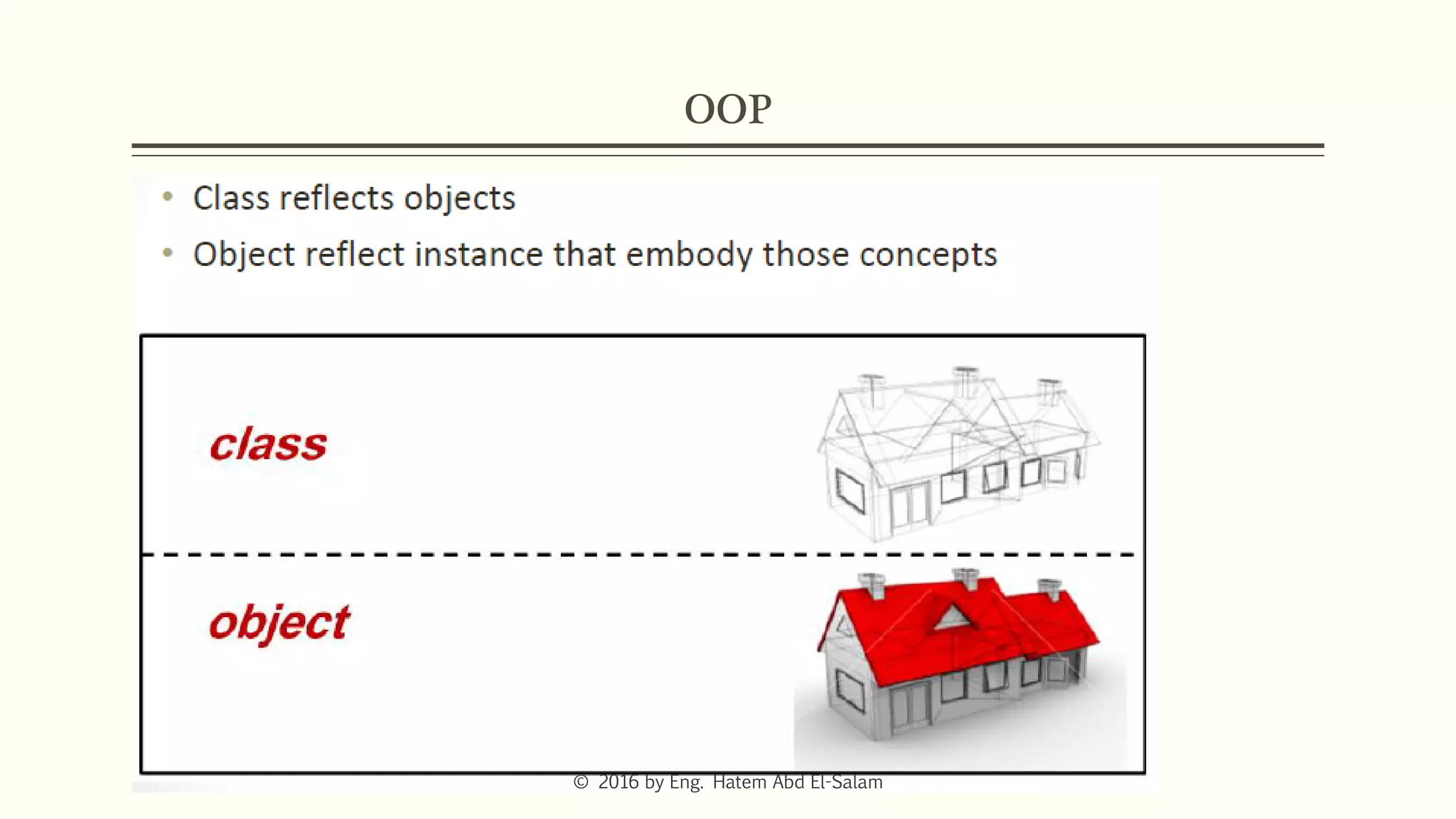
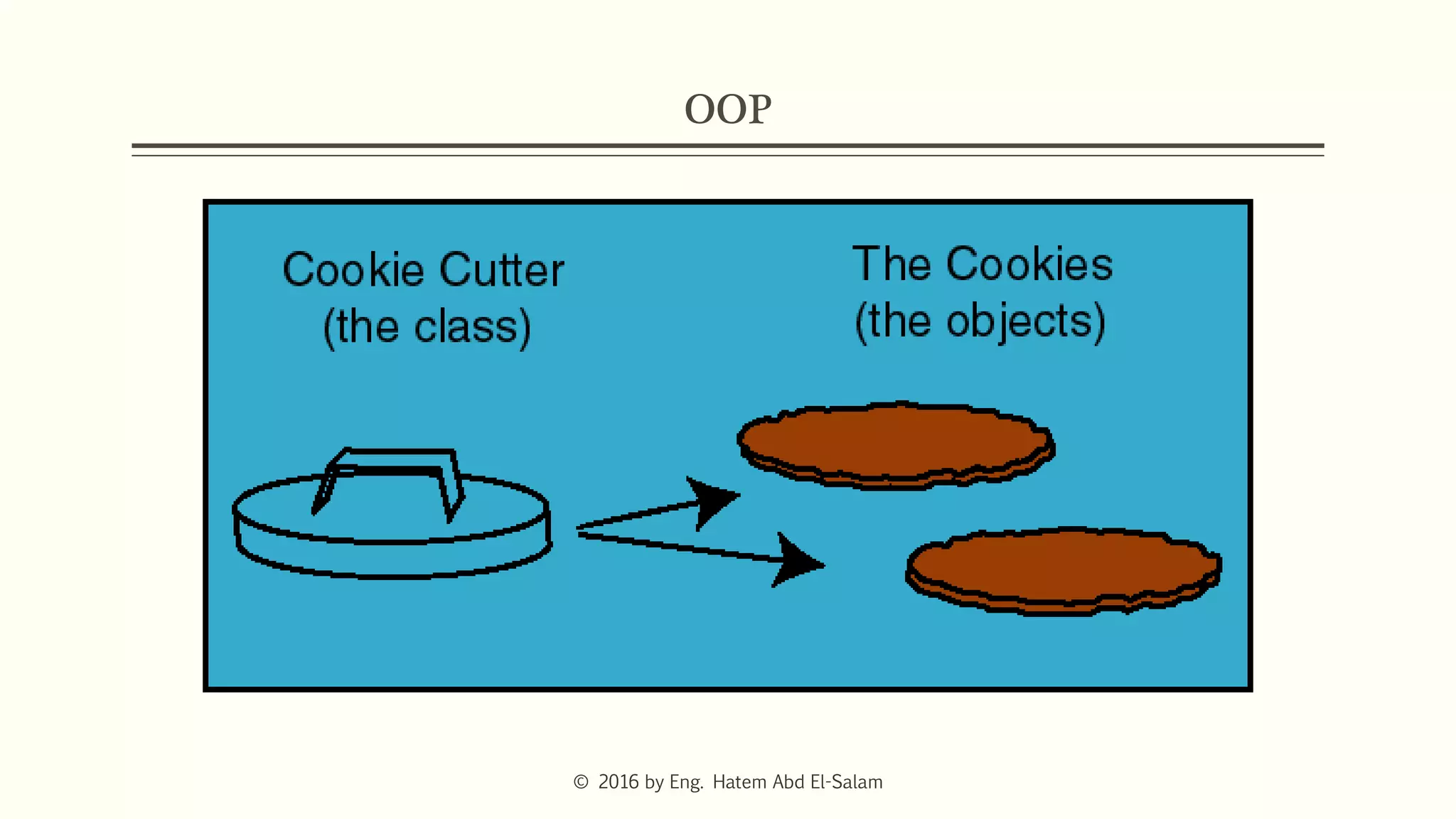
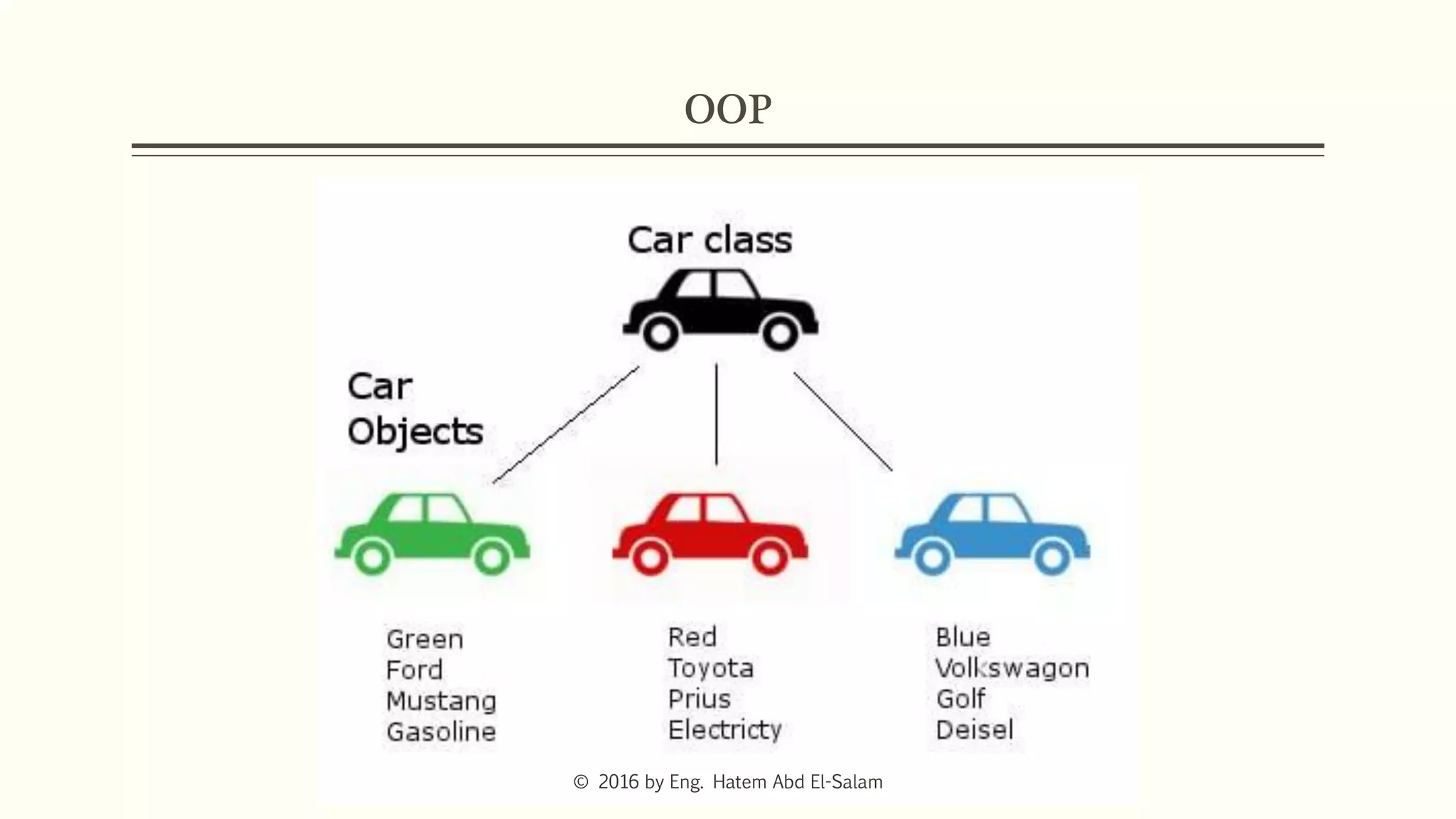
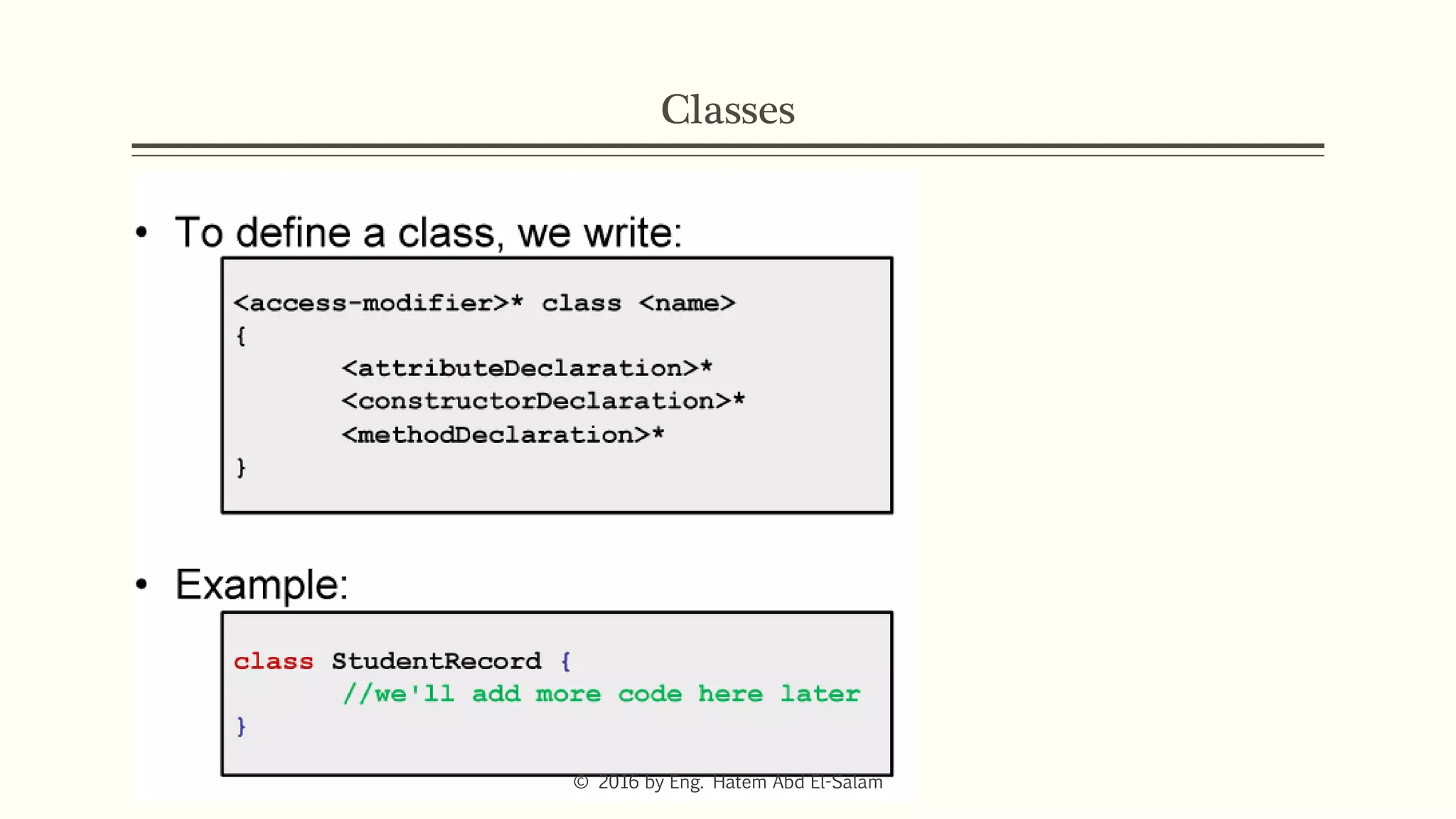
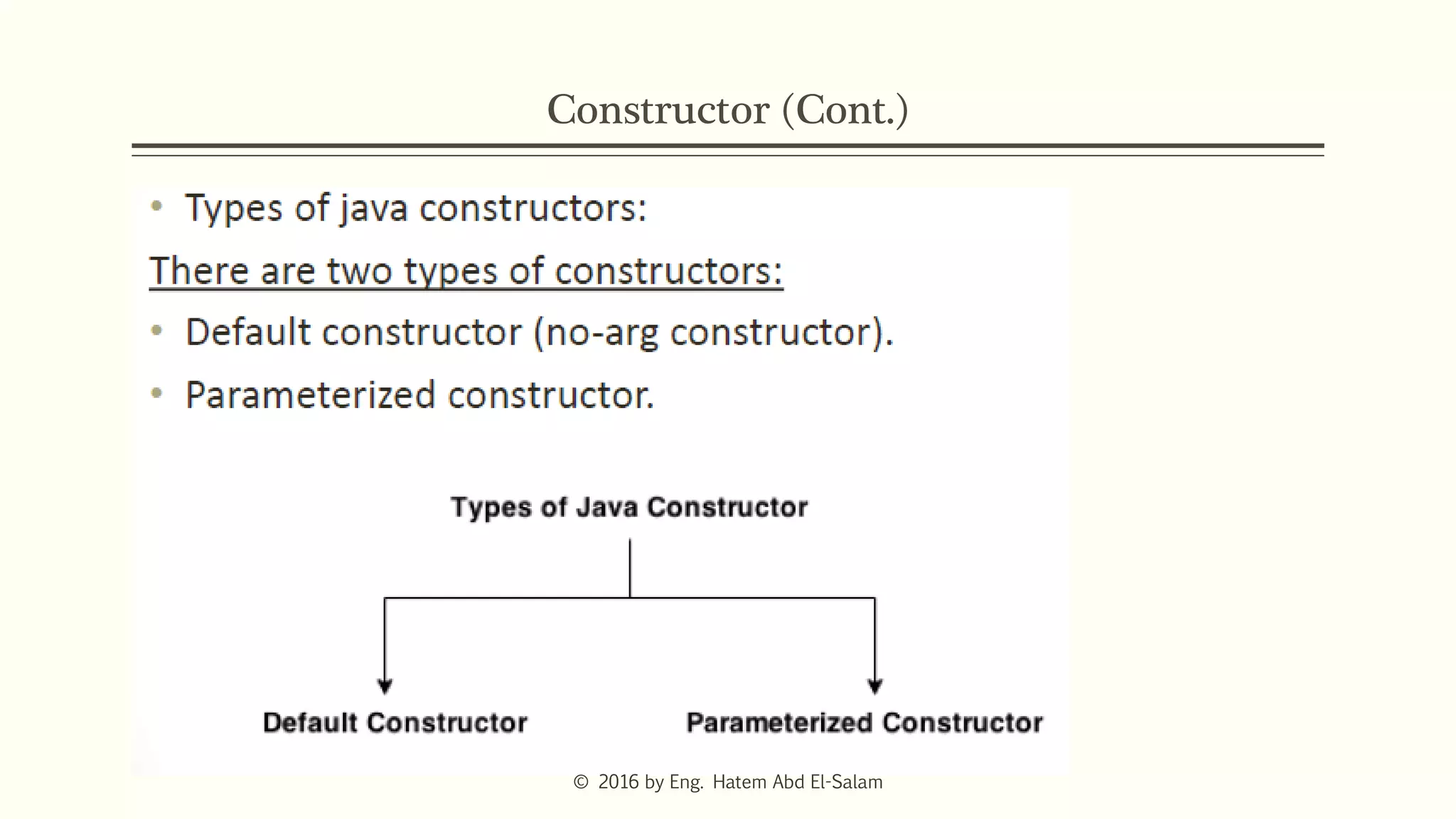
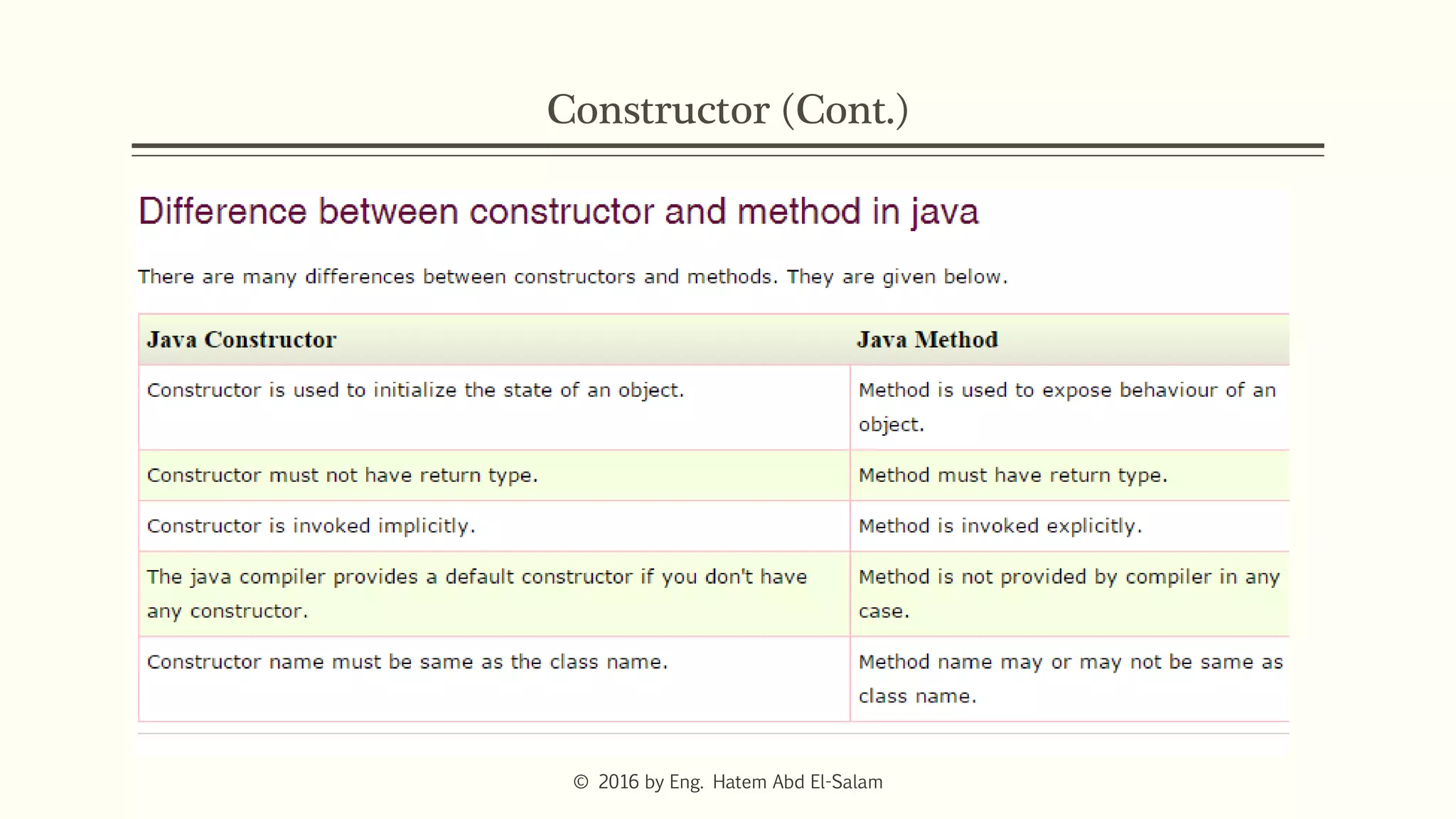
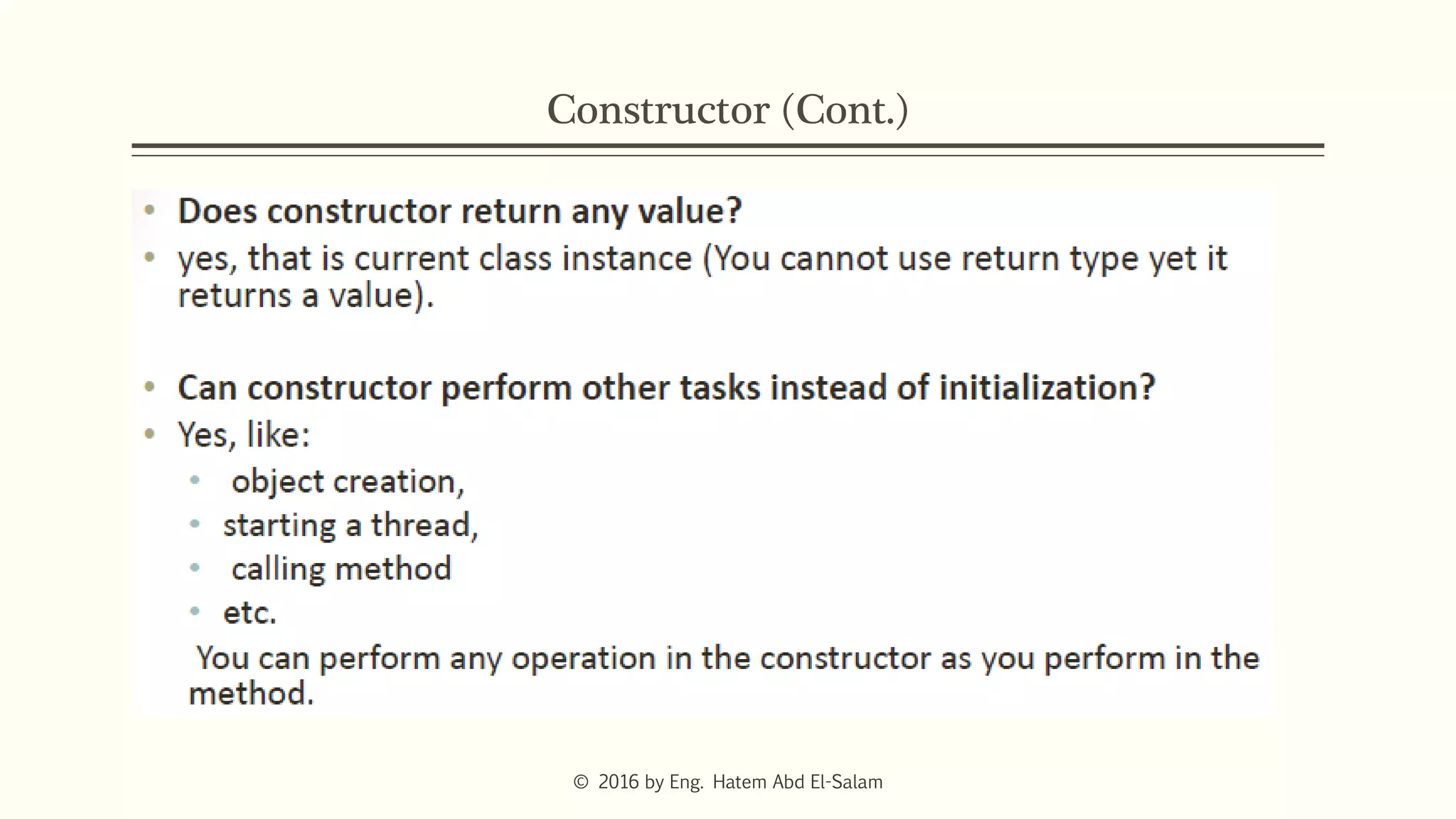
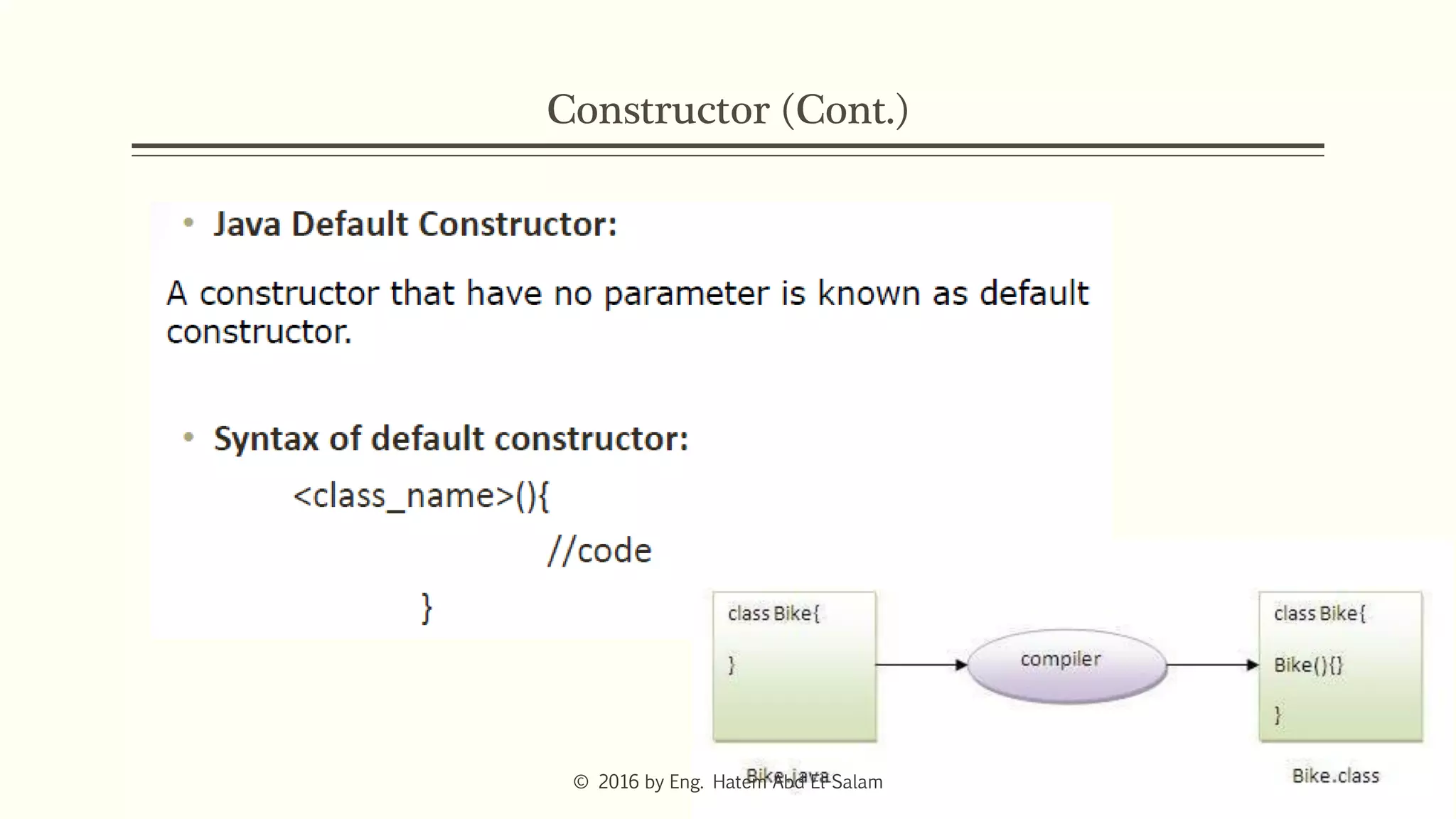
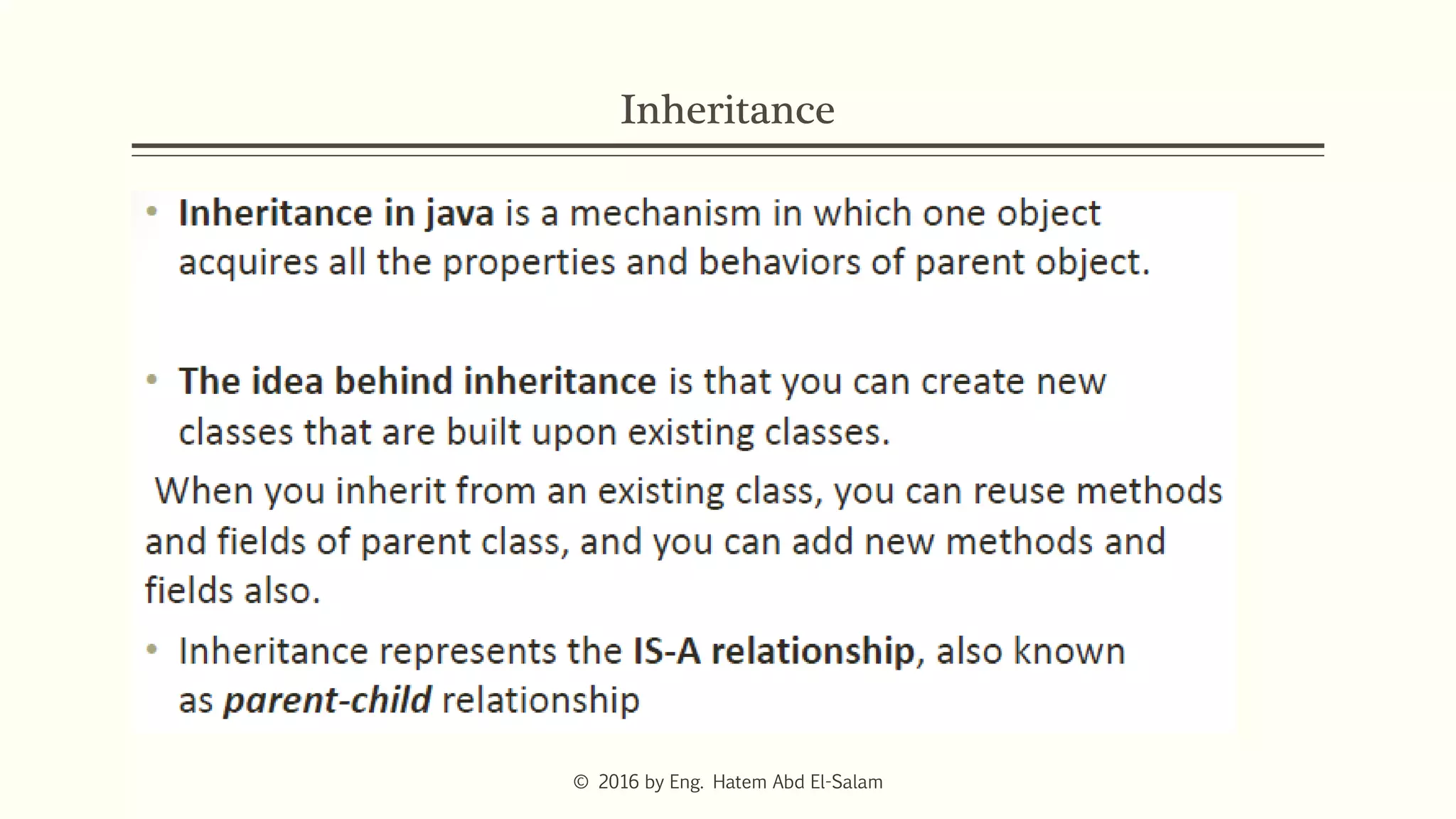
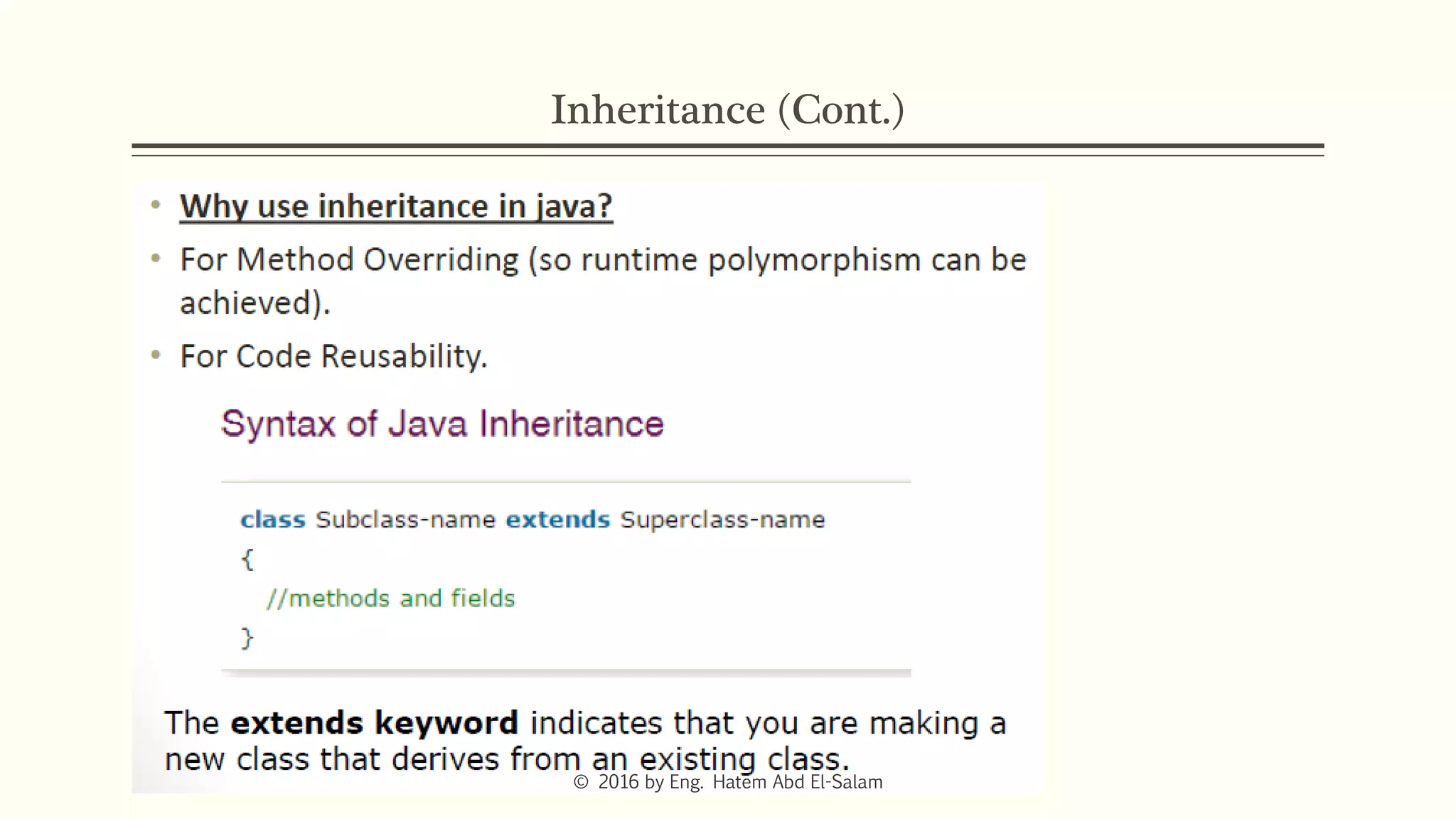
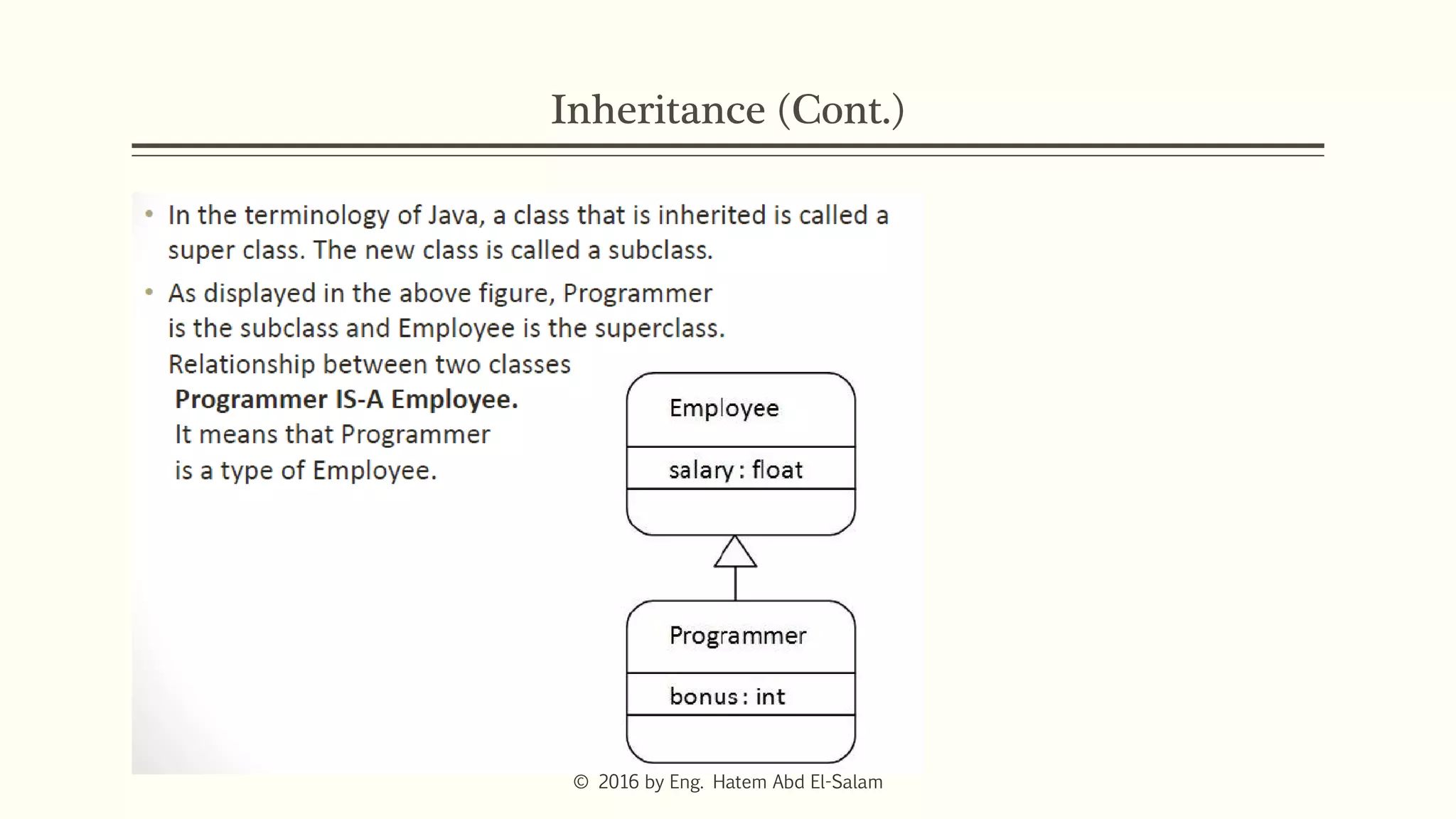
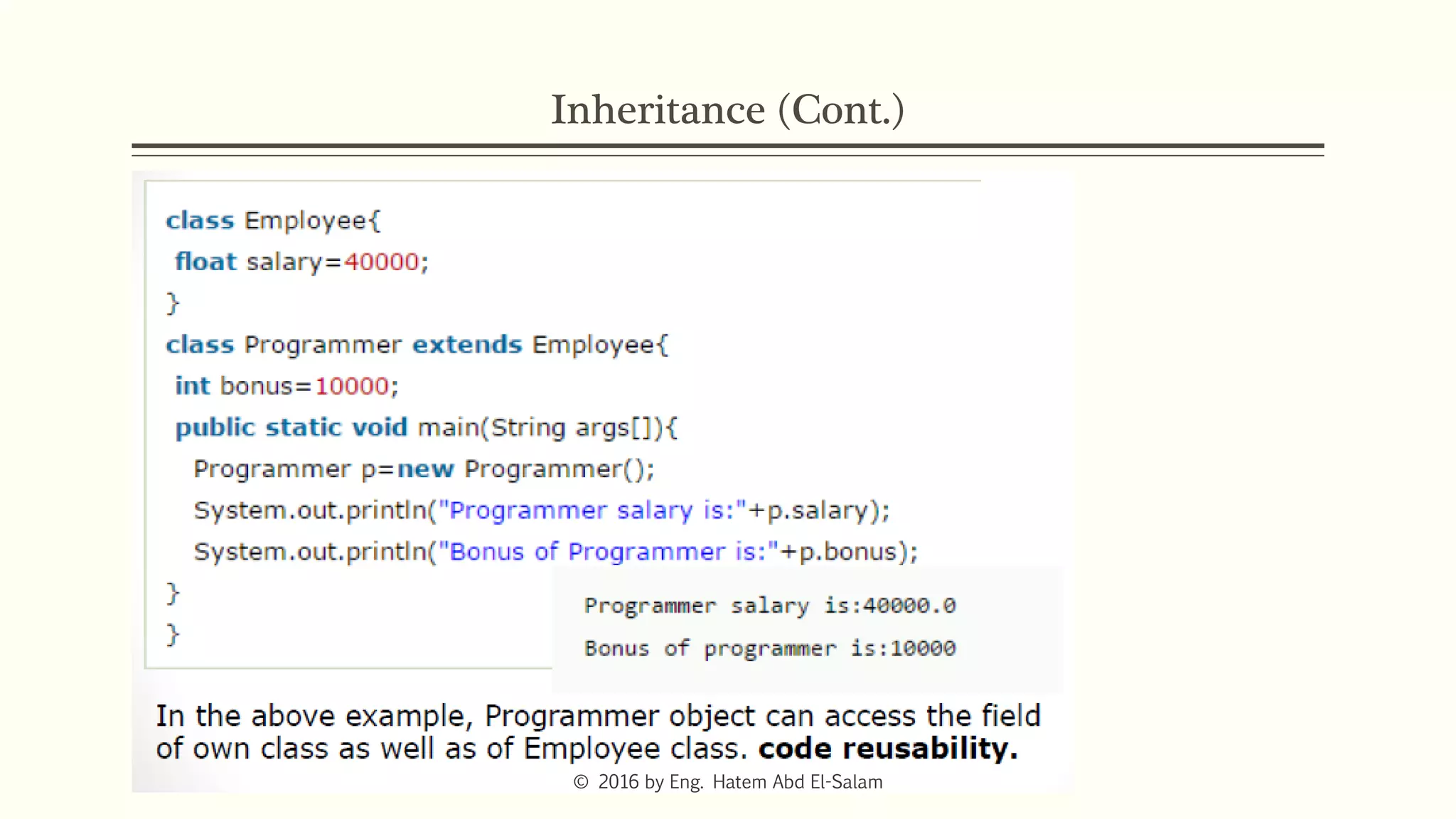
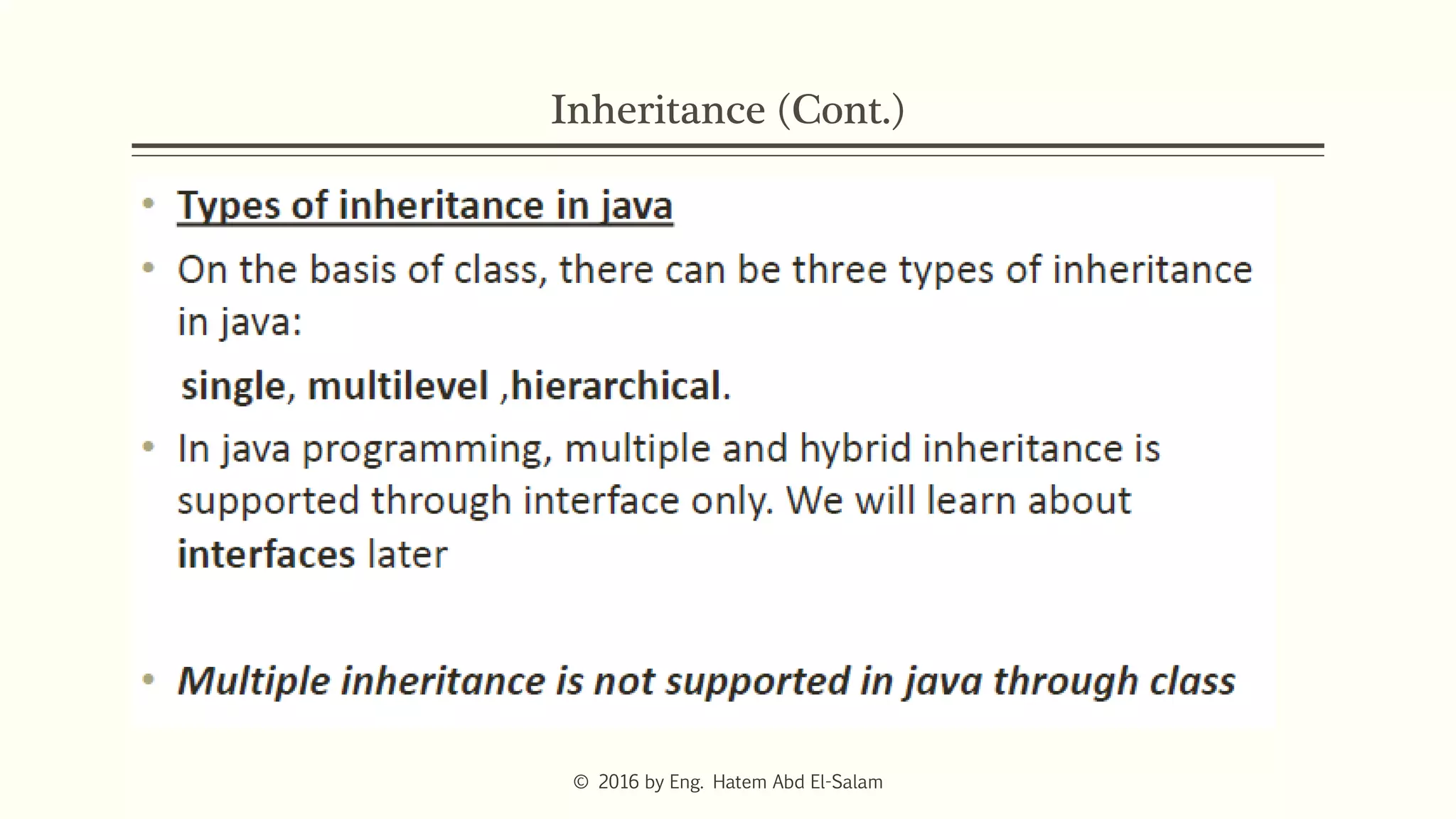
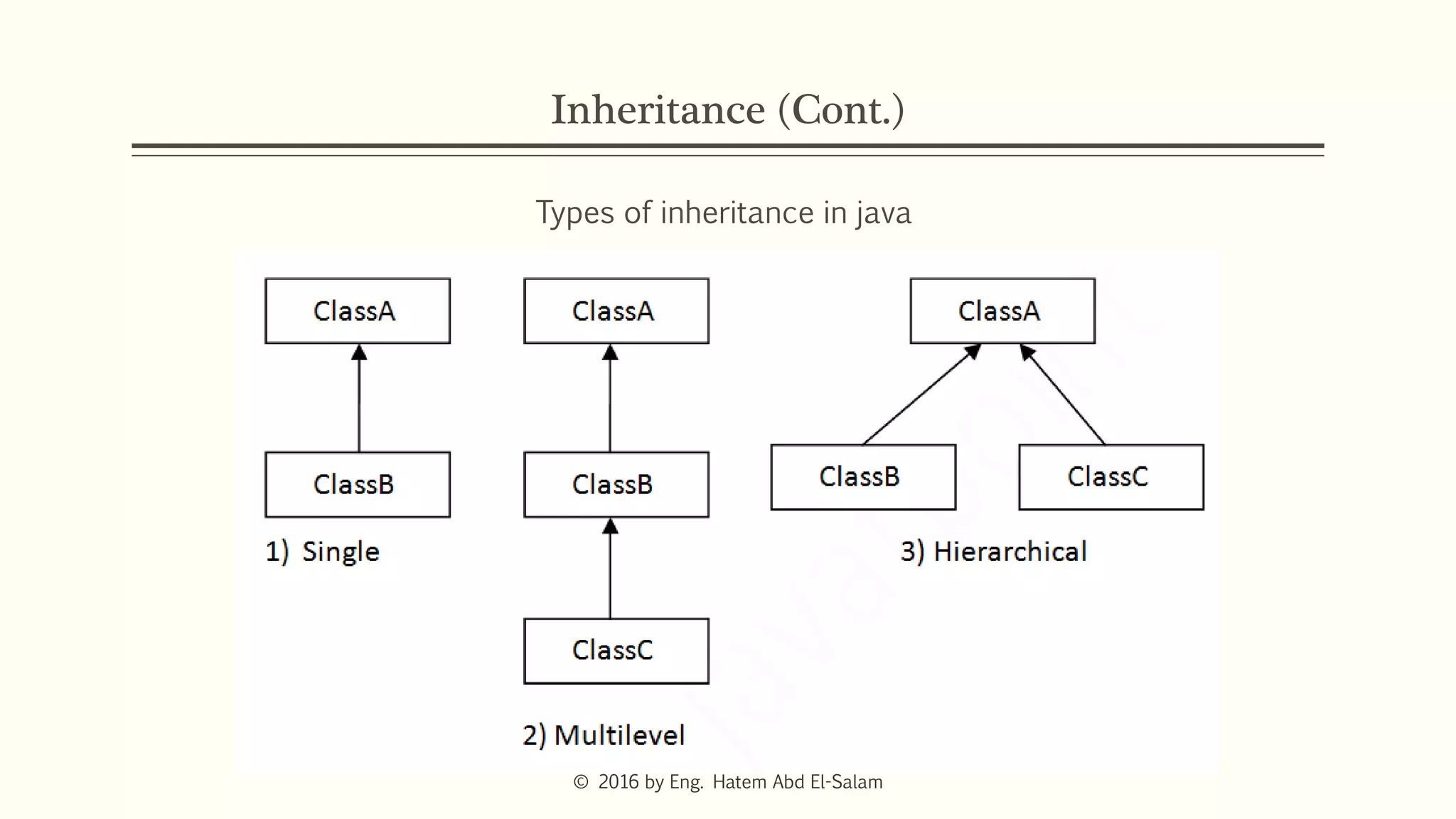
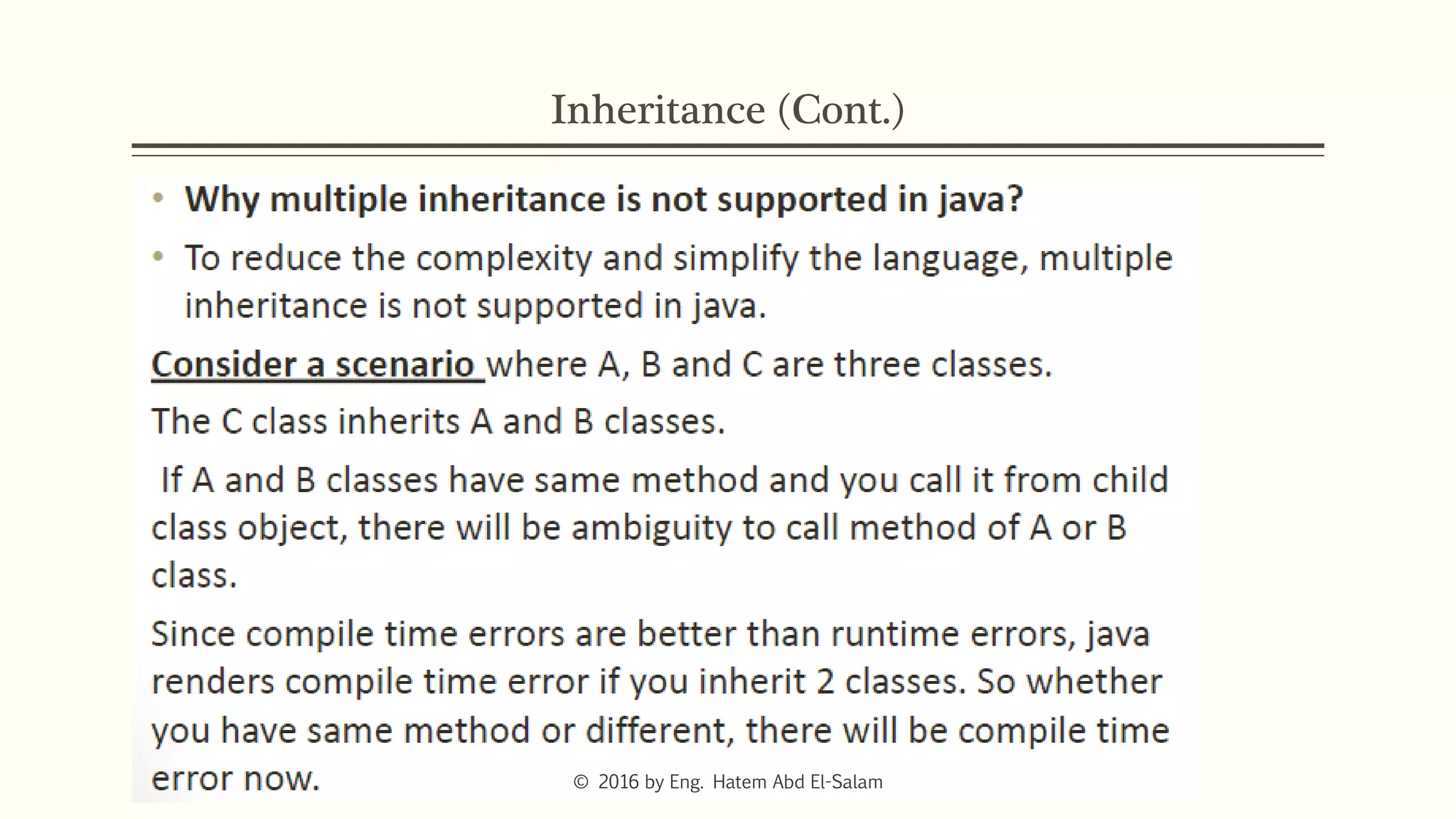
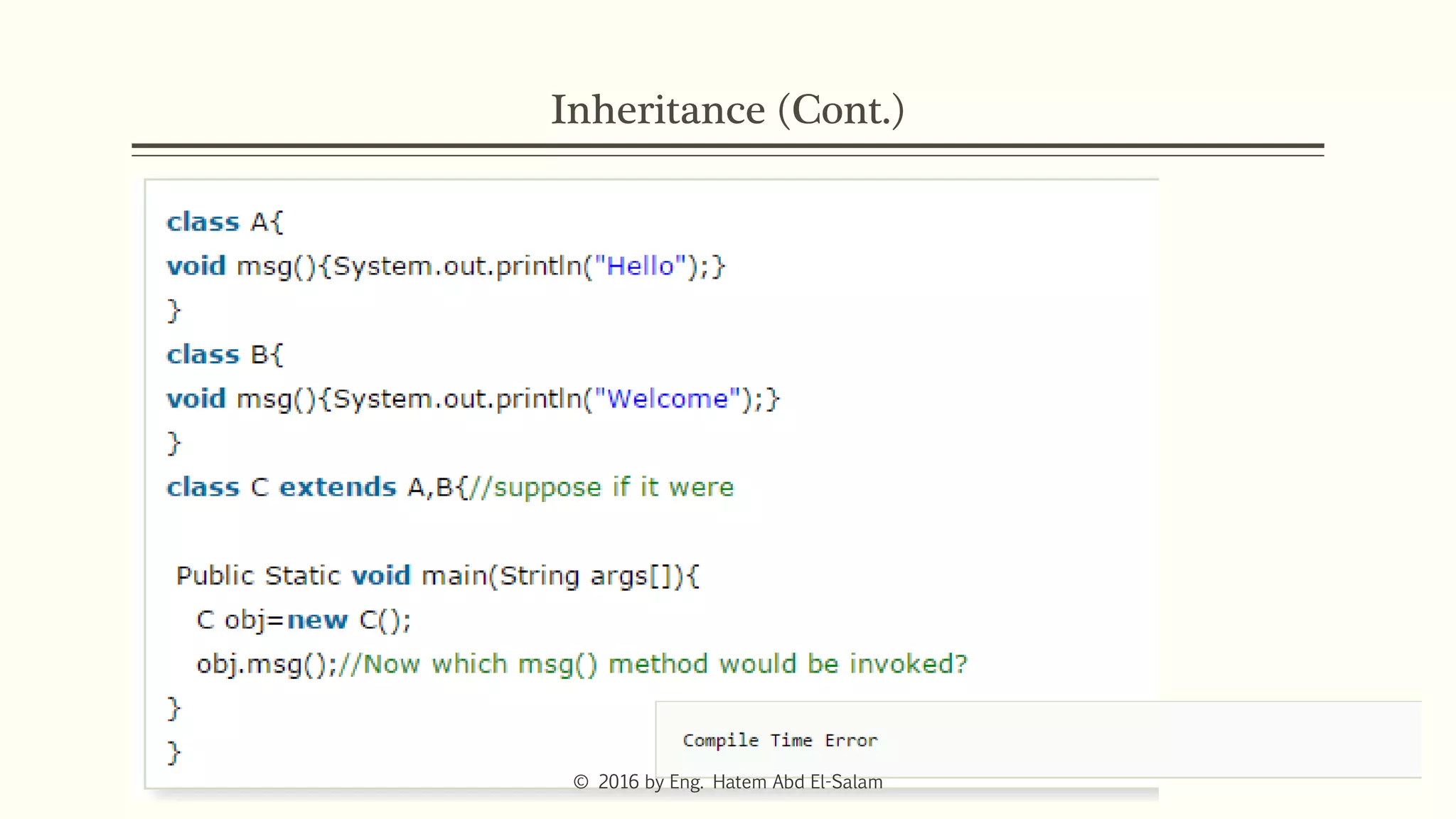
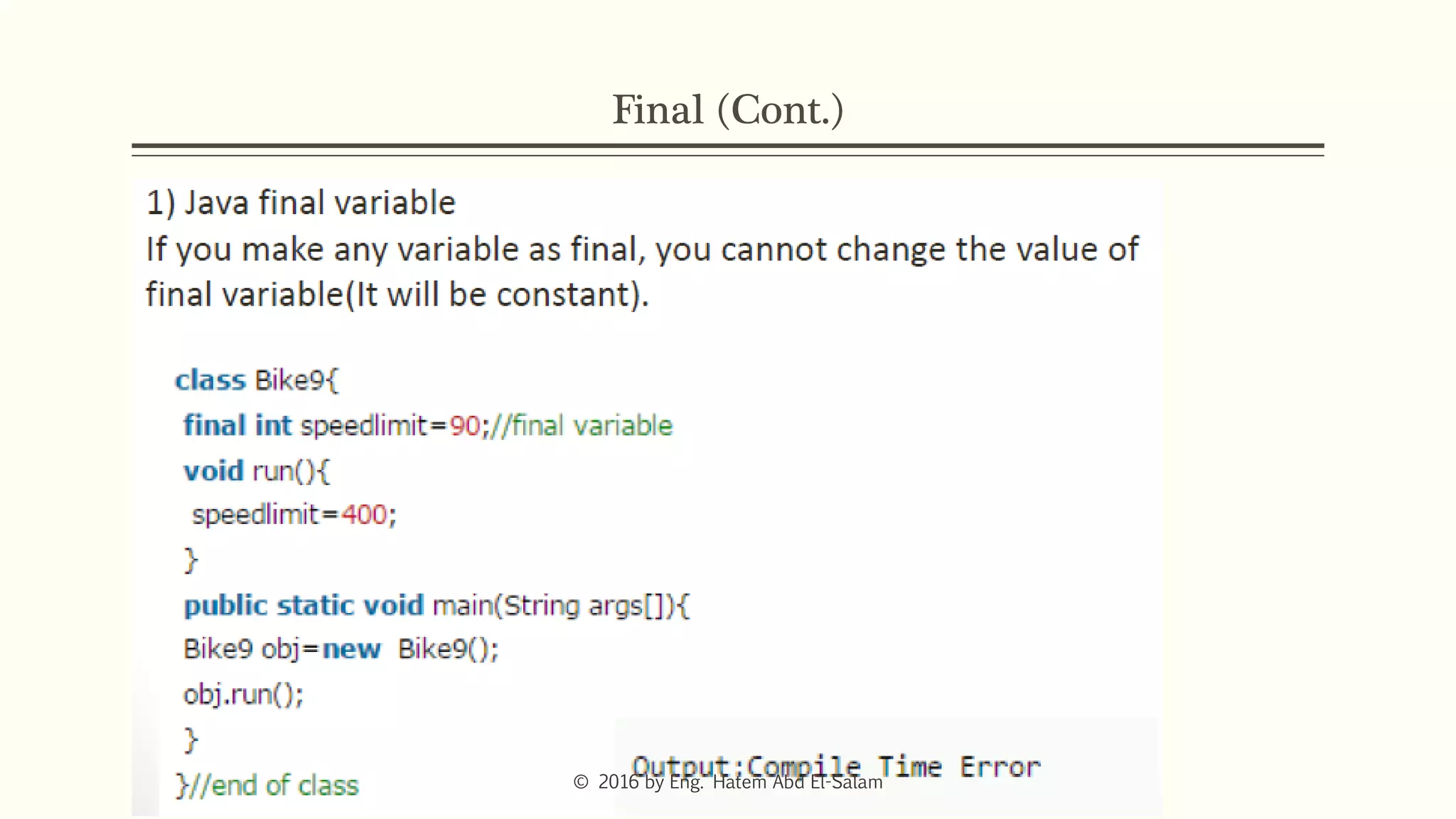
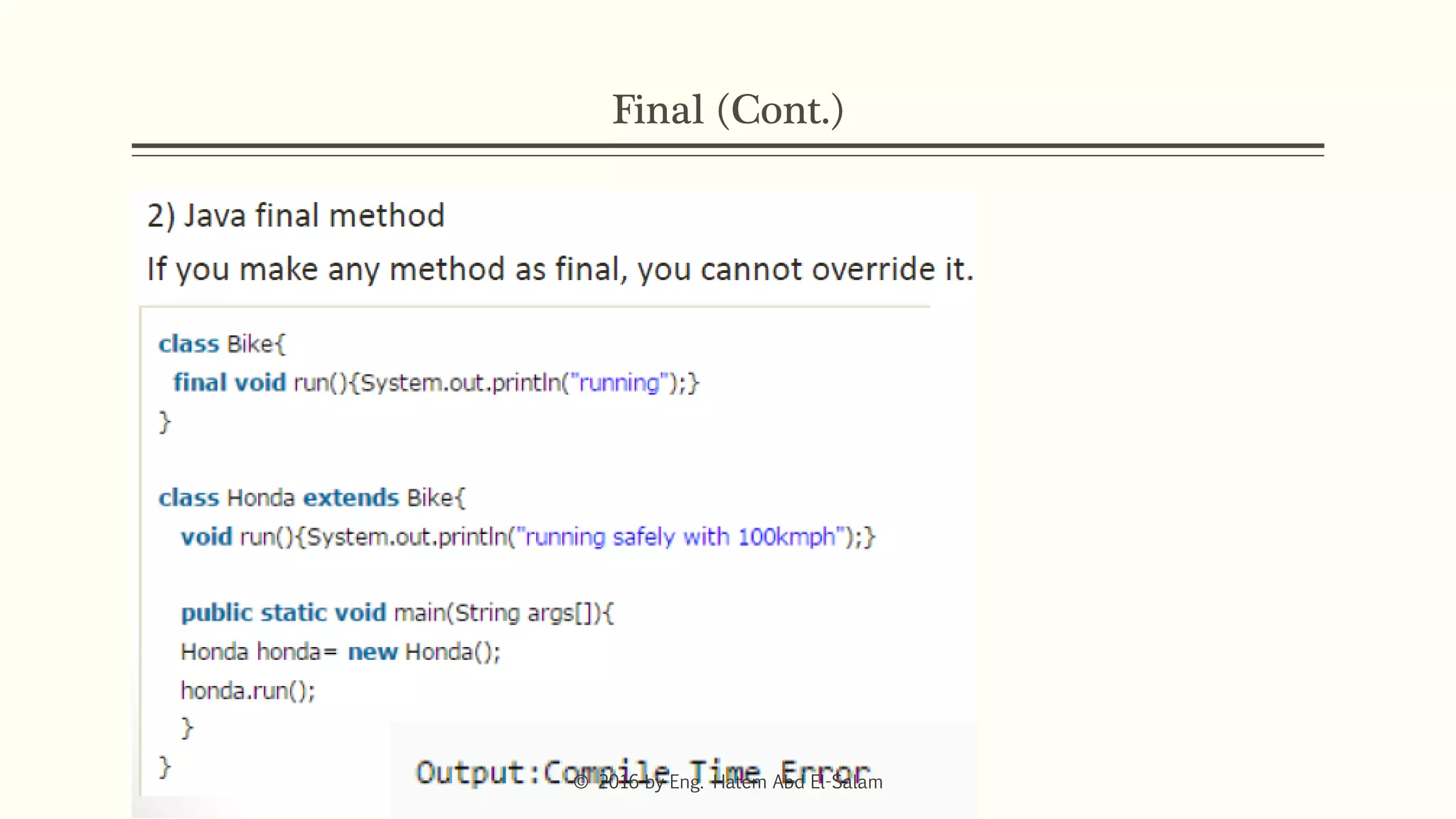
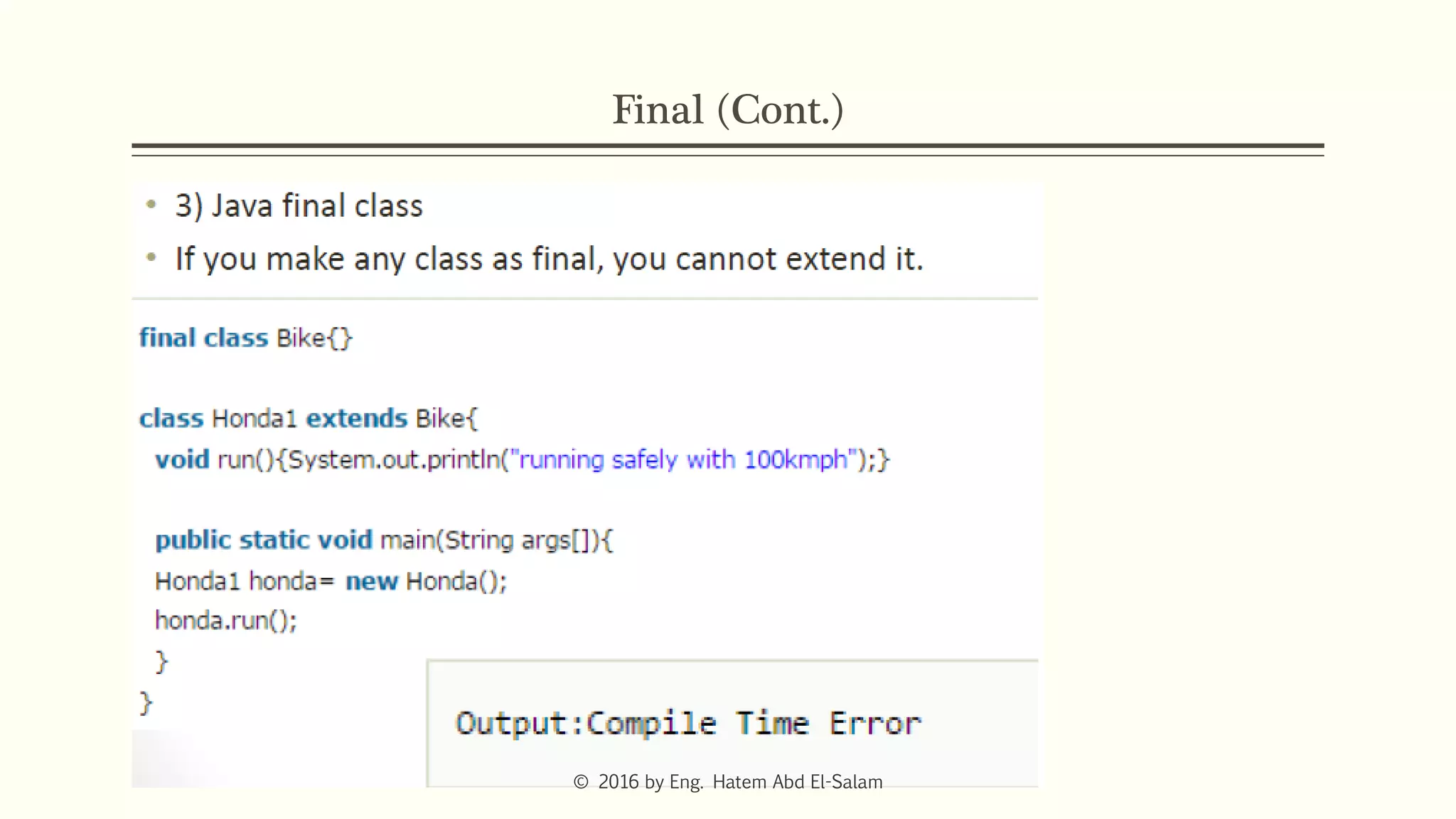
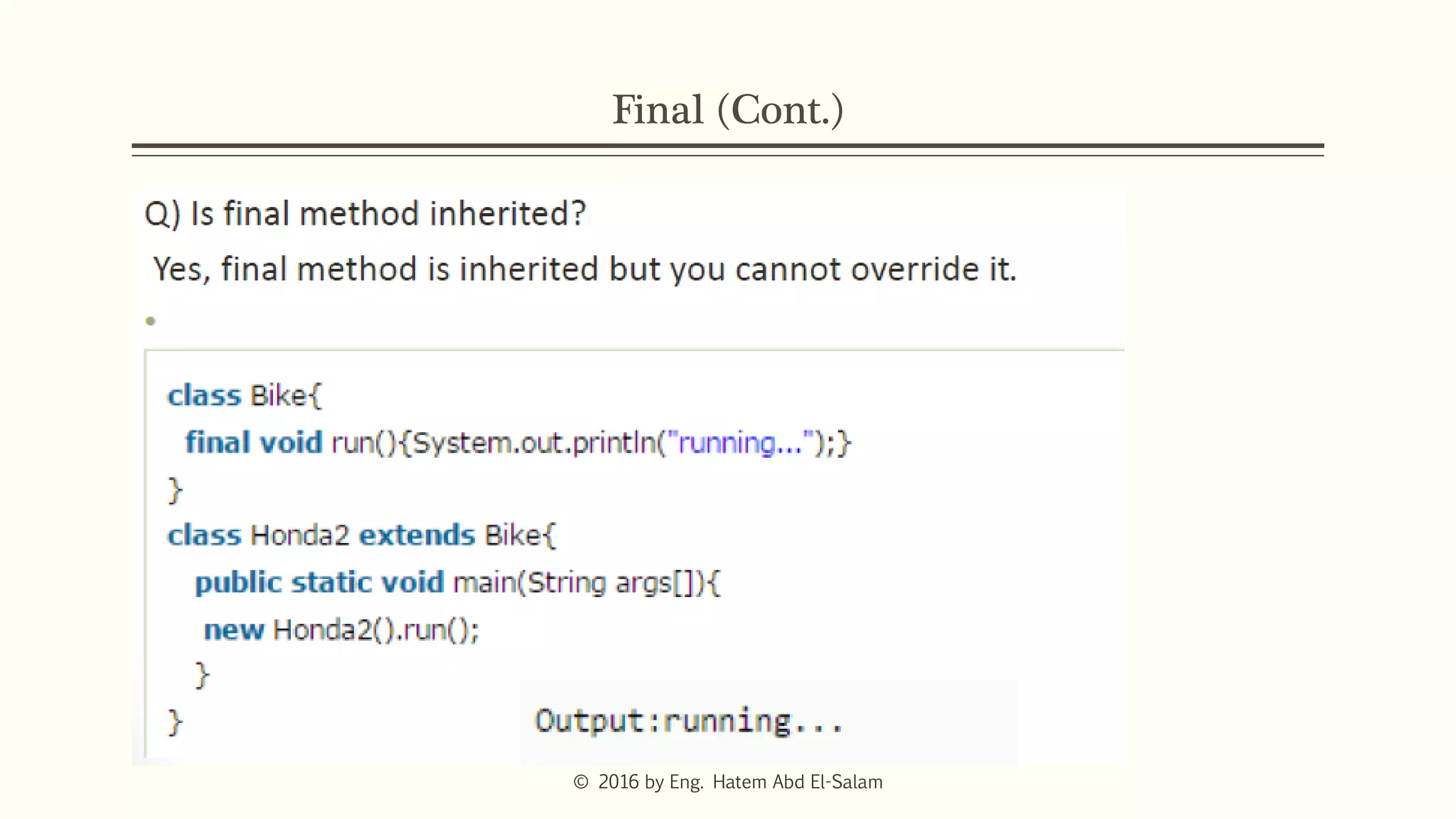
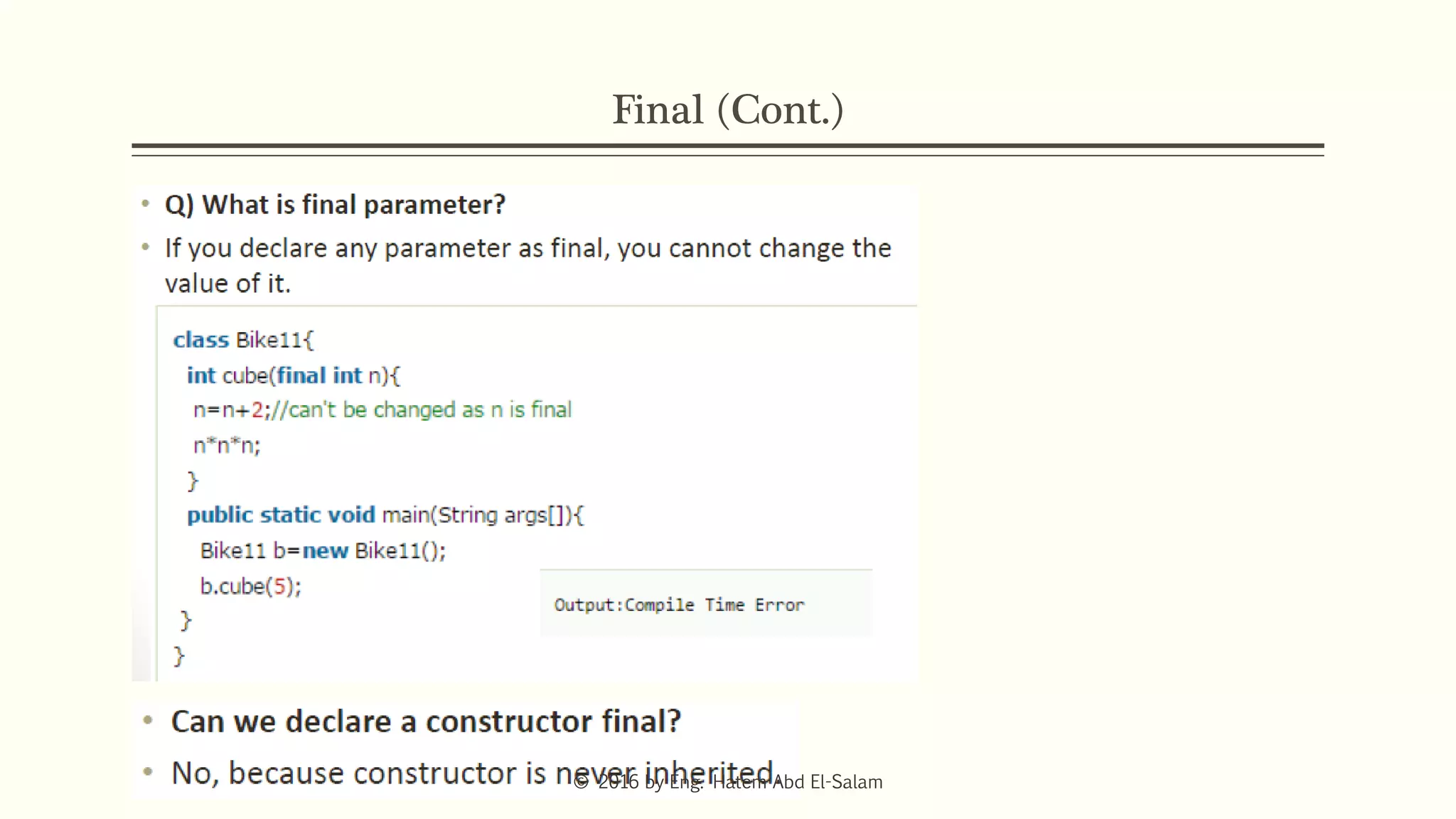
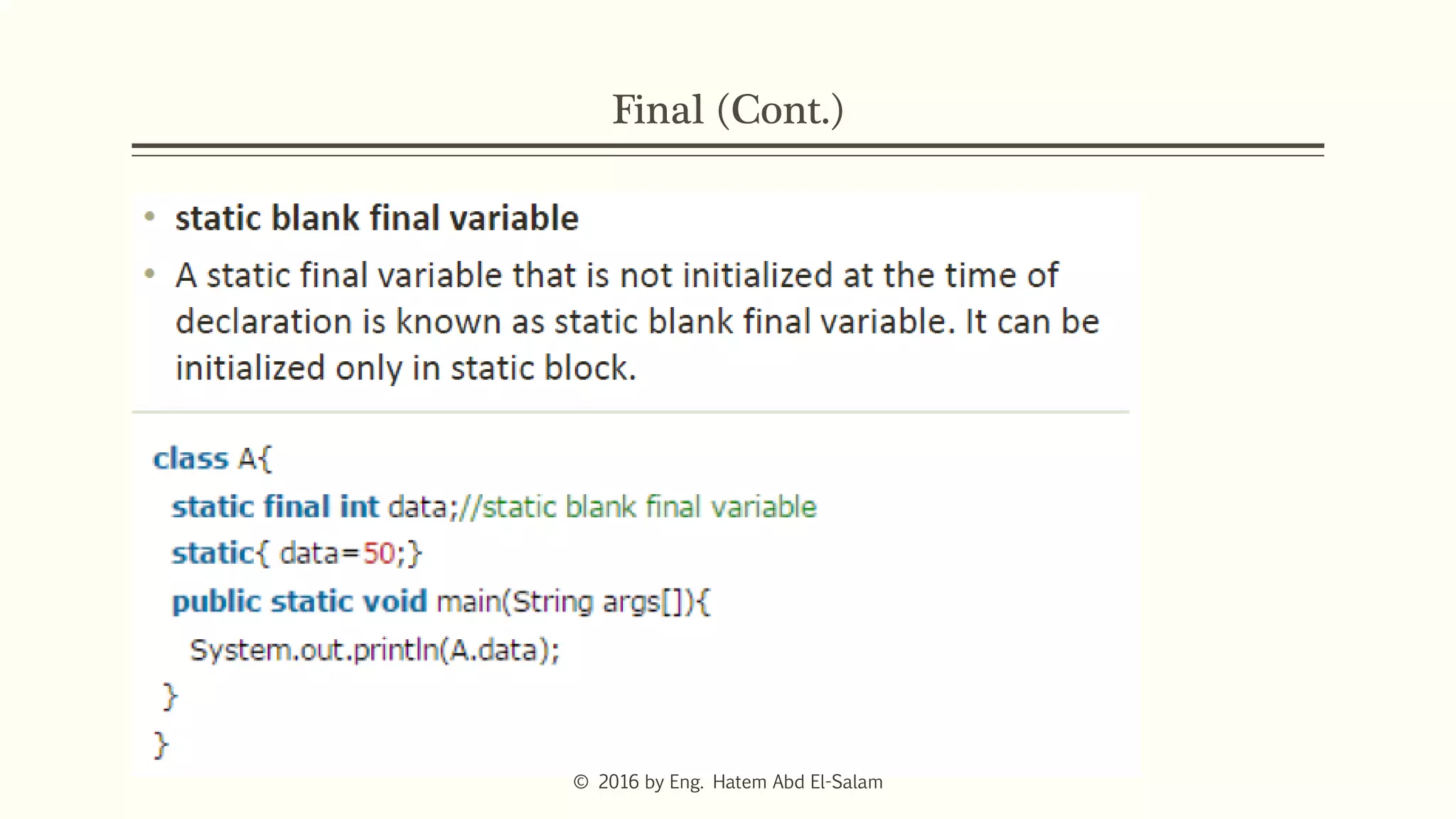
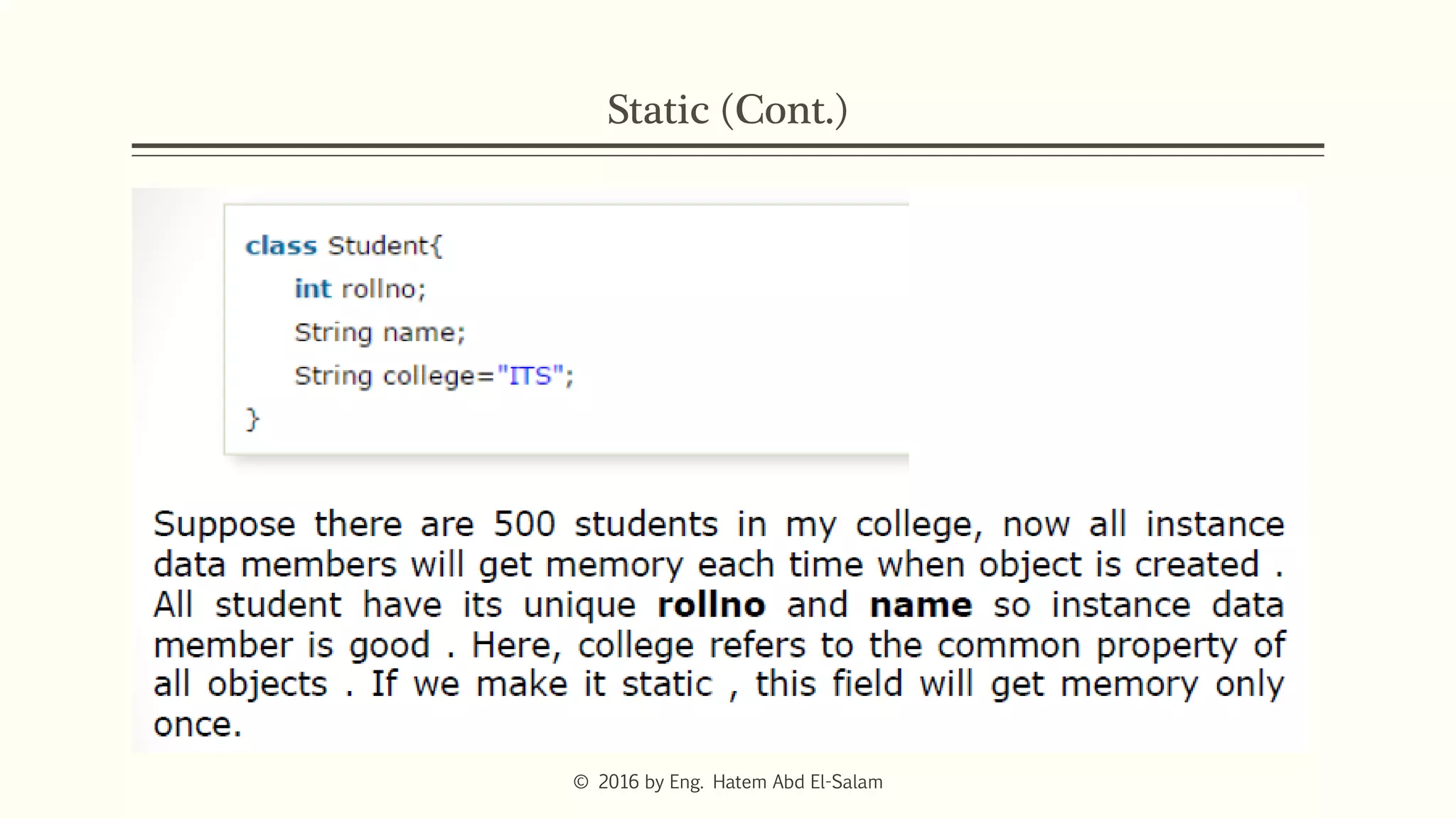
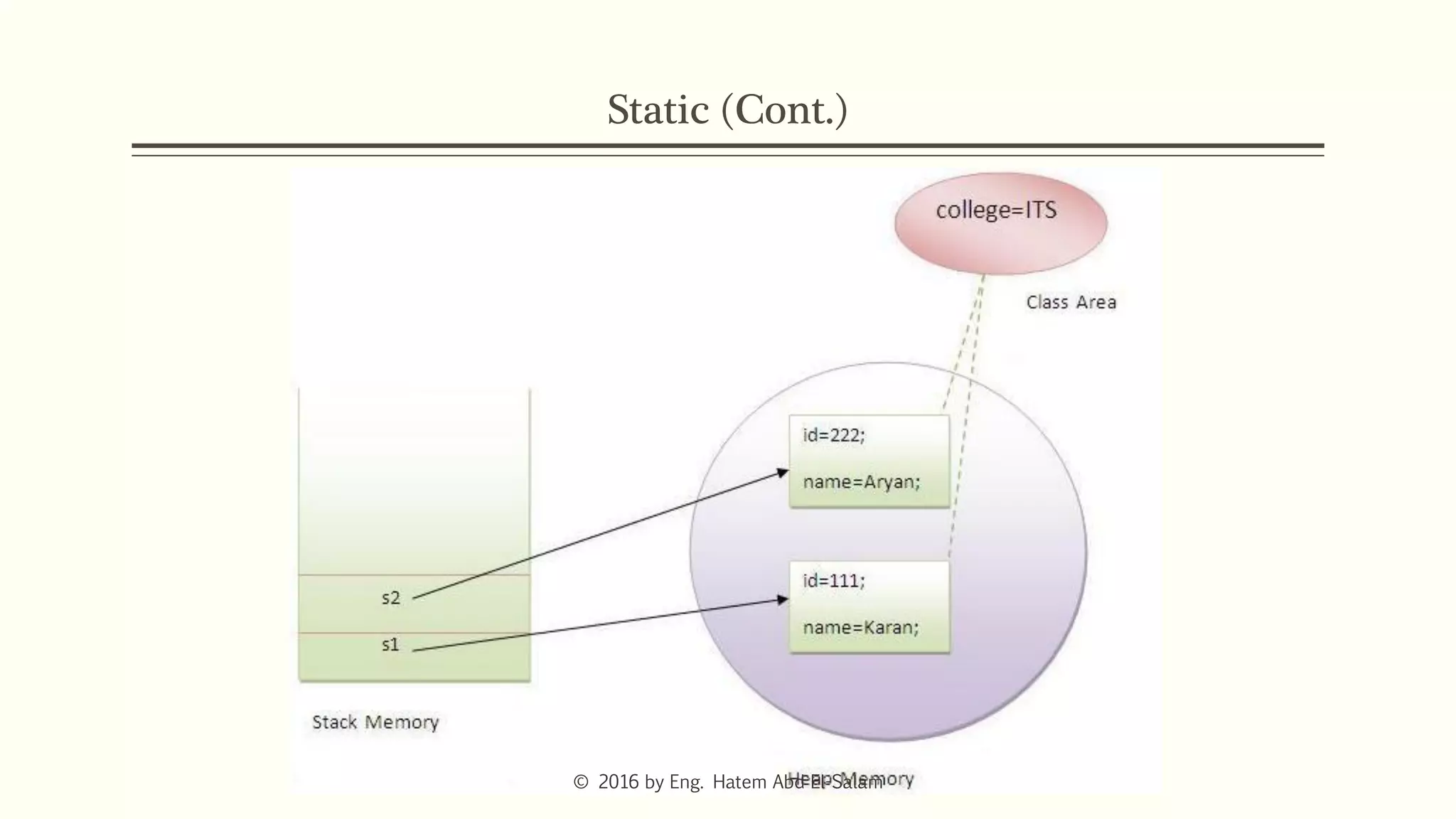
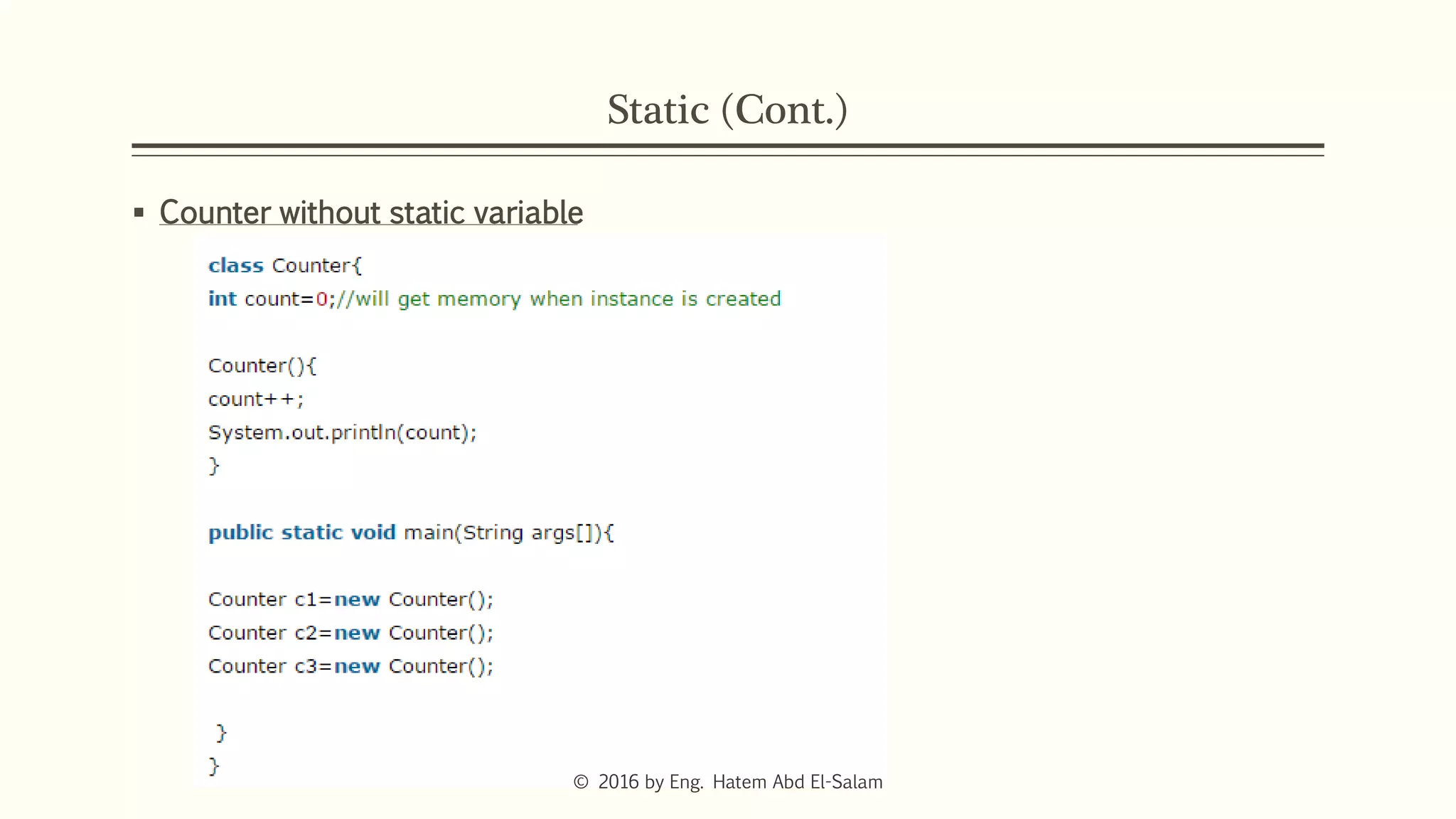
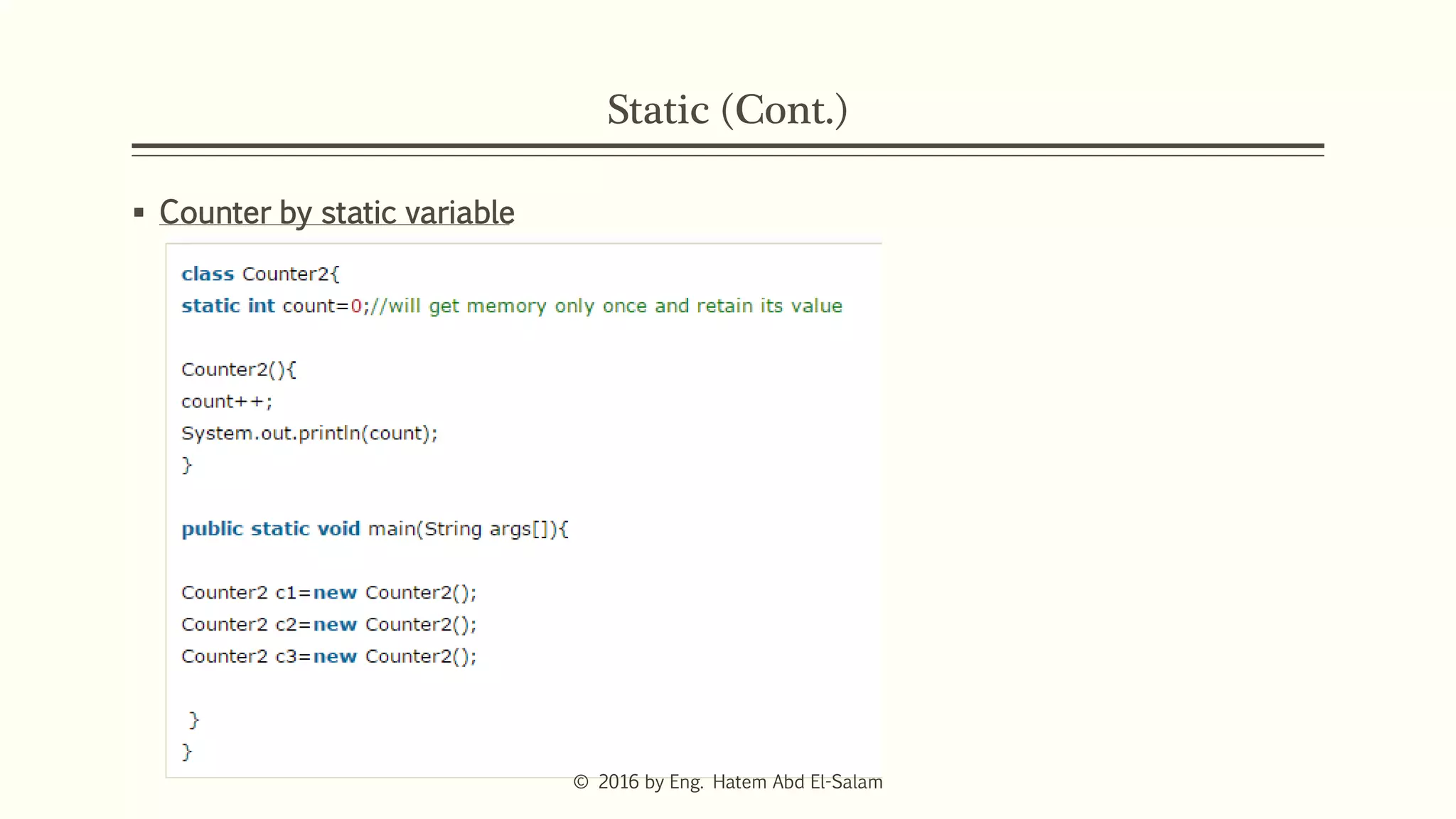
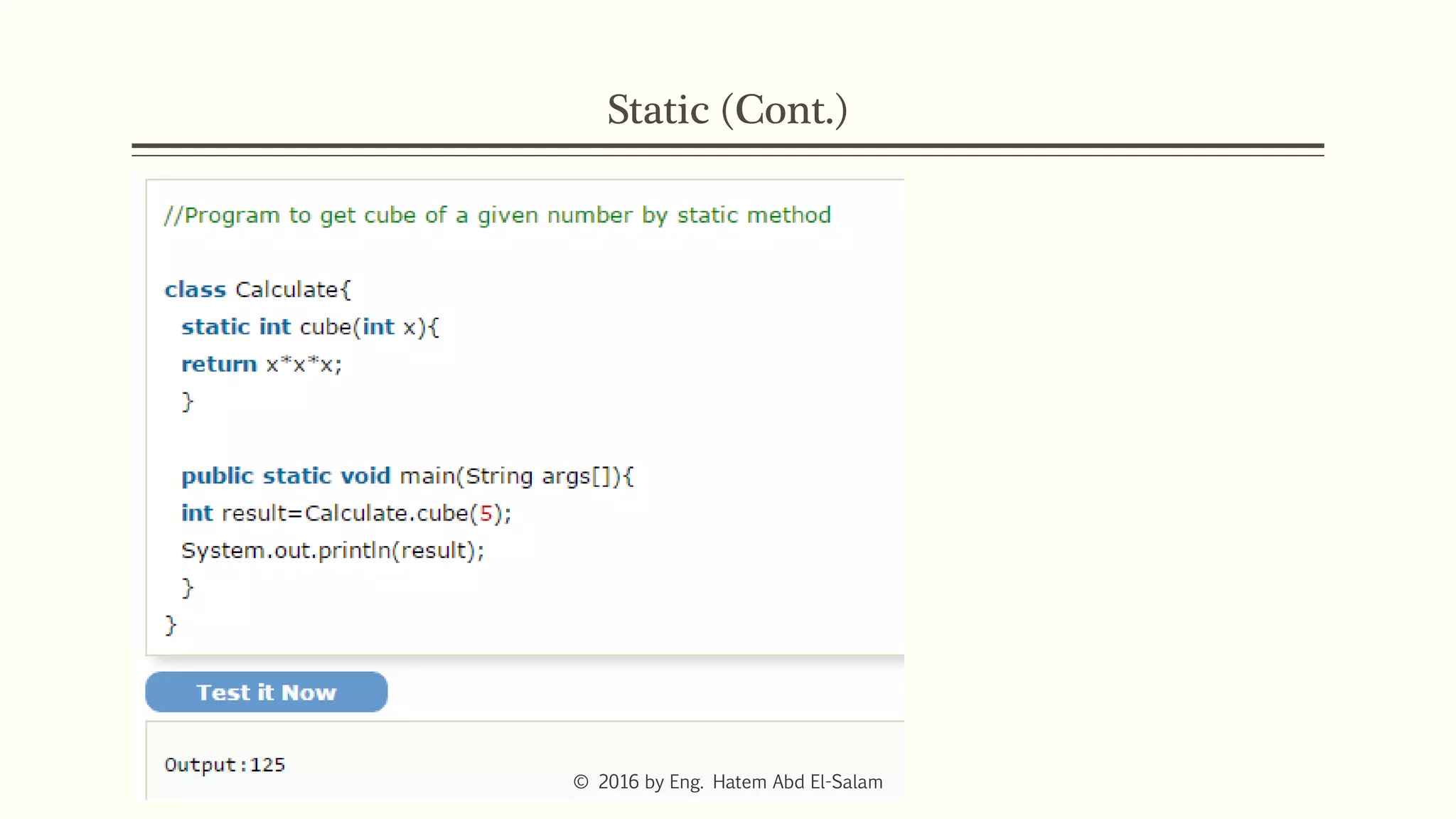
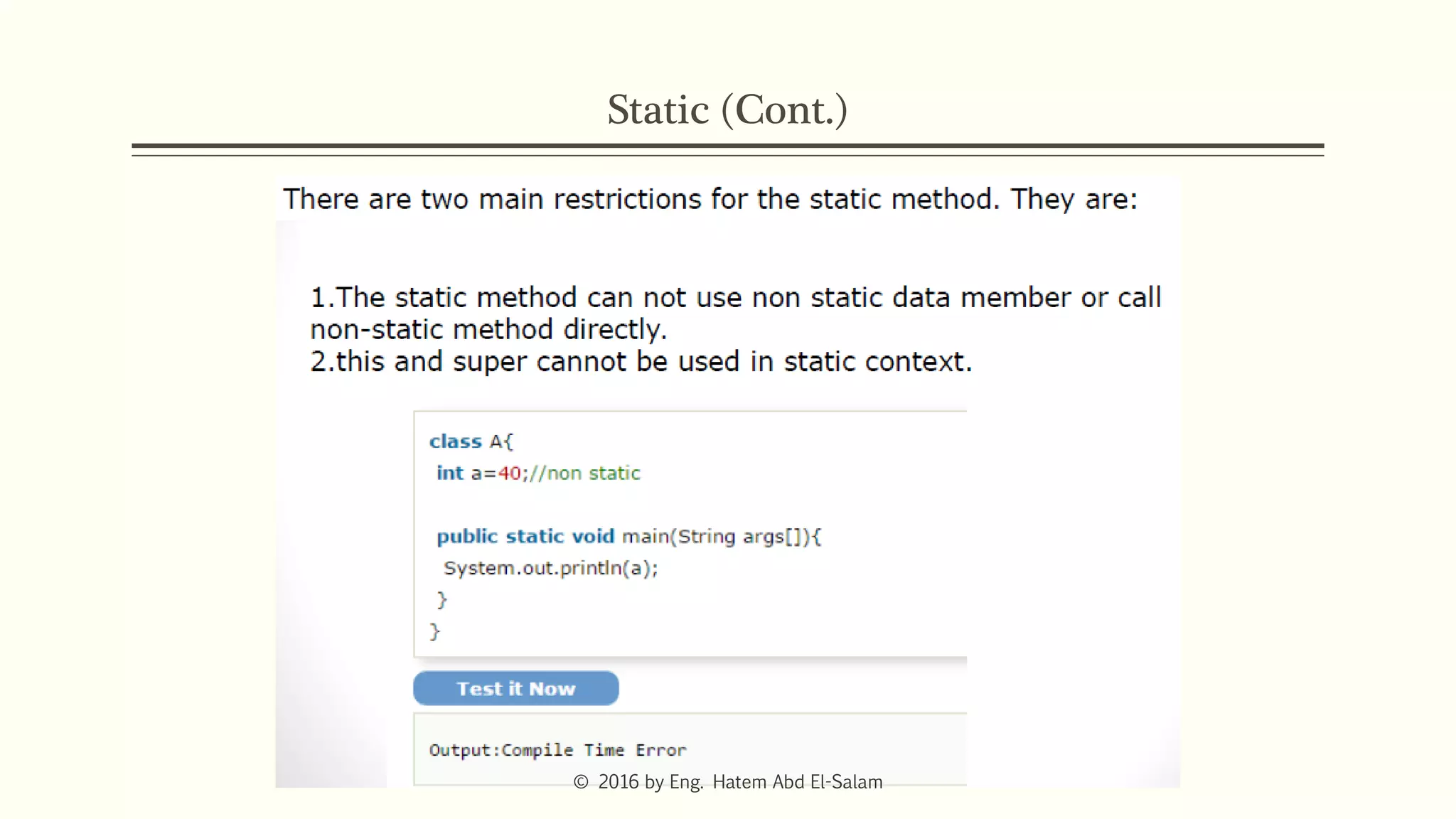
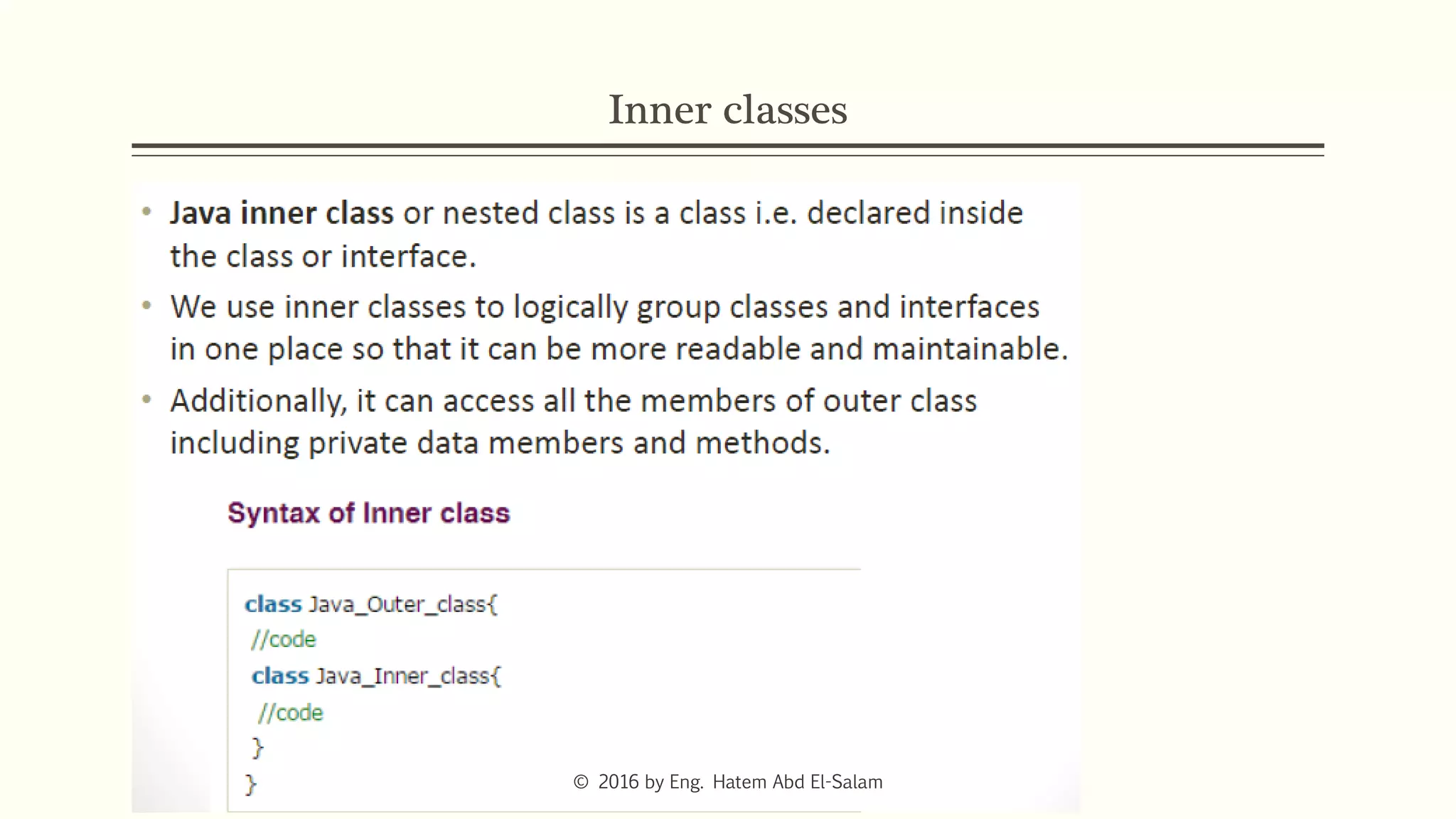
The document provides an overview of Java fundamentals, focusing on object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts such as classes, constructors, inheritance, static, and inner classes. It explains the importance of naming conventions for classes, the role of constructors in object initialization, and distinguishes between static and non-static elements. The lecture emphasizes how these concepts map real-world scenarios to software design.