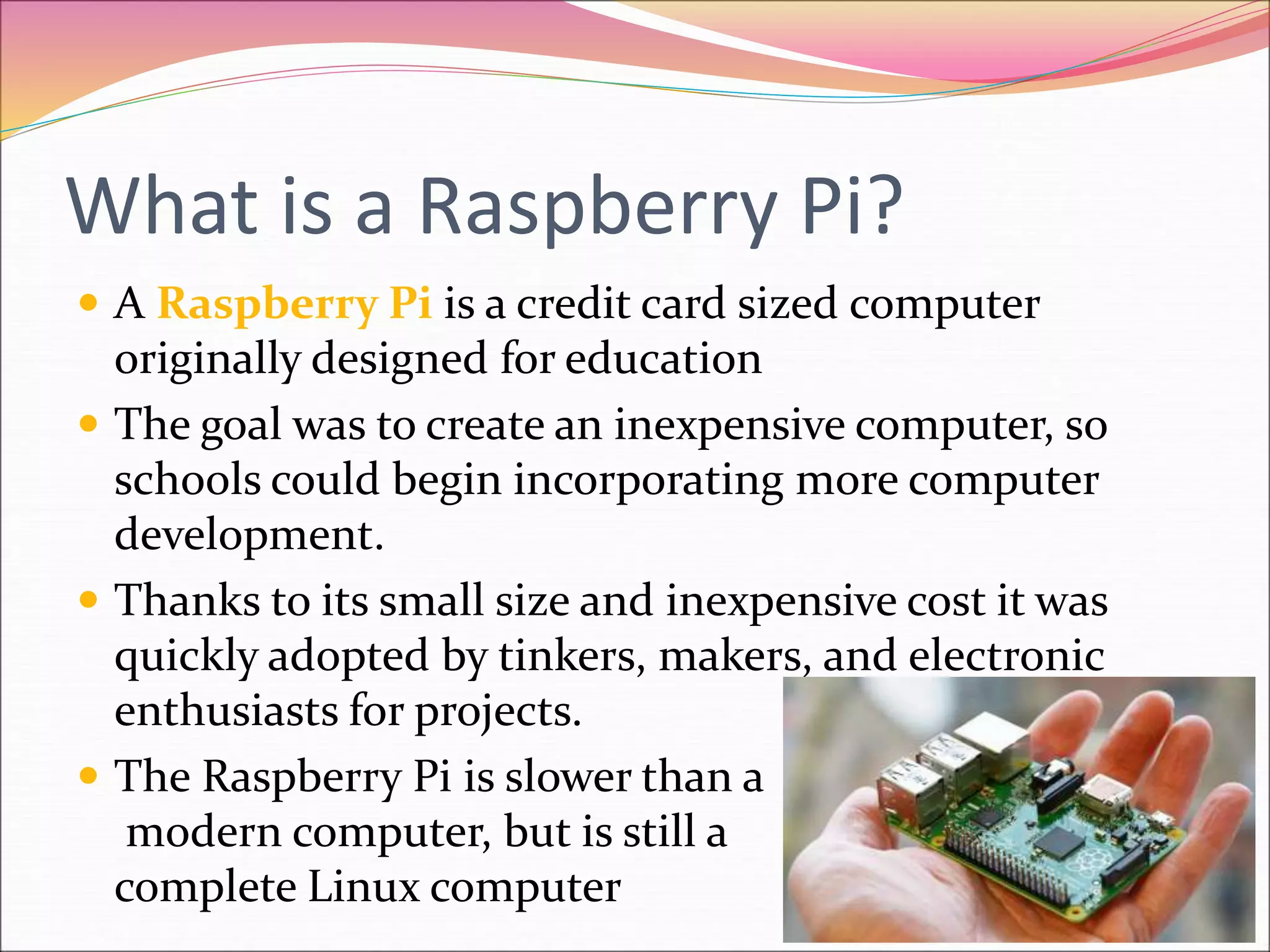
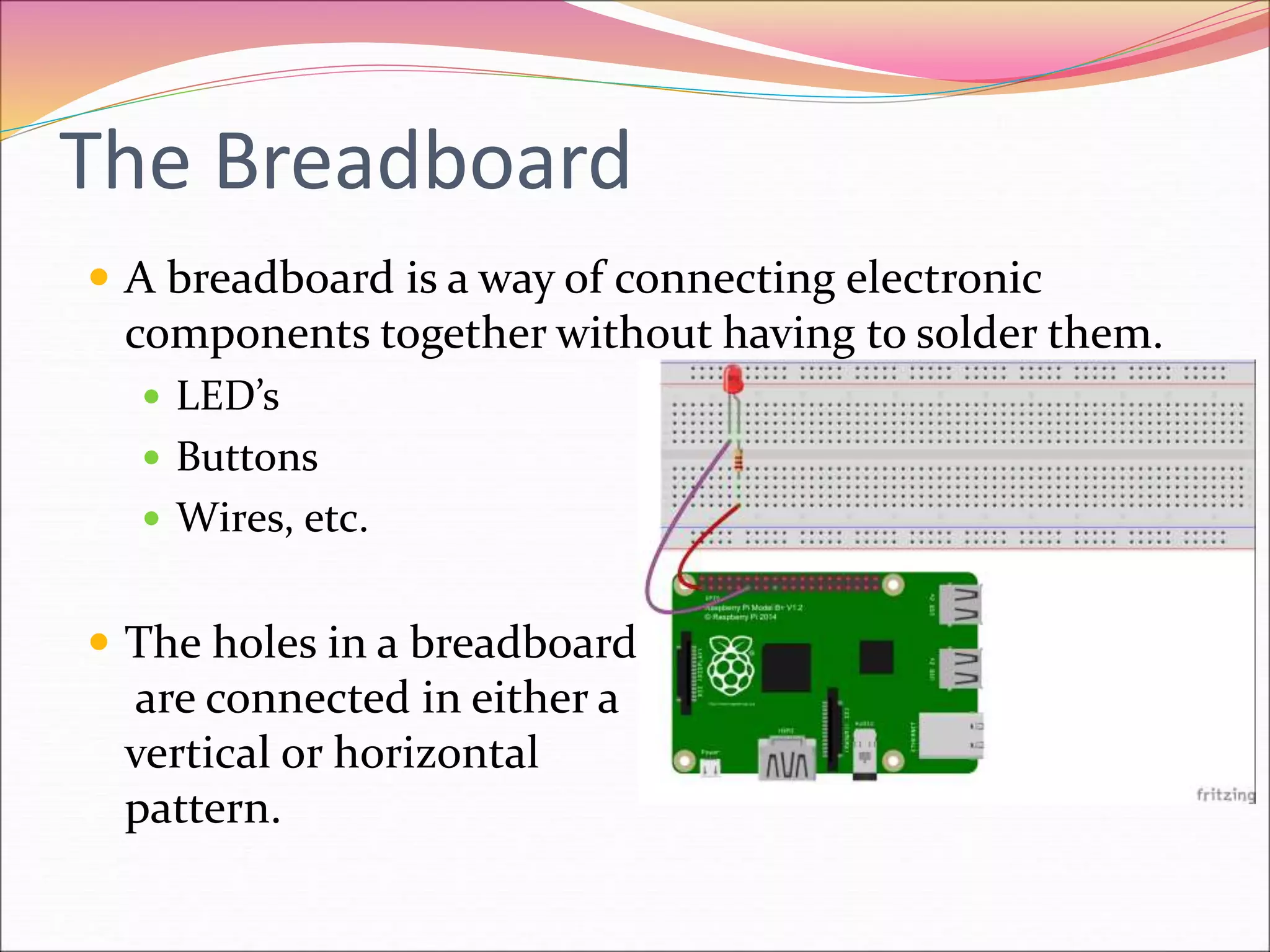
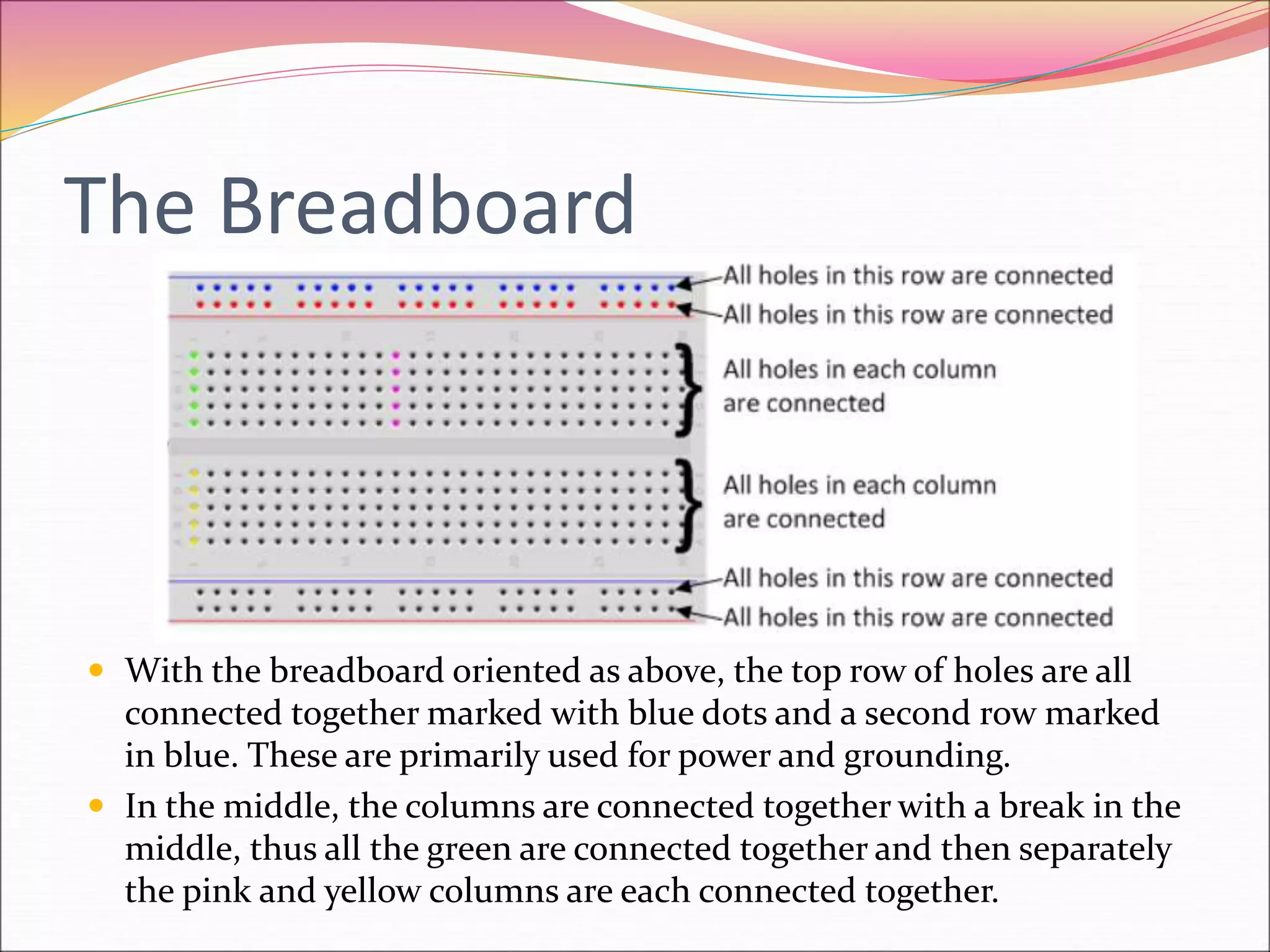
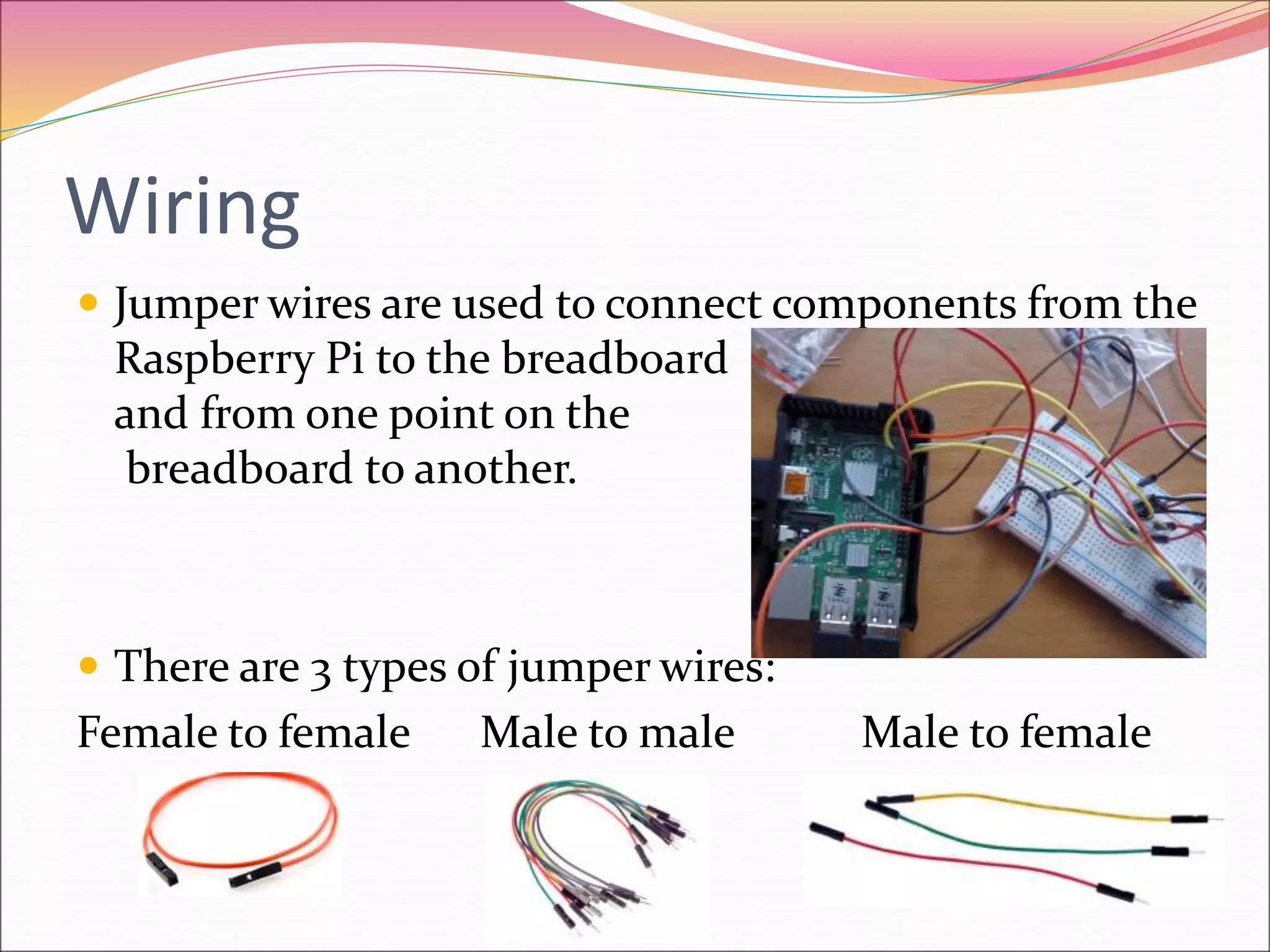
The Raspberry Pi is an inexpensive credit card-sized computer originally designed for education to allow schools to incorporate more computer programming. It was also quickly adopted by hobbyists for projects due to its small size and low cost. The document then provides information on why Raspberry Pis are useful, what types of projects can be built including game systems, assistants, weather stations and robots, and how components like breadboards, LEDs, resistors, jumper wires, and GPIO pins can be used in Raspberry Pi projects.