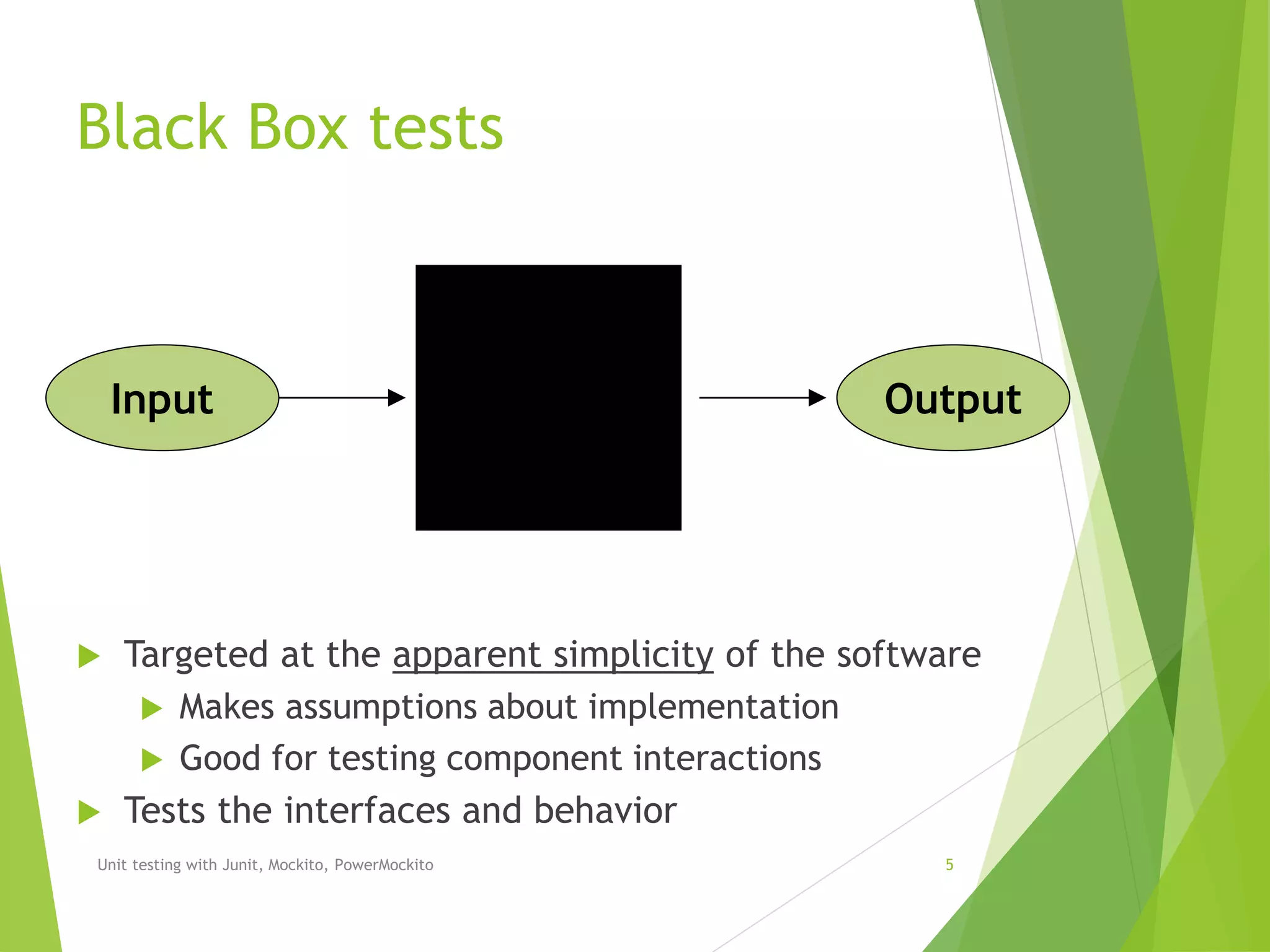
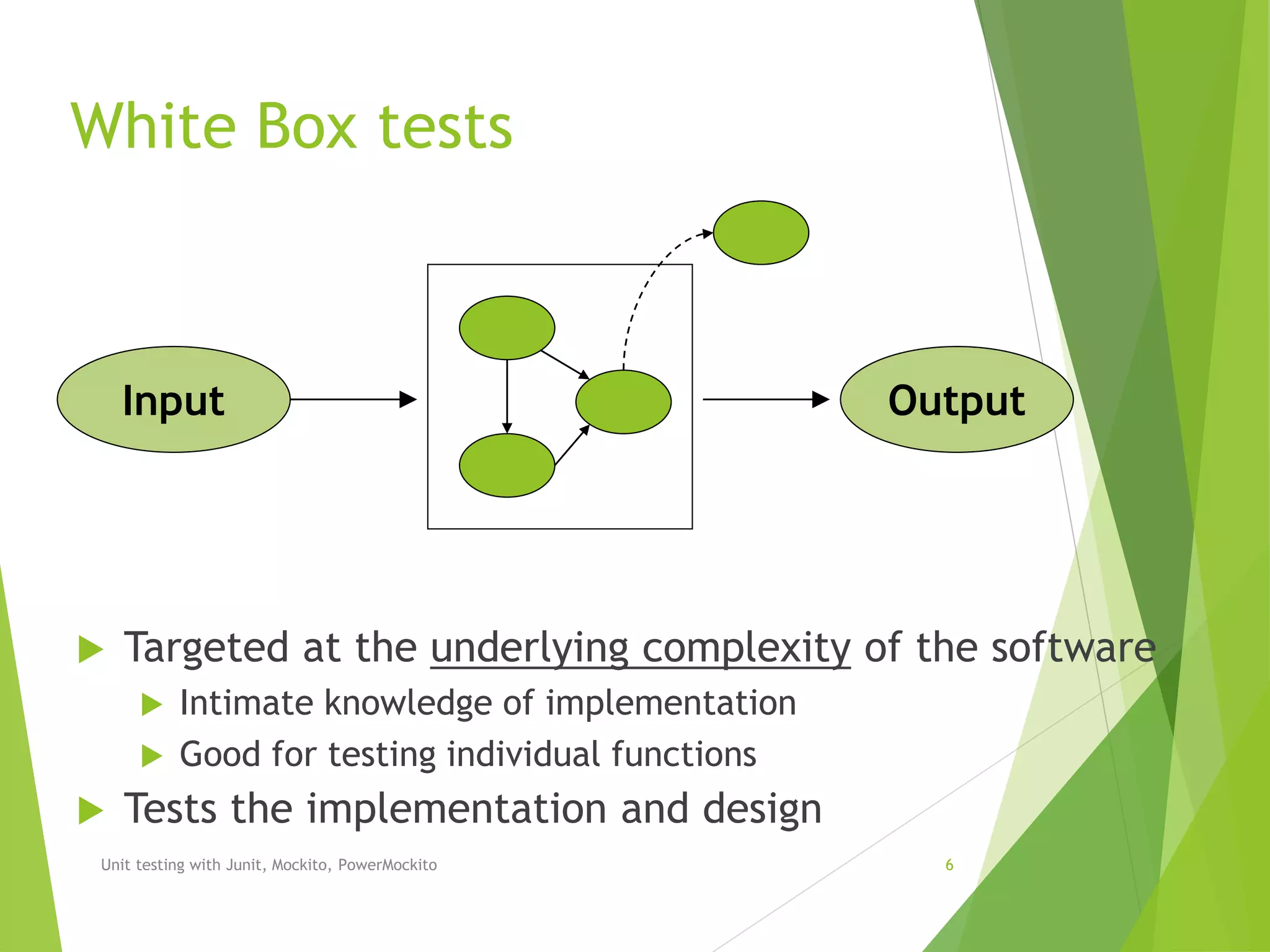
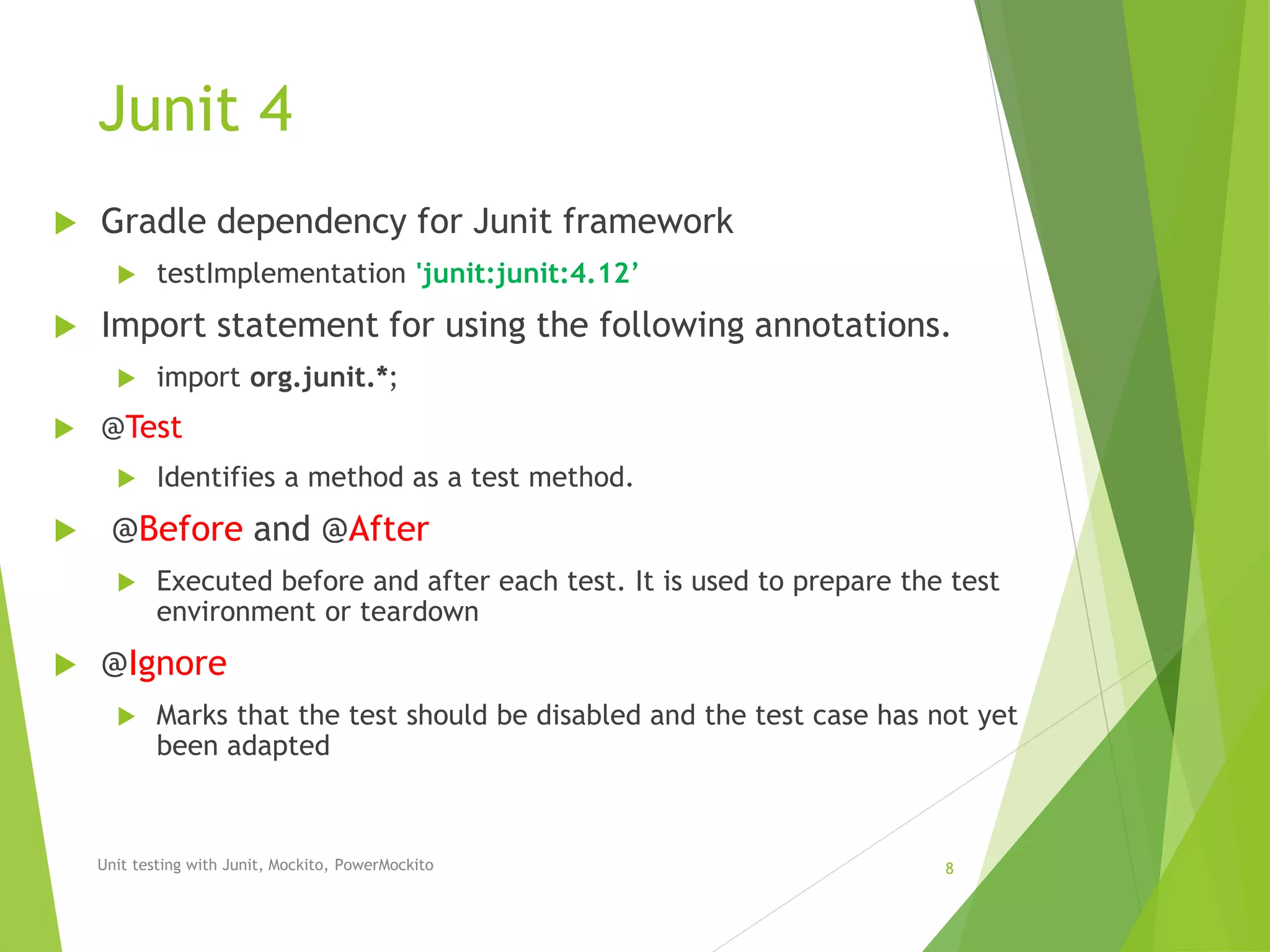
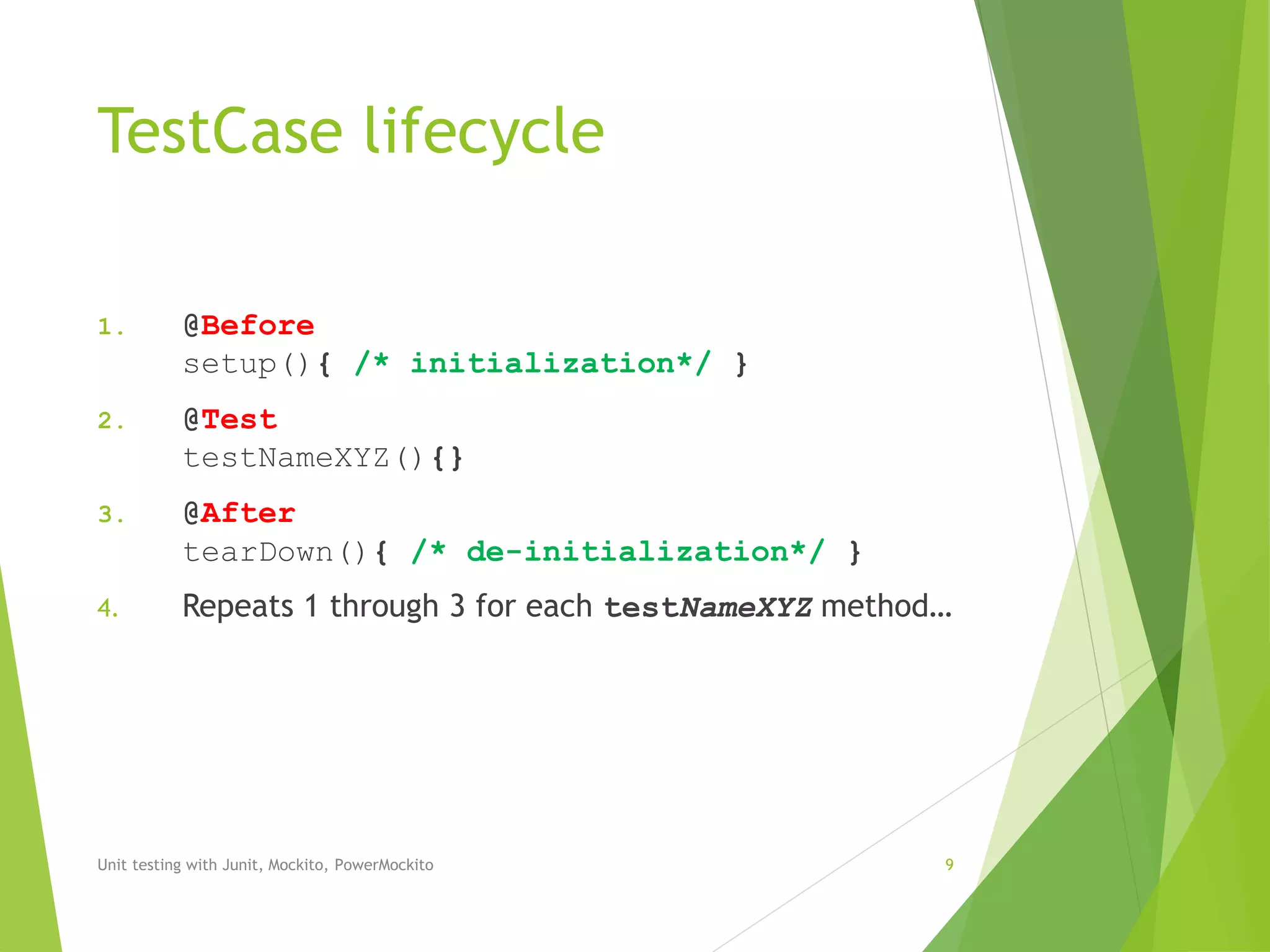
The document outlines unit testing methodologies using JUnit, Mockito, and PowerMockito, emphasizing frameworks, testing strategies, and specific annotations for test case design. It details black box and white box testing, including test case lifecycle, verification methods, and how to handle dependencies through mocking. Additionally, it discusses parameterized tests and the challenges of using JUnit with external dependencies, highlighting the capabilities of Mockito and PowerMockito for advanced mocking scenarios.




![JunitParams Framework
Parameterized test is to execute the same test over and over again
using different values
Gradle dependency for JUnitParams framework
testImplementation “pl.pragmatists:JUnitParams:1.1.1”
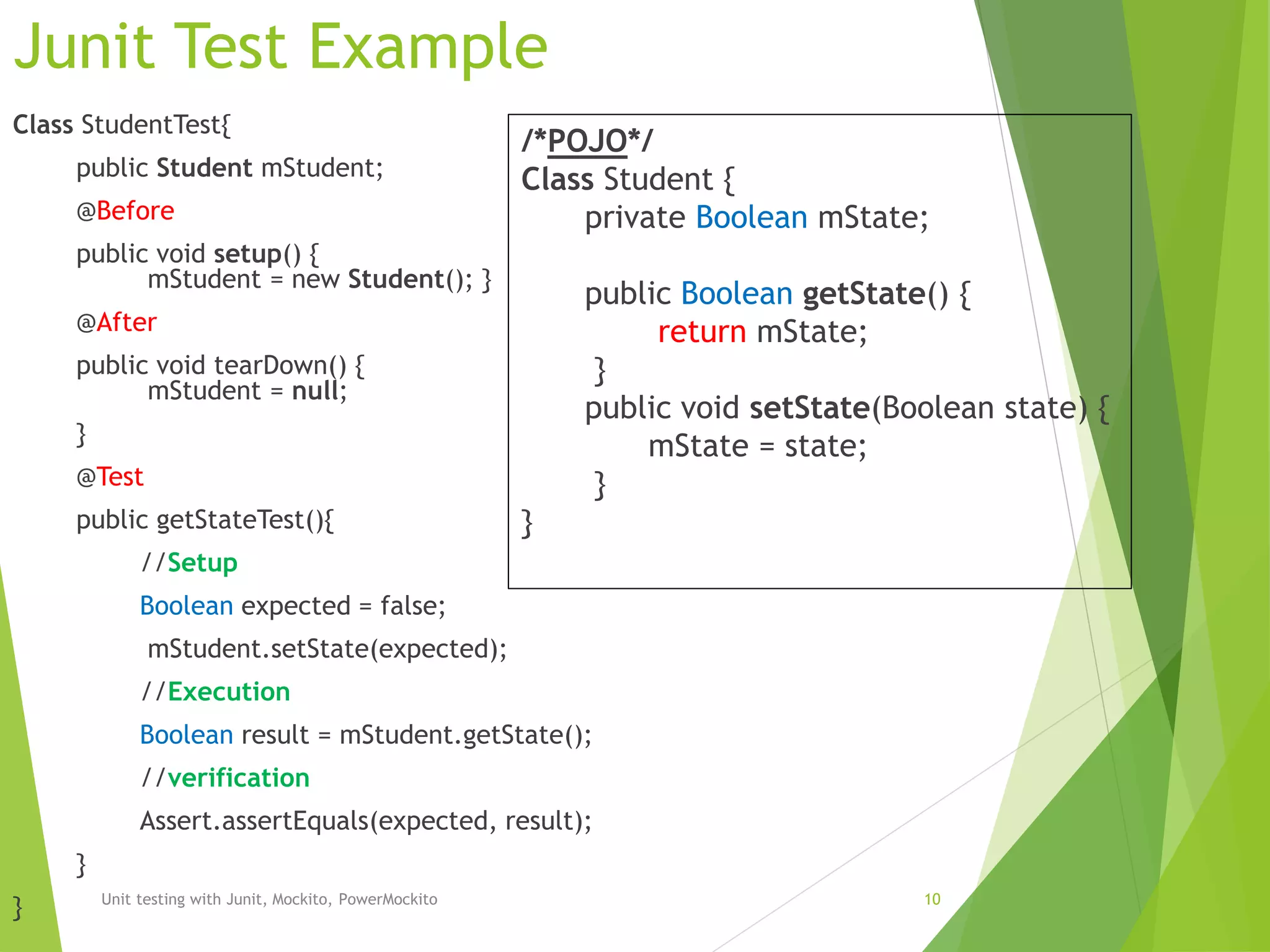
Example
public Object[] getScreenWidthParameters() {
return new Object[] {
new Object[] { 0, 0 },
new Object[] { 480, 480 },
new Object[] { -1, -1 },
new Object[] { null, null } };
}
@Test
@Parameters(method = "getScreenWidthParameters")
public void getScreenWidth(int mScreenWidth, int expected) throws Exception {
//setup
mStudent.setState(expected);
//Execution
int result = mStudent.getScreenWidth();
//Verification
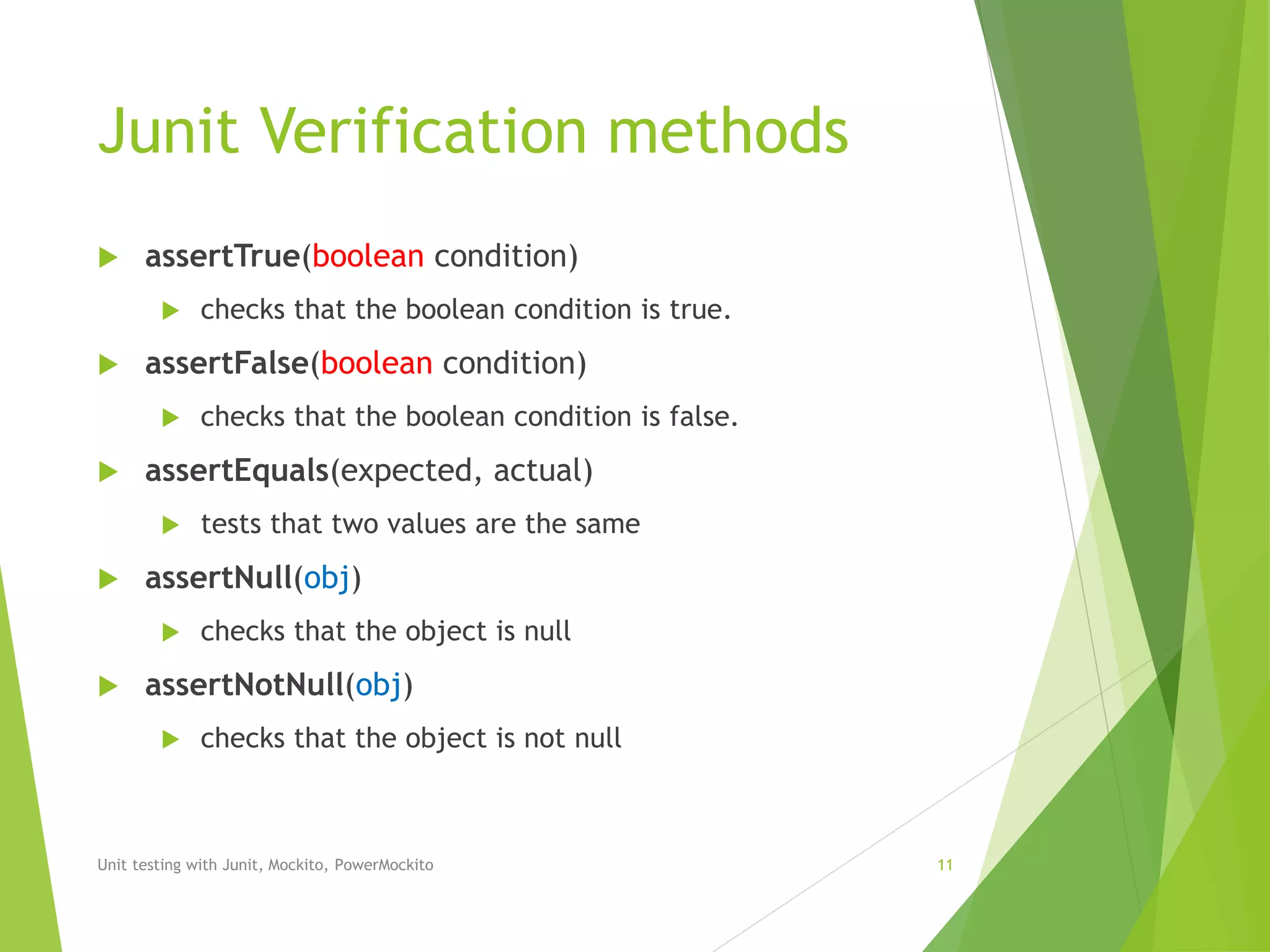
Assert.assertEquals(expected, result);
}
Unit testing with Junit, Mockito, PowerMockito 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junittesting-191105111211/75/Introduction-to-Testing-Frameworks-12-2048.jpg)