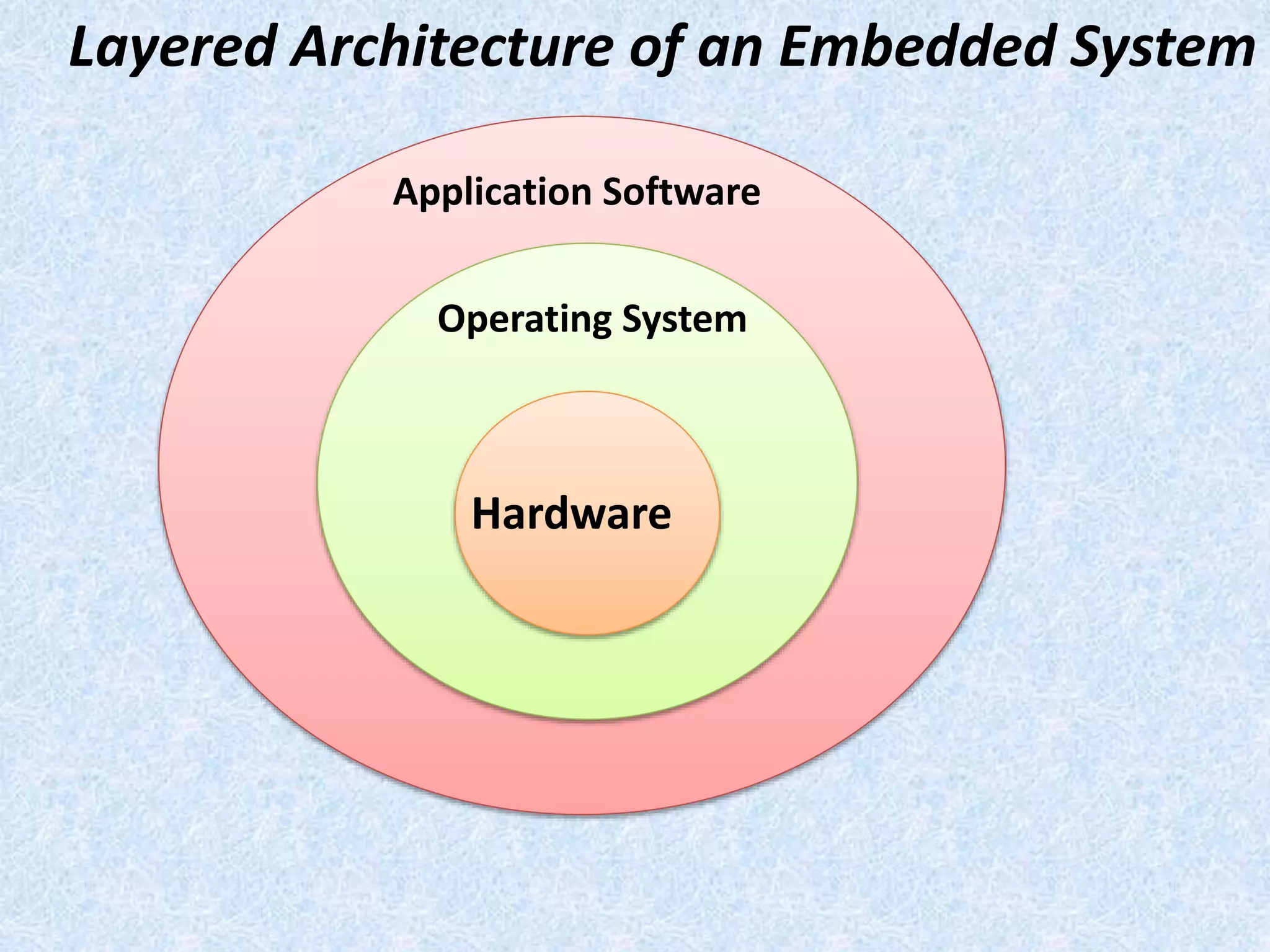
- An embedded system combines both hardware and software, with computer hardware and software embedded as a component.
- Early examples include NASA's Apollo guidance computer and the Autonetics D-17 guidance computer.
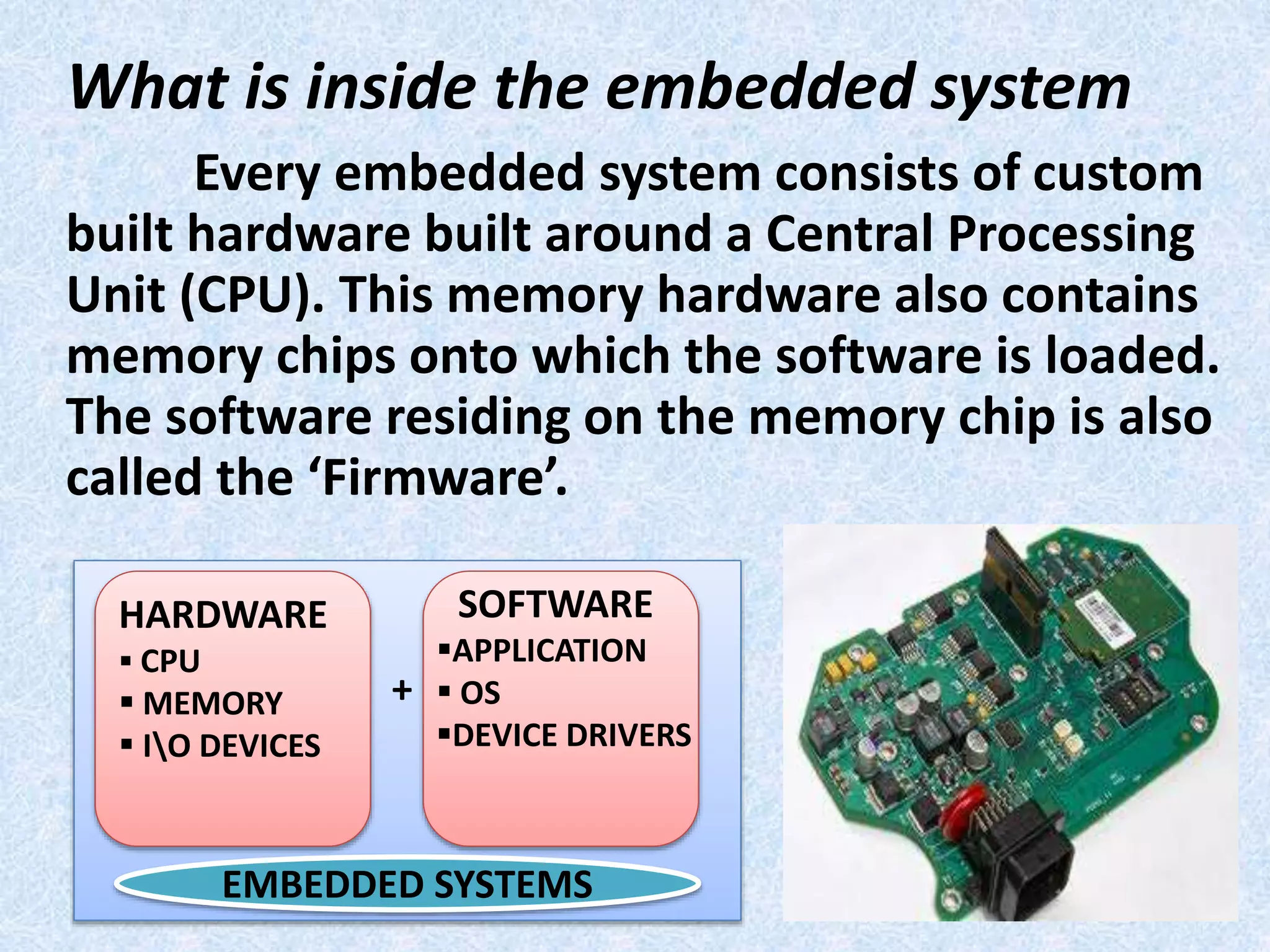
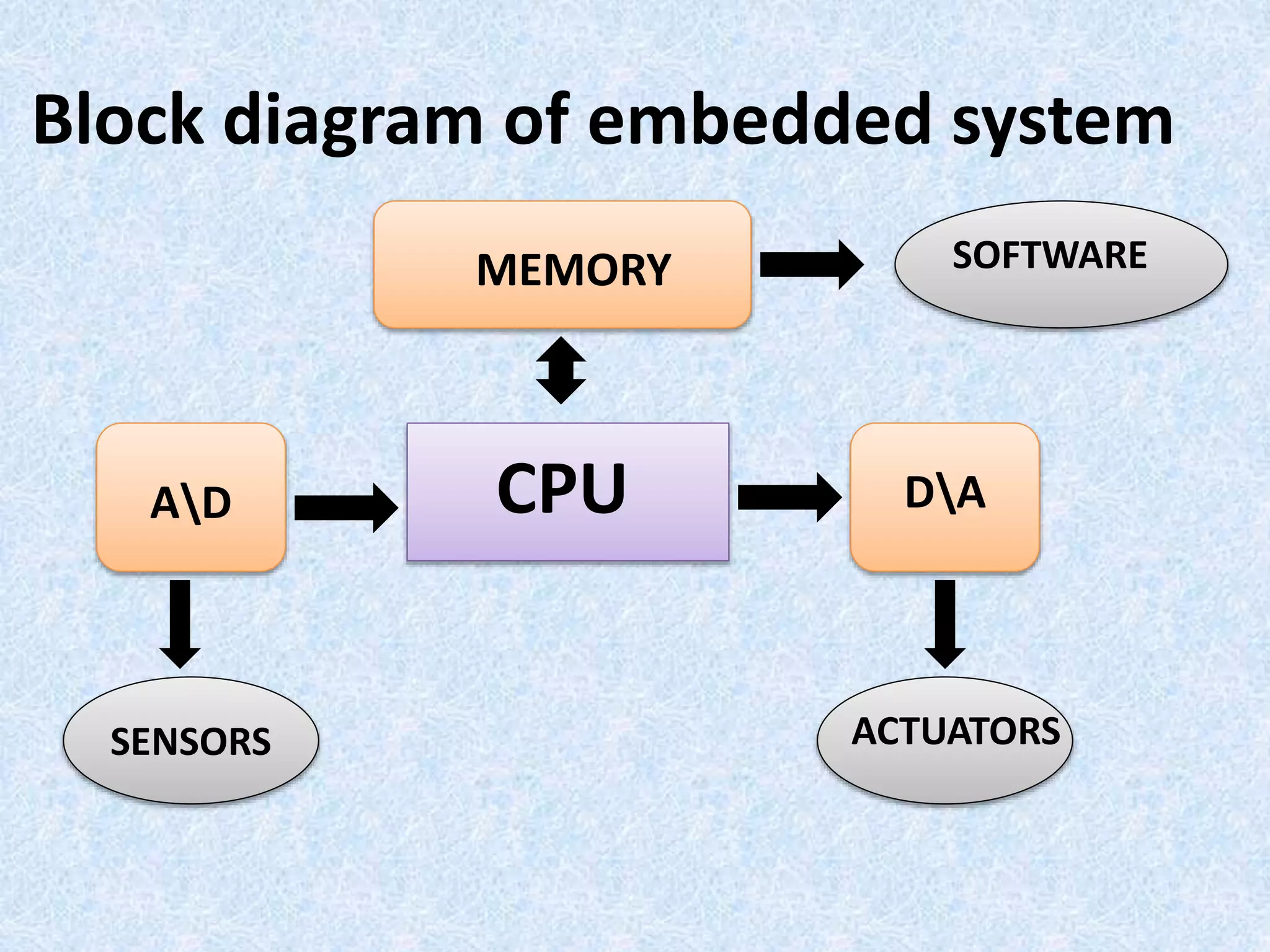
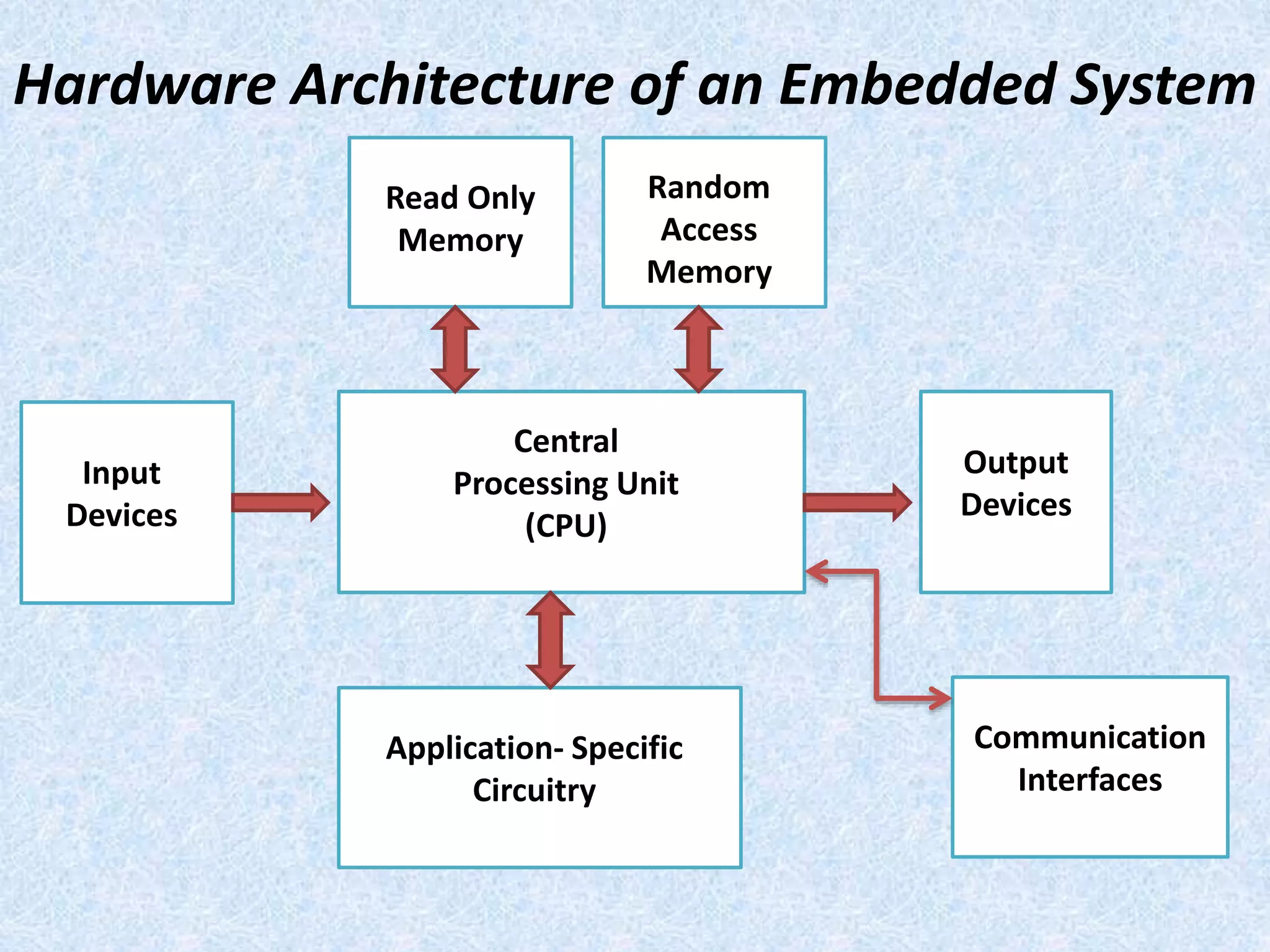
- Embedded systems typically include a CPU, memory, and input/output devices integrated into a single microprocessor-based unit.
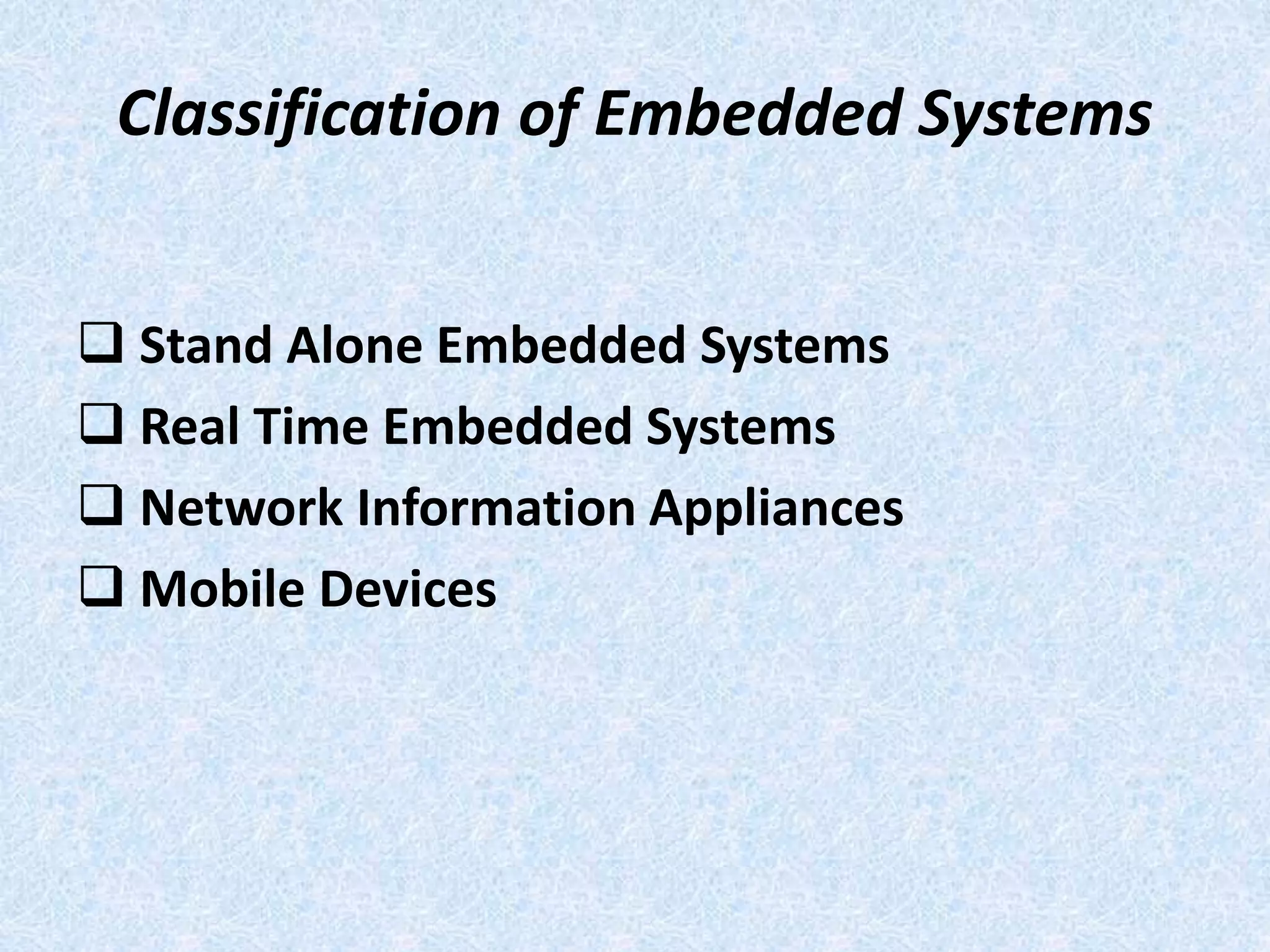
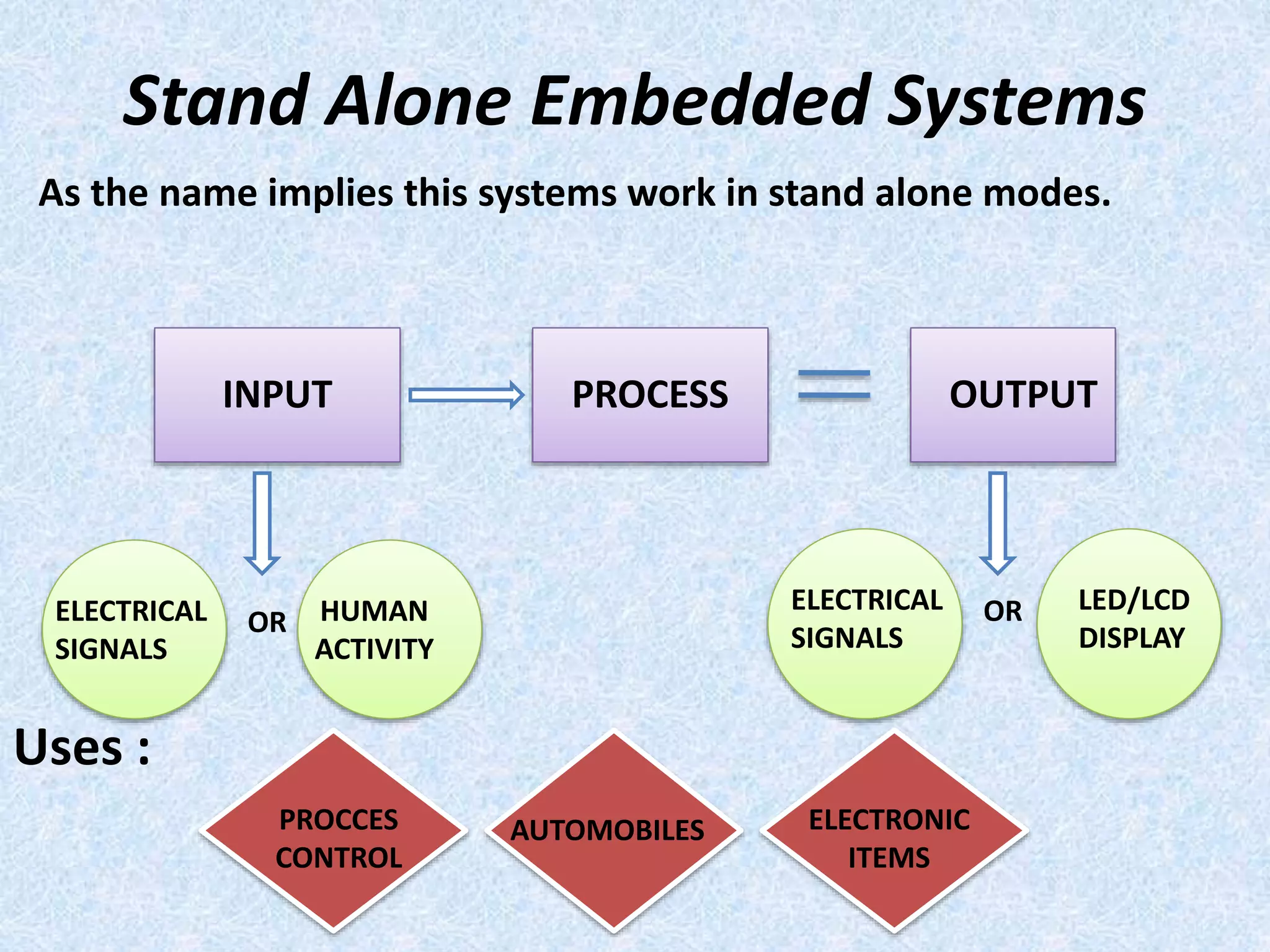
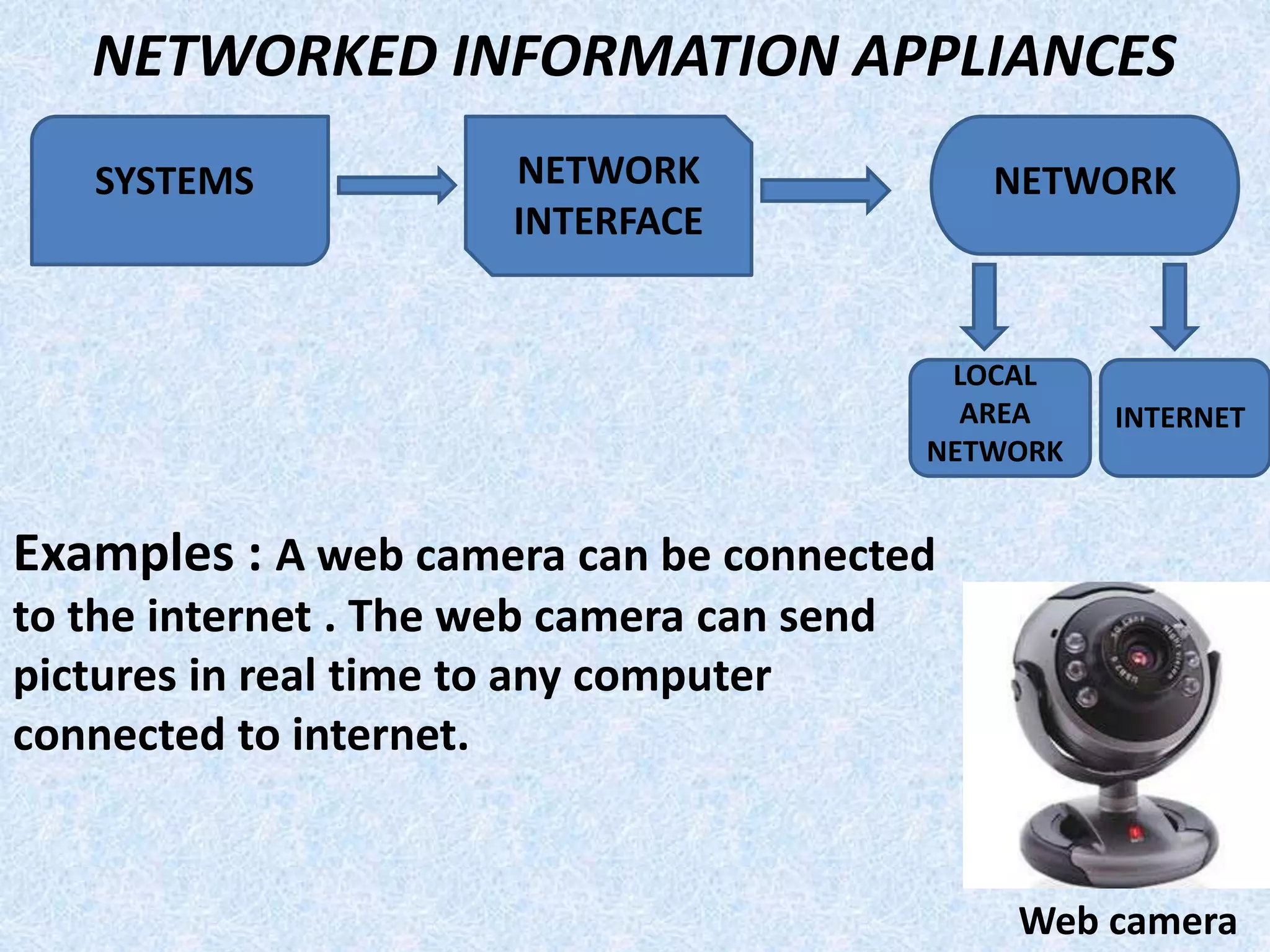
- They are classified as standalone, real-time, network information appliances, or mobile devices depending on their use and connectivity.
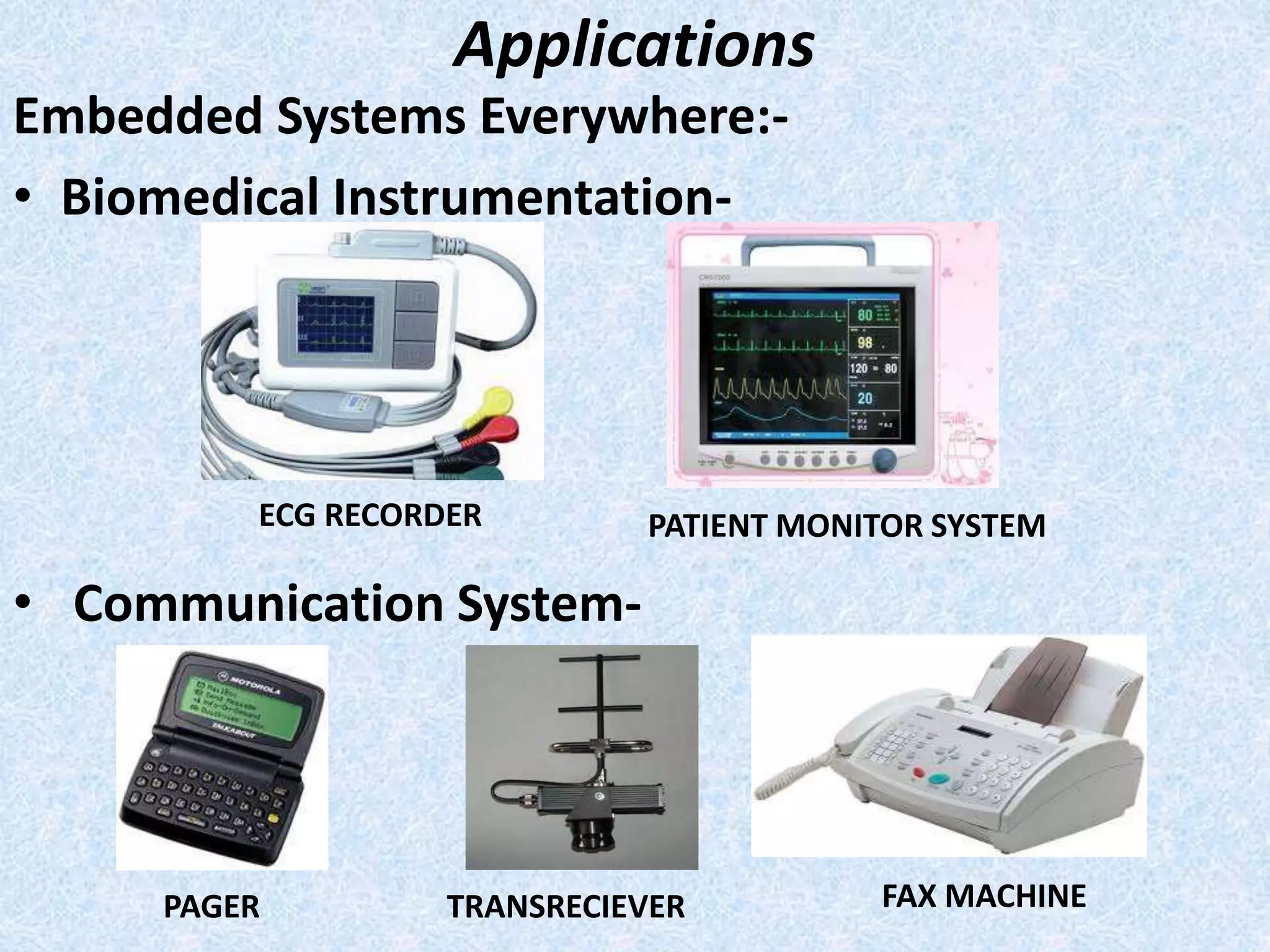
- Embedded systems have wide applications in areas like industrial control, scientific instruments, biomedical devices, mobile phones and more.