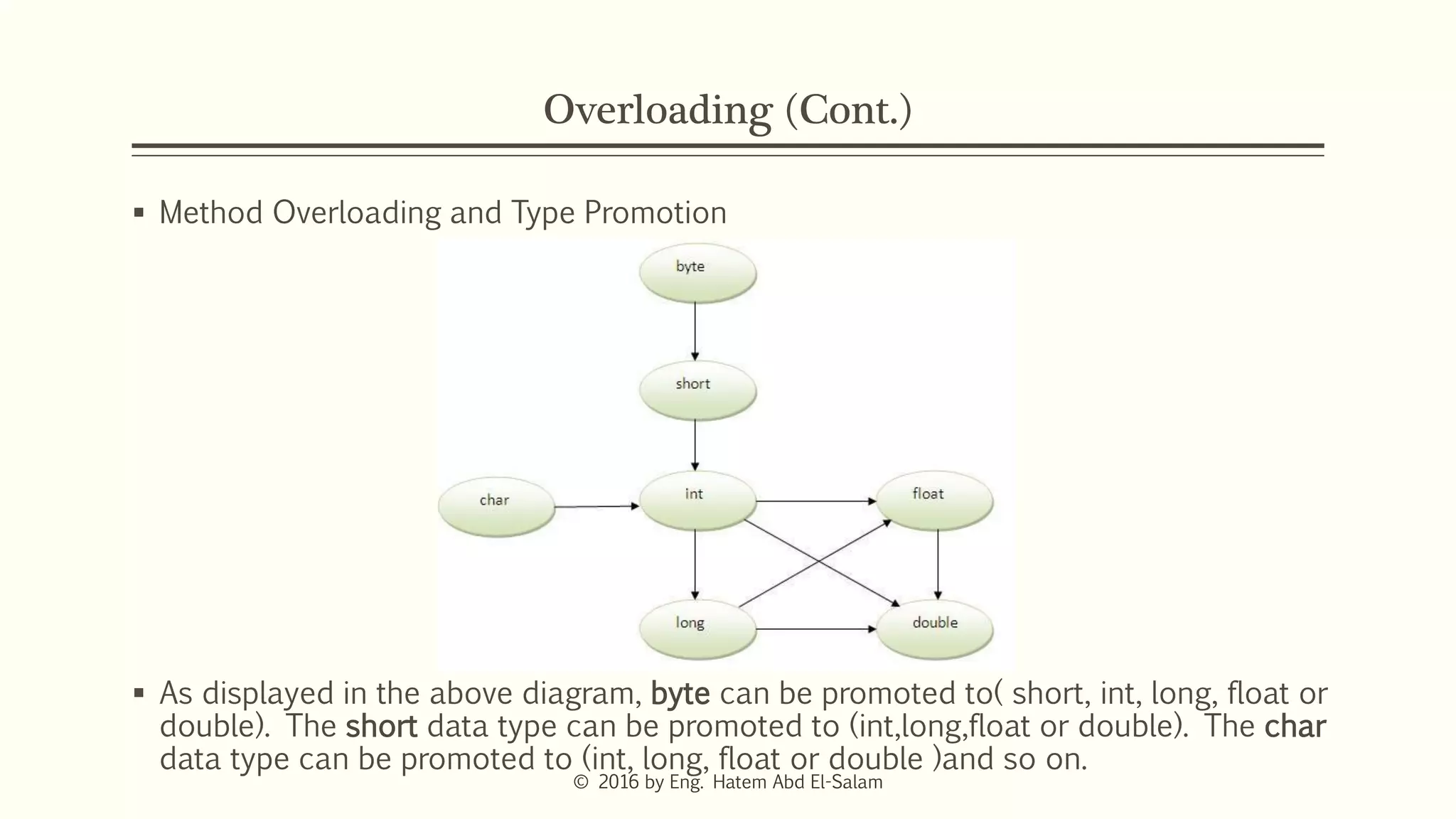
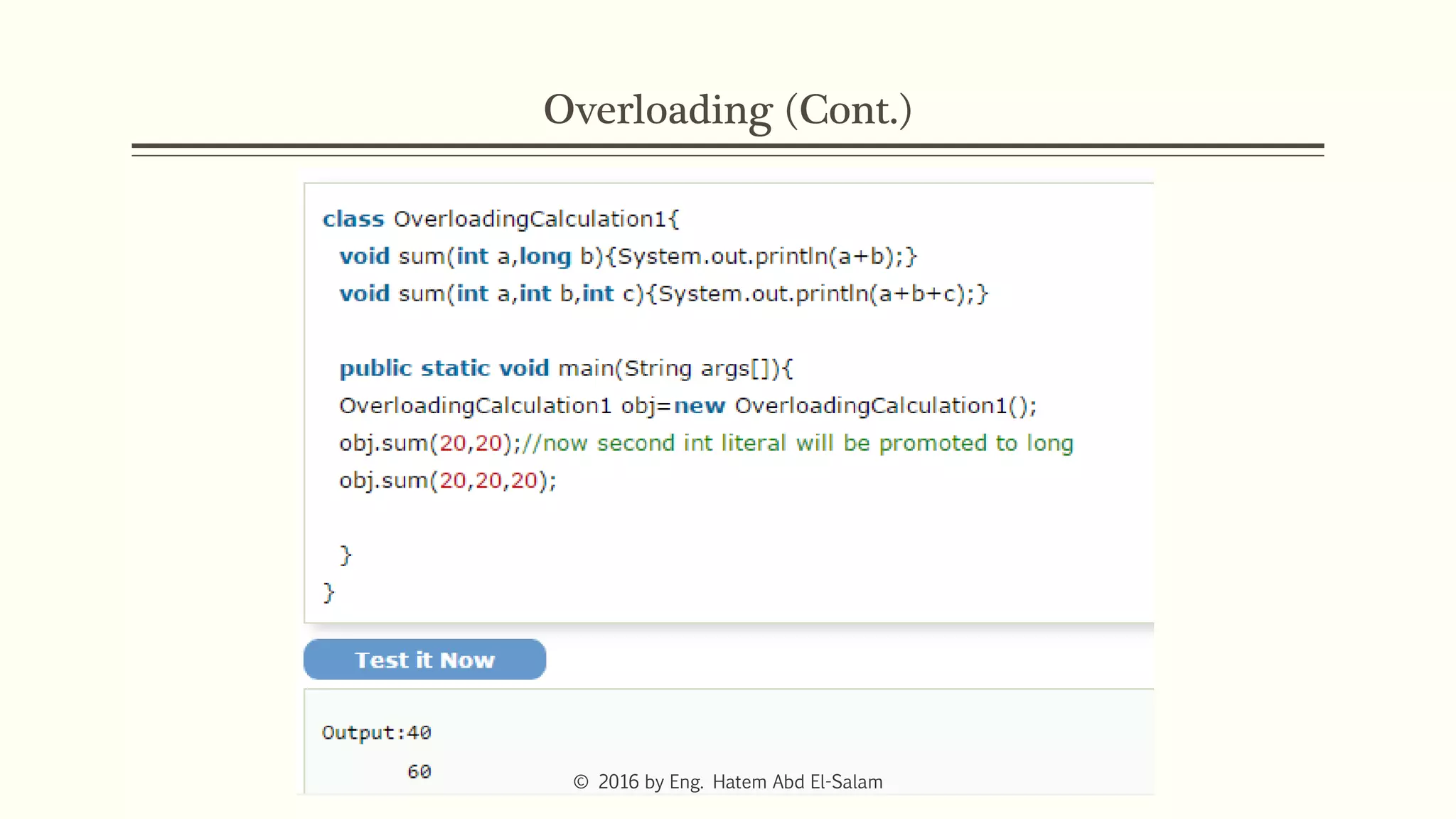
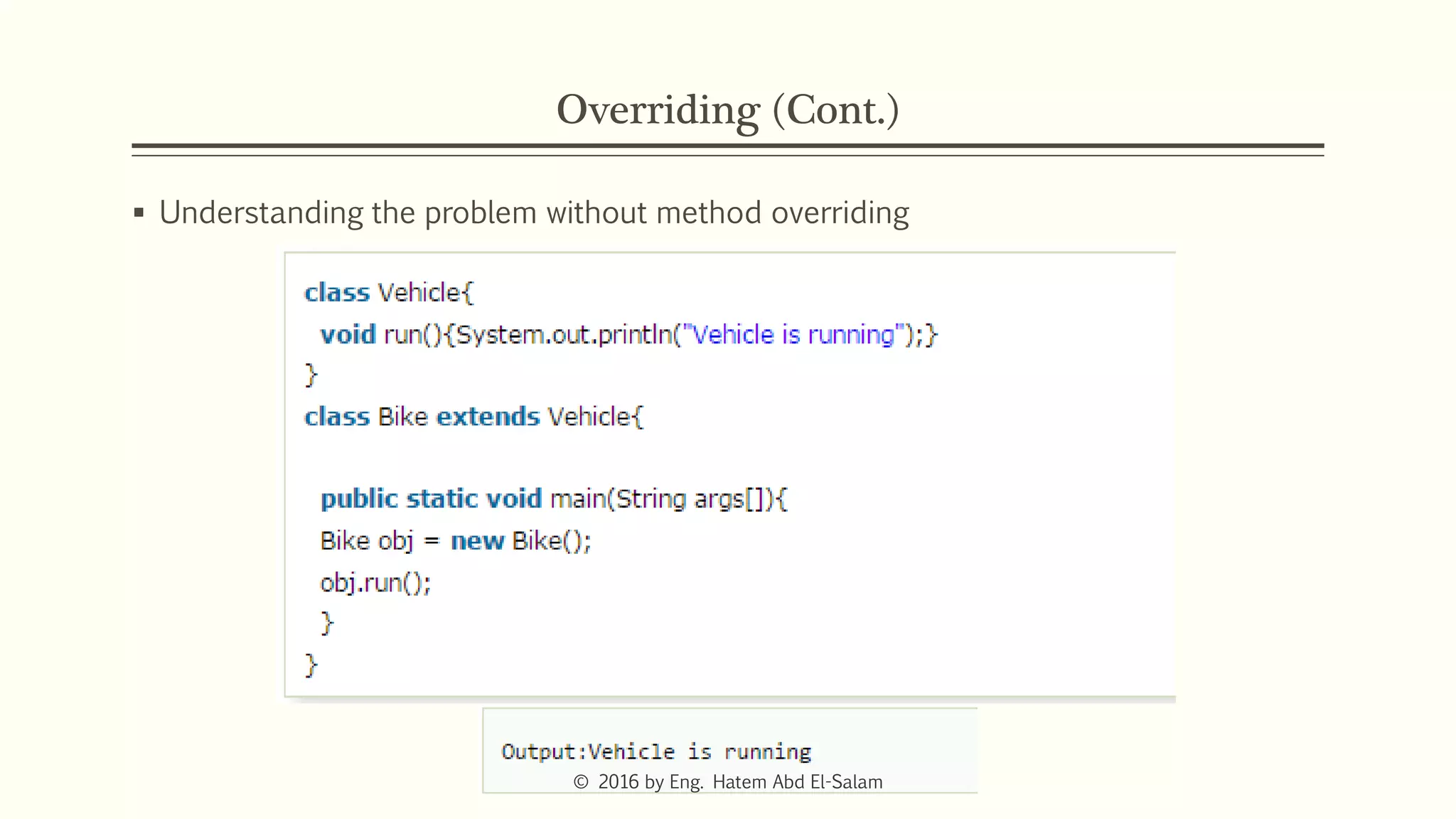
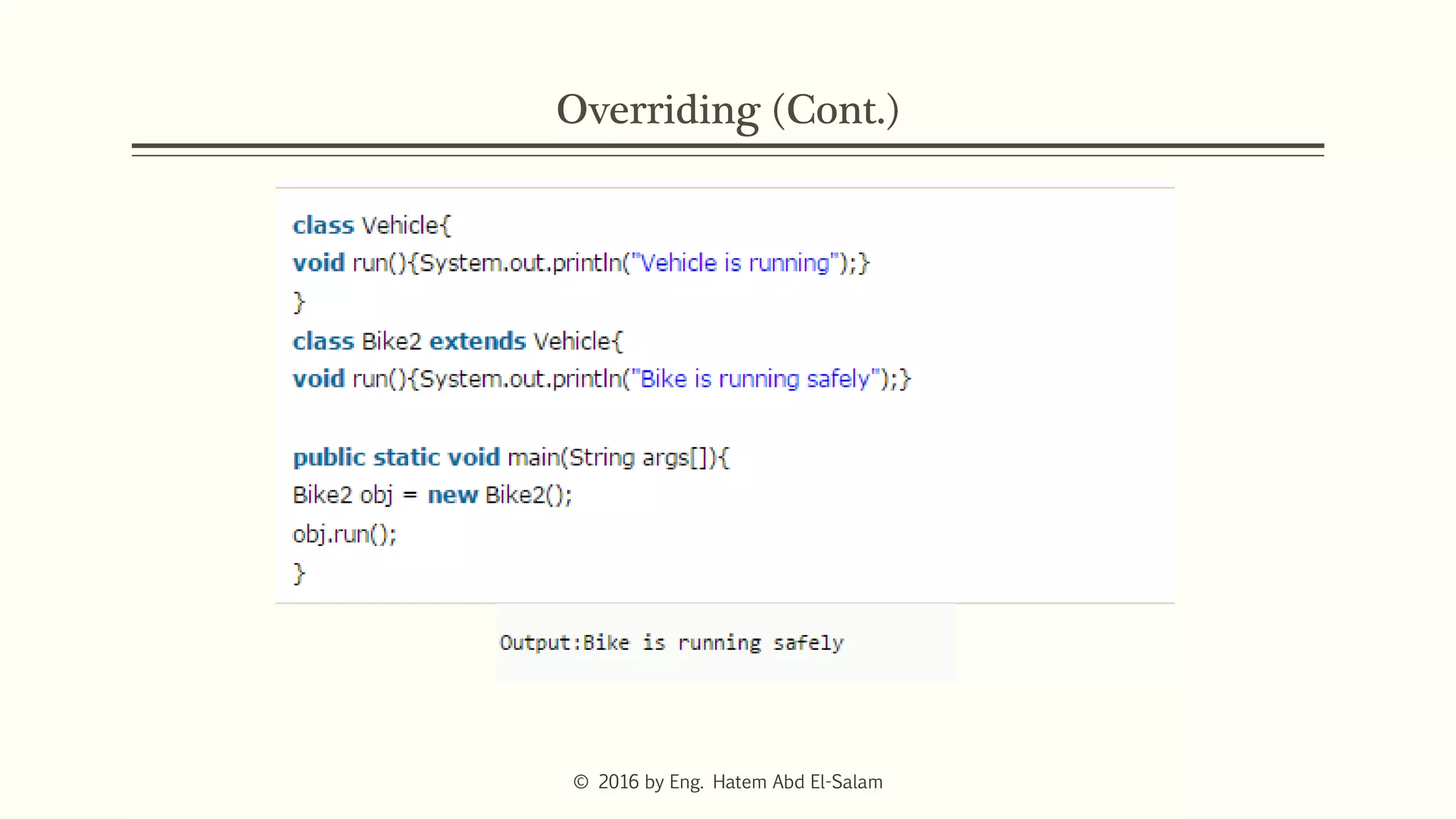
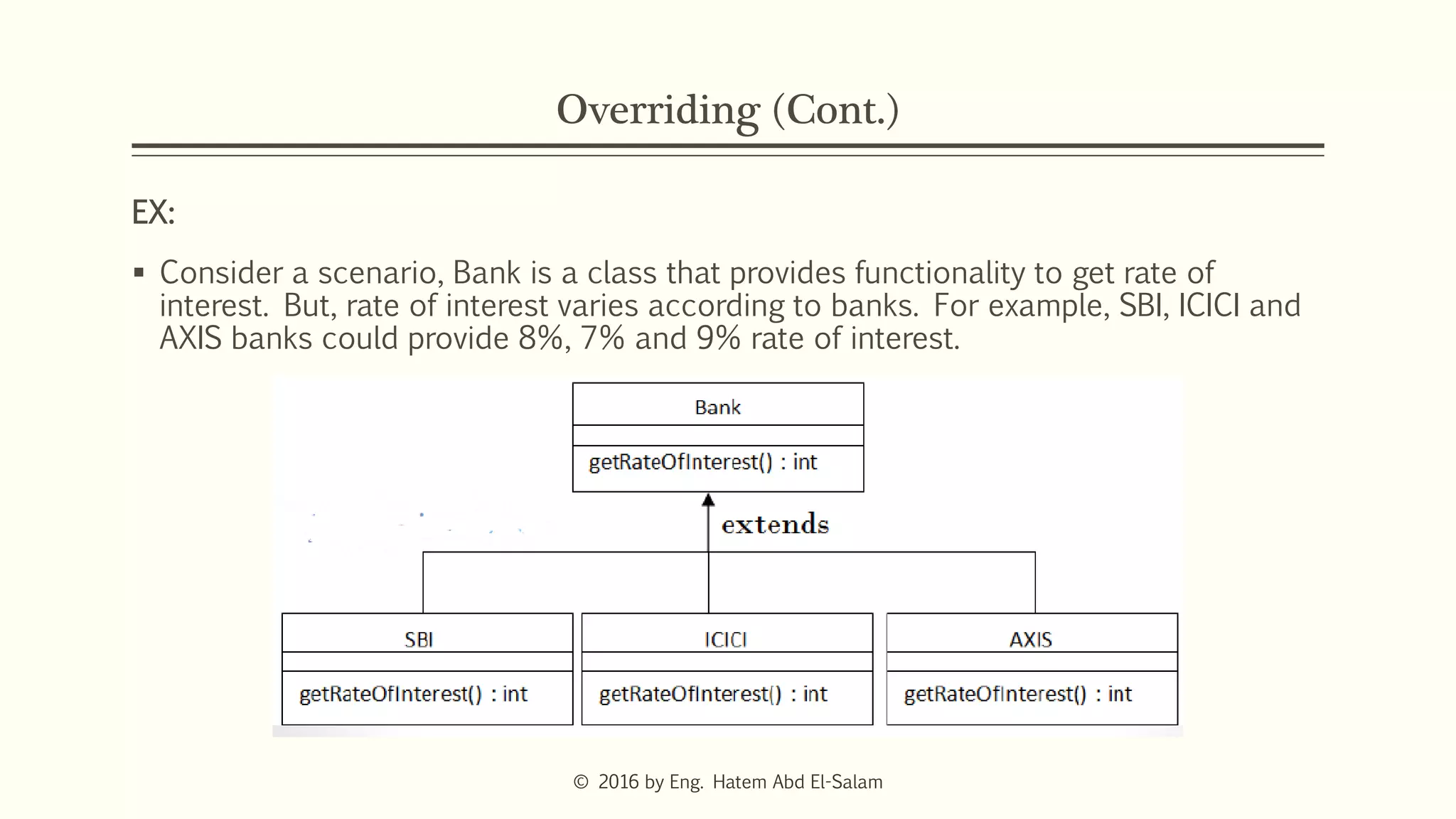
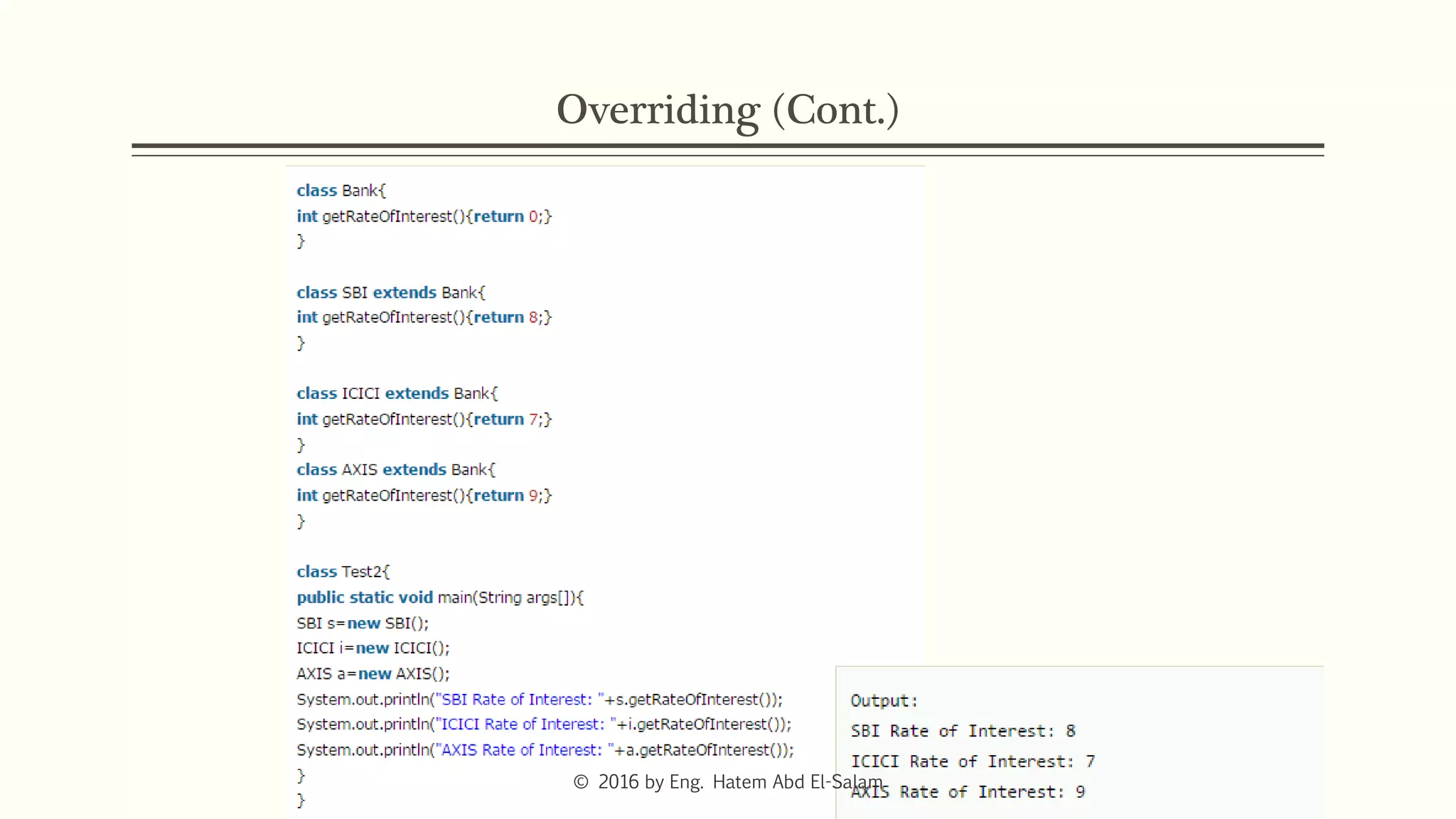
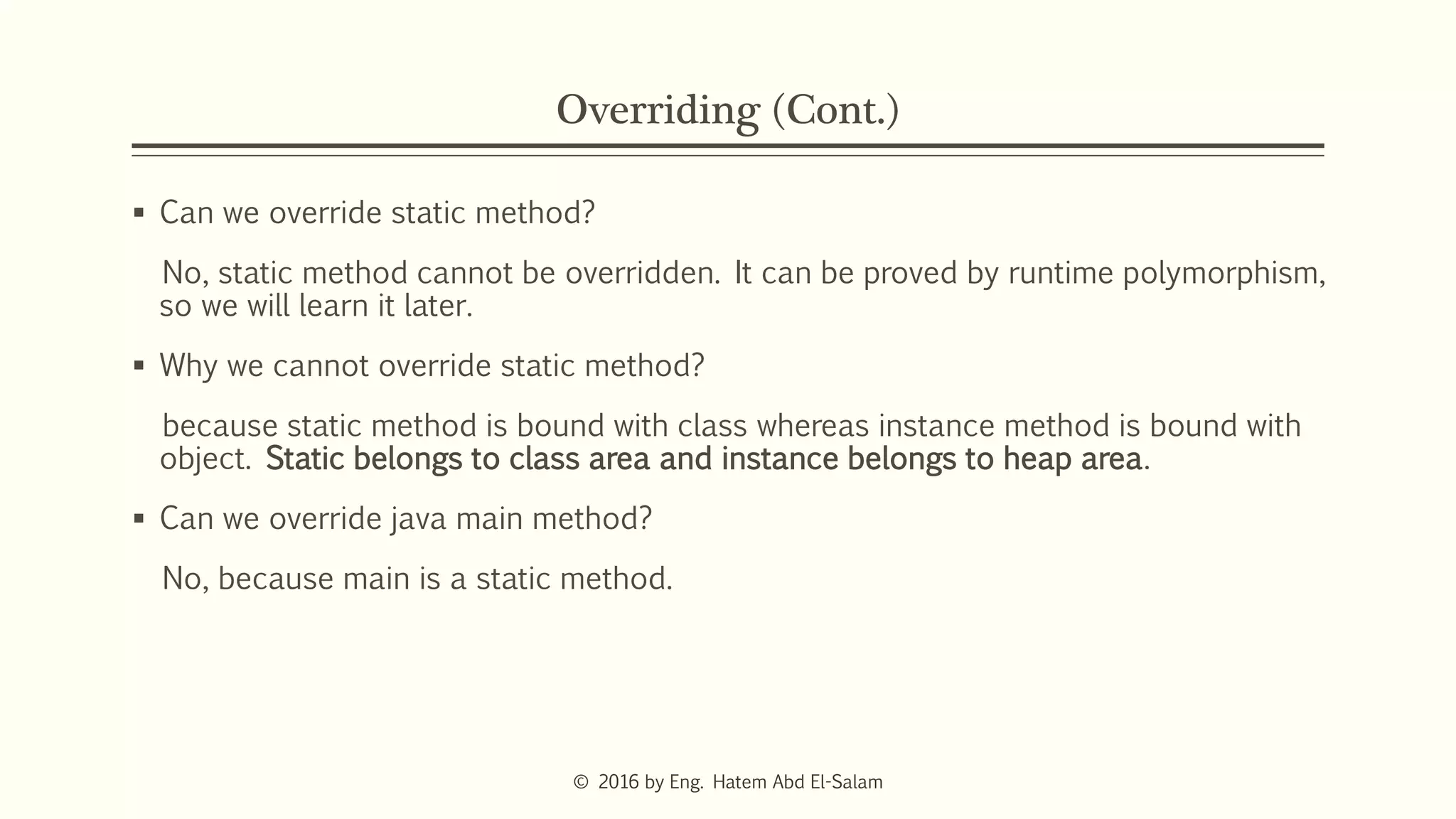
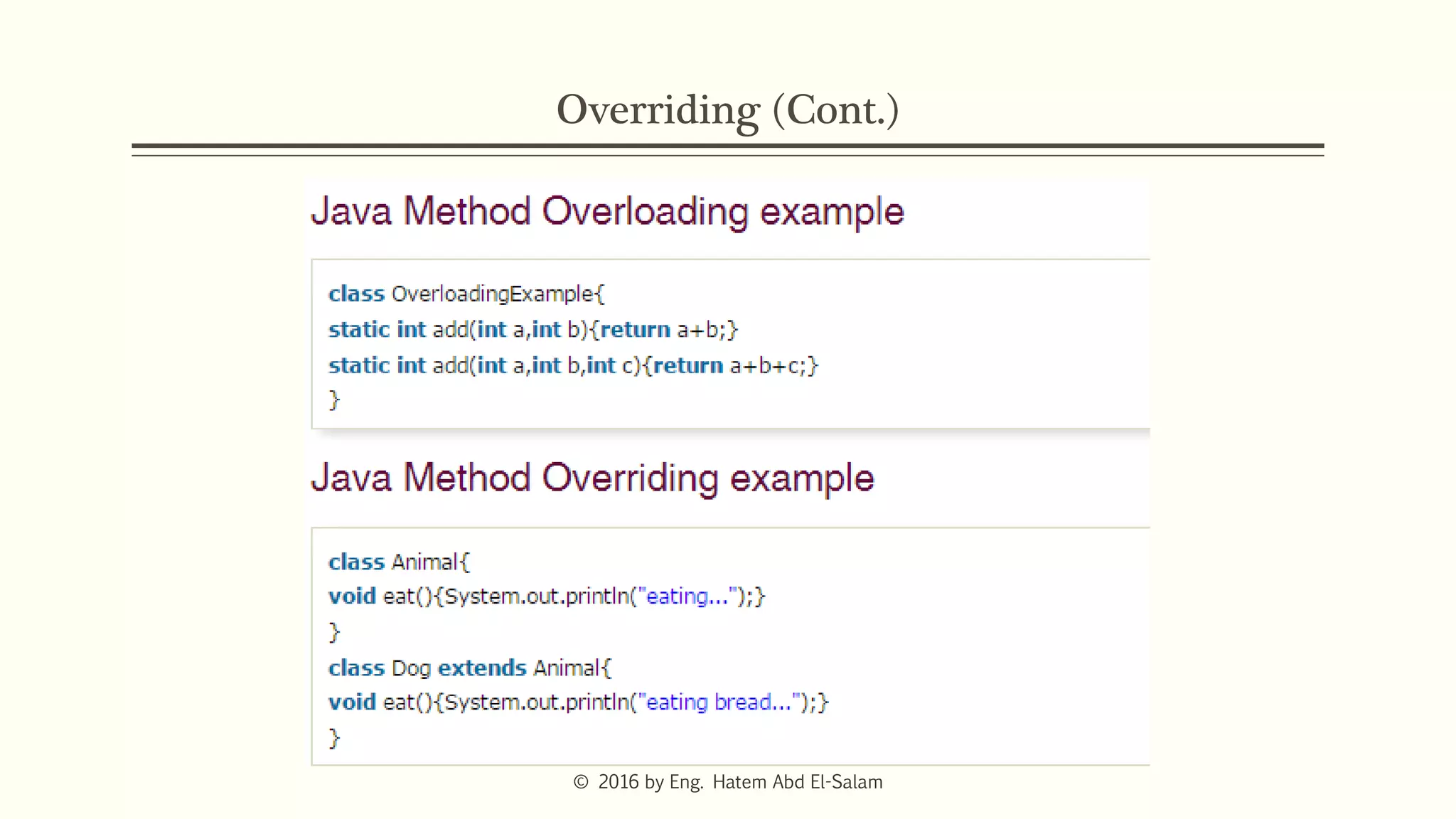
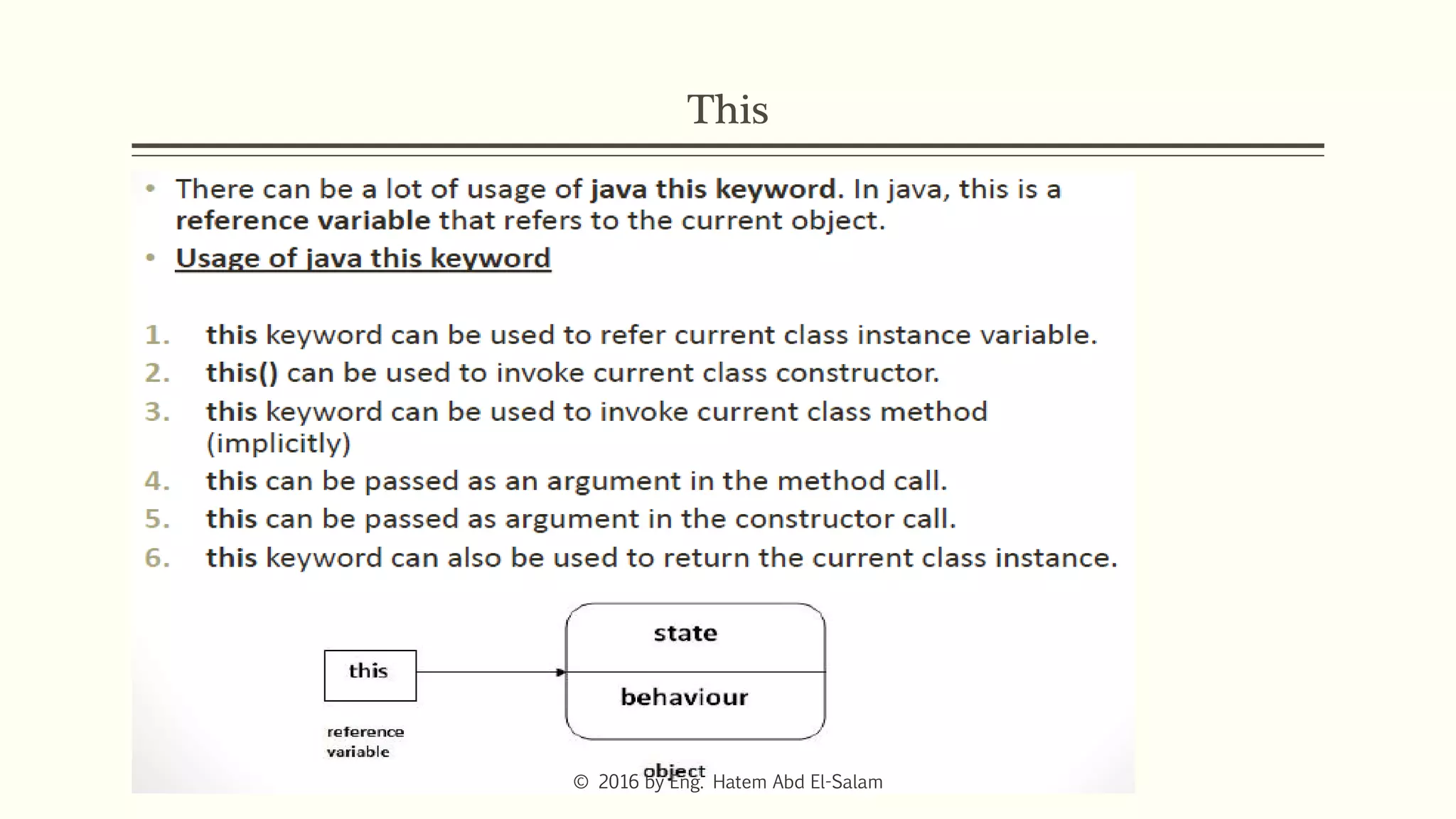
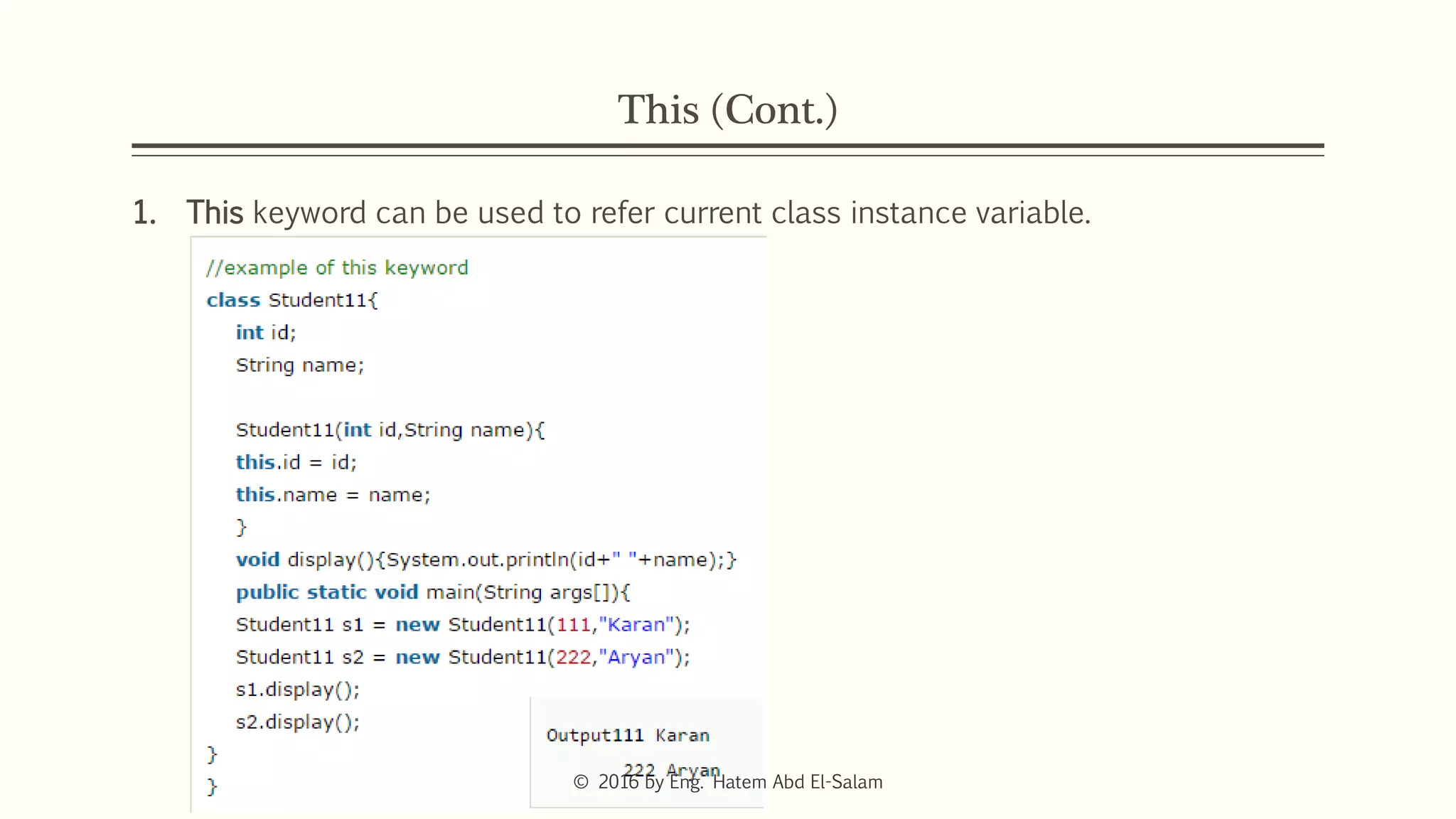
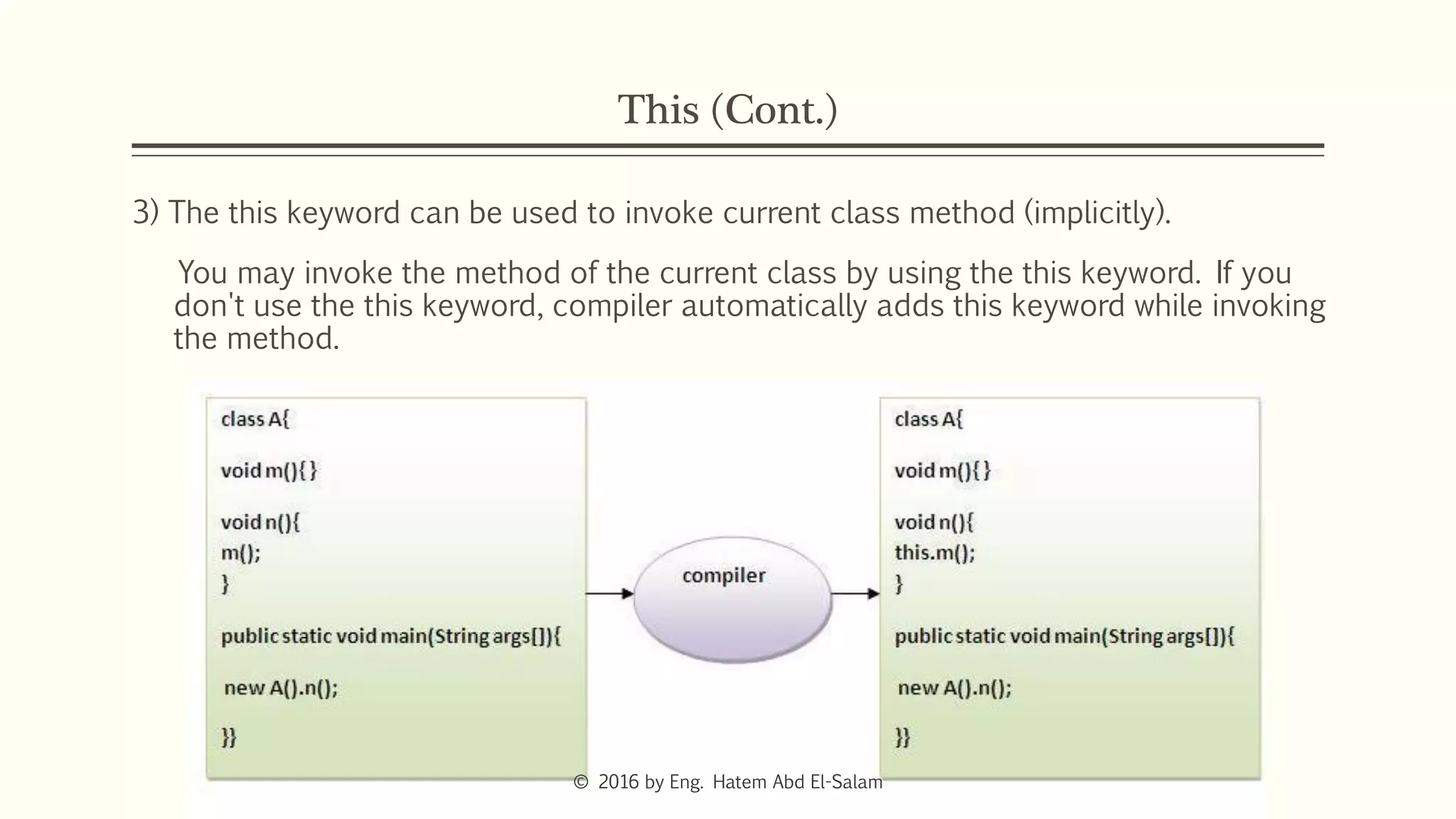
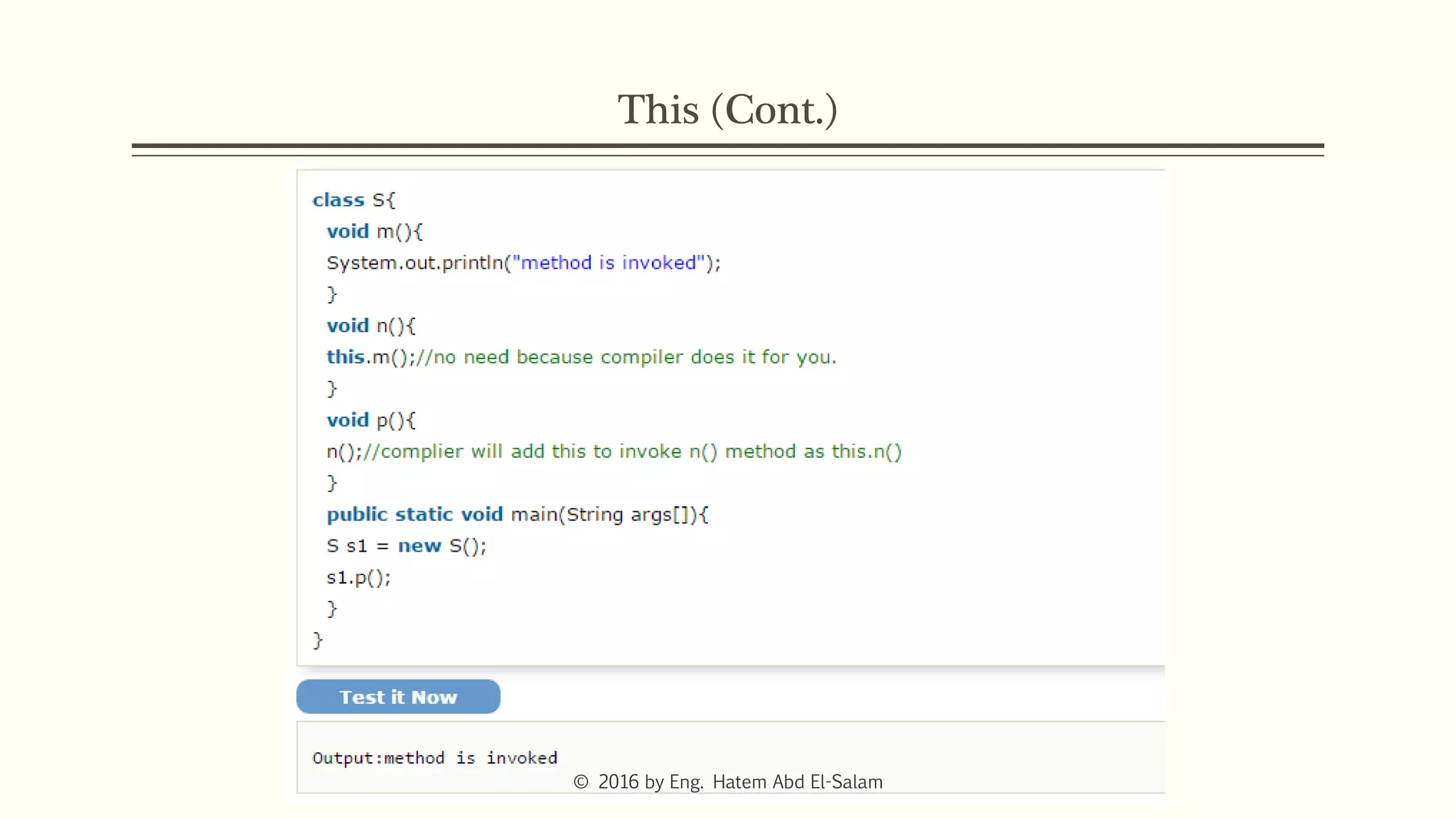
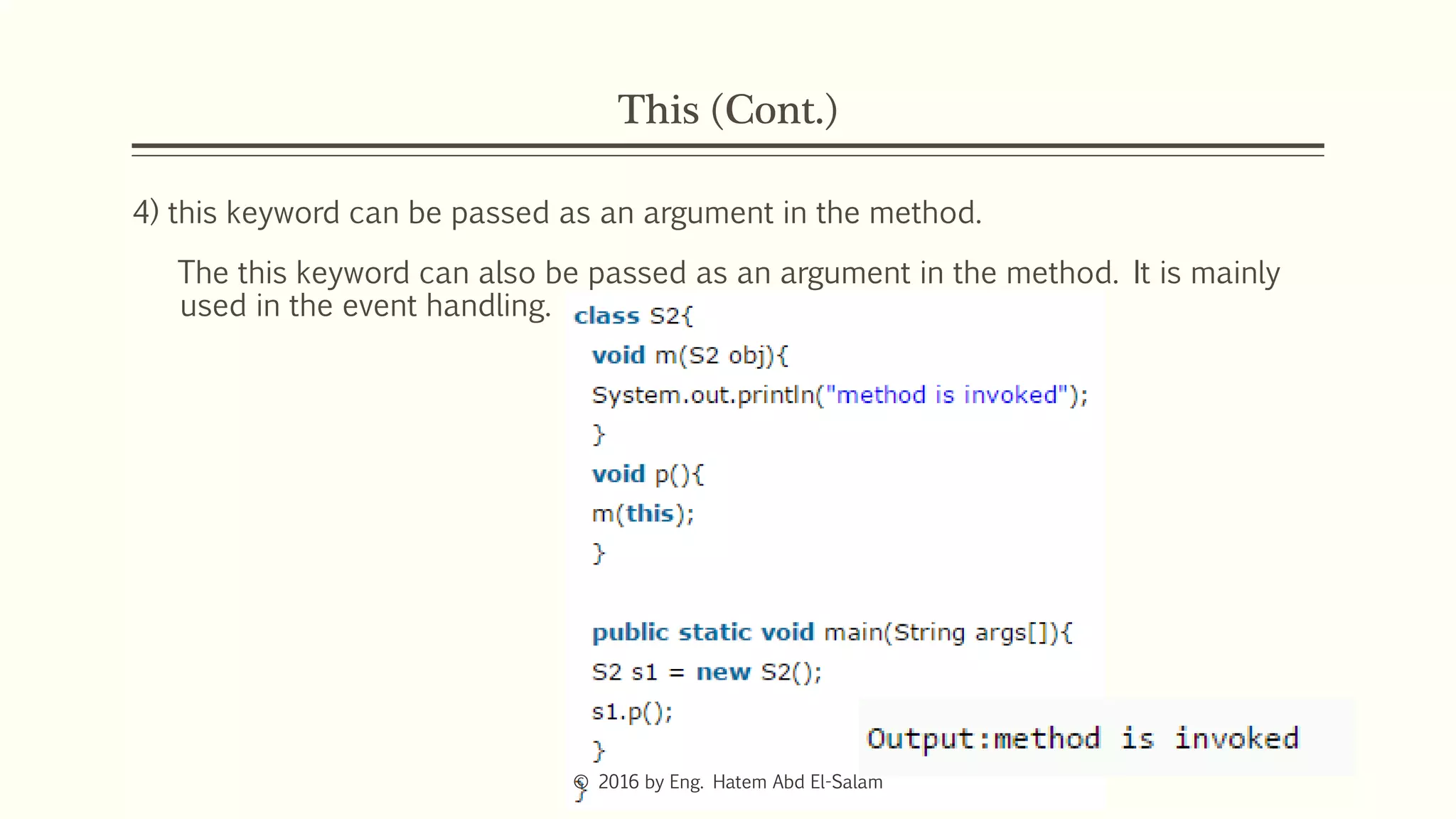
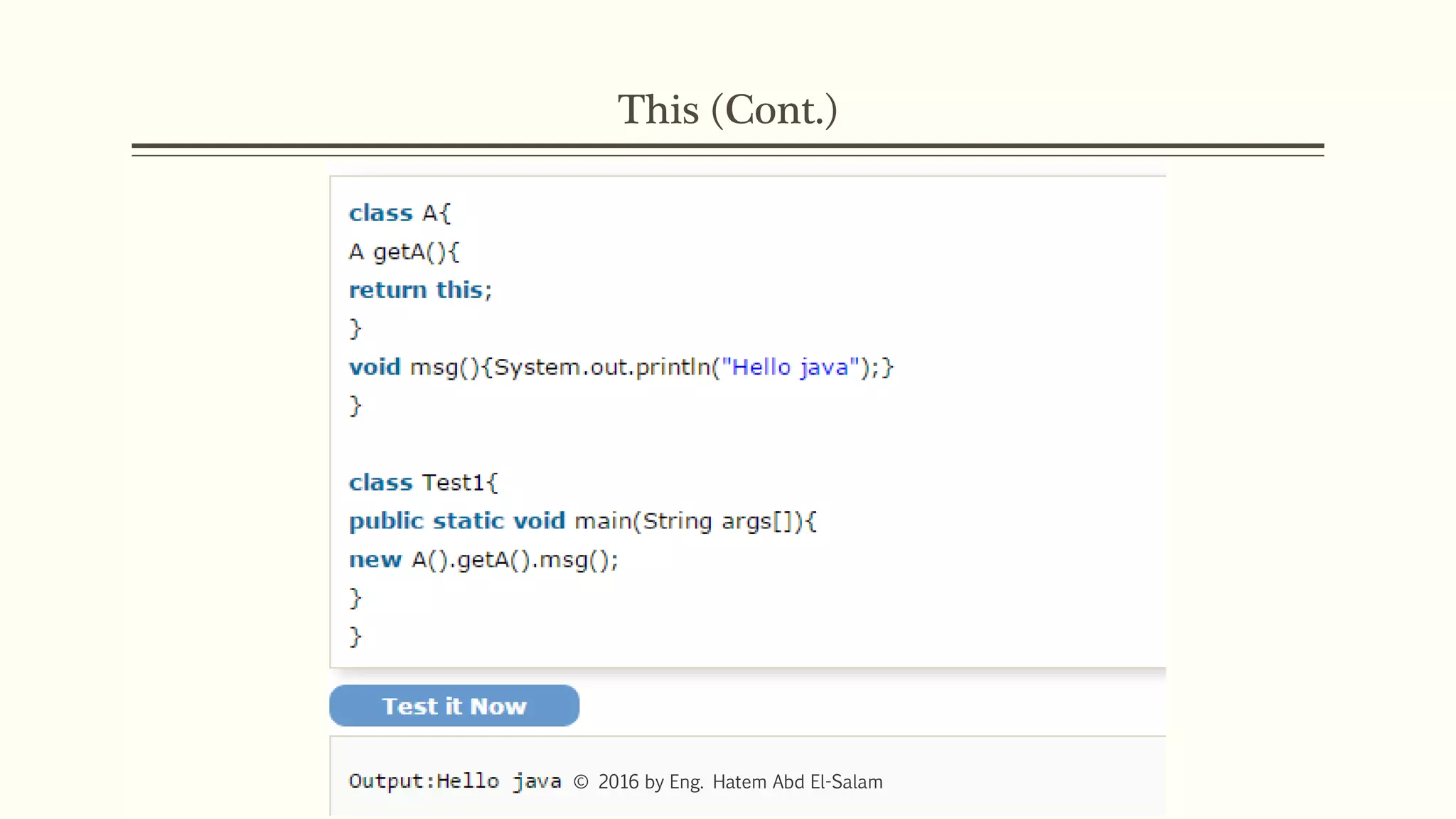
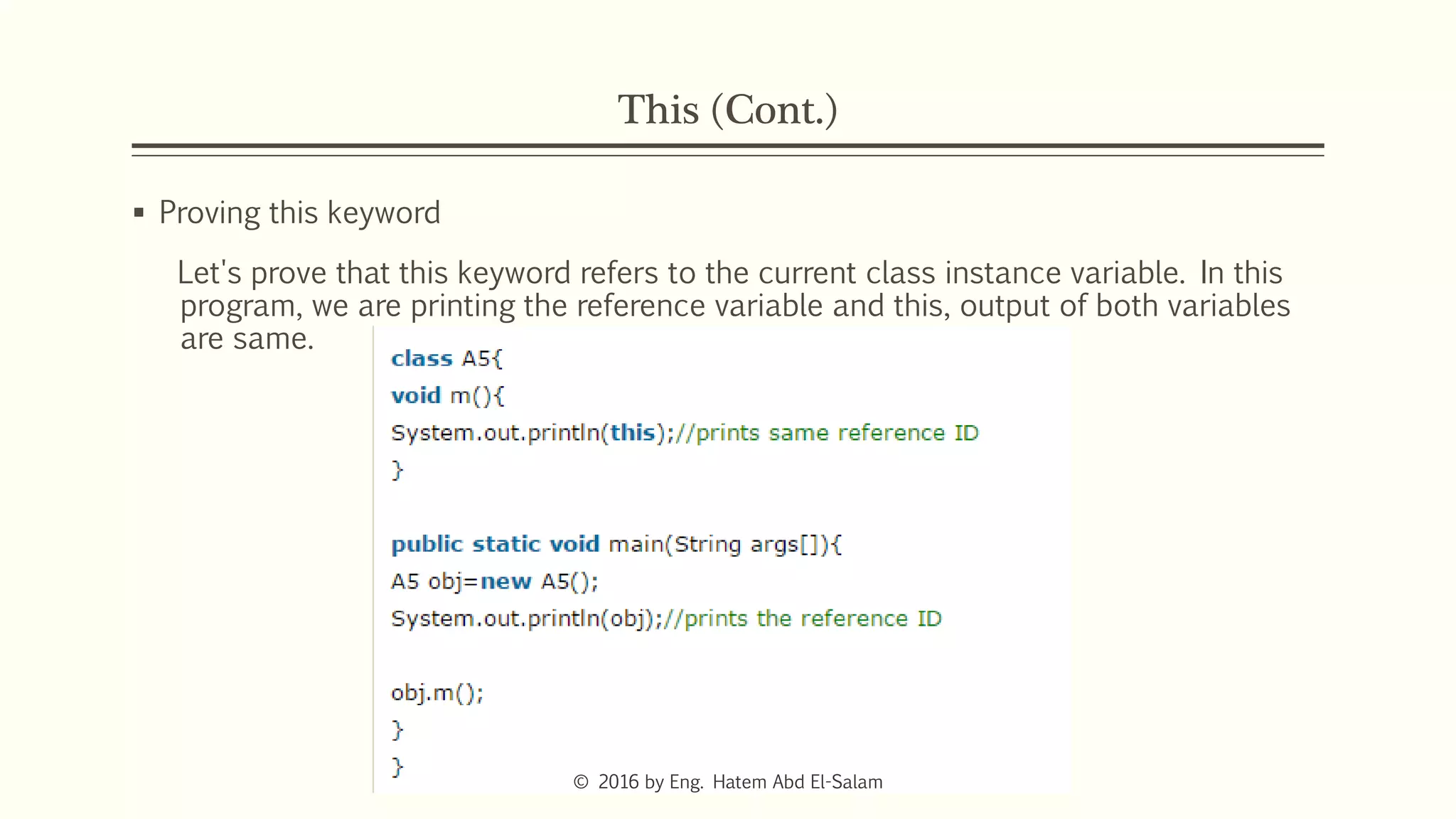
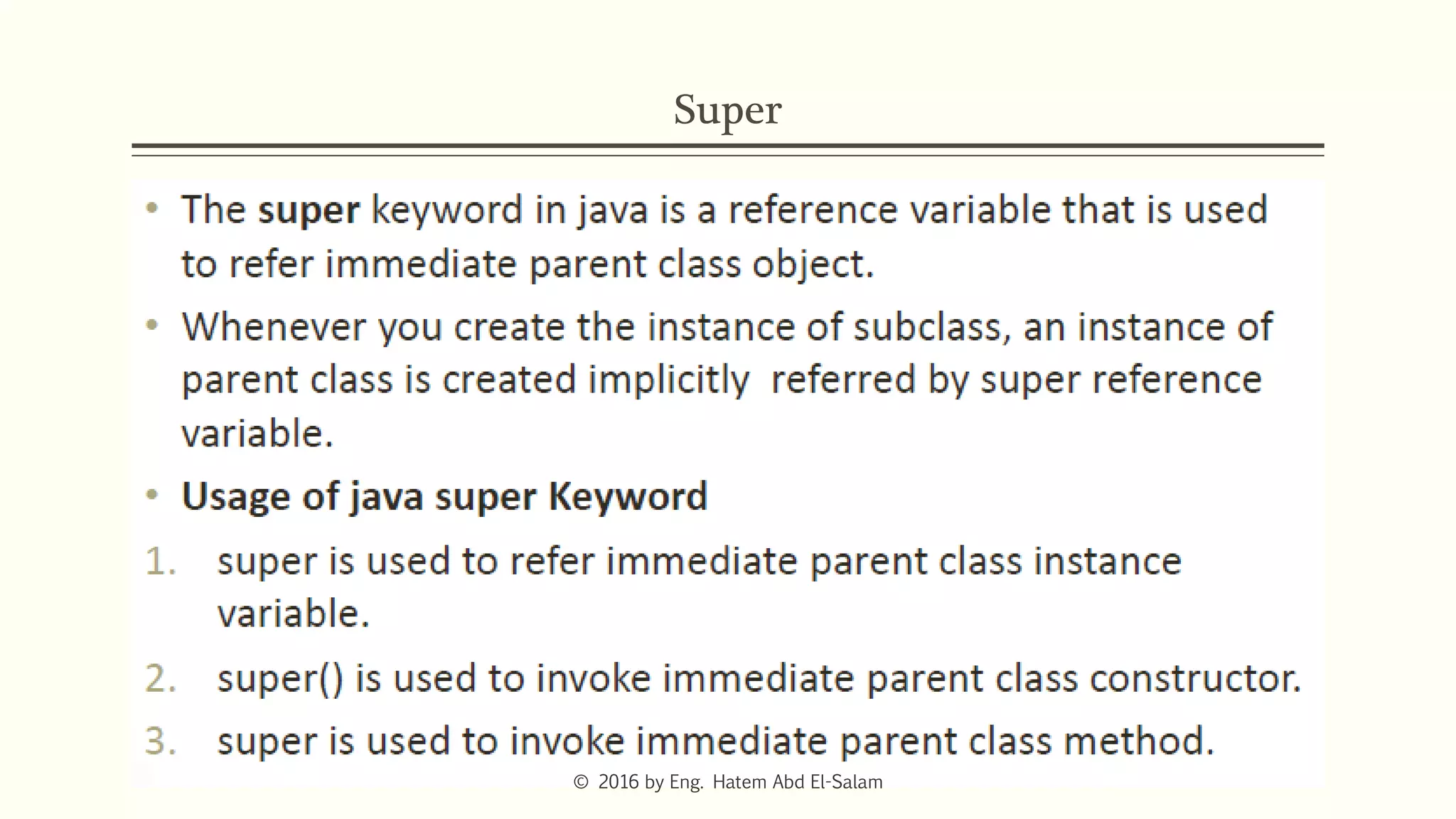
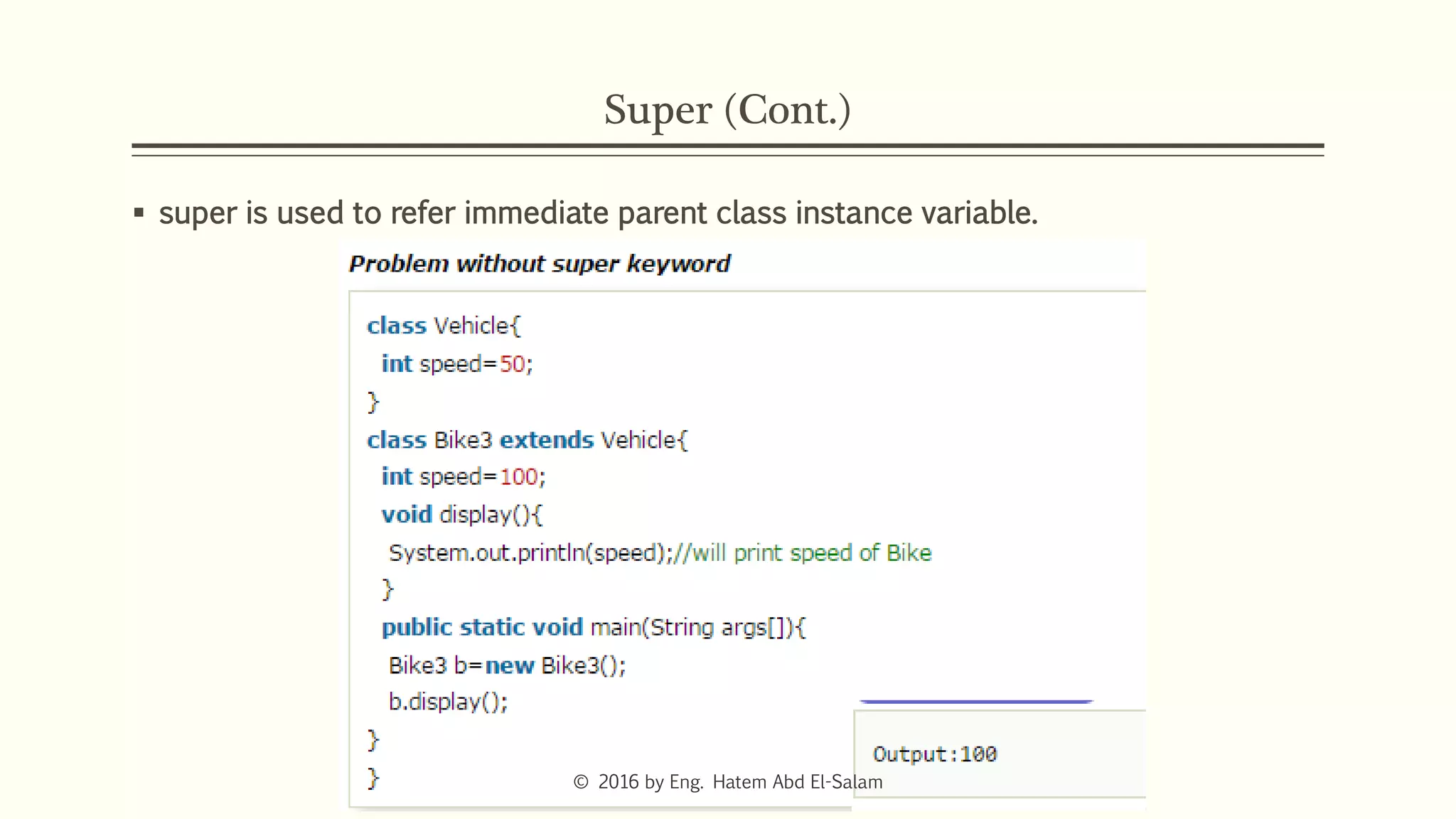
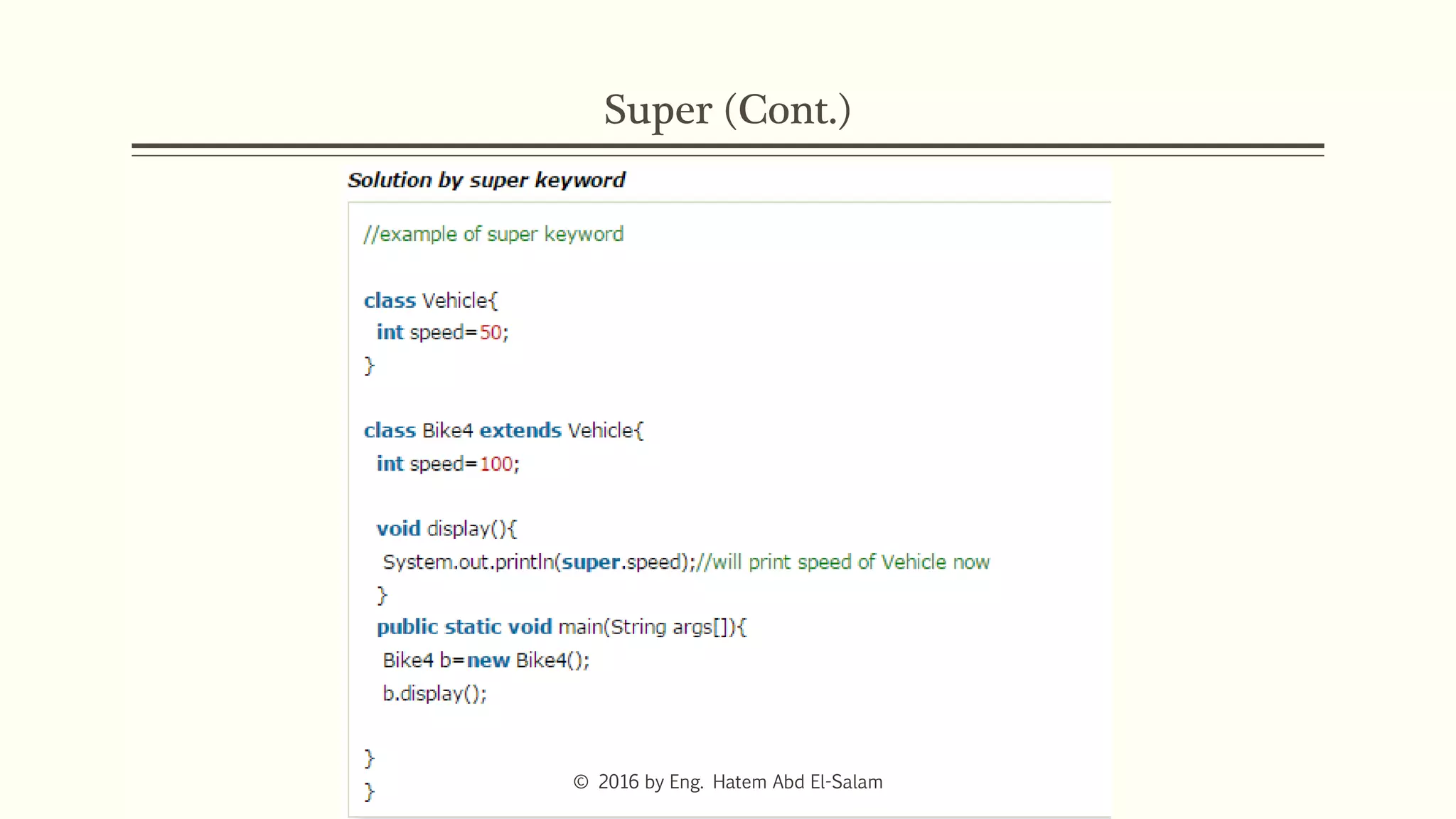
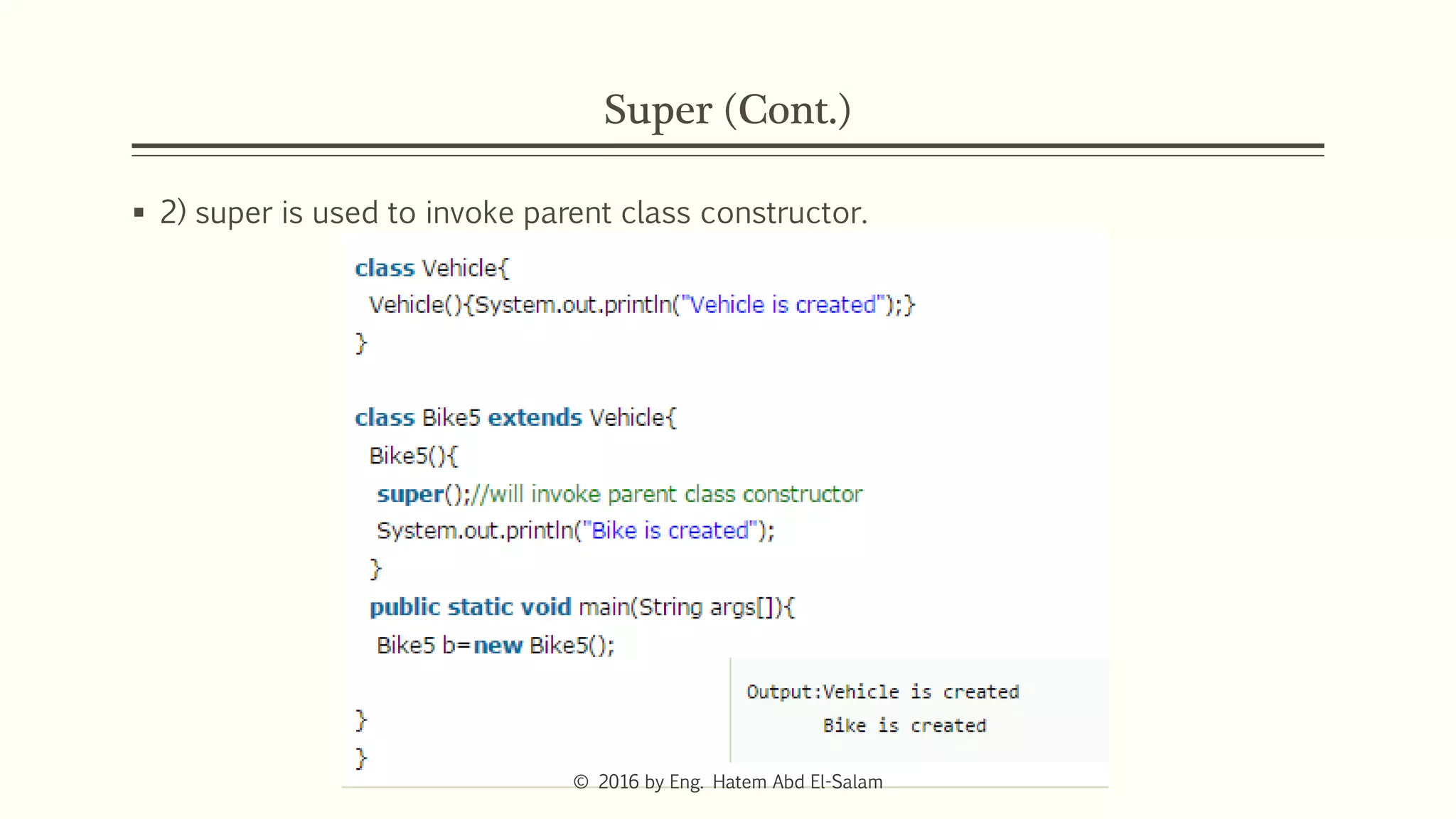
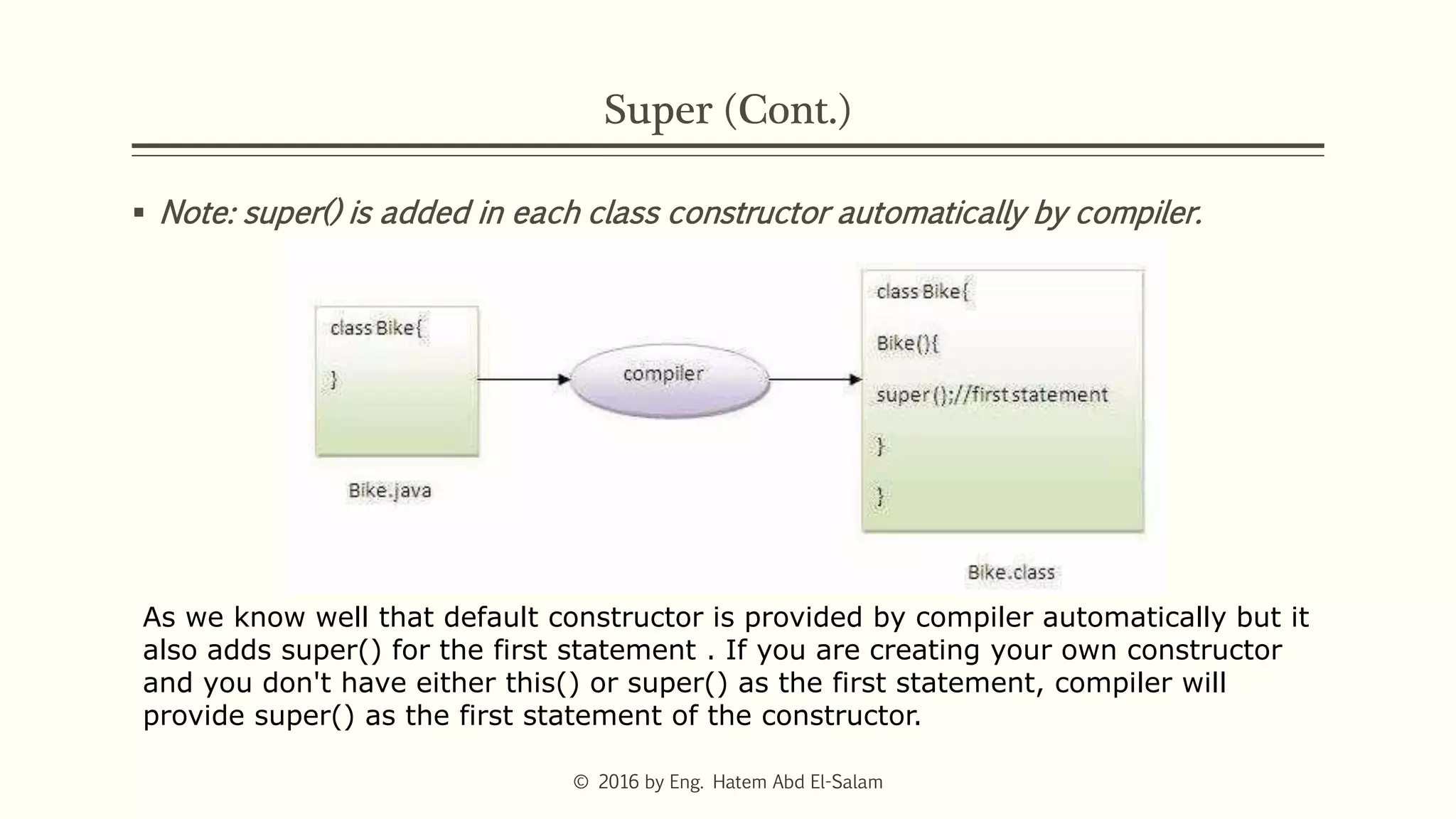
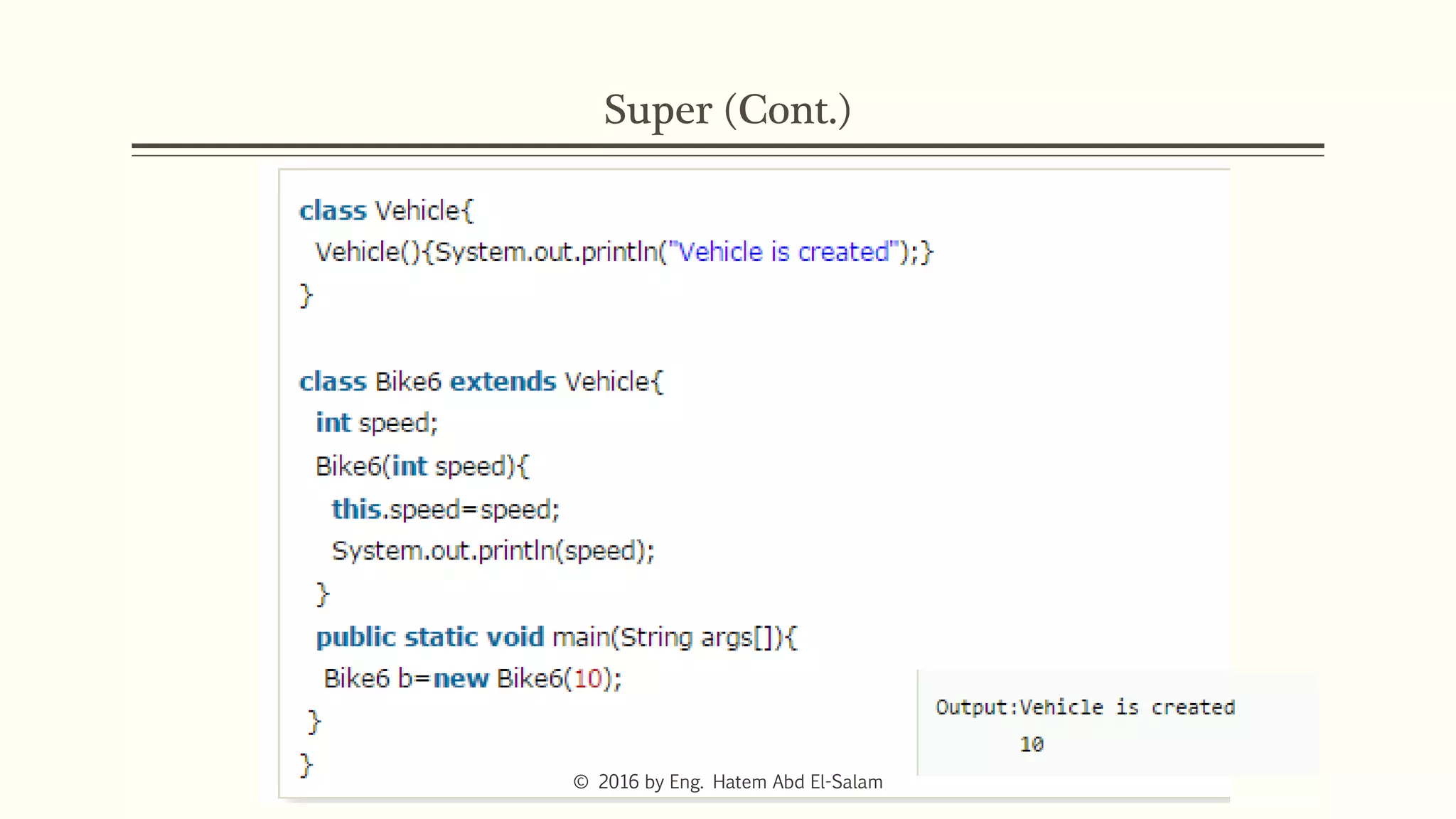
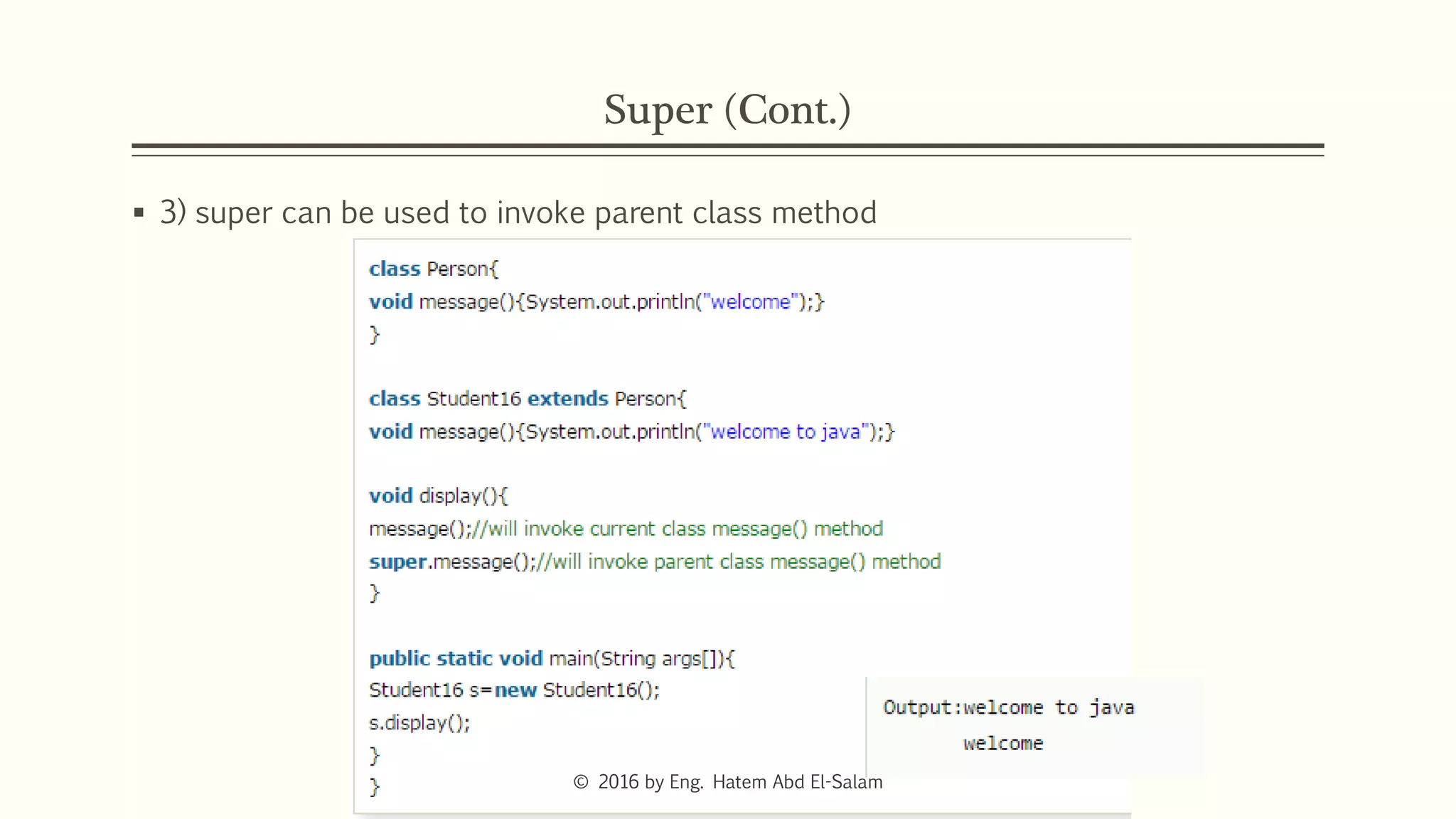
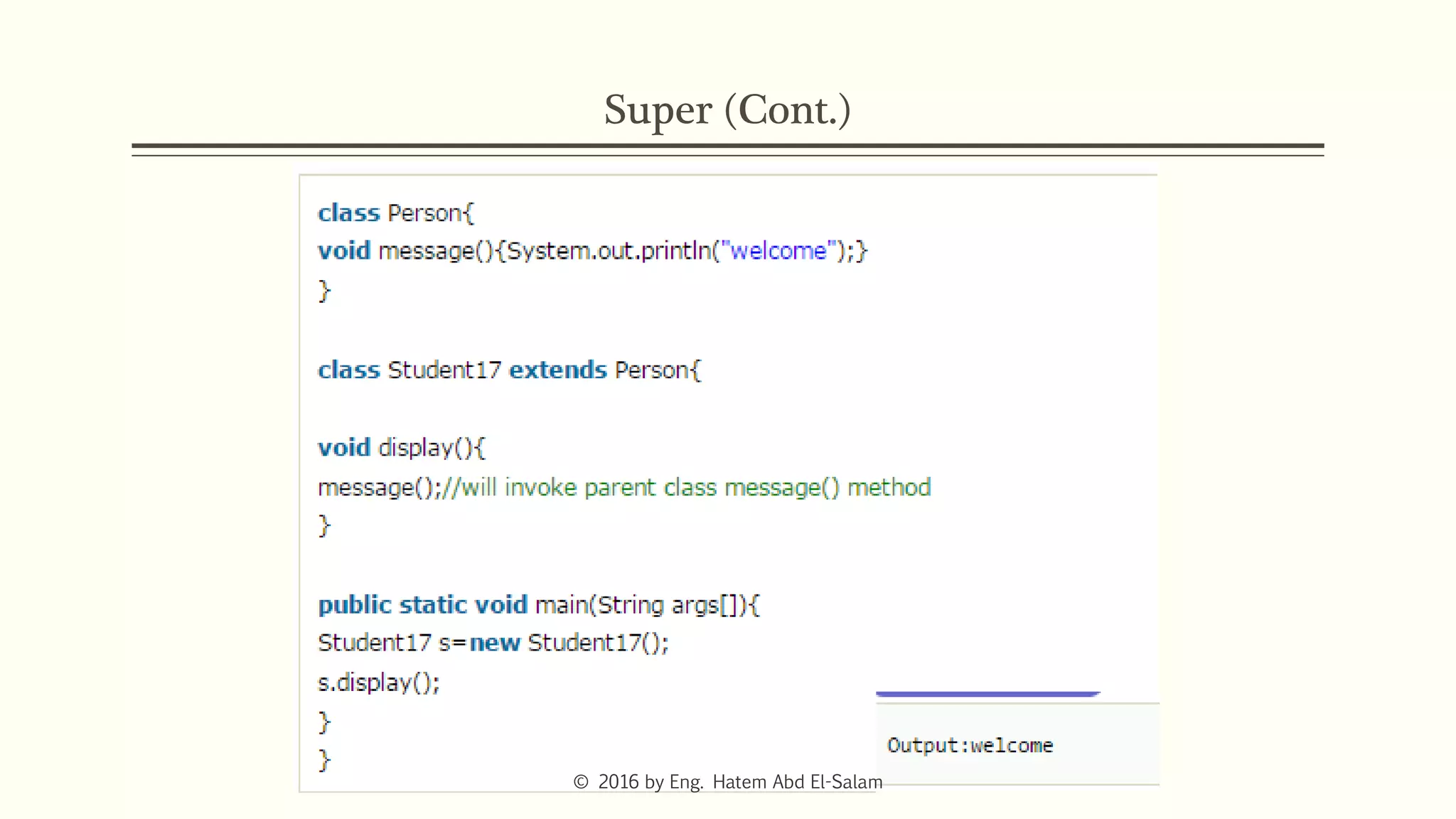
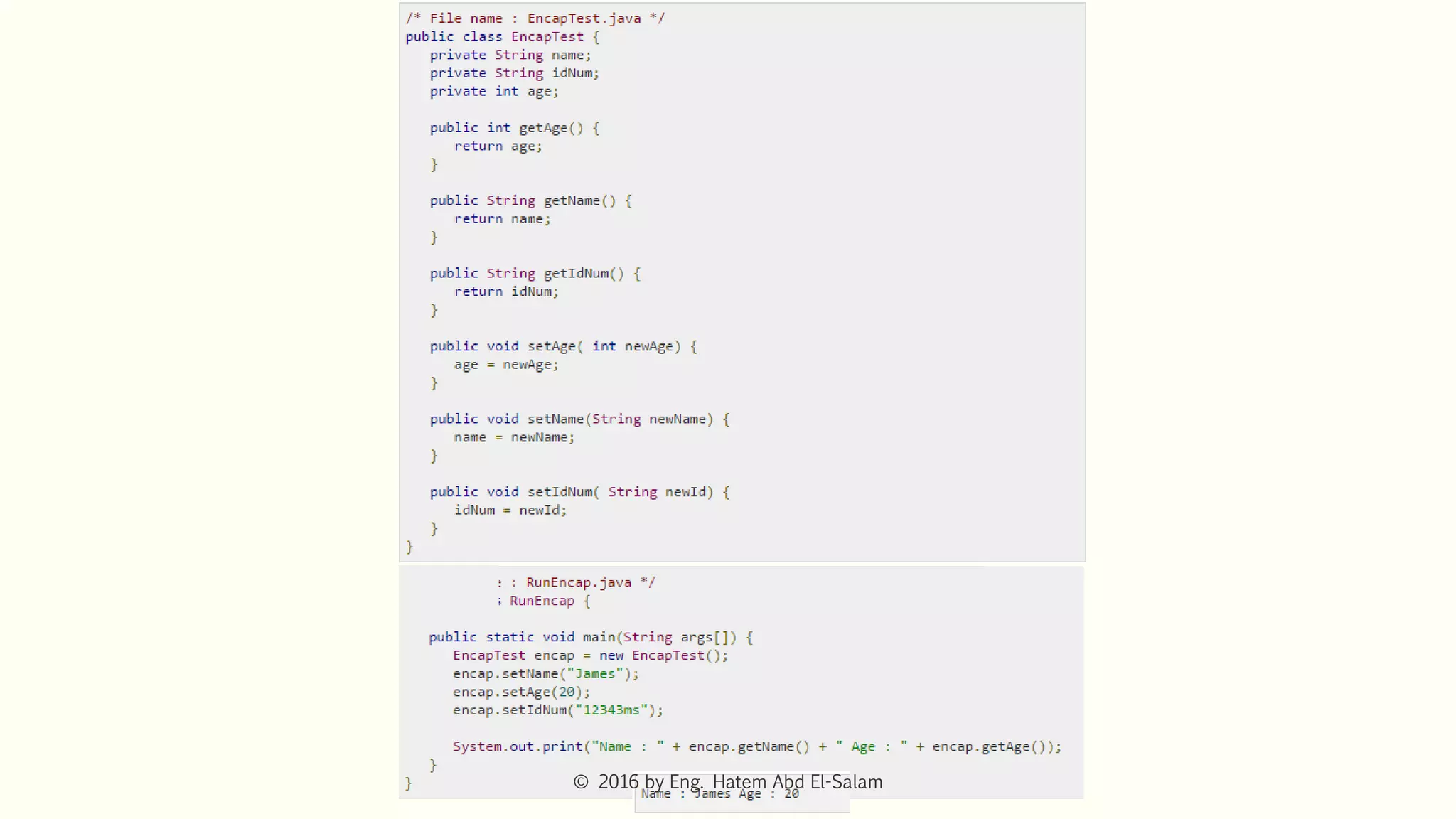
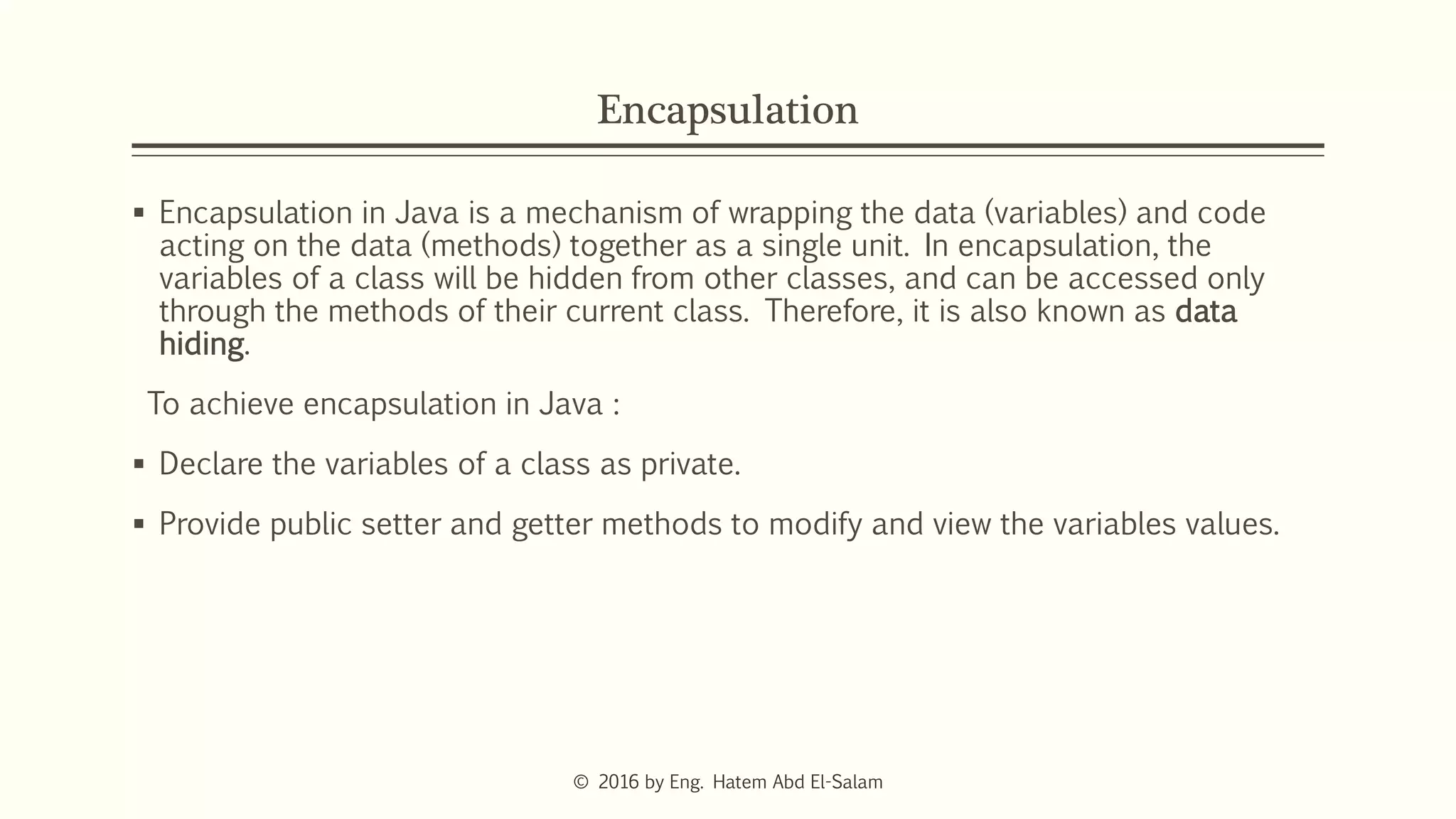
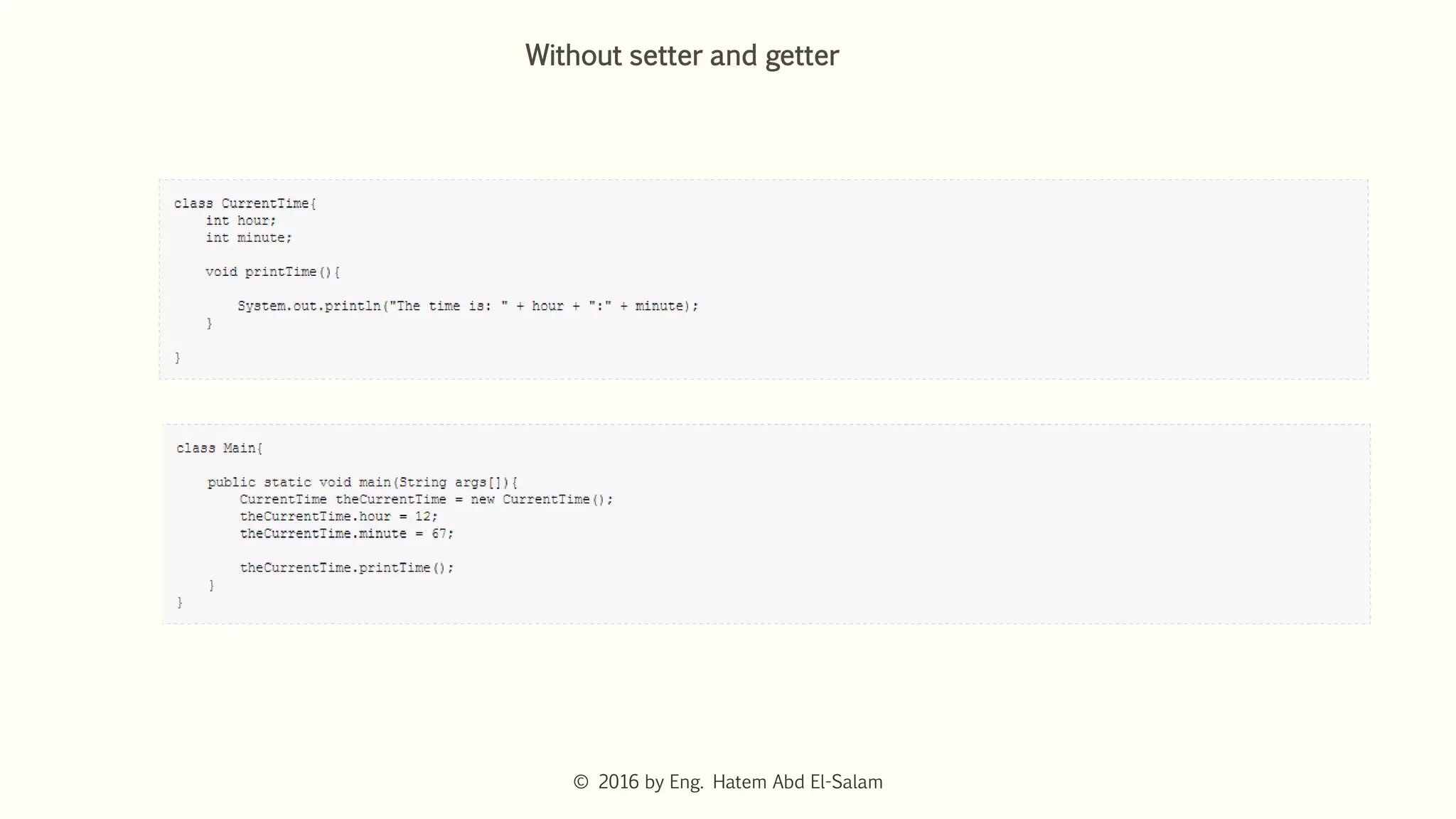
This document discusses Java fundamentals including method overloading, overriding, the 'this' and 'super' keywords, and getters and setters. It provides examples of overloading methods by changing parameters and data types. It also explains that overriding provides specific implementations of inherited methods. The 'this' keyword refers to the current class instance, while 'super' refers to the parent class. Getters and setters are used to access private variables through public methods.