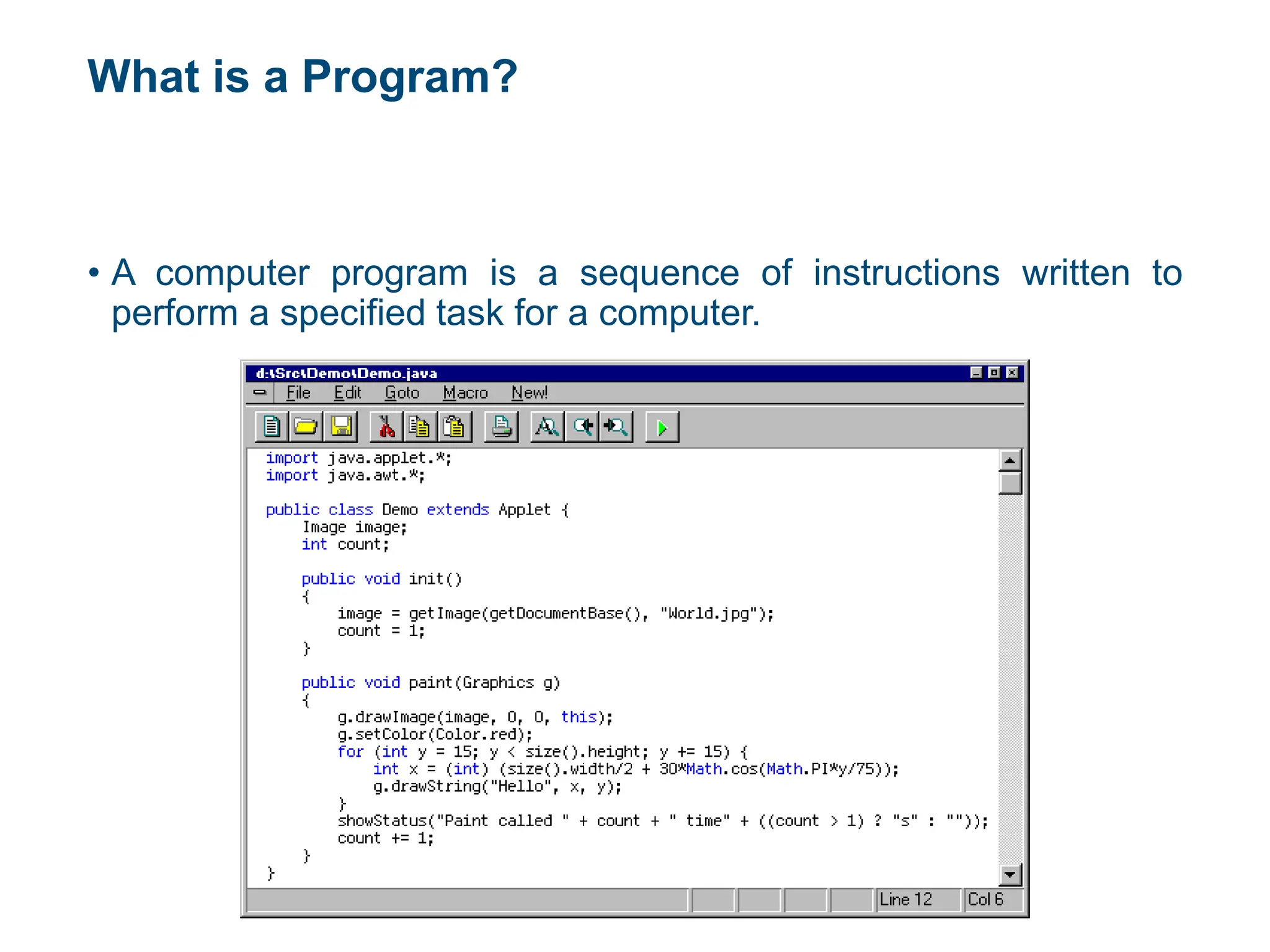
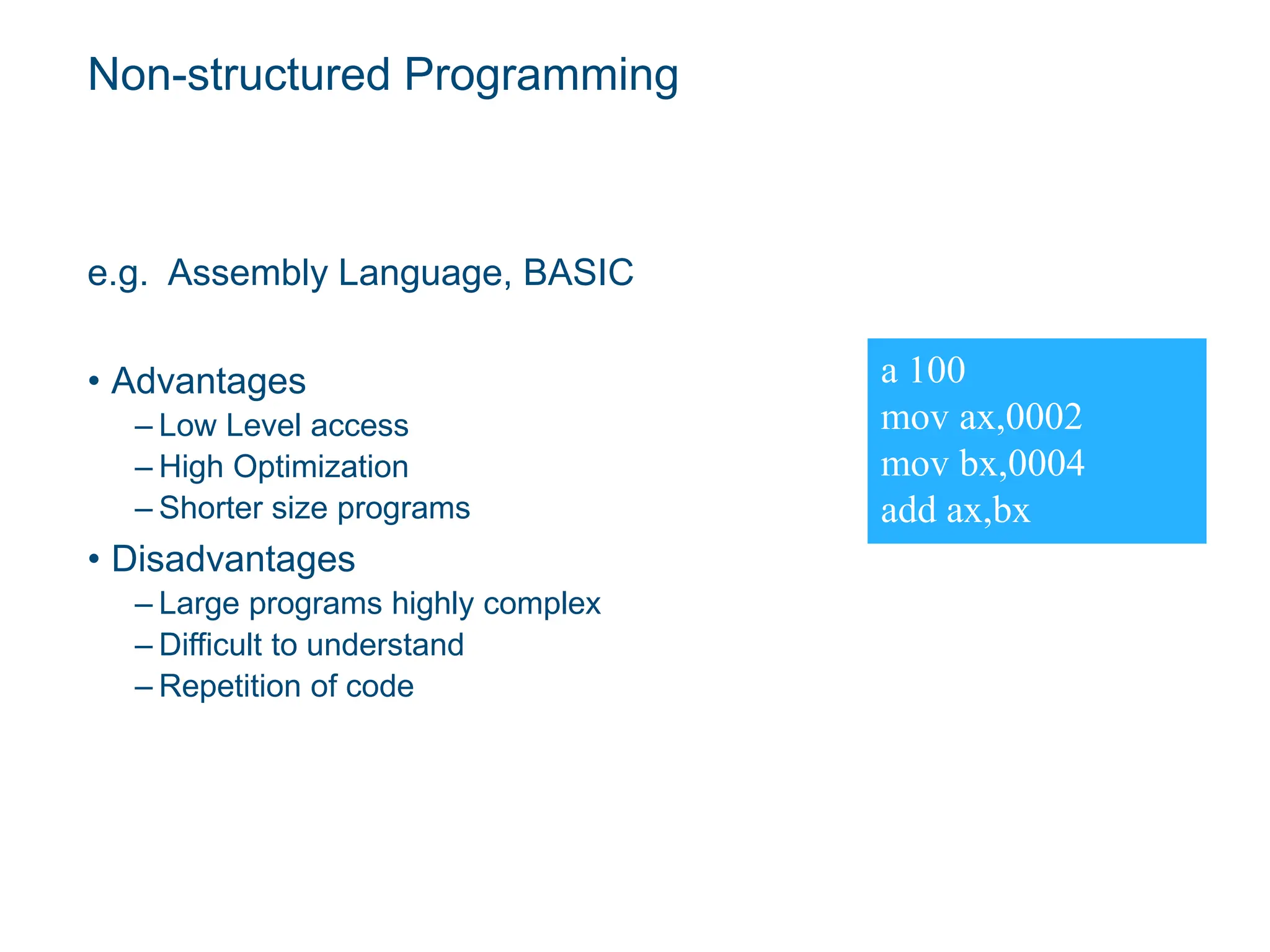
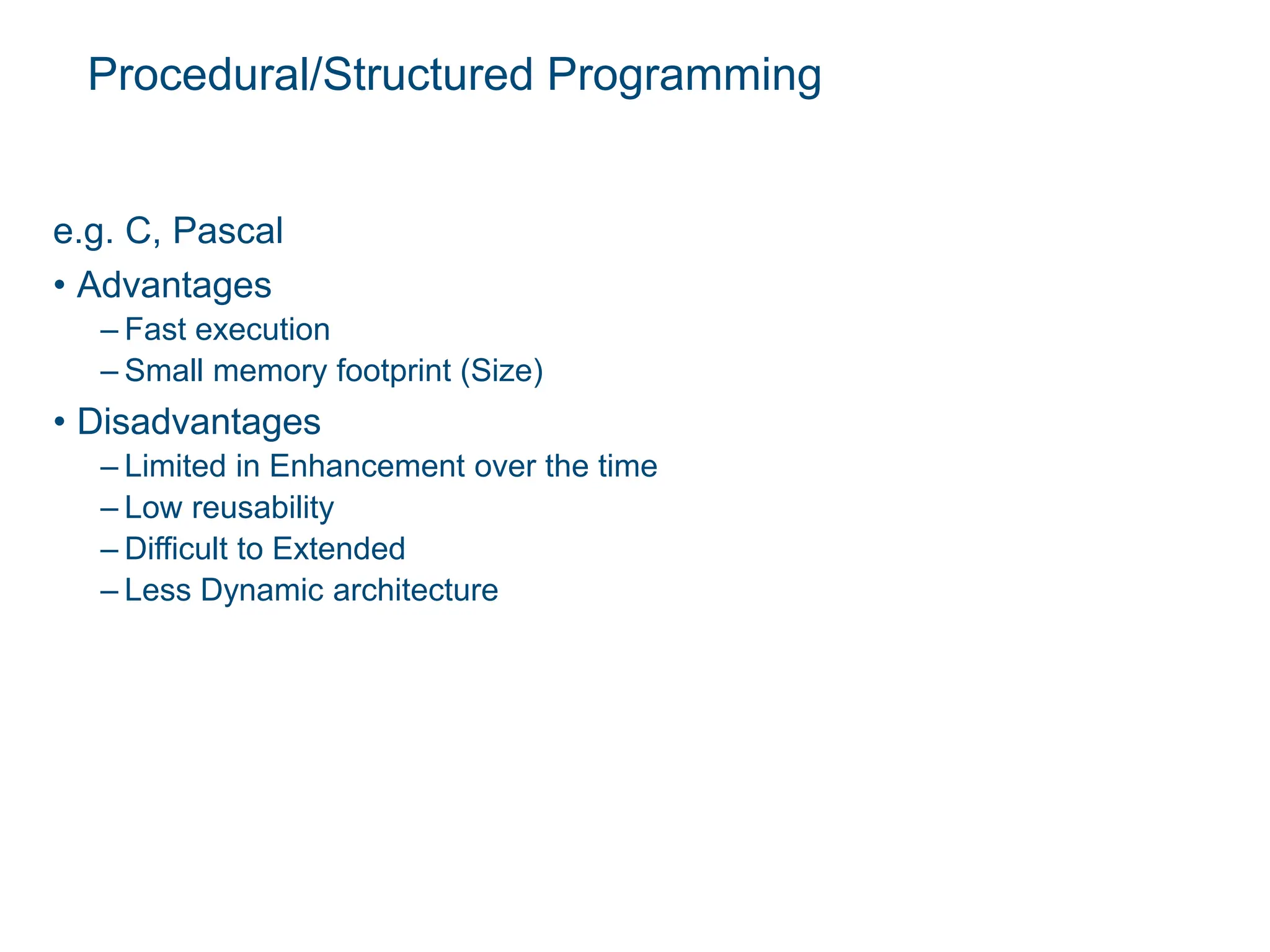
The document is an introductory lecture on Java programming, covering the evolution and features of programming languages, particularly focusing on Java's object-oriented nature. It outlines the history of Java, its versions, and the essential steps for creating and running Java programs. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of various programming paradigms and provides a brief overview of programming fundamentals.