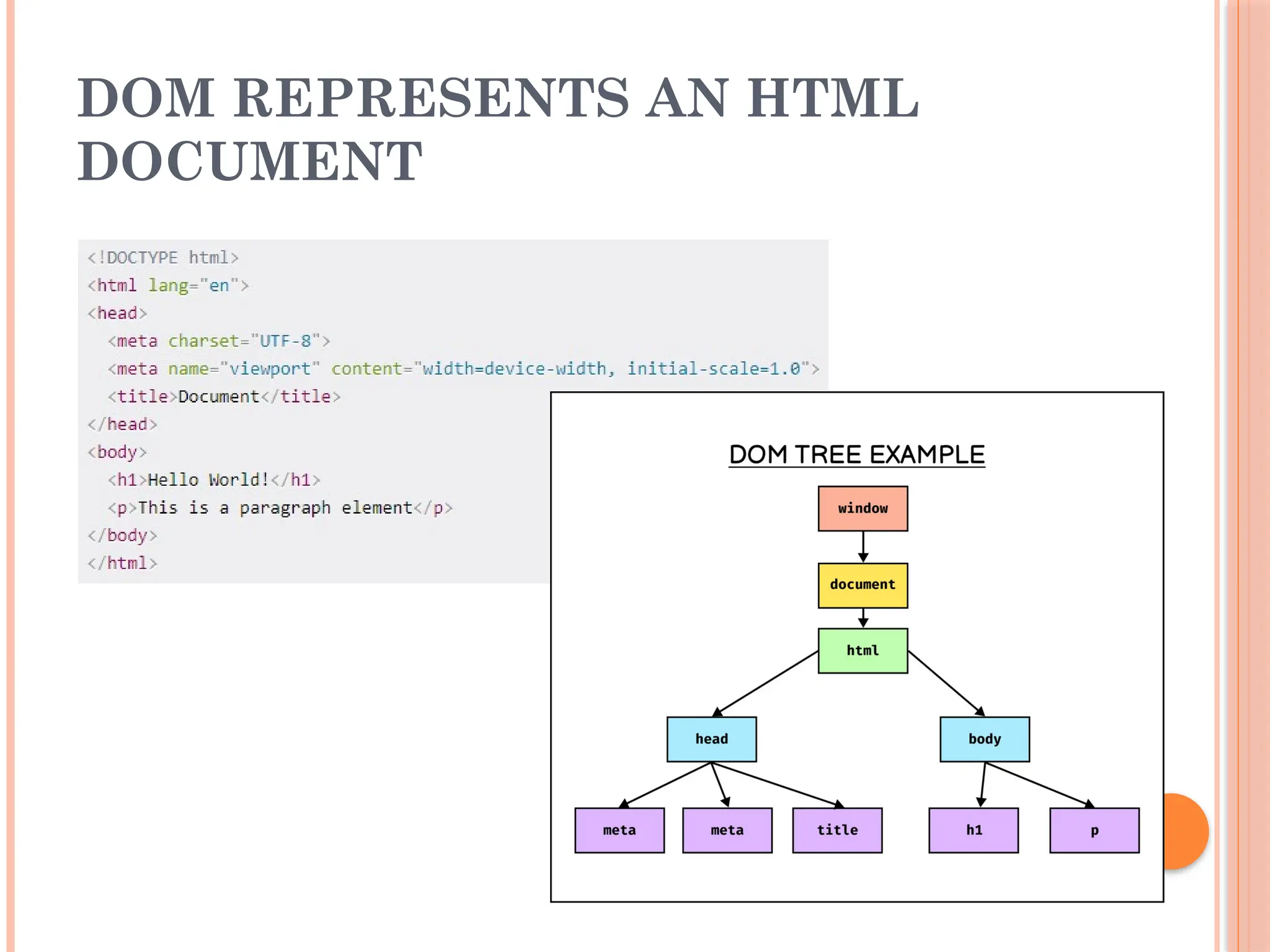
The document provides an introduction to JavaScript, focusing on the Document Object Model (DOM) and user input handling. It explains the significance of DOM manipulation for creating interactive web applications and details various methods for accessing and modifying DOM elements. The content also covers event handling in JavaScript, including event listeners and how to manage user input from HTML forms.