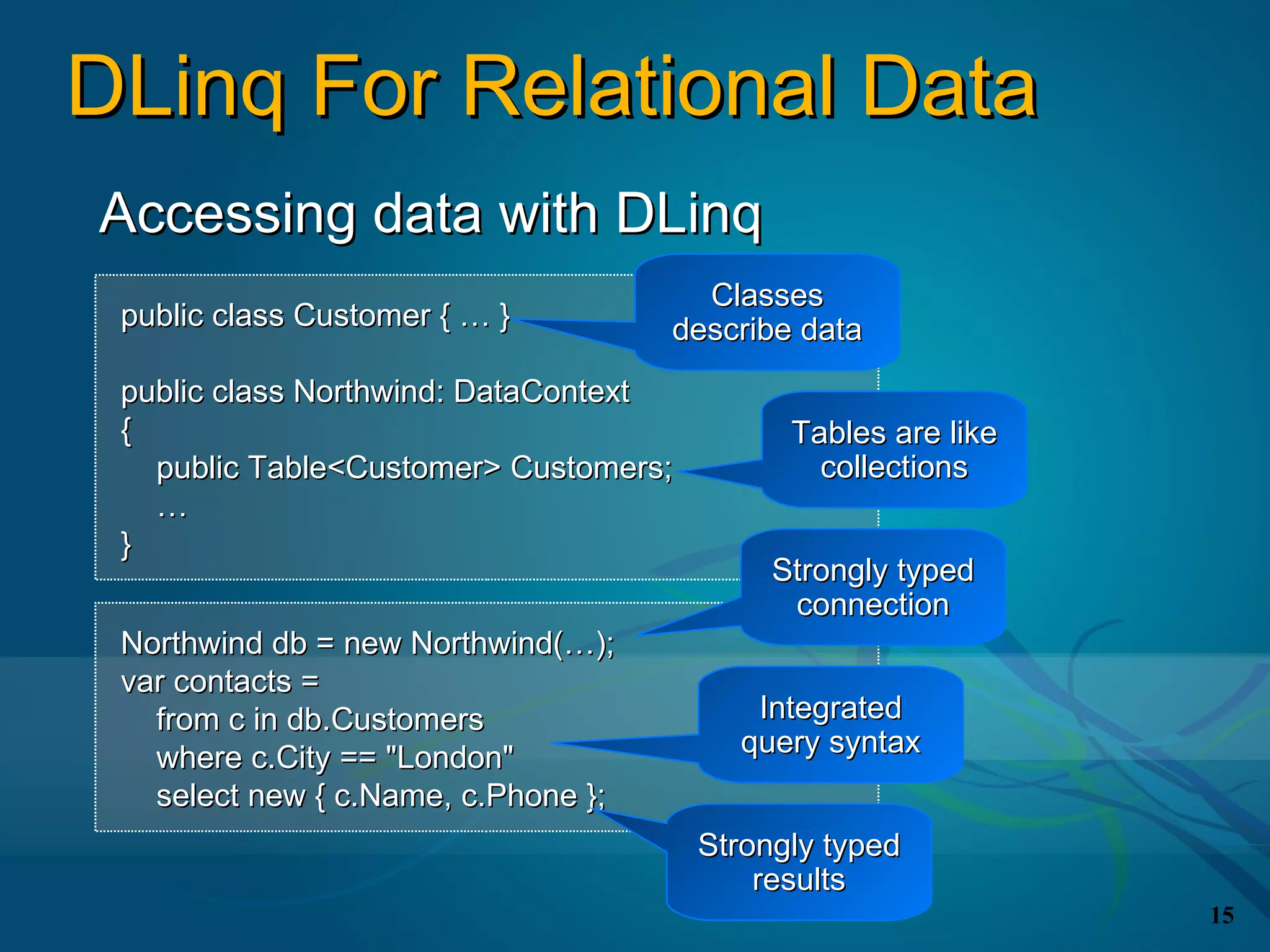
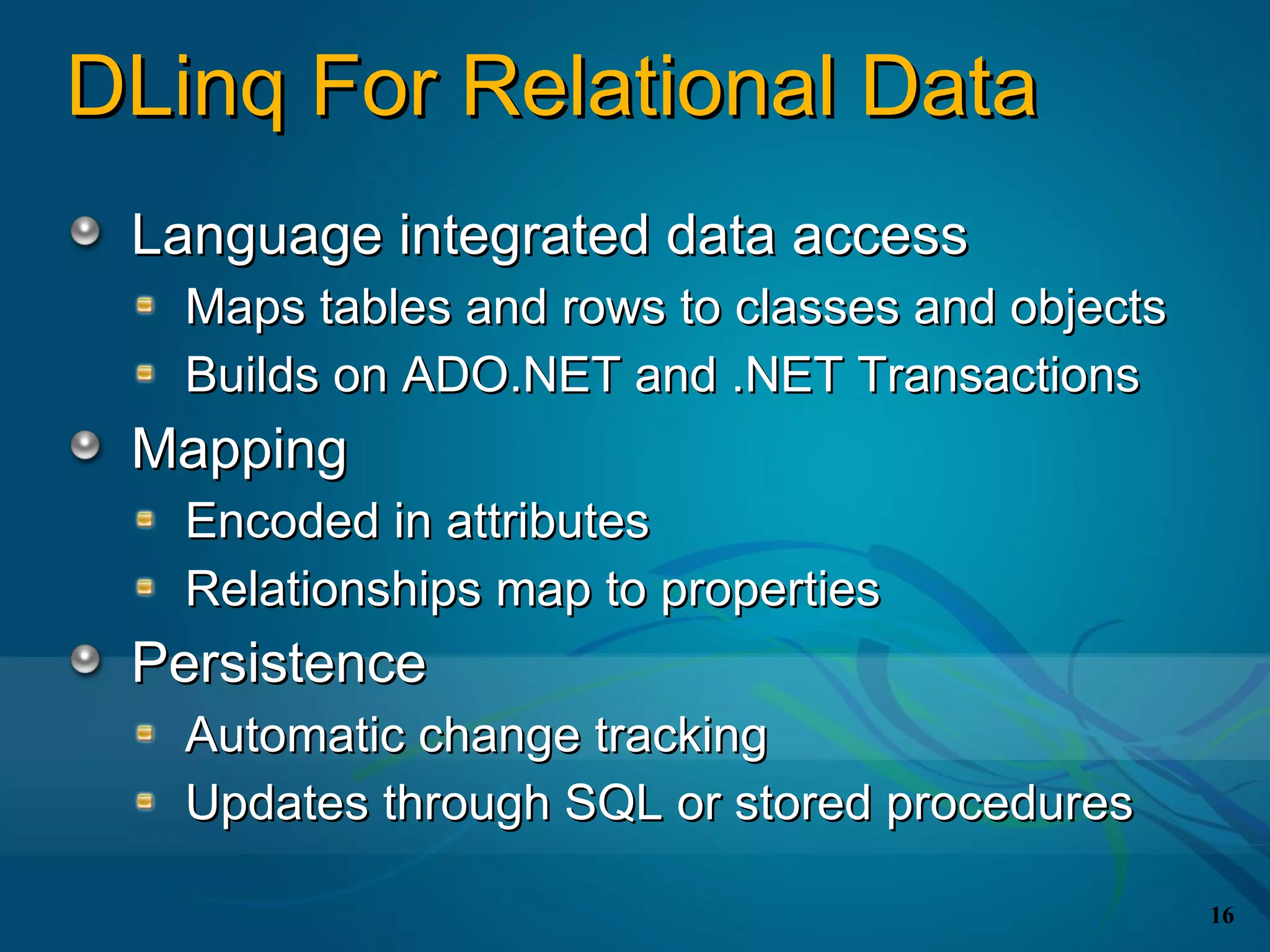
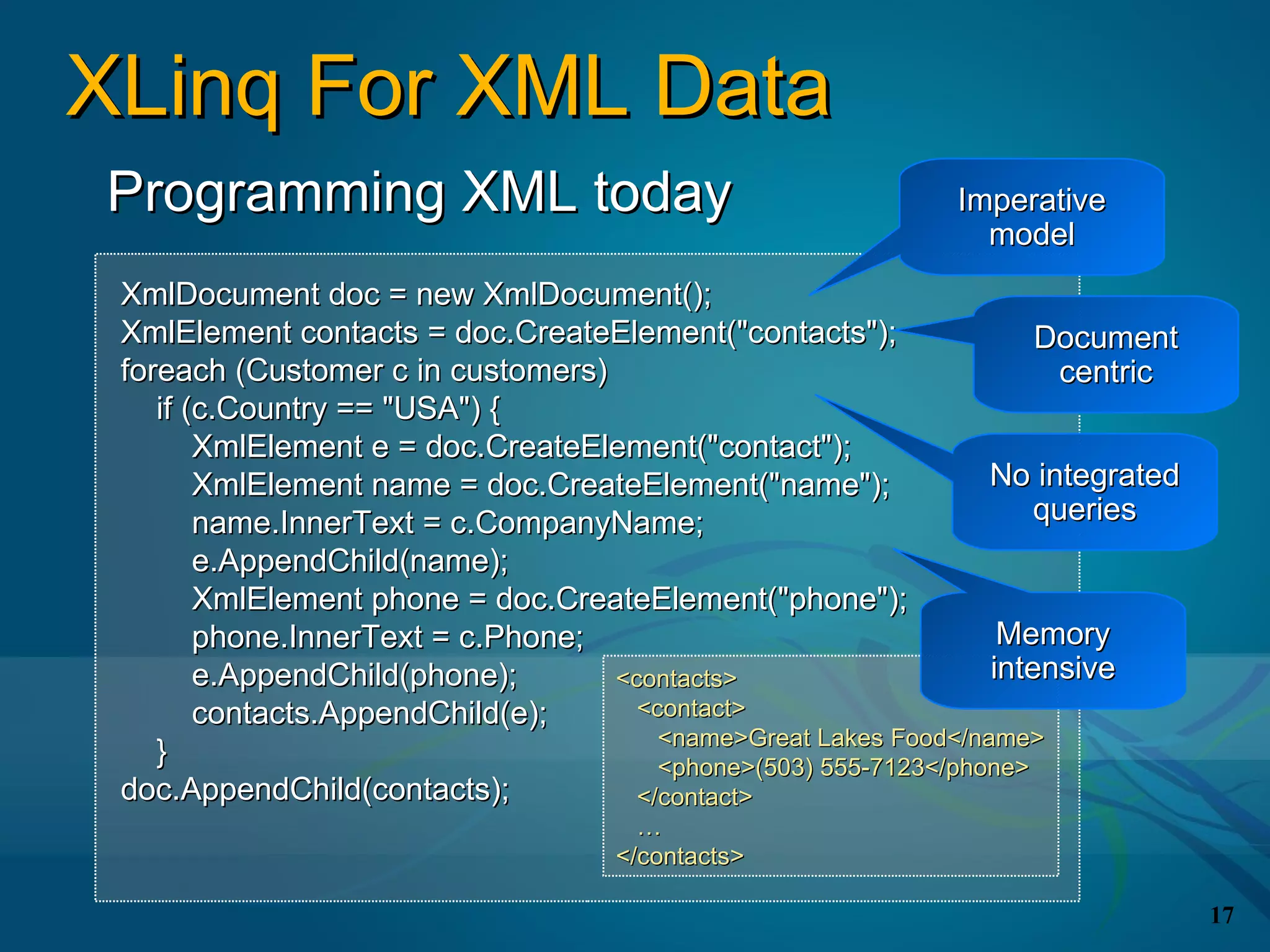
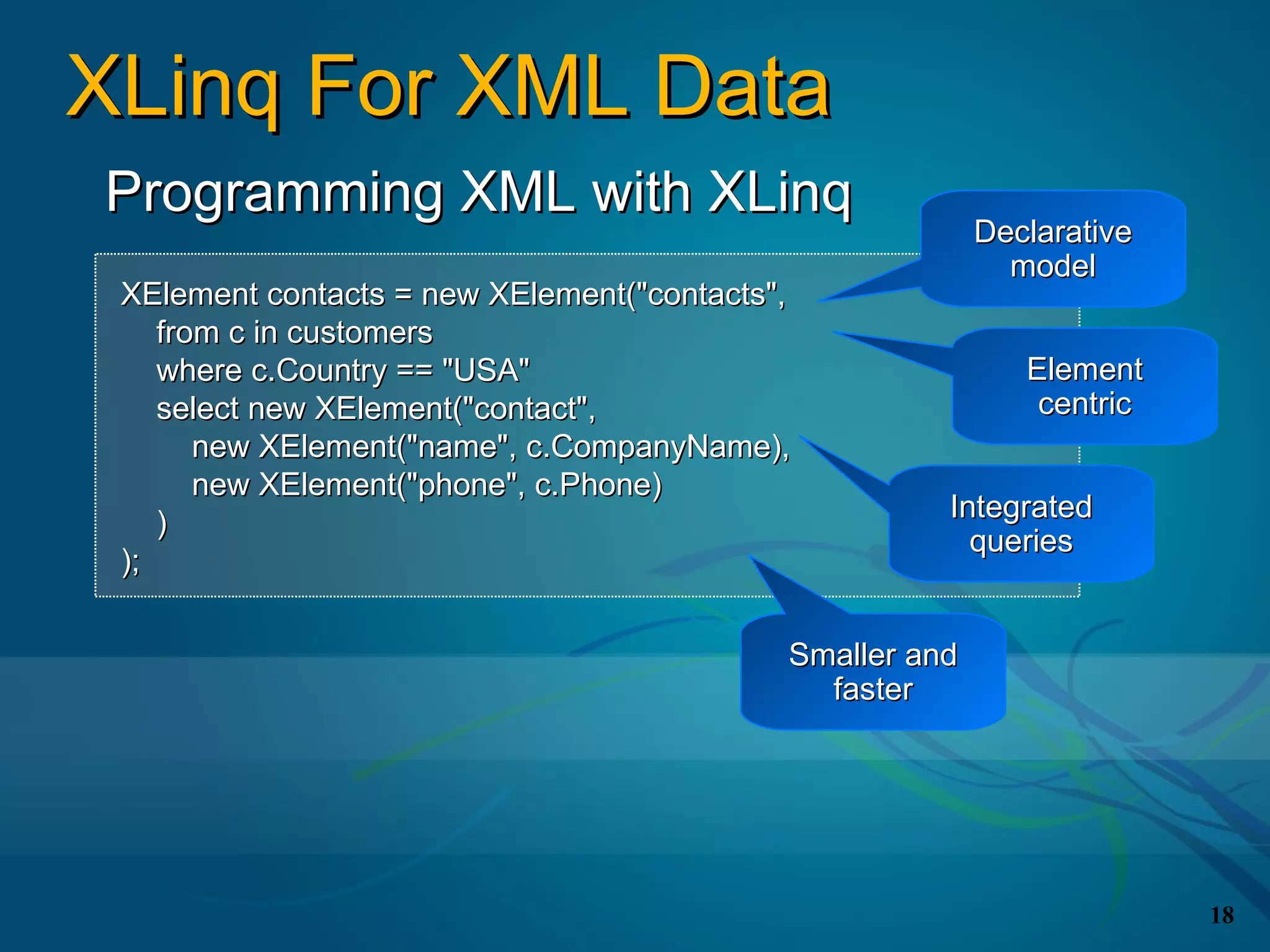
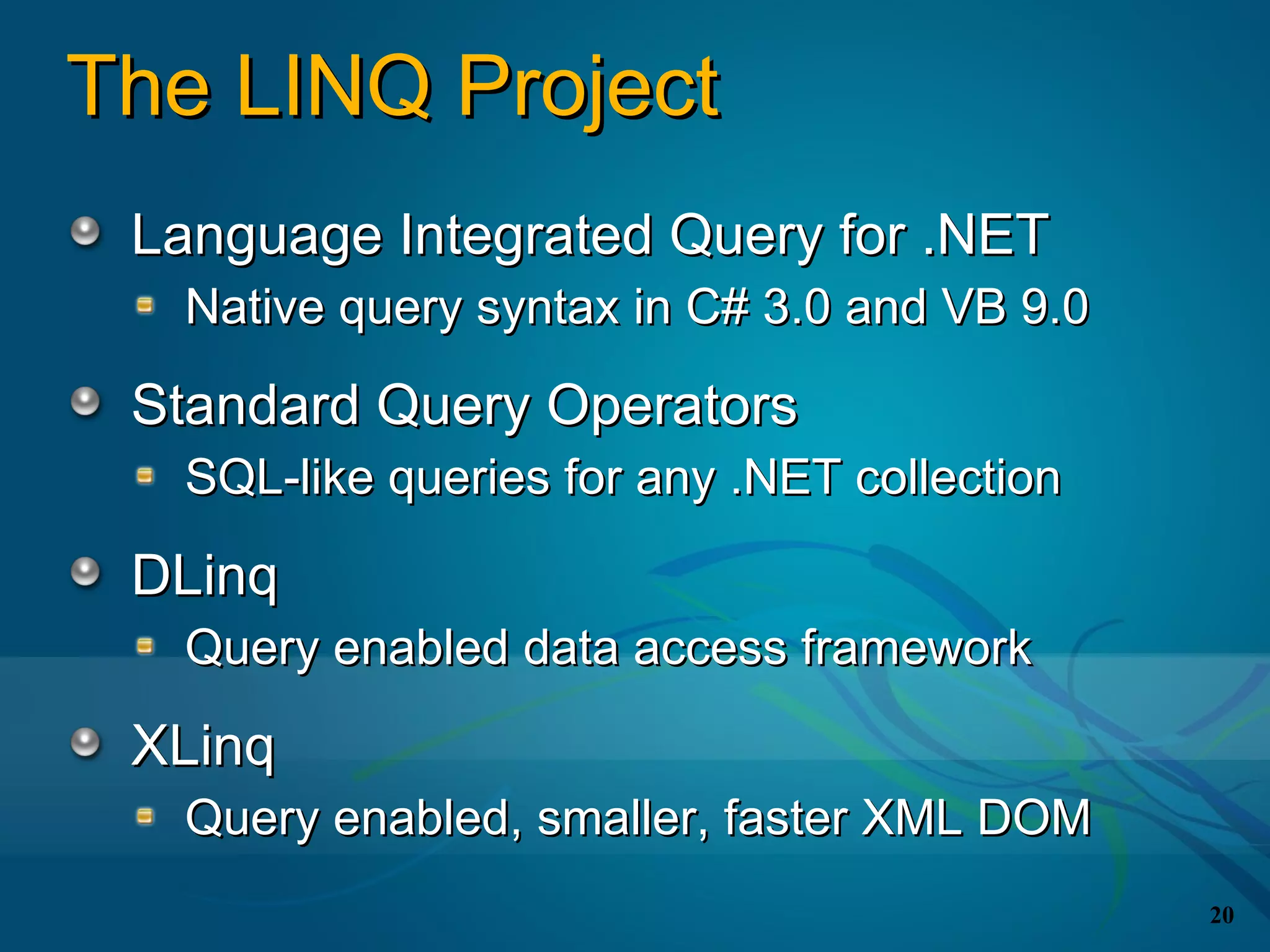
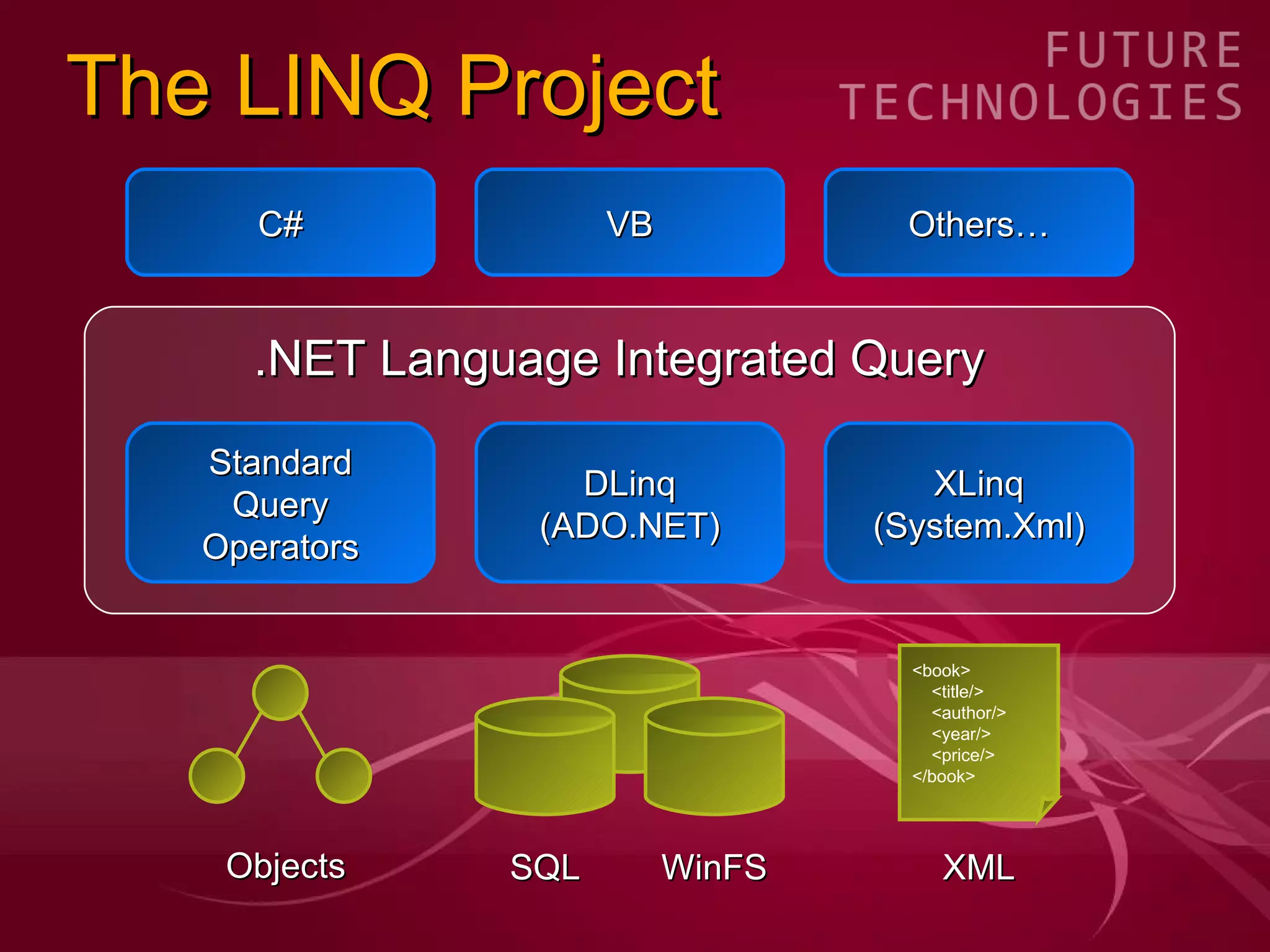
The document covers the LINQ (Language Integrated Query) project in .NET, detailing its components like DLINQ for relational data and XLINQ for XML data. It discusses C# 3.0 innovations including lambda expressions, query expressions, and type inference, emphasizing how LINQ unifies querying across different data types. Key features include standard query operators and the benefits of using LINQ for type safety, extensibility, and improved query capabilities.


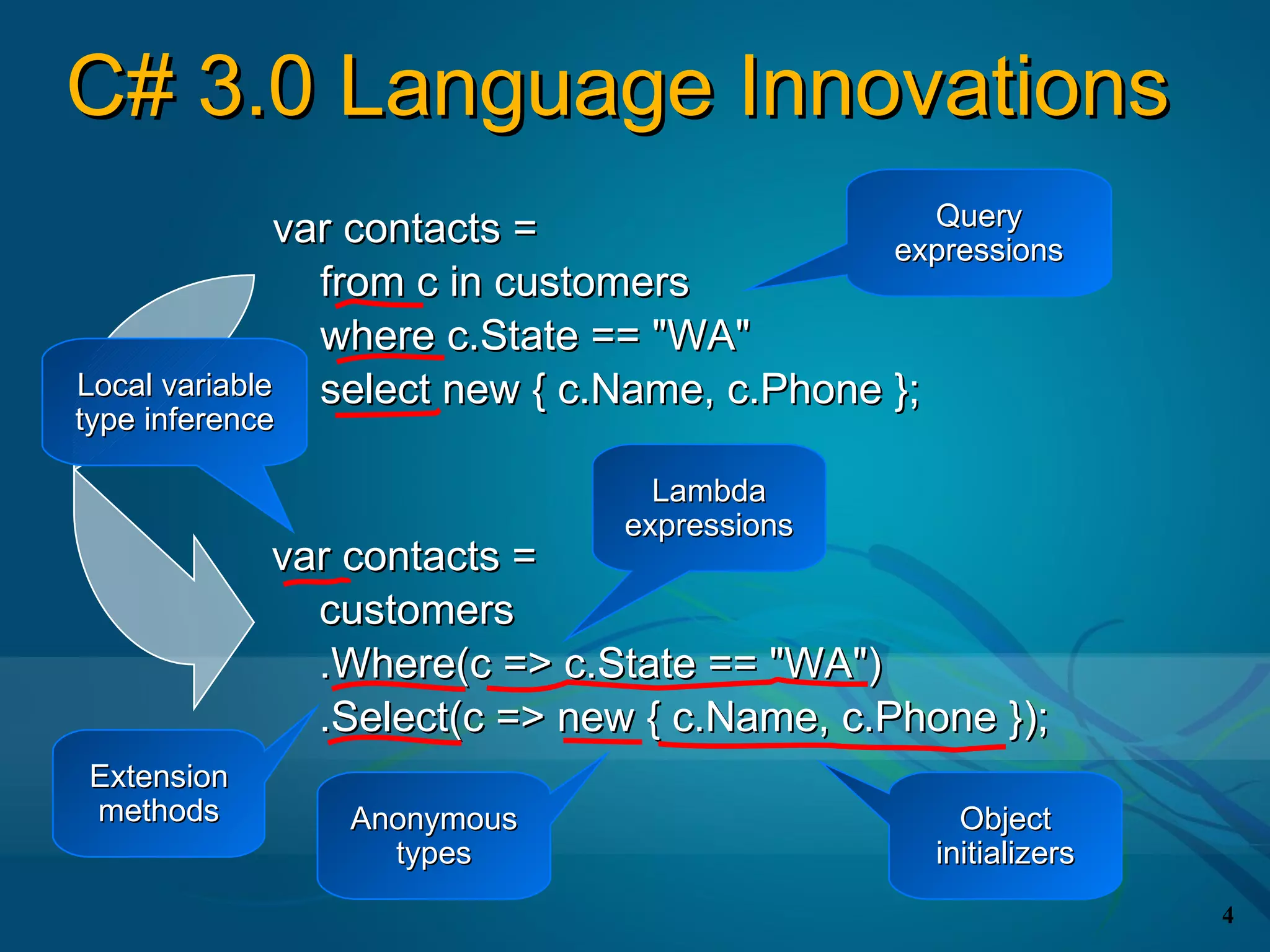

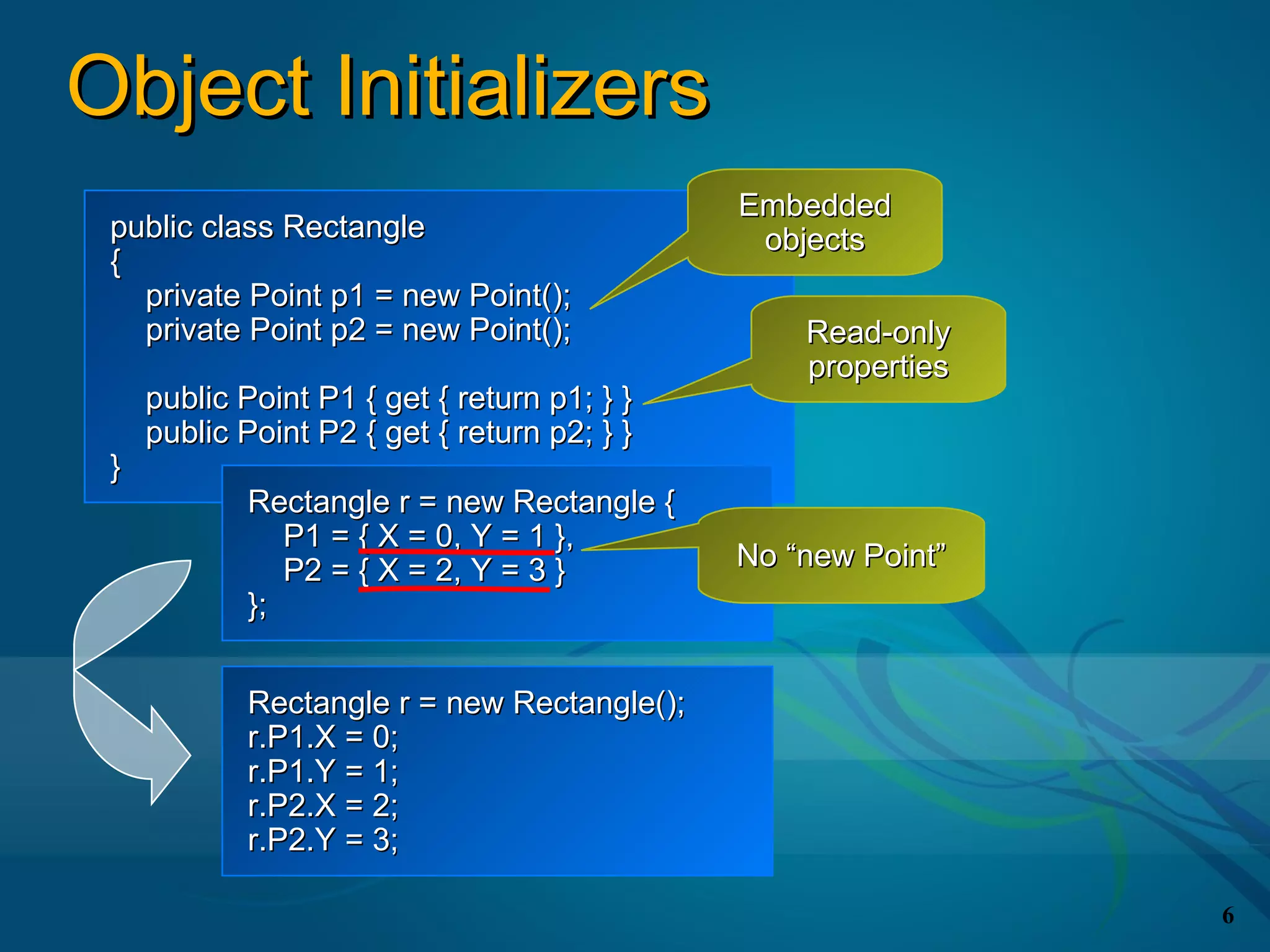
![Local Variable Type Inference
int i = 5;
string s = "Hello";
double d = 1.0;
int[] numbers = new int[] {1, 2, 3};
Dictionary<int,Order> orders = new Dictionary<int,Order>();
var i = 5;
var s = "Hello";
var d = 1.0;
var numbers = new int[] {1, 2, 3};
var orders = new Dictionary<int,Order>();
“var” means same
type as initializer
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-090701233237-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Linq-7-2048.jpg)
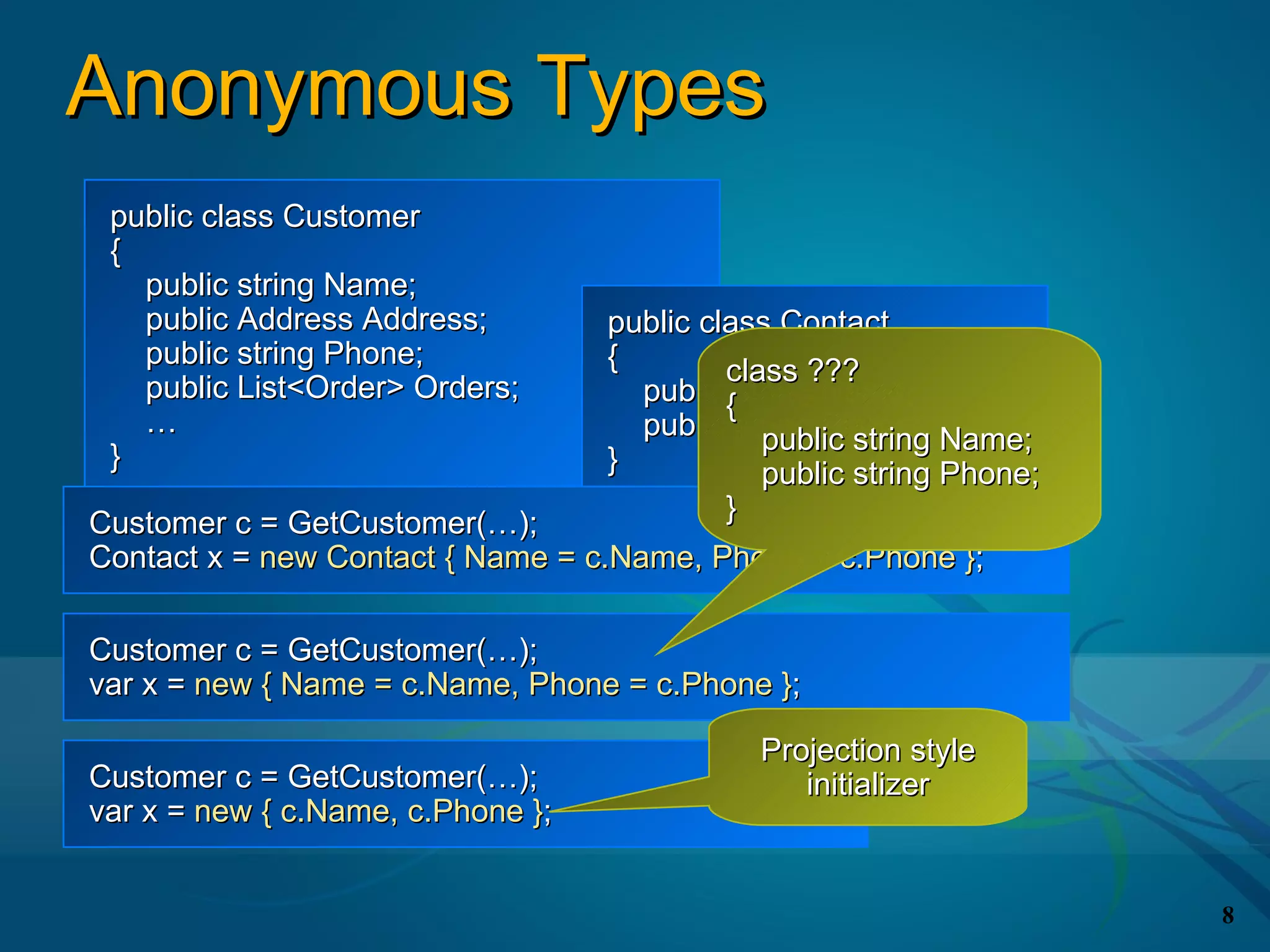
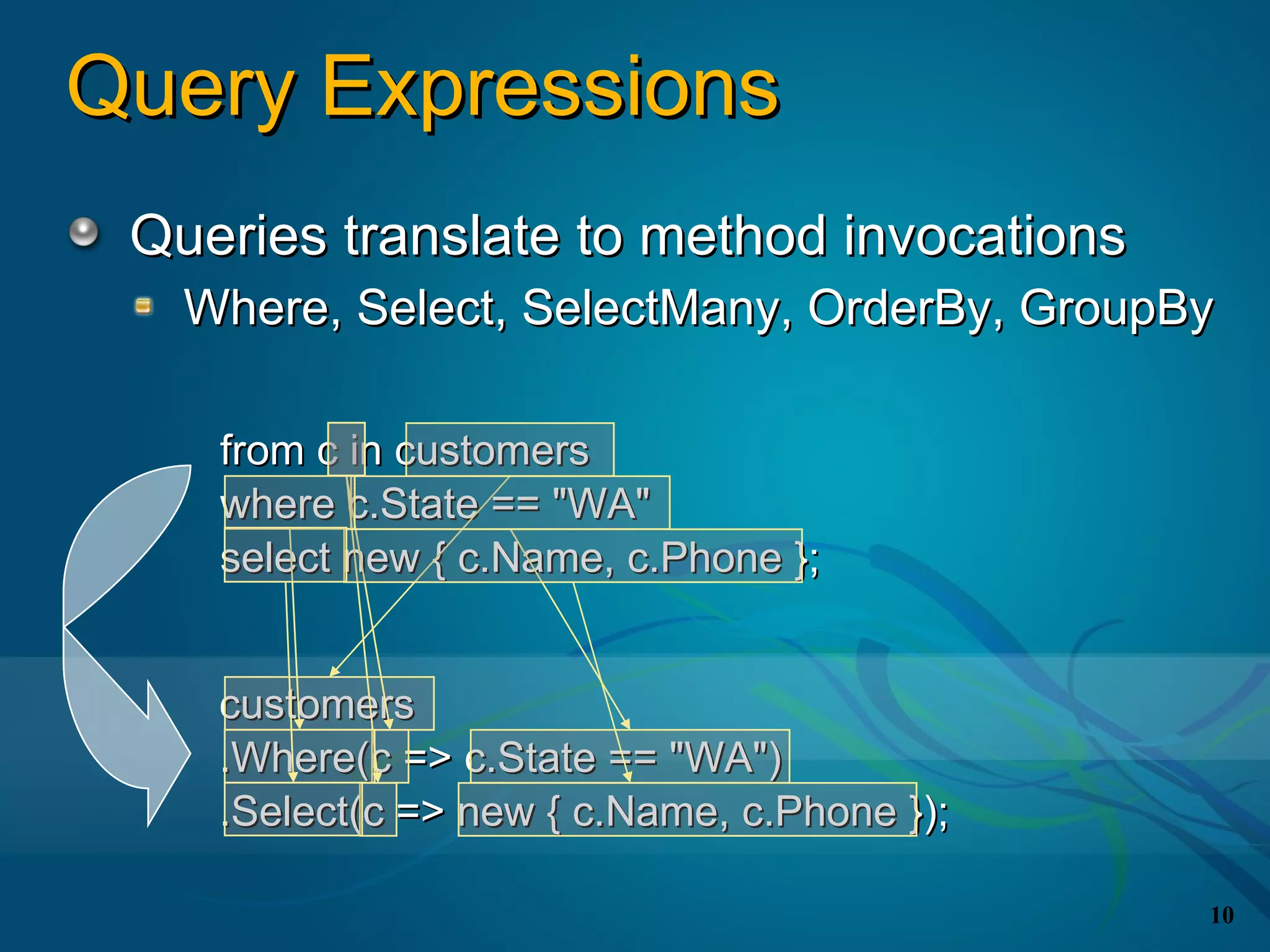
![Query Expressions
Language integrated query syntax
Starts with
from Zero or more
from or where
from id in source
{ from id in source | where condition } Optional
[ orderby ordering, ordering, … ] orderby
select expr | group expr by key
[ into id query ] Ends with select
Optional into or group by
continuation
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-090701233237-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Linq-9-2048.jpg)

![Deferred Query Execution
Customer[] custs = SampleData.GetCustomers();
var query = from c in custs where c.City == "London" select c.Name;
var query = custs.Where(c => c.City == "London").Select(c => c.Name);
string[] names = query.ToArray();
custs names
ID Name Phone
Where Select
c => c.City == "London" c => c.Name
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-090701233237-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Linq-13-2048.jpg)