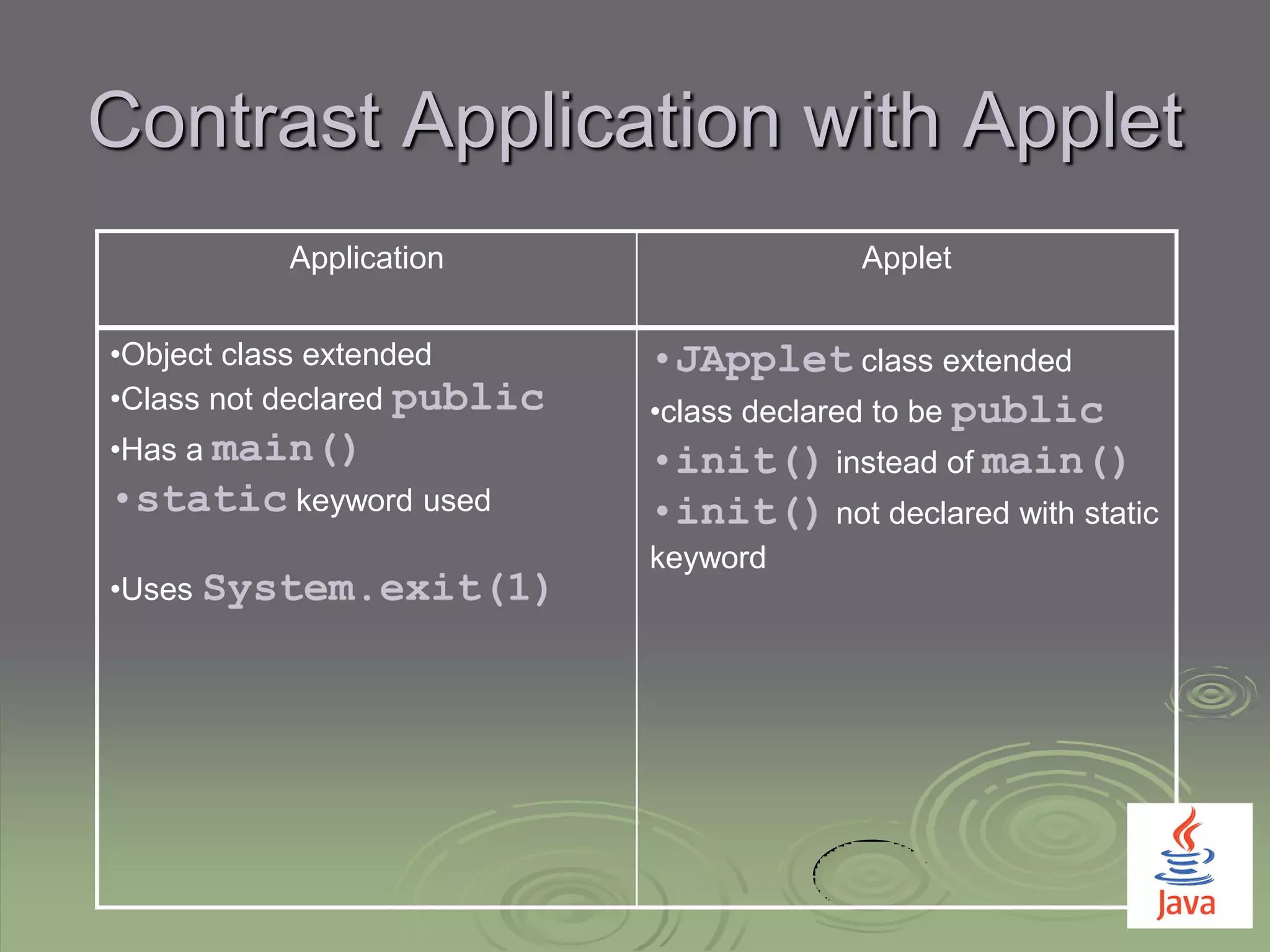
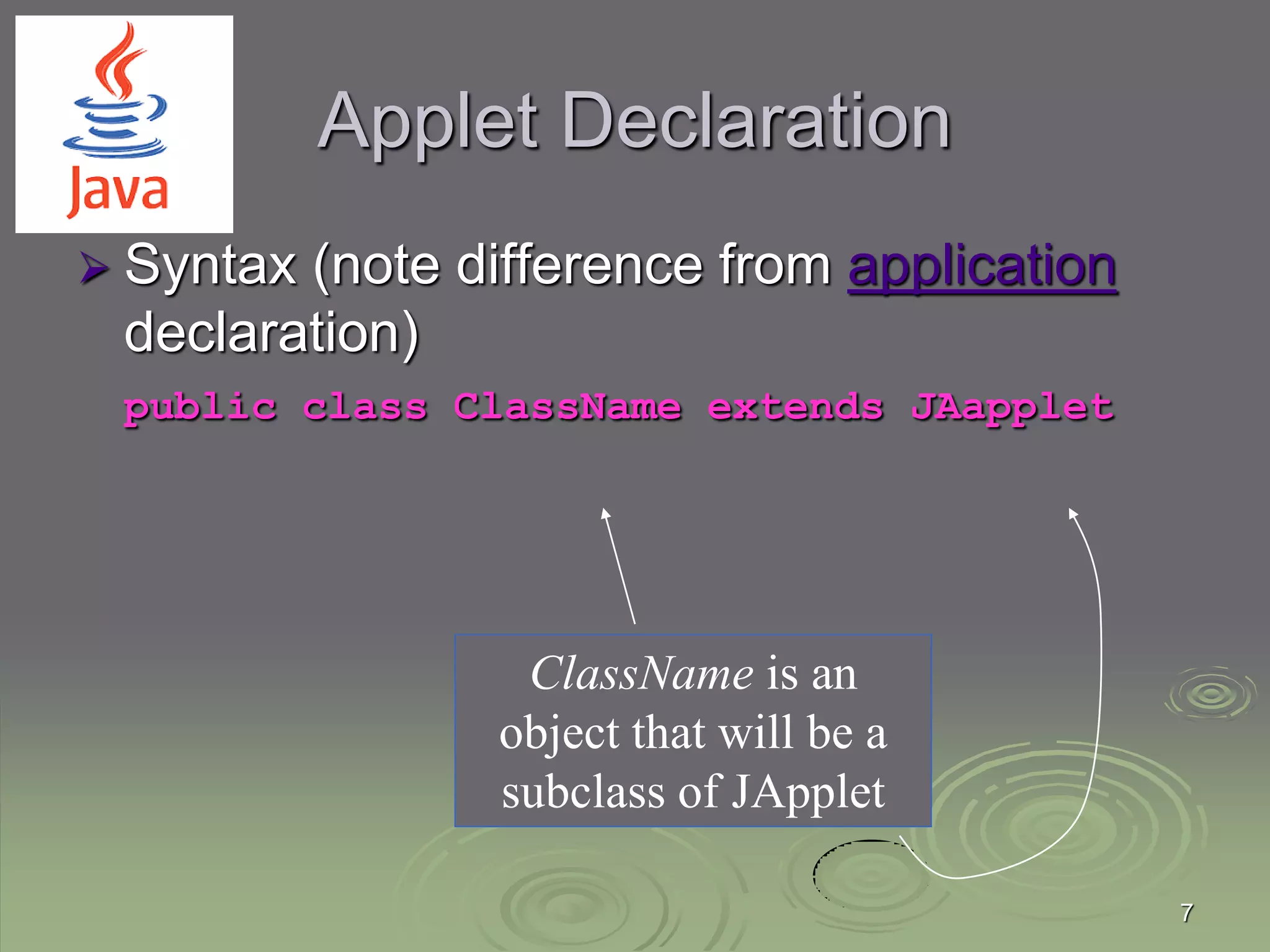
The document provides an introduction to Java applet programming, explaining that applets are embedded Java programs that run in web browsers and are executed through HTML files. It contrasts applets with standalone applications, highlighting differences in declarations, execution methods, and the use of graphical components. Additionally, it covers the process of embedding applets within HTML documents and emphasizes Java's object-oriented programming capabilities.