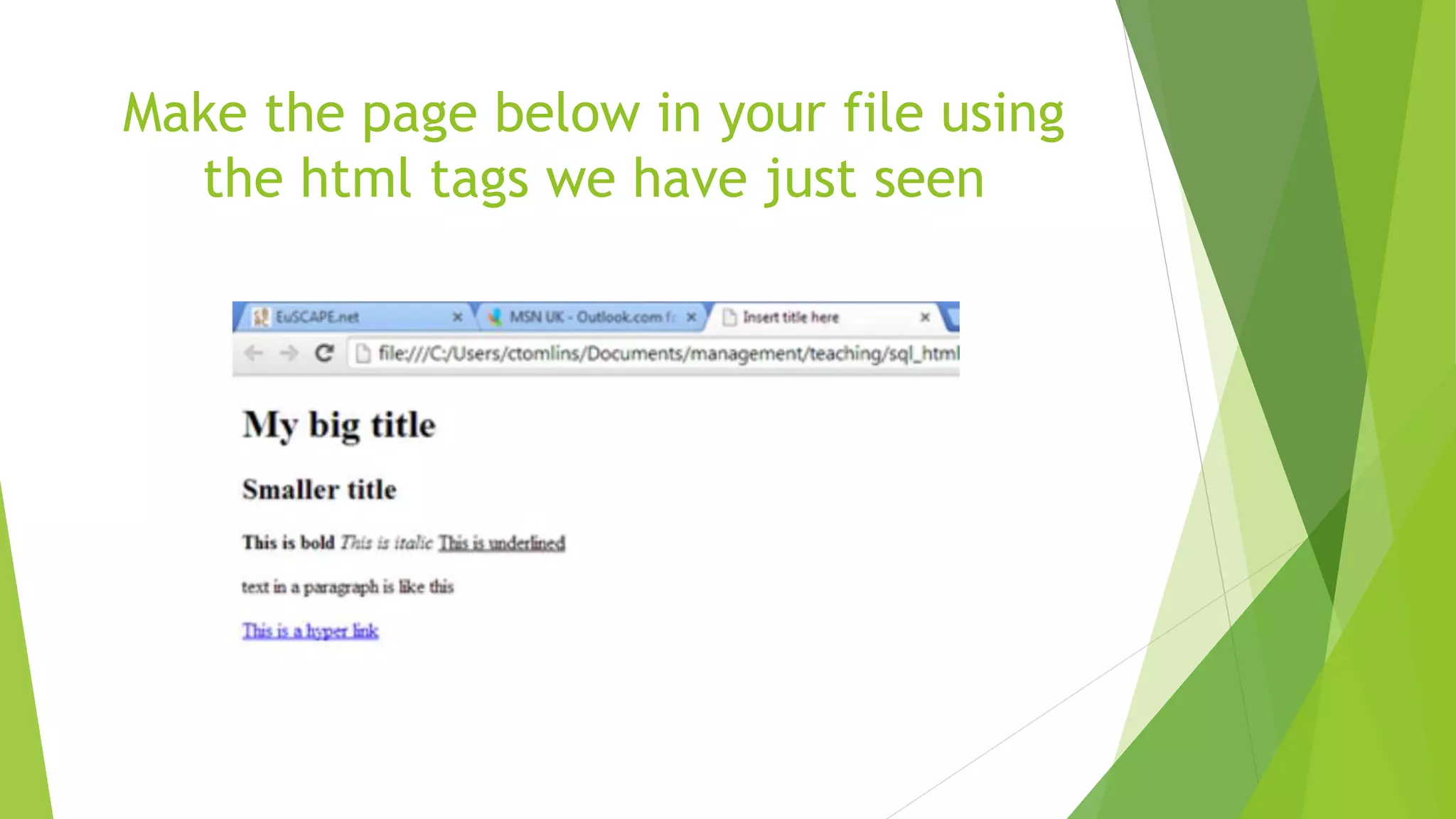
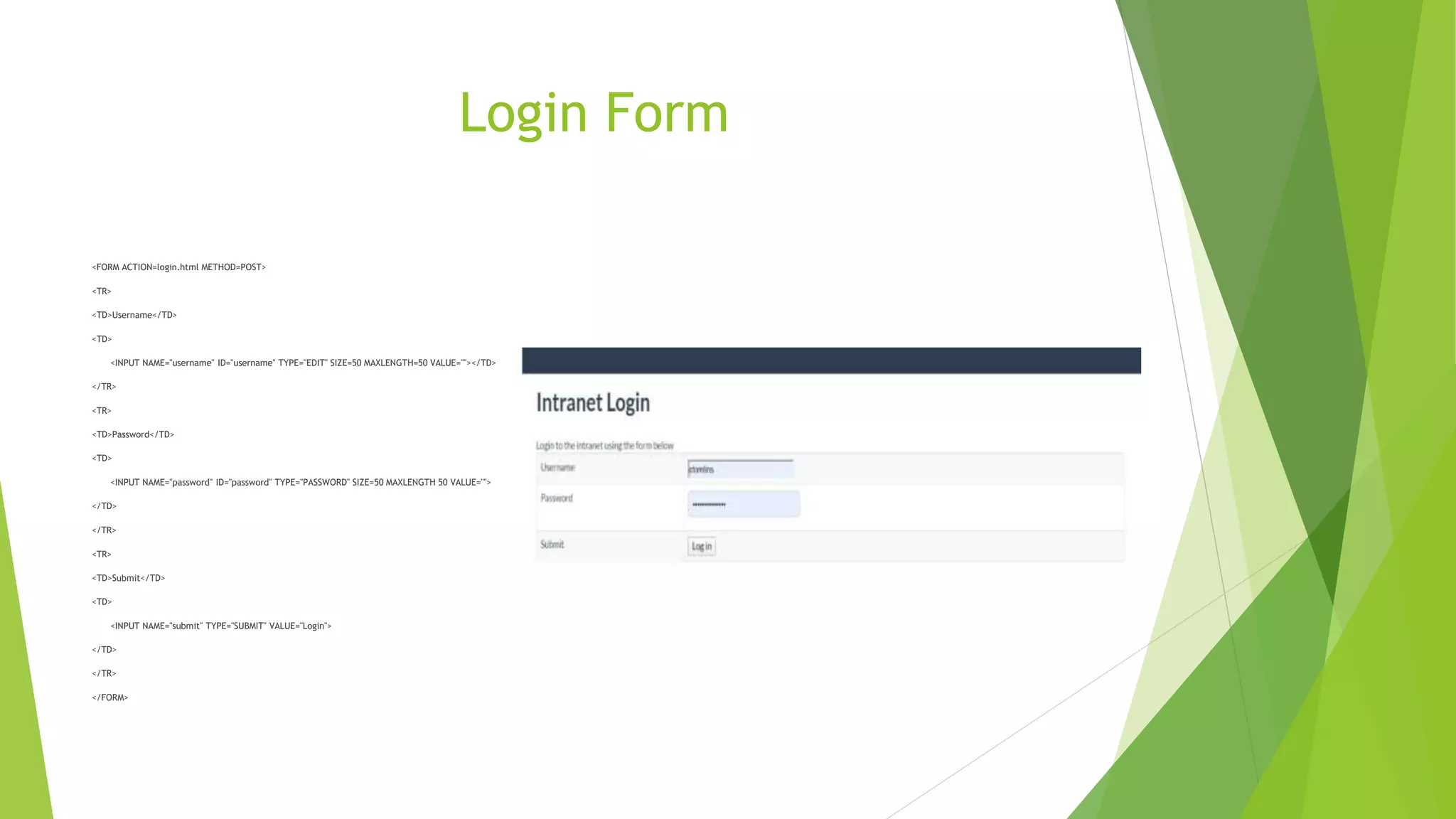
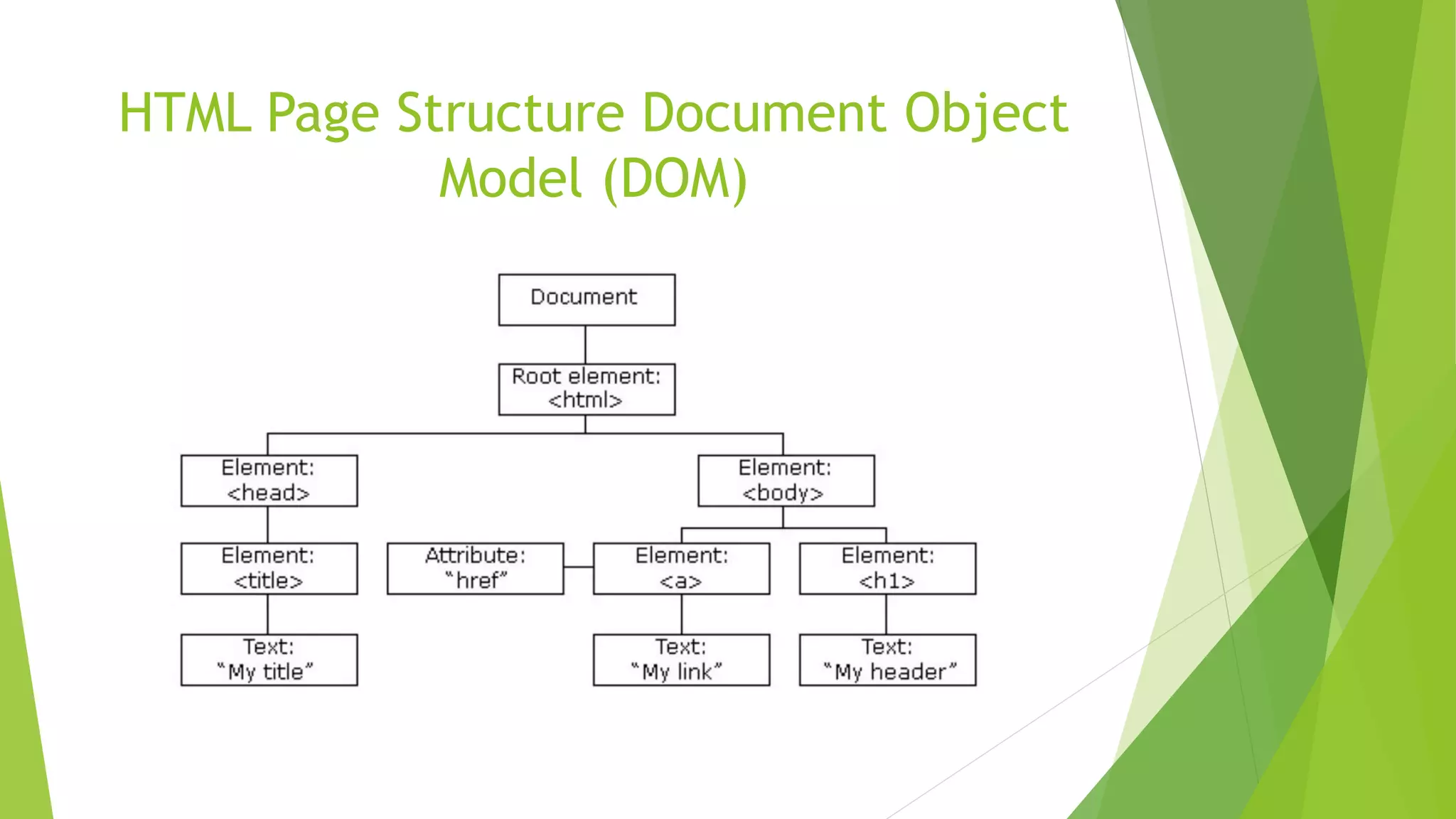
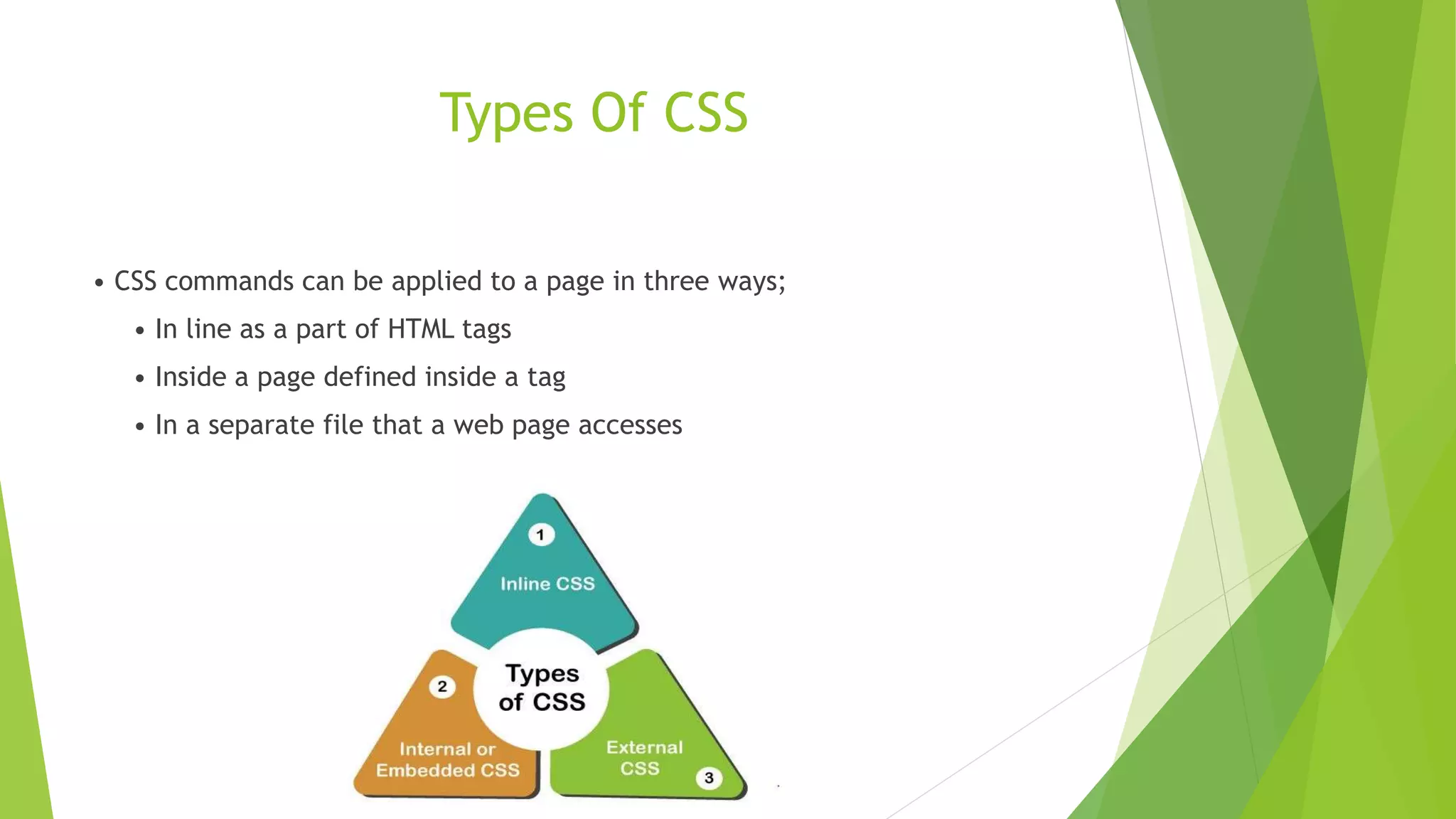
This document provides an introduction to HTML and CSS. It begins with an outline and then defines HTML as the language of the web, consisting of tags that format text. It describes common HTML tags like headings, paragraphs, links, and lists. It also covers HTML forms, tables, and the DOM tree. For CSS, it defines CSS as describing how HTML elements are displayed and types of CSS like inline, internal, and external stylesheets. It provides examples of using CSS selectors by ID, class, and element. In the end, it briefly introduces the Bootstrap framework for responsive web design across devices.