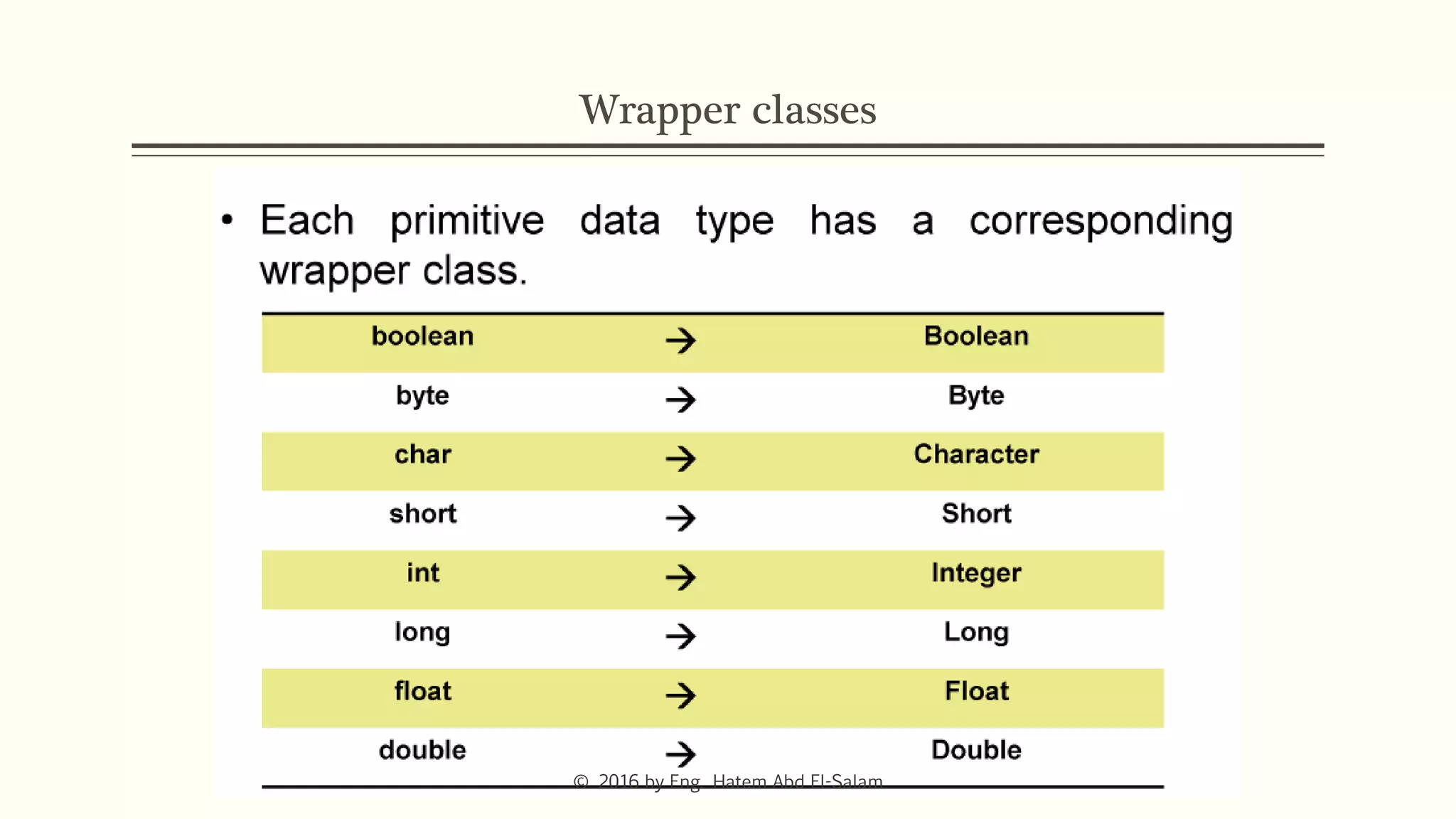
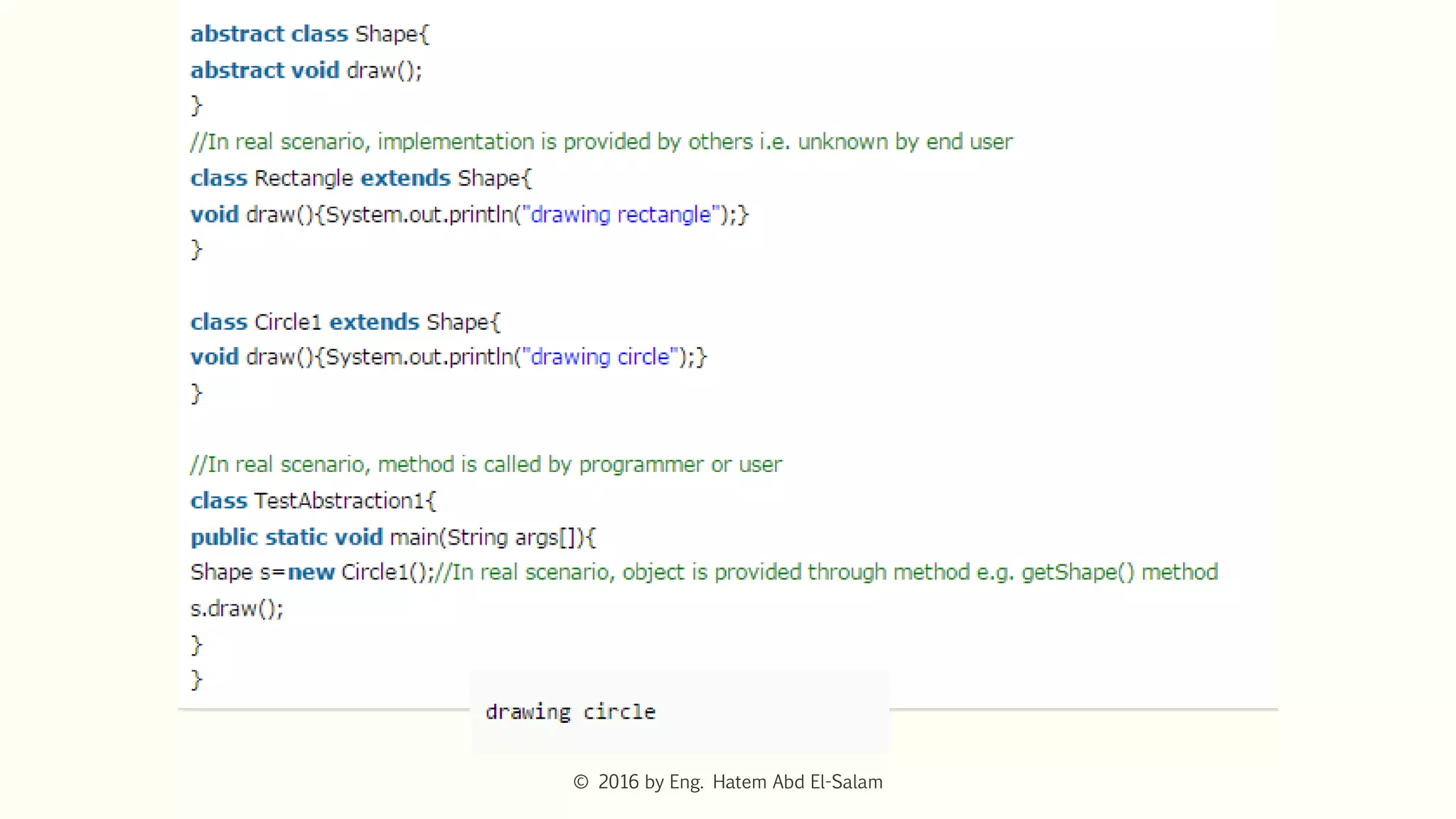
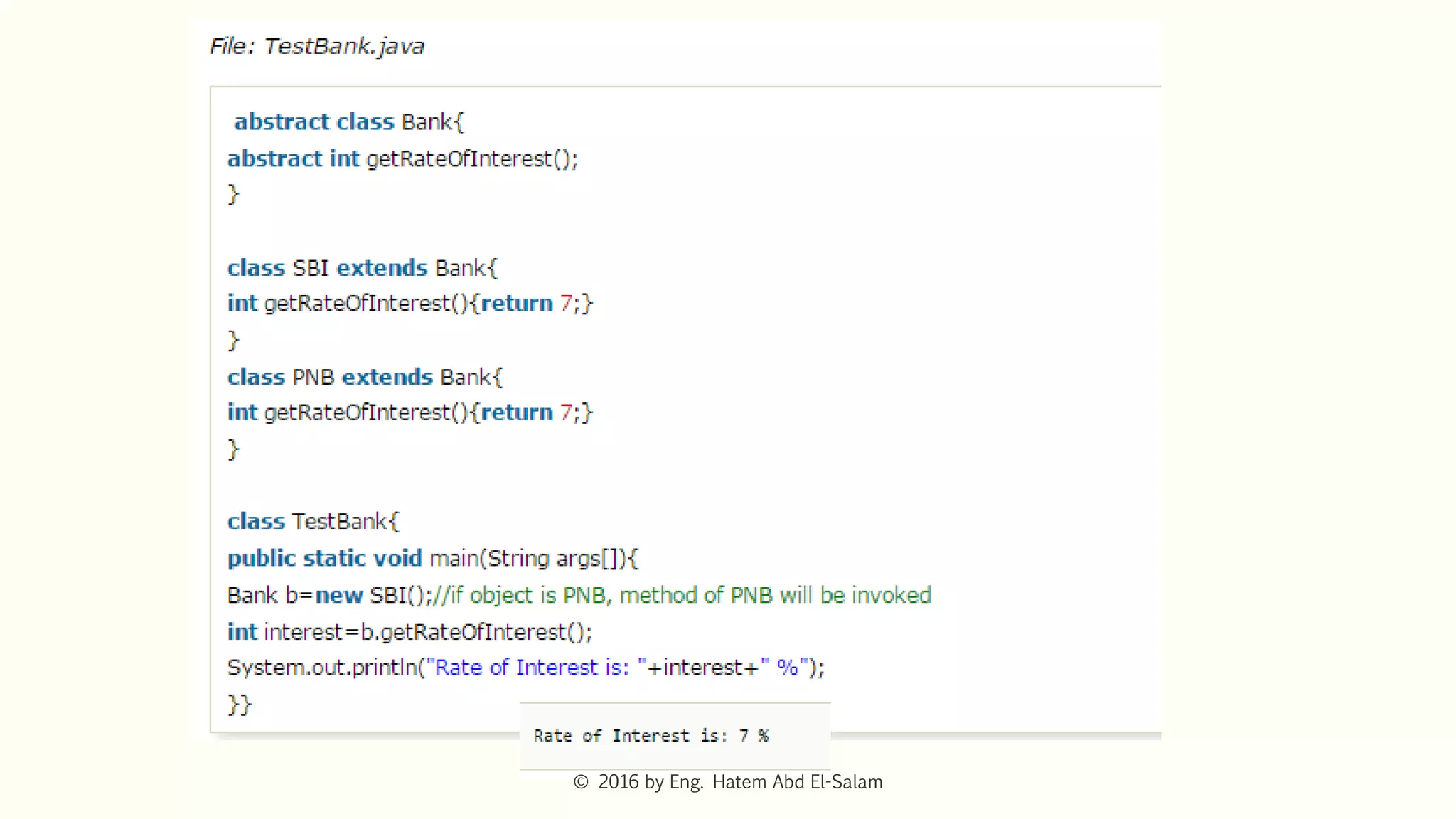
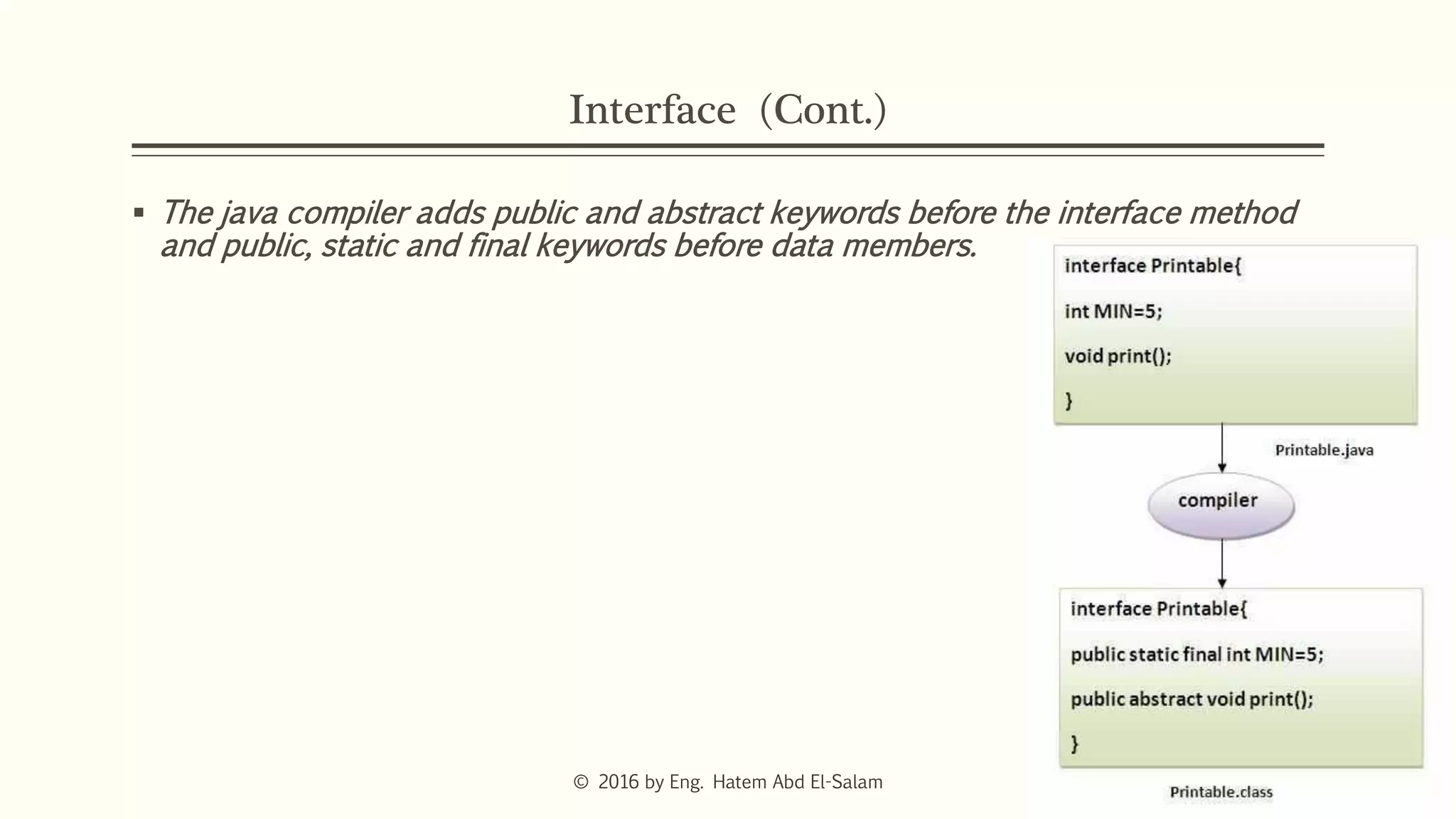
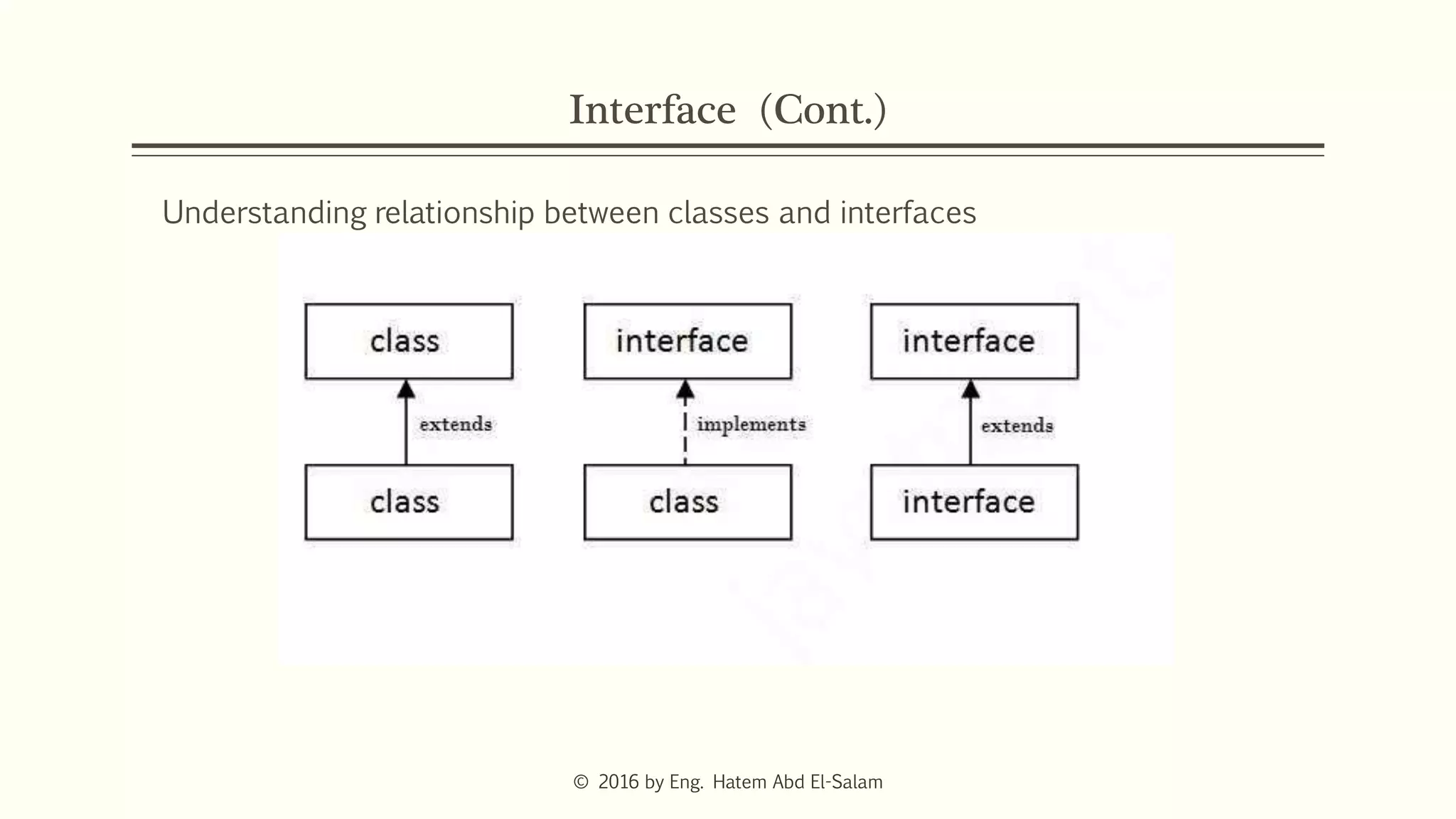
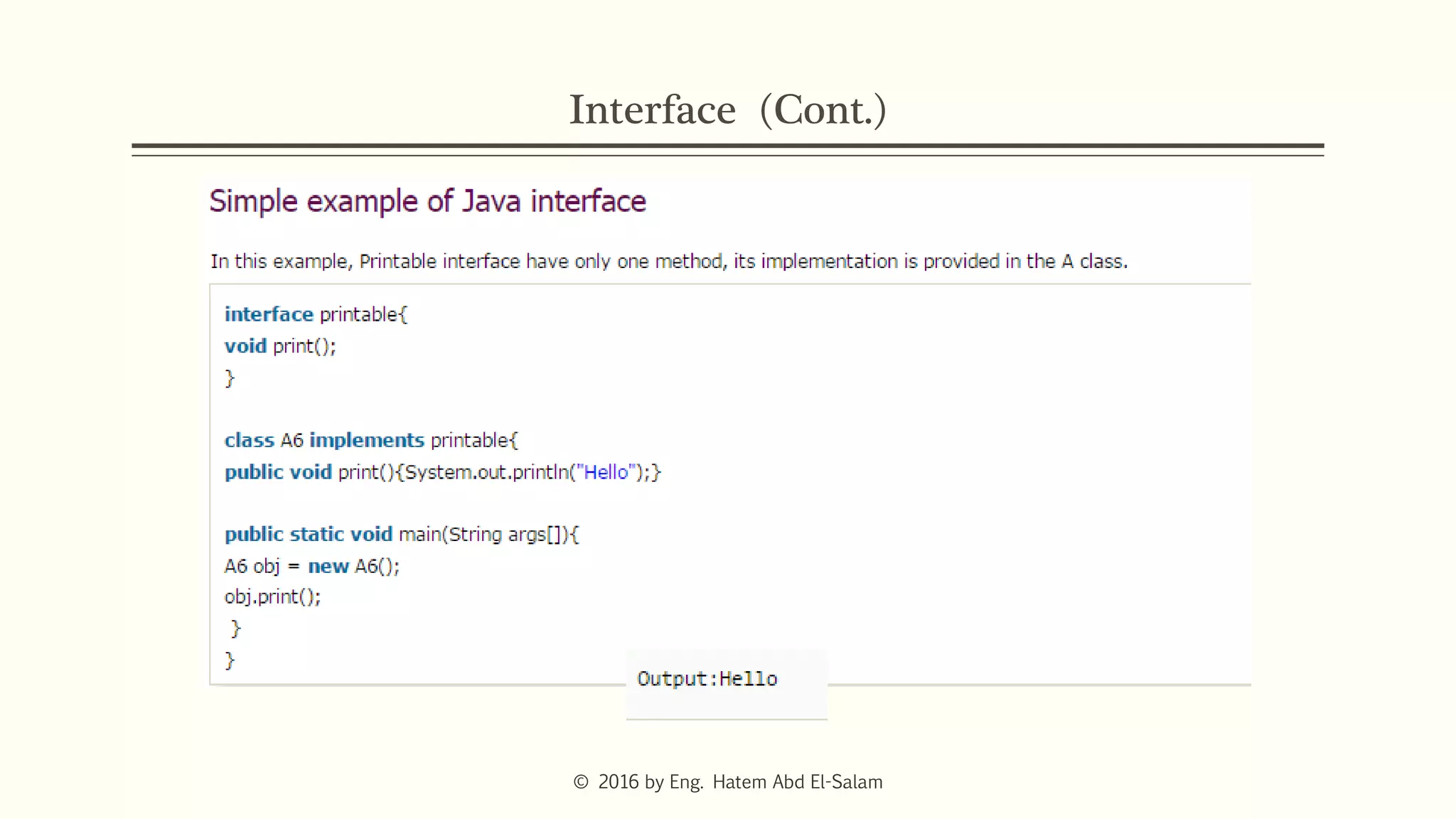
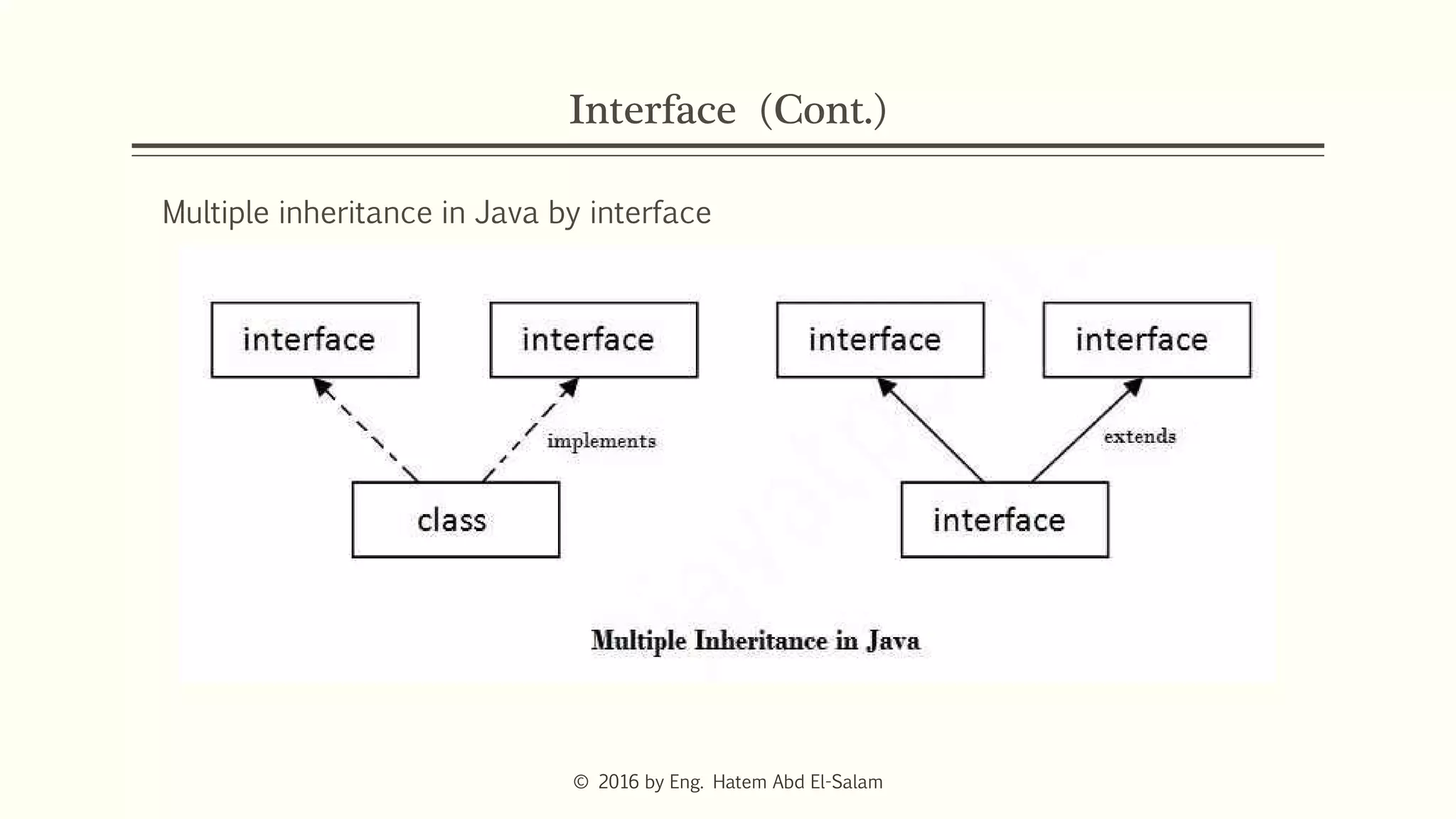
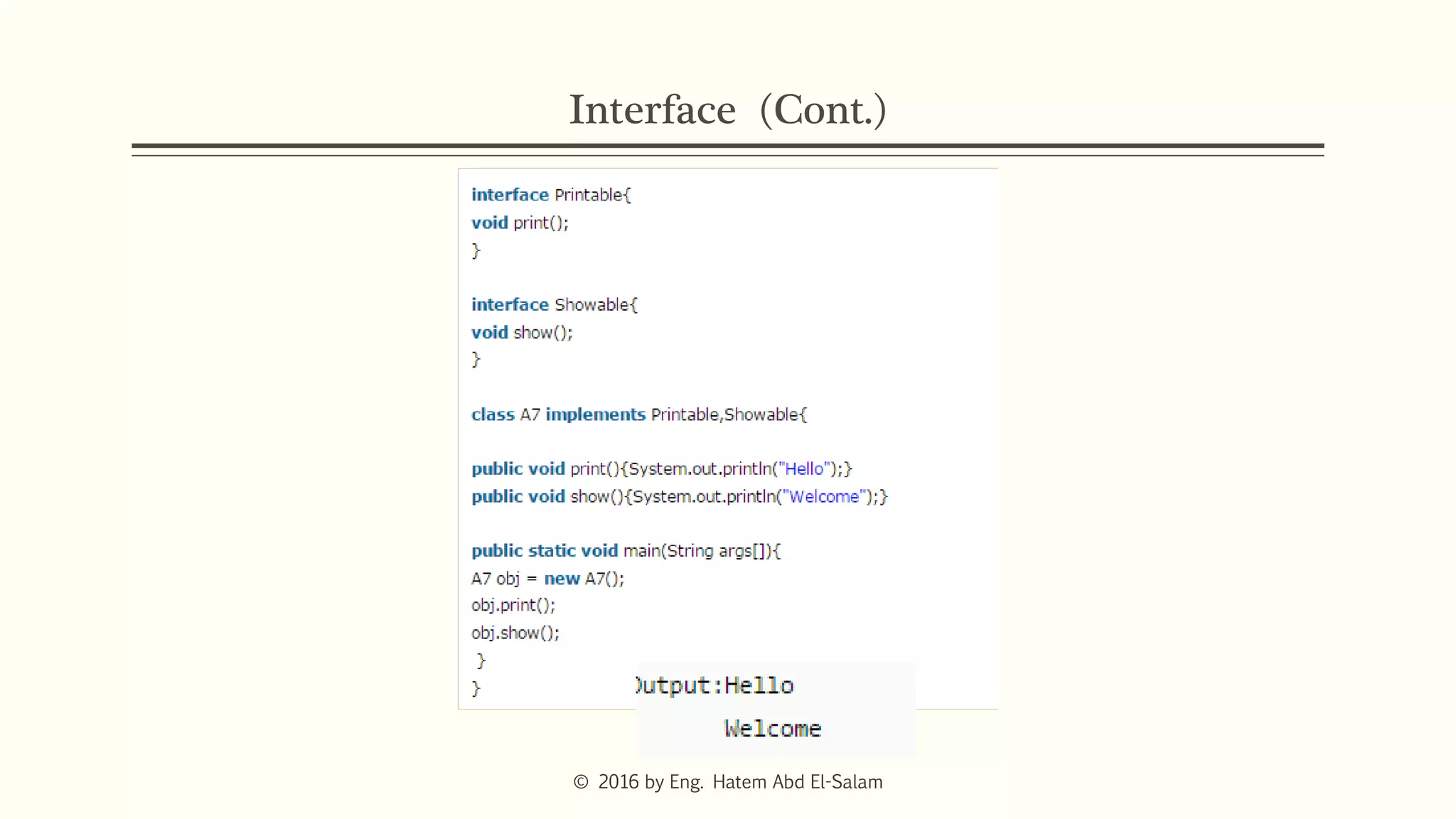
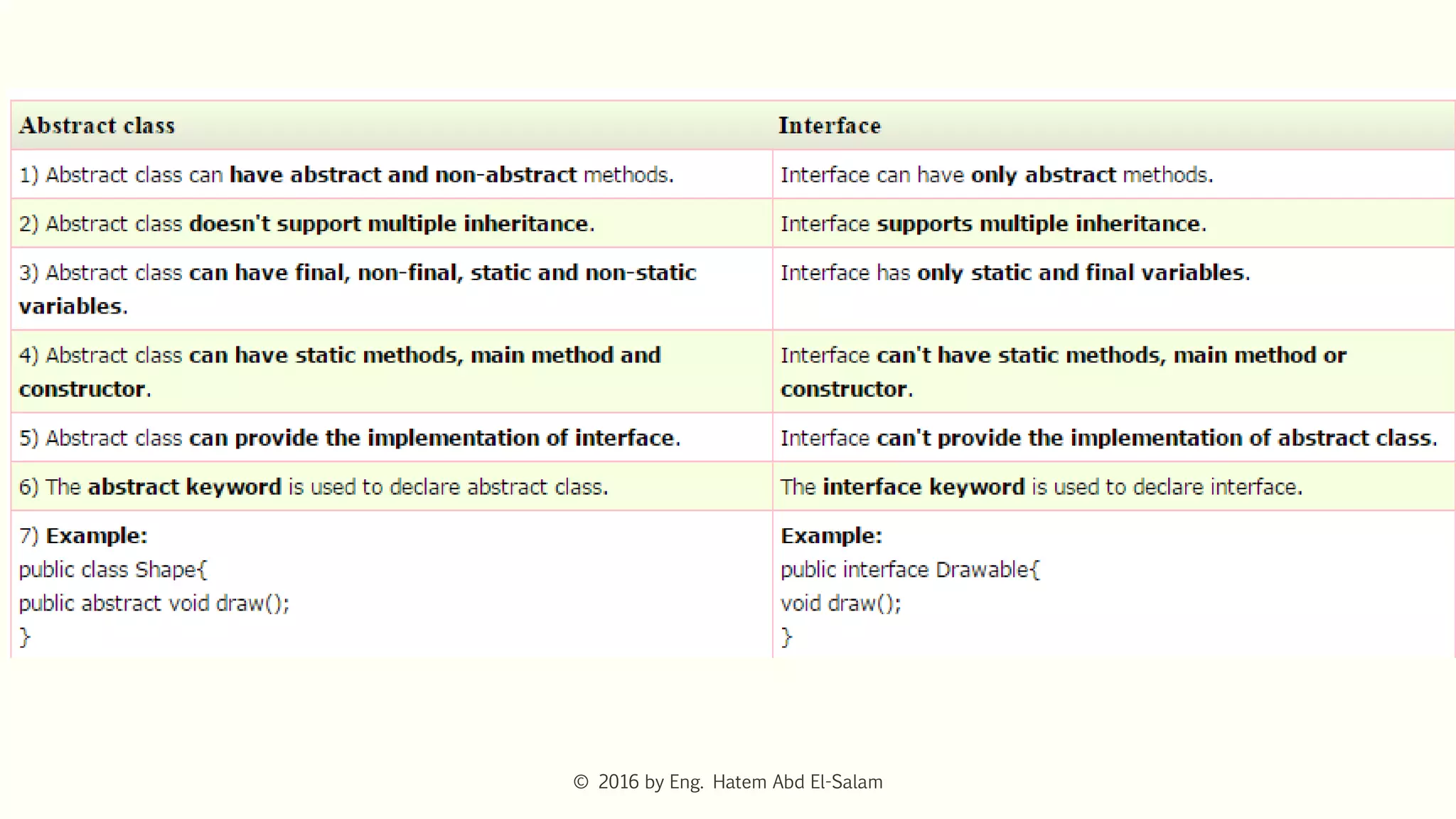
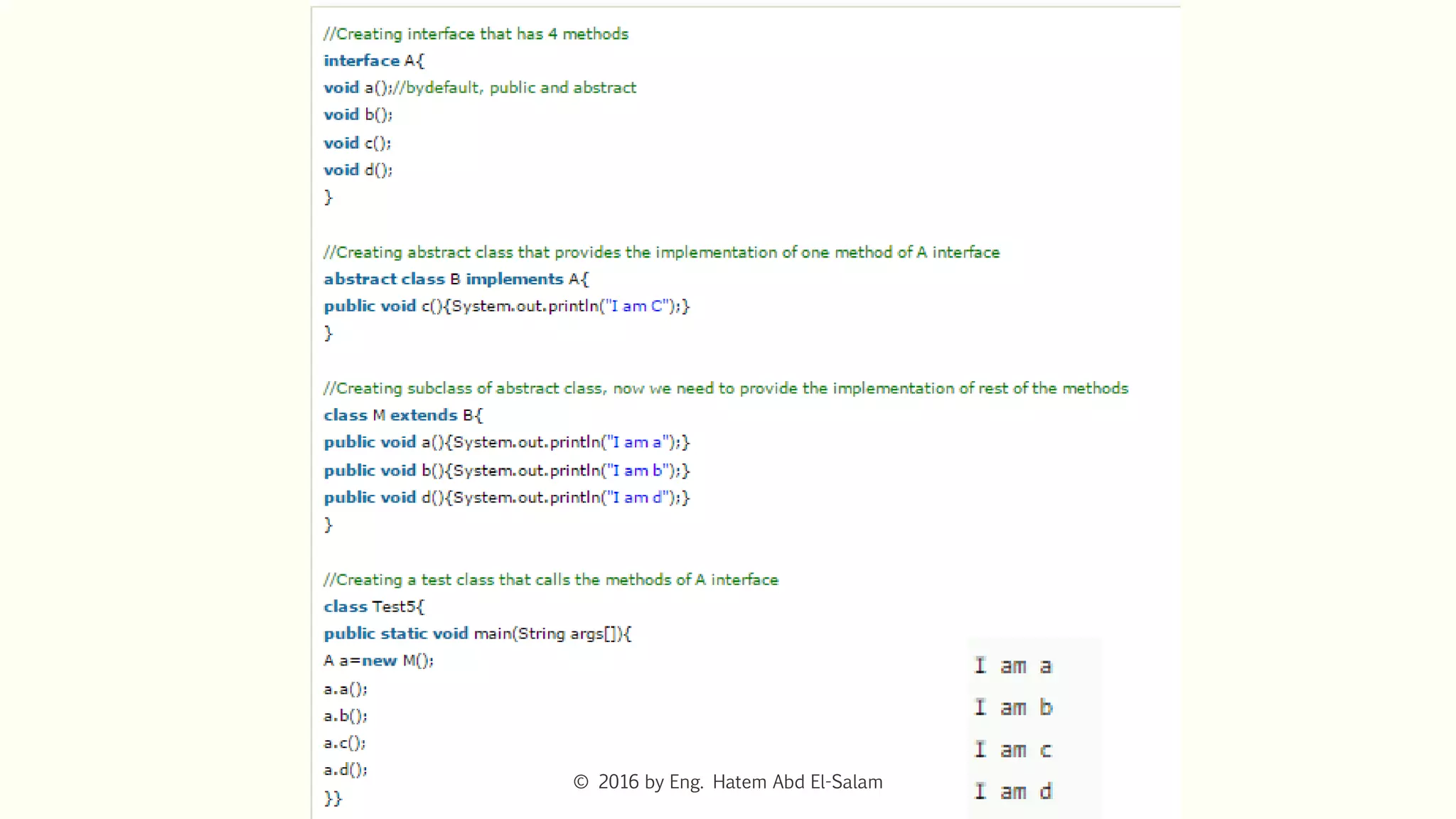
The document discusses Java fundamentals including wrapper classes, abstraction, interfaces, and delegation. It covers how wrapper classes allow primitive data types to be used as objects, abstraction hides implementation details and focuses on what an object does, interfaces provide a blueprint for classes and support multiple inheritance, and delegation allows an object to pass a request to another object to handle it.