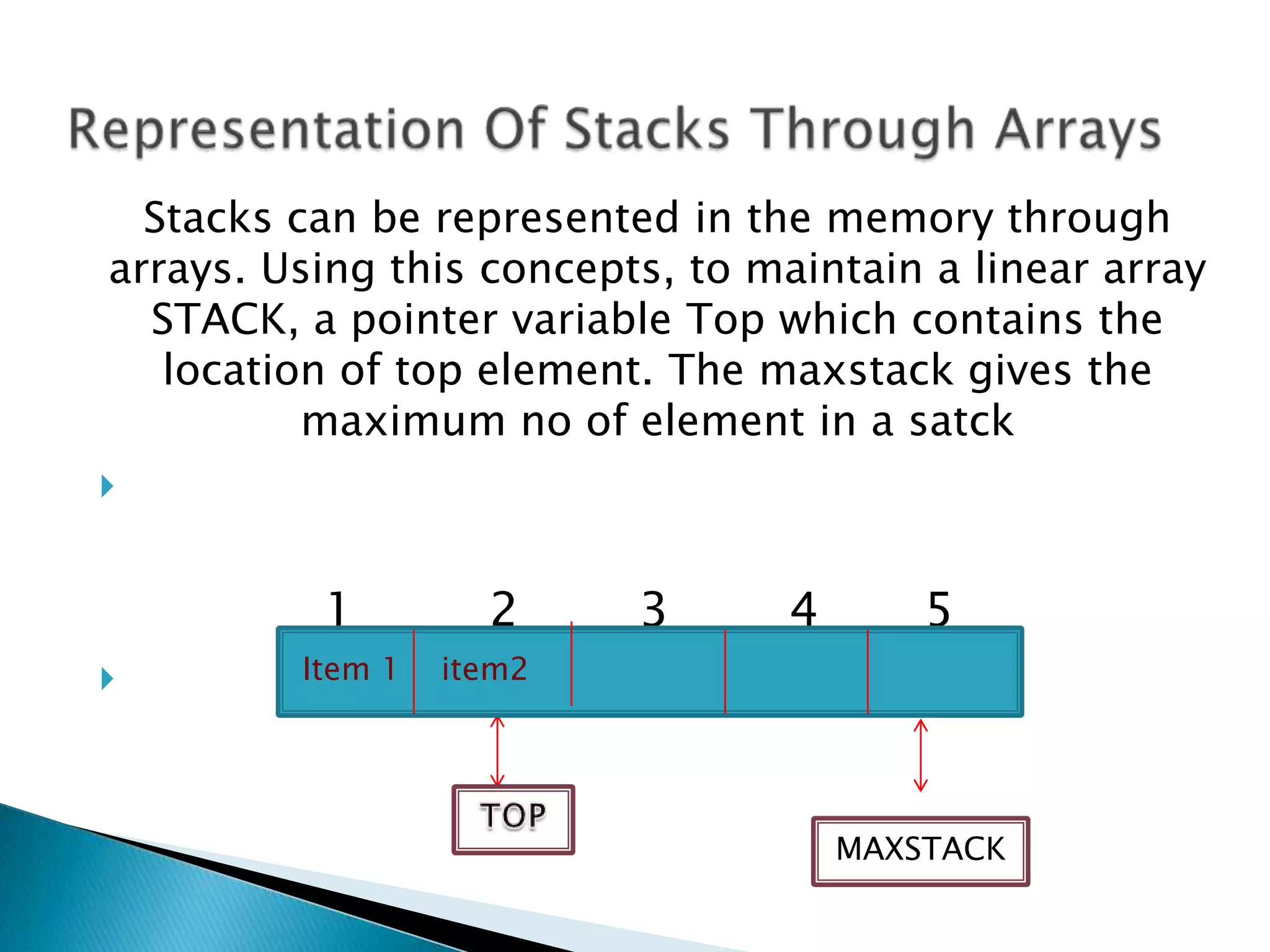
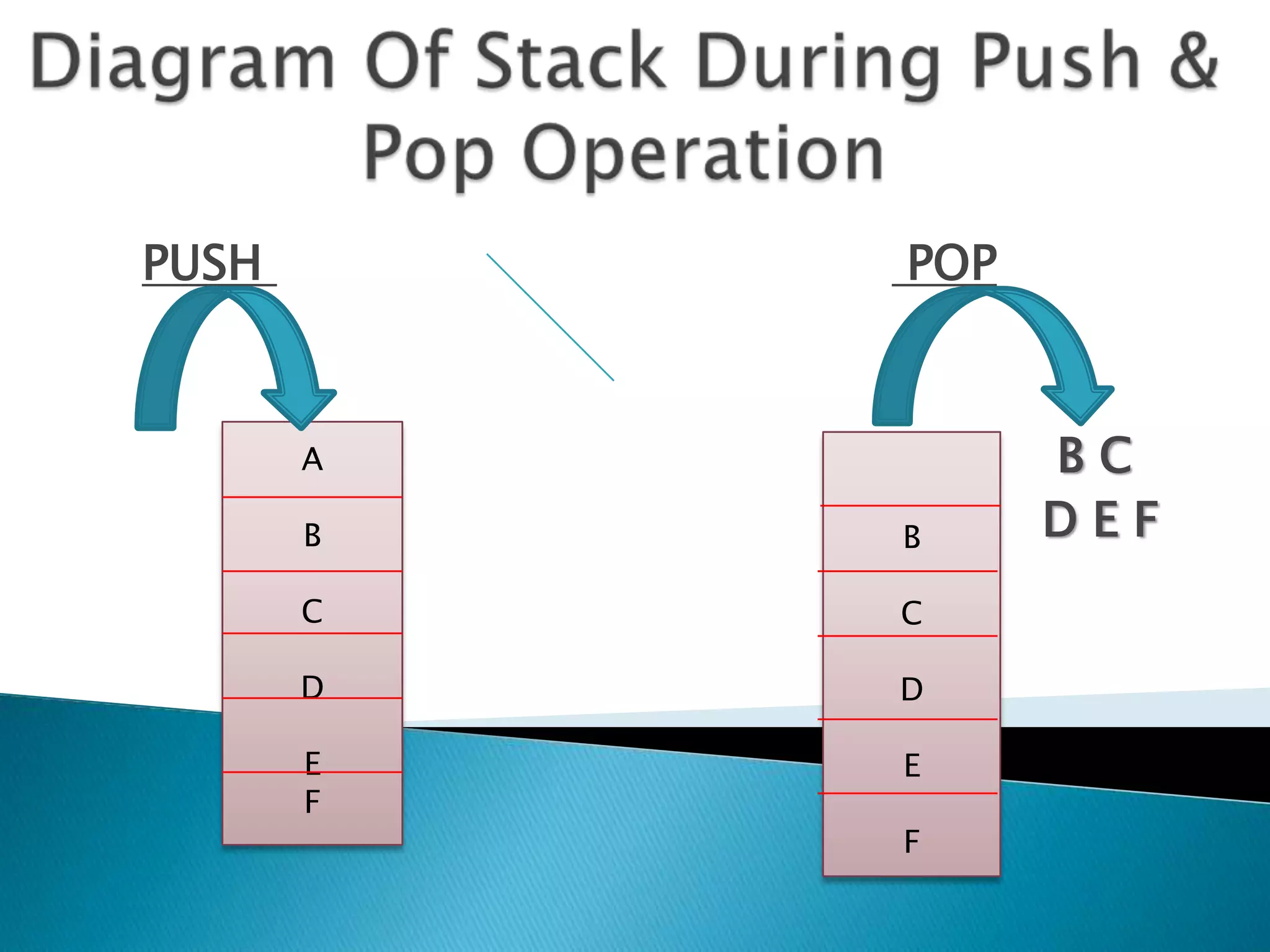
Stacks are linear data structures that only allow insertion and deletion of elements from one end, called the top. Elements are inserted via a push operation and deleted via a pop operation. Stacks can be implemented using arrays, with a pointer tracking the top element. Common applications of stacks include reversing the order of elements and evaluating mathematical expressions by treating them as a postfix notation.