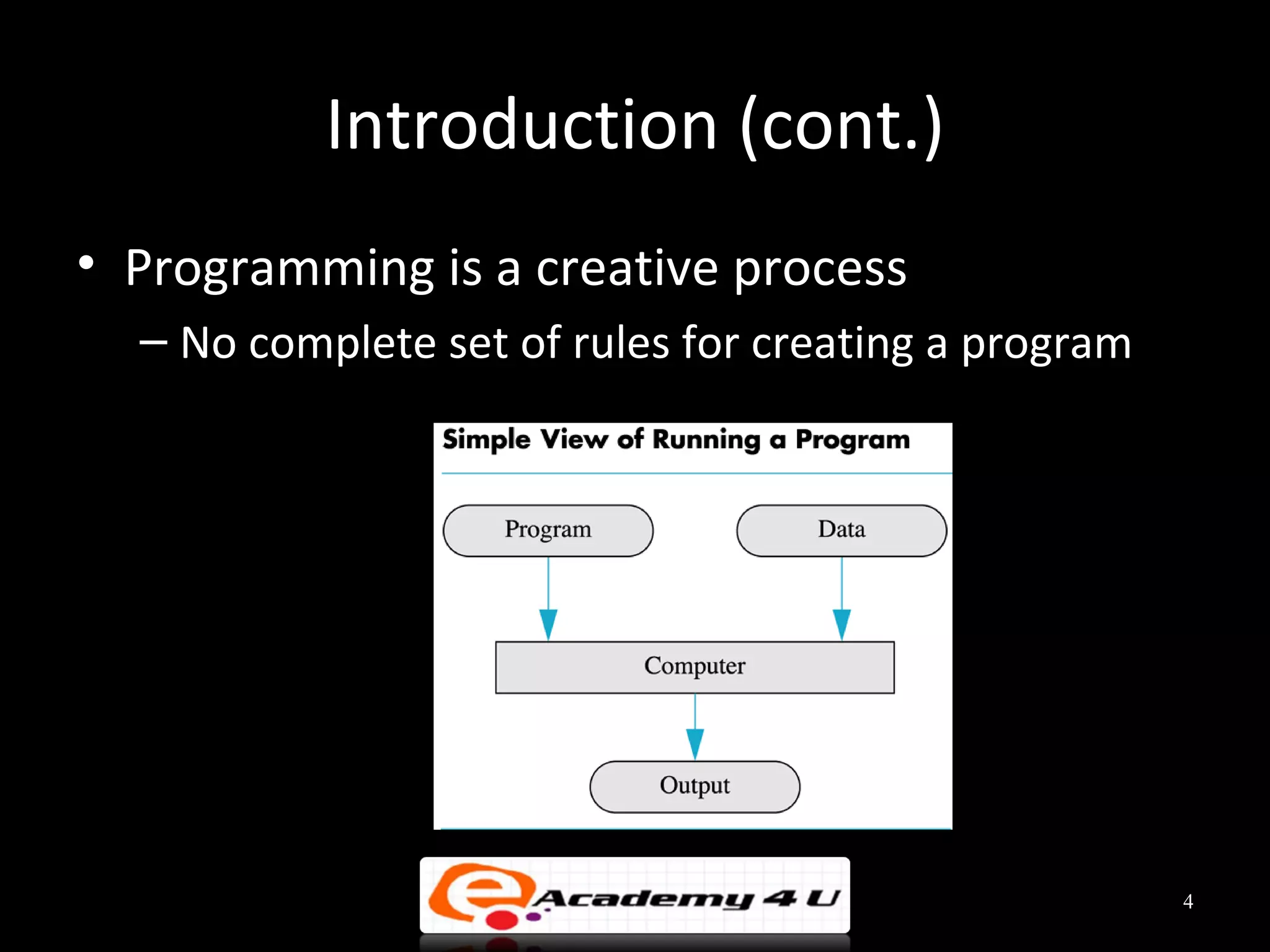
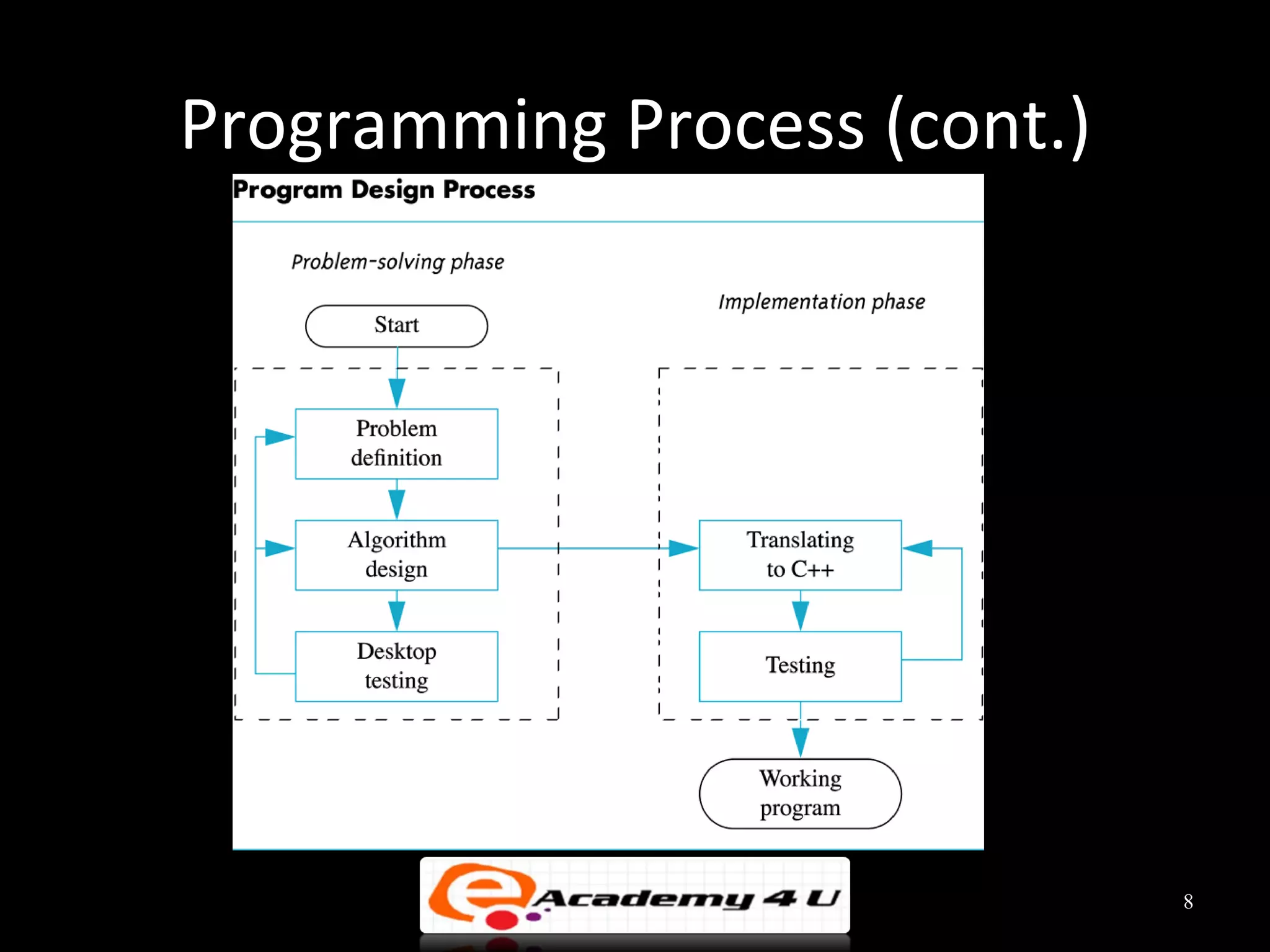
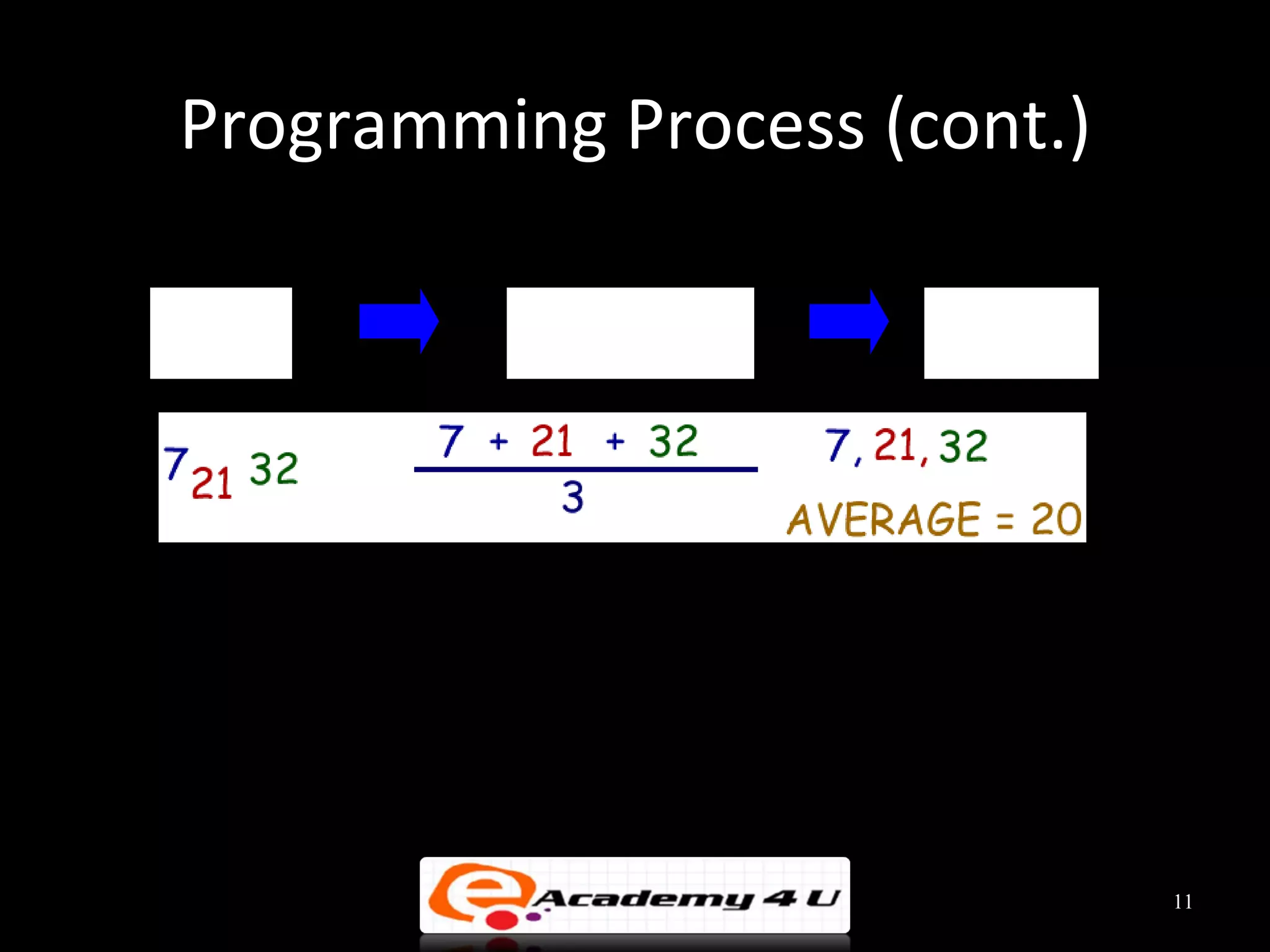
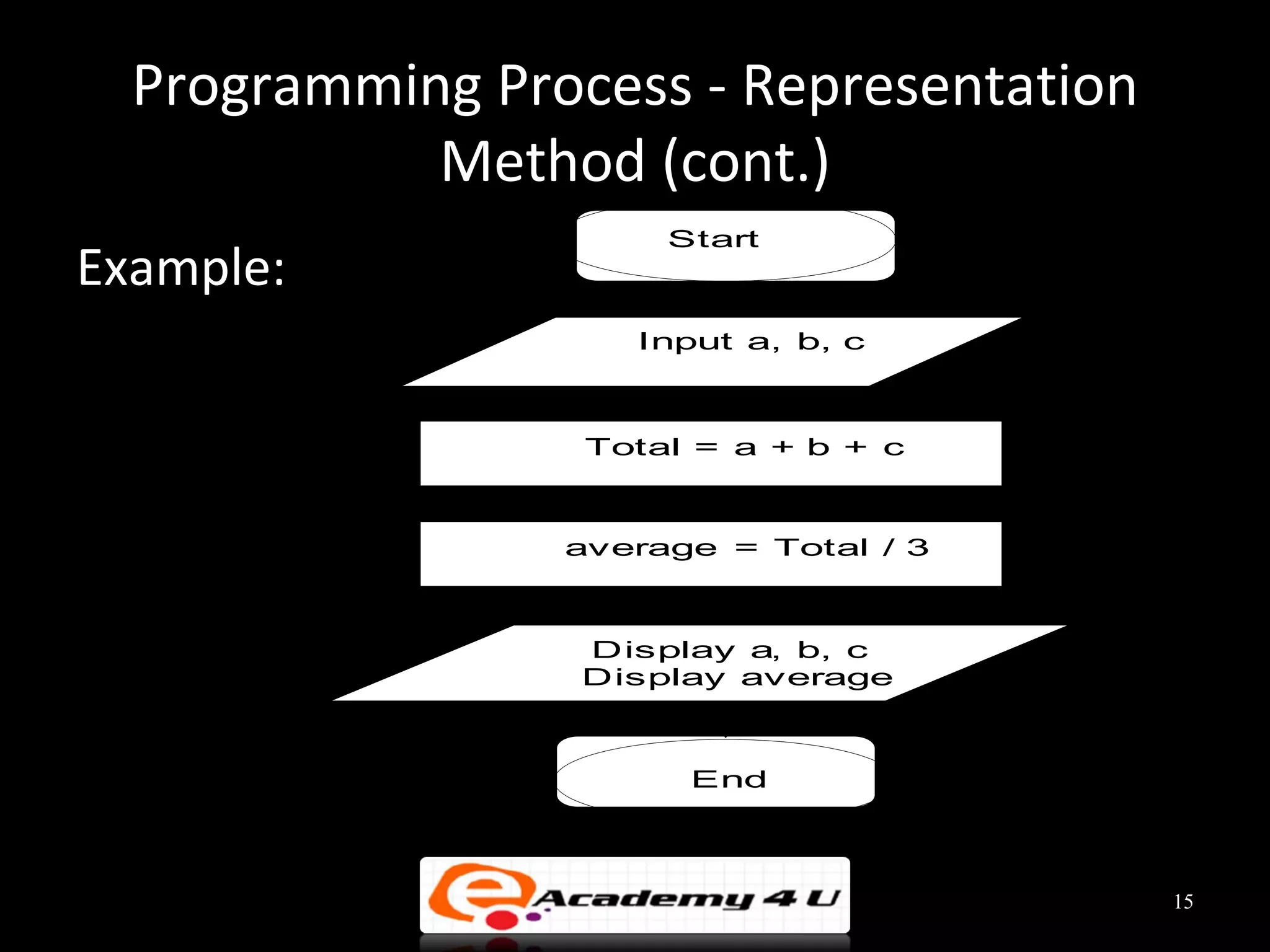
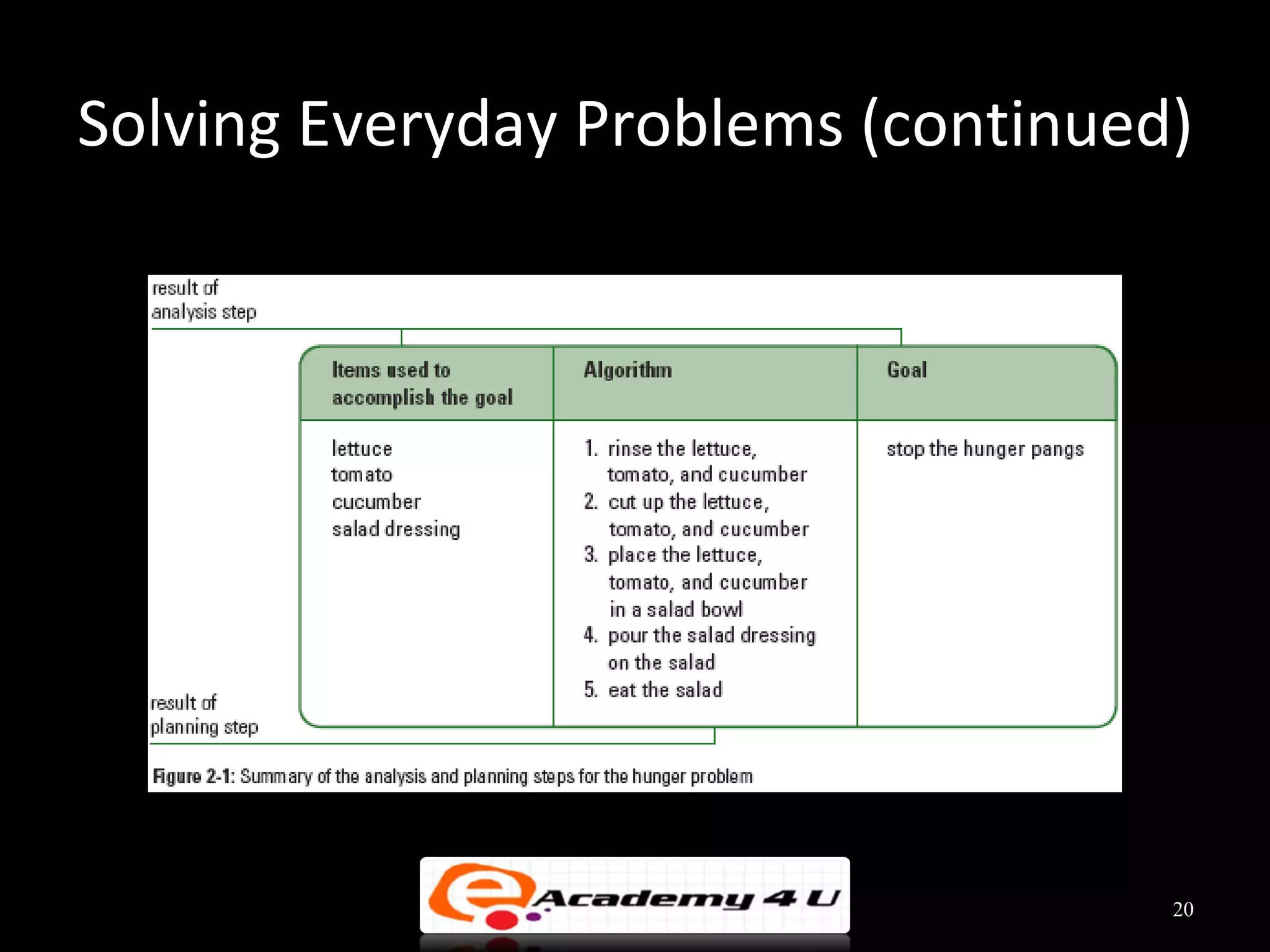
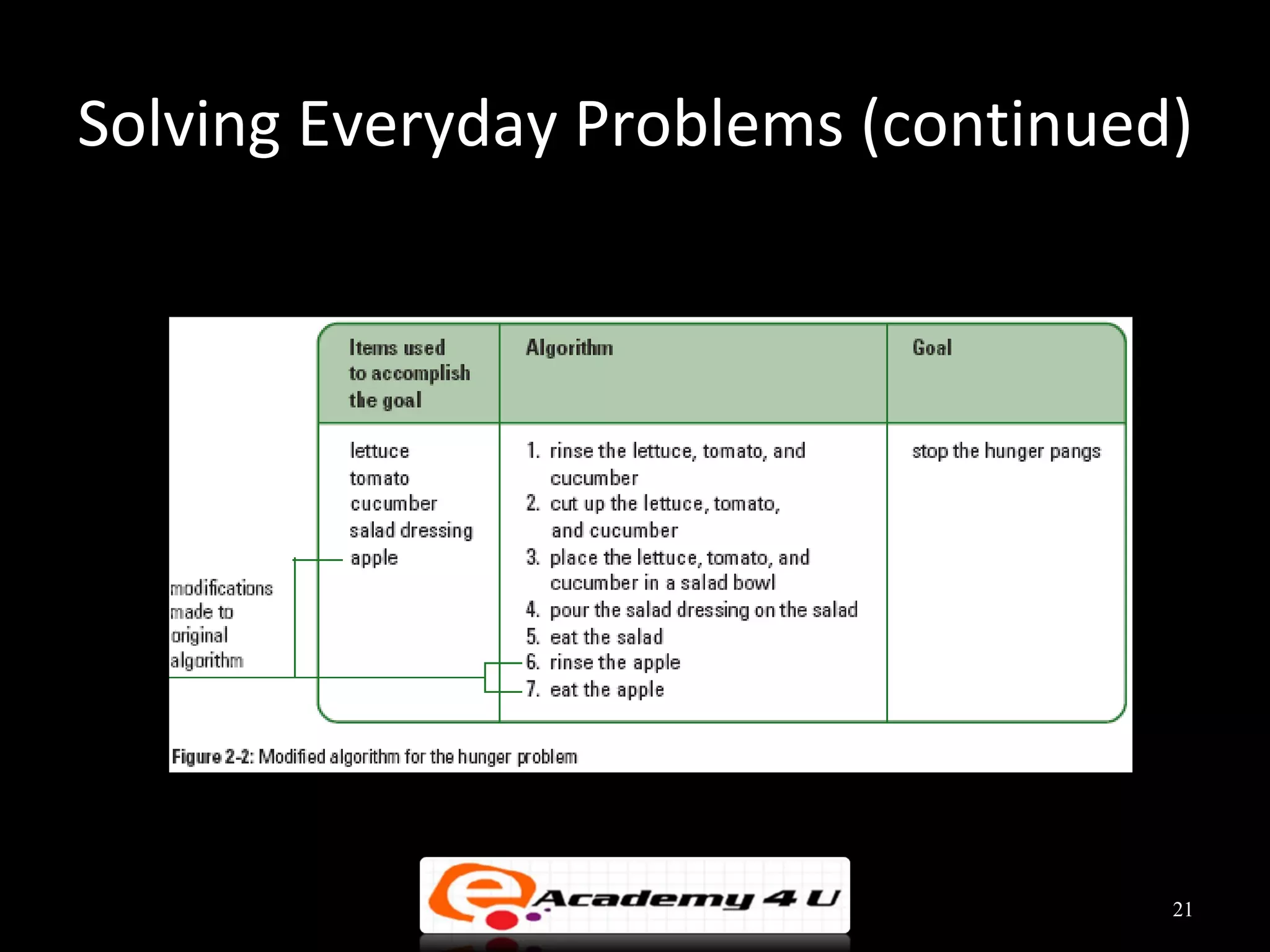
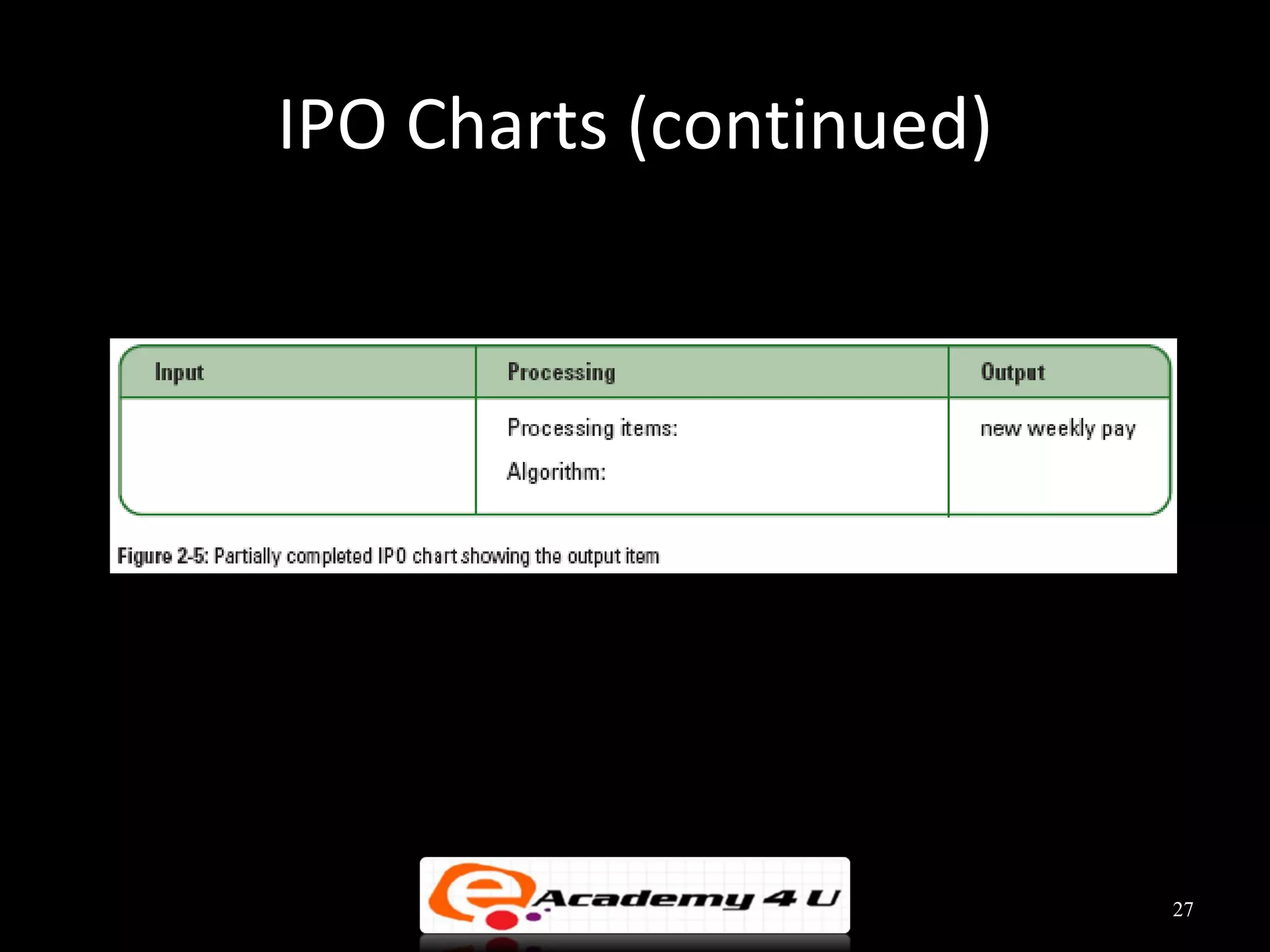
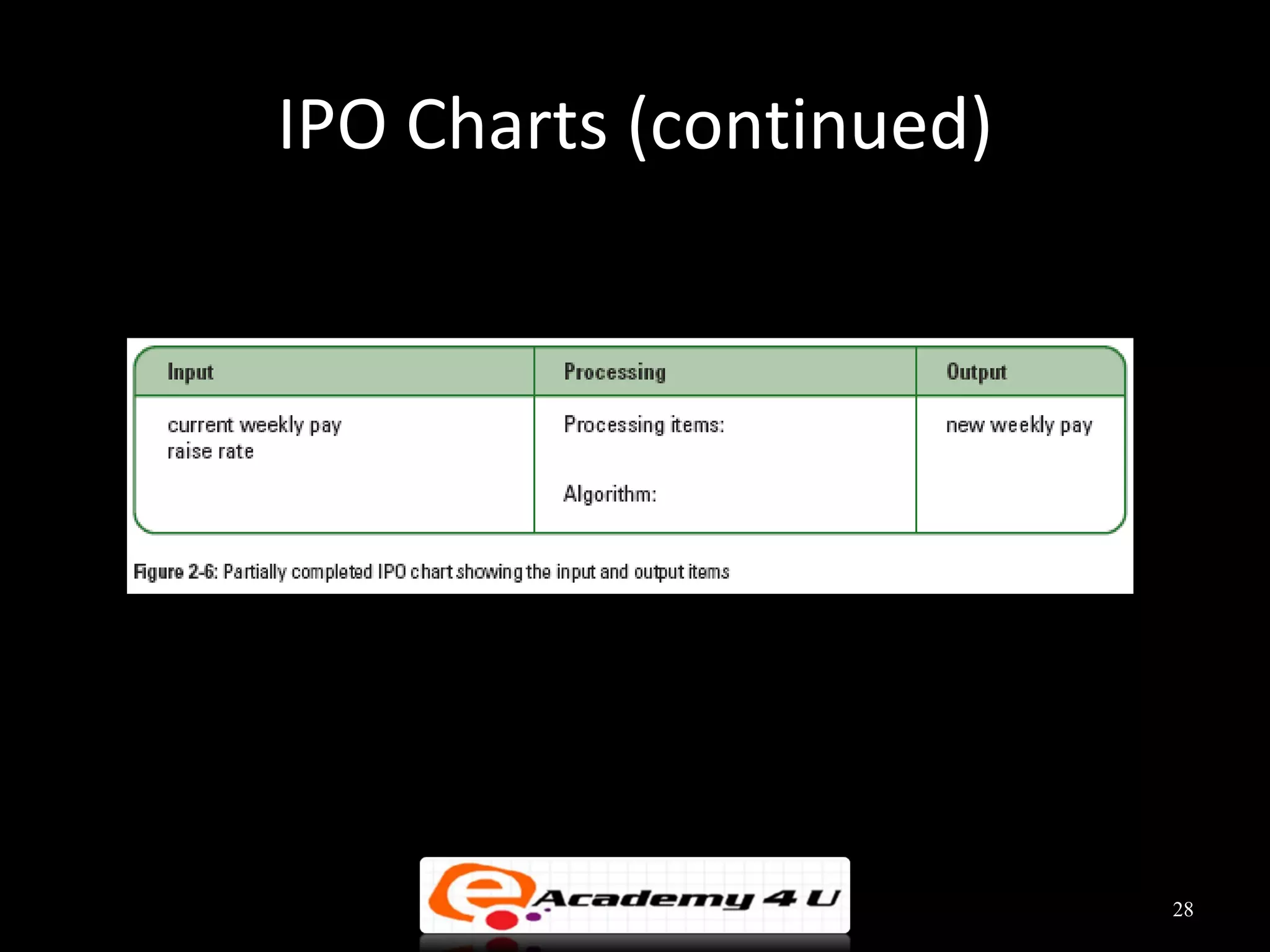
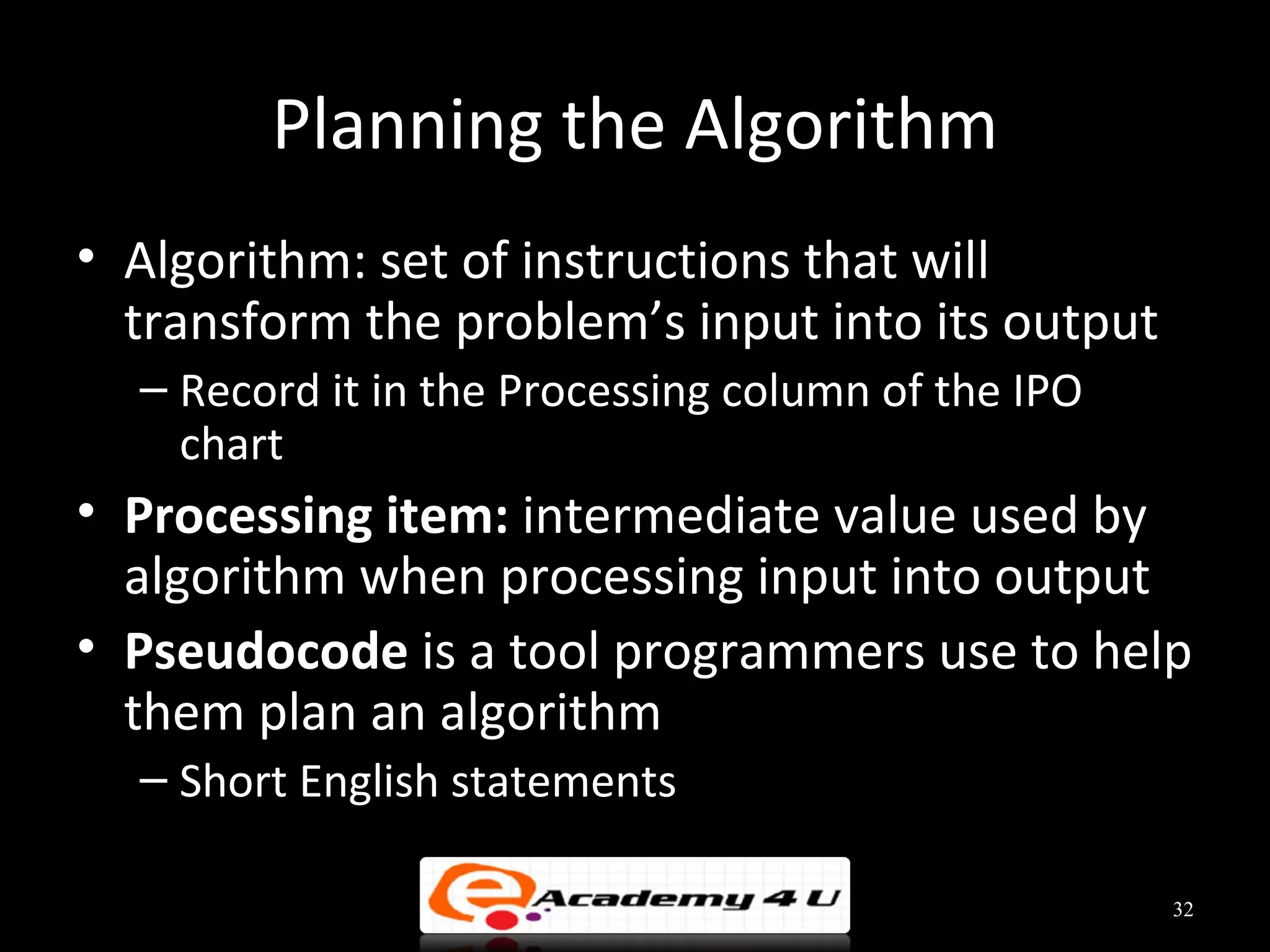
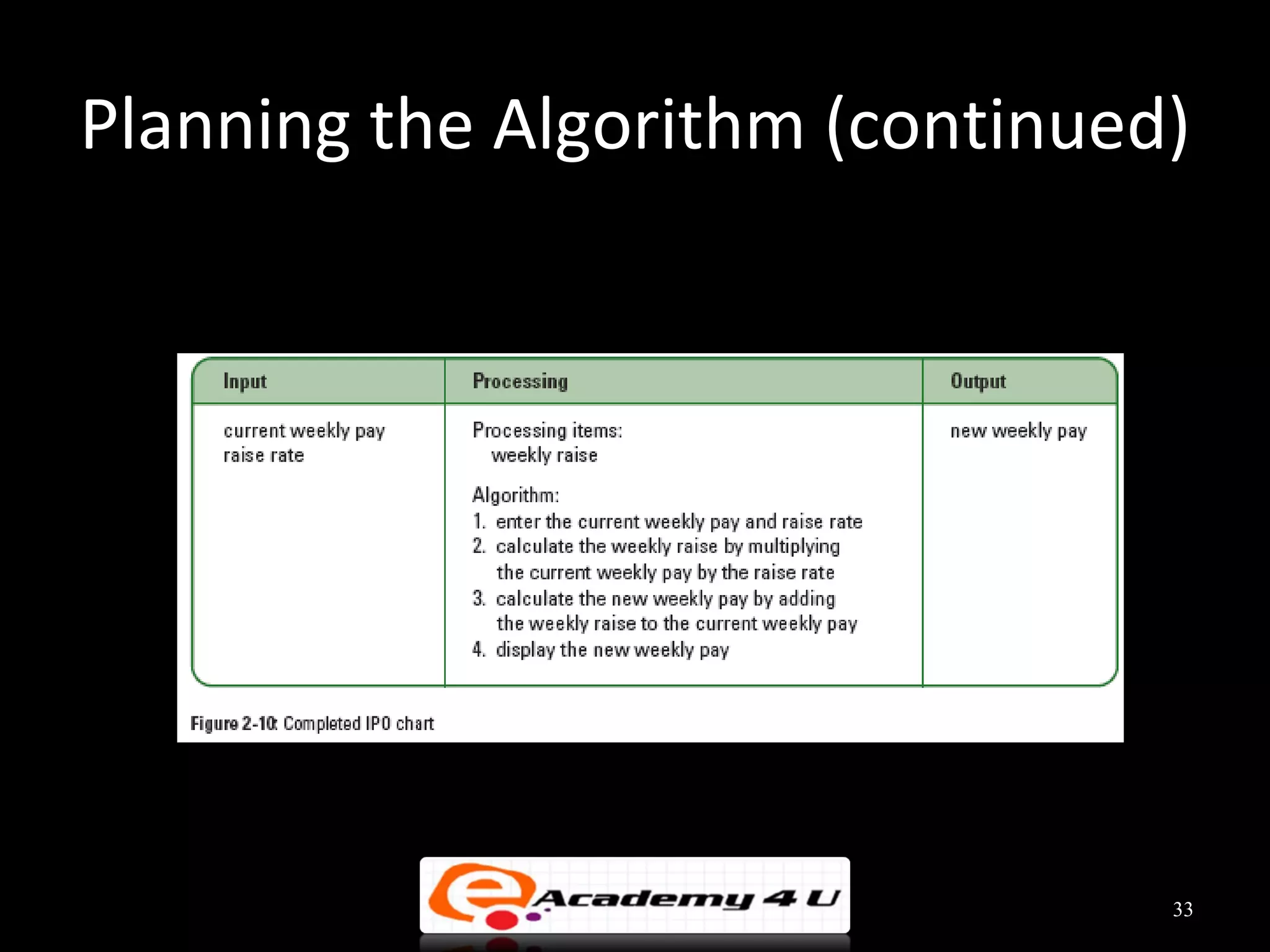
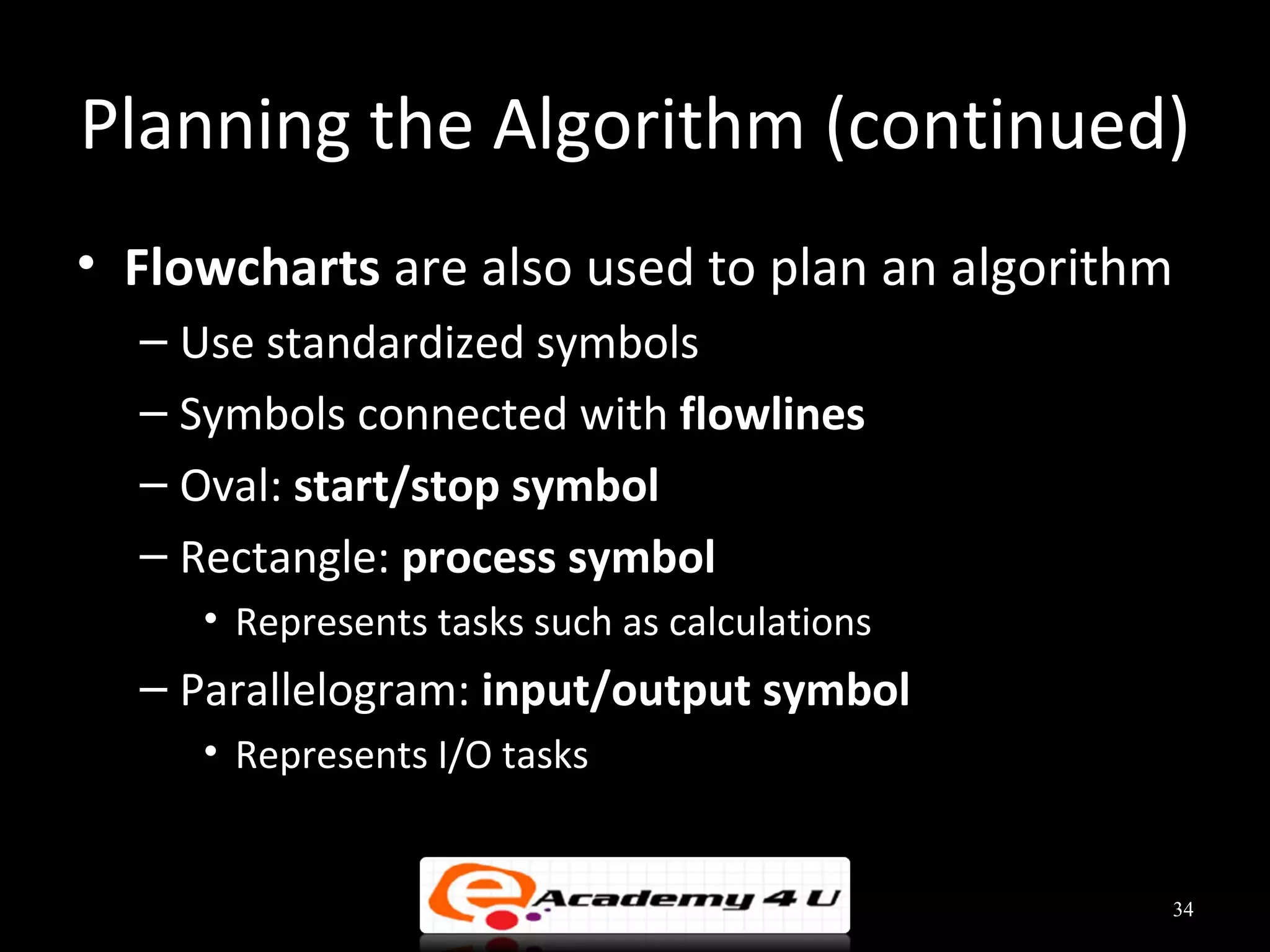
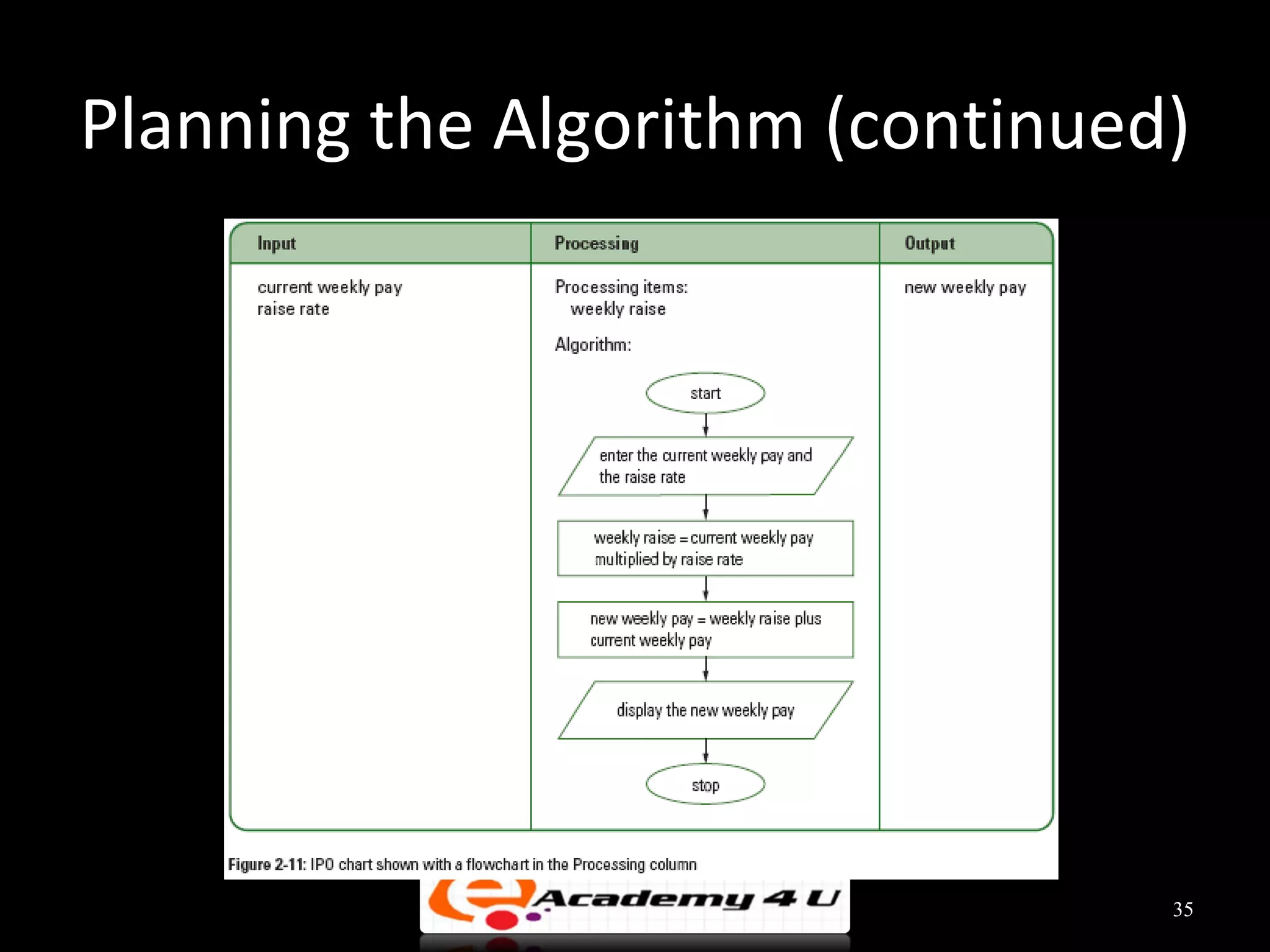
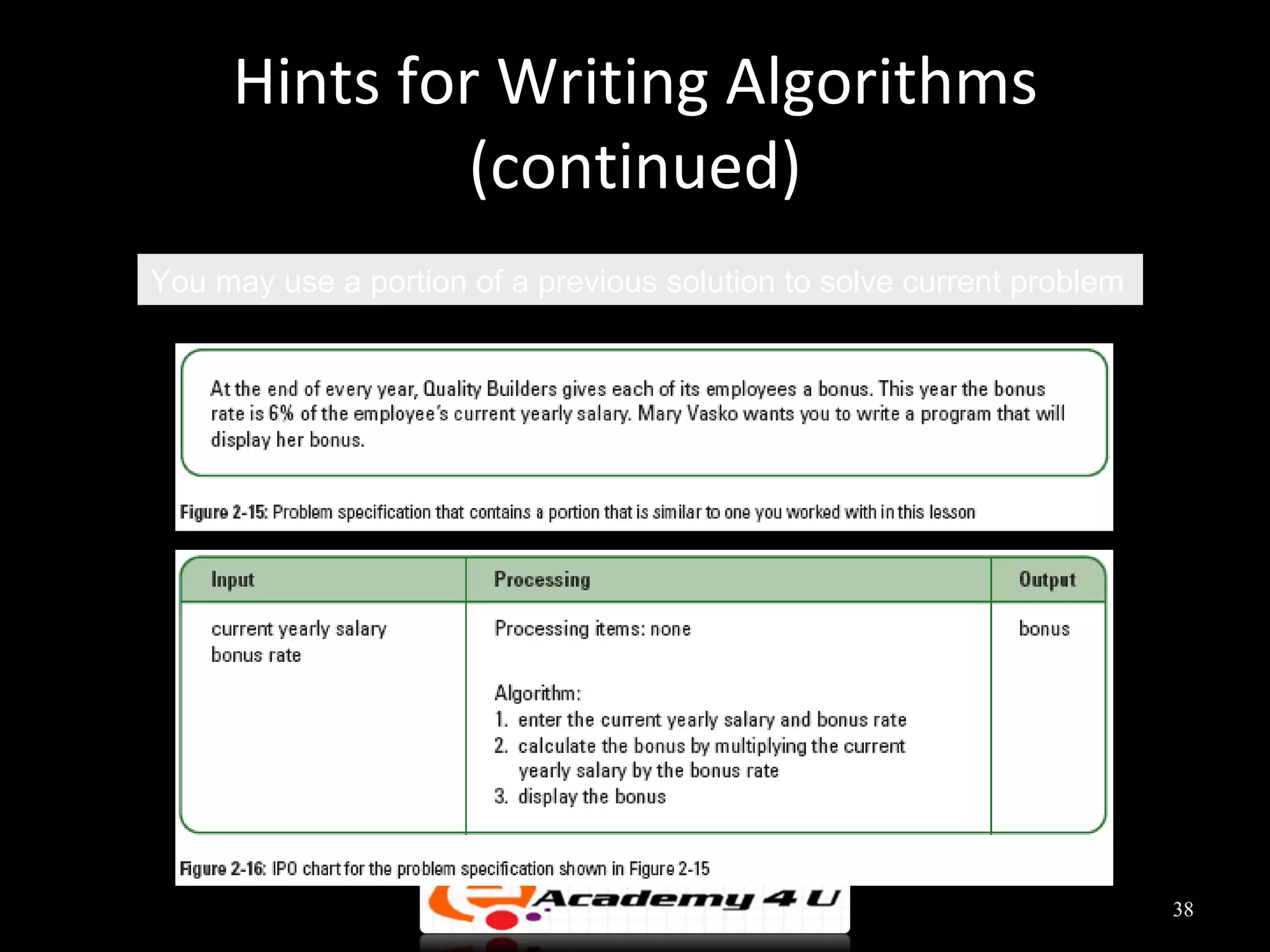
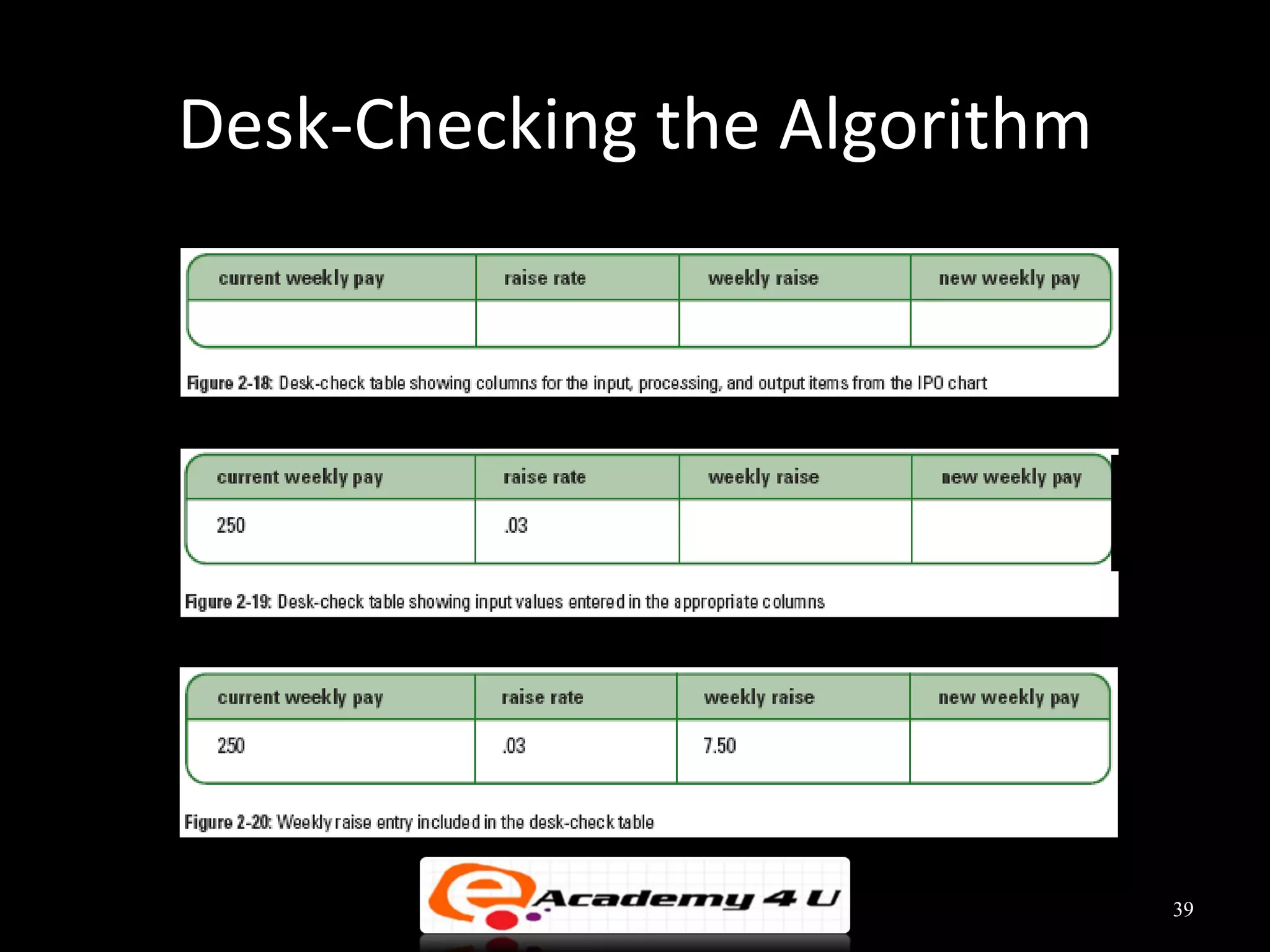
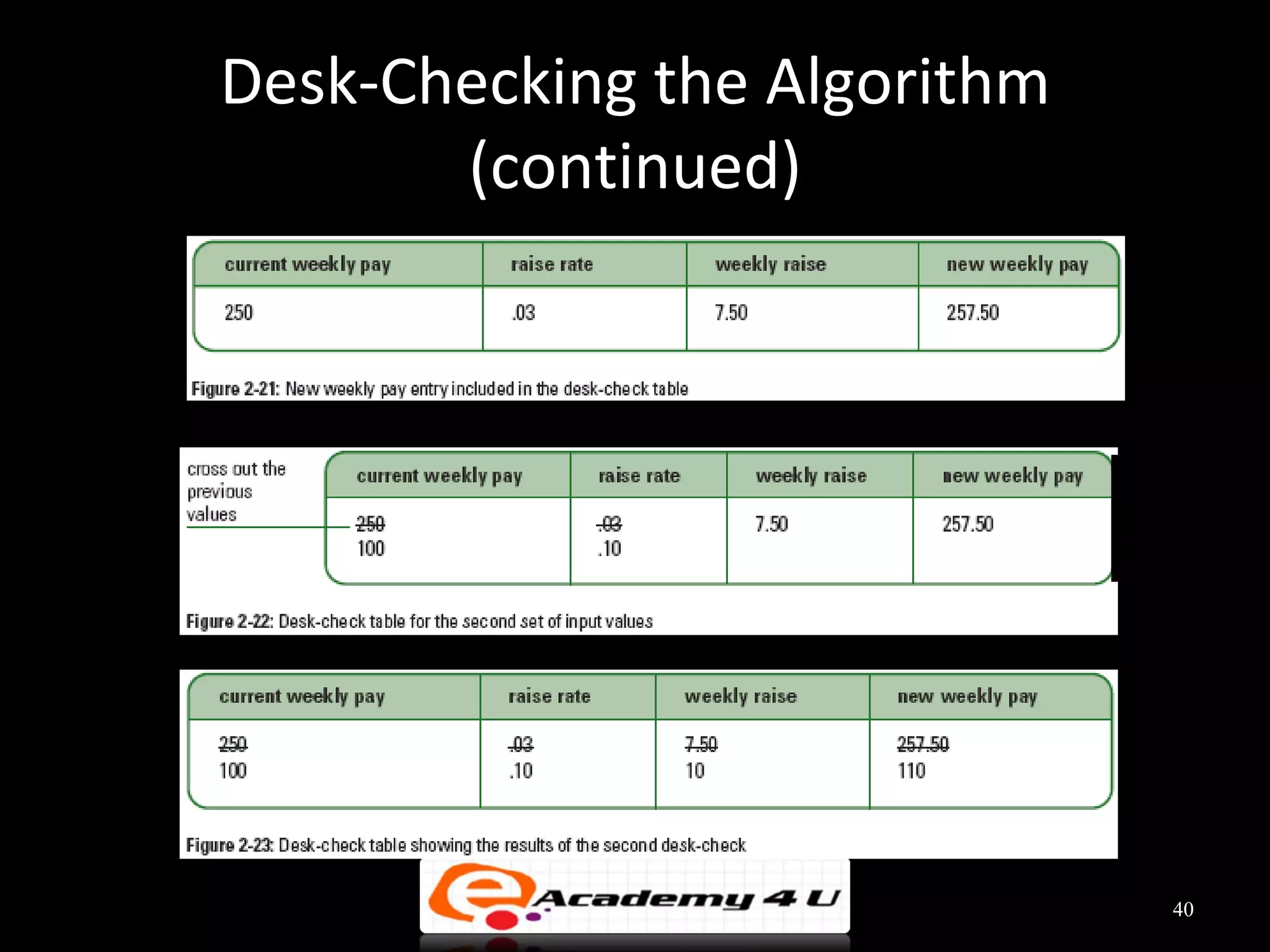
This document discusses the process of problem solving through programming. It begins by defining an algorithm as a sequence of instructions to solve a problem and a program as an algorithm expressed in a language a computer can understand. It then outlines the programming process of analyzing a problem to determine the input and output, planning an algorithm using tools like IPO charts and pseudocode, and coding the algorithm. It provides examples of analyzing problems, planning algorithms, and desk-checking algorithms on sample data.