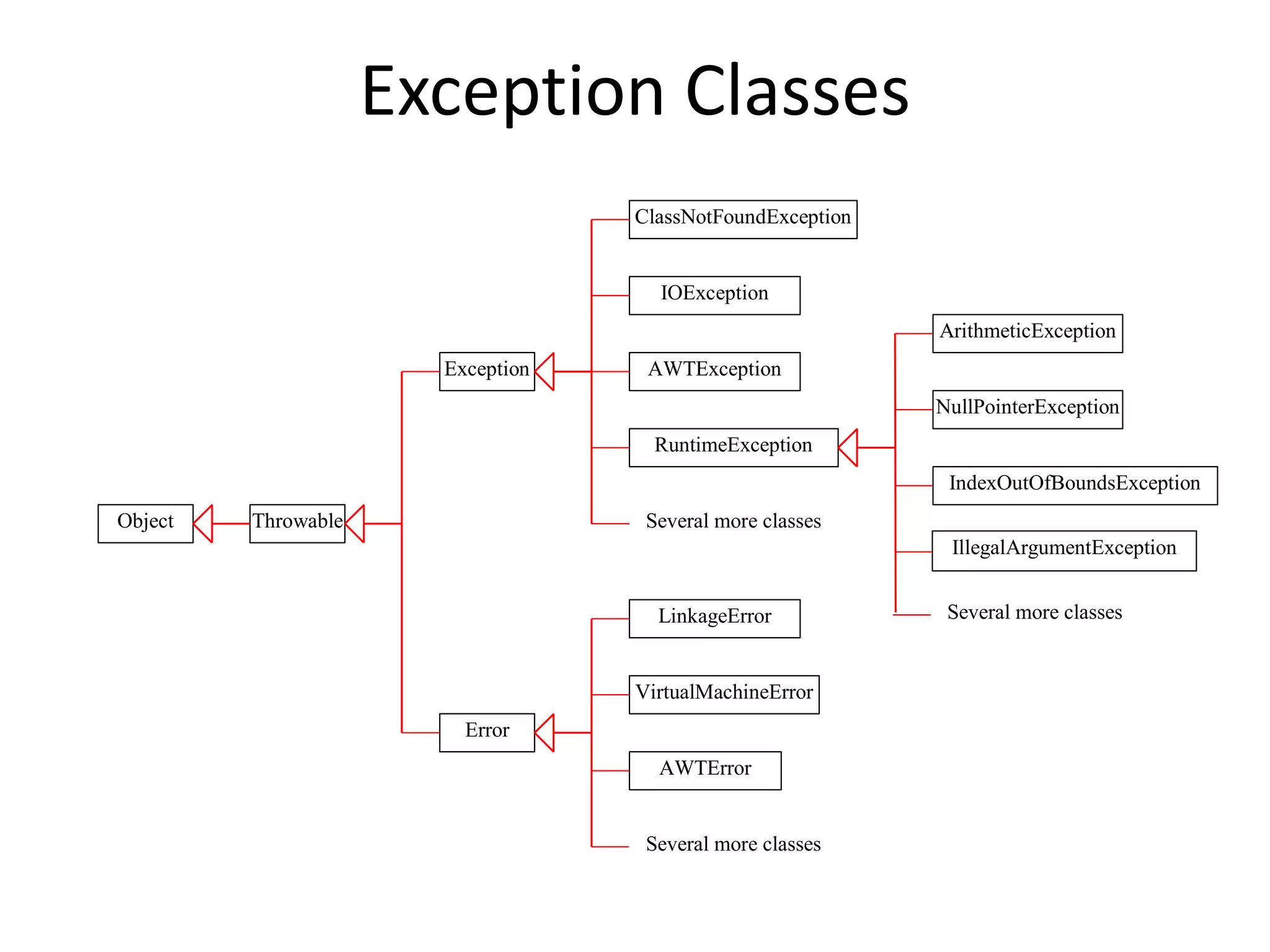
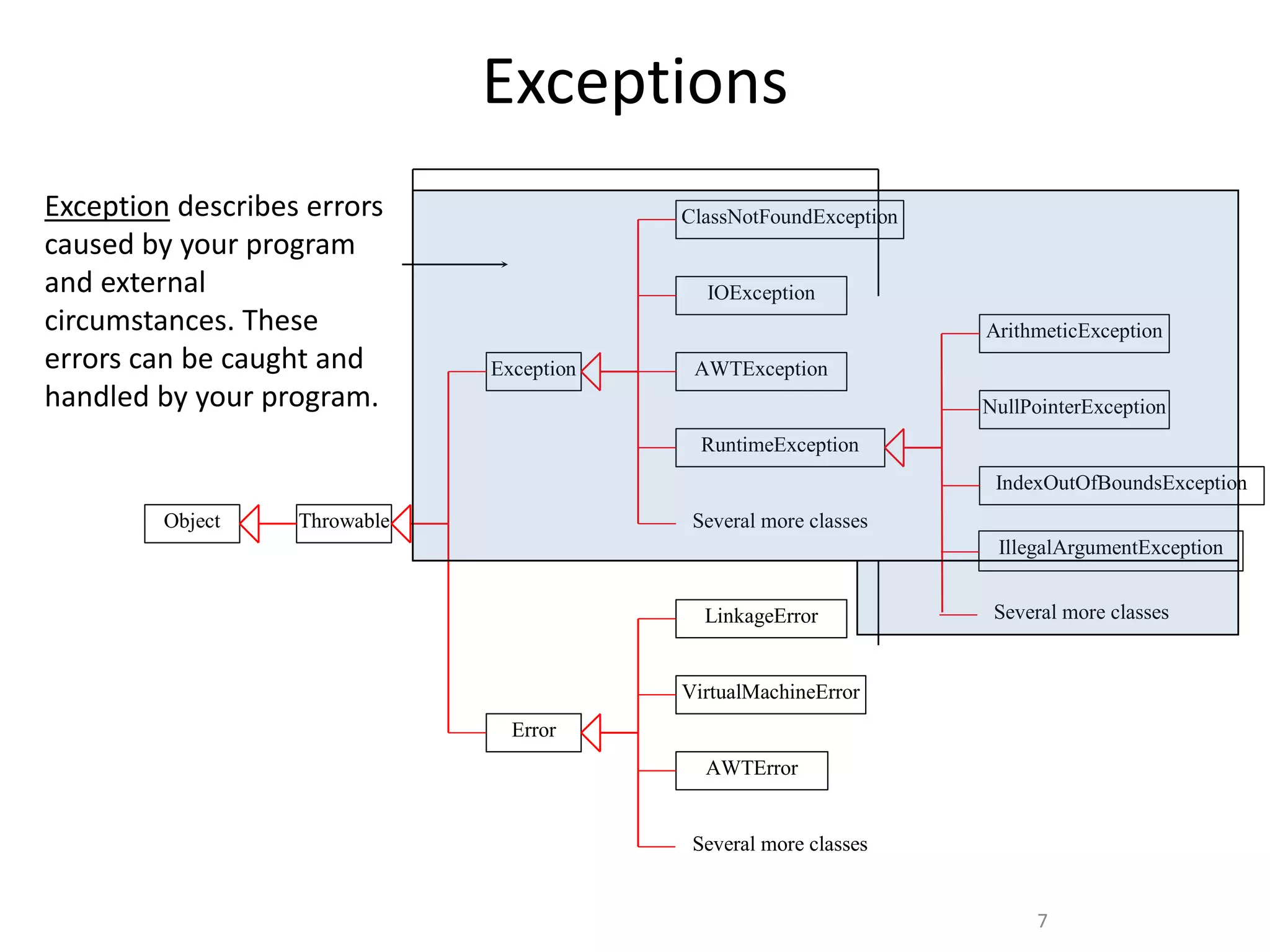
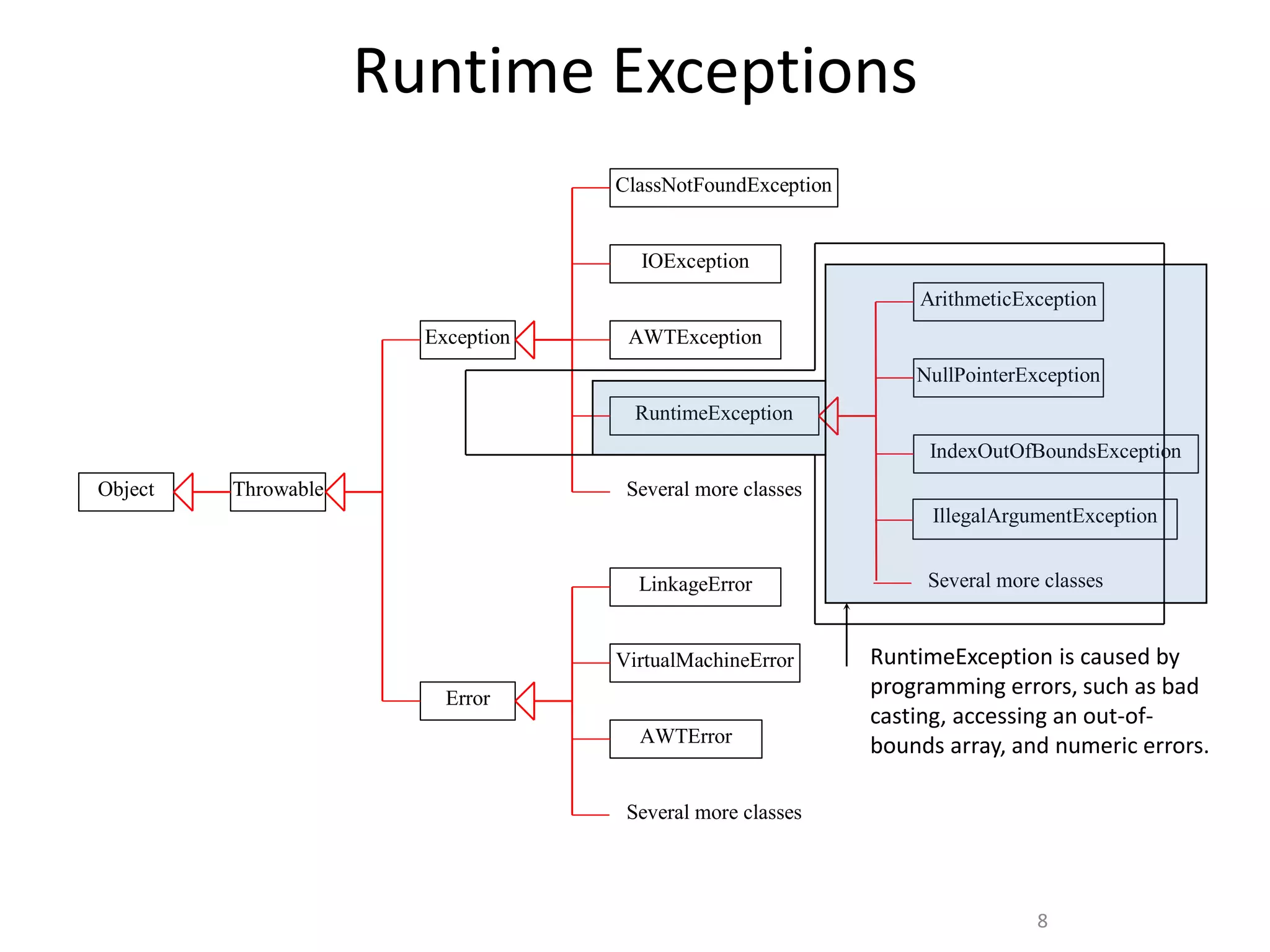
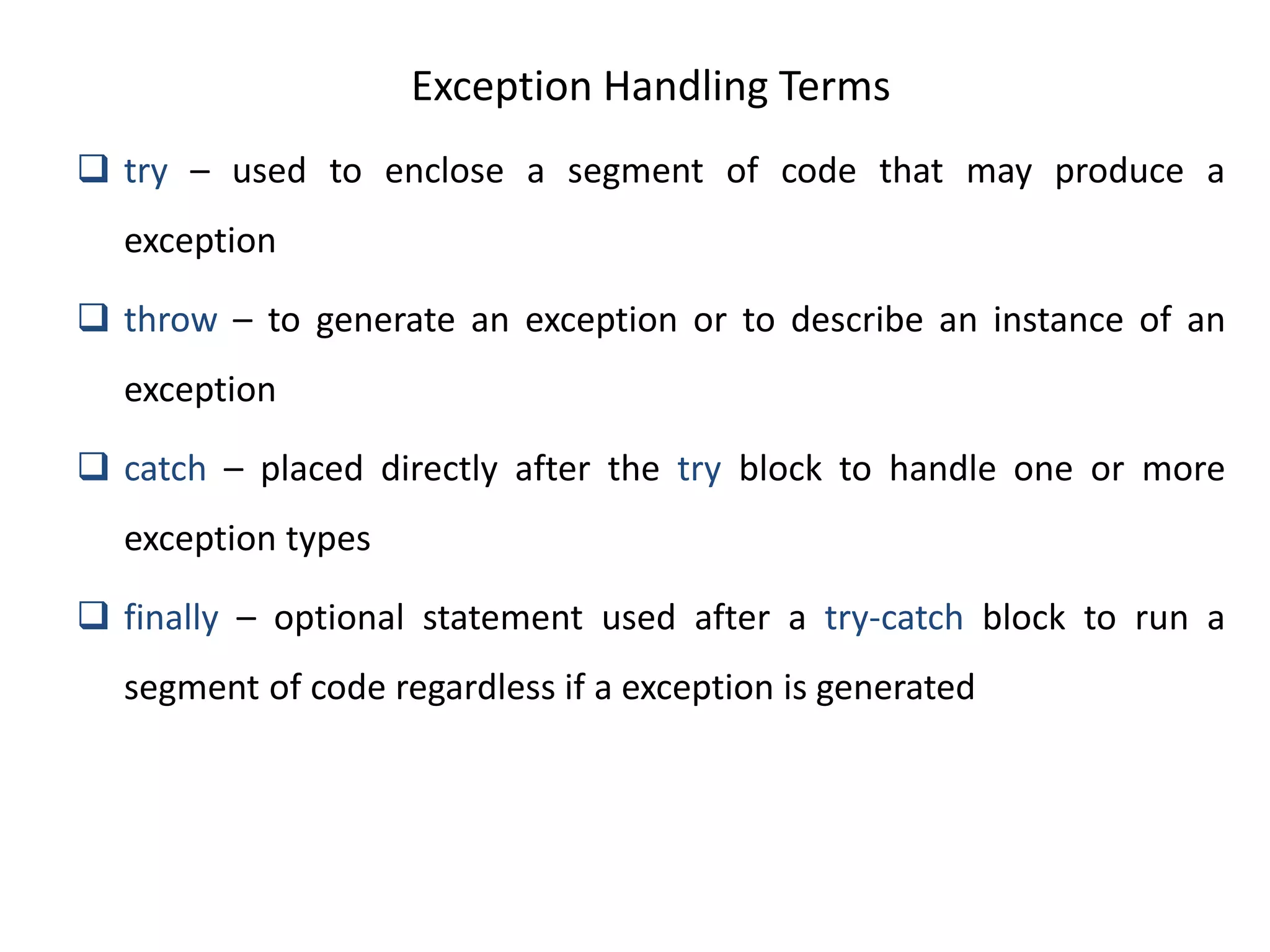
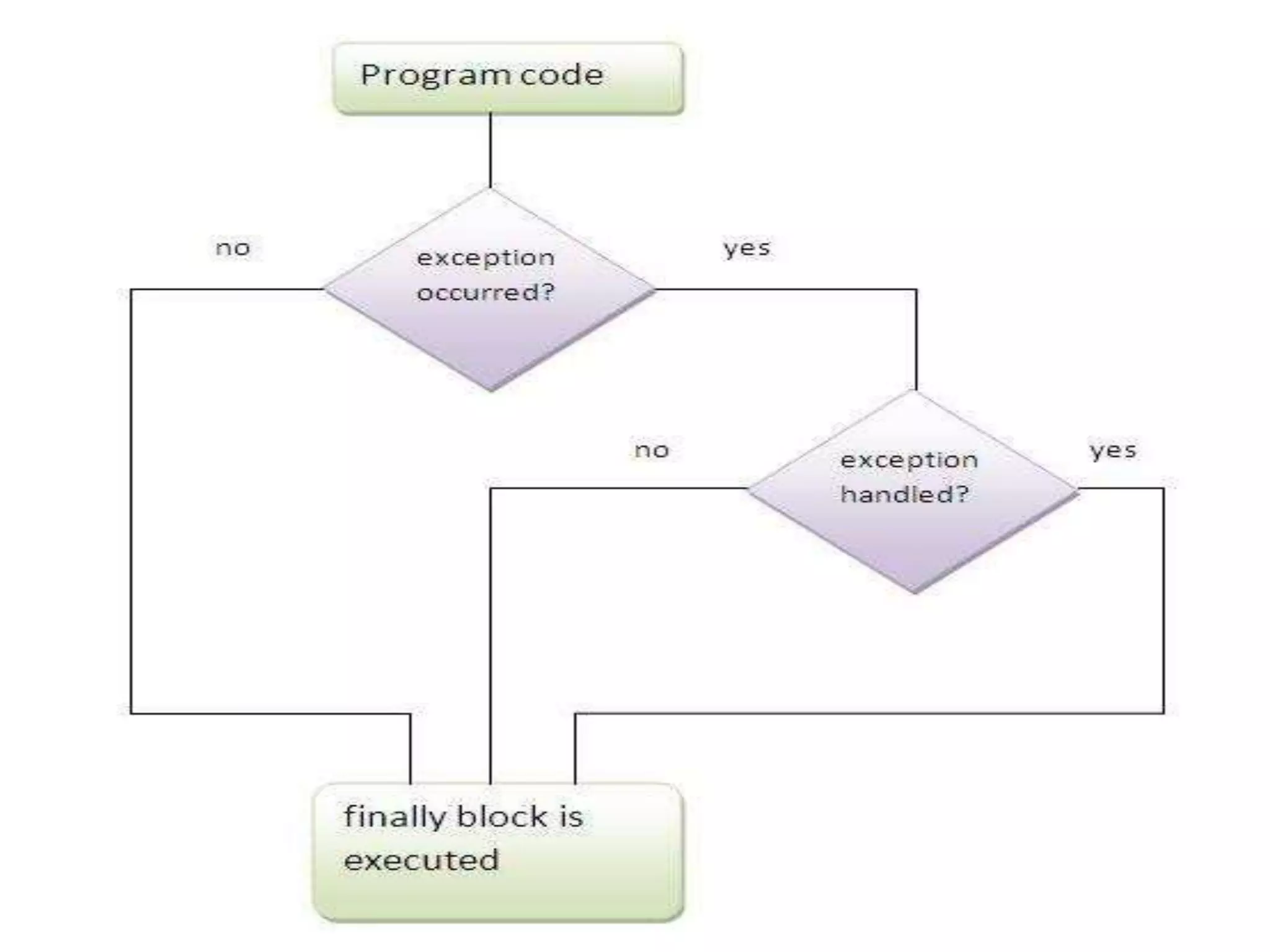
The document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines exceptions as abnormal conditions that arise during runtime and disrupt normal program flow. There are three types of exceptions: checked exceptions which must be declared, unchecked exceptions which do not need to be declared, and errors which are rare and cannot be recovered from. The try, catch, and finally blocks are used to handle exceptions, with catch blocks handling specific exception types and finally blocks containing cleanup code.





![class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int data=50/0;
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}
}
Output:
Exception in thread main java.lang.ArithmeticException:/ by zero
Rest of the code is not executed (rest of the code..)statement is not printed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-11-2048.jpg)

![class Simple1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
int data=50/0;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}}
Output:
Exception in thread main java.lang.ArithmeticException:/ by zero
rest of the code…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-13-2048.jpg)



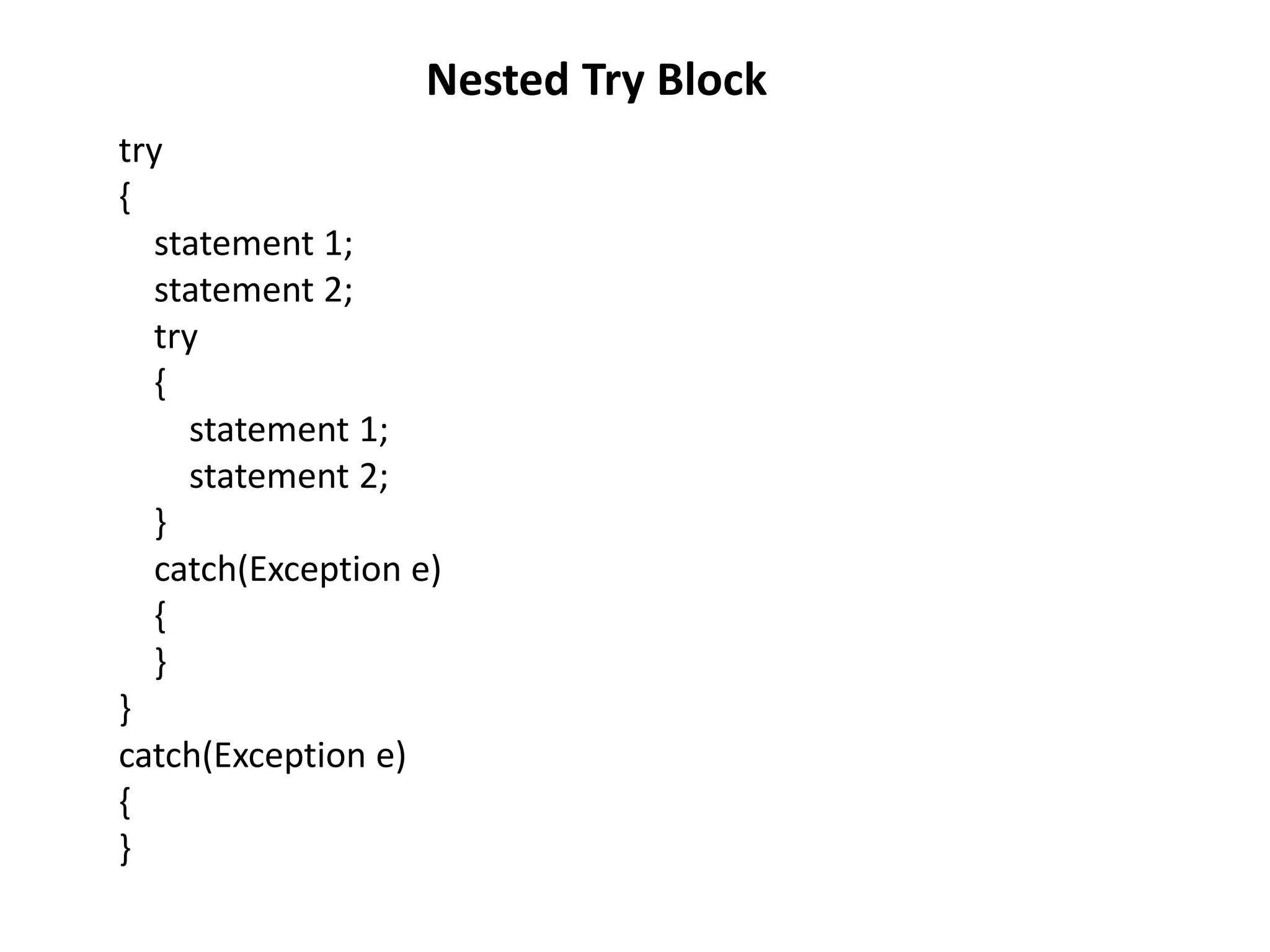
![class Excep6
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
try
{
S.o.p("going to divide");
int b =39/0;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
try
{
int a[]=new int[5];
a[5]=4;
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("other statement");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("handeled");
}
System.out.println("normal flow..");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-18-2048.jpg)

![class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
int data=25/0;
System.out.println(data);
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("finally block is always executed");
}
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-21-2048.jpg)

![public class bank
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int balance = 100, withdraw = 1000;
if(balance < withdraw)
{
//ArithmeticException e = new ArithmeticException("No money please");
//throw e;
//throw new ArithmeticException();
throw new ArithmeticException("No Money");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Draw & enjoy Sir, Best wishes of the day");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-23-2048.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(System.in);
int x = Integer.parseInt(dis.readLine());
if(x < 0)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
throw new IllegalArgumentException
("You have entered no"+" "+ x +" "+ "which is less than 0");
}
else
{
System.out.println("The no is"+x);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-24-2048.jpg)



![public class My_Exception
{
public static void main (String args [ ])
{
try
{
int x = 10;
if (x < 20 || x >100) throw new NumberRangeException( );
}
catch (NumberRangeException e)
{
System.out.println (e);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaexceptionhandling-150203104417-conversion-gate02/75/Java-exception-handling-28-2048.jpg)