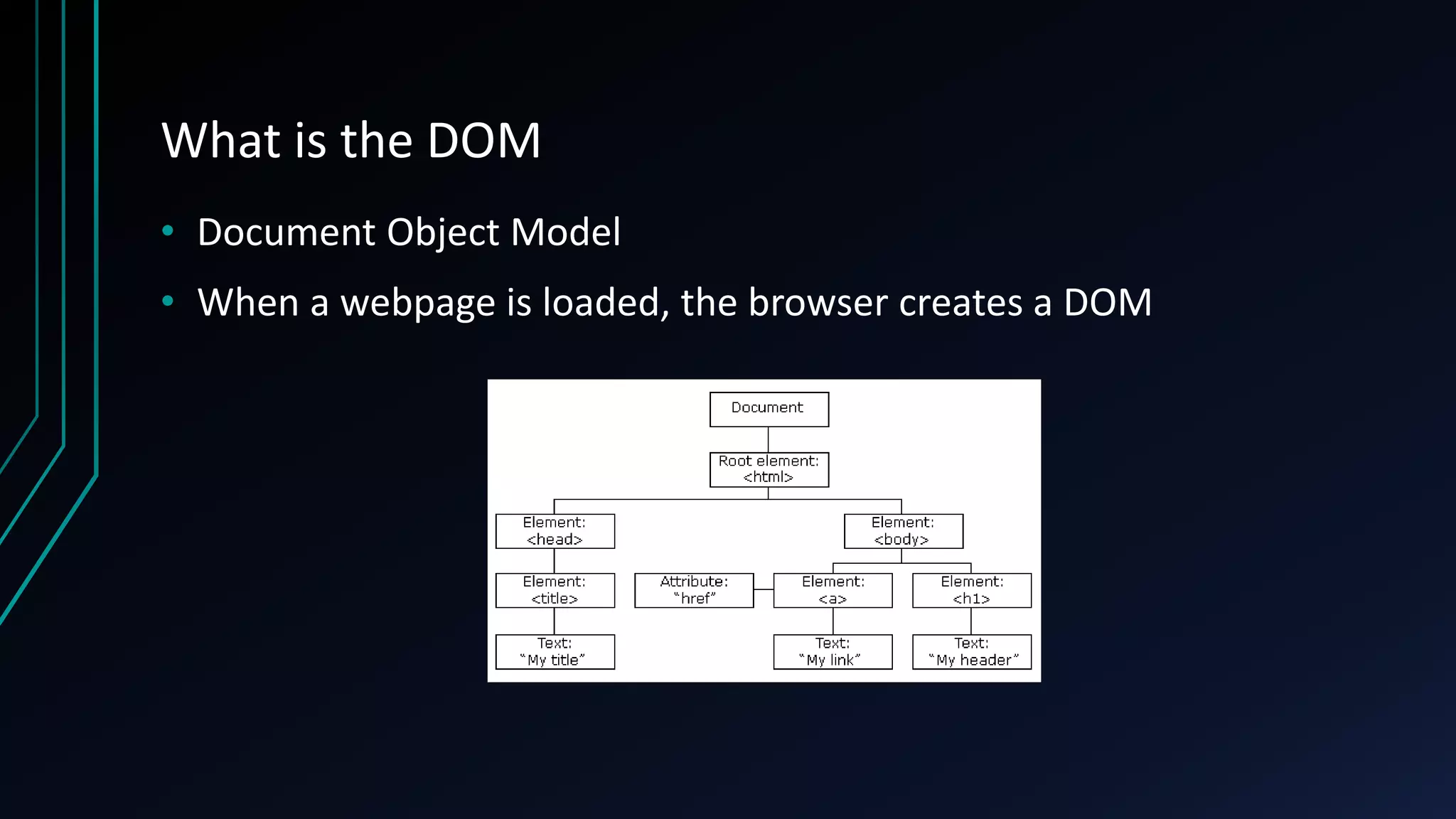
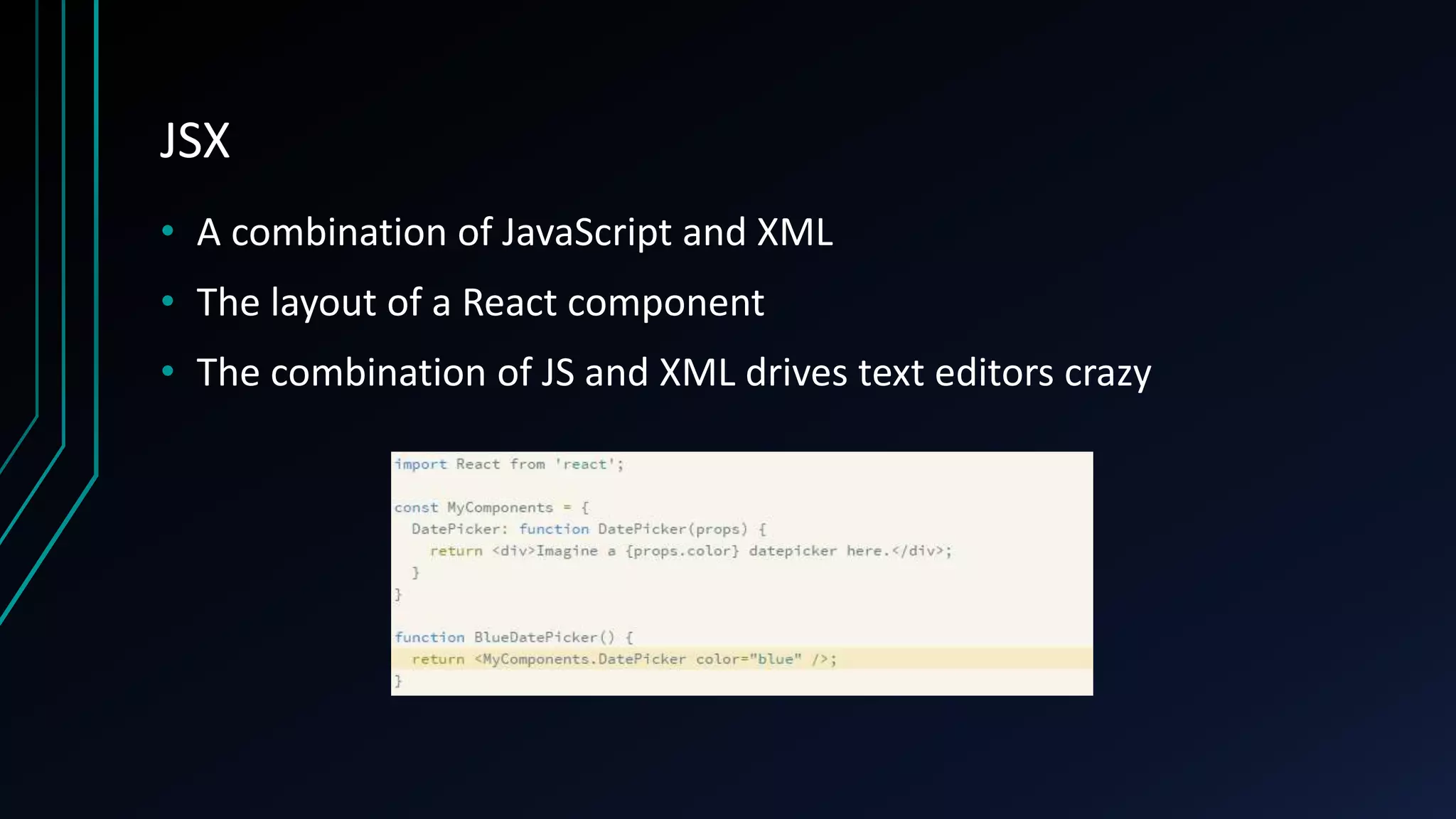
This document provides an overview of React, a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It discusses what React is, its benefits like allowing separate components to re-render independently without affecting other page elements. It also covers downsides like difficult error messages. Key concepts covered include JSX, components, properties, getting started with large single pages vs proper component-based development, integration with non-React software, and component lifecycles. Popular websites using React are also listed.