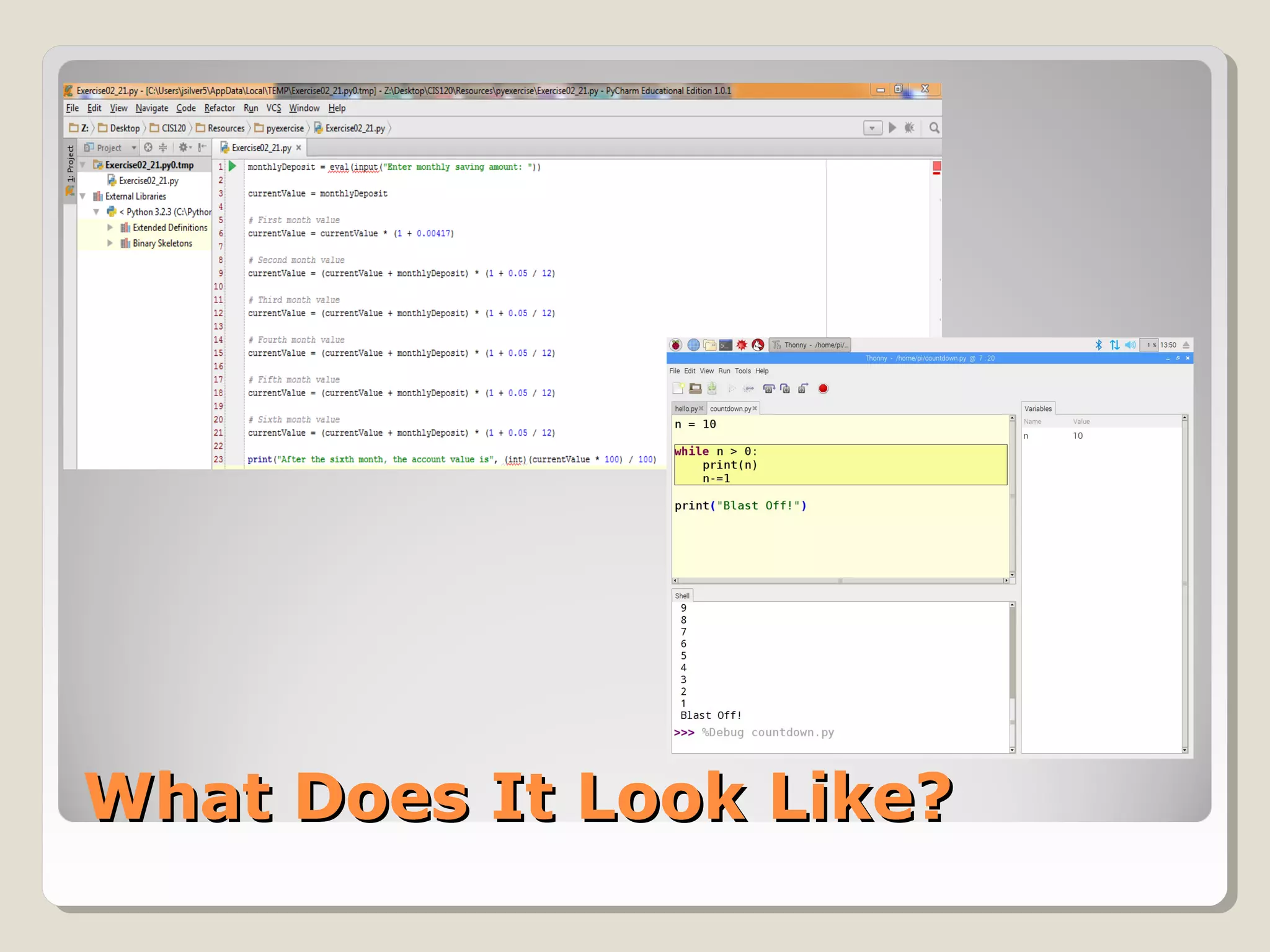
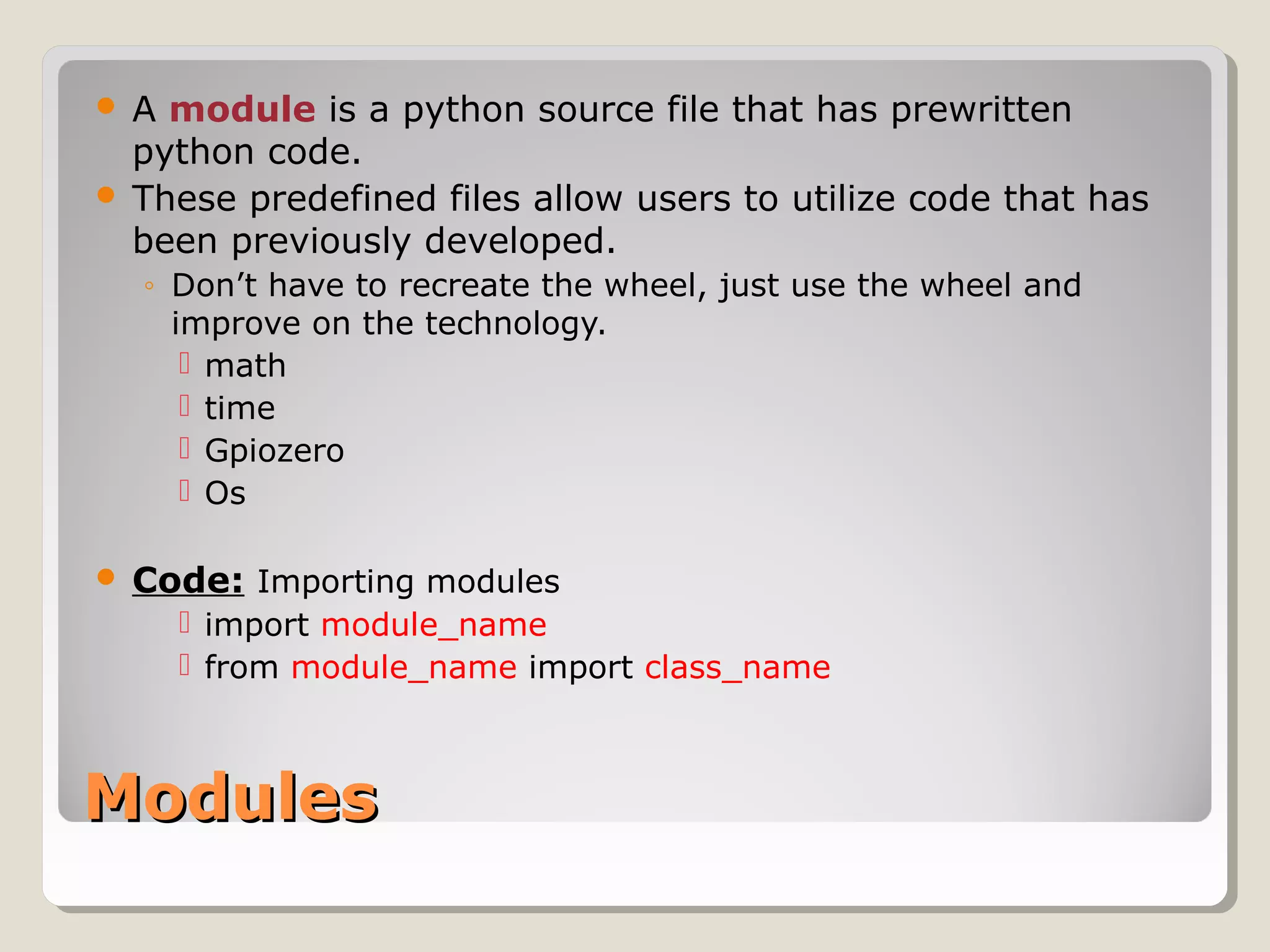
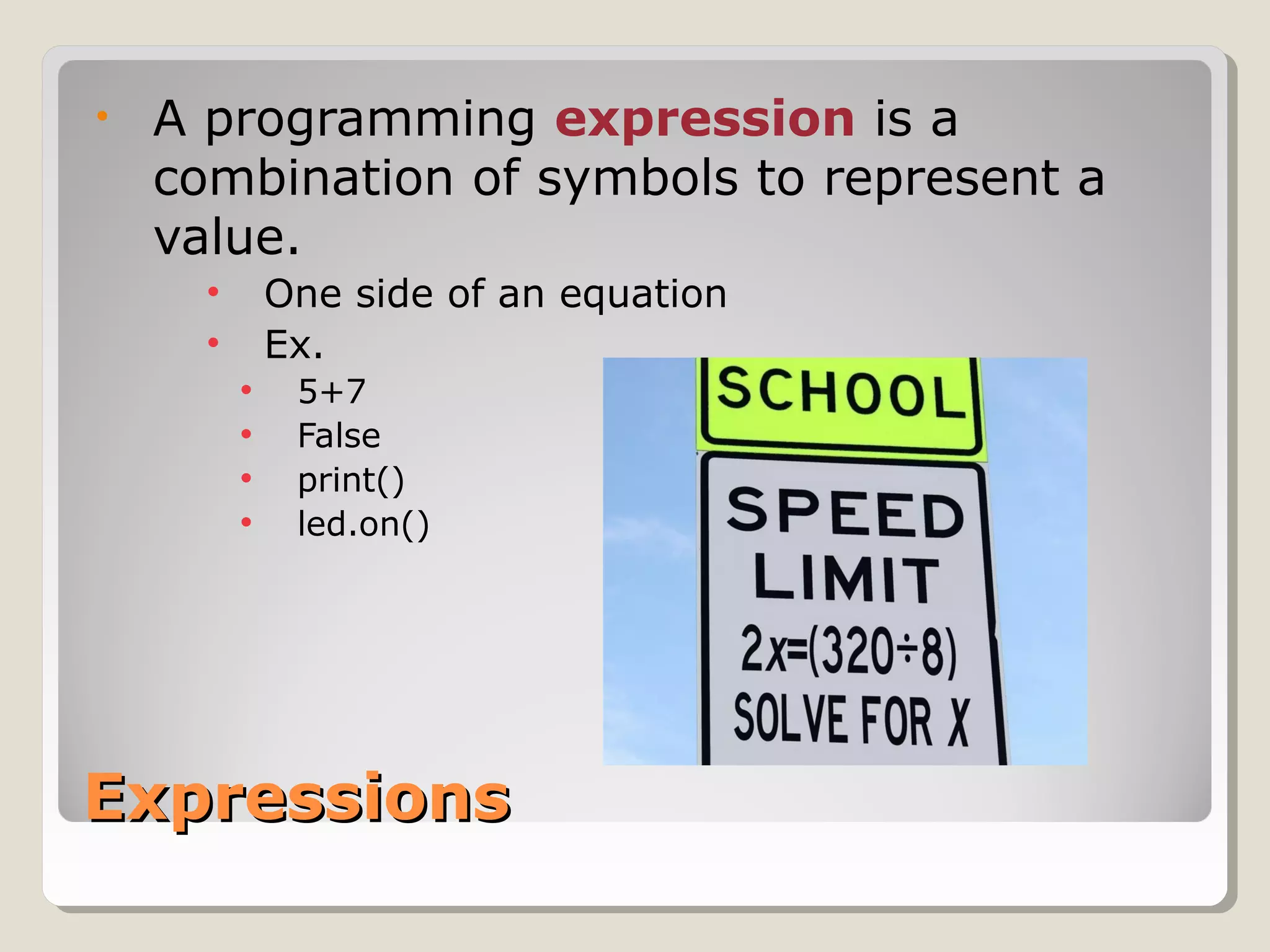
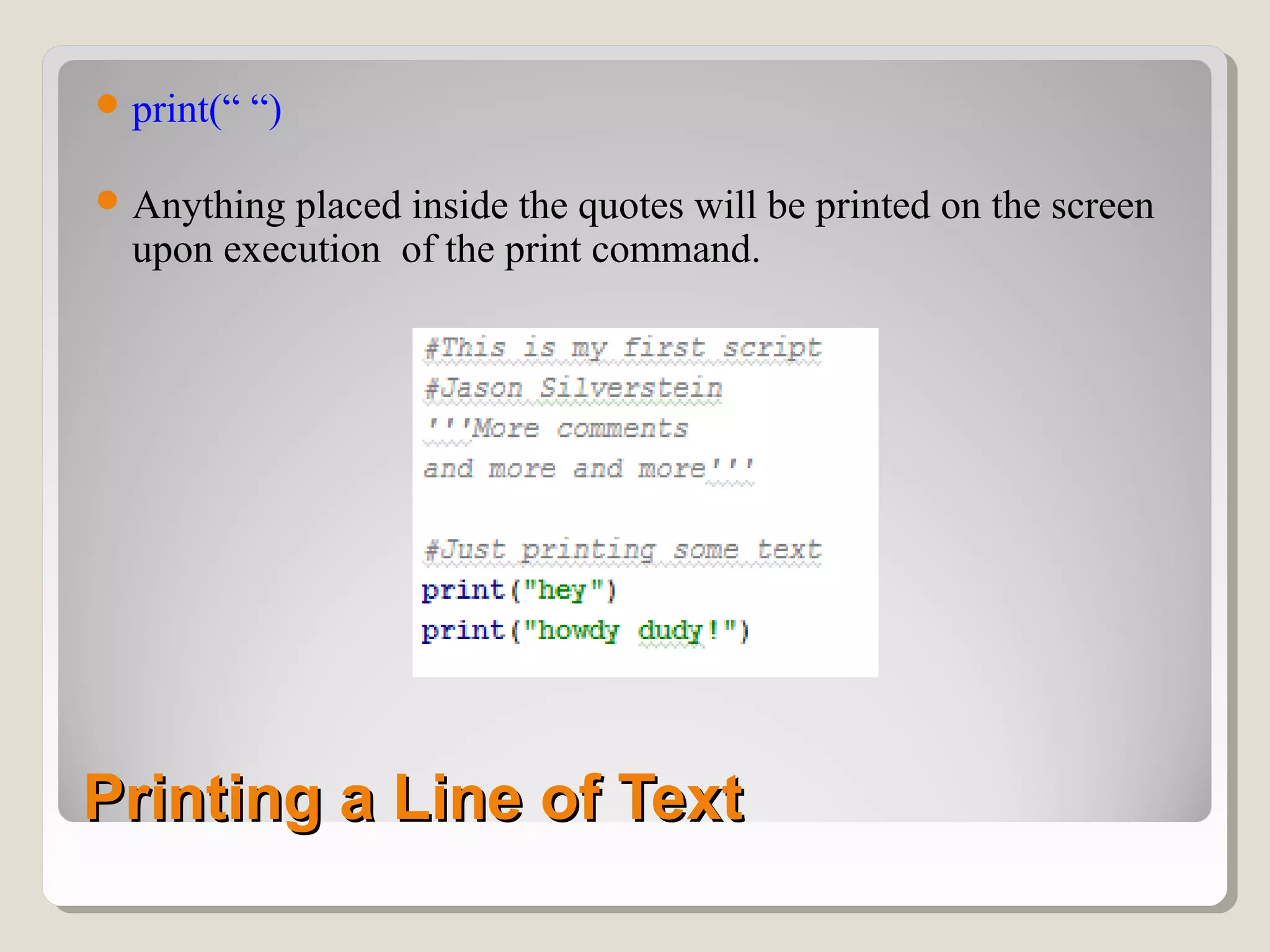
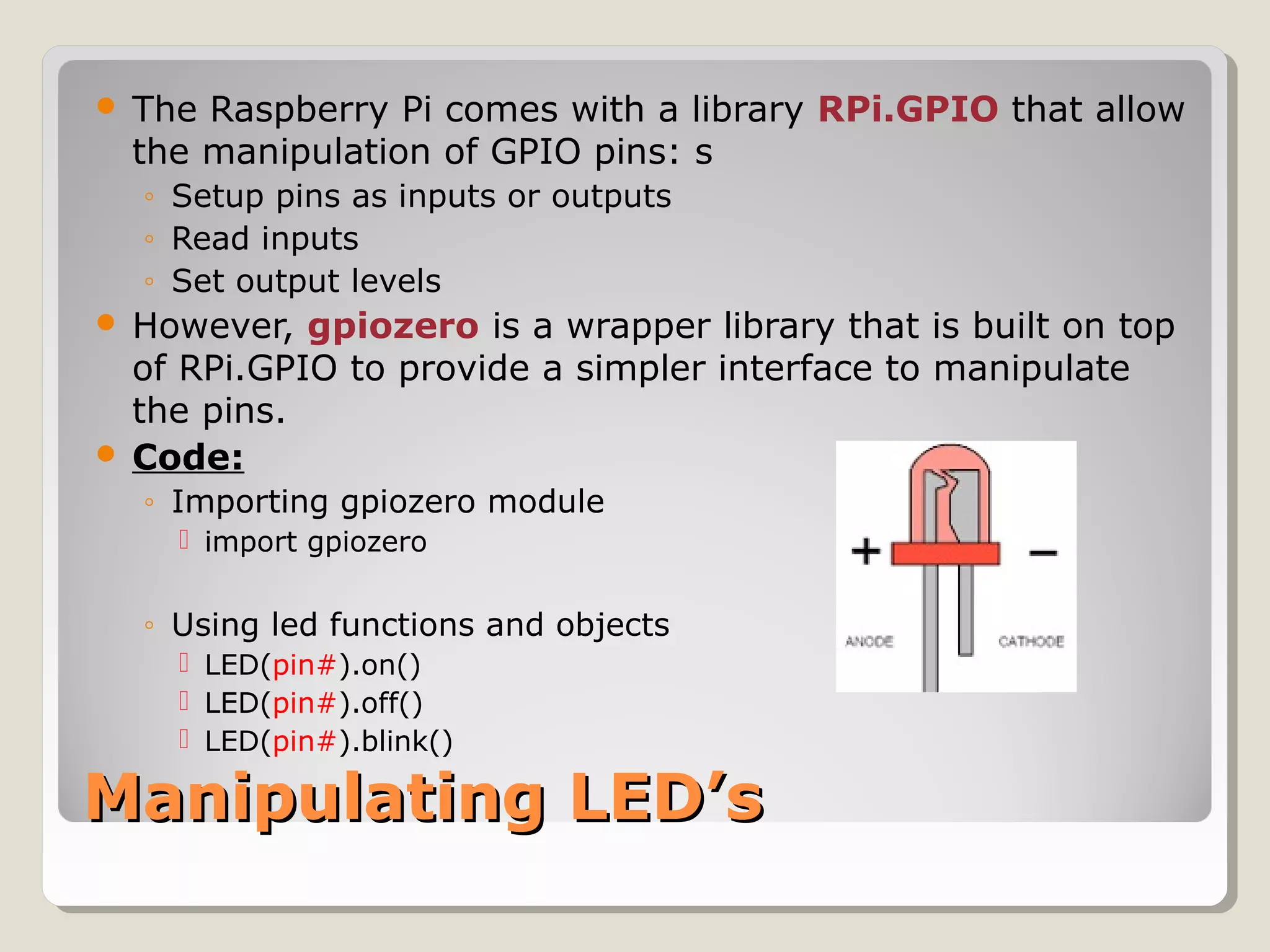
This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is an object-oriented and general purpose language used for tasks like web search, gaming, finance, and data analytics. It can be run through a command prompt, text file, or integrated development environment. The document reviews key Python concepts like its interpreted nature, program structure, modules, expressions, printing, and manipulating time and LEDs through importing modules.