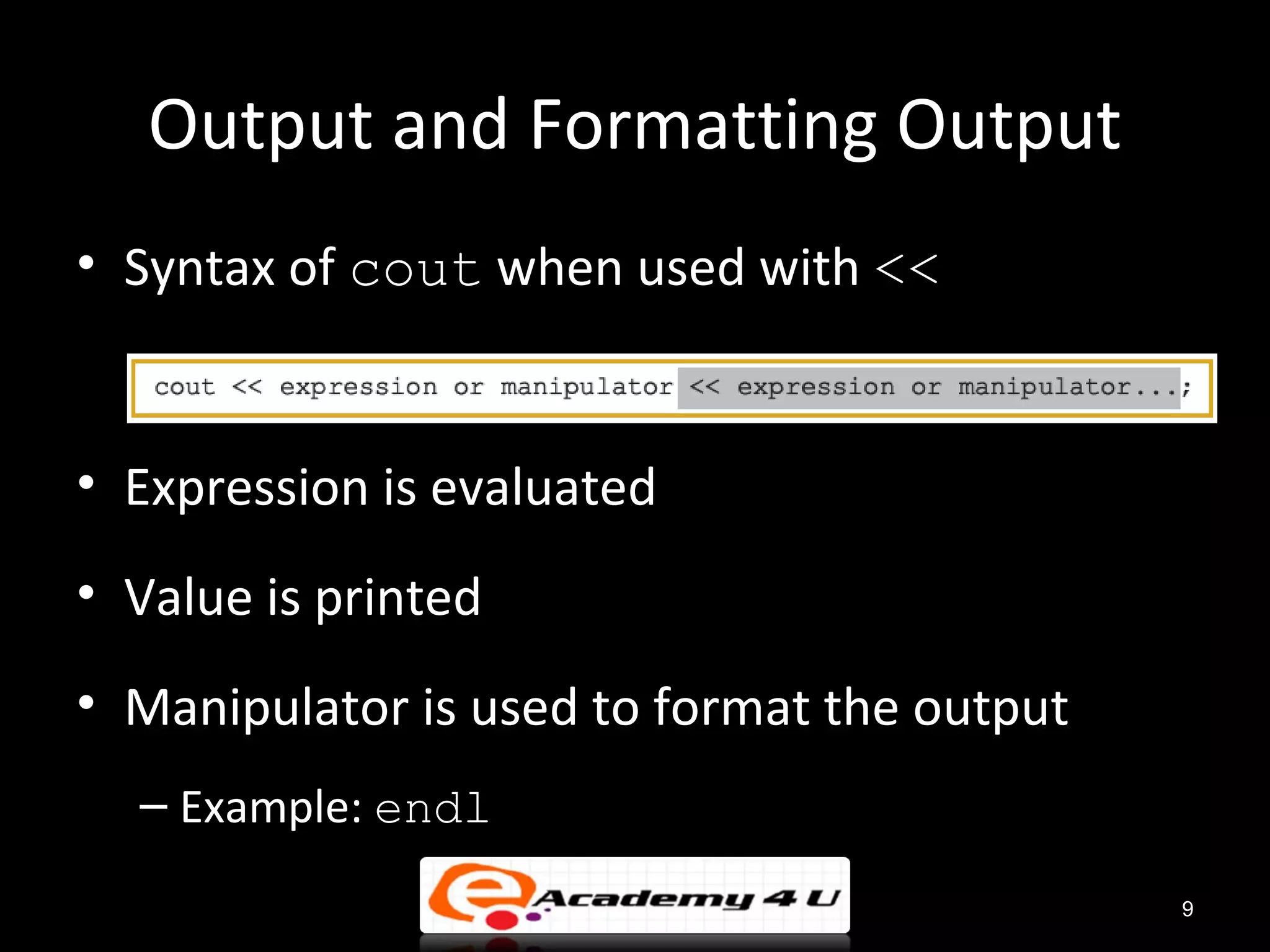
This document discusses input and output streams in C++. It explains that streams are sequences of characters that move from a source to a destination, and covers input streams from devices to a computer and output streams from the computer to devices. It also details the standard input stream cin and standard output stream cout, and how to use various manipulators to format output, such as setprecision, fixed, showpoint, setw, setfill, left, and right.