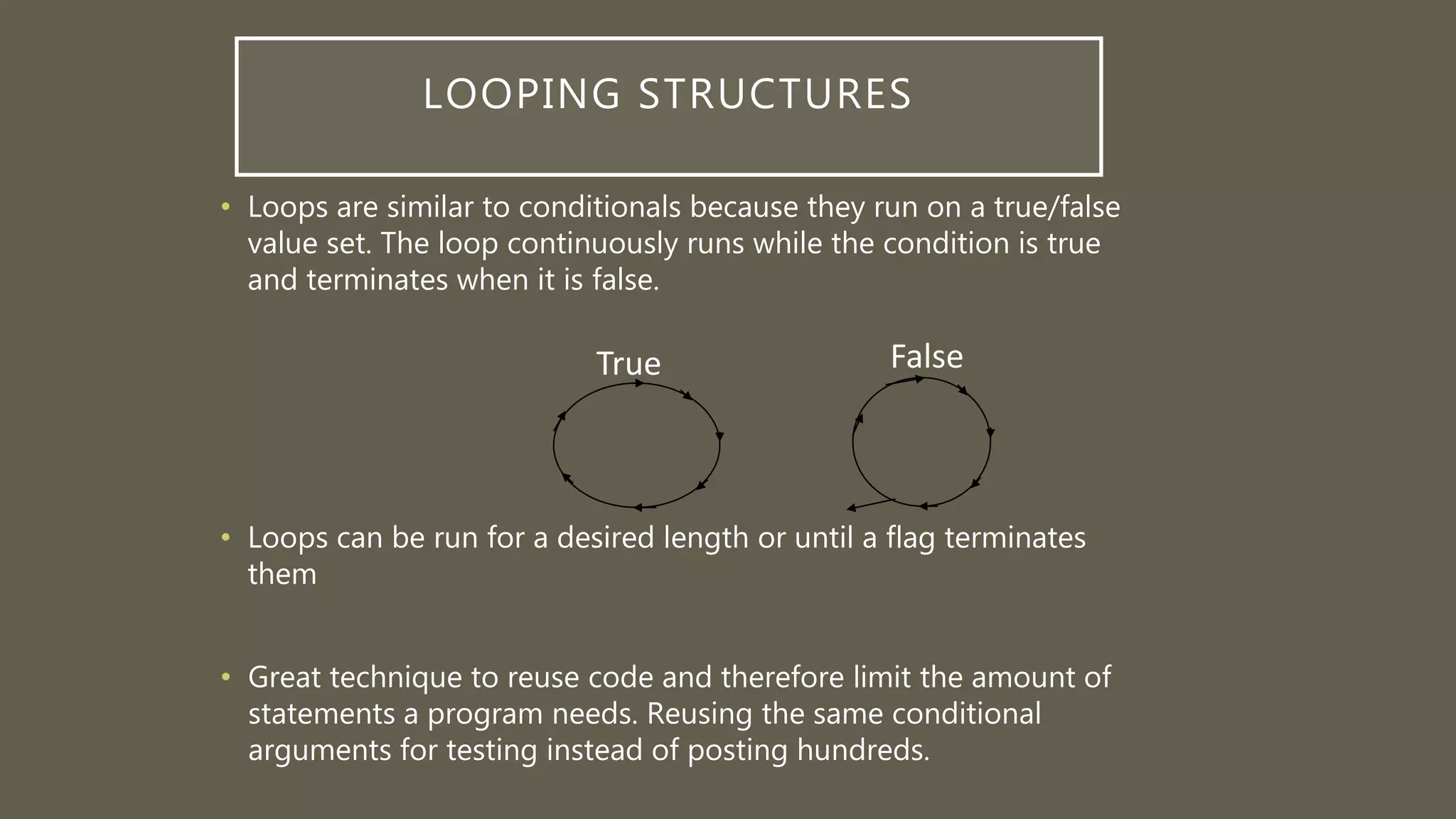
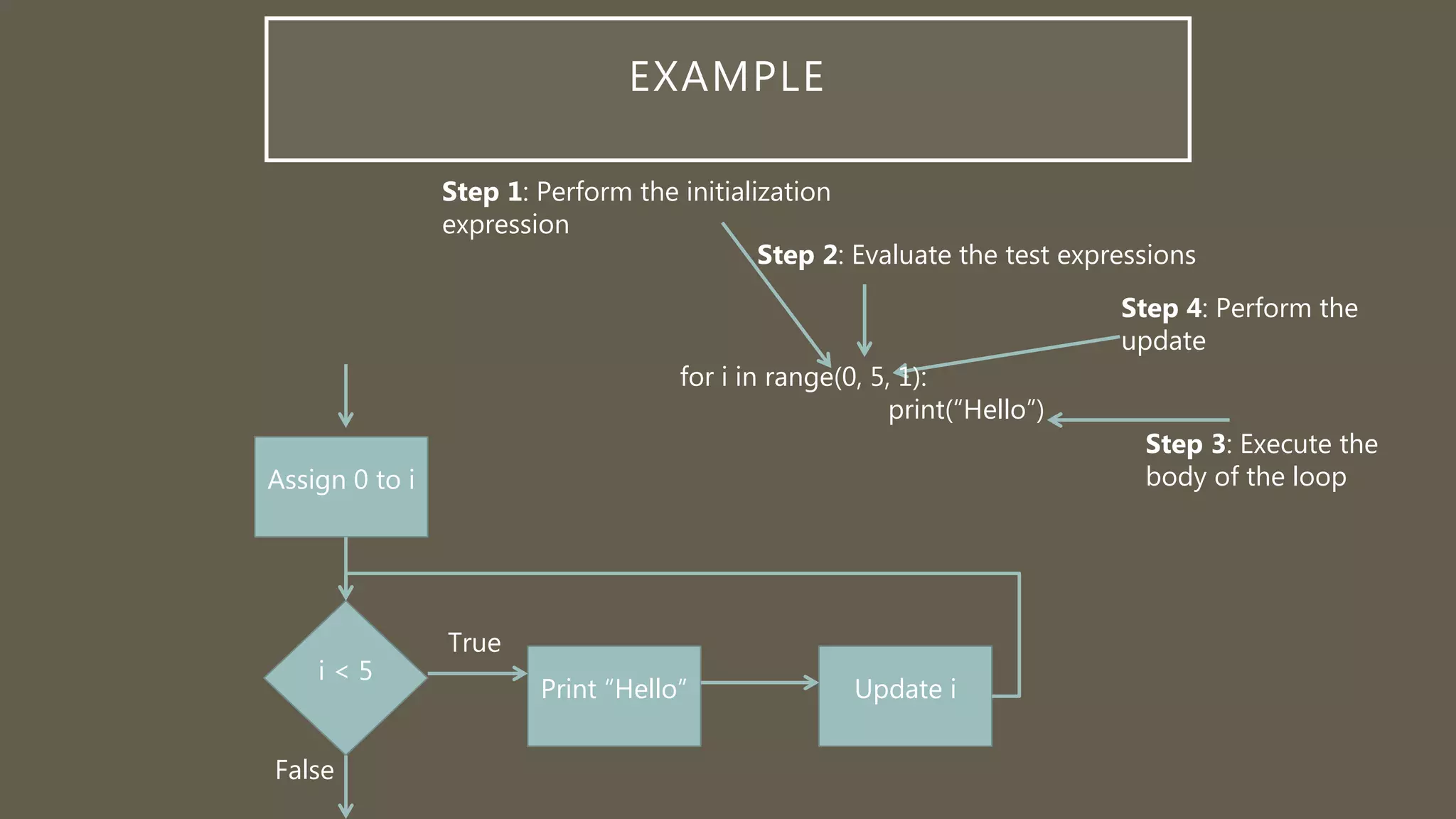
This document introduces looping structures in programming. There are several types of loops that allow code to be repeated, including for, while, and do-while loops. For loops are well-suited for problems that require iterating a specific number of times using a counter variable. The key components of a for loop are an initialization expression, a test expression, and an update expression. For loops iterate through code while the test expression is true, allowing efficient repetition of tasks like summing values or prompting a user multiple times.