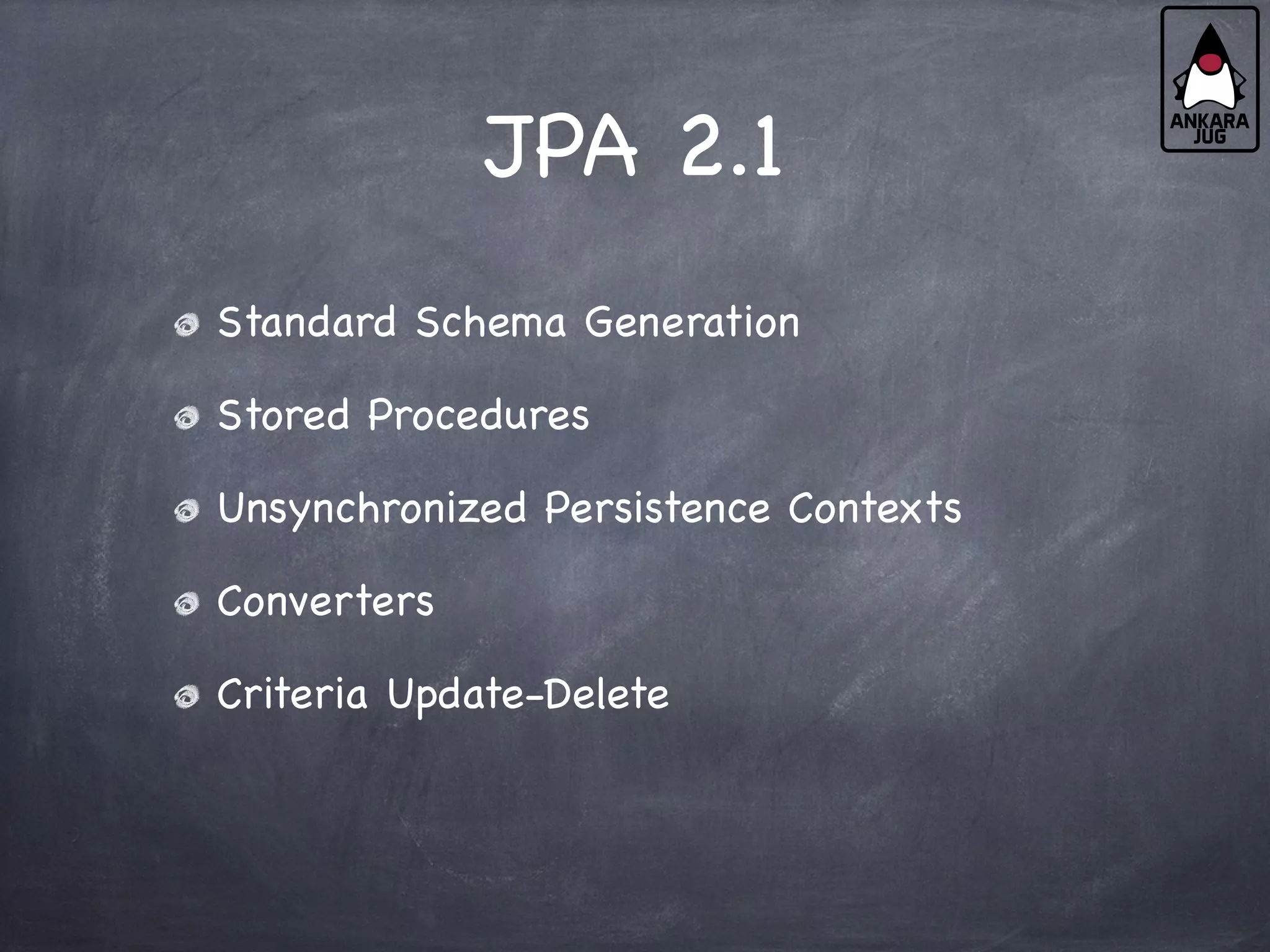
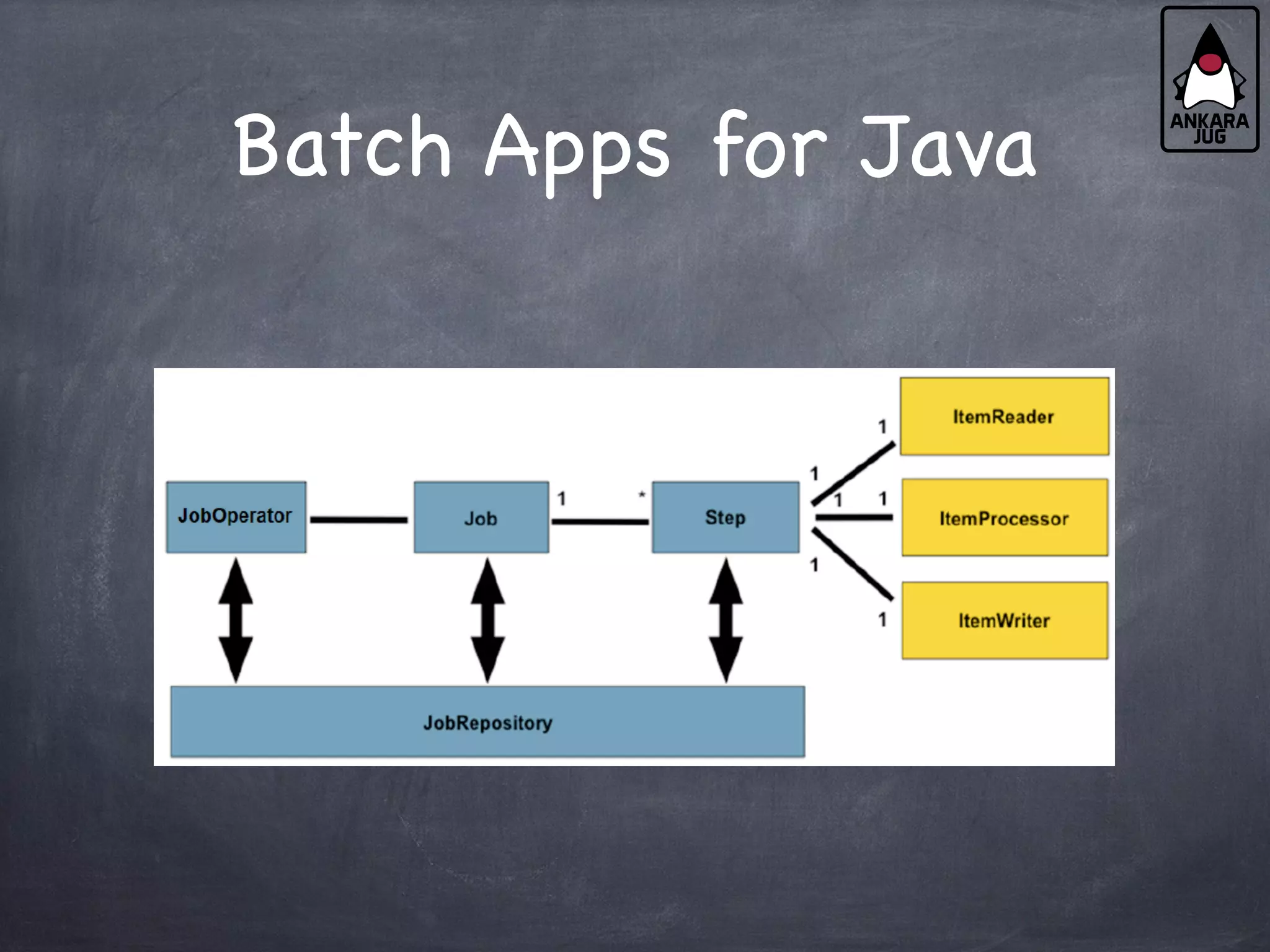
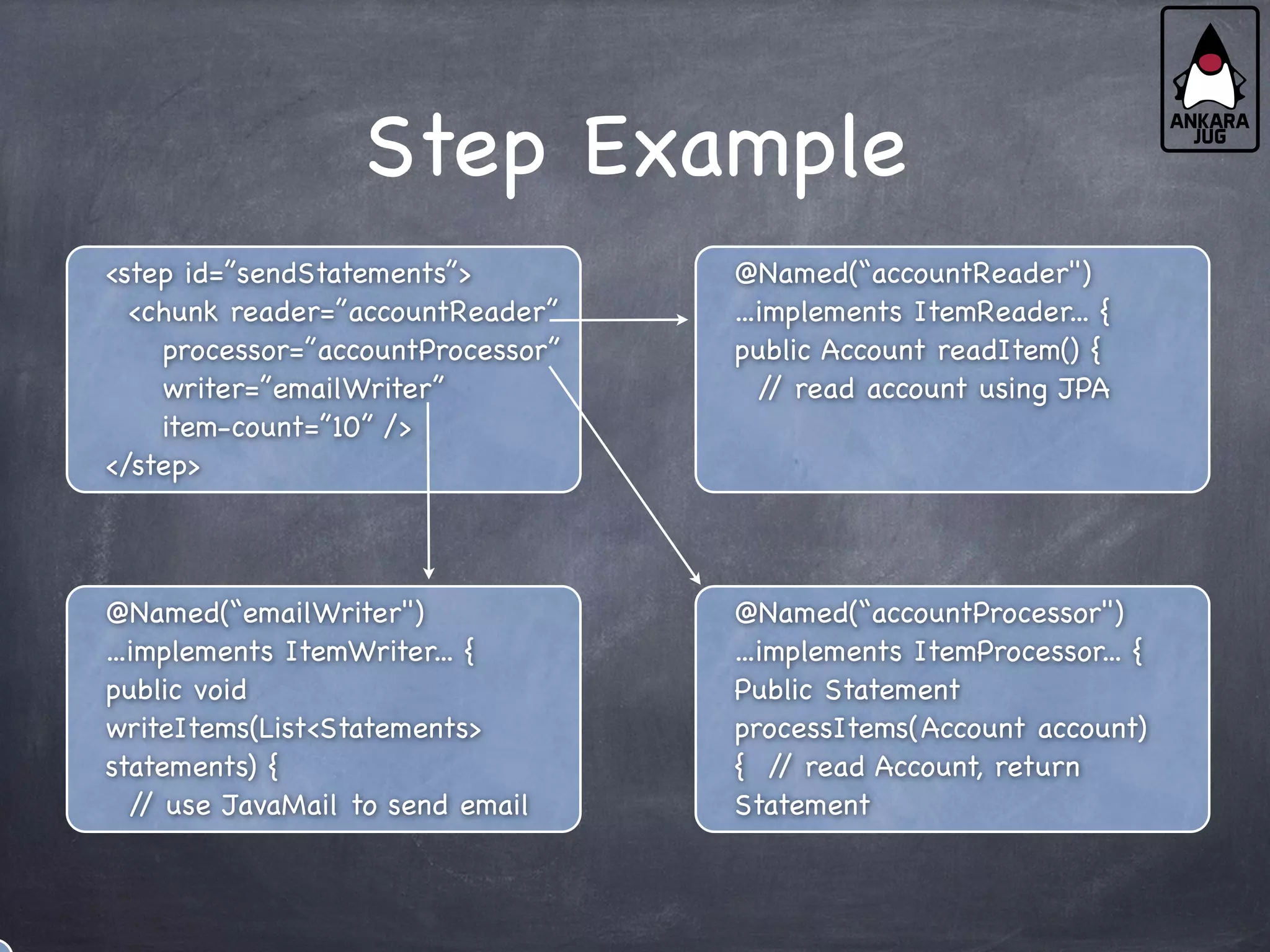
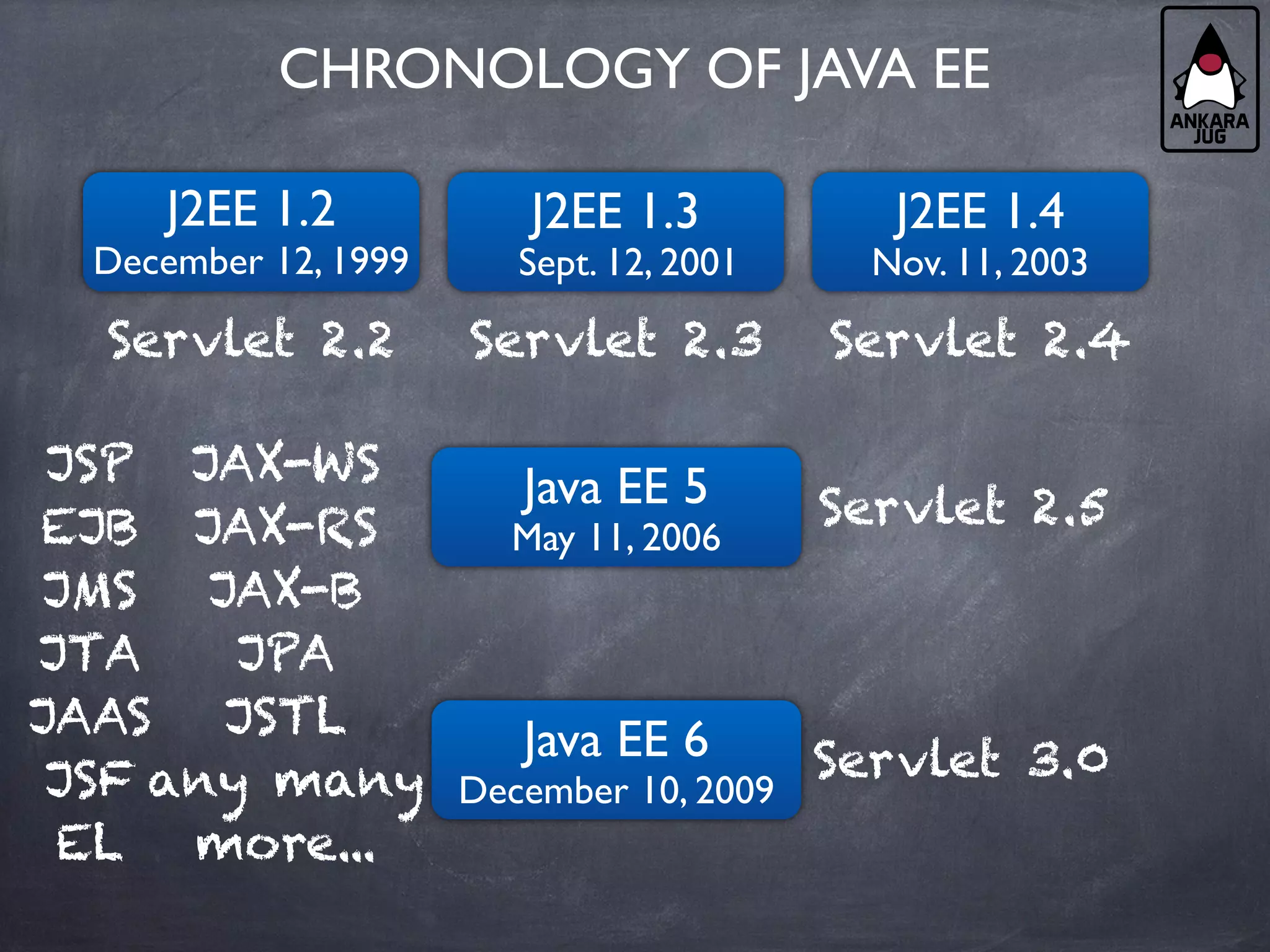
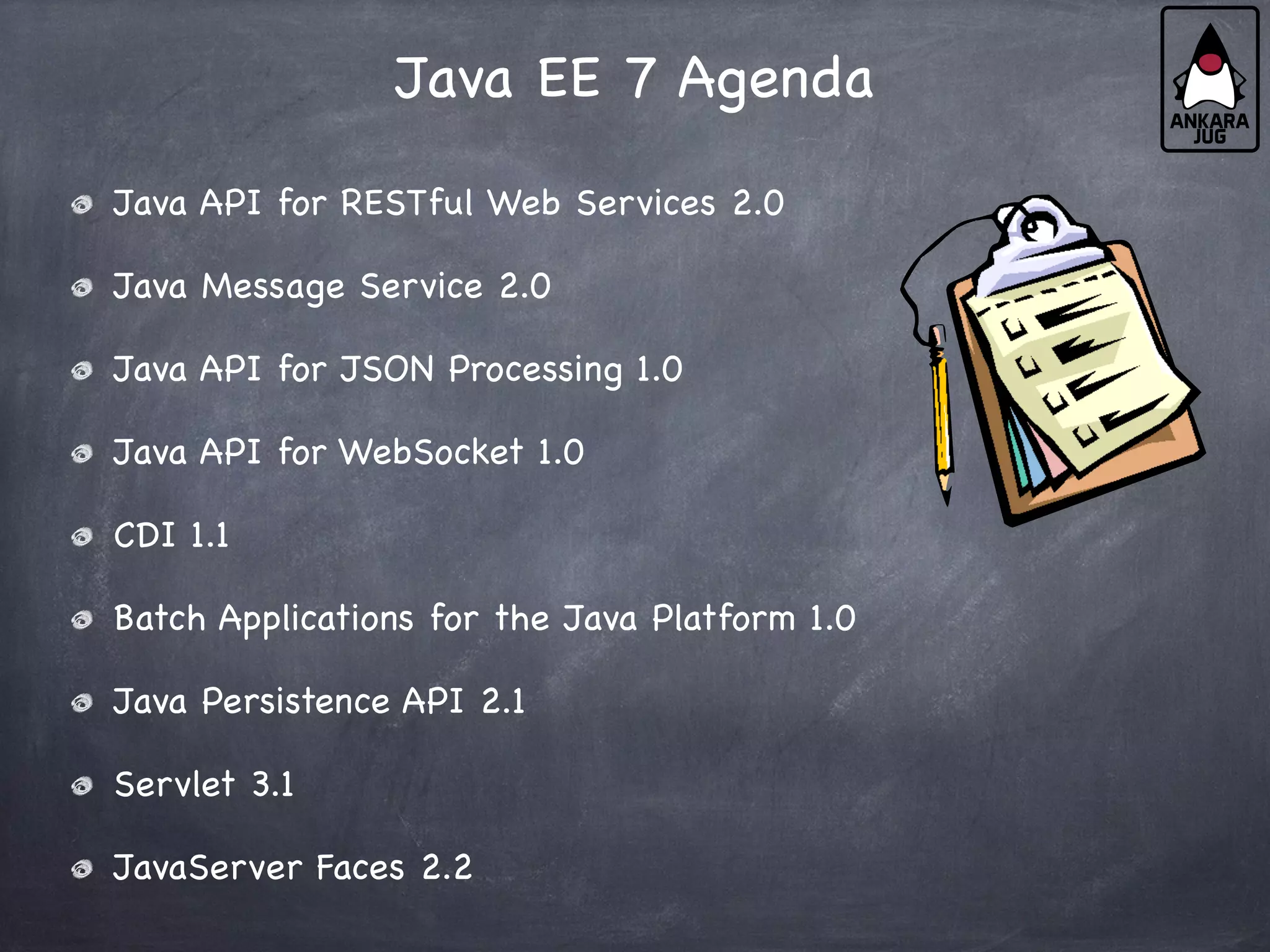
This document provides an overview of Java EE 7 technologies including Servlets, JSF, JMS, CDI, WebSocket, JSON, JPA, JAX-RS, and batch applications. It discusses the key features and changes in Java EE 7 for each technology compared to previous versions. These include enhancements to Servlets 3.1 like async processing, JSF 2.2 additions like file upload and HTML5 markup support, and JPA 2.1 features such as schema generation and stored procedures.




















![JSON
{
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Smith",
"age": 25,
"address": {
"streetAddress": "21 2nd Street",
"city": "New York",
"state": "NY",
"postalCode": 10021
},
"phoneNumbers": [
{
"type": "home",
"number": "212 555-1234"
},
{
"type": "fax",
"number": "646 555-4567"
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaee7demystified-130802020632-phpapp02/75/Java-EE7-Demystified-28-2048.jpg)
![Java API for JSON
JsonBuilderFactory factory = Json.createBuilderFactory(null);
JsonArray jsonArray = factory.createArrayBuilder()
.add(factory.createObjectBuilder().
add("type", "home").
add("number", "(800) 111-1111"))
.add(factory.createObjectBuilder().
add("type", "cell").
add("number", "(800) 222-2222")).build();
[
{
"type": "home”,
"number": "(800) 111-1111"
},{
"type": "fax”,
"number": "646 555-4567"
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaee7demystified-130802020632-phpapp02/75/Java-EE7-Demystified-29-2048.jpg)