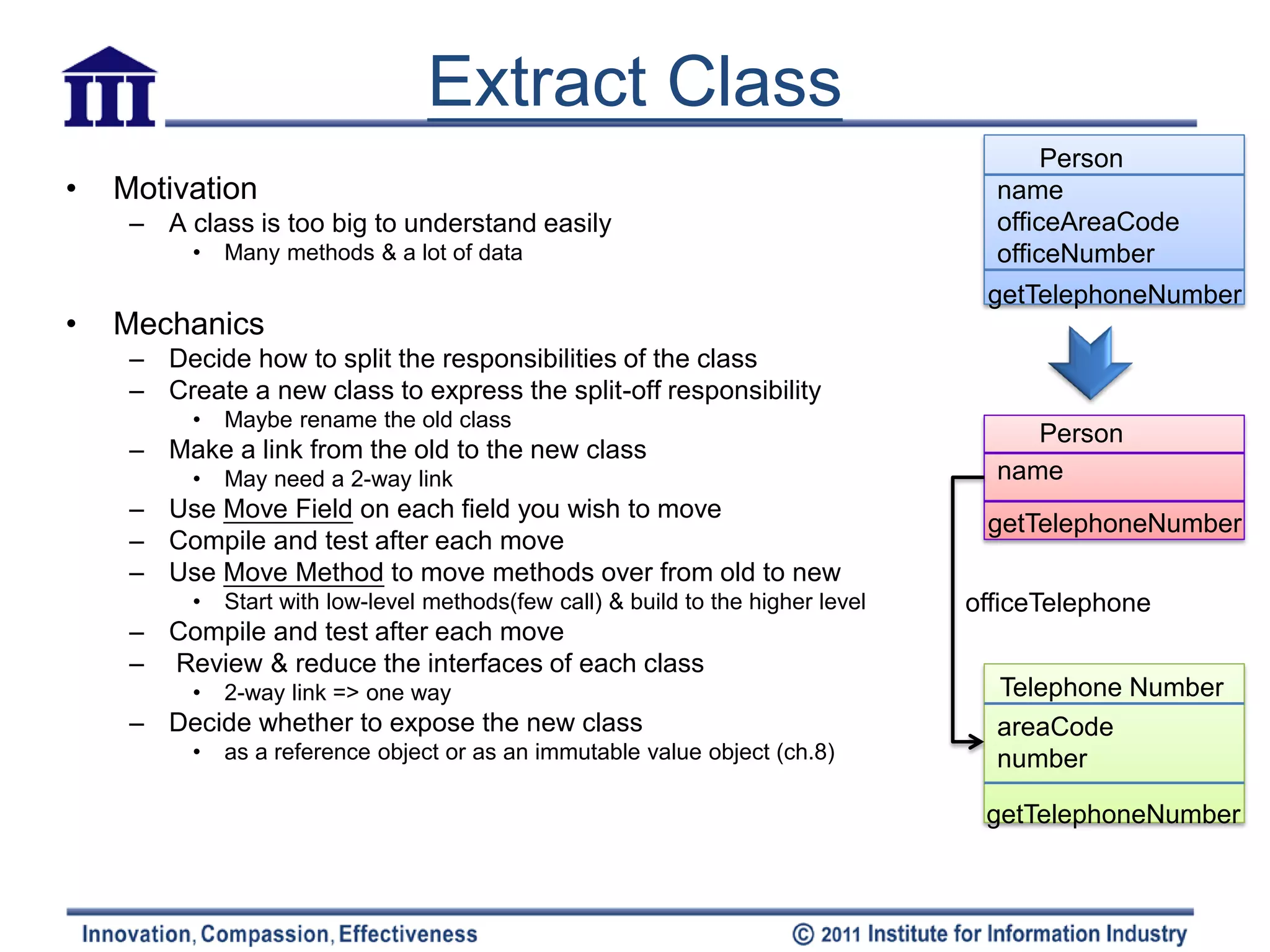
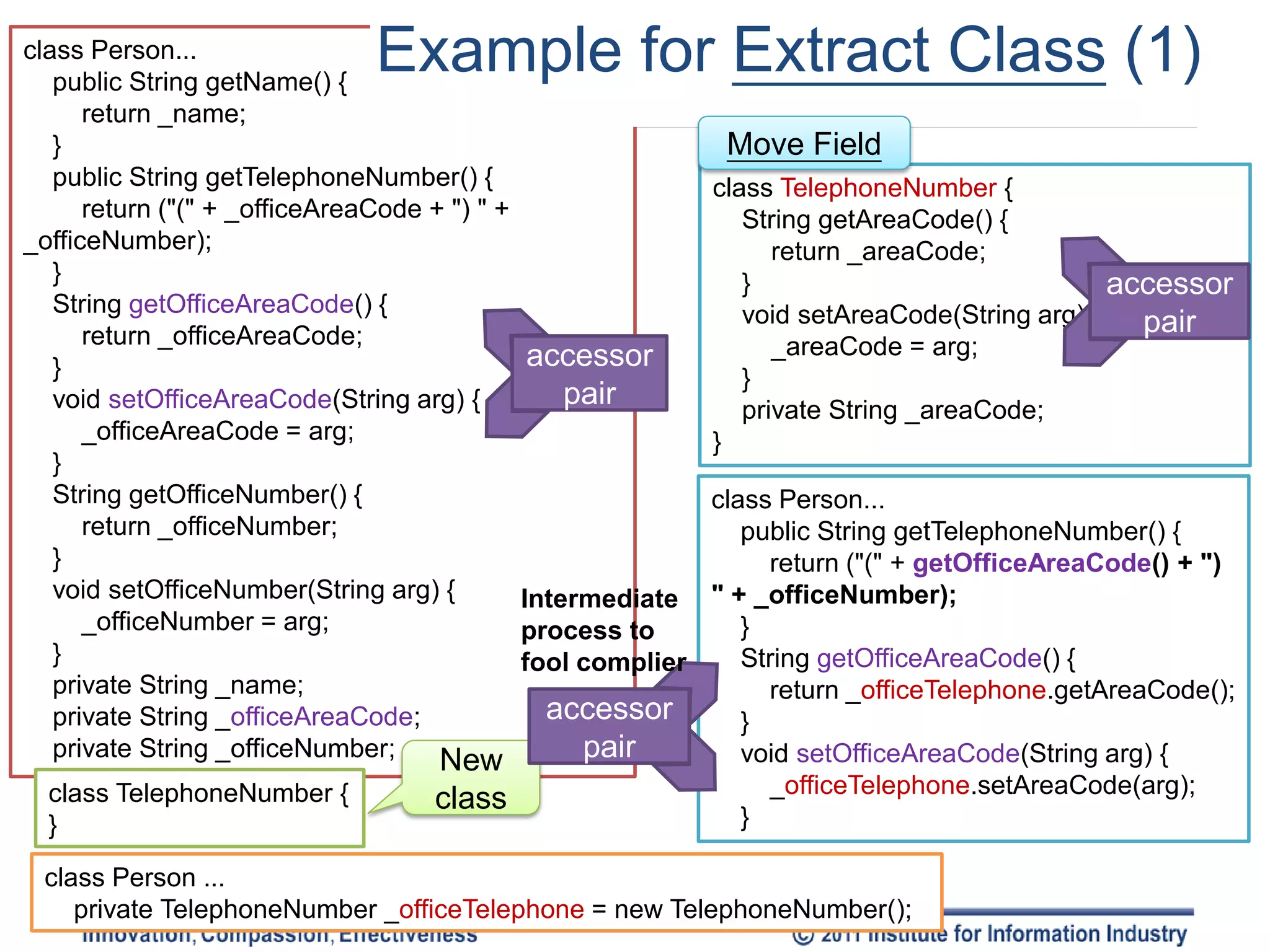
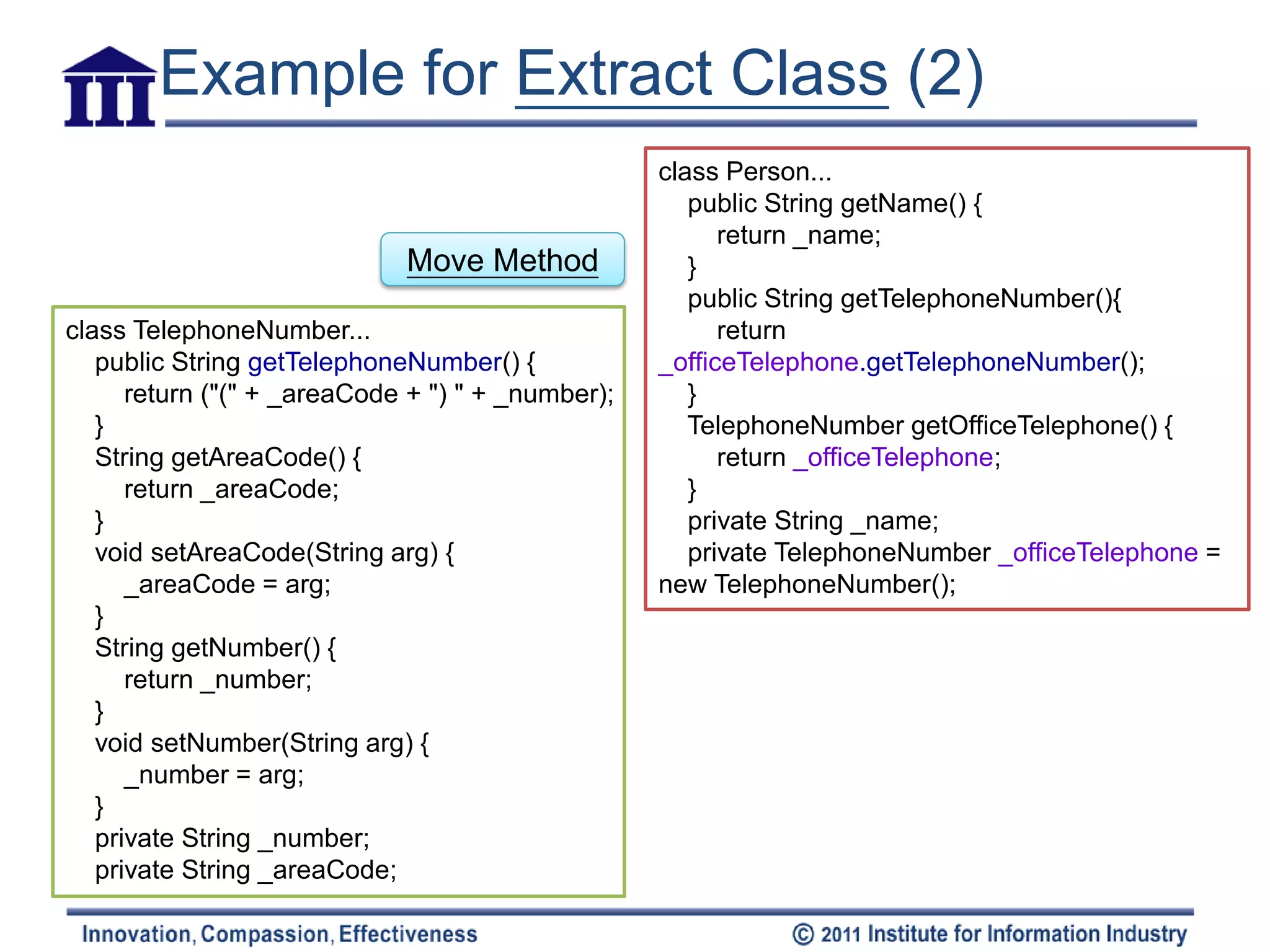
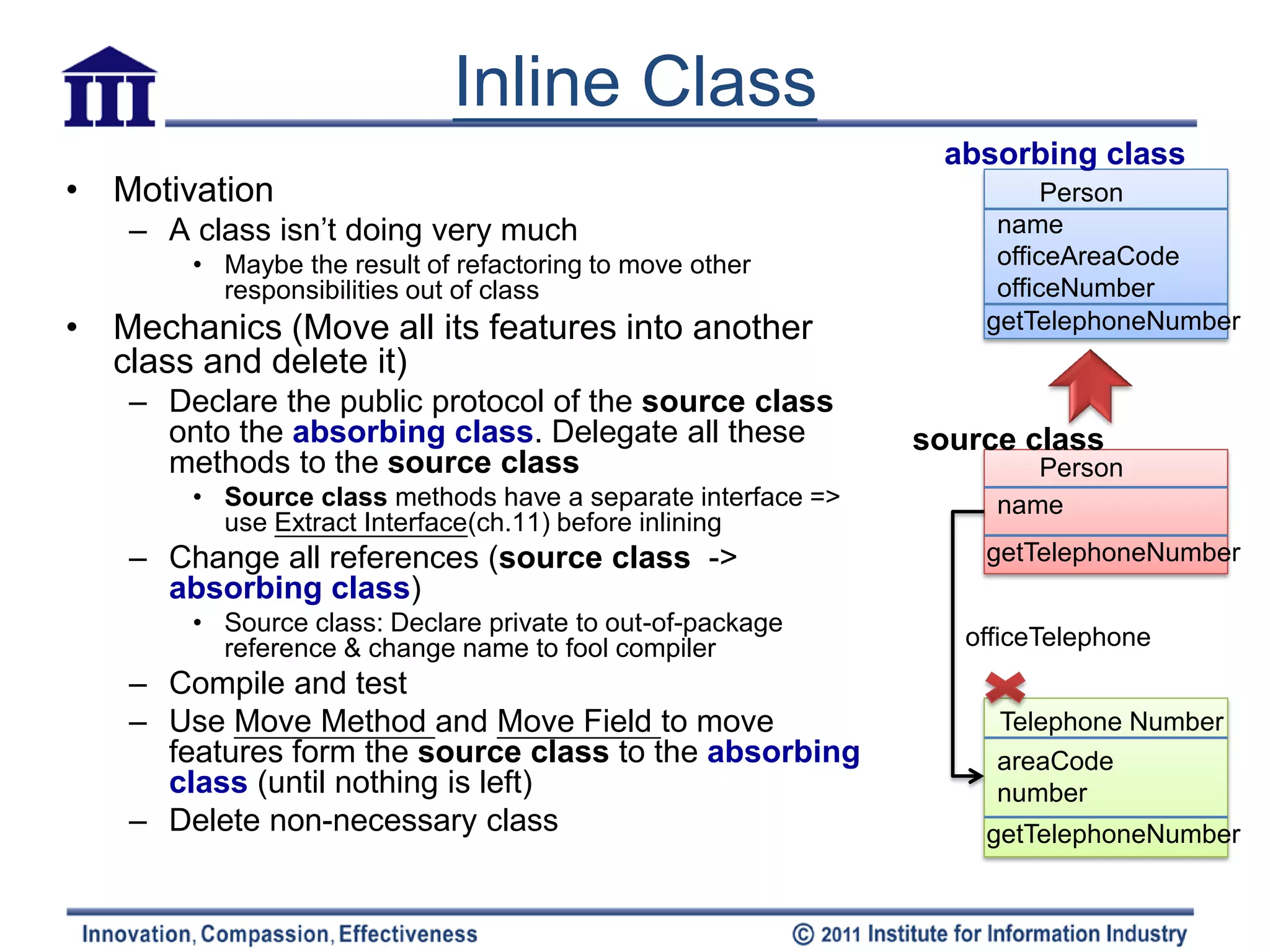
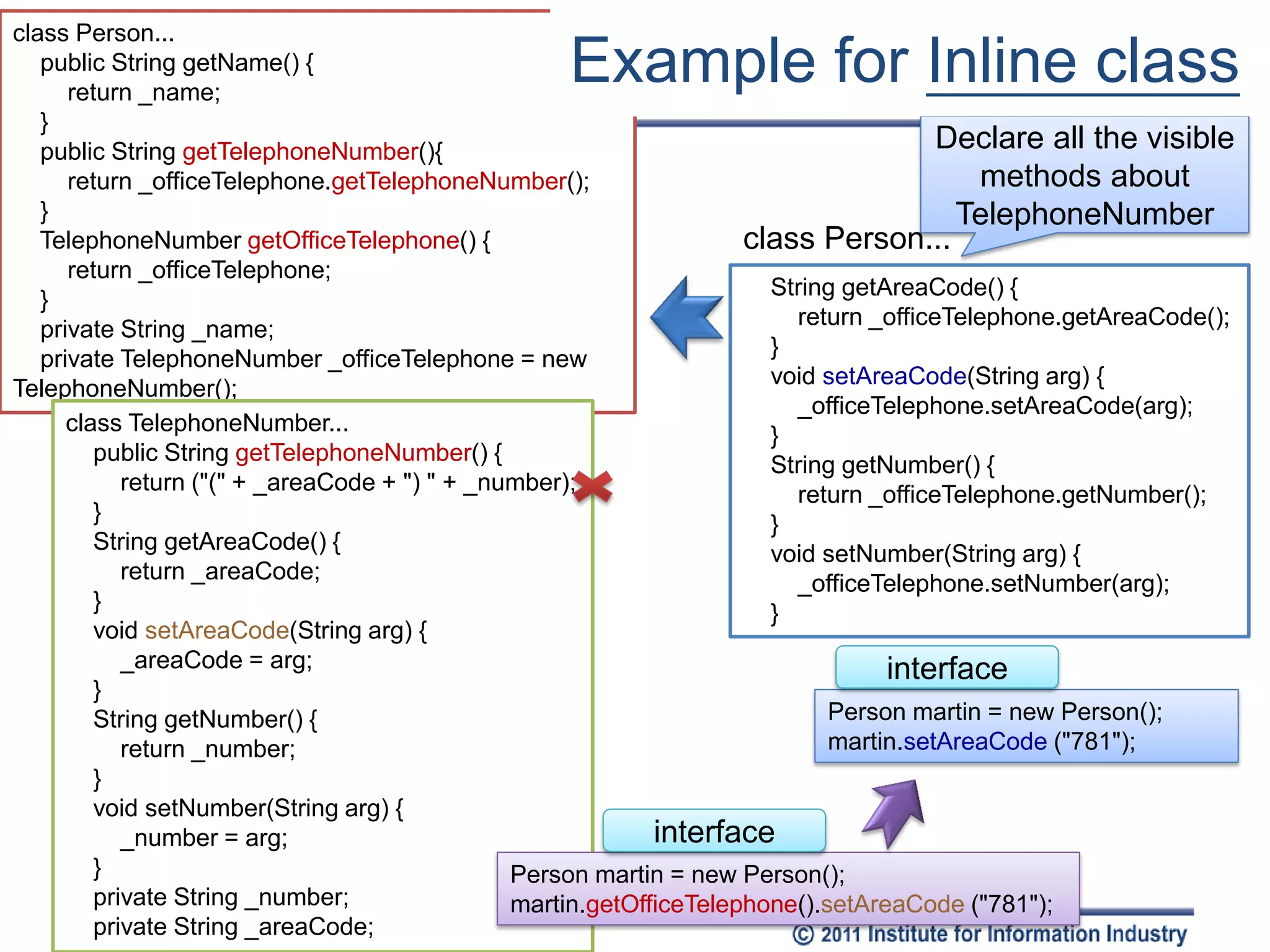
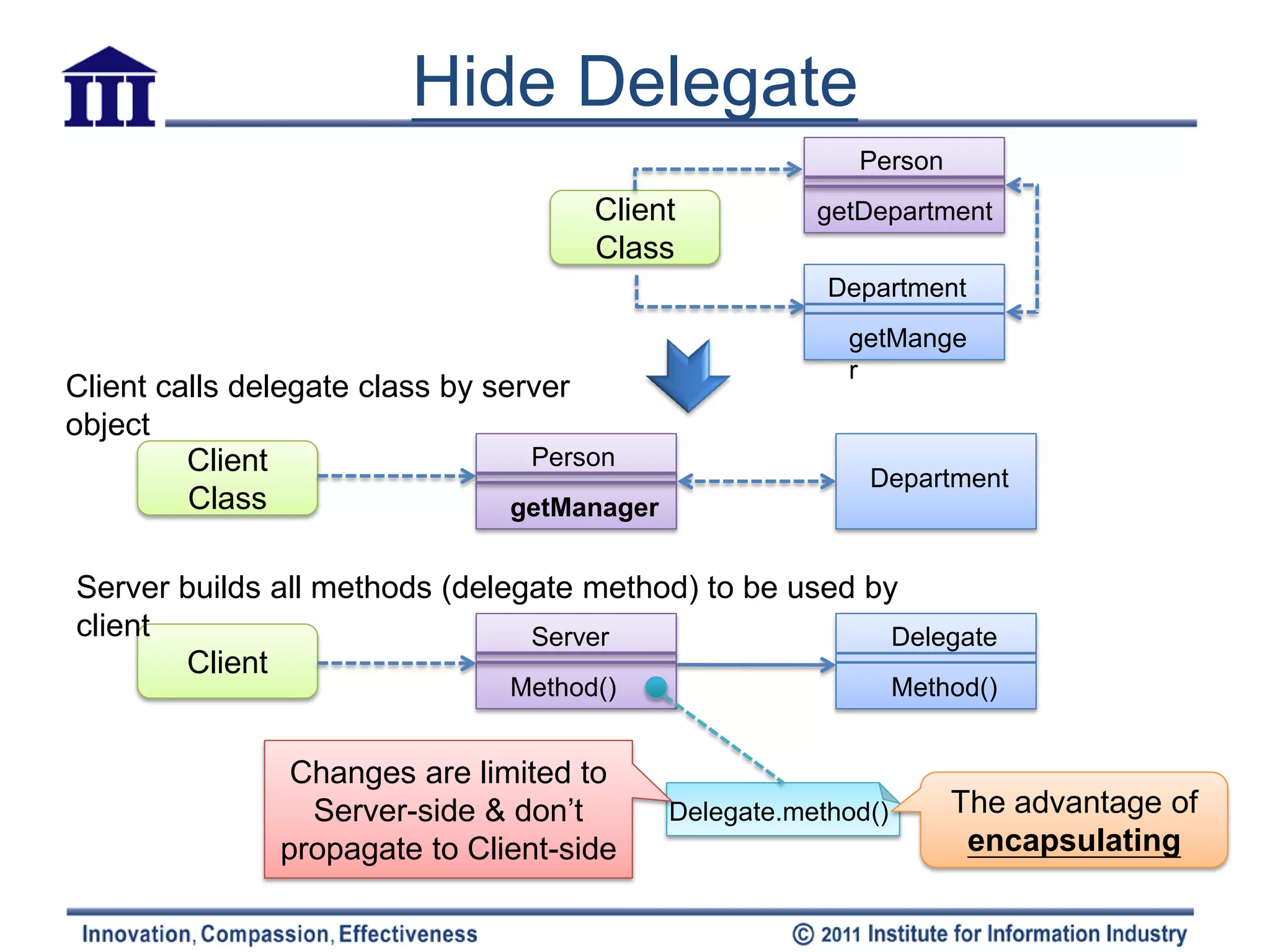
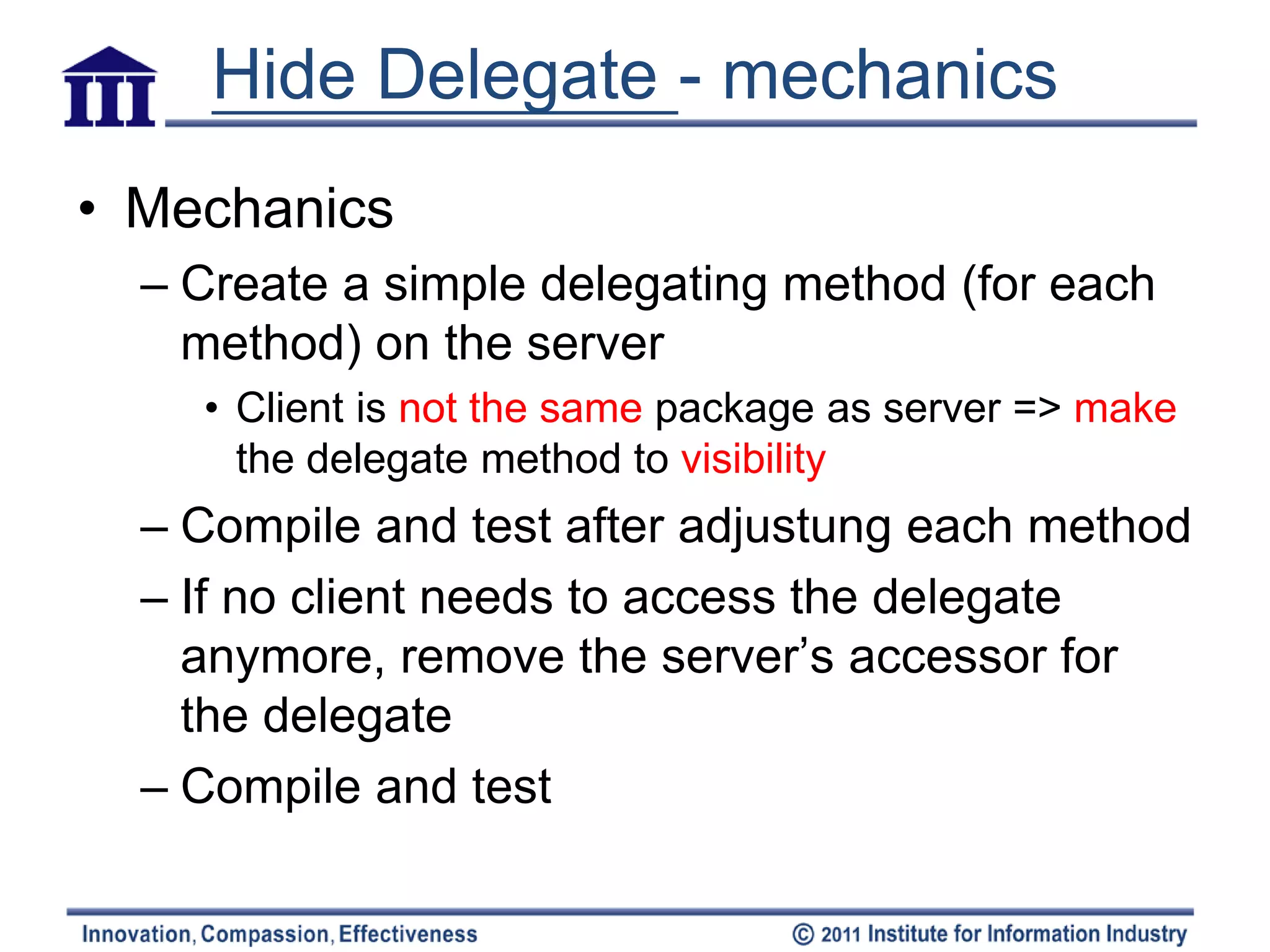
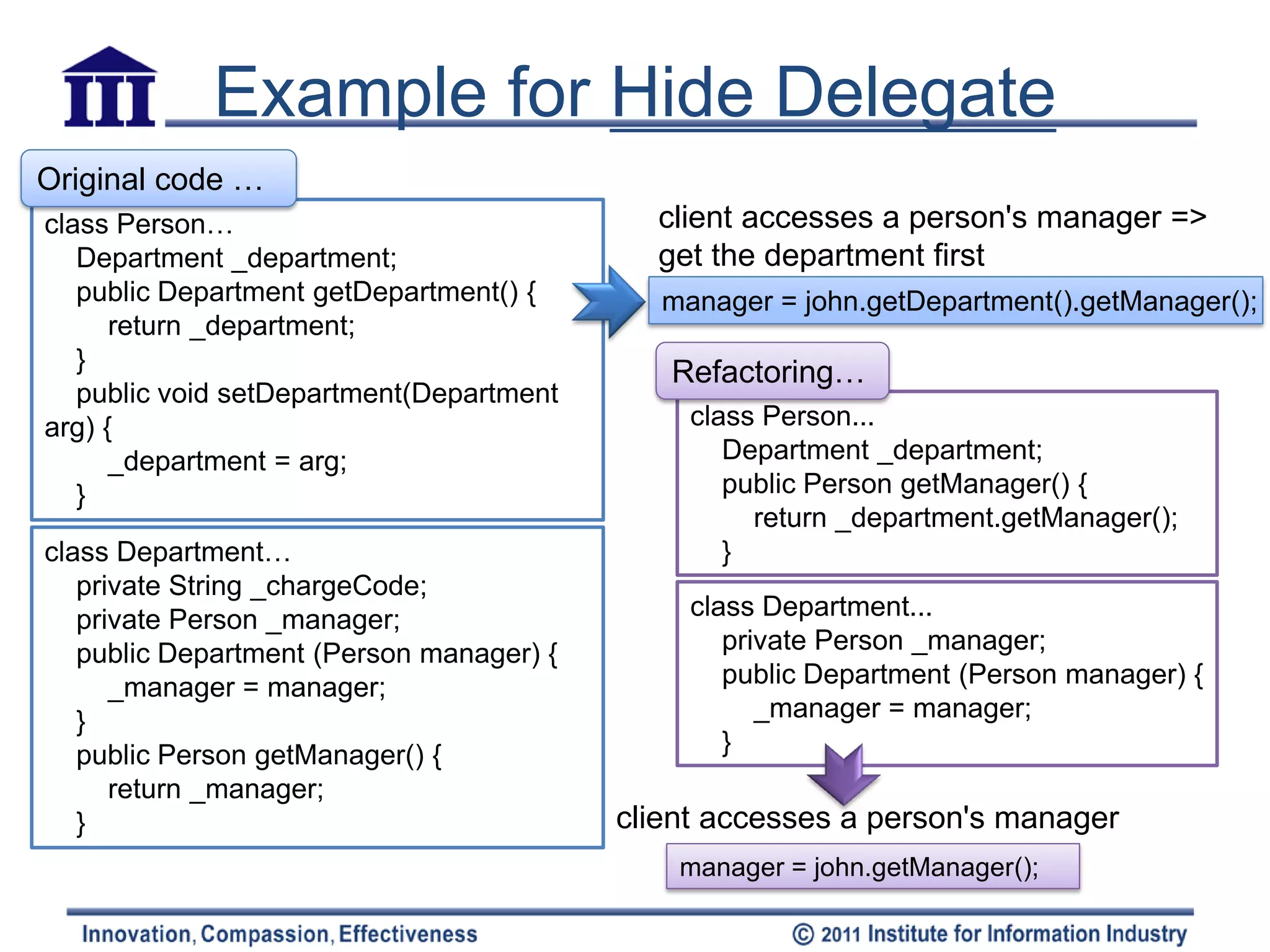
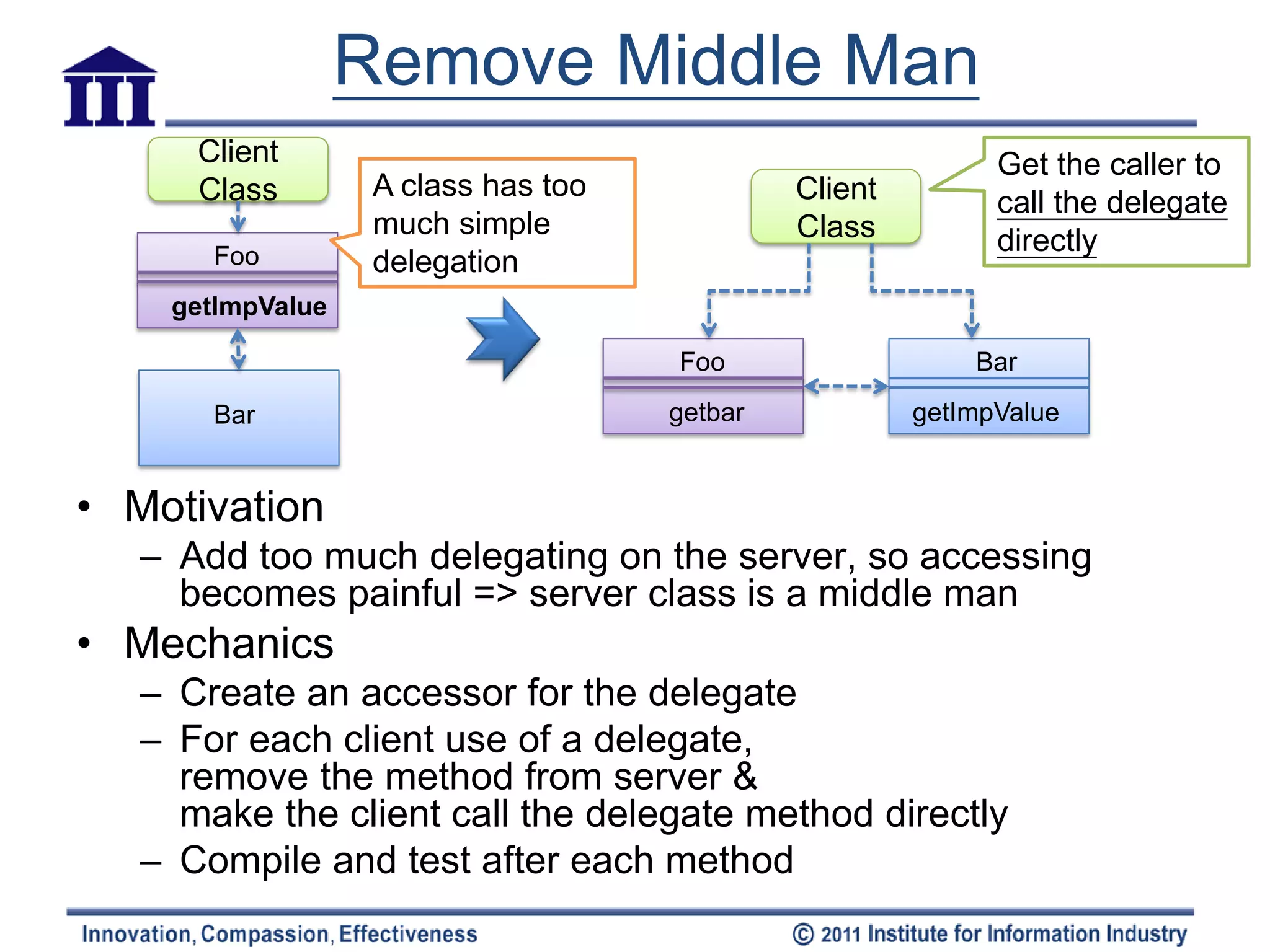
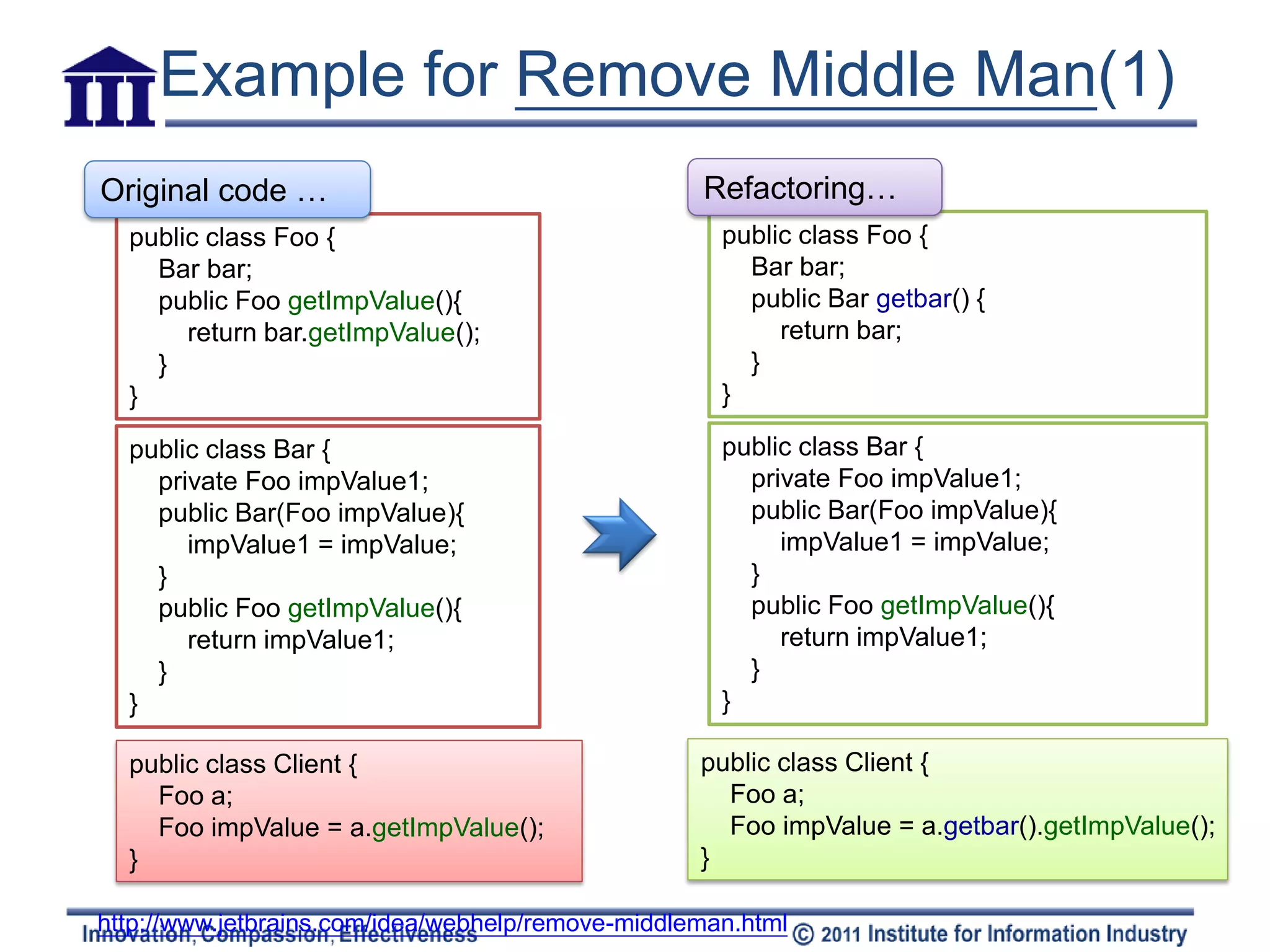
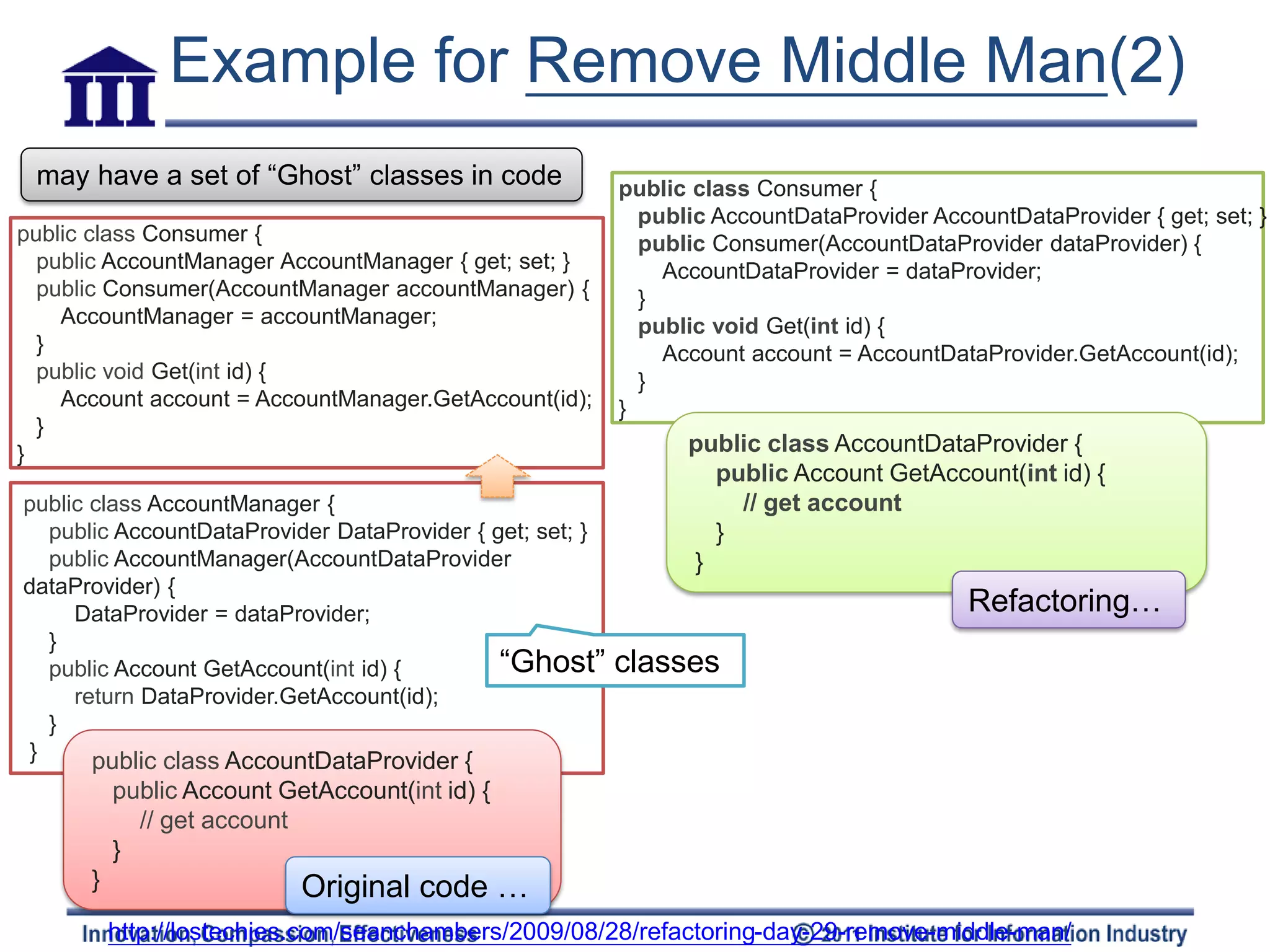
The document discusses various refactoring techniques for moving features between objects in object-oriented programming, including moving methods, moving fields, extracting classes, and inlining classes. It provides detailed mechanics for each technique, with examples illustrating the processes involved, such as copying code, adjusting references, and compiling. Additionally, it covers advanced concepts like hiding delegates and removing middlemen to streamline method calls and enhance code efficiency.
![Move Method
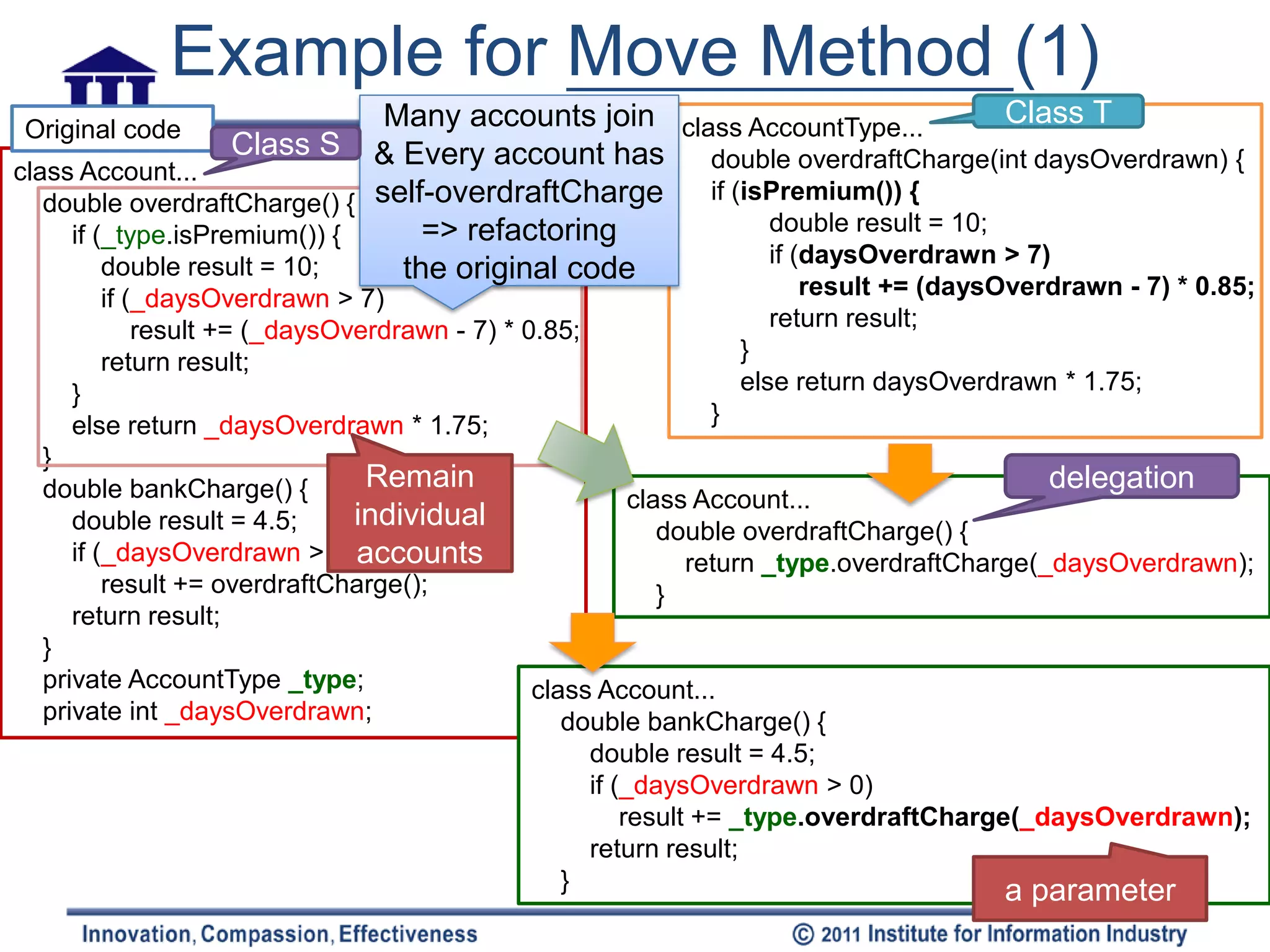
Motivation: Class S Class S
In Class S, method() used more features from Class T
Mechanics:
• Examine all features used by the method on Class S. Method()
– Consider what situation should be move? (one or more methods ?)
• Check the sub- & superclasses of Class S
– unless Class S and Class T are both the polymorphism
• Naming the method’ in Class T (more sense)
Class T Class T
• Copy the method code from Class S to Class T. Adjust the method’
to fit Class T
– Reference back Class S? just send a parameter from Class S
– Exception handler at Class S or Class T? Method’()
• Compile Class T
• Determine how to reference back Class S
– Class T has existing field or method
– If no existing, create a method in Class T
– or Create a new field (store the target object) in Class S [temporariness]
• Turn the source method into a delegating method
• Compile and test
• Decide whether to remove the source method or retain it as a
delegating method
– retain as a delegating method => many references
– If remove the source method, replace all the references and make the
reference to link Class T
• Compile and test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoring-ch7movingfeaturebtwobjects20110519-110518213234-phpapp02/75/Refactoring-ch7-moving-feature-btw-objects-3-2048.jpg)
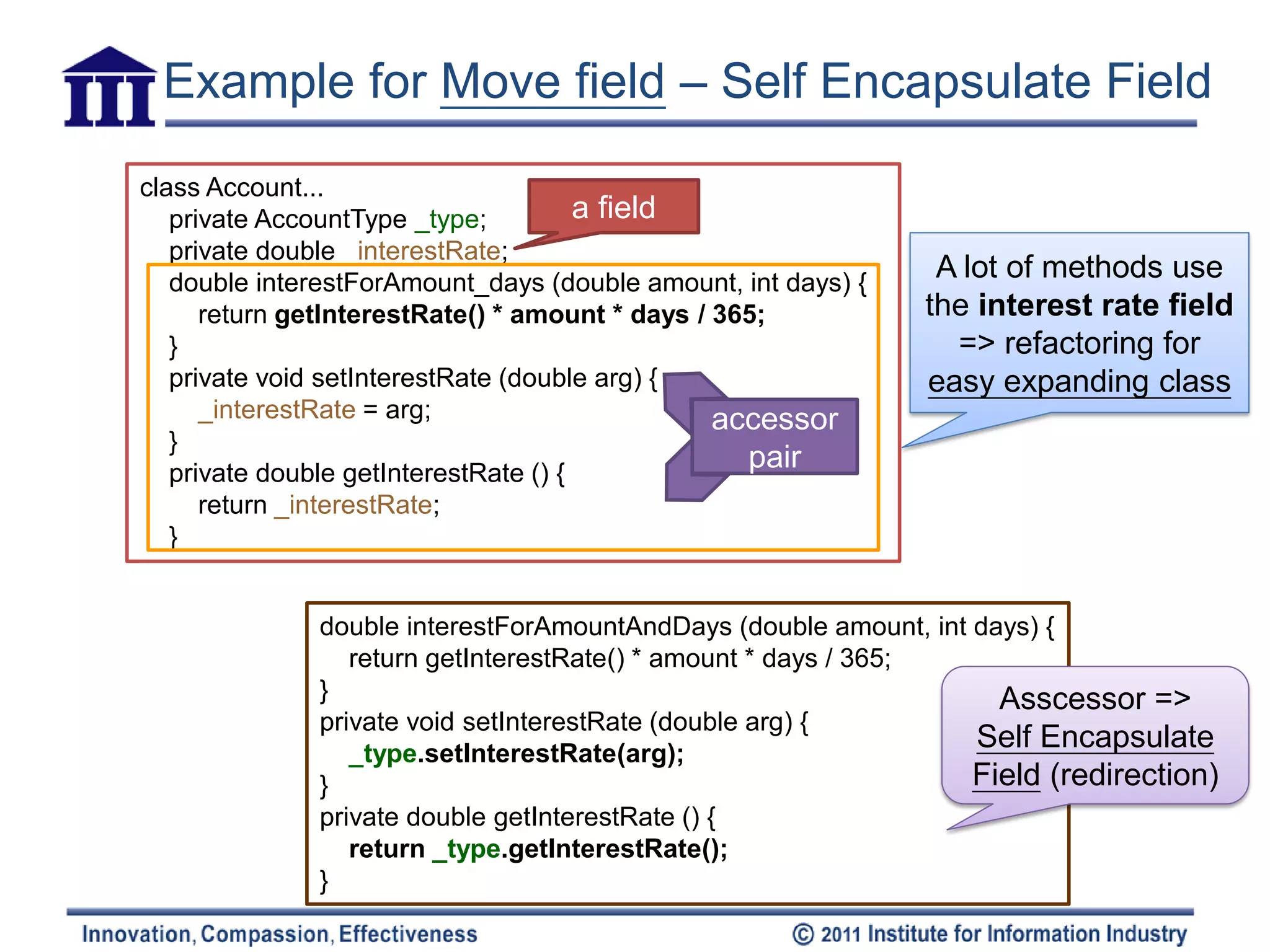
![Move Field
• Motivation Class S Class S
– Class S’s field(be used by more methods) is used frequently in
Class T
• If those methods seem sensible where they are => Move Field
– When doing Extract Class, must do Move Field
Field
• Mechanics
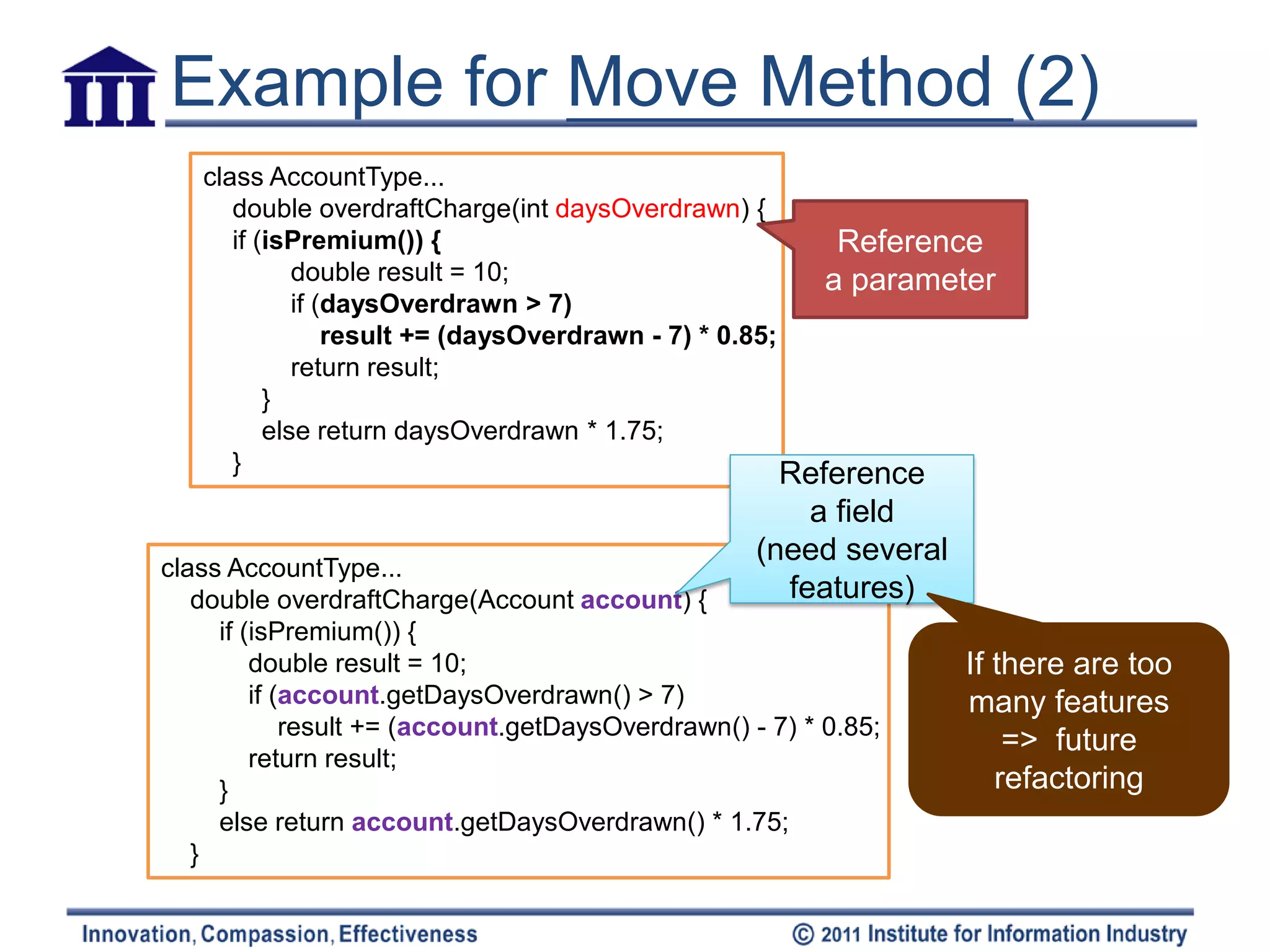
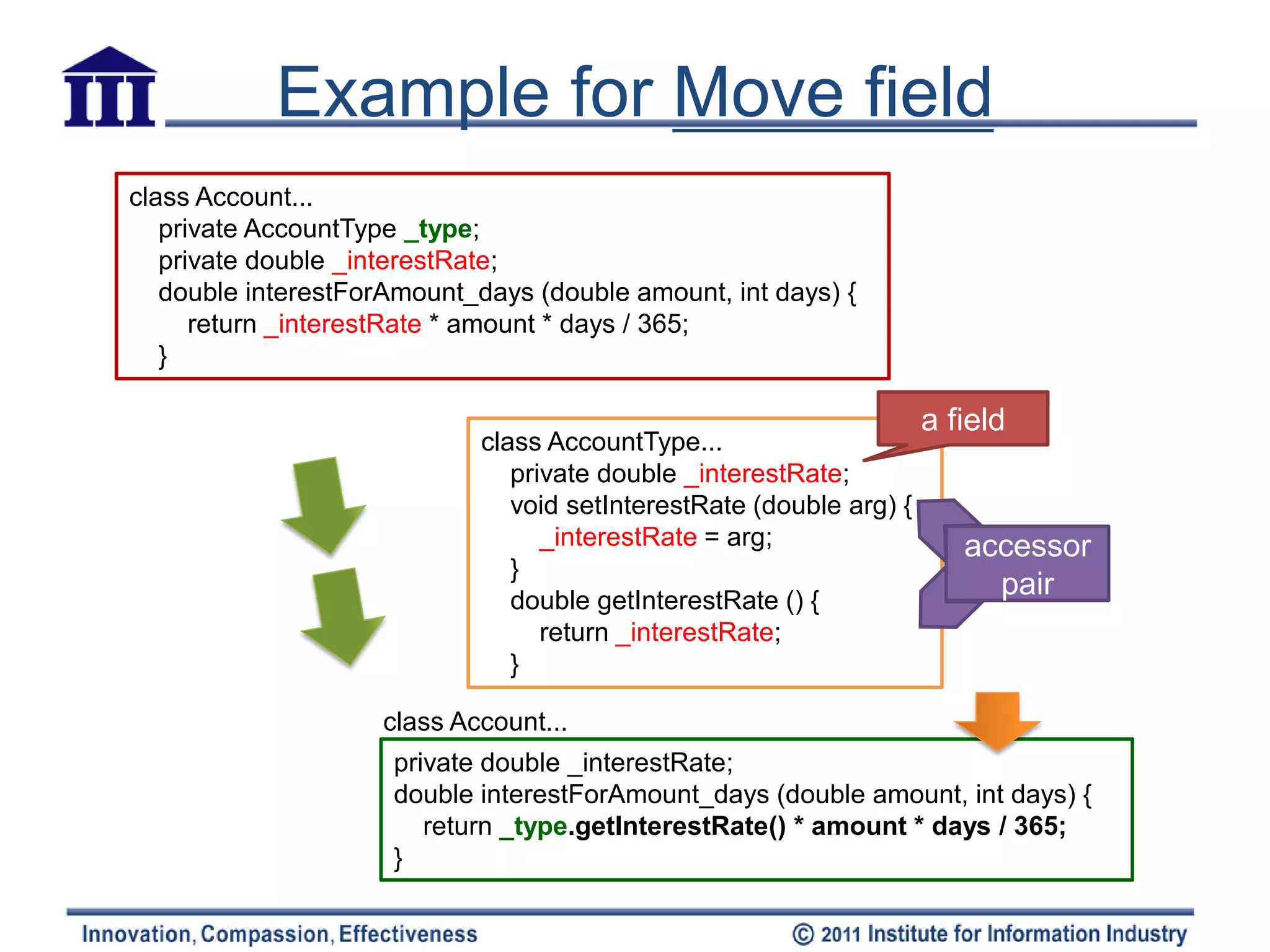
– Public field => use Encapsulate Field
• If the field be accessed frequently by many methods => use Self Class T Class T
Encapsulate Field
– Compile and test
– Create a field in Class T with getting & setting methods Field’
– Compile Class T
– Determine how to reference back Class S
• Class T has existing field or method
• If no existing, create a method in Class T
• or Create a new field (store the target object) in Class S
[temporariness]
– Remove Class S’s field
– Replace all field reference in Class S and chose the appropriate
link for Class T
• Access field is by variable => replace the reference with a call to the
target object’s getting method
• Access field by assignments => replace the reference with a call to the
setting method
• If field is not private => look in all subclass S for reference
– Compile and test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoring-ch7movingfeaturebtwobjects20110519-110518213234-phpapp02/75/Refactoring-ch7-moving-feature-btw-objects-6-2048.jpg)
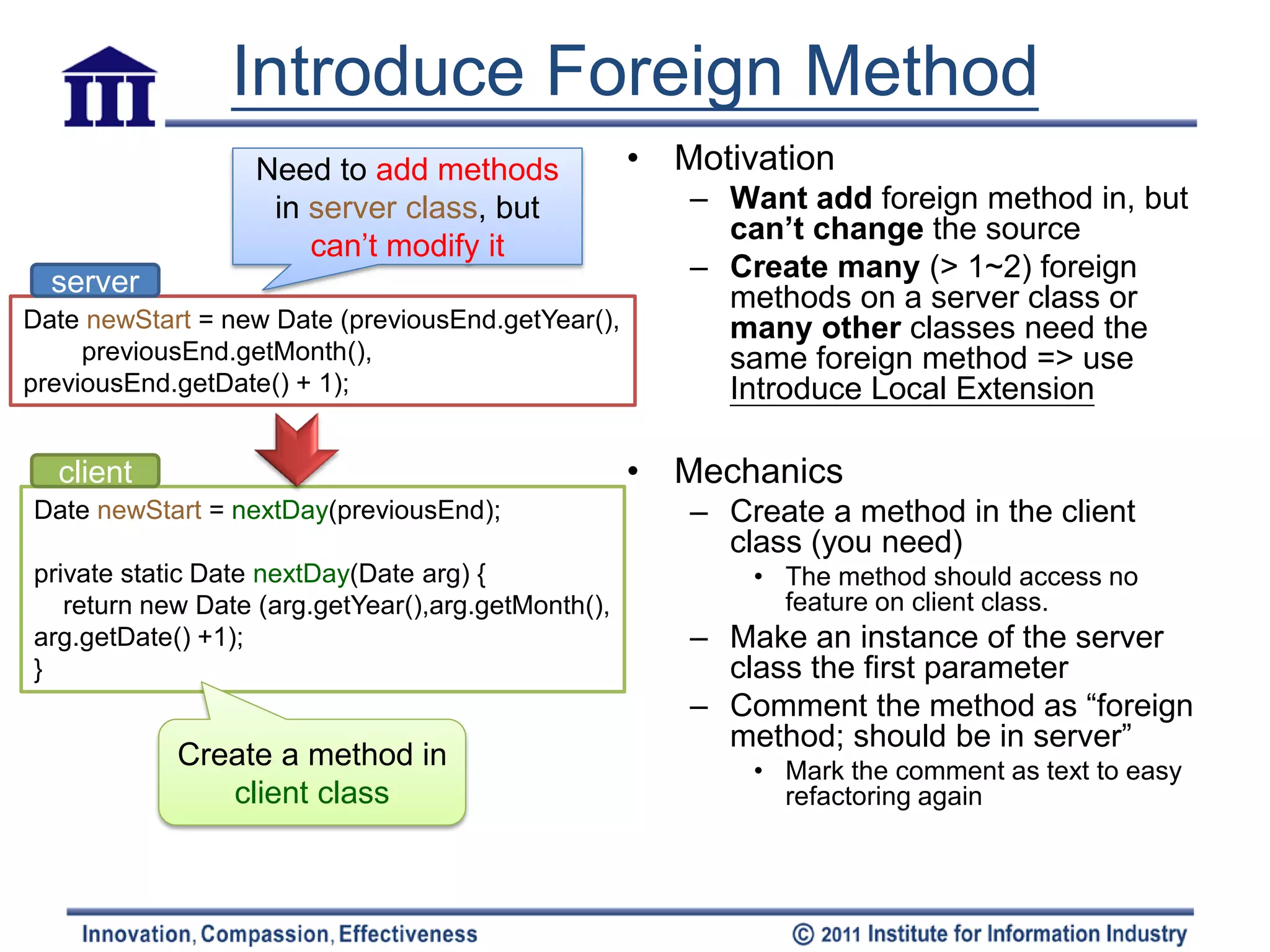
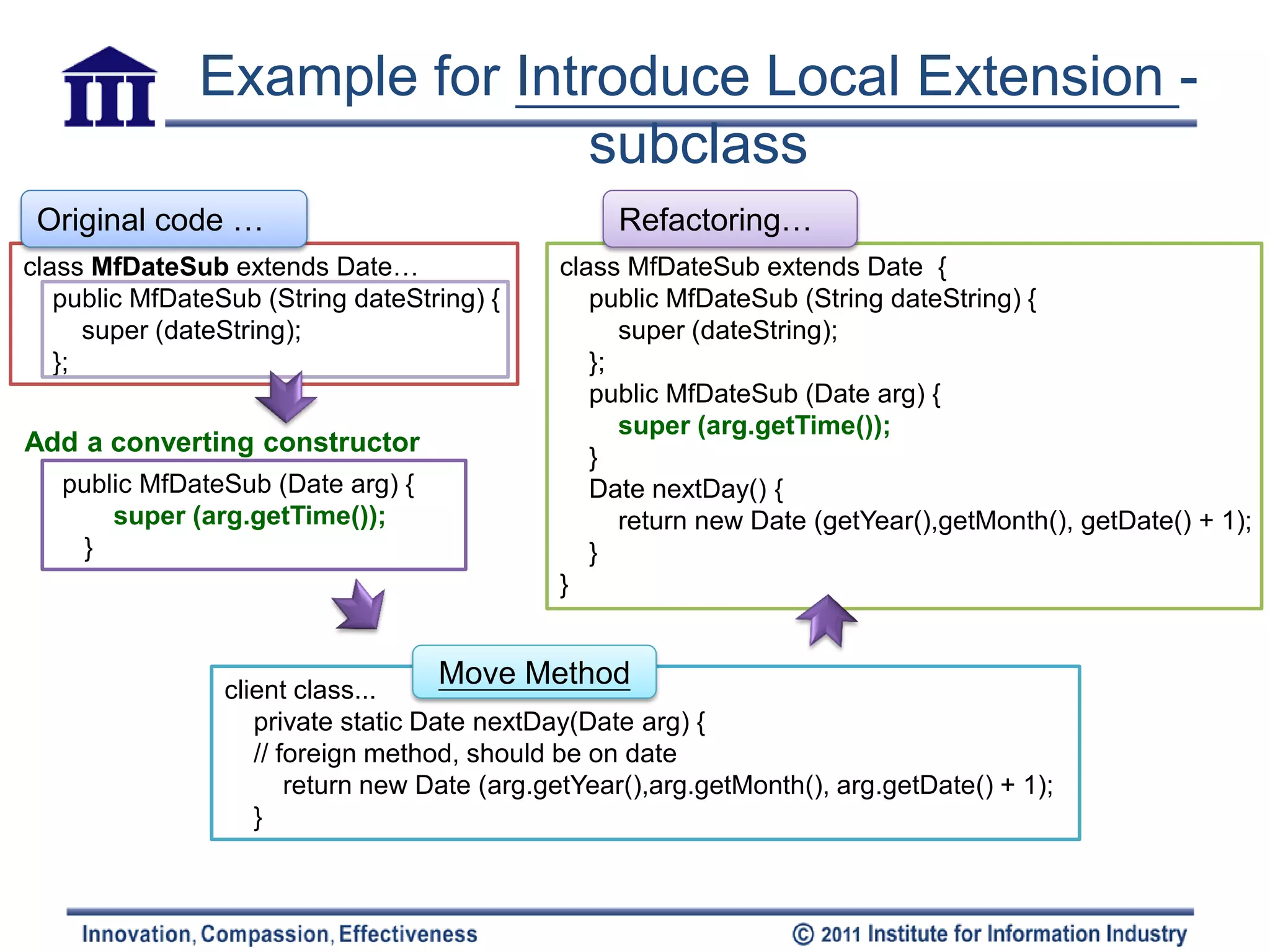
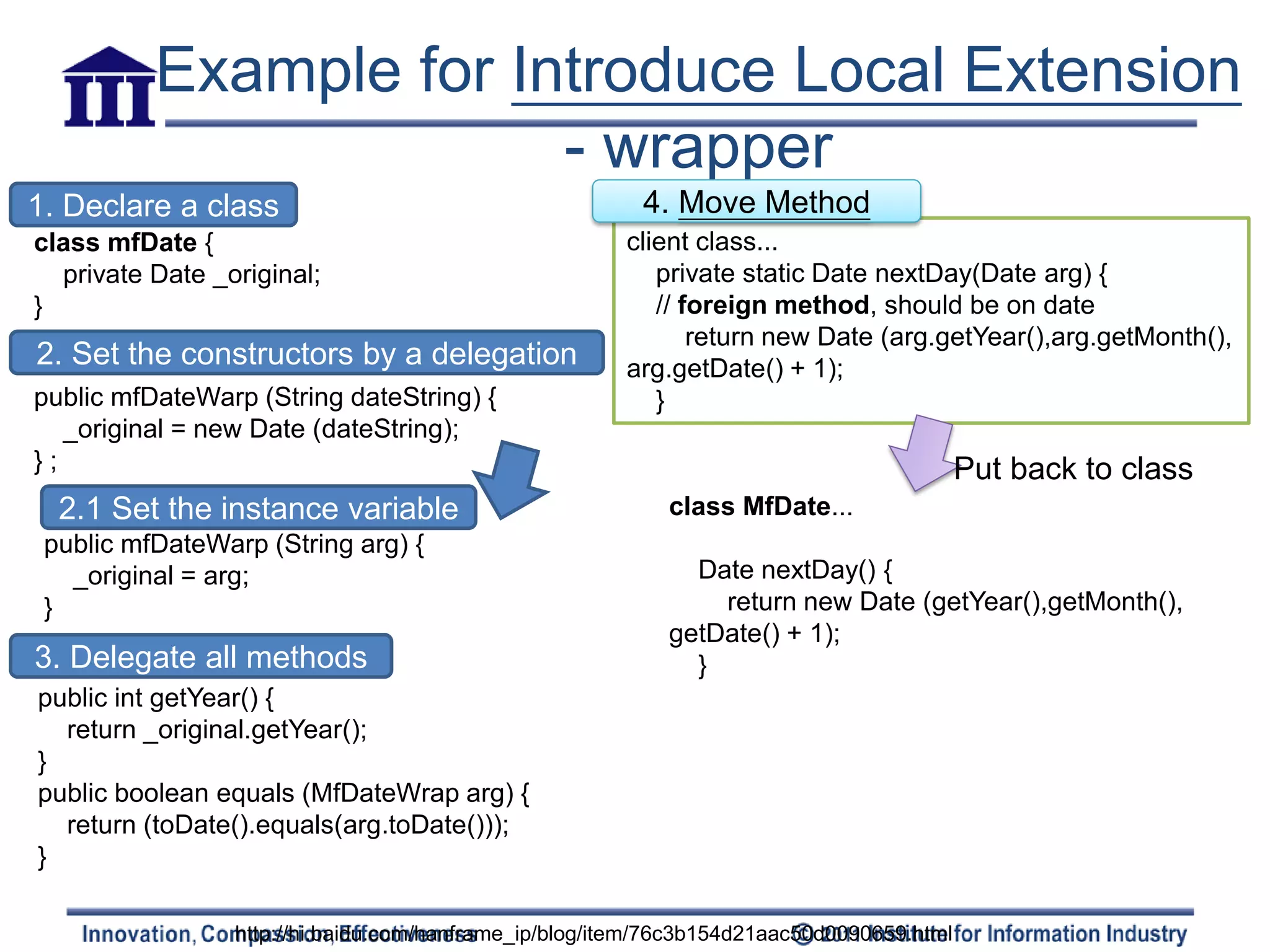
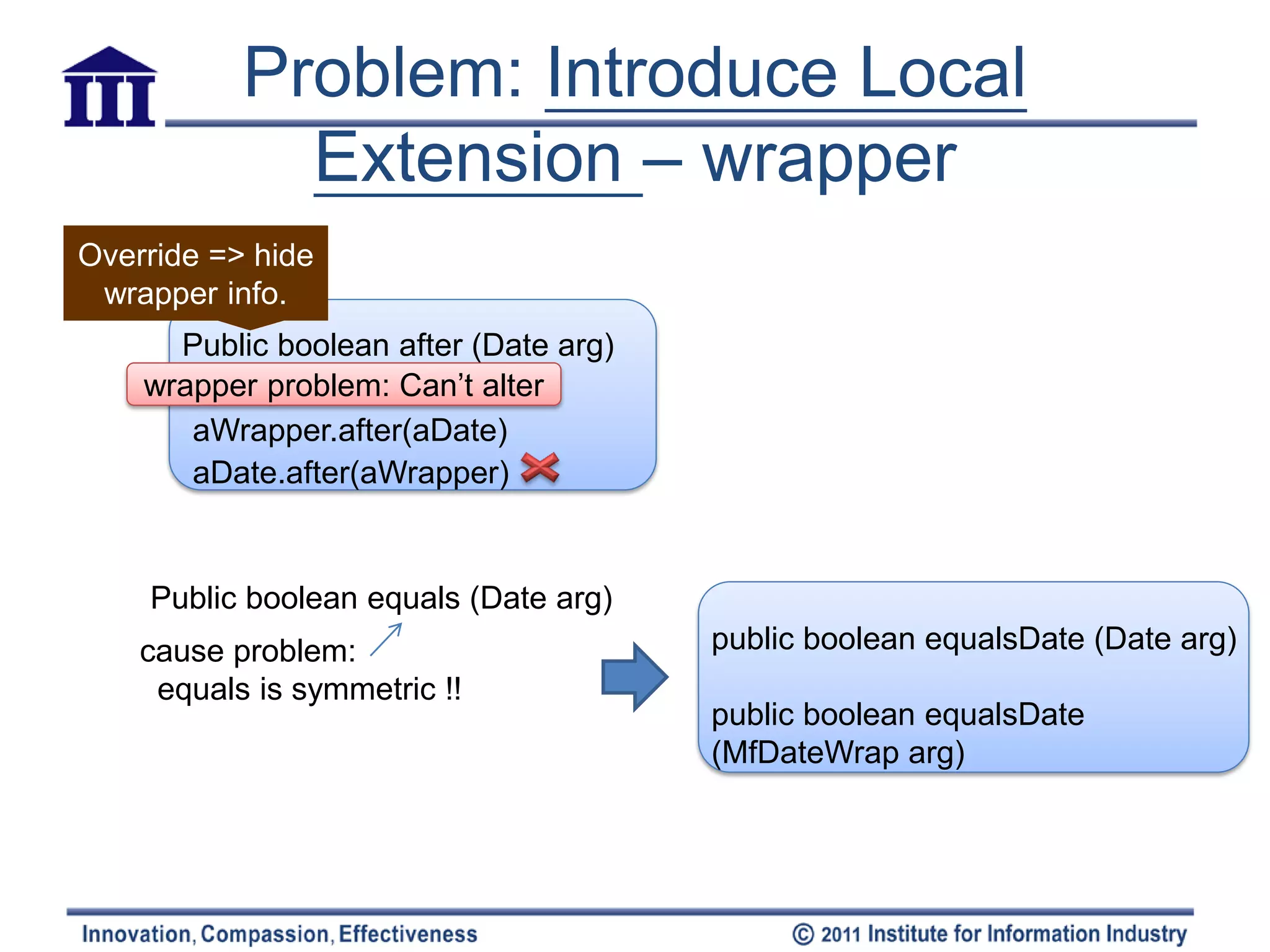
![Introduce Local Extension
Q: Need to add • Motivation
methods(>1~2) in server – Can’t modify => group the methods
together & using object-oriented
class, but can’t modify it techniques(subclass/ warp) to do (local
extension)
Date – Local extension
• A separate class & a subtype of extended
class
Client Class • [methods & data should be packaged into
well-formed units]
nextDay(Date):Date
• Mechanics
MfDate – Create an extension class either as a
subclass or a wrapper of the original
nextDay():Date
Create a new class – Add converting constructors to the
Subclass extension
that contains these • Constructor takes the original as an
extra method Class mfDate extends Date argument
{ • Subclass calls an superclass constructor
public nextDay()... • Wrapper sets the delegate field to the
Make this extension public dayOfYear()... argument
class a subclass or – Add new features to the extension
– Replace the original with the extension
wrapper of the where needed
original class mfDate { – Move any foreign methods defined for this
private Date _original; class onto the extension
Wrapper
(delegation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoring-ch7movingfeaturebtwobjects20110519-110518213234-phpapp02/75/Refactoring-ch7-moving-feature-btw-objects-21-2048.jpg)