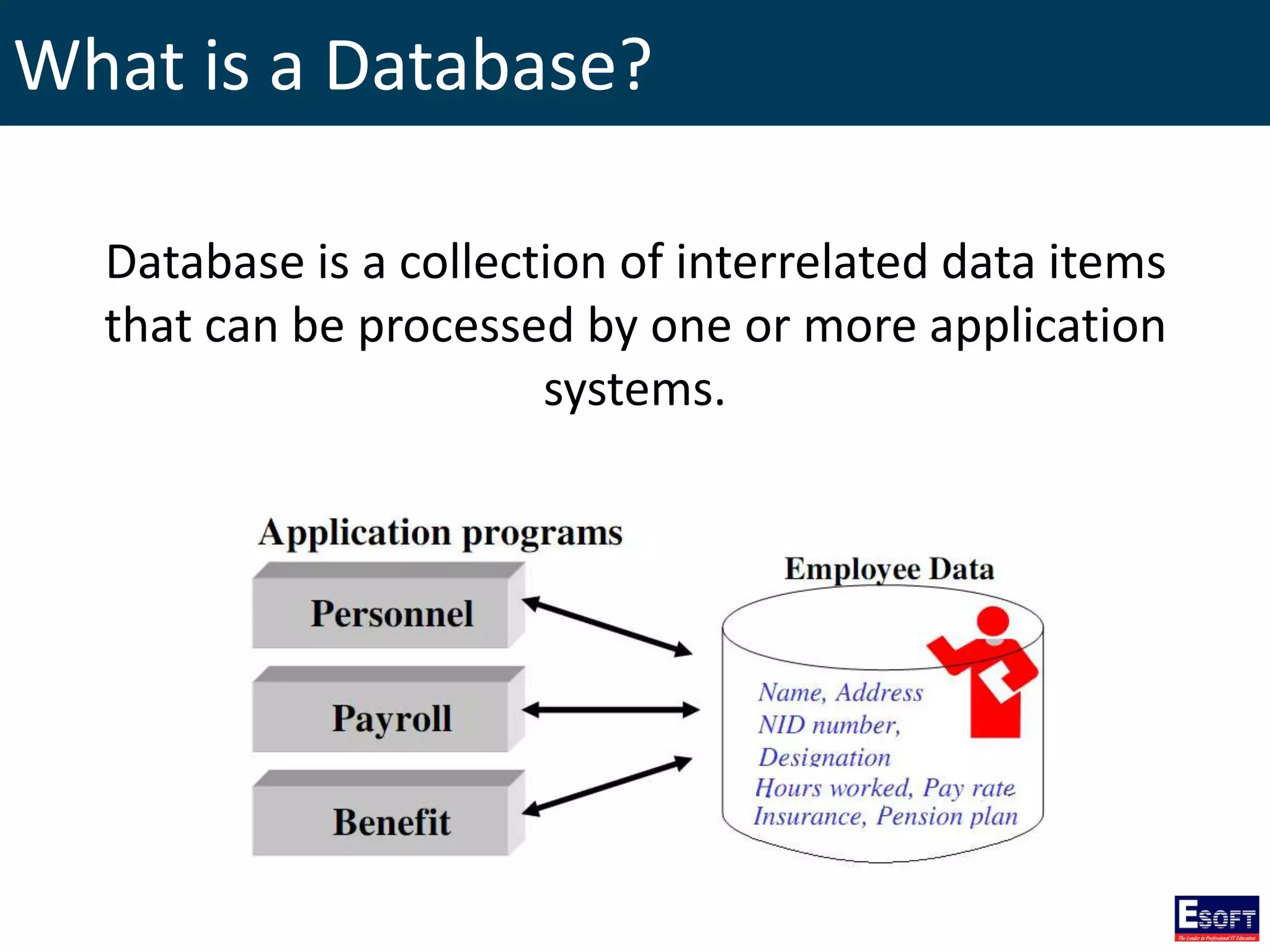
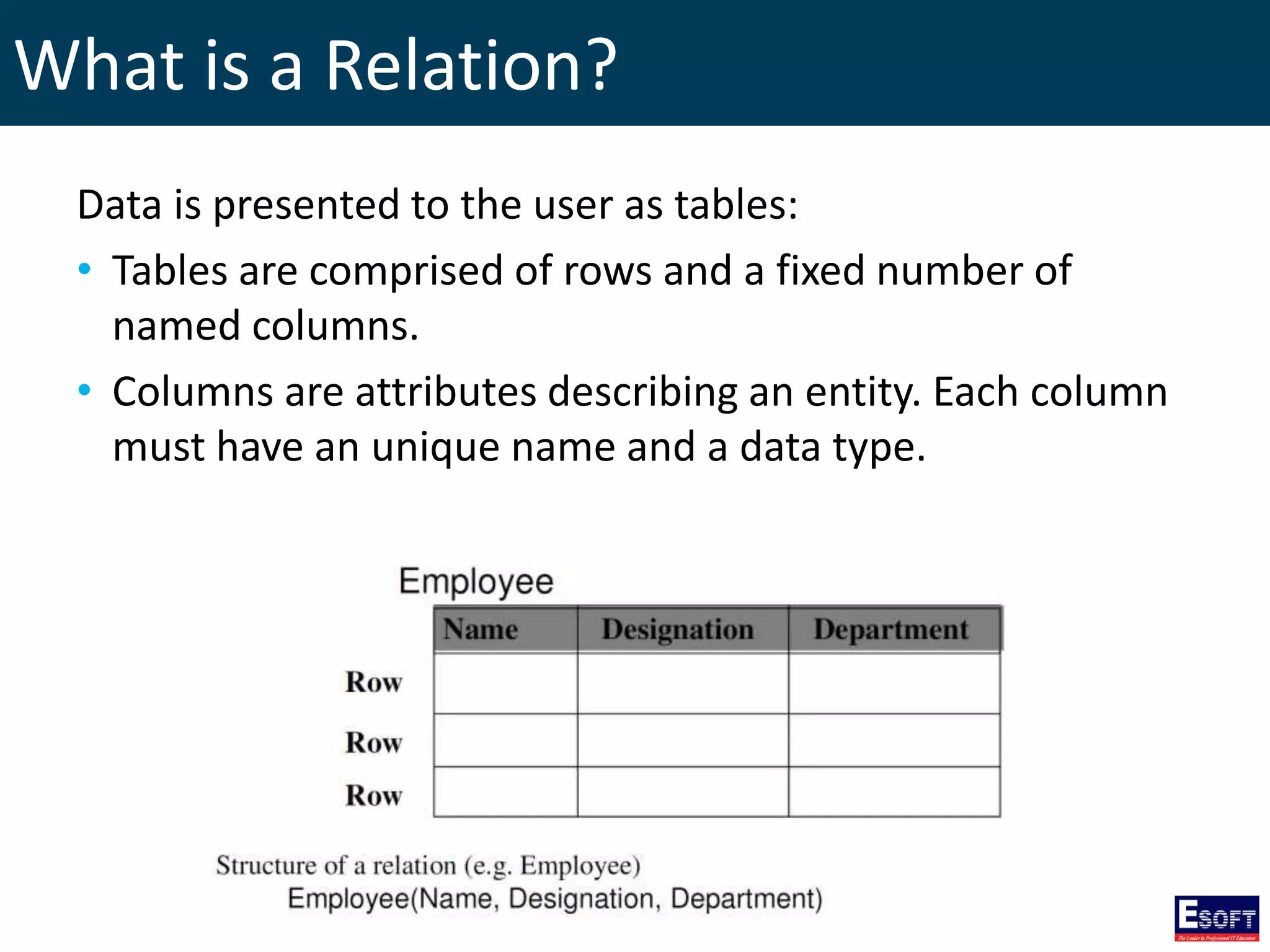
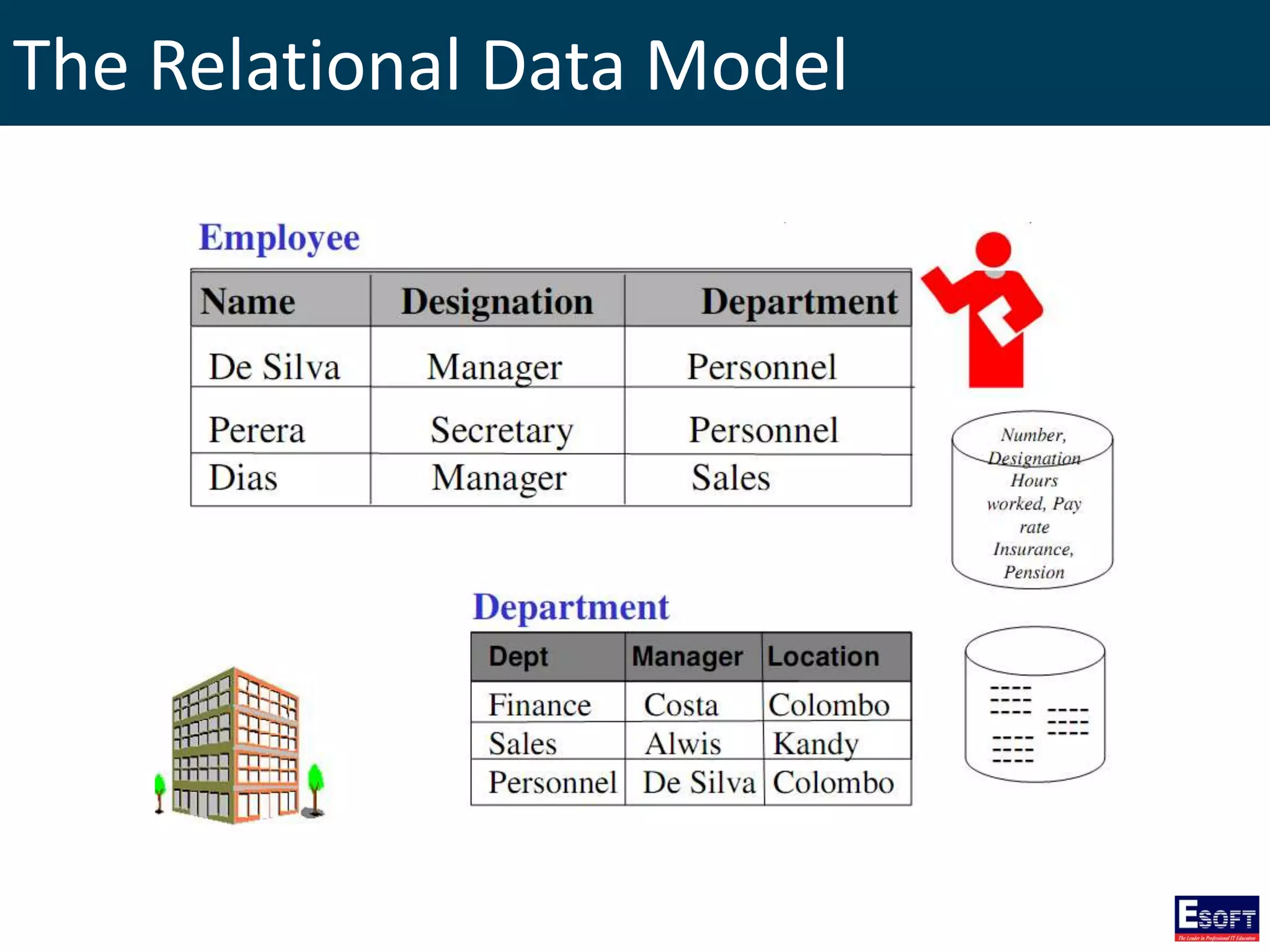
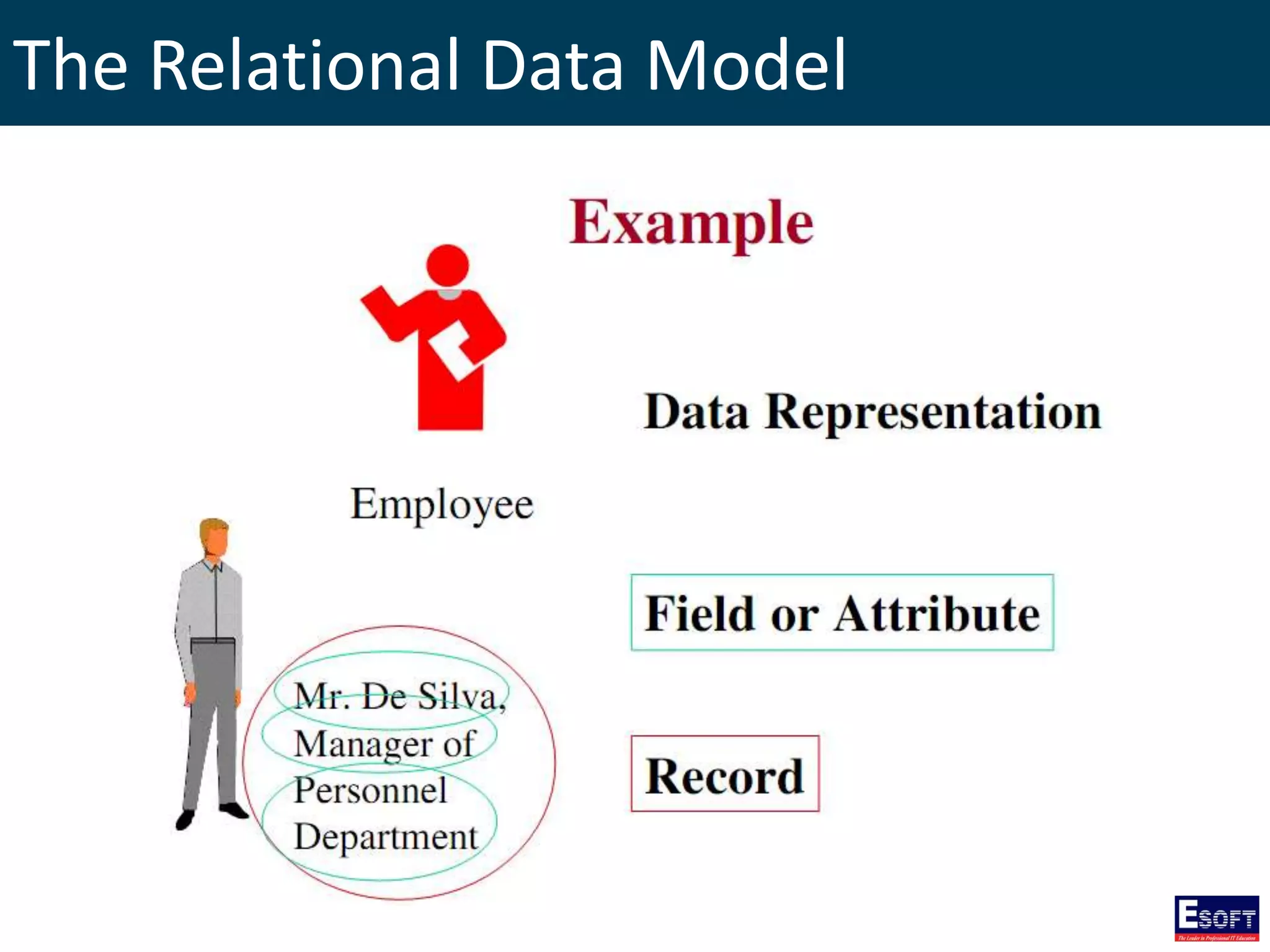
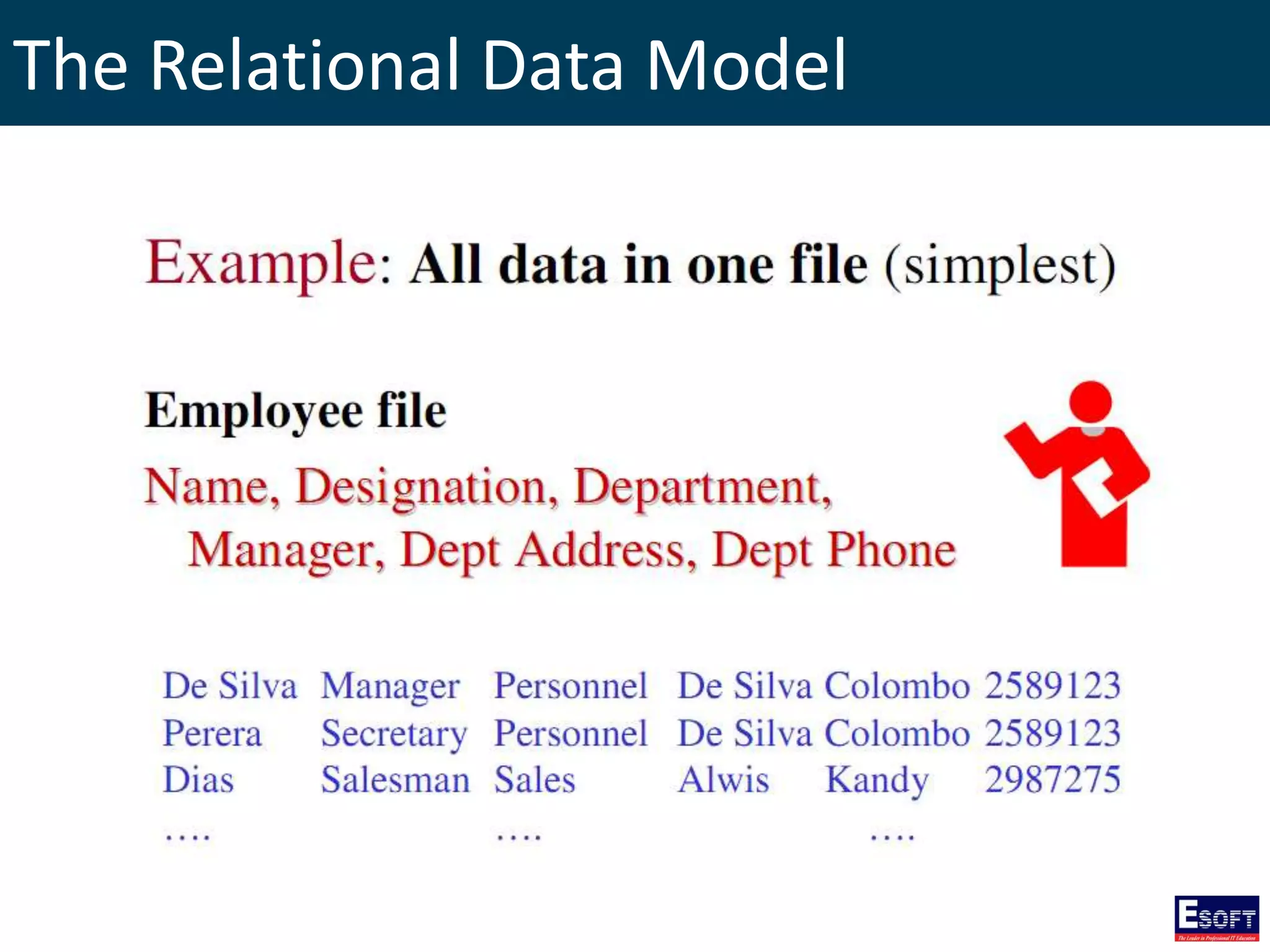
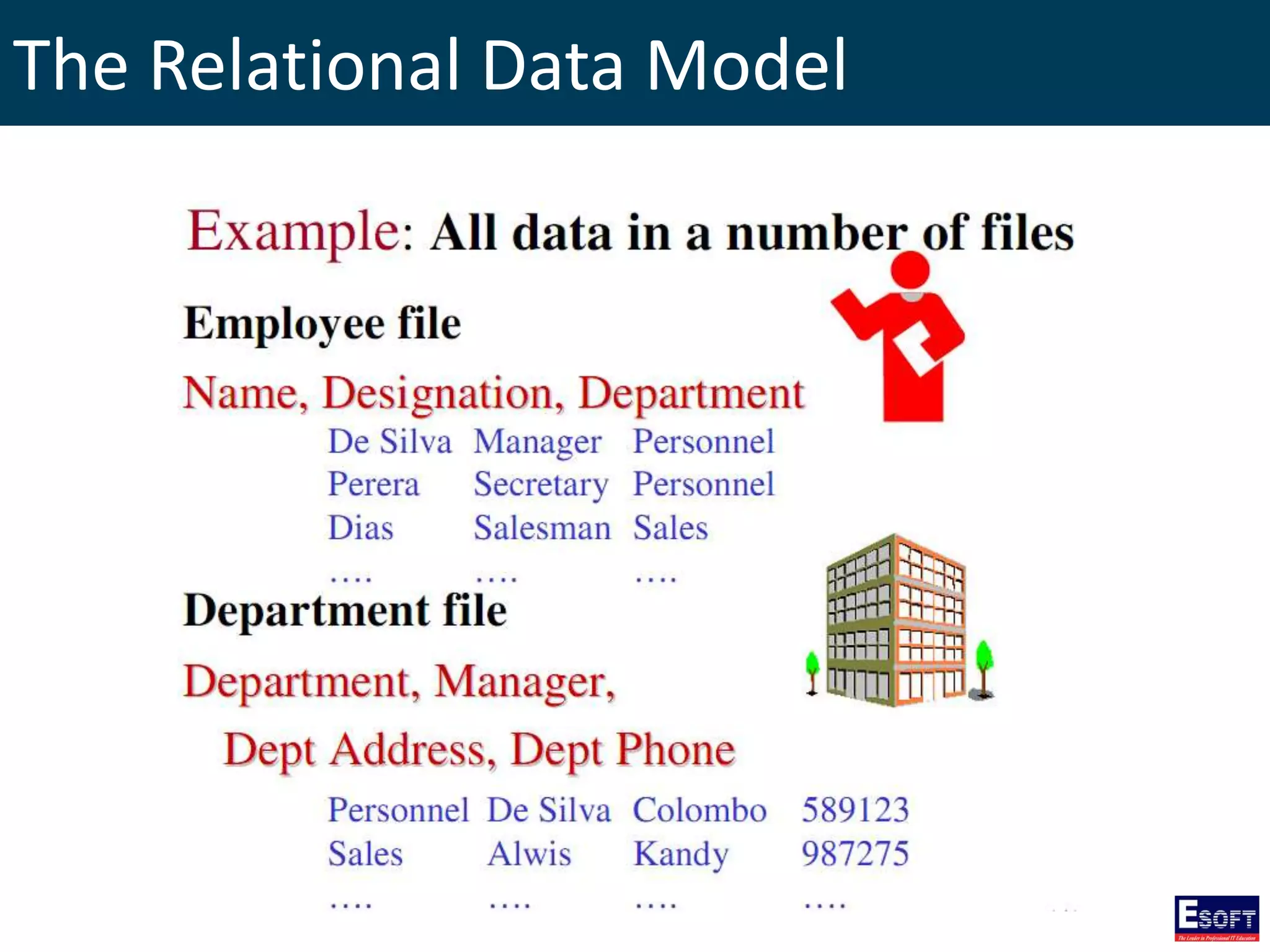
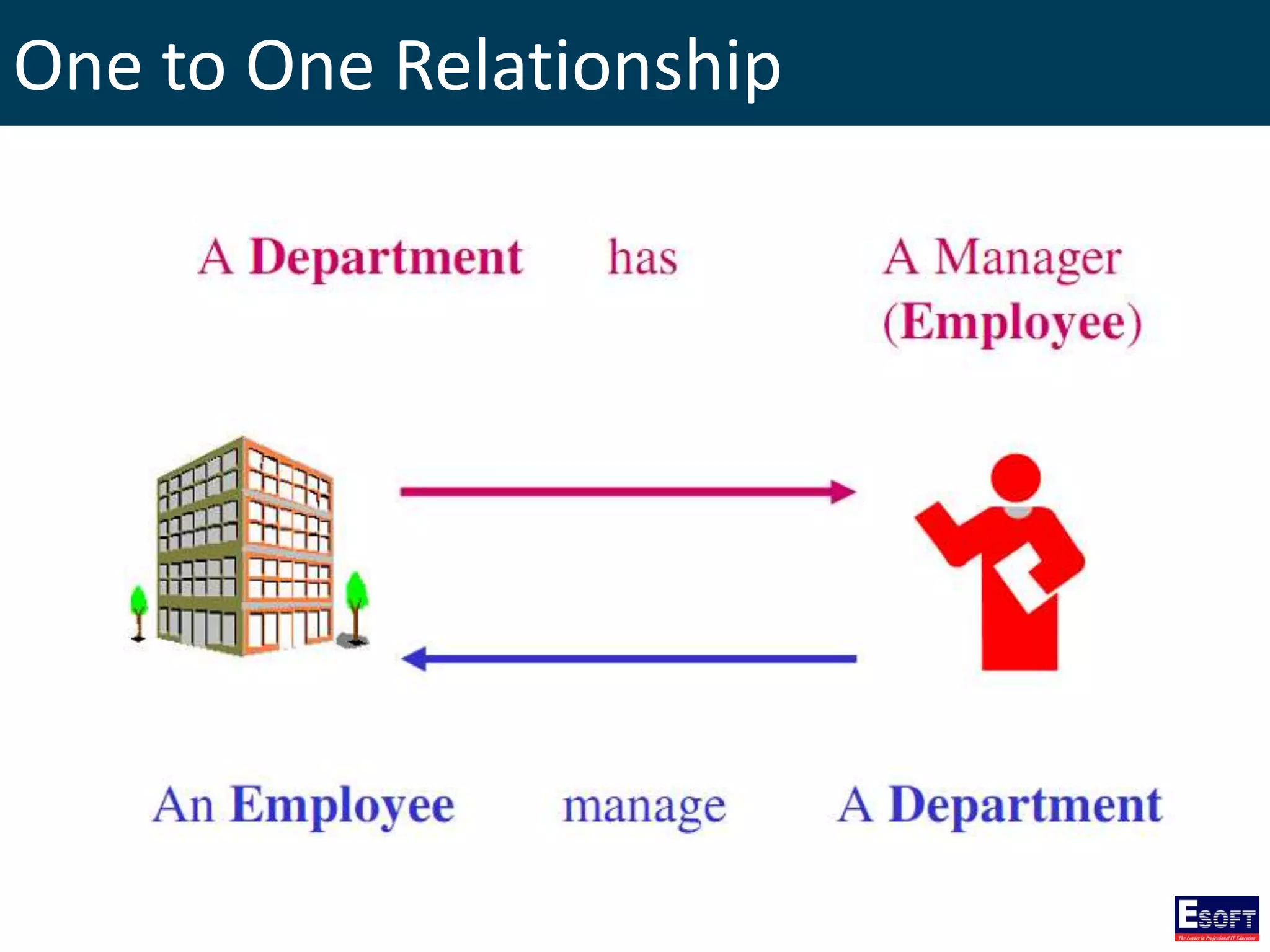
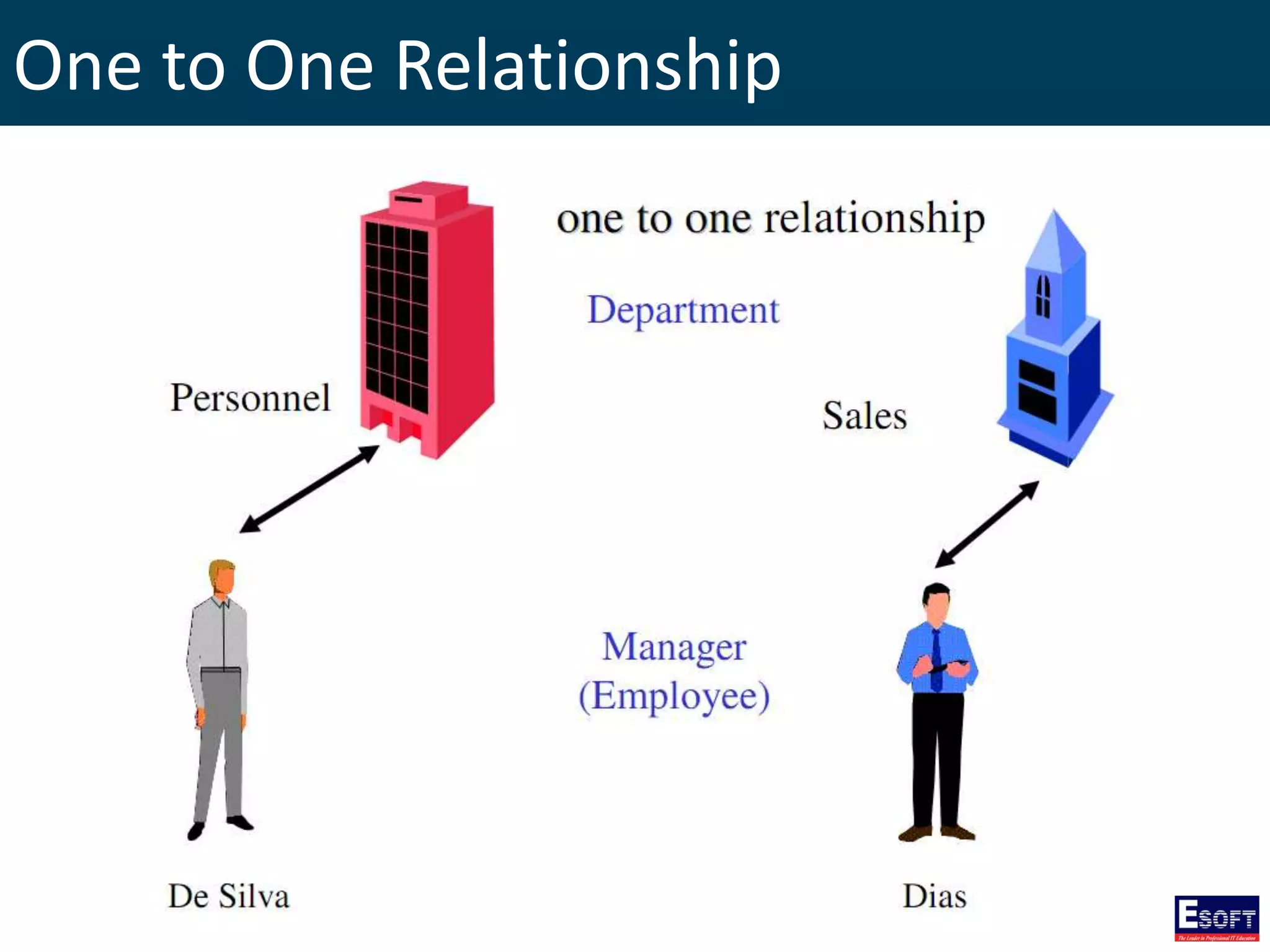
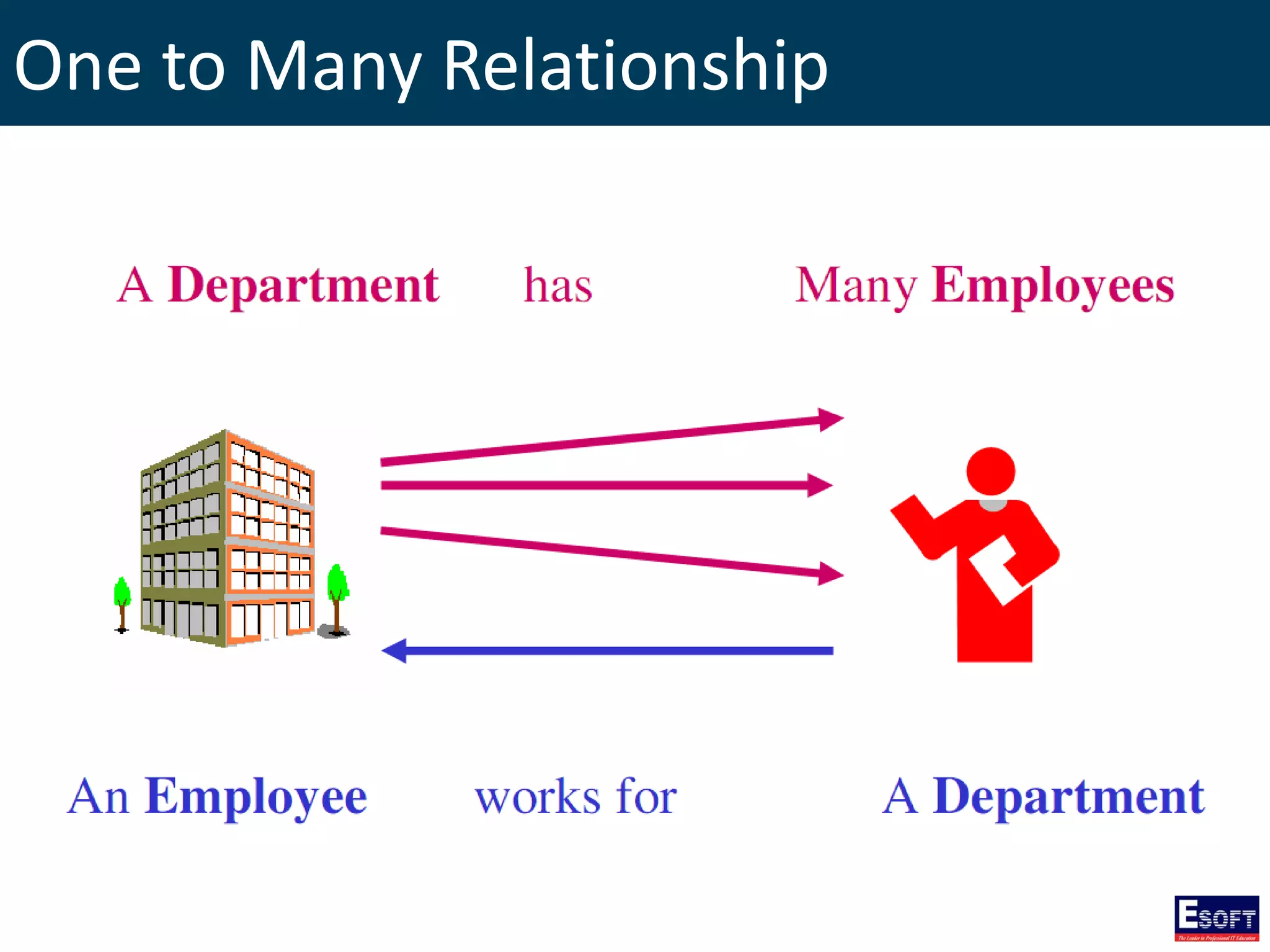
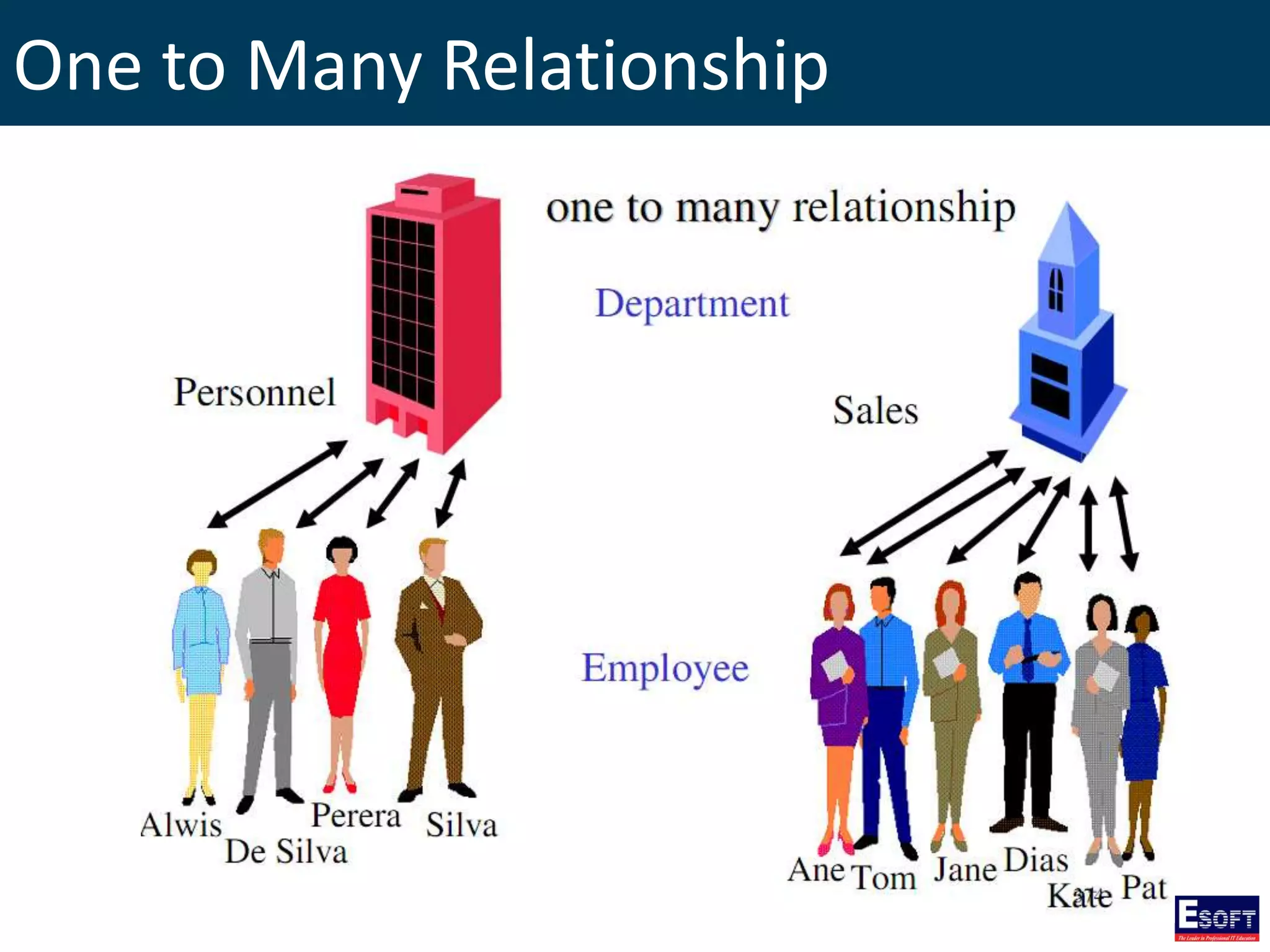
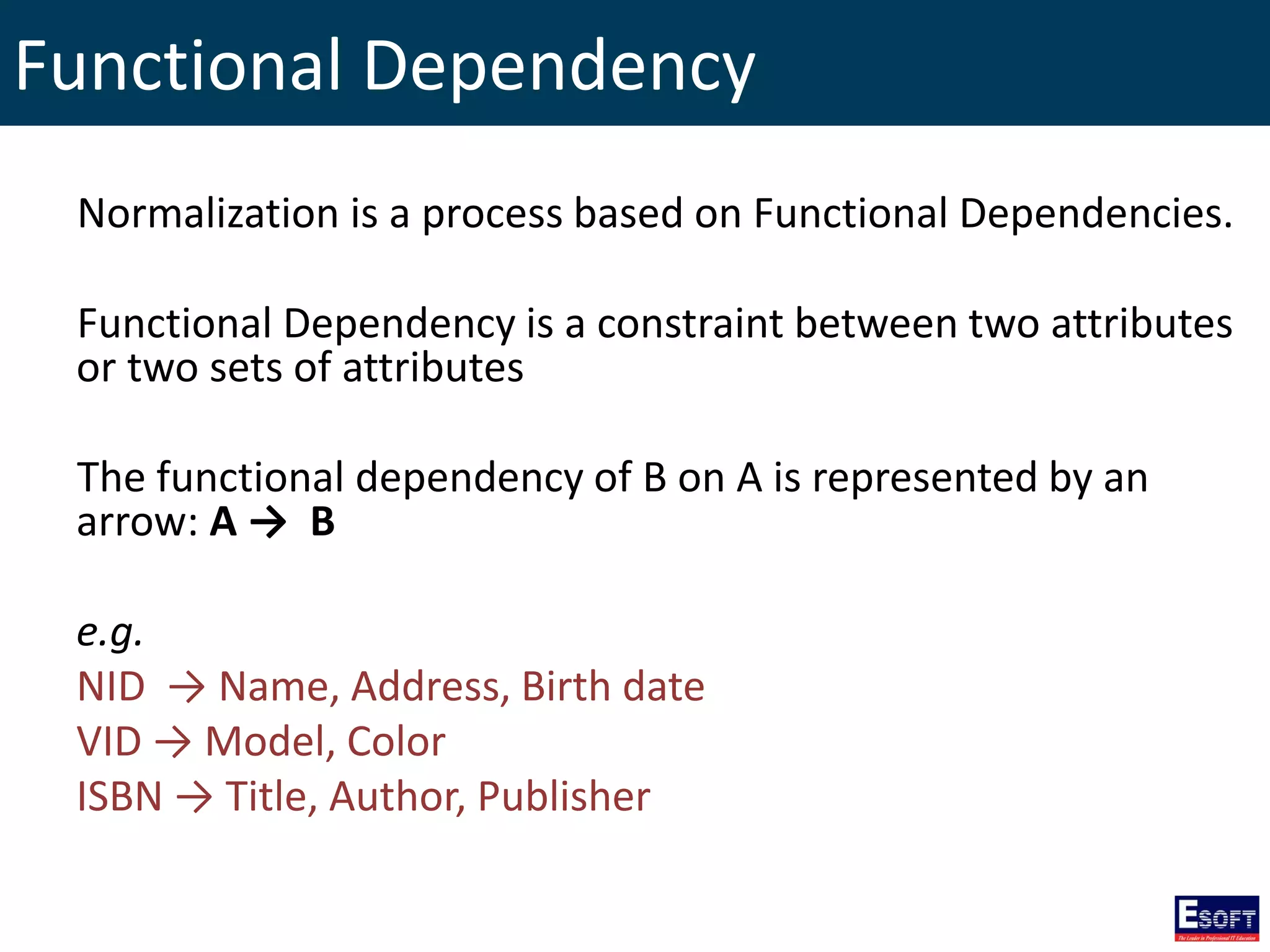
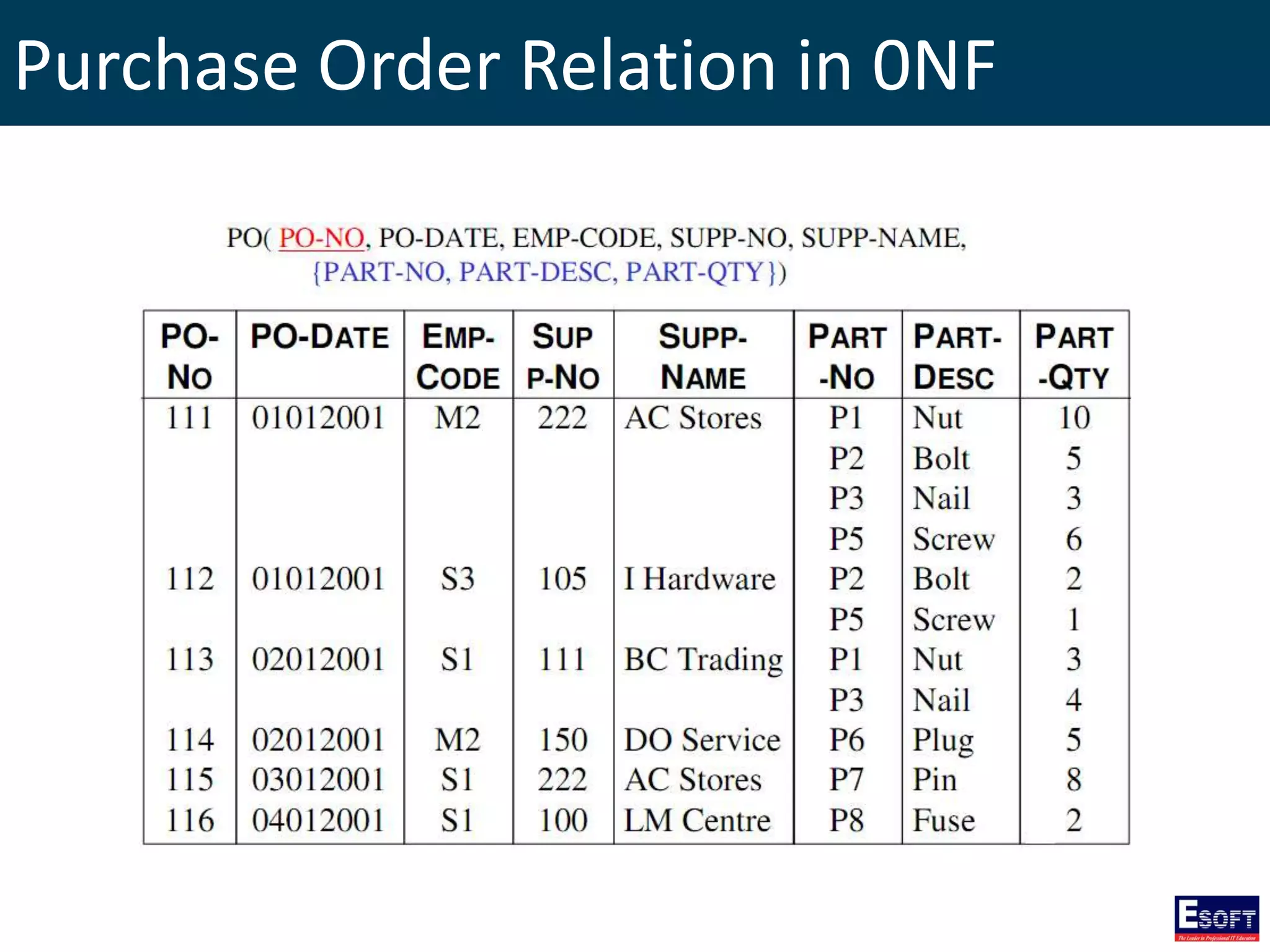
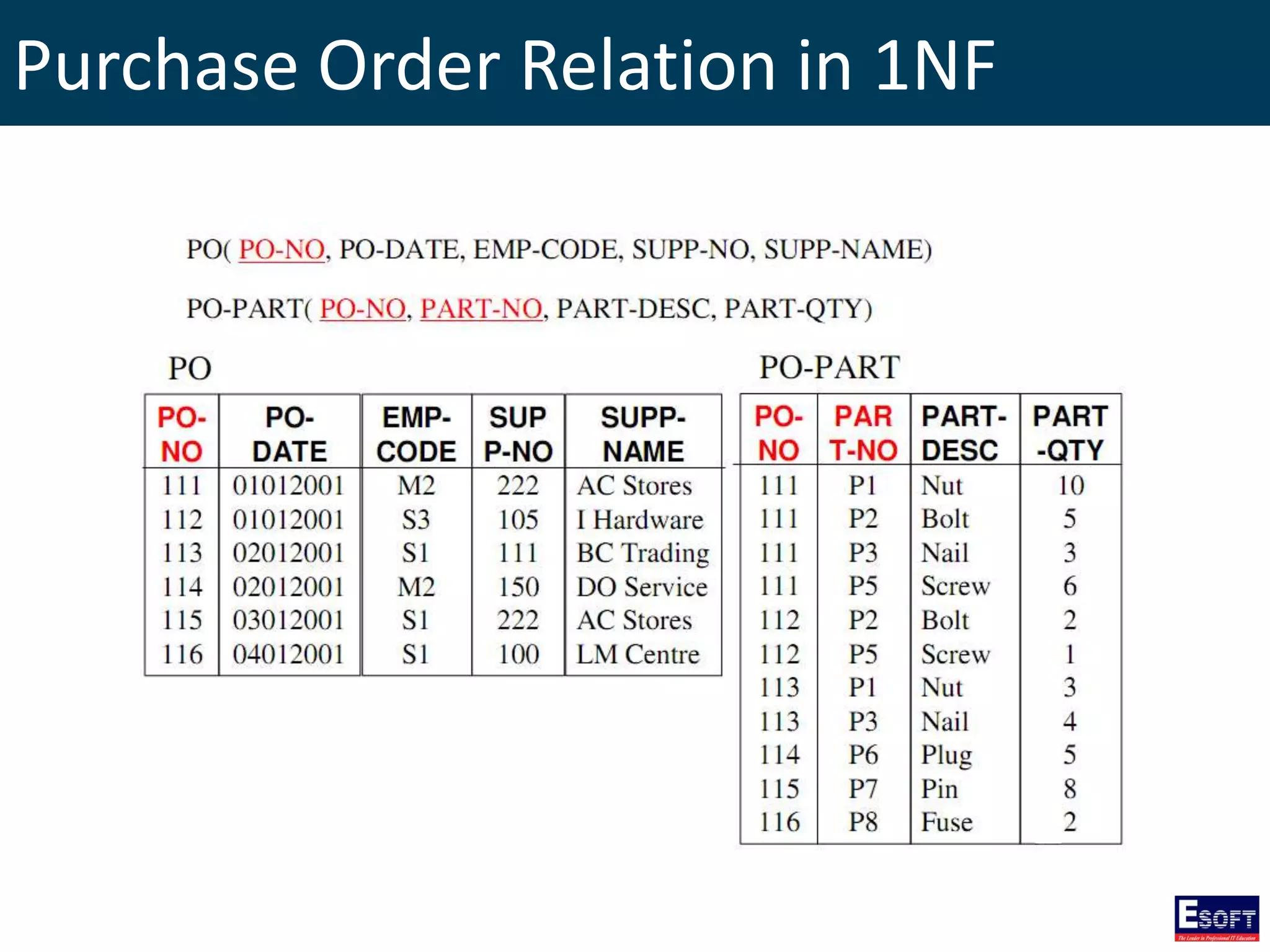
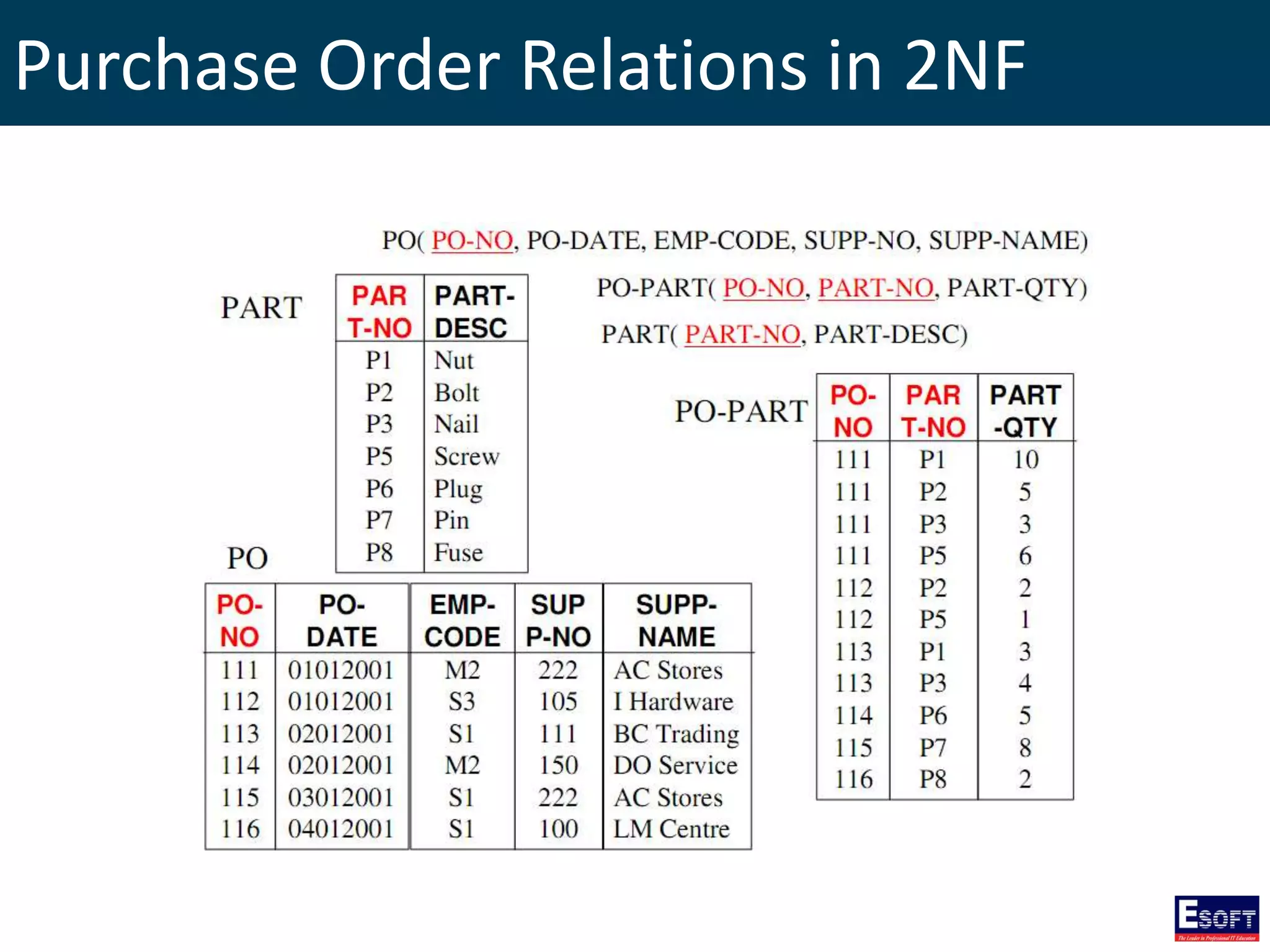
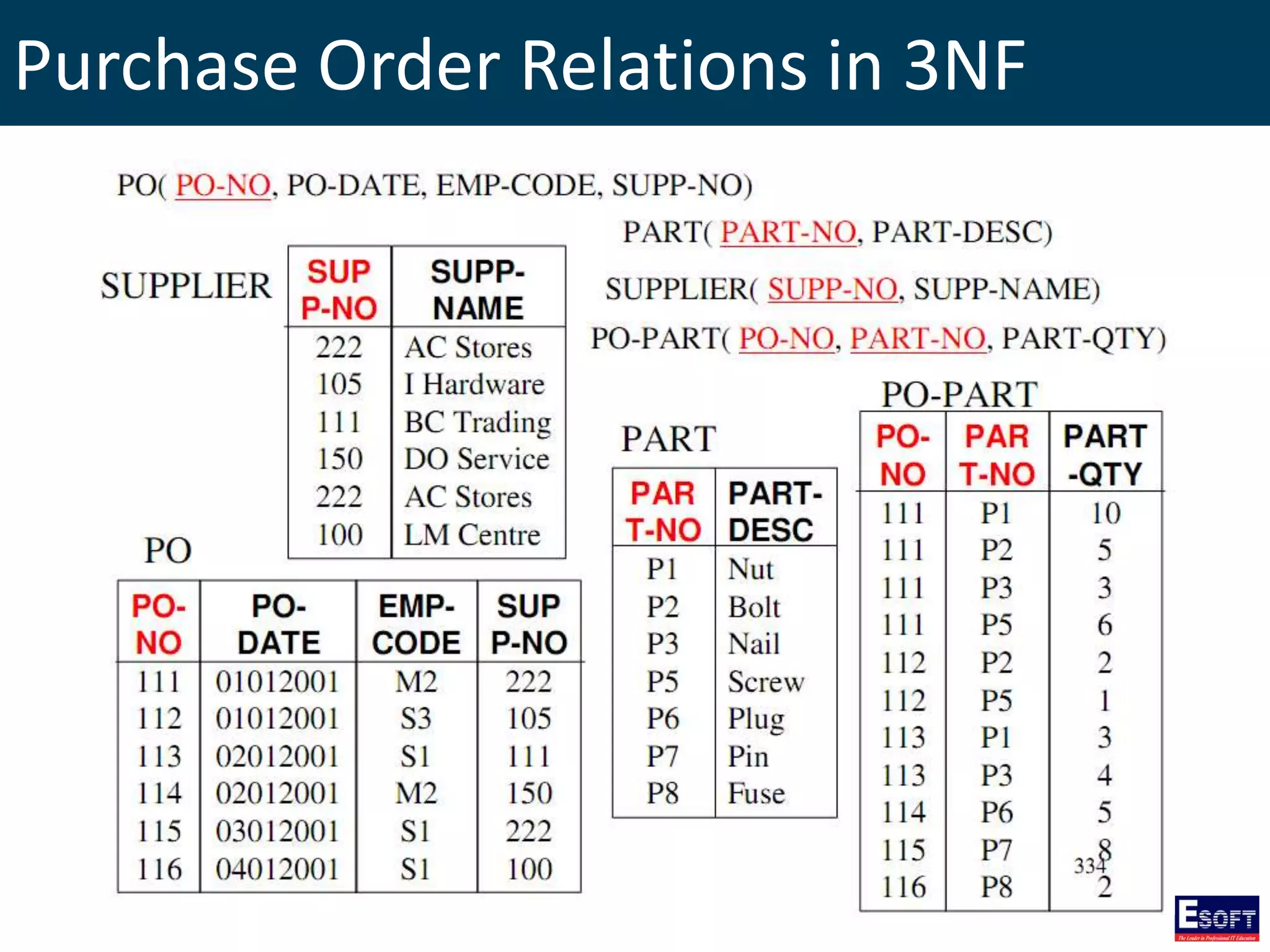
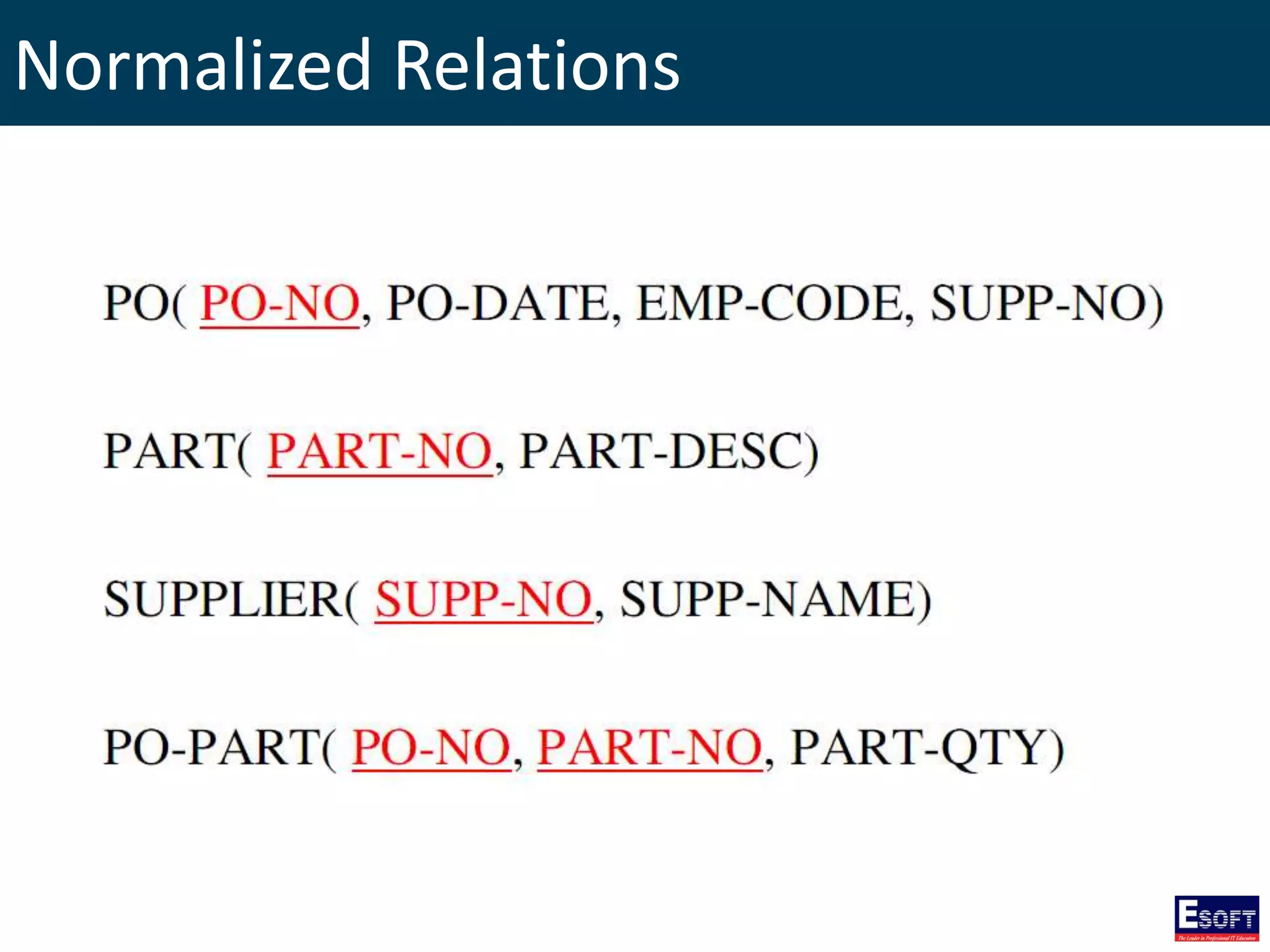
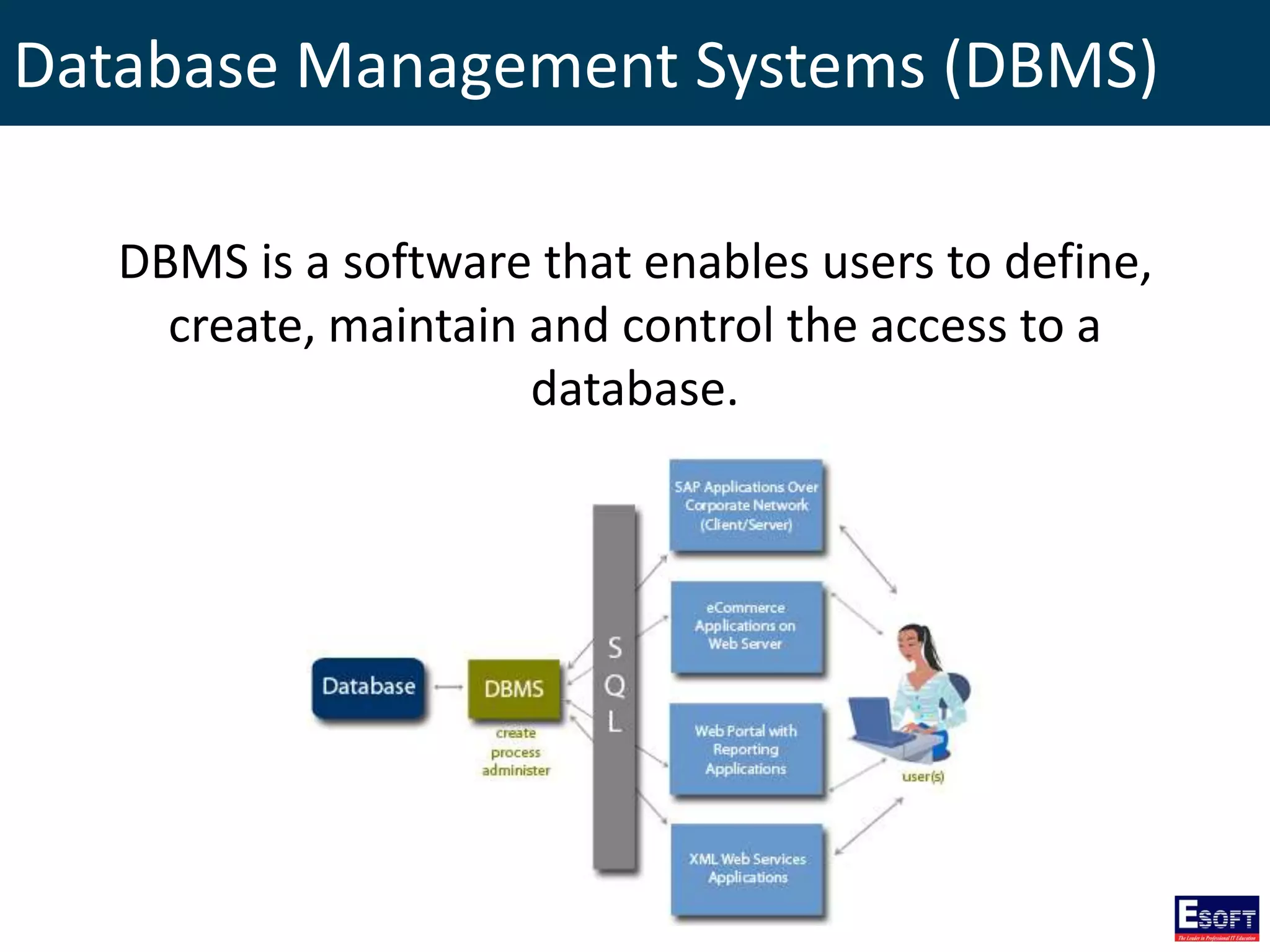
The document is a comprehensive guide on working with MySQL databases, covering foundational concepts like databases, relational data models, and normalization, followed by practical examples of PHP connection methods to MySQL. It includes detailed instructions on creating databases and tables, inserting, updating, and deleting records, as well as using prepared statements for enhanced security. Additionally, it discusses the role of a Database Management System (DBMS) and the advantages of normalization in reducing data redundancy.








![Select Data From MySQL (object oriented)
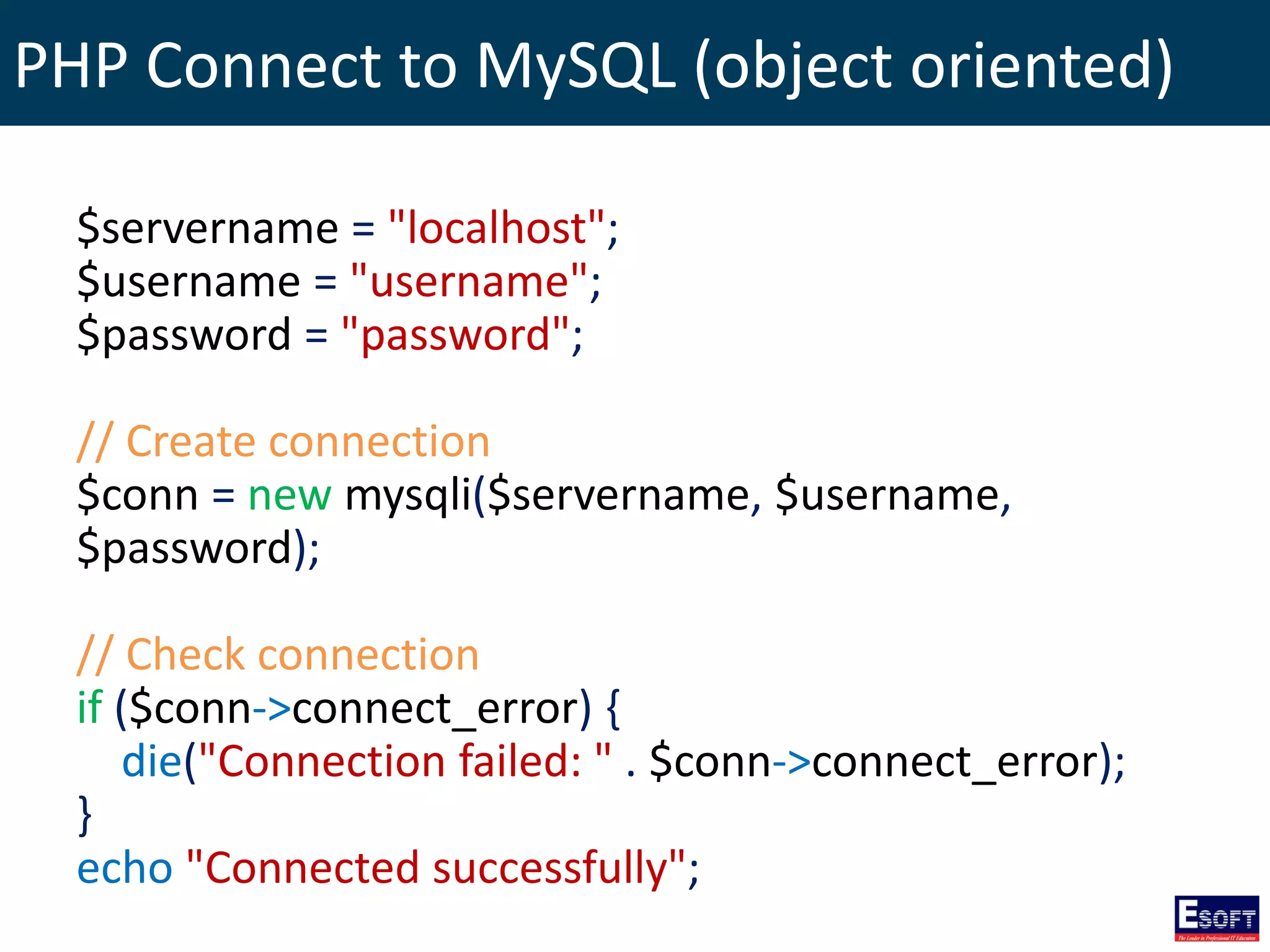
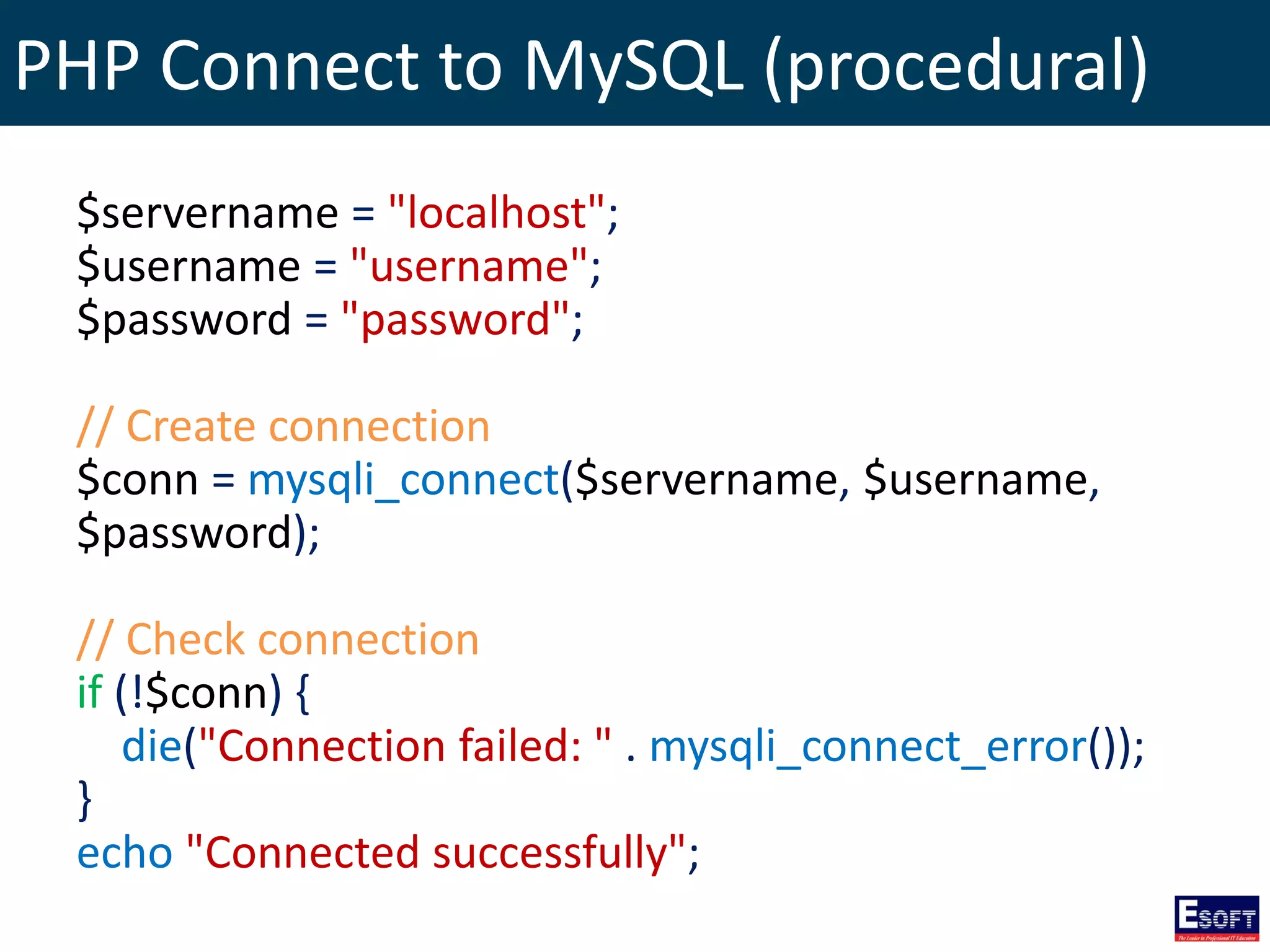
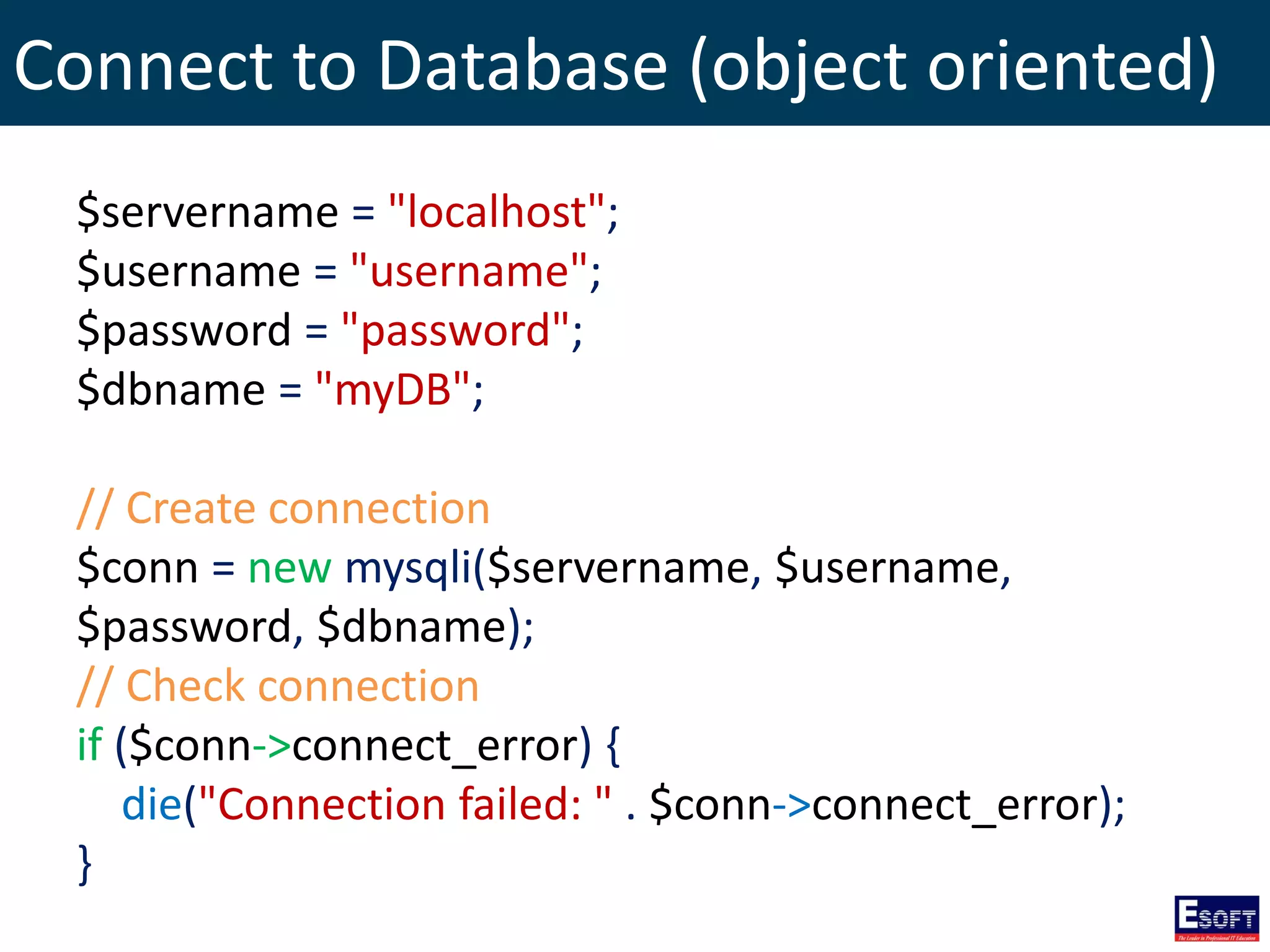
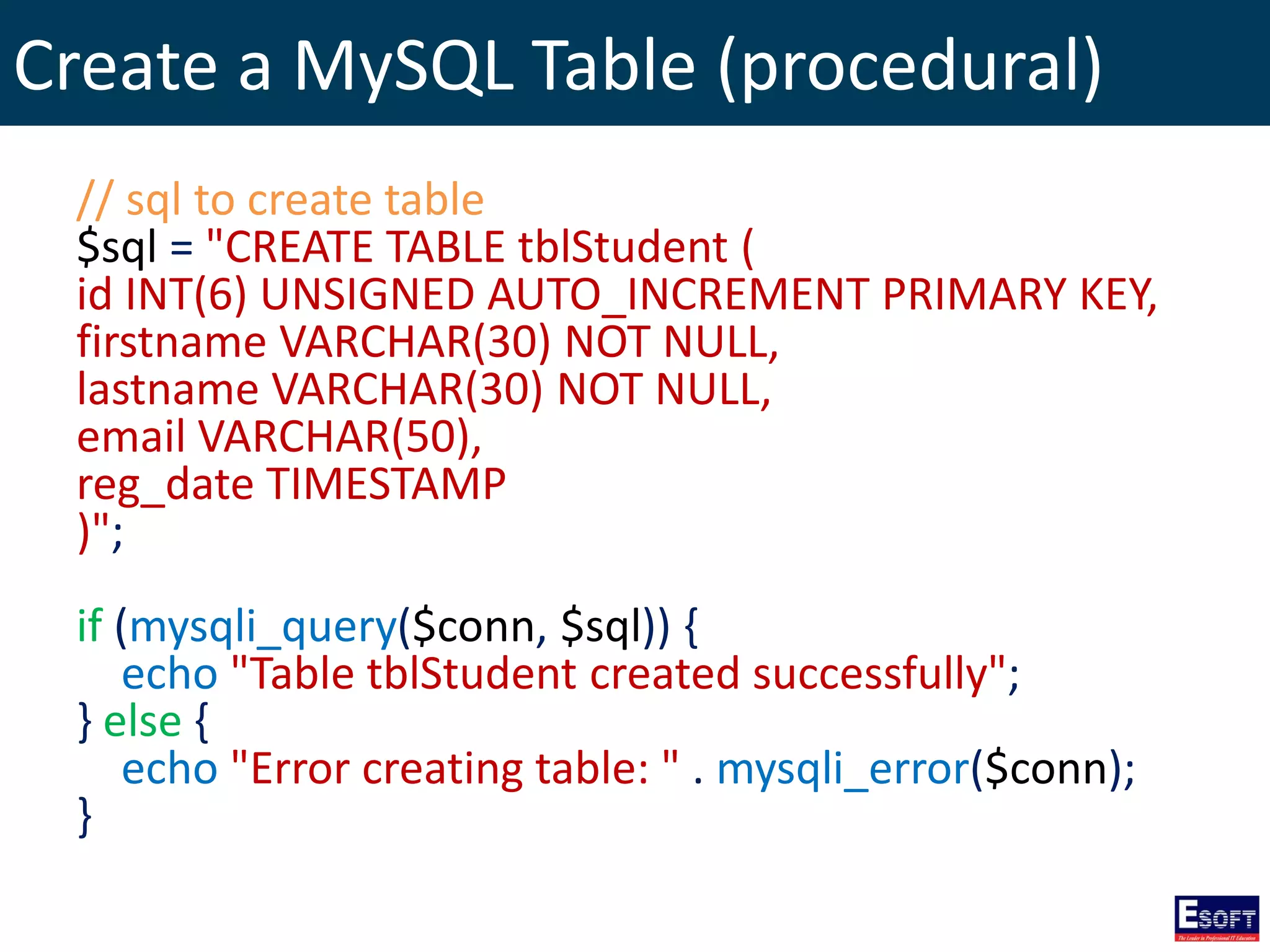
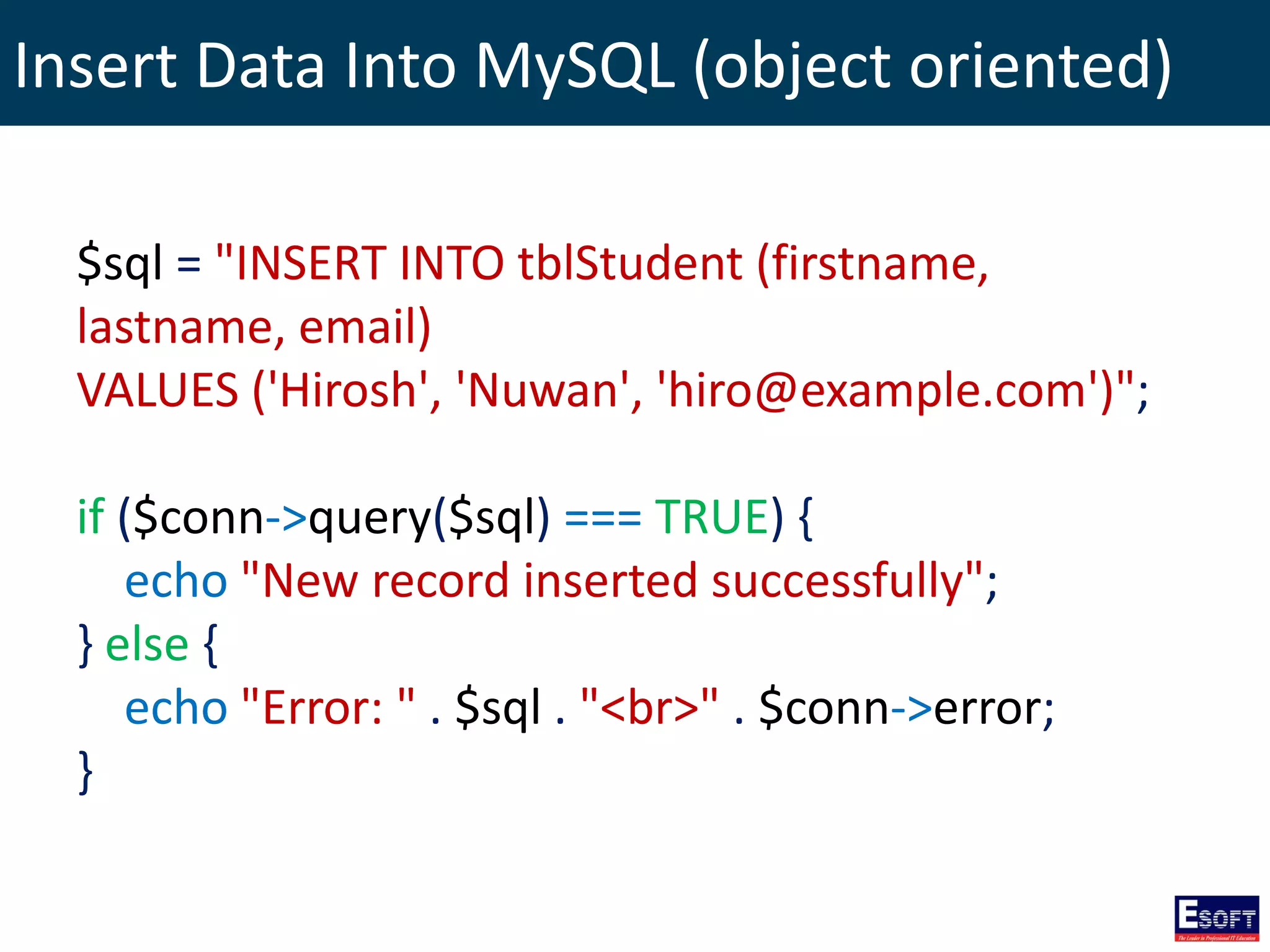
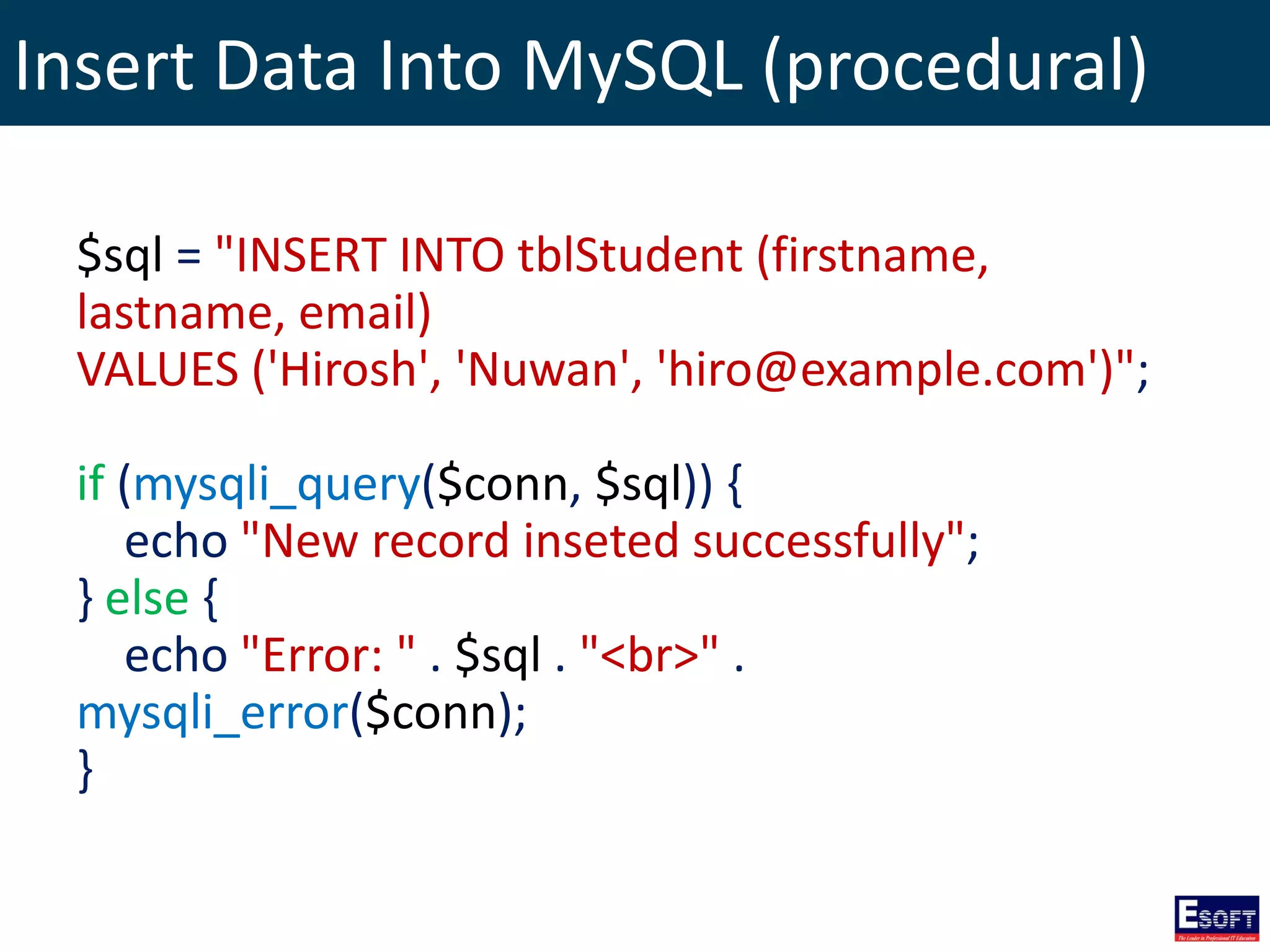
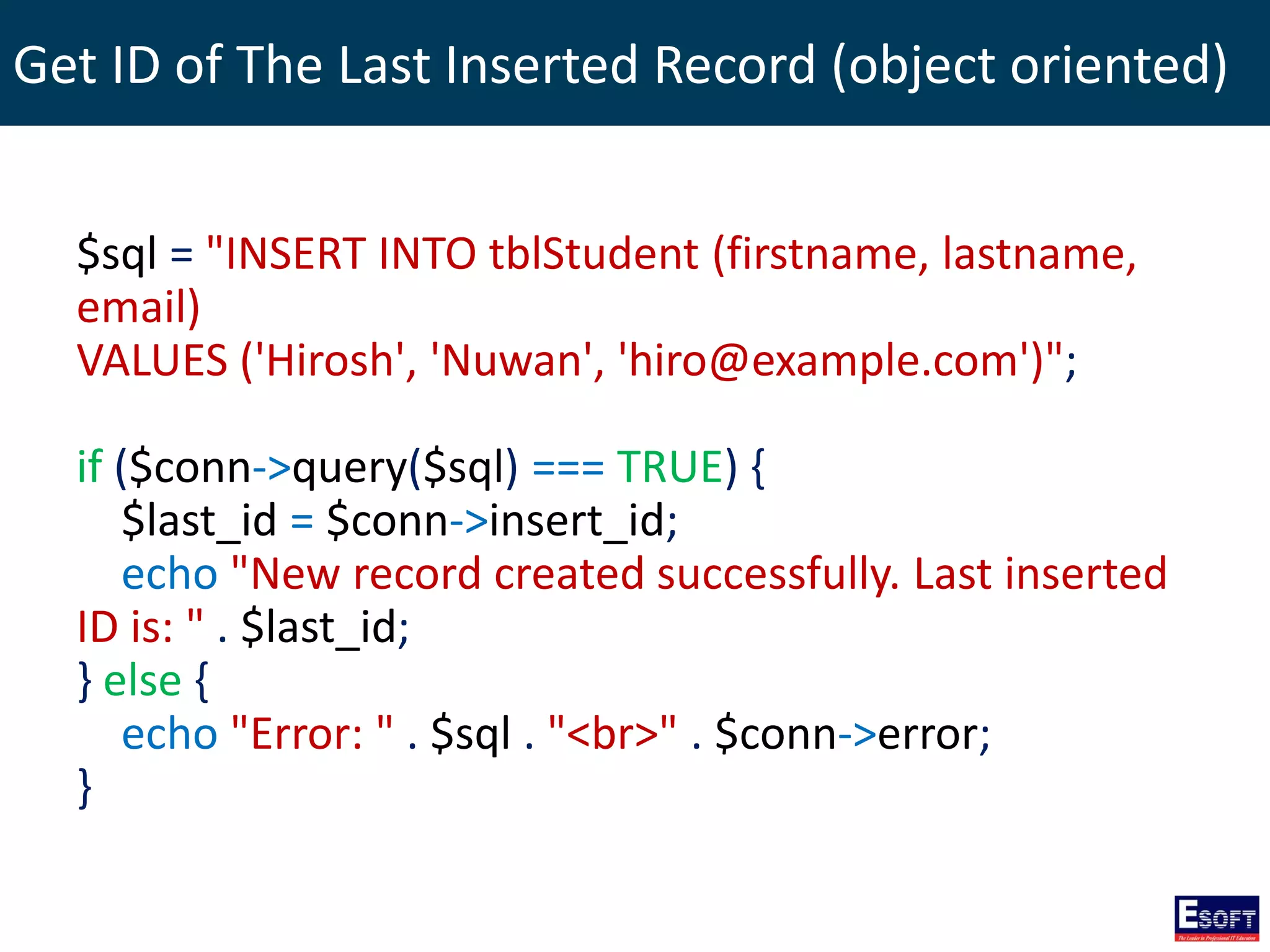
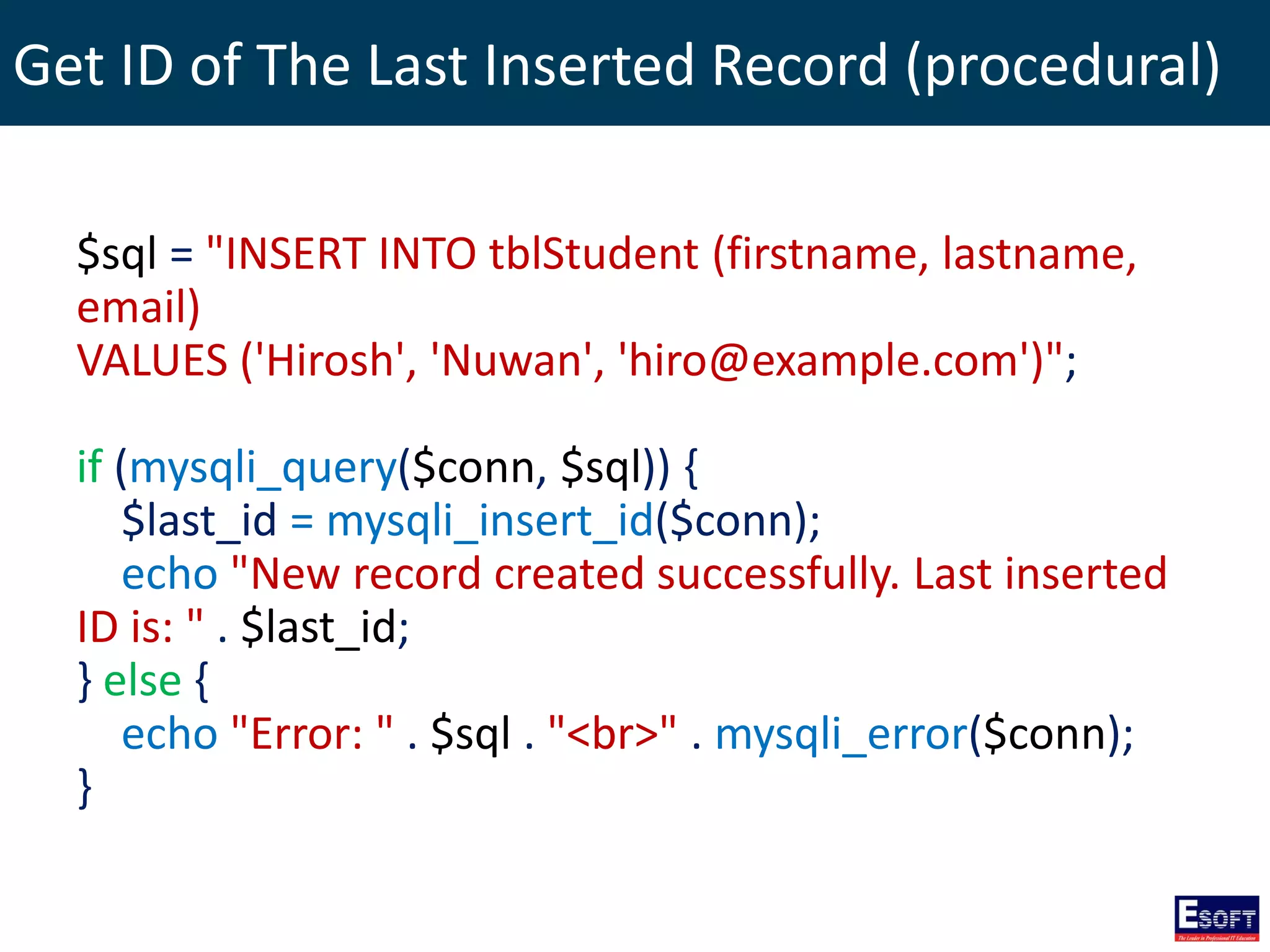
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM tblStudent";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " .
$row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulex-170204095037/75/DIWE-Working-with-MySQL-Databases-50-2048.jpg)
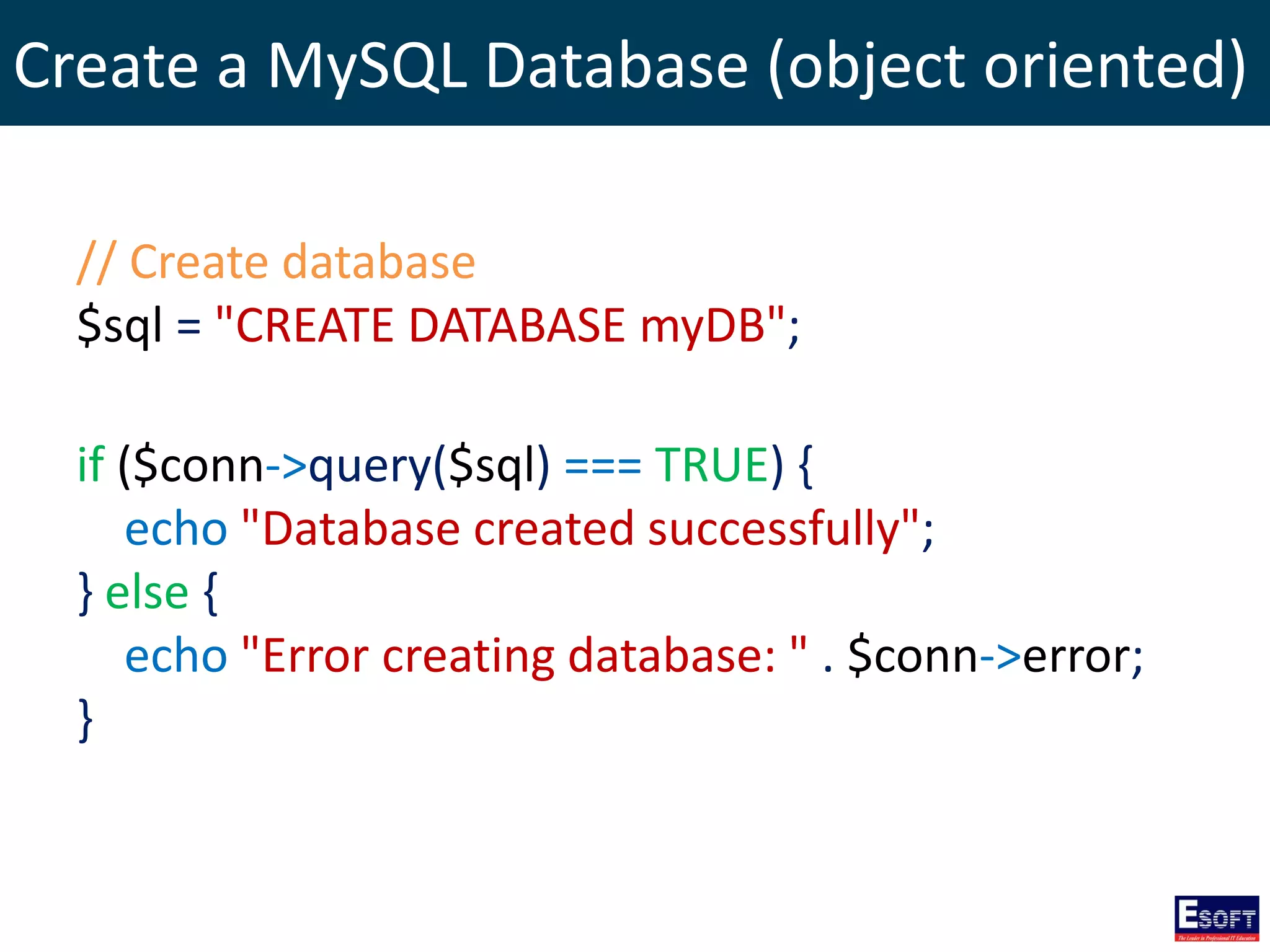
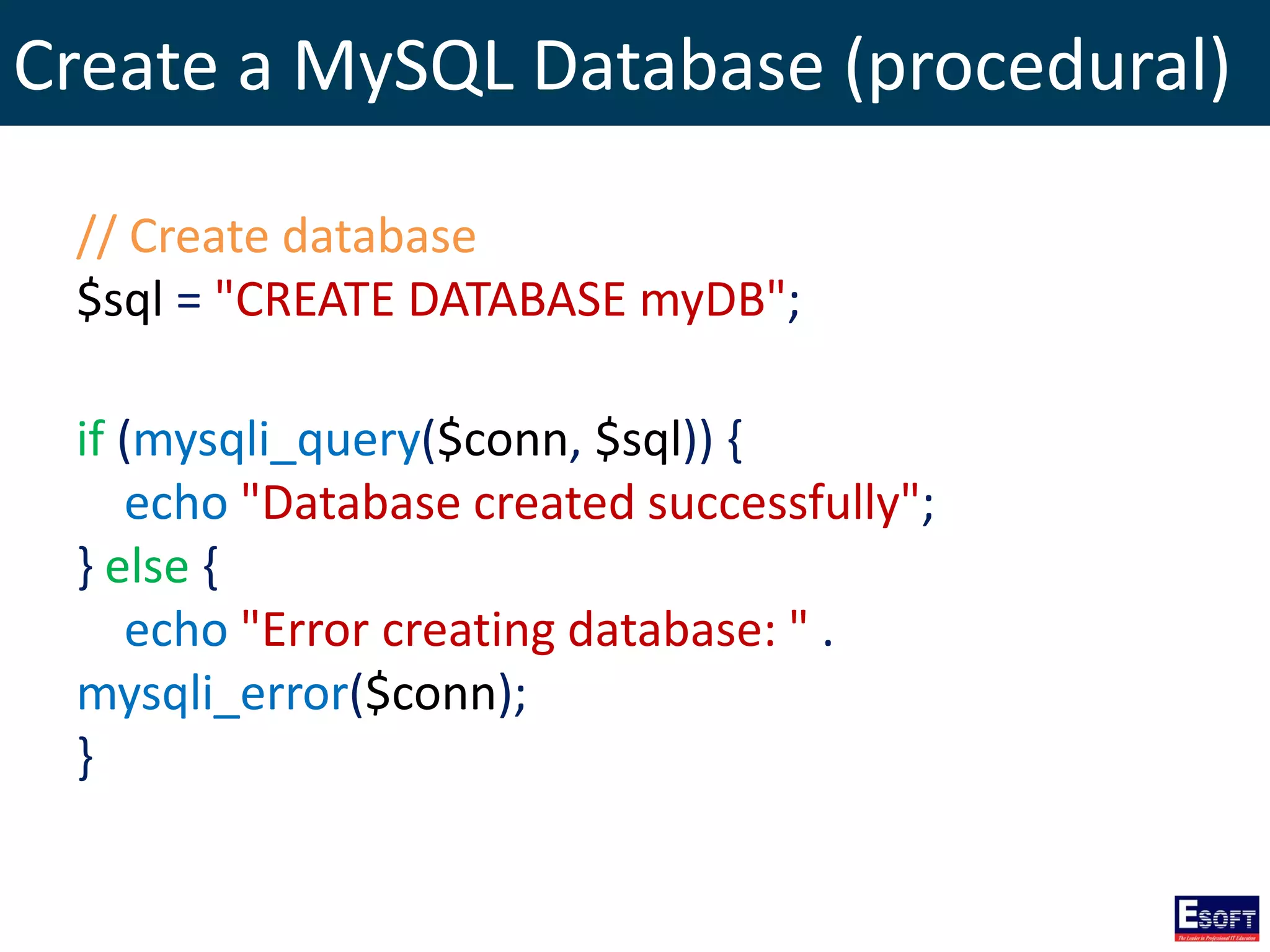
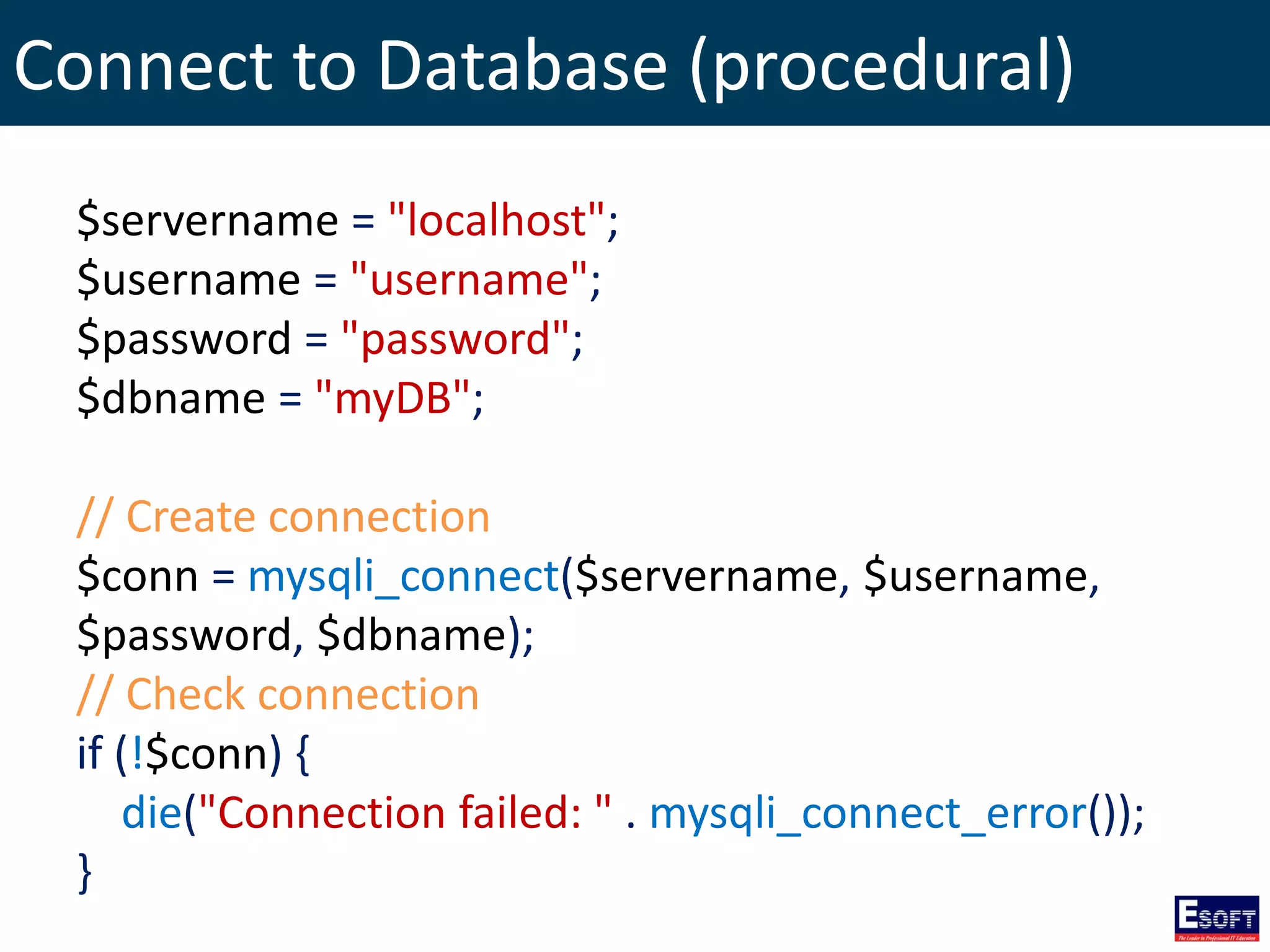
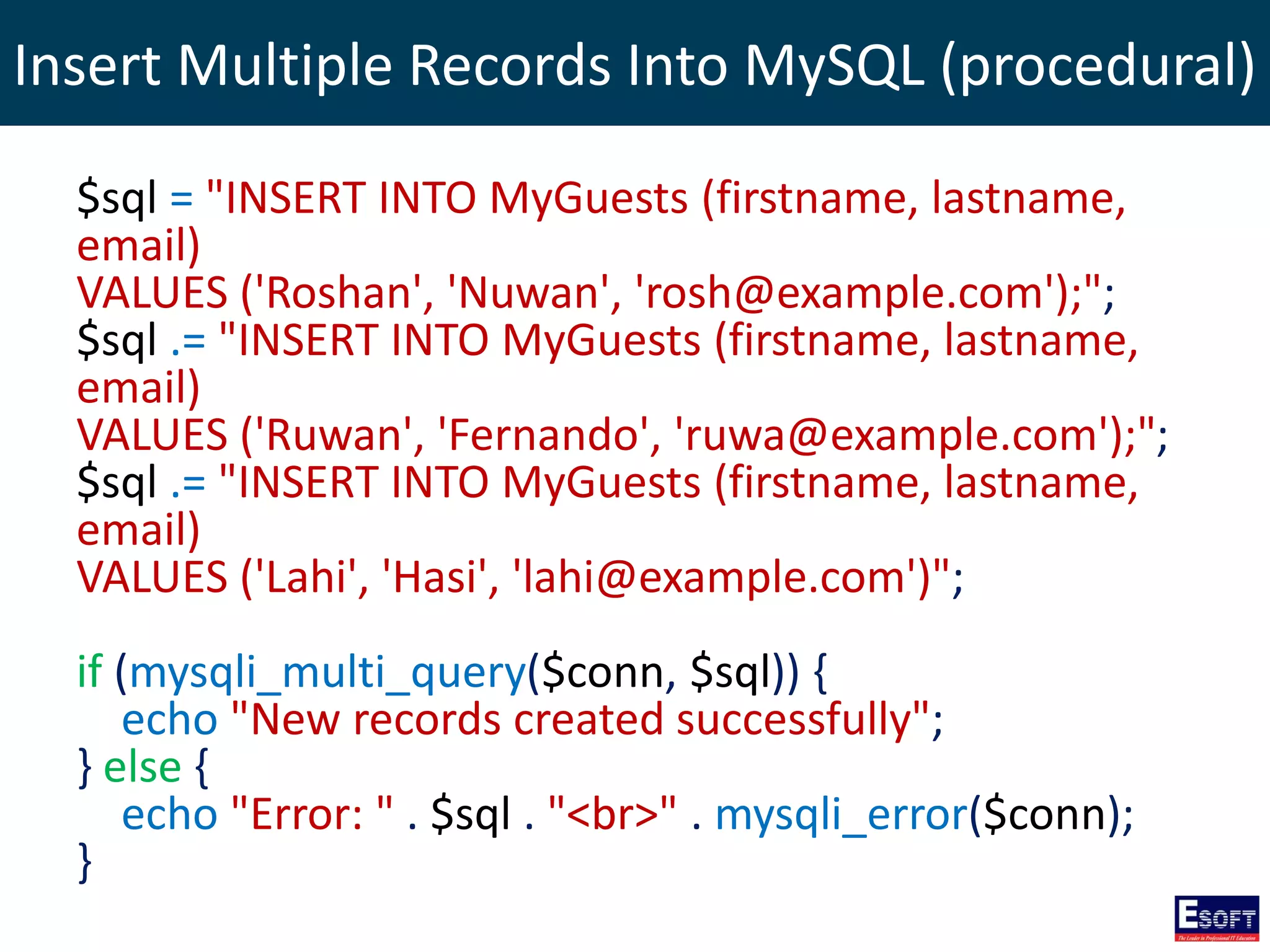
![Select Data From MySQL (procedural)
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM tblStudent";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " .
$row["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulex-170204095037/75/DIWE-Working-with-MySQL-Databases-51-2048.jpg)